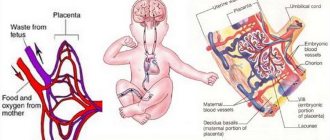
During various laboratory examinations, which a pregnant woman repeatedly undergoes during the entire period of bearing a child, she often hears from doctors that certain urine and blood parameters are abnormal. But this does not always mean that things are bad: numerous changes are characteristic of the body of the expectant mother - there is nothing surprising in this. And yet, this is why tests have to be taken so often, because these very changes can promptly warn the doctor about serious disorders that pose a danger to the unborn child and mother. One of these may be thick blood during pregnancy.
Even if it turns out that your blood is thick, do not rush to worry! Obstetricians assure that this condition is typical for pregnant women and often does not pose any danger. However, in some cases it will be necessary to undergo appropriate treatment to prevent possible risks.
Examination for thick blood during pregnancy
Very often, thick blood is determined “by eye”: when taking tests, a laboratory technician may notice that a pregnant woman has very thick blood - the hole in the needle is clogged, or it is simply clear from the viscosity that it is too thick. However, it should be understood that thick blood during pregnancy is not a disease or a diagnosis. Rather, it is a manifestation of some disorder caused by or leading to a disease state.
The blood becomes thick due to deviations in certain indicators of homeostasis (blood clotting system). And the prognosis and treatment depend on which particular norm is violated. That is why, before drawing any conclusions, much less taking any measures, it is necessary to send the pregnant woman to a coagulogram (or hemostasiogram) - a comprehensive study of the blood coagulation system, which is carried out strictly on an empty stomach!
The reason for such an analysis may be the result of a general blood test that shows an increased number of formed elements.
The following coagulogram indicators are of decisive importance for thick blood:
- fibrinogen - normally it should not go beyond 2.0-4.0 g/l, and there should be no fibrinogen B in the blood at all. But during pregnancy, the level of fibrinogen naturally increases throughout the entire period and by the end can reach 6 g/l;
- APTT - activated partial thromboplastin time or blood clotting time - is normally 24-35 s, but due to the increase in fibrinogen levels in pregnant women, blood clotting naturally accelerates somewhat (by 17-20 s);
- TV - thrombin time is normally 11-18 s; due to an increase in the level of fibrinogen during pregnancy, it also increases, but still does not go beyond the norm;
- lupus anticoagulant - normally should be absent, its presence indicates the development of pathologies, autoimmune disorders and is accompanied by an increase in aPTT;
- prothrombin - normally within the range of 78-142%; exceeding the norm in pregnant women may indicate premature placental abruption.
What is the danger?
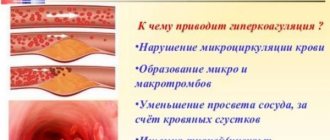
Many people do not know the danger of a condition in which the blood becomes much thicker. One of the most dangerous consequences of this condition is the risk of blood clots forming in the lumens of blood vessels.
We suggest you read: Why during pregnancy the navel can come out, darken and become hot, what to do
As a rule, blood clots form in small vessels. But when they form in large arteries, where blood moves much faster, the risk of a blood clot breaking off and blocking a coronary artery or vessel located in the brain increases. As a result of such thrombosis, tissue necrosis occurs in the affected organ, and the patient may suffer from a heart attack or stroke.
Other consequences of high viscosity include the development of hypertension, atherosclerosis, and intracerebral bleeding.
Pregnant women with high blood viscosity are more likely to develop blood clots, placental abruption, prematurity, or even fetal death.
The occurrence of a particular complication is influenced by the reason due to which the blood has become thicker than normal. Therefore, in order to cure a complication, you must first eliminate the underlying disease.
Why is this pathology dangerous?
Very often, doctors do not even attach importance to the fact that a pregnant woman has thick blood. This condition may be a physiological norm and go away on its own after childbirth. By the way, even iron supplements, which are often prescribed to pregnant women with low hemoglobin, can increase blood density.
However, if a woman is found to have thick blood during pregnancy, then a few weeks before giving birth she will need to take an additional test to monitor the indicators (they, by the way, tend to change constantly throughout the entire period).
More on the topic
Blood thinners during pregnancy
Blood after sex during pregnancy
Blood in urine during pregnancy
Blood during ovulation
Nosebleeds during pregnancy – should you worry?
