How to prevent thrombosis? How to find out whether there is a probability of this disease, in what percentage? – the answer to these questions worries many.
First of all, you should be sensitive to your health, listen to your body and, naturally, take all “concerns” seriously.
Prevention of the formation of any disease is necessary for every person. In the modern world, there are many ways in which you can maintain your health and avoid blood clots. The problem of thrombosis development is widespread and has acquired social significance. Dissemination of information about thrombosis prevention is necessary.
The cause of the formation of blood clots can be any factor, the main ones being injuries to the extremities (upper and lower), pregnancy and childbirth, acute respiratory viral infections, even a perfectly performed operation.
This leads to pathological diseases (thrombosis, strokes, heart attacks, angina pectoris), which result in deterioration of health (disability) and death.
Reasons for appearance
It is important to understand what thrombosis is, how it manifests itself, the reasons for its manifestation and occurrence?
Thrombosis is not only an unpleasant disease, but also very dangerous. Lack of treatment leads to a huge number of complications. This disease is characterized by the formation of thrombi (blood clots) inside blood vessels. In most cases, clots attach to their walls, increasing in size. This prevents blood from flowing normally and clogging occurs. Prevention of deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities is extremely necessary. Rarely do such formations resolve without intervention.
The causes of these formations can be a variety of factors:
- injuries;
- age categories;
- bad habits;
- heredity;
- overweight;
- various circulatory disorders;
- changes in the amount of cholesterol;
- disturbances in the proper functioning of the kidneys;
- spread of the infectious process;
- taking hormonal medications;
- oncology;
- chemotherapy;
- period after surgery;
- decreased activity;
- a sharp drop in body temperature;
- blood vessel disorders (pathologies);
- long-term stay in one position of the body and limbs (forced postures).
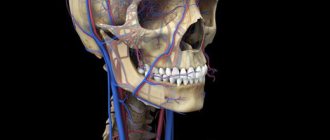
It is important to know that the vessels of the heart and the veins of the lower extremities are most susceptible to thrombosis!
The second name for thrombosis is “disease of the lower extremities.” Blood circulation is disrupted by the resulting blood clot. Lack of timely treatment is the result of inflammatory processes and damage to vascular tissue. But the worst thing is thromboembolism (the most dangerous complication of the disease, leading to the death of a person). This is why prevention of deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities is important.
Therapy: how to avoid blood clots in blood vessels?
Treatment varies depending on whether the thrombosis is venous or arterial. But the right therapy can help dissolve blood clots and restore normal blood flow. The treatment regimen for thrombosis is aimed at preventing plaque growth or the formation of new blood clots: this reduces the risk of complications or late consequences.
Dissolution of a blood clot - thrombolysis - is possible for a short period: in the initial phase of thrombosis. Therefore, treatment should begin as soon as possible. In case of vein thrombosis, the doctor prescribes heparin. This active ingredient inhibits blood clotting and may help dissolve the clot. Heparin is prescribed to the patient for about a week. This acute treatment is followed by long-term administration of anticoagulant tablets (phenprocoumon). To avoid the formation of new blood clots, continue treatment for three months.
The patient should continue compression treatment and wear special stockings. To support venous reflux, move regularly and do calf muscle exercises.
In arterial thrombosis, the blood clot is first tried to dissolve with coagulation inhibitors. Microinvasive interventions are used for arterial thrombosis. For surgical removal of a blood clot (thrombectomy), two surgical methods are available, combined with medication:
- Open thrombectomy: The doctor locates the plaque in the blood vessel and removes it. The method is suitable when it comes to small calcium-cholesterol deposits.
- Balloon catheter: The doctor inserts a balloon catheter with a stent into the damaged vessel. The specialist places a catheter near the plaque. The catheter and balloon are then inflated, air expands the vessel, and a stable stent is placed.
A penchant for education
Of course, anyone can be susceptible to thrombosis. But there are certain types of people who are most prone to this disease. Let's look at their reasons:
- heart diseases - stroke, heart attack, varicose veins, thrombophlebitis;
- age - after forty years;
- menopause period;
- overweight;
- haemorrhoids;
- alcohol consumption;
- smoking;
- immobile or sedentary lifestyle;
- oncological diseases;
- surgical intervention;
- blood clotting diseases;
- hormonal disorders and stressful situations.
It is necessary to be able to recognize these types. This will help prevent the appearance of clots, determine in time whether there are already blood clots, or significantly reduce their number through timely prevention.
Prevention. Medicines
The right thing to do is to seek help from a specialist in time, at the first signs of discomfort. It is the doctor who knows how to diagnose a blood clot, how to determine thrombosis in general. Prevention of this disease involves taking certain medications, with some basic points:
- Thinning of the blood composition. Prescription of drugs containing acetylsalicylic acid.
- Strengthening blood vessels. It is recommended to take a drug that contains ascorbic acid or vitamin C.
- Blood purification.
We should not forget - in no case should you self-medicate or prescribe such drugs yourself! This is dangerous for your health!
Naturally, medications help reduce the risk of developing the disease, but everything is harmonious as a whole. Prevention of deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities is an integral part of the procedure.
Drug interactions
Consider Tsiprolet and Albucid
Tsiprolet is a drug that contains a broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent. It is suitable for treating bacterial infections. Its effect is milder, since it does not contain dexamethasone.
