© Author: Ilya Vitalievich Soldatenkov, general practitioner, especially for SosudInfo.ru (about the authors)
Angiodystonia is a disorder of vascular tone caused by impaired adaptation of arteries and veins to changing conditions of the external and internal environment. As a result of inadequacy, insufficiency or redundancy of vascular function, regional or general blood flow is disrupted.
Angiodystonia is a syndrome of a number of pathologies characterized by a sudden transient change in the tone of blood vessels. Angiodystonia has different origins, localization, and pathogenesis. The disease affects individual vessels or the entire circulatory system. The main reason for this condition is negative changes in the structure of the vascular walls.
The disease is classified according to several principles:
- By origin - primary or neurogenic angiodystonia and secondary or symptomatic angiodystonia;
- According to the location of the focus - limited and systemic angiodystonia;
- According to the level of blood pressure - angiodystonia of the hypertensive, hypotensive or mixed type.
The diagnosis of angiodystonia is usually made in older people. In recent years, the disease has become “younger” and has become increasingly diagnosed in schoolchildren. In children, the pathology tends to heal quickly. In order to prevent the development of serious illnesses in a child in the future, it is necessary to consult a specialist when the first signs of angiodystonia appear.
Causes
Angiodystonia is a disease of a secondary nature that develops against the background of the underlying pathology. The cause of venous angiodystonia is a violation of the tone of the veins, and arterial angiodystonia is a violation of the tone of the arteries.
Angiodystonia develops against the background of the following pathologies:
- Endocrinopathy, hormonal imbalance;
- Infectious and inflammatory processes;
- Cardiopsychoneurosis;
- Somatic diseases;
- Traumatic brain injury;
- Sedentary lifestyle, excess body weight;
- Emotional stress, stress;
- Poisoning;
- Tuberculosis, syphilitic and herpetic infections;
- Emotional instability;
- Alcoholism, smoking, drug addiction;
- Varicose veins;
- Climax;
- Transitional age;
- Osteochondrosis, spondylosis;
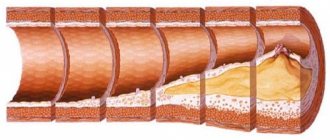
- Atherosclerosis.
The causes of angiodystonia in children are: birth trauma, toxicosis of pregnant women, maternal illness, protracted labor.
Under the control of neurohumoral regulation, arteries and veins expand and contract in a given situation. Vasodilation occurs after excessive stress on the muscles, brain and internal organs, due to which blood flow and oxygen supply increase to them. The venous system must respond to the entire process accordingly: through the veins, waste blood enters the lungs, where it is enriched with oxygen. The coordinated work of the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts of the autonomic nervous system ensures the correct response of blood vessels to external and internal factors.
If a malfunction occurs in the body, a spasm of the arteries occurs, the tone of the veins increases, the blood supply to the internal organs is disrupted, and oxygen deficiency develops.
Angiodystonia most often develops in people who sleep little and work a lot, sit up at night at the computer, and are often exposed to stress at work and at home.
Symptoms
Manifestations of angiodystonia are very diverse. The clinical picture of the pathology consists of several syndromes: asthenic, respiratory, angina, mental, neurogastric, cerebrovascular.
The main clinical signs of angiodystonia are:
- Hypertension or hypotension
- Dizziness,
- Dyspeptic symptoms
- Numbness of the limbs,
- Pain in the muscles of the neck and back, aches throughout the body,
- Cardialgia that occurs in attacks at rest and during physical activity;
- Tachycardia or bradycardia,
- Insomnia,
- Decreased concentration,
- Mnestic disorders,
- Impaired vision, smell, touch,
- Depressive state
- Dyspnea.
Headache is the main symptom of the pathology, occurring at any time of the day after physical activity or even at rest. The pain is concentrated in the temples or at the back of the head and varies from dull, pressing to intense, shooting. Against the background of a painful, debilitating headache, depression develops, reducing performance and knocking the patient out of the normal rhythm of life.
Characteristic symptoms of the pathology
With the described pathology, the following symptoms are observed:
- Headaches of an aching or “shooting” nature, which are localized in the back of the head, as well as in the temporal or parietal regions. Unpleasant sensations arise spontaneously, regardless of physical or emotional stress. Severe headache, which occurs with cerebral angiodystonia and causes decreased performance, is also called cephalgia;
- Insomnia or drowsiness;
- Dizziness;
- Arrhythmia;
- Pain in muscles, back;
- Numbness of the upper and lower extremities;
- Increased fatigue;
How to cure vascular diseases of the brain? Watch the video below for more details:
- Feelings of noise in the head;
- Presyncope and fainting;
- Pain in the heart area;
- Attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- Dyspnea;
- Emotional depression;
- Decreased concentration.
