Hypoplasia (hypoplasia) is a developmental defect consisting in underdevelopment of the tooth or its tissues. The extreme expression of hypoplasia is aplasia - the congenital absence of a tooth, part or all of the enamel.
In dental practice, the most common occurrence is tooth enamel hypoplasia - damage to teeth of non-carious origin.
According to some authors, hypoplasia of hard dental tissues occurs as a result of both a violation of the formation of enamel by enameloblasts and a weakening of the process of mineralization of enamel prisms.
What is cerebral hypoplasia
Hypoplasia of the brain is the formation of vessels and elements of the circulatory system that are lagging behind. An abnormal phenomenon that provokes ischemic lesions, destructive and atrophic processes. Often contributes to the occurrence of stroke and ischemia.
The left and right vertebral vessels form a blood pool, which transmits 20% of the blood volume. The carotid aorta is responsible for the remaining 80%.
As a result of circulatory disorders, parts of the head, such as the cerebellum, occipital lobes and trunk, do not receive enough oxygen. The patient's general health deteriorates and vascular insufficiency develops, which affects the entire cardiovascular system.
Treatment
Medicines are used that dilate the left artery and stabilize blood circulation. Thanks to their use, there is a decrease in the intensity of migraines and restoration of normal functioning of the vestibular apparatus.
Hypoplasia can manifest itself against the background of the formation of blood clots in the arteries; for this, medications are used that make the blood more liquid. In addition to taking medications, the patient will be able to independently stabilize his health by adhering to the following recommendations:
- You need to get a good night's sleep; orthopedic pillows are used for this purpose.
- Work behind the monitor should be kept to a minimum.
- Increase the number of sports activities, the lifestyle should be more active.
- You need to try not to get into stressful situations, not to tense up.
- Hypoplasia often occurs in the area of the cerebral artery in the fall and spring. This requires preventive measures.
Surgery should be performed after treatment procedures if there are no results. Doctors organize endovascular intervention, which involves implanting a stent into the artery. This makes it possible to expand the vessel and stabilize blood flow.
The length of the problem area largely determines the outcome of treatment.
With brain hypoplasia, you can lead a full life. The likelihood of negative consequences increases in old age. Therefore, regular use of medications, physical activity, and prevention of circulatory problems can turn hypoplasia of the blood vessels of the head into a disease with which people live for a long time.
Classification of the disease
Vascular disease affects and damages all areas of the brain. They provoke slow tissue development. The pathology may be congenital or appear with age.
Hypoplasia of the cervical artery most often begins to develop in the fetus in the womb.
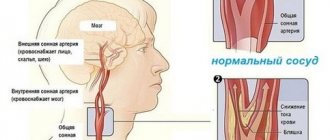
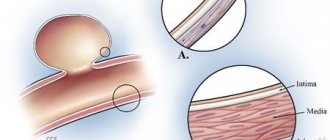
The circle of Willis ensures normal blood supply to the brain. It is formed by large aortas of the spine with two branches. Usually the vessels develop evenly. A branched artery is responsible for natural blood supply. Vascular hypoplasia can be left-sided, right-sided or bilateral.
Hypoplasia of neck vessels disrupts blood supply and prevents normal nutrition of brain cells.
If you do not undergo diagnosis in time, cardiovascular failure and serious malfunction of the vestibular apparatus may develop.
First, you should undergo certain therapy, due to which the blood flow will return to normal.
Corpus callosum of the brain
Hypoplasia of the corpus callosum of the brain in a child is a most dangerous disease, which consists in the absence of the corpus callosum ─ a section in which there are accumulations of nerve fibers that carry out neural interaction between the right and left hemispheres of the brain. This disease is not acquired, but only congenital. It is diagnosed both in the prenatal period and within 2 years from birth. In 70–75% of cases, underdevelopment of the corpus callosum in a child leads to disability, schizophrenia and seizures. The causes of the disease have not yet been clarified, but unfavorable factors include intoxication of the expectant mother during pregnancy.
Right artery lesion
Hypoplasia of the right vertebral vessel is somewhat more common. Symptoms of hypoplasia of the right vertebral artery are similar to fatigue or malaise, the emotional background is unstable.
The right vessel in the spine is 2 times smaller than the left one, so if the lumen is narrowed, then the anomaly is not obvious.
