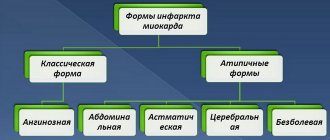
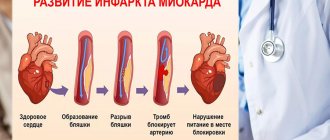
The ability of the myocardium to contract (inotropic function) ensures the main purpose of the heart - pumping blood. It is maintained due to normal metabolic processes in the myocardium, sufficient supply of nutrients and oxygen. If one of these links fails or the nervous, hormonal regulation of contractions and the conduction of electrical impulses are disrupted, then contractility decreases, leading to heart failure.
Physiological patterns
The level of pressure in the arterial bed is determined by the tone of the vessels, their ability to create resistance to blood flow, as well as the force of myocardial contraction.
Heart rate reflects the function of automatism (generation of impulses) of the conduction system, the speed of impulse propagation and contractility.
The regulation of cardiac activity and arterial condition is mediated by effects on alpha and beta adrenergic receptors. Stimulation of the 1st subgroup leads to vasoconstriction with a corresponding increase in pressure. 1-receptors are located in the nodes where impulses are formed that determine the rhythm of heart contractions.
These receptor molecules are also responsible for vascular tone and the force of contraction of cardiomyocyte layers. By influencing similar structures scattered throughout the cardiovascular system, as well as receptors of other compounds (NO, acetylcholine, etc.), mediator and endocrine regulation of heart function occurs.
Vegetative influence
With active stimulation of the vagus, a decrease in the frequency and strength of heart contractions occurs. However, with a decrease in its activity, opposite effects develop.
The phenomenon is caused by constant sympathetic impulses and the action of catecholamines on the adrenal receptors of the organ.
Variation in the relationship between the activity of the vagus and the sympathoadrenal component of the autonomic system normally leads to changes in heart rhythm, as well as in the strength of myocardial contractions.
The functioning of the cardiovascular system (CVS) is influenced not only by catecholamines (adrenaline and norepinephrine), but also by other endogenous biologically active compounds.
There is a connection between pulse and blood pressure with hormonal levels:
| Hormones and mediators | Impact on cardiovascular system |
| Glucagon | Increase in heart rate |
| Thyroid derivatives (T3, T4) | |
| Angiotensin II | |
| Serotonin | |
| Prostaglandins | Acceleration of heart rate, increasing the force of contractions by improving blood flow in the heart’s own vessels, normalizing metabolism in the myocardium |
| Kinins | Helps increase heart rate and systolic output through stimulation of the sympathetic-adrenal system |
| Calcium | Participates in the contraction of smooth muscles, accordingly maintains vascular tone (increased pressure) |
| Potassium | Reduces heart rate and its strength |
The question of whether blood pressure depends on the pulse is quite difficult. Since norepinephrine/adrenaline are universal stimulants of the receptors of the sympathetic system, the increase in vital signs under the influence of catecholamines occurs simultaneously.
There are no direct indications of a possible relationship between blood pressure and pulse.
Causes and treatment of changes in blood pressure that do not coincide with heart rate
28.08.2019
Both pulse and blood pressure (BP) are important indicators of overall health. It is these values that are determined in the patient during the initial visit to the therapist.
They help to identify the degree of dysfunction of the cardiovascular system and the level of quality of cellular nutrition.
If the heart rhythm and its contractility are disturbed, the load on the arteries and vessels increases, as a result of which heart diseases subsequently develop and the general condition of the patient worsens.
Bradycardia often occurs due to high blood pressure
Bradycardia is often observed in people prone to hypertension. You should find out from a specialist how to raise your pulse with high blood pressure. You should not take special medications without the recommendation of a therapist.
The concept of pulse and blood pressure
Blood pressure shows the degree of blood pressure in the arterial system. To determine the state of functioning of the body, two values are important:
- Systolic. Measured at maximum contraction of the heart muscle.
- Diastolic. Shows pressure during the period of maximum relaxation of the myocardium.
With high blood pressure values, determined using a special device - a tonometer, a person must take certain measures, since the risk of strokes and heart attacks, the appearance of chronic heart dysfunction and other diseases of the vascular system significantly increases.
The normal blood pressure is 120/80
The optimal blood pressure reading is considered to be 120/80. When they increase above 140/90, observed over a long period, the doctor diagnoses “hypertension”.