A child who suffers from cerebral angiodystonia experiences a decrease in appetite and physical activity, emotional instability, and a feeling of lack of air.
The main symptom of the pathology is cephalgic syndrome: severe headache causes depression and significantly reduces performance. In the most severe cases, depression is replaced by apathy or panic.
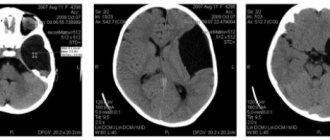
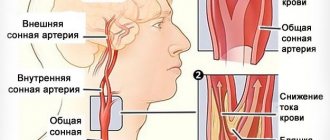
Angiodystonia of the brain
Cerebral angiodystonia is the most common and quite severe form of pathology, developing under the influence of endogenous or exogenous factors and usually occurring against the background of migraine, hypertension, congenital or acquired endocrinopathies, diseases of the digestive system, and allergic reactions.
Spasm of cerebral vessels leads to disruption of the trophism of brain centers and manifests itself as headache syndrome. When veins and venules expand, the outflow of blood from certain areas of the brain becomes difficult. Such processes contribute to the development of ischemia, hypoxia, and damage to brain neurons. After some time, the vascular wall returns to normal, and the general condition of the patients is completely restored.
There are 3 variants of the course of angiodystonia:
- According to the hypertensive type - spasm of the arteries is manifested by sudden attacks of headache, pulsation in the temples, cardialgia, arrhythmia, hypertension;
- Hypotonic type - dilation of the blood vessels of the head is manifested by a gradually increasing, dull headache localized in the occipital, parietal or temporal region, blurred vision, short-term memory loss, disability, fainting;
- According to the mixed type, angiodystonia manifests itself alternately with symptoms of the first two types.
Symptoms of cerebral angiodystonia:
- Fatigue,
- Dizziness,
- Noise in my head
- Throbbing, aching or dull pain in the temples and back of the head,
- Nausea,
- Vomit,
- Insomnia,
- Drowsiness,
- Presyncope,
- Weakness,
- Malfunctions of the endocrine system,
- Short-term memory lapses
- Pronounced changes in emotions - from prolonged feelings of depression, anxiety, fear to euphoria;
- Lack of control over your emotional state.
In severe cases, depression and irritability are replaced by apathy, anxiety, and panic. Without treatment, crises may develop.
If the above symptoms are detected, you should seek medical help, undergo a comprehensive diagnosis and begin treatment immediately. If headaches and other asthenic symptoms do not go away even after a long rest, encephalopathy may develop. At the same time, in patients, depression becomes chronic, consciousness is impaired, initiative disappears, and mood swings occur. It is extremely unacceptable to treat angiodystonia of cerebral vessels on your own at home.
During pregnancy
Management of pregnancy with such a disease should be more scrupulous. This pathology is an absolute indication for a cesarean section. If a woman decides to give birth on her own, such a load can cause severe dilation and rupture of the blood vessels of the fundus, after which the likelihood of vision loss increases significantly.
The specialist may allow a natural birth if the type and degree of the disease does not pose a threat to the health of the woman in labor. The decision on admission to independent delivery is made by an ophthalmologist.
Most medications cannot be prescribed during pregnancy. The exception is those medications that a woman is forced to take constantly. To maintain health, your doctor may recommend physical therapy. If the risk of deterioration in the pregnant woman’s well-being exceeds the risks to the fetus, taking the necessary medications is indicated.
As a rule, with a complicated medical history, a woman should visit the doctor much more often than the average woman in labor. This is necessary for disease control and early detection of deteriorating health.
Special prevention of angiopathy should be carried out for women during pregnancy. It is at this stage that the body is as weak and defenseless as possible, and the load on the vessels increases several times. Edema and late toxicosis can serve as a signal of violations. If such symptoms occur, you should seek immediate medical attention. Most often, a pregnant woman is hospitalized in a hospital for a course of treatment.