The nutrition of the occipital region of the head is disrupted, so the emotional background will malfunction, and visual impairment is observed.
In rare cases, it affects the general condition of the patient, constant fainting, impaired coordination of movement, and dizziness after getting out of bed.
Hypoplasia of this side is dangerous because the resulting blood clot can block the lumen, which will lead to a stroke.
What is vertebral artery hypoplasia
The medical term itself refers to the underdevelopment of any organ or tissue.
With hypoplasia of the vertebral arteries, one of the vessels (rarely both) is underdeveloped, and their lumens are narrowed in a certain area. There are three forms of the disease:
- Hypoplasia of the right VA;
- The left vessel is underdeveloped;
- Bilateral hypoplasia of the vertebral artery is a development option when both arteries are deformed.
Location of the vertebral artery
Both arteries supply different parts of the brain and cervical part of the body, so each type of disease has its own characteristics.
Doctors have not decided on the exact causes of the congenital disease.
Left artery lesion
The disease is not easy to recognize in the early stages. It develops for several years and does not make itself felt. Impaired blood circulation provokes stagnation of blood in the cervical region, causing pain syndromes in the neck area. Sudden movements are accompanied by unpleasant sensations.
Damage to the left-sided aorta leads to abnormal blood pressure. Due to improper blood supply, the body changes, and the disease begins to gradually develop. The clinical picture of damage to the left transverse sinus occurs due to the immature left vertebral artery.
In mild cases, the problem cannot be noticed, only with the help of MRI images. At night there are severe headaches, nausea and even vomiting. There is a risk of having a heart attack or stroke.
It is more dangerous for health when the work of both the left and right arteries is disrupted. This leads to lifelong disability.
When the vertebral - basilar artery is affected
The right and left vertebral vessels, entering the cranium, are connected into a single artery. The main reason for the narrowing of its lumen is hypoplasia of the vertebral artery. It leads to the development of a serious disease ─ vertebral-basilar insufficiency. The pathology has serious consequences and threatens ischemic stroke. A thrombus that completely blocks an already narrow lumen leads to cessation of blood flow and stroke.
Hypoplasia of the vertebral artery usually develops against the background of cervical osteochondrosis. There is even a special term “Leaning Tower of Pisa syndrome”: it happens to tourists who sightsee with their heads thrown back. The posterior communicating artery is compressed and the person experiences symptoms:
- dizziness accompanied by nausea,
- numbness of hands and feet,
- seeing double,
- lack of coordination.
Treatment of narrowing of the vertebral vessels is carried out in the neurological department, because the disease in advanced cases is fatal.
Causes of pathology
The problem may begin to form in the womb. When planning pregnancy, it is recommended to study all the factors that influence the occurrence of hypoxia. Many factors can provoke hypoplasia of the right transverse sinus. Main reasons:
- bruises and injuries;
- ionization and radiation waves;
- genetic predisposition.
Cases have been recorded when changes appeared without clearly defined reasons. Experts could not explain this phenomenon. In adults, pathology can occur as a result of:
- osteochondrosis in acute or chronic form;
- dislocation of the vertebrae;
- overgrowth of the nape membrane with bone tissue;
- thrombosis;
- a strong blow to the head;
- spinal bruise;
- atherosclerosis.
Age-related changes provoke progression of the disease. Doctors often make incorrect diagnoses, since the disorder is influenced by many factors.
Causes of hypoplasia
Hypoplasia can affect any organ, but the causes of hypoplasia are usually standard.
Hypoplasia is most often congenital. The causes of underdevelopment of various parts of the body are very often alcohol or drug addiction of future parents. The use of certain medications that adversely affect the development of the fetus is of great importance for the development of pathologies.
In addition, various infectious diseases suffered during pregnancy often serve as a background for the defective development of various organs. Infection of the mother with rubella, viral diseases, cytomegaly, toxoplasmosis, polio and other infections often lead to underdevelopment of organs.
Hypoplasia can also be caused by man-made factors, such as ionizing radiation.
To endogenous causes, i.e. causing hypoplasia at the level of the primary embryonic development include oligohydramnios, fusion of the egg membranes with the surface of the fetus, neuroendocrine disorders and other anomalies.
