Reasons for development
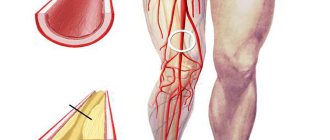
Diabetic gangrene of the lower extremities is the death of tissues and cells due to metabolic disorders. The risk of developing the disease increases if there is an increase in blood sugar levels over a long period.
Gangrene in diabetes mellitus develops due to the influence of the following factors:
- non-compliance with prescribed treatment;
- bad habits;
- wearing narrow and uncomfortable shoes out of season;
- neglected condition after minor damage to the skin caused by infection;
- obesity;
- influence of temperature changes;
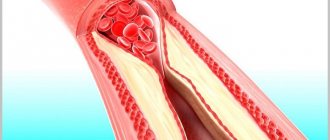
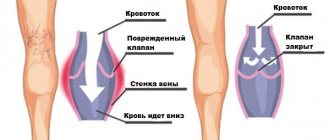
- ischemia, atherosclerosis - with such diseases, blockage or narrowing of small vessels occurs, which leads to oxygen starvation;
- change in regeneration processes;
- decreased immune defense;
- polyneuropathy.
The first signs of gangrene in diabetes
Patients with diabetes have a significantly lower threshold for sensitivity to pain; they do not immediately pay attention to discomfort in the foot area - cuts, abrasions, calluses, cracks. Gradually, a sluggish inflammation occurs, caused by the penetration of infection into the wounds, and an ulcer forms. Further, the process can develop rapidly, and the patient develops diabetic gangrene.
Several signs that should alert a patient with diabetes:
- Constantly felt fatigue in the legs;
- Tingling in the feet;
- Numbness of the legs;
- Pain in the leg muscles;
- The color of the foot has changed - it has become bluish or red;
- The foot is cold to the touch.
Detection of such phenomena indicates disorders of peripheral circulation.
What a diabetic should pay attention to so as not to miss the onset of gangrene:
- Constant pain in the legs;
- Dark skin in the affected area (purple or black);
- Copious purulent discharge in the affected area (not always);
- Pulsation in the limb is not palpable;
- High temperature, chills, nausea.
If you notice the above symptoms, you should consult a doctor and undergo a thorough examination.
Forms of the disease
Gangrene is usually divided according to the accompanying factors:
- damage to the nerve fiber (neuropathic);
- vascular changes (angiopathic);
- destruction of bone tissue (osteopathic).
There are also two forms of pathology - we will consider them below.
Dry gangrene
The degenerative process begins gradually with an itching or burning sensation in the toes and can last for several years. Over time, the sensitivity of the skin decreases, convulsive muscle twitching occurs, and intense pain appears, sometimes going away on its own.
The difference between the source of the disease and healthy integument is visible visually: the affected area peels off, and the process of mummification is observed. There are no unpleasant odors.
The general condition of the patient often does not worsen, since the disease resolves without an infectious process. In most cases of diabetes, dry gangrene affects the toes.
The pathology does not harm the functional state of a person’s internal organs, but one of the treatment methods is amputation of part of the foot.
Wet gangrene
A dangerous type of complication that threatens the life of a diabetic. The disease has an abrupt onset and pronounced symptoms.
The affected limb increases in size, swells, becomes greenish or purple in color, and the skin becomes covered with small blisters. The area of necrosis quickly grows, drawing bones and muscle tissue into the process. A strong unpleasant odor emanates from the feet.
When palpating the affected area, crepitus is felt due to the filling of the subcutaneous tissue with hydrogen sulfide. The patient's general condition deteriorates sharply, and symptoms of intoxication appear.
The wet type of gangrene of the leg in diabetes mellitus requires urgent amputation of the limb to save the patient’s life.
Why do trophic ulcers appear on the legs with diabetes and how to treat them
- About ulcers in diabetes
- About symptoms
- About treatment
- About prevention
With a disease such as diabetes, the human body as a whole needs special attention, and adequate treatment in particular is no less necessary. The lower extremities require especially careful care, since blood flow to them is weakened. As a result, diabetic ulcers often form in the legs. What it is, what are the symptoms and methods of treating this manifestation are discussed further in the text.
About ulcers in diabetes
According to statistical studies, trophic type ulcers in diabetes mellitus account for no more than 3% of the total number of ulcers. This may not seem like much, but up to 80% of diabetics face problems not only with small vessels, but also with nerve endings. Therefore, their treatment is necessary and not only in the legs. Sometimes a minimal injury to the skin of the foot is more than enough for it to transform into a slowly healing wound, or, in fact, a trophic ulcer. For what reasons does this happen? The explanation for this phenomenon is quite simple - with long-term diabetes mellitus, complications occur such as:
- angiopathy (exclusively small vessels are affected);
- neuropathy, which involves damage to small nerve endings in the legs.
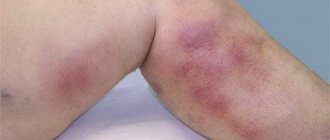
All this becomes a catalyst for disruption of the integrity and condition of tissues, as well as the formation of a diabetic foot. This pathological condition also provokes the formation of not just trophic ulcers, but also gangrene - as can be seen in the photo. Healing them and restoring the skin of the feet becomes possible, not least thanks to competent care, which speeds up treatment.
About symptoms
In the vast majority of cases, ulcers in diabetes mellitus are formed on the phalanges in the area of the nail and toes. In much rarer cases, it occurs on the heels. Their formation is largely facilitated by such manifestations as corns and microscopic injuries received while wearing uncomfortable shoes.
They can also be the unfortunate result of an unprofessional pedicure, foot burn, abrasion and much more.