Retinal angiopathy during pregnancy is a common phenomenon that is encountered by both new and experienced mothers in the 2-3 trimester. Most often, the problem occurs during the 9th month of pregnancy. Vascular angiodystonia during pregnancy is usually a consequence of hypertension, atherosclerosis or diabetes mellitus.
Hypertensive angiopathy in a pregnant woman has the following characteristic differences:
- periodic narrowing of the arteries due to toxicosis;
- vascular sclerosis;
- circulatory disorders;
- rapid restoration of the visual system after childbirth.
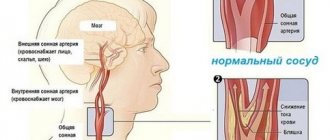
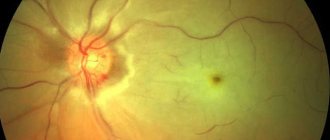
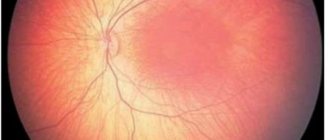
Angiodystonia of the retina
Angiodystonia of the retina is detected by ophthalmologists during ophthalmoscopy, which reveals hemorrhages, hematomas, overstretched veins, and vascular branching.
Patients' pupils become enlarged, the shine in their eyes increases, chills and a feeling of fear occur. Patients complain of decreased visual acuity, “flickering spots” before the eyes, pain and pain in the eyeballs, and a feeling of “sand” in the eyes. Trophic disturbances and tissue hypoxia lead to the progression of eye diseases, dystrophy, and complete loss of vision.
Angiodystonia of retinal vessels usually develops in individuals with hypertension or hypotension and neurotic disorders of varying severity. Retinal angiodystonia usually develops in both eyes at once.
Diagnostics
After listening to the patient’s complaints, collecting an anamnesis of life and illness, and a visual examination by a specialist, they move on to instrumental research methods. The most significant among them are:
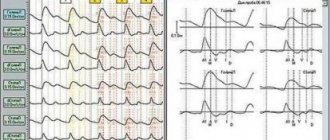
- Rheoencephalography is a non-invasive technique that involves examining the blood vessels of the brain using weak, high-frequency electrical impulses. This method allows you to determine the condition of the blood vessels of the brain.
- Ultrasound of peripheral vessels.
- Electrocardiography.
- Electroencephalography.
- Ophthalmoscopy, during which the doctor detects changes in the lumen of blood vessels, their narrowing, dilation, tortuosity, and plethora.
- Consultation with a psychiatrist or neurologist.
To exclude organic pathology, laboratory tests of blood and urine, ultrasound of the thoracic and abdominal organs, and examination of the stomach, intestines, and lungs are performed.
If the disease was detected in childhood, it can be completely cured. After establishing a reliable clinical picture of angiodystonia, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment and recommends, if necessary, lifestyle changes.
conclusions
Violation of the autonomic regulation of vascular tone in the brain is a common cause of neurological symptoms in people of all ages. Angiodystonic symptoms include headache, sleep disturbance, numbness, and autonomic disorders. Diagnosis is carried out taking into account complaints, examination by a neurologist and other specialists, as well as additional methods. Treatment is prescribed in accordance with the identified changes.
The following sources of information were used to prepare the material.
Treatment
Treatment of angiodystonia is complex, including elimination of the underlying disease and normalization of vascular tone. The treatment regimen is selected by the doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Physical therapy will help normalize vascular tone. To reduce and relieve the symptoms of the disease, patients are recommended to optimize their work and rest schedule, eat right, and fight bad habits.
Water procedures tone blood vessels: baths with aromatic oils relax, contrast showers stimulate. Patients with antidystonia are prescribed sanatorium treatment, massage, swimming, physiotherapeutic measures - electrophoresis, galvanization, magnetic therapy, reflexology.
Drug treatment of cerebral angiodystonia consists of prescribing the following groups of drugs to patients:
- Vasoactive substances - Clonidine, Methyldopa, Propranolol,
- Painkillers – “Pentalgin”, “Bral”, “Ketonal”,
- Sedatives - “Corvalol”, “Persen”, “Tenoten”, “Seduxen”, “Novo-Passit”,
- Sleeping pills - "Melaxen", "Donormil",
- Antihypertensive drugs – “Captopril”, “Bisoprolol”, “Tenorik”,
- For hypertension - “Eufillin”,
- Antidepressants - Amitriptyline, Flucosetine,
- Antiarrhythmic drugs – “Verapamil”, “Diltiazem”,
- Drugs that improve cerebral circulation - Piracetam, Pentoxifylline, Pantogam, Vinpocetine,
- Vitamins, antioxidants,
- Vascular eye drops for retinal angiodystonia - “Taufon”, Mildronate”, “Emoxipin”, eye vitamins in tablet form - “Lutein Complex”, “Anthocyan Forte”,
- Herbal remedies - herbal mixtures of mint, lemon balm, valerian, motherwort for a tendency to hypertension, lemongrass and echinacea for hypotension.
