WHY DO HEART ATTACKS HAPPEN? IS IT POSSIBLE TO PREDICT AND PREVENT ITS APPEARANCE?
A heart attack cannot occur on a healthy heart; it only affects a diseased, crippled organ.
Unfortunately, heart disease does not immediately make itself felt. As a rule, a person feels normal, even if the blood vessels are half overgrown with cholesterol plaques.
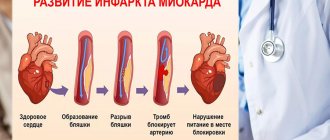
With atherosclerosis, a cholesterol plaque can periodically ulcerate and a blood clot forms on it. It grows rapidly until it finally closes the entire lumen of the artery. The blood flow through it stops, oxygen starvation and cell death begin: this is how myocardial infarction develops.
Its first sign is a hard, sharp, severe pain behind the sternum, which can radiate to the arm, shoulder, back, jaw, neck.
Features of repeated attacks
It is impossible to determine exactly why a recurrence of myocardial infarction occurs. Patients who strictly follow the doctor's instructions, follow their diet and exercise, suffer a secondary heart attack no less often than those who adhere to the recommendations selectively.
It is impossible to predict what the prognosis will be after the 2nd or even 3rd myocardium. For some, this does not bring significant changes, and they continue to live after the disease for decades. For others, the second heart attack turned out to be fatal.
Recurrent and repeated: what is the difference
Doctors distinguish between recurrent and repeated heart attacks. For many it is the same thing. In fact, experts call recurrent an attack that develops in the first months after the initial one.
A heart attack that develops several months or more later is considered recurrent. It can be localized in the same place as the previous one, or it can affect completely different areas of the muscle.
DOES A PERSON ALWAYS EXPERIENCE SEVERE PAIN DURING A HEART ATTACK?
Read more…
No not always. It happens that only by using a cardiogram can a doctor determine whether a patient has suffered a heart attack, although the patient already has huge scars on his heart. And the patient recalls that he recently felt bad, it was difficult to walk, his chest ached, but then it became easier.
By the way
What to feed your heart
It has been proven that eating fish 2 times a week reduces the risk of developing heart disease by 30%. Fish is a record holder for the content of polyunsaturated fatty acids Omega-3, which regulate the level of lipids and cholesterol in the blood.
A fish diet prevents the development of atherosclerosis (one of the main culprits of cardiac accidents) and has a beneficial effect on the condition of the heart and blood vessels. Foods rich in potassium (legumes, grains, nuts) and fiber (vegetables and fruits) are also good for the heart.
Article on the topic
Reduce the temperature to death. Cold medicines can cause heart attacks
IS IT POSSIBLE TO HELP YOURSELF WITH SOMETHING IN A HEART ATTACK BEFORE THE AMBULANCE ARRIVES?
If chest pain occurs, you should immediately put a nitroglycerin tablet under your tongue or use nitromint (an aerosol drug). The main task of these drugs is to dilate the blood vessels so that the heart attack is minimal.
If the ambulance arrives quickly, then you can hope for a better prognosis. Hospitals now use medications to dissolve newly formed blood clots. But after a few hours such treatment will be ineffective.
Treatment of recurrent heart attacks
Emergency treatment after a heart attack includes two procedures:
- thrombolysis;
- angioplasty.
These techniques are effective only in the first 12 hours after necrotic processes in the myocardium.
Thrombolysis refers to the administration of drugs that dissolve the formation that caused the blockage. The procedure is contraindicated in cases of bleeding from internal organs and hemorrhagic stroke. The method is prohibited for intracranial tumors and aneurysms. If there is a history of such events, at least six months must pass before thrombolysis can be used.
Angioplasty is a procedure in which a balloon is inserted into the vessels using a special catheter. It expands and restores normal lumen inside the vessel. Blood supply is quickly restored, and myocardial nutrition improves.
Angioplasty is performed not only after an attack, but also later. If thrombolysis is acceptable, it is performed immediately. After 5-6 days, delayed angioplasty is possible. Sometimes this procedure is performed as planned. This technique has virtually no contraindications. On the contrary, it is used as an effective emergency aid.
IS IT POSSIBLE TO RETURN TO HUMAN LIFE AFTER A HEART ATTACK?
Life after a heart attack
It is possible, but for this you need to undergo a rehabilitation course.