Do not forget that a slight increase in values during physical activity is the norm and is considered an acceptable reaction of the body. It is very important to measure your blood pressure at rest.
It is important to remember that blood pressure levels may increase after drinking caffeinated drinks and smoking.
The flow of blood through the arteries is uneven. Its movement occurs in impulses, which are provided by contractions of the heart muscle. The pulse can be determined by pressing the thumb against the radial artery located in the wrist. Modern tonometers show all the necessary values at once.
A weak pulse and low blood pressure can indicate various diseases associated with both blood disease and dysfunction of certain organs.
Such indicators are often observed with reduced thyroid function. Some people have normal blood pressure but exhibit bradycardia.
The question of how to raise the pulse without raising blood pressure is decided by a specialist after a complete examination of the patient.
Pulse and blood pressure are inextricably linked
Relationship between blood pressure and heart rate
Heart rate (HR) should always be measured at rest. This indicator, as well as blood pressure values, normally increases during physical activity.
The relationship between pulse and blood pressure is explained as follows: with an increase in blood pressure, intracranial pressure increases, which leads to activation of the vagus nerve and provoking bradycardia.
Pulse for hypertension
Hypertension is rarely accompanied by bradycardia, a state of the body in which the heart rate does not exceed 50 beats/min. The most common causes of a low pulse are pathologies such as:
- cardiosclerosis and myocarditis;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- infectious diseases;
- dysfunction in the endocrine system;
- hypovitaminosis;
- blood diseases.
Low heart rate may be caused by cardiosclerosis
Heart problems and bradycardia can be caused by long-term use of certain medications, atherosclerosis, and the presence of scars after heart attacks.
Prolonged stress conditions accompanied by nervous breakdowns and intracranial hypertension also play a certain role in reducing heart rate. Physiological reasons can also influence the weakening of the pulse.
Thus, bradycardia can appear when a person moves from heat to cold.
In cases where such phenomena occur rarely and are accompanied by mild symptoms, there is no need to worry. But with severe bradycardia, in which the heart rate is less than 40 beats/min, starvation of brain cells occurs, which is dangerous for the development of irreversible changes in the vascular system. A decrease in heart rate due to hypertension in older people sometimes leads to a heart attack or stroke.
It is important to know how to increase your heart rate without increasing your blood pressure. Most often, specialists prescribe medications belonging to the group of ACE inhibitors to hypertensive patients with symptoms of bradycardia.
Such drugs act smoothly and sparingly. Strong antihypertensive drugs are contraindicated in this case, as they can cause loss of consciousness and respiratory arrest.
Beta blockers are also dangerous for these patients.
A common symptom of high blood pressure is tachycardia.
Hypertensive patients often suffer from tachycardia. This condition is also dangerous because the load on the heart increases significantly.
The reasons for a sharp increase in blood pressure and pulse most often lie in excessive physical exertion, disruptions in the endocrine system, and serious stress.
In this case, general weakness, severe headaches, redness of the skin, dizziness, and difficulty breathing may occur. If this condition occurs, you should seek medical help.
If you are prone to bradycardia and hypertension, the patient should definitely ask the therapist how to increase the pulse without increasing the blood pressure.
Pulse with hypotension
There is no need to worry if blood pressure is slightly reduced and heart rate is normal. As a rule, a person with this condition most often feels stable and does not even realize the presence of hypotension.
With low blood pressure and bradycardia, nausea and weakness may occur
In some cases, low blood pressure is diagnosed due to bradycardia. In this case, the patient complains of dizziness, nausea, weakness, fatigue, depression, and chills. The doctor will definitely tell you what to do if you have low blood pressure and a low pulse after examination and a full examination.
Hypotension is often accompanied by tachycardia. Typically, patients note the appearance of nausea, anxiety, migraines, and sweating. Pain in the chest area may occur. To identify the cause of increased heart rate and hypotension, you should undergo an examination.
Sometimes patients with vegetative-vascular dystonia experience sudden changes in blood pressure. In this case, it is necessary to observe what the pulse is like at high blood pressure.
The causes of low blood pressure and low pulse are most often the same as with hypotension accompanied by tachycardia:
- diseases of endocrine organs;
Anemia may be one of the causes of hypotension
- diseases of the nervous system;
- respiratory type of arrhythmia;
- anemia;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- serious blood loss;
- infectious diseases;
- heart damage.