How it develops
The disease appears as a result of a disorder in the structure of the aorta. Defects develop during embryonic maturation. Pontocerebellar hypoplasia occurs due to a lack of CDG (carbohydrate glycoprotein). This deviation is clearly visualized.
The pathology refers to an autosomal recessive disease. There is a delay in the child's development and obvious microcephaly.
The cervical vessels are responsible for supplying blood to the brain; they form a dense circle. If the lumen narrows, life-threatening diseases appear.
Even with minor damage, the cerebellum ceases to receive normal nutrition. The child’s fine motor skills suffer and handwriting cannot be developed. If the brain stem is damaged, facial expressions of the entire face are disrupted, and the swallowing process fails.
With the development of microcephaly, the patient loses weight and volume of the head. The development of internal elements changes and defects appear.
The convolutions lag behind in development and are not deep. The visual tubercle does not protrude and looks smaller. The trunk and pyramid of the oblong part are also much smaller, which affects the size of the skull.
During the process of growth, the facial part of the child grows quickly and the brain part of the skull grows more slowly. As a result, the deformation of the head can be seen with the naked eye.
Causes
The disease can be genetically determined or acquired in the early stages of development of the organism. At the same time, depending on the timing of the manifestation of the pathology, the list of its causes may vary.
Attention! Genetic hypoplasia is transmitted through a damaged gene on the sex X chromosome and is inherited as a dominant trait. In the case of the father's illness, it affects only daughters (100% of girls are born with hypoplasia, boys are healthy), and in the case of the mother's illness, it affects 50% of all children of both sexes.
In addition to heredity and spontaneous mutations, the main pathogenic factors for hypoplasia of primary teeth are disorders in the mother’s body and neonatal complications. Other factors:
- hormonal imbalances;
- viral infections (rubella, syphilis, toxoplasmosis, etc.);
- discrepancy between the Rh factor of the mother and the fetus - hemolytic disease of the newborn develops;
- severe toxicosis;
- alcohol abuse;
- irradiation - one-time or cumulative;
- lack of vitamins, micro- and macroelements;
- prematurity, asphyxia and birth injuries - due to the high risk of developing encephalopathies with disruption of the regulatory functions of the central nervous system.
The impact of these causes disrupts the formation of tooth germs or disrupts metabolism, which immediately affects the future of various dental structures, including enamel.
Attention! Pregnancy infections disrupt the formation of hard tissues of the fetus, including tooth enamel. Research confirms that severe cases of aplasia are more common in children whose mothers suffered from rubella, toxoplasmosis, “banal” ARVI or toxicosis during pregnancy. Moreover, statistics show that various manifestations of enamel hypoplasia occur today in every third child of preschool age.
Hypoplasia of the enamel of permanent teeth begins in childhood, starting from 5–6 months, and is often associated with metabolic disorders:
- Failures in the central nervous system disrupt the metabolism of essential minerals. The skeleton, including teeth, does not receive enough of the necessary elements to build its structure.
- Hormonal diseases - hypothyroidism and parathyroid insufficiency reduce the calcium and phosphorus content in bones, nails, and teeth.
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract - various types of dyspepsia and enzyme problems reduce the ability to absorb essential microelements.
- Hypovitaminosis, especially with a deficiency of vitamins D, C, E, affects the normal formation of the skeleton as a whole (up to rickets).
- Acute infectious diseases in the first years of life slow down mineral metabolism and inhibit the natural development of the body.
The condition of baby teeth also affects the condition of permanent teeth developing in their immediate vicinity. Chronic periodontitis or trauma due to unsuccessful removal with damage to the tooth germ can cause disruption of enamel formation.
Symptoms
Signs of hypoplasia are observed in older age, such as migraines, high blood pressure, drowsiness, psychological disorders and decreased sensitivity. The blood supply gradually returns to normal on its own. In such cases, the patient consults a doctor.
Possible symptoms:
- dizziness and pain;
- nerve dysfunction;
- disturbances of sensitivity, speech and motor apparatus;
- hallucinations.
Diagnostics
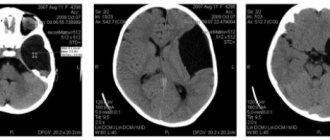
In order for the doctor to make a correct diagnosis, neurological examinations should be completed, the results of which determine the presence of the disease. The patient will need to consult a neurologist, therapist, cardiologist and ophthalmologist.