As a result, even such minor mechanical damage does not heal for several weeks. Over time, they become much larger in size and deepen, becoming precisely a trophic ulcer in the legs, the treatment of which is necessary as soon as possible. The characteristics and differences of such ulcers in the case of diabetes mellitus are as follows:
- Even with small ulcers, quite noticeable pain can be observed, which tends to intensify at night. However, the completely opposite state is also possible. It finds the following expression: with a trophic ulcer with obvious diabetic polyneuropathy, there may be no painful sensations. This occurs even with significant and fairly deep ulcers. However, both of these types are distinctive characteristics of trophic ulcers in the legs, the treatment of which is recommended to begin as soon as possible;
- never heals on its own and even with the use of medications it will take a very long time;
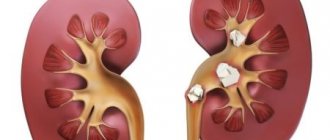
- Such ulcers in diabetics can become deeper and turn into gangrene, which will require amputation.
In this regard, preventive measures and treatment of presenting ulcers in diabetics are extremely important. They should be carried out as soon as possible after their discovery, as well as diabetes mellitus.
Diagnostics
Identification of a pathological process consists of several stages:
- visual examination of the skin of a diabetic’s leg, palpation of the foot, the affected area;
- bacteriological culture of wound surfaces;
- analysis for sugar level, biochemistry, OAC with formula. Determination of urea, creatine, ESR in blood;
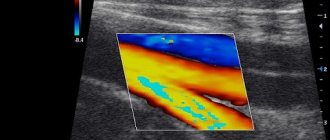
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the lower extremities, assessment of blood flow velocity;
- neurological examinations;
- MRI and radiography as indicated.
Treatment methods
There are several methods of treating gangrene.
No amputation
The measures are aimed at reducing blood sugar, taking antibiotics with a wide range of effects, and using vitamin complexes.
During therapy, it is important to reduce the load on the legs (even to bed rest), monitor personal hygiene and not overcool the feet.
It is advisable to use physiotherapeutic procedures aimed at removing dead tissue cells and increasing regenerative processes.
Therapeutic gymnastics helps during the rehabilitation process to restore normal blood flow in the leg and prevent muscle atrophy.
Surgical method
Surgical intervention is prescribed in cases of rapid spread of the pathological process and severe intoxication of the body.
Treatment options include:
- limb amputation;
- local treatment of the wound surface;
- dressing the affected area;
Operations to normalize blood flow:
- Prosthetics – characterized by the restoration of blood circulation using a prosthesis that is installed in the vessel. Cell nutrition is normalized, which leads to healing of ulcers and eliminates the recurrence of gangrene.
- Shunting. The method is aimed at ensuring that blood can flow to the tissues through special shunts formed from the tissues of another vessel.
- Endovascular method. The operation involves inserting a catheter with a balloon, which moves through the vessel and expands it. A stent is installed to prevent relapse.
The main goal of therapy is to transform wet gangrene into dry gangrene, which avoids amputation of part of the leg.
Concomitant treatment
Sometimes the gangrenous process can be stopped with a course of fasting. This alternative must be strictly under the supervision of a specialist and has a number of contraindications.
Simple tips for treating gangrene of the lower extremities
- During the treatment of gangrene, you should not eat salty, fatty, or smoked foods.
- Avoid constipation - the intestines should be cleansed daily.
Remember that gangrene is a very dangerous disease that can lead to serious complications. When deciding which treatment methods to give preference to (traditional or folk medicine), evaluate all possible consequences. In any case, you should definitely see a doctor.
How to prevent gangrene from developing
Prevention of complications is carried out using simple preventive measures:
- normalization of blood glucose levels;
- regularly undergoing the necessary examinations and consulting a specialist in the presence of the first symptoms;
- careful adherence to the rules of personal hygiene - treat your feet with antibacterial soap, use moisturizing creams;
- therapeutic exercises to restore blood flow to the lower extremities;
- compliance with the prescribed diet and therapy;
- conduct evening self-massage sessions for 10 minutes after a hard day at work;
- give your legs an elevated position more often to reduce pastosity;
- getting rid of bad habits;
- keep your feet warm and choose comfortable shoes;
- timely treatment of minor abrasions, calluses and wounds;
- frequent walks in the fresh air, swimming.
Folk remedies for the treatment of gangrene of the lower extremities
Various traditional methods of treatment are used for gangrene on the legs. You can combine or alternate some of them so that the result pleases you faster.
Means for oral administration
The disease can be affected from the inside - for this you need to prepare a decoction. The use of pine tincture shows good results. Grind young needles of any coniferous tree (they should not exceed 1 cm in length). You can dry them and store them in a paper bag, or you can use them fresh. Soak the pine needles (about 5 tbsp) in a liter of water, add a little onion peel and rose hips (1 tbsp is enough). Bring the product to a boil, keep on fire for 6 minutes. Let it brew for 8 hours. Filter and use instead of water throughout the day. You can take up to 600 ml per day.
Ointments and compresses for gangrene
- Multicomponent ointment. Combine rosin, unsalted lard, honey, laundry soap, sunflower oil (50 g of each component). Boil the mixture. When the mixture has cooled, add finely chopped aloe, onion and garlic (50 g each). Mix thoroughly. Before use, warm the ointment in a water bath and apply warm to the affected areas.
- Rye bread. Salt fresh rye bread well and chew it thoroughly. Make a compress from the resulting mass on the sore spots. If you grind the components in another way, the effect will not work. It is important that the bread and salt react with saliva