What are platelets needed for?
Cells called platelets have important functions in the human body. Being in the vascular bed, they perform the following tasks:
- Stop bleeding. Due to adhesion and aggregation, blood cells form a thrombus and also cause a narrowing of the lumen of the vessel in the place where its integrity is compromised.
- Saturation of the walls of blood vessels with nutrients. When platelets are destroyed, germ factors are formed that promote the healing of damaged endothelium.
- Protection from bacteria and foreign organisms. This happens due to their gluing.
Many women's platelet levels decrease during pregnancy. This may occur normally or indicate a problem in the body. To avoid trouble and not miss the development of a serious disease, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations and blood tests.
Thrombocytopenia during pregnancy - causes and symptoms. Treatment of thrombocytopenia during pregnancy
A normal ratio of all blood parameters is an important diagnostic criterion for health.
Numerous tests that the expectant mother undergoes are performed primarily for preventive purposes. The importance of regularly taking a general blood test cannot be overestimated.
In addition to the level of ESR and hemoglobin, which are strictly controlled, the doctor also pays attention to the content of cells such as platelets.
You should not wait until the pathology manifests itself as specific complaints. Platelets - colorless blood cells - are one of the most important components of blood. A deviation in the content of this type of cell, either in the direction of increase or decrease, can have very serious consequences for both the pregnant woman and her baby.
Causes of thrombocytopenia
Low platelets during pregnancy can be a marker of serious diseases. You should undergo regular examinations with a doctor and get tested so as not to miss pathology.
The number of blood platelets decreases with:
- Viral infections (flu, ARVI).
- Systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Congenital pathologies of the coagulation system.
- Malignant neoplasms of bone marrow and cancer metastases.
- Late gestosis of severe degree.
- Allergic diseases.
- Pathologies of the endocrine system.
- Poor nutrition (lack of folic acid).
- Incorrect use of medications (with antibiotic therapy, overdose of antiplatelet agents).
- Bad habits (abuse of alcoholic beverages and smoking).
- Exposure to radiation (during radiation therapy).
Having determined a low platelet level, the doctor conducts additional diagnostics - prescribes a thrombophilia test and a coagulogram. After a thorough examination, collecting anamnesis and deciphering laboratory parameters, a hematologist or therapist makes the correct diagnosis and prescribes effective treatment.
Reasons for the decline
Low platelets during pregnancy are detected in the presence of the following pathologies:
- Allergic manifestations. When the body reacts incorrectly to certain substances, the composition of the blood changes. The platelet count may increase or decrease.
- Autoimmune pathologies. The reason lies in the production of antibodies that destroy healthy blood cells. A decrease in platelets during pregnancy in this case indicates the need to correct the functioning of the immune system.
- Poor nutrition. Blood composition deteriorates with a lack of vitamins and nutrients in the diet. Quantitative indicators can deviate from the norm either to a smaller or larger direction. A lack of vitamin B12 and folic acid contributes to disruption of platelet maturation processes.
- HIV infection. In immunodeficiency states, the amount of all formed elements in the blood decreases. Even if the first test was negative, there is a chance that the second will be positive. The incubation period lasts at least six months, and infection could occur after registration.
- Diseases of the endocrine system. If the thyroid gland produces too much or too little hormone, it can negatively affect the bone marrow.
- Pathologies of the hematopoietic system. Some diseases, such as leukemia, are characterized by a sharp decrease in the number of cells responsible for blood clotting. In this case, consultation with a hematologist is required.
- Oncological diseases. Malignant tumors in pregnant women are being detected more and more often. Oncological pathologies lead to a rapid decrease in the number of platelets, especially if the tumor metastasizes to the bone marrow.
- Chronic pathologies and acute infections. Exacerbation of diseases leads not only to a decrease in the number of blood cells, but also to a change in their size.
- Taking certain medications. Antibacterial, antihistamine, anti-inflammatory and painkillers can provoke thrombocytopenia.
Important information: Why are leukocytes in the blood elevated after childbirth?
Symptoms of low platelets
A low platelet level can be suspected by a number of external manifestations, including:
- The appearance of bruises and hemorrhages.
- Bleeding gums, which often occurs when brushing teeth).
- Nose and gastrointestinal bleeding.
- The appearance of blood in the urine.
Prolonged thrombocytopenia can lead to a number of serious complications, such as stage 3 preeclampsia, HELLP syndrome and massive blood loss during and after childbirth.