At the site of damage to the heart muscle, a scar gradually forms, around which muscle tissue grows. The heart adapts to new conditions over time, but it needs to be carefully and regularly trained, since reserves are already limited.
The goal of rehabilitation is to “patch up” the heart muscle so that the heart can function optimally. To do this, dosed physical activity is used with a gradual increase (under the supervision of a doctor).
Physical activity
People who are overweight should try to reduce it, but should not go on strict diets to do this. They are usually accompanied by stress, which is unacceptable in the post-infarction state. Emotional shocks should generally be avoided, trying not to think about something negative. This is not easy to do, but it is possible if you use psychological training and meditation. To restore the body's functioning after a heart attack, gentle physical activity is required.
To restore the body's functioning after a heart attack, gentle physical activity is required. The most basic of them is walking in the fresh air, which is recommended to be done in any weather, with the exception of too hot and cold days. Physical therapy exercises prescribed by a doctor play a major role in health rehabilitation.
And finally, people who have suffered a myocardial infarction should not forget to constantly take medications, because without them, heart complications are inevitable. They should be taken strictly as prescribed by your doctor.
Alarming symptoms
Read more…
A feeling of unbearable pain in the chest is a classic picture of a heart attack . However, sometimes the symptoms of a heart attack are confusing.
For example, the nerve that controls pain in the heart sends signals to the stomach, neck, and left arm . And instead of causing pain in the heart, the disorder in the coronary arteries leads to pain in other parts of the body. The consequences of these misunderstood symptoms can be very serious.
Of course, not every bout of abdominal or shoulder pain means a heart attack is on the way. We all have these minor ailments from time to time. But you should be wary if such vague symptoms last longer than 15-20 minutes and are not alleviated by taking home remedies that previously helped in such cases.
Read more…
- ❗ a feeling of oppressive pressure in the chest, compression or pain in the center of the chest, lasting longer than two minutes - “as if an elephant had stepped on the chest”;
- ❗ spreading pain from the chest to the left arm or left side of the neck;
- ❗ shortness of breath, profuse sweating and fatigue, sometimes accompanied by fainting, dizziness or nausea.
First aid for recurrent MI
If a person experiences pain in the chest, heavy sweating, heart rhythm disturbances, or general malaise, you should give him a Nitroglycerin tablet and immediately call an ambulance.
We must remember that the sooner qualified medical care is provided for recurrent myocardial infarction (ICD-10 code I 22), the greater the chances of successful treatment. The patient must be hospitalized and undergo a cardiogram. It would be good to be able to compare the results with previous research.
Using existing methods, cardiologists can immediately restore blood flow through the affected artery, reducing myocardial damage. To do this, special medications are used to help dissolve blood clots, or angiography is performed followed by stenting of the damaged vessel. Both methods give a positive effect only in the first hours after the onset of an attack. This once again suggests that the patient needs to be urgently taken to a medical facility, and not wait until the end of the attack.
Three main signals
They should make you take your condition seriously
- First : it seems to you that the attack of pain is unusual in nature or intensity.
- Second : severe pain does not go away and is not relieved immediately.
- Third : chest pain wakes you up at night and lasts longer than a few minutes.
Remember!
The most dangerous time is the first hour from the onset of a heart attack. As a rule, at this time, fatal arrhythmia or asystole (a sharp weakening of heart muscle contractions) occurs, which can lead to cardiac arrest. Therefore, such patients must be taken to the hospital, to the intensive care unit as early as possible, and the treatment process must be constantly monitored.
Remember!
If you have not yet reached the doctor, but you are worried about heart pain, you should definitely have a bottle of nitroglycerin in your pocket. Nitroglycerin is the only remedy that can quickly relieve suffering. As a rule, in a matter of seconds it relieves pain and dilates the blood vessels of the heart, but not for long.
A person who has had a heart attack needs to take responsibility for their health
The consequences of a heart attack are eliminated or reduced either with medication or through surgery. How exactly the issue will be resolved is determined by the doctor. If the form of the heart attack is small-focal, medications can also help, but if the heart attack is extensive, then you need to operate.
While the patient is in the hospital, he is being monitored by doctors, and outside of it, he must take responsibility for his health. Anyone who has had a heart attack should continue to take aspirin, which is necessary to prevent blood clots from forming. And in principle, a person must change his life and start eating differently.