If you are prone to low blood pressure, it is recommended to take courses of Eleutherococcus tinctures, drink green tea and coffee daily. If the cause of this condition is identified, the patient is prescribed medication.
What is arrhythmia
Blood pressure and pulse may decrease or increase in patients with cardiac arrhythmia, in which its rhythm and regularity of contractions are disrupted. A similar condition is detected in patients with heart attacks, dysfunctions of the nervous system, and intoxications. Arrhythmia does not always occur in sick people.
Heart rhythm disturbances can occur with severe fatigue or excessive physical exertion. However, the symptoms of this phenomenon often go unnoticed. Arrhythmia is not always associated with disorders in the heart itself.
It can occur with hyperthyroidism (thyroid disease) and some other diseases.
Blood pressure problems are often observed in patients with arrhythmia
Irregular heart rhythm is accompanied by a rare, rapid or irregular pulse. With reduced thyroid function, increased intracranial pressure, and certain types of infections, sinus bradycardia may be observed. With atherosclerosis and intoxication conditions, premature heart contractions (extrasystoles) may occur.
Arrhythmia accompanied by ventricular tachycardia occurs not only in older people. This phenomenon is sometimes observed at a young age, when the right ventricle of the heart undergoes structural changes.
The danger of arrhythmia lies in the increased likelihood of its transformation into atrial fibrillation, which is more dangerous for the patient. In this case, contractions of the ventricles occur defectively, which leads to disruption of the blood supply to the brain and other body systems.
See your doctor so he can confirm that you have an arrhythmia.
If signs of arrhythmia appear, you should consult a doctor. You can monitor and determine the dependence of pulse on pressure using automatic tonometer devices. All patients suffering from blood pressure disorders must have such devices for home use.
Blood pressure and pulse in children
Blood pressure levels and heart rate in children of different ages vary significantly. If in one-year-old babies blood pressure should not exceed 90/50, then in children over two years old it is normally 100/60. In adolescents, blood pressure values reach the adult norm – 120/80.
Heart rate also changes depending on age. Thus, newborns have a pulse from 120 to 160 beats/min. In two-year-old children, the indicator should not exceed 150. Normally, in children 7-8 years old, the heart rate is on average 97, in adolescents - 70 beats/min.
Children should also have their blood pressure and pulse checked.
Experts advise measuring blood pressure and pulse in children regularly. If deviations from normal values are detected, you should definitely show the child to the pediatrician. In children, it is easiest to determine the pulse in the cervical area in the area of the carotid artery. In older children, you can calculate your heart rate by placing your thumb on your wrist.
There is no need to worry if you notice an increase or decrease in heart rate once.
Observation must be carried out within a week. It is important to remember that the reliability of the data will be higher if the child is at rest. You should not determine your heart rate after eating, in the cold, in a hot room, or after physical activity.
Tachycardia, as well as increased blood pressure in children, occurs with a viral infection, emotional overload, anemia, malfunction of the endocrine organs, respiratory system, and impaired cardiac function. After treatment, such disorders usually disappear.
If your child complains of dizziness and weakness, be sure to show him or her to the doctor.
It is necessary to measure blood pressure and heart rate for some time if the child develops weakness, fatigue, dizziness, or pale skin.
You should undergo an examination if your baby shows signs of bradycardia or hypotension. Such signs can be observed with hypothyroidism, anemia, infectious disease, and parasitic infestations.
It is important to remember that the danger of chronic bradycardia lies in the development of heart failure.
Source:
Heart rate and blood pressure
- The pulse rate, along with the tonometer readings, are important values that allow us to evaluate the functioning of the body, in particular the heart muscle.
- In medical practice, heart rate and blood pressure have a direct relationship with each other.
- Accordingly, the dependence of the pulse on blood pressure makes it possible to determine the quality of nutrition of the body’s cells and prevent the development of possible pathological processes in general.
Source: https://dp3.ru/serdtse/prichiny-i-lechenie-izmenenij-ad-ne-sovpadayushhih-s-chastotoj-pulsa.html
Physiological patterns
The level of pressure in the arterial bed is determined by the tone of the vessels, their ability to create resistance to blood flow, as well as the force of myocardial contraction.