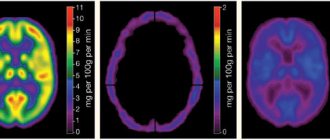
The doctor prescribes an MRI, then ultrasound scanning, Dopplerography and angiography. All methods will help determine the shape, size and structure of blood vessels. Experts also look at the state of the circulatory system.
The diagnosis is confirmed if:
- the internal lumen in diameter is less than 2 mm;
- blood flow moves at a speed of less than 40 ml/min;
- there is no stenosis.
As a result of the examination, patients observed:
- stroke anomaly in approximately 9% of cases;
- stenosis – 20%;
- deformation – 40%;
- extravascular compression 10%;
- blockage at 4%.
Basically, damage to the blood supply to the left side is diagnosed when a person experiences cardiovascular failure. Even if you regularly visit a specialist, it is impossible to notice the disorder.
Damage to the left side appears in adults, and symptoms should be closely monitored. The first sign is pain in the neck. Other symptoms may be absent and making an accurate diagnosis difficult.
About 25% of people have a disorder in the circulatory system, half of them can live their whole lives and not know about it. The initial stage of the pathology does not cause serious manifestations.
Who's at risk
People whose relatives have been diagnosed with cerebral hypoplasia are most susceptible to the disease. Children are at particular risk; the disease can appear in the womb.
In a relative risk group, people over 35 years of age have reduced immune defenses and are at risk of developing the disorder. In a man over 40 years of age, sperm may be genetically affected; a woman's body over 35 years of age does not recognize the changes.
Children with the disease may be born to a mother with chronic thyroid disorders or to a diabetic.
Right transverse sinus disease
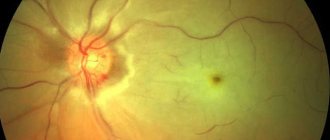
The right transverse sinus is a collector vein that connects the internal and external vessels of the brain. Reabsorption of cerebrospinal fluid from the cavities of the meninges takes place in them. From the transverse sinus, blood enters the jugular veins, which drain blood from the intracranial space. Hypoplasia of the right transverse sinus leads to a decrease in the lumen of the vein, which, in turn, is a threat of hemorrhagic cerebral infarction. Left transverse sinus disease Hypoplasia of the left transverse sinus causes vision complications. The left transverse sinus lies symmetrically to the right, located in the transverse groove of the cranium. If the outflow of blood is impaired, swelling of the optic nerve head is observed. The patient complains of headache, dizziness and fatigue, but it is the sharp drop in visual acuity that indicates that the patient has hypoplasia of the left transverse sinus.
Treatment methods
Treatment may be necessary if severe deformation occurs, patency is impaired and blood flow begins to flow poorly. The patient requires surgical treatment if there is a threat of ischemic stroke.
Drug treatment
Glycine tablets Phezam (capsules) Mexidol injections
Complex therapy is prescribed with the help of pharmacological drugs. They help blood circulation function normally, strengthen the walls of blood vessels, and stimulate metabolism in cells. Medicines prescribed by a specialist:
- nootropics;
- blood flow regulators;
- metabolism accelerators;
- vasodilators.
If the tissues are affected, the patient has severe hypoxia, then the following drugs are suitable: Actovegin, Reomacrodex.
Surgery
Surgery is necessary for people whose large aortas are damaged. The size and type of deformity is diagnosed, and then specialists decide whether surgery is necessary. The decision is influenced by the patient’s well-being and possible risks.
During the operation, deficiencies are corrected. After about 3 months, it is necessary to check the operated area. Doctors do this using the instrumental method.
Folk remedies
Recipes for folk remedies are used for symptomatic treatment at the initial stage of pathology.
In severe cases, traditional medicine methods do not bring the desired effect. For additional therapy that will improve immunity, you can prescribe decoctions or tinctures, lemon, olive oil and chamomile flowers help. Folk remedies have sedative, antihypertensive and vasodilating properties. Suitable:
- infusions and decoctions of rose hips and hawthorn;
- lemon balm and mint teas;
- extract of valerian, motherwort.