Smoking, drinking strong alcoholic drinks and fatty foods is prohibited at all. Potatoes and bread should be a minimum in the diet. You must include sea fish, herbs and vegetables (not potatoes) in your diet. It is also useful to drink dry red wine occasionally. These products are useful for improving blood composition and preventing the formation of cholesterol plaques.
YOU HAVE FOUR HOURS
Cardiologists estimate that only a quarter of patients with heart problems correctly recognize the warning signs of a myocardial infarction.
Statistics show that women and older people are especially slow to call a doctor. In the case of a heart attack, such a delay is literally like death, because timely provision of medical care for this disease is a decisive condition for saving life. This assistance should be provided, if possible, in the first four hours after the onset of severe symptoms.
Symptoms of a heart attack are often similar to those of other diseases. How not to confuse one with the other and avoid mortal danger?
DIGESTION DISORDER
Read more…
Unlike the pain that occurs with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, the abdominal pain that occurs during a heart attack is rarely acute.
In this case, the area where the pain is felt is not sensitive to touch. The patient is more likely to suffer from bloating, which is sometimes accompanied by a dull ache, burning sensation or nausea. Taking digestive medications or having a bowel movement may provide some relief, but the discomfort usually does not go away.
Such symptoms may appear if damage occurs to the posterior wall of the heart due to blockage of the right coronary artery. The fact is that the nerves coming from the back wall of the heart are located very close to the nerves that transmit the pain signal to the stomach.
PAIN IN THE LOWER JAW AND NECK
It spreads to both sides of the jaw and sometimes to both sides of the neck. It also happens that the pain initially occurs in the neck.
ARM OR SHOULDER PAIN
Read more…
Although the left side usually hurts, the pain or heaviness may spread through the shoulder and into the right arm. The pain is usually pressing rather than sharp and spreads down the arm, down to the wrist and fingers. At the same time, it is difficult to pinpoint the exact location where it hurts, as can be done with an injury.
DYSPNEA
Some heart attack victims suddenly begin to breathe heavily and suffocate after the most ordinary exertion. This breathing disorder is sometimes described as “oxygen starvation” and does not disappear with rest.
The patient can sit for several minutes, and breathing seems to be restored. But as soon as he continues walking, the shortness of breath returns. Trouble breathing is a symptom that is often ignored, especially by older people who believe that “it’s just being old.”
FEELING TIRED
Shortness of breath is often accompanied by fatigue that affects the entire body.
Remember!
The most successful treatment is when started within an hour of the onset of a dangerous symptom. And after twelve hours, medicine, unfortunately, is already powerless to help...
Life threatening!
All complications of myocardial infarction are life-threatening; their occurrence significantly reduces the prognosis and hope for a successful outcome.
Particularly dangerous complications include:
- Acute (in the acute period of the disease) and chronic (after scarring of the infarction area) heart failure, that is, a violation of the pumping function of the heart, which is aggravated by cardiac asthma and pulmonary edema.
- Disorders of heart rhythm (arrhythmias) and impulse conduction (blockades).
- Cardiogenic shock, in which there is a sudden decrease in the contractility of the left ventricle of the heart and at the same time a strong expansion of the arterial bed, which leads to a sharp drop in pressure.
- Embolism (blockage of blood flow) in the pulmonary artery or systemic circulation.
- Acute aneurysm of the left ventricle of the heart (the condition threatens heart rupture).
How to avoid relapse and recurrence of myocardial infarction?
Have you been struggling with HYPERTENSION for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure hypertension by taking it every day...
Read more "
Although recurrent and repeated myocardial infarction generally indicate the resumption of necrotic processes in the muscle tissue of the heart, there are differences between them. So recurrent is a process that began less than two months after myocardial infarction. The second one develops after more than two months.
- How to distinguish a relapse from a repeat using an ECG
- Characteristic signs of relapse
- Characteristic signs of recurrent infarction
- How to avoid repetition
The classification of cardiac muscle infarctions is quite extensive. It is distinguished by shape, zone of localization, flow, speed of development, and so on. Thus, recurrent processes can begin regardless of the existing pathological process. But acute MI is a rapidly developing pathology (both primary and secondary). Without proper treatment, follow-up and prevention, it is impossible to determine how beneficial the consequences will be. After all, MI is a very dangerous disease, bordering on a fatal risk to the patient’s life.
The danger of MI is also that, in addition to serious consequences, none of the patients is immune from a second, third or more inflammation. Which only aggravates the condition of the patient’s cardiovascular system. Statistics indicate at least 25-29% repetitions. Moreover, it is impossible to say who is more insured - the patient who follows the protective regime or leads a normal lifestyle.