Heart rate reflects the function of automatism (generation of impulses) of the conduction system, the speed of impulse propagation and contractility.
The regulation of cardiac activity and arterial condition is mediated by effects on alpha and beta adrenergic receptors. Stimulation of the 1st subgroup leads to vasoconstriction with a corresponding increase in pressure. 1-receptors are located in the nodes where impulses are formed that determine the rhythm of heart contractions.
These receptor molecules are also responsible for vascular tone and the force of contraction of cardiomyocyte layers. By influencing similar structures scattered throughout the cardiovascular system, as well as receptors of other compounds (NO, acetylcholine, etc.), mediator and endocrine regulation of heart function occurs.
Vegetative influence
With active stimulation of the vagus, a decrease in the frequency and strength of heart contractions occurs. However, with a decrease in its activity, opposite effects develop.
The phenomenon is caused by constant sympathetic impulses and the action of catecholamines on the adrenal receptors of the organ.
Variation in the relationship between the activity of the vagus and the sympathoadrenal component of the autonomic system normally leads to changes in heart rhythm, as well as in the strength of myocardial contractions.
The functioning of the cardiovascular system (CVS) is influenced not only by catecholamines (adrenaline and norepinephrine), but also by other endogenous biologically active compounds.
There is a connection between pulse and blood pressure with hormonal levels:
| Hormones and mediators | Impact on cardiovascular system |
| Glucagon | Increase in heart rate |
| Thyroid derivatives (T3, T4) | |
| Angiotensin II | |
| Serotonin | |
| Prostaglandins | Acceleration of heart rate, increasing the force of contractions by improving blood flow in the heart’s own vessels, normalizing metabolism in the myocardium |
| Kinins | Helps increase heart rate and systolic output through stimulation of the sympathetic-adrenal system |
| Calcium | Participates in the contraction of smooth muscles, accordingly maintains vascular tone (increased pressure) |
| Potassium | Reduces heart rate and its strength |
The question of whether blood pressure depends on the pulse is quite difficult. Since norepinephrine/adrenaline are universal stimulants of the receptors of the sympathetic system, the increase in vital signs under the influence of catecholamines occurs simultaneously.
There are no direct indications of a possible relationship between blood pressure and pulse.
Reflex patterns
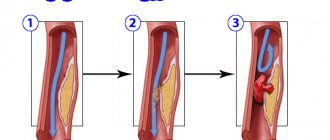
The study of the circulatory system at the time of the formation of physiology revealed how the pulse depends on the pressure in large venous vessels. At the end of the 19th century, it was established that stretching the veins with a large volume of blood provokes an increase in heart rate. The effect is aimed at unloading the right parts of the heart and normalizing the blood supply to the body.
Human circulatory system
The appearance of tachycardia is typical for untrained individuals when performing increased physical activity.
Thanks to this property, it is possible to cover unusual energy and oxygen costs during intense physical activity.
In athletes, due to constant training, the cardiomyocytes themselves undergo restructuring: the heart muscle thickens (“increases” its mass).
Myocardial hypertrophy covers the need of body tissues due to the ability to release a larger volume of blood into the vascular bed. Long-term adaptation is manifested by the fact that under conditions of increased load in athletes, the usual human connection between pulse and blood pressure changes towards an increase in blood pressure while maintaining a standard, sometimes even reduced heart rate.
The body's response to disturbances
With the development of pathological conditions, the inclusion of compensatory mechanisms is noted. Decreased renal blood flow results in the release of renin.
Additional production of angiotensin and aldosterone is triggered, promoting arteriolar spasm and water retention in the body. This can lead to the development of hypertension.
Massive bleeding threatens a significant decrease in blood volume. In such conditions, the body tries to maintain tissue perfusion and supply the organs with necessary substances by increasing the heart rate.
In such cases, there is an inverse relationship between pulse and pressure. The inability to maintain blood pressure due to loss of blood volume is compensated by an increase in heart rate.
Transfusion of blood components or blood substitutes, taking into account stopped bleeding, eliminates hypovolemia. At the same time, the pressure begins to recover, and the rhythm gradually normalizes.
How are pulse and blood pressure related in children?
At birth, the child has a predominance of vagotonia. The sympathetic link begins to mature later than the parasympathetic.