Symptoms and manifestations
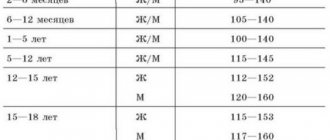
In a healthy state of the body, the number of flat bodies constantly fluctuates. The lower and upper limits of normal range from 180*109/liter of blood to 400*109/l. During pregnancy at different stages, the level of cells also changes.
| Gestational age | Platelet count |
| First trimester | 170-340*109/l |
| Second trimester | 160-330*109/l |
| Third trimester | 140-320*109/l |
There may be a physiological decrease in the level of squamous cells. In this condition, constant monitoring of blood tests for coagulation and platelets is necessary; no specific treatment is required. Thrombocytopenia is said to occur if the lower level of the limit becomes 100*109/l or less.
In this case, symptoms appear that depend on the cause, as well as on the acute or chronic nature of this pathology.
- Frequent nosebleeds, sometimes for no reason, that are difficult to stop;
- Bleeding gums: while brushing your teeth, as well as after tooth extraction, bleeding may not stop for a whole day or more;
- Subcutaneous pinpoint hemorrhages;
- Although the number of cells decreases, the platelets increase in size, and a rash may appear in the form of reddish or bluish spots, which may be isolated or occupy a large area of the body;
- Gastric and intestinal bleeding, which may be associated with fragility of blood vessels, even roughage can cause this condition;
- Blood appears when urinating, due to the fact that the vessels of the urinary tract are also damaged.
In a blood test, in addition to platelets, the quantitative composition of red blood cells decreases, reticulocytes, on the contrary, increase, the leukocyte formula shifts to the left, blood clotting decreases, and a blood clot forms slowly during bleeding.
Normalization of blood platelet levels
Many people are concerned about the question “how to increase platelets in the blood?” Treatment should be prescribed by a doctor after a thorough examination and determination of the cause of the disease.
A mild degree of the disease does not require special therapy; to correct it, it is necessary to improve nutrition and eliminate harmful factors (smoking, alcohol, stress).
Treatment of severe and moderate (in the presence of risk factors) thrombocytopenia should take place in a medical institution. The therapy uses drugs such as prednisolone, etamsylate, vitamin B12 and many others.
Traditional ways to increase platelets
With a slight decrease in the number of blood platelets in the blood, they can be increased using folk remedies. Buckwheat porridge, red meat, beef liver, fish and eggs have proven themselves well.
Sesame oil, which should be consumed 1 tbsp, will also help raise the level of platelets in the blood. l. 3 times a day (before breakfast, lunch and dinner).
Treatment methods
Treatment of thrombocytopenia in pregnant women should be aimed at normalizing platelet levels and maintaining the hemostatic system. When platelets decrease, women require special therapy, taking into account its effect on the fetus.
Medicines
The basis of systemic therapy for thrombocytopenia in pregnant women is glucocorticosteroids. In medical practice, Prednisolone and Dexamethasone are most often used. Treatment is carried out in short courses, with a gradual reduction in dosage, until a positive result is achieved.
The development of a treatment regimen and selection of dosage is carried out individually for each patient.
If corticosteroids are insufficiently effective and there is no clinical effect, women are prescribed intravenous injections of immunoglobulin. The drug is administered 3 or 4 times during gestation, during and after delivery.
Severe thrombocytopenia may require emergency platelet transfusion. In practice, this method is used extremely rarely.
Surgical methods
If necessary, starting from the second trimester of pregnancy, a woman may be given a splenectomy - an operation to remove the spleen. Taking into account pregnancy, the laparoscopic method of intervention is recommended.
The issue of the progress of labor resolution is decided in each case individually, but a caesarean section is the least traumatic for the child. Its implementation is advisable when the level of platelets in a newborn decreases.
Why is thrombocytosis dangerous?
In some cases, women may experience the opposite symptom - increased platelets during pregnancy. A persistent increase in platelet levels may indicate the presence of:
- Inflammatory diseases (tuberculosis, liver diseases).
- Diseases of the spleen or condition after splenectomy.
- Malignant neoplasms.
- Drug therapy (taking glucocorticoids).
- Iron deficiency anemia.
Thrombocytosis can be suspected if a pregnant woman has a headache, numbness in the extremities, or blurred vision. A general blood test helps identify it. If thrombocytosis is detected in the blood during pregnancy, the doctor prescribes medications designed to reduce the number of blood platelets in the blood - anticoagulants (Fraxiparine) and antiplatelet agents (Curantil).
Platelets are low during pregnancy due to various diseases, so treatment is selected by the doctor individually in each specific case.
Why does it occur
In addition to the physiologically determined process during pregnancy, the disease can develop under the influence of various factors. The main causes of thrombocytopenia are:
- fetal freezing;
- allergy;
- infectious diseases of viral etiology;
- vitamin deficiency with vitamin B12 deficiency;
- destruction of red blood cells due to hormonal disorders;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- poisoning of the body with medications, alcohol, salts of heavy metals and other toxic substances;
- uterine bleeding due to placental abruption;
- autoimmune diseases;
- neuropathic conditions;
- hereditary predisposition;
- gene mutations;
- a drop in the percentage of platelet cells due to an increase in blood volume.