Albucid is an antibacterial agent that copes with moderate conjunctivitis. The active ingredient is Sulfacetamide, it fights bacterial infection caused by staphylococcus or streptococcus.
The course of treatment is 1-2 weeks. Albucid is used in dosages of 2-3 drops 5-6 times a day.
A complete substitute for a similar drug
A complete substitute for Dexona drops is the drug Dexa-Gentamicin, which contains the antibiotic gentamicin and the glucocorticosteroid dexamethasone. In some cases it will be more effective than its closest analogue.
Gentamicin is effective against Micromonospora bacteria. The medication is used in dosages of 1-2 drops 4-6 times a day for 1-2 weeks.
Release form and compositionDosage form: solution-drops for the eyes and ears (5 ml each in dark glass bottles complete with a dropper, 1 set in a cardboard box).
Content of active ingredients in 1 ml:
- Neomycin sulfate – 5 mg;
- Dexamethasone sodium phosphate – 1 mg.
Excipients: disodium hydrogen phosphate, benzalkonium chloride (preservative), disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, creatinine, sodium chloride, propylene glycol, sodium metabisulfite, water for injection.
Pharmacological properties Let's consider the drug in the context of pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics.
Pharmacodynamics
Neomycin is an antibiotic from the aminoglycoside group. Produced by Streptococcus fradiae. It acts bactericidal, disrupting protein synthesis in microbial cells.
Active against gram-negative and gram-positive microorganisms, including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Shigella, E. coli and Proteus. It has little effectiveness against streptococci and P. aeruginosa.
Neomycin has no effect on anaerobic microorganisms, viruses and pathogenic fungi. Antibiotic resistance develops slowly and to a small extent. Dexamethasone is a glucocorticosteroid.
It has a desensitizing, antiallergic and pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. Actively suppresses the process of inflammation, inhibiting the migration of mast cells, the release of inflammatory mediators by eosinophils and reducing capillary permeability.
In the case of a combination of Dexona with other topical ophthalmic drugs, the interval between their instillations should be 10 minutes.
READ MORE: Eye drops for inflammation - classification, principle of action and price
When prescribing neomycin together with local systemic aminoglycoside antibiotics or vancomycin, it is necessary to monitor the level of the drug in the blood serum, as the risk of nephro- and ototoxicity increases.
Data on drug interactions with Dexona are not provided.
No drug interactions have been established.
Prohibited foods for thrombosis
There are foods that need to be strictly limited. Prevention of blood clots is aimed at reducing and eliminating the following foods from the diet:
- smoked meats;
- bread made from white flour;
- cream;
- meat broths;
- fried foods;
- fatty foods.
This list of food products is strictly not recommended, as these products thicken the blood:
- sausages;
- mango;
- bananas;
- salt.
To avoid blood clots, experts do not recommend overusing decoctions:
- rosehip;
- St. John's wort;
- nettle;
- valerian.
Treatment with various infusions and decoctions is certainly useful, but not in all cases. You especially need to follow all the rules, instructions, and proportions. Everything is fine! Abuse of herbal decoctions leads to the opposite effect. We need to remember this!
The most harmful actions for thrombosis are drinking alcohol, smoking, using diuretics, hormonal and contraceptive drugs . They significantly increase the possibility of blood clots.
Proper nutrition
A proper diet reduces the risk of blood clots by controlling blood sugar and cholesterol and helps maintain normal weight.
List of prohibited products for patients at increased risk of thrombosis:
- Salo.
- Margarine and butter.
- Chocolate.
- Smoked meats.
- Hard cheeses.
- Fatty meat broths.
- Fast food.
- Fried foods;
- Coffee.
- Alcohol.
Plant foods and soups made with vegetable broths are included in the diet. Potatoes, bananas and mangoes are also good for the cardiovascular system, as they are rich in potassium.
The menu should include dishes with omega fatty acids (fatty fish). Useful greens: parsley, dill, lettuce and so on.
They also pay attention to the amount of liquid you drink. It is best to drink clean water, but dried fruit compotes and green tea will also be useful. An adult needs to drink about 1.5-2 liters of water per day. This improves blood flow, thereby facilitating the passage of blood vessels and improving blood circulation.
The diet should be enriched with vitamins necessary for normal life. To strengthen the vascular wall, vitamins C, A, E, P, and group B are important. They can increase the strength and elasticity of the vascular wall.
A thrombus is a blood clot that is a block in the path of blood flow. If a blood clot blocks the blood vessels of the heart, the person will have a heart attack; if it blocks the blood vessels of the brain, the person will have a stroke.

Prevention during surgery
Particular attention is required to prevent vascular thrombosis during any surgical interventions.
How to check for blood clots? - this procedure should be performed for all patients who are prescribed surgical treatment, regardless of the likelihood of thrombosis in general.
This prevention requires a special approach:
- use of special compression clothing, elastic knitwear;
- limb massage;
- getting up quickly after surgery, walking;
- positive attitude of the patient himself;
- It is preferable to perform shorter operations with minimal damage to skin tissue.
Modern medicine has come a long way. A patient at risk of blood clots in blood vessels must be provided with maximum protection. It is accompanied by new generation drugs.
—