Features of autonomic innervation are reflected in the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Children are characterized by decreased vascular tone, with corresponding low blood pressure values.
The needs of a growing organism for blood supply at a high level are covered by physiological tachycardia. Each period has a certain framework of functional constants, the actual values of which help to navigate the condition of a small patient.
There are tables showing the relationship between pressure and pulse with the child’s age:
| Years | Heart rate | HELL |
| Newborns | 120-140 rpm | 60-80/40-50 mm Hg. |
| Up to a year | 110-130 rpm | 80-85/45-50 mm Hg. |
| 1-5 years | 100-120 rpm | 90-105/50-60 mm Hg. |
| 6-10 years | 85-90 per minute | 95-115/55-65 mm Hg. |
| 11-14 years old | 70-90 per minute | 105-120/65-70 mm Hg. |
Deviations from the average statistical indicators, up or down, may indicate the presence of pathology.
Cardiovascular activity and medication use
Practical medicine uses many drugs that directly or indirectly affect the tone of the vascular wall, the functioning of the myocardium, as well as the brain centers responsible for the functioning of the circulatory system.
Moreover, these drugs can exhibit cardiotropic and vasoregulatory effects, causing not only the main, but also an undesirable side effect. The dependence of pulse and blood pressure on the use of non-selective adrenergic blockers was revealed.
When using adrenergic blockers as antihypertensive drugs, patients experience a slowdown in rhythm, up to the development of blockades.
That is why, for hypertensive patients with bradyarrhythmia, the use of cardioselective beta-blockers, which affect only the vascular wall, is indicated. It should be noted that drugs that suppress the activity of the parasympathetic nervous system (anticholinergics) give an effect similar to stimulation of the sympathetic system.
Drugs such as Caffeine, Lobelin, Cititon can cause tachycardia and a hypertensive state.
on this topic
video about the relationship between blood pressure and pulse:
Heart rate and systemic blood pressure have a common basis of regulation. Various hormones influence heart performance. In some situations where it is necessary to maintain tissue perfusion limits, there is a correlation between pulse and blood pressure.
Knowledge of the basic physiology of the heart, main and peripheral vessels allows us to understand the dependence of the pulse on pressure, which is an important component in the choice of therapy with certain medications, since this understanding allows us to predict the body’s possible negative response to a particular drug.
Source: https://feedjc.org/arterialnoe-davlenie-zavisit-ot-chastoty-sokrashhenij-serdca/
Reflex patterns
The study of the circulatory system at the time of the formation of physiology revealed how the pulse depends on the pressure in large venous vessels. At the end of the 19th century, it was established that stretching the veins with a large volume of blood provokes an increase in heart rate. The effect is aimed at unloading the right parts of the heart and normalizing the blood supply to the body.
Human circulatory system
The appearance of tachycardia is typical for untrained individuals when performing increased physical activity. Thanks to this property, it is possible to cover unusual energy and oxygen costs during intense physical activity. In athletes, due to constant training, the cardiomyocytes themselves undergo restructuring: the heart muscle thickens (“increases” its mass).
Myocardial hypertrophy covers the need of body tissues due to the ability to release a larger volume of blood into the vascular bed. Long-term adaptation is manifested by the fact that under conditions of increased load in athletes, the usual human connection between pulse and blood pressure changes towards an increase in blood pressure while maintaining a standard, sometimes even reduced heart rate.
Diagnosis of myocardial ventricular contractility
To determine myocardial strength, the ejection fraction is used. It is calculated as the ratio between the amount of blood entering the aorta and the volume of contents of the left ventricle in the relaxation phase. It is measured as a percentage, determined automatically during ultrasound by a data processing program.
It is considered normal if the value is within 55 - 60%. If contractility is insufficient, it drops to 35 - 40%.
Increased cardiac output can occur in athletes, as well as with the development of myocardial hypertrophy at the initial stage. In any case, the ejection fraction does not exceed 80%.
In addition to ultrasound, patients with suspected decreased cardiac contractility undergo:
- blood tests - electrolytes, oxygen and carbon dioxide content, acid-base balance, kidney and liver tests, lipid composition;
- ECG to determine myocardial hypertrophy and ischemia; standard diagnostics can be supplemented with exercise testing;
- MRI to detect defects, cardiomyopathy, myocardial dystrophy, consequences of coronary and hypertension;
- X-ray of the chest organs - increased cardiac shadow, congestion in the lungs;
- radioisotope ventriculography shows the capacity of the ventricles and their contractile capabilities.