Cerebral angiodystonia: consequences of the development of the disorder
Angiodystonia does not appear as an independent disorder in the functioning of cerebral vessels. It “accompanies” existing diseases.
It is not at all necessary that it will be associated with brain activity, the nervous system or the psychological characteristics of a person. Sometimes the mechanism of development of cerebral angiodystonia is triggered due to the fact that:
- there are disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract;
- allergic reactions;
- overwork and stressful situations;
- hormonal disruptions or changes (relevant during adolescence and menopause).
The disease does not develop immediately, so not every person can understand in a timely manner that violations are occurring.
In order to better understand the causes of the disease, you should know that a disorder in the blood vessels is divided into primary and symptomatic (a response to another disorder in the body).
It is also important to remember that the disease also develops under the influence of external unfavorable circumstances, among which in the first place is poor nutrition, as well as constant stress on the nervous system. If these factors exist, then it is best to get examined by a doctor.
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- disruptions in the autonomic nervous system;
- amyloidosis;
- various types of gastrointestinal disorders;
- diseases and disorders of the central nervous system;
- pancreatitis;
- concussions of varying severity;
- physical inactivity;
- varicose veins;
- Addison's disease;
- increased ICP;
- presence of bad habits (especially long-term smoking);
- increased irritability;
- impressionability;
- age-related features (hormonal imbalance).
Cerebral angiodystonia can occur in several types:
- for hypertensive;
- according to hypotonic;
- according to mixed.
More details about each type of angiodystonia:
- When vascular spasm occurs, a person may experience attacks of sharp and sudden pain. A characteristic feature of the hypertensive type is pulsation in the temples, pain in the heart, the presence of arrhythmia and hypertension.
- The hypotonic type is caused by vasodilation, which leads to migraines and fainting. Loss of strength also occurs, a person loses the ability to perform any type of work - physical or mental. Memory loss (short-term) is sometimes possible.
- The mixed form differs in that its manifestations may coincide with the first two types. At this time, a person may experience a decrease in hearing and vision acuity, and a decrease in sense of smell. The patient also loses the ability to perceive new or complex information. Pain in the back and joints appears.
It is important to remember that pain with any type of disease can occur at any time of the day. This factor is not influenced by fatigue, overwork or emotional stress. Main area of pain:
- whiskey;
- parietal region;
- forehead.
Signs of cerebral angiodystonia syndrome are varied in their manifestations. The main ones are severe, sometimes unbearable pain.
They can occur both during the day and at night, when a person is calm. Symptoms of the syndrome also include:
- dizziness (may occur several times a day);
- sleep disturbance (insomnia, light sleep);
- pressure changes;
- heaviness in the head;
- noise in ears;
- weakening of memory and attention;
- hearing and vision impairment.
Specialists are also able to identify such unpleasant and serious symptoms as:
- vasoconstriction (manifested in varying degrees of severity);
- depletion and weakening of blood flow;
- displacement of veins or arteries.
That is why it is very important to begin the process of diagnosis and therapeutic therapy in a timely manner.
Diagnosis of the disease
As soon as a person discovers symptoms associated with angiodystonia, it is necessary to immediately contact a specialist so that he can carry out all the necessary diagnostic measures. There are several methods and methods for determining a violation, so the likelihood of error is minimized.
So one of the techniques is rheoencephalography - a procedure that involves examining the blood vessels of the brain.
The doctor monitors changes in resistance values in tissues when they are exposed to electrical impulses of high frequency, but weak in impact. By comparing the data obtained, the specialist can use objective and complete information about the state of health at the time of the study.
Monitoring allows you to determine the following vascular conditions:
- tone;
- reactivity;
- elasticity of the walls of blood vessels;
- the amount of hematopoiesis produced.
Also used in the diagnosis of angiodystonia:
- ultrasound examination (arterial and peripheral vessels are diagnosed);
- studies of ischemic changes occurring in the heart (myocardium, for this purpose an ECG device is used).