The secondary form of thrombocytopenia in pregnant women develops against the background of radiation sickness and may be caused by toxic brain damage. The occurrence of such conditions is observed in viral diseases - scarlet fever, chickenpox, measles.
Insufficient platelet synthesis is observed in women with leukemia or with a pathological increase in the size of the spleen.
Traditional methods of increasing blood cells during pregnancy: 3 effective recipes
Traditional medicine will help expectant mothers normalize their indicators.
The most effective medicinal recipes that can be prepared at home include the following:
- nettle infusion Take 10 grams of herb per 200 ml of water. Mix, boil and cook over low heat for 5 minutes. Divide the drink into two doses. Take morning and evening. The course of treatment is 14 days;
- milk with nettle juice. You need to chop the fresh leaves of the plant, squeeze them through cheesecloth until you obtain juice. Mix 50 ml of milk with 5 ml of the resulting nettle liquid. You will get a single dose. Drink three times a day for a month;
- Sesame oil. Drink 1 tbsp. spoon 30 minutes before meals. Course - 4 weeks.
Traditional medicine also helps well if a pregnant woman has elevated red blood cells. In this case, it is recommended to use dill seeds. They need to be ground into flour and eaten 1 teaspoon twice a day with a glass of water. Take a course of 2 months.
How to increase platelets during pregnancy
Thrombocytopenia is a symptom that characterizes a wide range of diseases of the circulatory system and is manifested by a low platelet count in the blood.
The range of normal values for this indicator varies from 180-400x10 9 /l.
If the number of platelets in the blood decreases, symptoms of bleeding gums, increased duration of menstruation, nosebleeds, and hemorrhages in internal organs or under the skin may occur.
Diagnostics
The simplest, most convenient and reliable method for diagnosing thrombocytopenia during pregnancy is a general blood test. This study is usually performed on an empty stomach in the morning. Often an additional chemical blood test is prescribed. To make a correct diagnosis and identify the cause of thrombocytopathy, the doctor must conduct an external examination of the patient for the presence of rashes, bruises and minor hemorrhages in the oral cavity. Conjunctivitis may also indicate a problem.
The following diagnostic measures may also be prescribed:
- Lee-White study (for blood clotting);
- analysis according to Sukharev;
- coagulogram;
- genetic tests;
- sternal puncture.
Additionally, a urine test for hemosiderin, antibody tests, and radiographic examination may be recommended. If necessary, other studies are carried out to determine the cause of the pathology.
Why does platelet count increase?
Thrombocytosis can occur due to:
- prolonged toxicosis, complicated by attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- indigestion accompanied by loose stools;
- insufficient water consumption;
- lack of iron;
- infectious diseases (toxyplasmosis, pulmonary inflammation, infection with pathogenic microorganisms, hepatitis, viral intestinal damage);
- inflammatory processes caused by arthritis and liver diseases;
- the occurrence of malignant tumors;
One of the reasons
Therapeutic nutrition during pregnancy: normalizing platelet levels with diet
For pregnant women, the doctor will definitely tell you which foods can further increase the level of blood platelets, and which, on the contrary, should be eaten when platelets are low in order to increase their number. The diet is based on eating foods high in vitamins and microelements.
Foods that increase platelets are:
- chicken eggs;
- lean meats;
- mushrooms;
- nuts;
- vegetables - carrots and beets predominate;
- fruits - especially pomegranate, bananas, apples and peaches;
- sea fish;
- seafood;
- greenery;
- legumes;
- dairy products.
It is necessary to exclude sausages and confectionery products, smoked and canned foods, and chocolate from the diet. The diet will also help the expectant mother keep in shape and even lose extra pounds if she is overweight. If you add to this high-quality care for your body and face, you will probably be able to avoid psychological problems.
The LUNA mini face brush will help you stay attractive while pregnant and after childbirth, as it effectively removes makeup, cleanses the skin of dirt, improves blood microcirculation and removes blackheads.
What is thrombocytopenia?
Platelets, small plate-shaped red blood cells that form in the brain, play an important role in the blood clotting process. They are responsible for rapid blood clotting and maintain it in a liquid state, preventing the formation of blood clots. In the event of damage to vascular cells, many platelets travel to the site of damage in a few seconds and restore tissue. A healthy person should normally have 150-400 thousand/μl of blood cells, which are renewed every 7-10 days.
If the results of a blood test show a platelet count less than the established norm, then thrombocytopenia is diagnosed - a pathological condition in which the level of red cells decreases and bleeding increases. With this disease, the process of stopping bleeding slows down, resulting in a large loss of blood even with a small cut.
Depending on the duration of the pathology, acute and chronic thrombocytopenia are distinguished. In the first case, the pathological effect on the body occurs for up to 6 months, and in the second – more than six months.