How to distinguish a relapse from a repeat using an ECG
ECG for recurrent myocardial infarction
Sometimes the localization zone is located in maximum proximity to the old scar, at a distance or in the area of another wall. And in these cases, the EC-gram will already indicate fresh infarction changes.
In case of relapse, the pathological process begins anew in each new lesion. It proceeds independently, regardless of the primary manifestation of myocardial infarction (that is, when the initial infarction has not yet completely healed). Visible on the EC-gram in 70% of cases.
Characteristic signs of relapse
Recurrent MI is insidious and can be confused with a prolonged course. But an experienced doctor will be able to expose the “deceiver” during the diagnostic process. With a prolonged course, the localization zone of the primary manifestation increases, the acute and acute periods drag on and drag on. And in new foci the inflammatory process begins anew. Therefore, the impression of “marking time” is created.
Primary infarction is considered here as large-focal or extensive, and is an acute violation of the coronary circulation. Its course is long, divided into four periods:
- Acute (0.5-2 hours) – decreased blood supply to the area, signs of tissue death appearing;
- Acute (2-10 days or more) – formation of a necrotic area, softening of muscles;
- Subacute (up to 4 weeks) – the initial stage of scarring;
- Post-infarction (3-5 months) – full formation of the scar, adaptation of the myocardium to new working conditions.
Stenosing atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries is the most likely cause of relapse
As a result of numerous observations, conclusions were drawn about the most likely causes of relapses. The main condition for this form of MI is severe stenotic atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries with damage to collateral vessels. Not only does the coronary artery “turn off” due to thrombosis, but its ability to adequately expand is also impaired. Functional burden of the myocardium leads to the formation of new necrosis.
At the same time, we should not exclude the fact that the recurrent process can begin not only in the periphery, but also in the infarction zone. This is explained by the discrepancy between the need for blood supply and the state of coronary blood flow. As a result, the percentage of recurrent course ranges from 4% to 30%.
The following is observed:
- reduction in the mass of contractile myocardium;
- increase in the incidence of chronic blood supply failure;
- exacerbation of heart rhythm disturbances;
- increasing the duration of inpatient treatment (due to recurrent infarction processes, an acute period is observed for a long time);
- the risk of death increases, including for inpatients (up to 35% of cases).
Variants of the clinical picture of relapse:
Why do you feed pharmacies if hypertension is afraid of the usual like fire...
Tabakov has revealed a unique remedy against hypertension! To reduce blood pressure while preserving blood vessels, add to…
- arrhythmic;
- gastralgic;
- asthmatic;
- asymptomatic;
- anginal.
This causes some difficulties in laboratory and hardware diagnostics. So, for example, if the attacks of pain during the initial heart attack were mild, and the patient was not hospitalized. Then, with subsequent attacks and hospitalization, the primary infarction will not be noticeable on the ECG, while recurrent inflammation is better visible. The patient is diagnosed with “myocardial infarction” without specifying a relapse, and the initial symptoms are defined as a manifestation of angina pectoris. This may further affect the entire treatment process.
Another relapse can be “hidden” under the pretext of complications of MI, for example, arrhythmia. Recurrent processes of necrosis negatively affect the condition of the patient’s body. There may be:
- swelling of the respiratory system;
- cardiogenic shock;
- extensive necrotic lesion.
Characteristic signs of recurrent infarction
As mentioned, repeated myocardial infarction develops 2 or more months after the first incident. Middle-aged men who have had this disease are at risk. The repeated course is severe; asthmatic and arrhythmic variants are often detected. Symptoms are less pronounced, since in previously affected areas of MI pain sensitivity is reduced.
The most common cause of any myocardial infarction is atherosclerosis with the formation of plaques on the walls of the coronary arteries. A gradual decrease in the lumen and sedimentation of thrombotic formations leads to complete occlusion. The supply of oxygen and beneficial substances contained in the blood to the tissue stops, which is why, in fact, cell death begins.
With repeated MI, atherosclerotic plaques do not go away, and sooner or later occlusion cannot be avoided. If the same blood vessel is involved in the process, then necrosis forms in the area of the scar of the first infarction, but if other vessels are involved, then a repeated infarction affects other walls of the heart.