It is also necessary to distinguish between the symptoms of this disease and existing signs of nervous disorders and changes.
Treatment of the disease
Based on the diagnostic data obtained, the doctor prescribes therapeutic therapy. It is based, first of all, on normalizing vascular tone indicators. Timely and properly selected treatment will not only relieve symptoms, but also cure the source of cerebral angiodystonia.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with What is cerebral palsy?
It is important to choose the right mode that suits your biorhythms, which will allow you to work and rest for the optimal amount of time. We should not forget about proper nutrition, which is why the treatment program includes a diet compiled by a professional specialist in this field.
The healing process will be accelerated if you do not forget about walking and giving up bad habits (if you had them before the onset of the disease). An individual rehabilitation program is often developed.
The most effective medications will be the following:
- Clonidine, Methyldopa, Propranolol are vasoactive agents;
- Pentalgin, Bral, Ketonal - provide good relief from pain;
- Corvalol, Persen, Tenoten, Afobazol, Seduxen, Novo-Passit - sedatives;
- Melaxen, Donormil - help to sleep peacefully and fully;
- Captopril, Bisoprolol, Tenorik - are prescribed as good antihypertensive drugs;
- Eufillin - if hypertension is noted;
- Amitriptyline, Fluoxetine are effective remedies for depression;
- Verapamil, Diltiazem - relieve arrhythmia;
- Piracetam, Pentoxifylline, Pantogam, Vinpocetine - improve the flow of blood into the brain and regulate blood circulation.
You should also use vitamins and antioxidants to generally strengthen the body. All drug dosages are calculated by a specialist.
Advice from the people
Traditional methods of treatment can be used as preventative measures, as well as in combination with basic (medicinal) therapy prescribed by a doctor. The main bias is towards sedatives, since it is necessary to relieve nervous tension, which contributes to the development of tone.
Recommended:
- daily walks in the fresh air;
- tinctures of knotweed, valerian or motherwort;
- physical training;
- walking (from 2 to 5 km);
- warm relaxing baths (2-3 times a week);
- sleep (at least 8 hours) daytime rest (40-60 minutes).
If you do not take any measures to treat vascular angiodystonia, then a number of dangerous ailments may develop against its background.
This can lead to the development of encephalopathy, a brain disease of a vascular nature. Its main features:
- depression;
- dizziness;
- memory impairment.
Fatigue increases, mood swings are noted. In order to prevent the onset of the disease or its complications, timely prevention is required.
The most effective way to stay healthy is to lead a healthy lifestyle. Rest, moderate physical and emotional stress, sports - all this will help a person get rid of the negative manifestations of increased vascular tone in the brain.
Cerebral angiodystonia can develop both as a result of various disorders in the body (internal factors) and due to the influence of external factors (for example, stressful situations, eating heavy foods).
Cerebral angiodystonia requires careful diagnosis. In cases of lack of adequate treatment against the background of angiodystonia, encephalopathy, a non-inflammatory brain disease, may develop. Encephalopathy against the background of cerebral angiodystonia is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Chronic depression;
- Frequent headaches due to stress, fatigue;
- Disorders of consciousness, memory;
- Dizziness;
- Lack of initiative.
Concomitant symptoms may also include increased fatigue, mood swings, heaviness in the head, sleep disturbance and other signs inherent in angiodystonia.
If angiodystonia is suspected, a comprehensive examination is necessary. The main methods for diagnosing angiodystonia are non-invasive techniques, one of which is rheoencephalography - a study of cerebral vessels based on monitoring changes in tissue resistance values when exposed to weak high-frequency electrical impulses.
The following methods are also used in the diagnosis of angiodystonia:
- Ultrasound examination of arterial and peripheral vessels;
- Screening for ischemic changes in the myocardium using ECG.
Also, if angiodystonia is suspected, it is necessary to differentiate symptoms from signs of psychosomatic diseases.
Prevention
Preventive measures for angiodystonia include:
- Maintaining proper rest and sleep patterns
- Proper nutrition,
- Normalization of weight,
- Sports activities,
- Stabilization of the nervous system,
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle,
- Hiking,
- Regularly undergoing prescribed tests,
- The use of herbal tinctures with a moderate calming effect.
Thus, angiodystonia does not pose a great threat to human health, but significantly reduces the quality of life.