If necessary, an ultrasound scan of the liver and kidneys is also prescribed.
Watch the video about heart examination methods:
The body's response to disturbances
With the development of pathological conditions, the inclusion of compensatory mechanisms is noted. Decreased renal blood flow results in the release of renin.
Additional production of angiotensin and aldosterone is triggered, promoting arteriolar spasm and water retention in the body. This can lead to the development of hypertension.
Massive bleeding threatens a significant decrease in blood volume. In such conditions, the body tries to maintain tissue perfusion and supply the organs with necessary substances by increasing the heart rate.
In such cases, there is an inverse relationship between pulse and pressure. The inability to maintain blood pressure due to loss of blood volume is compensated by an increase in heart rate.
Transfusion of blood components or blood substitutes, taking into account stopped bleeding, eliminates hypovolemia. At the same time, the pressure begins to recover, and the rhythm gradually normalizes.
Causes
Congenital malformations such as tetralogy of Fallot can lead to right atrial hypertrophy.
Right atrium pressure overload is characteristic of tricuspid valve stenosis. This is an acquired heart defect, in which the area of the opening between the atrium and the ventricle decreases. Tricuspid valve stenosis may be due to endocarditis.
With another acquired heart defect, tricuspid valve insufficiency, the right atrium experiences volume overload. In this condition, blood from the right ventricle, when it contracts, flows not only into the pulmonary artery, but also back into the right atrium, causing it to work under overload.
The right atrium is enlarged in some congenital heart defects. For example, with a significant atrial septal defect, blood from the left atrium enters not only the left ventricle, but also through the defect into the right atrium, causing its overload. Congenital heart defects accompanied by the development of HPP in children - Ebstein's anomaly, tetralogy of Fallot, transposition of the great vessels and others. Right atrium overload can occur quickly and manifest primarily on the electrocardiogram. This condition can occur during an attack of bronchial asthma, pneumonia, myocardial infarction, or pulmonary embolism. Subsequently, with recovery, the signs of HPP gradually disappear.
Sometimes electrocardiographic signs of HPP appear when the heart rate increases, for example, against the background of hyperthyroidism. In thin people, electrocardiographic signs of HPP may be normal.
How are pulse and blood pressure related in children?
At birth, the child has a predominance of vagotonia. The sympathetic link begins to mature later than the parasympathetic.
Features of autonomic innervation are reflected in the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Children are characterized by decreased vascular tone, with corresponding low blood pressure values.
The needs of a growing organism for blood supply at a high level are covered by physiological tachycardia. Each period has a certain framework of functional constants, the actual values of which help to navigate the condition of a small patient.
There are tables showing the relationship between pressure and pulse with the child’s age:
| Years | Heart rate | HELL |
| Newborns | 120-140 rpm | 60-80/40-50 mm Hg. |
| Up to a year | 110-130 rpm | 80-85/45-50 mm Hg. |
| 1-5 years | 100-120 rpm | 90-105/50-60 mm Hg. |
| 6-10 years | 85-90 per minute | 95-115/55-65 mm Hg. |
| 11-14 years old | 70-90 per minute | 105-120/65-70 mm Hg. |
Deviations from the average statistical indicators, up or down, may indicate the presence of pathology.
Cardiovascular activity and medication use
Practical medicine uses many drugs that directly or indirectly affect the tone of the vascular wall, the functioning of the myocardium, as well as the brain centers responsible for the functioning of the circulatory system.
Moreover, these drugs can exhibit cardiotropic and vasoregulatory effects, causing not only the main, but also an undesirable side effect. The dependence of pulse and blood pressure on the use of non-selective adrenergic blockers was revealed.
When using adrenergic blockers as antihypertensive drugs, patients experience a slowdown in rhythm, up to the development of blockades.
That is why, for hypertensive patients with bradyarrhythmia, the use of cardioselective beta-blockers, which affect only the vascular wall, is indicated. It should be noted that drugs that suppress the activity of the parasympathetic nervous system (anticholinergics) give an effect similar to stimulation of the sympathetic system.
Drugs such as Caffeine, Lobelin, Cititon can cause tachycardia and a hypertensive state.