Influencing factors:
- gender of the patient: men are more likely than women to develop heart disease;
- age: for men there is a risk at any age, for women - after menopause; average indicators range from 45-50 years and older, by the age of 70 the percentage of men and women levels off;
- genetic predisposition;
- overweight;
- chronic endocrine diseases;
- high blood cholesterol levels;
- high blood pressure;
- improper lifestyle: nutrition, regime, bad habits;
- psychoemotional disorders, stress;
- inadequate prevention of atherosclerotic disease or its absence;
- non-compliance with a doctor’s prescription for a gentle regimen after a heart attack: nutrition, exercise, smoking, alcohol.
Repeated heart attack is characterized by pressing or sharp pain in the heart area
A second heart attack can develop in the same way as the first case, have the same course and symptoms. It is characterized by prolonged pain in the heart area, radiating to the left arm, forearm, interscapular space, neck, and lower jaw. Their character is sharp or oppressive. The pain is not relieved by nitroglycerin, or is relieved partially, not for long. There is a general feeling of weakness, paleness of the skin, and hyperhidrosis.
The nature of the pain this time may differ somewhat from the previous manifestation of the pathology. A heart attack usually has consequences, which leaves a negative imprint on each new outbreak.
Repeated myocardial necrosis can occur without pain in the heart, but with signs of an arrhythmic, abdominal or asthmatic variant:
- shortness of breath;
- breathing problems, pulmonary edema;
- cyanosis;
- loss of consciousness;
- a sharp drop in blood pressure.
How to avoid repetition
In addition, you need to reconsider your lifestyle and try to eliminate all possible influencing factors.
Patients suffering from diabetes are at risk, so regular cardiac monitoring is essential.
For prevention and rehabilitation, doctors recommend constant use of beta-blockers, antiplatelet agents and statins
Prevention and rehabilitation after a heart attack are necessary to prevent post-infarction angina and repeated necrosis. Medical recommendations include:
- Constant, continuous, lifelong use of beta-blockers, antiplatelet agents and statins.
- Lifestyle correction: regimen, nutrition, giving up bad habits, moderate physical activity.
- Prevention or treatment of psycho-emotional state.
- Bed rest (in the acute period and with recurrent myocardial infarction).
- Exercise therapy as prescribed.
- Regular non-exhausting walks in the fresh air.
- Sanatorium-resort recreation and treatment.
- Temporary disability: long-term sick leave or transition to light forms of work. Note that a conditional period of 90-120 days has been established for repeated MI. But in the case of vascular reconstructive surgery, sick leave is provided for a year.
- Those who have suffered a heart attack are not recommended to return to work afterward if these are the following professions: pilot, pilot, driver of any type of transport, dispatcher, postman, courier, crane operator, high-altitude fitter, and so on. Daily employment and night shifts are also contraindicated.
Myocardial infarction has recently become significantly “younger”. This disease does not occur suddenly; it is preceded by many unfavorable factors, including vascular diseases. An acute heart attack requires an emergency response, since in the absence of adequate treatment in the first six hours the patient may simply die. Therefore, it is important for people at risk to regularly attend routine examinations with a cardiologist. And the rest too. After all, the heart is the main engine of the human body!
– by leaving a comment, you accept the User Agreement
- Arrhythmia
- Atherosclerosis
- Varicose veins
- Varicocele
- Vienna
- Haemorrhoids
- Hypertension
- Hypotension
- Diagnostics
- Dystonia
- Stroke
- Heart attack
- Ischemia
- Blood
- Operations
- Heart
- Vessels
- Angina pectoris
- Tachycardia
- Thrombosis and thrombophlebitis
- Heart tea
- Hypertension
- Pressure bracelet
- Normalife
- Allapinin
- Asparkam
- Detralex
Emergency situation: what to take?
If acute pain occurs, it is recommended to take 1-2 tablets of nitroglycerin (if there is no significant decrease in blood pressure) under the tongue. You can repeat taking nitroglycerin after 20-30 minutes or use long-acting drugs (sustak, nitrong, nitrogranulong, sustonite, erinite, etc.).
Inside, you need to take any ANALGESIC available at hand (1-2 tablets of pentalgin, baralgin or spazgan, analgin, etc.).
CORVALOL, VALOCORDIN - up to 50-60 drops or any calming sedative drug (for example, phenazepam, 1-2 tablets) can help.
If you have panangin (asparkam, potassium orotate), you can take 2-3 tablets. Be sure to try to control your blood pressure.
If blood pressure is high, antihypertensive drugs can be added to treatment in the patient’s usual dosage (if he has taken them before). However, do not try to suddenly and significantly reduce blood pressure - this may impair blood flow to the heart.
What to do before the ambulance arrives
During a heart attack, a person may instantly lose consciousness, breathing and heartbeat may stop. In this case, it is necessary to immediately begin resuscitation measures, without waiting for the ambulance to arrive.
Moreover, you first need to start resuscitation, and then ask someone around you to call an ambulance.
If the patient has no reaction to external stimuli, it is necessary:
✅ 1. LAY THE PERSON ON THE BACK on a flat surface and throw back his head, ensuring airway patency. If he is vomiting, you need to turn his head to the side and clear the contents from the oral cavity using any tissue.
✅ 2. CHECK IF THERE IS BREATHING . If there is no spontaneous breathing, artificial ventilation of the lungs must be done using the mouth-to-mouth method. At the same time, do not forget that the patient’s nose should be pinched at the moment of blowing air.
✅ 3. CHECK IF THERE IS A HEARTBEAT . Don't try to feel the pulse on your wrist - place your fingers on the carotid artery (the area of the neck under the jaw). If there is no pulsation, begin chest compressions. That is, place your palms on top of each other in the middle of the sternum and, using the weight of your body, rhythmically press down with the base of your palms, moving the sternum towards the spine. Rhythm - slightly more often than once per second (80 clicks per minute).
If resuscitation is carried out alone, every 15 compressions, two consecutive blows of air should be made into the patient’s lungs.
SPECIAL ATTENTION TO DIABETICS
Myocardial infarction in patients with diabetes mellitus occurs equally often in both men and women, but it develops much earlier than in people who do not suffer from diabetes mellitus, and is more severe and longer lasting.
Diabetics are more likely to have heart rhythm disturbances, pulmonary edema, and gastrointestinal bleeding. The most dangerous thing is that in patients with diabetes, myocardial infarction often occurs without pain.
It can be suspected only by a sudden deterioration in the patient’s general condition, the appearance of shortness of breath, weakness, and heart failure. At the same time, thirst increases, appetite disappears, nausea and vomiting occur.
Prevent recurrence
Read more…
When a person is discharged from the hospital after a myocardial infarction, they are given a list of medications to take with them at home.
For what? For one purpose - to prevent repeated exacerbations of coronary artery disease.
Medicines used to compensate for impaired blood supply to the heart muscle in the post-infarction period are called antianginal drugs. As a rule, they have a wide range of effects on the body: they prevent the occurrence of angina attacks, improve myocardial contractility, lower blood pressure, affect the heart rate, and provide other pharmacotherapeutic assistance.
The most effective and currently widely used antianginal drugs are nitrates in various dosage forms: for example, tablets that slowly dissolve in the gastrointestinal tract (“retard tablets”) of nitroglycerin (patented name sustak, nitrong, etc.), isosorbide dinitrate (nitrosorbide) .
These include calcium antagonists - verapamil (finoptin, corinfar, cordafen), diltiazem. And also beta blockers - propranolol (synonyms: anaprilin, obzidan, inderal), atenolol.
Important!
Each patient, upon returning home from a medical institution, should know the names and doses (by hour of day) of taking medications, the purpose of their administration, the duration of the treatment course, and the expected therapeutic effect. Moreover, even possible side effects of prescribed medications.
Lifetime tablet
You can slow down the development of pathological processes (and thereby reduce the risk of a second stroke) with the help of medications.
“A patient who has suffered a vascular accident will have to take medications for the rest of his life,” says Simon MATSKEPLISHVILI, Deputy Director of the Medical Research and Educational Center of Moscow State University, Corresponding Member of the Russian Academy of Sciences . “But convincing patients of this can be difficult.”
Sometimes a person who has had a heart attack needs 5-7 medications daily. In the language of patients, this is called “poisoning the body with chemistry.” And since taking heart medications does not have an obvious effect (like taking antipyretics or painkillers), some consider them useless and therefore unnecessary. In addition, after studying the package insert for the drug (which lists even once recorded side effects), the patient sometimes comes to the conclusion that it is better to drink charged water and whisper conspiracies - these remedies, as is known, have no known side effects.
However, practice shows: refusal to take medications is the main cause of a second heart attack, in which the patient’s risk of death increases by 2.7 times!”