Therefore, dear women, do not panic if the doctor, based on the results of the coagulogram, decided not to do anything. However, be sure to listen to his recommendations when he prescribes you treatment for thick blood during pregnancy. The fact is that such a condition can also pose a great danger to the baby and his mother. This is mainly the risk of blood clots (after childbirth, varicose veins often “come out” if there was thick blood during pregnancy) and blockage of blood vessels, as a result of which both suffer: the fetus experiences a lack of oxygen, the risk of miscarriage, heart attack, stroke increases, and in general disruption of normal blood circulation is fraught with multiple consequences.
But the good news in this case is that the situation can be corrected.
Precautionary measures
It is advisable to plan each pregnancy so that the expectant mother is prepared for the increasing load on her and physiological changes. Prevention of poor coagulation during pregnancy involves preliminary strengthening of the walls of the vascular bed.
This is done through the following actions:
- Complete cessation of smoking and even passive presence next to a smoker.
- The use of gentle traditional medicine: rosehip tincture, fresh lemon, honey and its by-products. All of them enrich the body with citron, a substance that directly strengthens the vascular system.
- Nutrition should be complete and balanced to avoid vitamin deficiency and other substances necessary for the synthesis of coagulation components.
If pregnancy has already occurred, for the purpose of prevention it is necessary to adhere to these rules.
For expectant mothers, it is important to especially monitor the drinking balance, since excess fluid will thin the blood, and coagulation factors will not be able to react in a diluted form if necessary.
Therapeutic tactics to compensate for abnormal coagulation are prescribed by a hematologist. A timely individual program gives a high percentage of success in carrying a healthy child to the required gestational age. As a rule, synthetic drugs prescribed by a doctor do not have any negative effects on the child or the woman in labor. They naturally increase the chance of successful pregnancy and reduce the risk of intrapartum and postpartum hemorrhage and their complications.
What to do if your blood is thick during pregnancy?
It should be said that thick blood is formed not only in pregnant women. But the piquancy of the situation lies in the fact that many blood thinning medications are prohibited for the expectant mother. Therefore, if the situation allows, the doctor will prescribe you a diet, or rather slightly adjust your diet.
First of all, you will be advised to drink more. It has long been proven that it is not water, but salt that contributes to fluid retention in the body, so you will have to limit the consumption of the latter (if you cannot completely eliminate it) and increase the consumption of the former. You definitely need to drink enough, that is, at least one and a half liters a day, although the exact volume should be calculated for yourself individually. In this case, only water is drinkable: certainly purified and without gas, but not distilled! Buy yourself an organic plastic bottle and keep it handy at all times, taking a few sips every 20-40 minutes. Please note that more than 70 ml of water drunk at one time is not absorbed by the body - the excess can just go into edema. Make sure that by the end of the day you drink the entire bottle (if it is 1.5-2 liters) or the appropriate volume.
You will have to exclude fatty, salty, spicy foods from your diet if you have not done so before. In return, you will need to introduce products that have a blood thinning effect into the menu. Among these are mainly those containing vitamin C and orange-red vegetables, fruits and berries and juices from them:
- berries (mulberries, raspberries, black currants, strawberries, plums, cranberries, viburnum, sea buckthorn);
- citrus fruits (grapefruit, orange, lemon, lime);
- dried apricots;
- pomegranate;
- a pineapple;
- tomatoes;
- beet;
- mushrooms;
- garlic, onion;
- cocoa, chocolate;
- birch sap, birch bark and buds;
- vegetable oils: olive, flaxseed, rapeseed;
- spices: turmeric, oregano, curry, cayenne pepper, dill, paprika, thyme, ginger, cinnamon.
Plant foods should be consumed in season. Do not forget that pregnant women should not eat too many raspberries and viburnum, and you also need to be careful with mushrooms. In addition, many products can cause allergies - you should not abuse anything.
You should also reduce the consumption of foods that thicken the blood: potatoes, buckwheat, bananas, carbonated and alcoholic drinks (which goes without saying), etc.
To improve blood circulation throughout the body, start exercising. Just a few simple exercises a day, along with proper drinking habits, can significantly improve your well-being. Soon you will notice that drowsiness and lethargy have disappeared, the pain in your legs has decreased, and vigor and cheerfulness have appeared instead. Sleep will become more complete, normal performance will return and mental activity will improve.
However, first consult your doctor to see if you have any contraindications to drinking large quantities of fluids and to moderate physical activity.
Decoding the results
The level of coagulation is determined by taking blood from a vein. The study is done on an empty stomach; the time interval between donating the biomaterial and eating should be at least eight hours. The coagulogram contains the following indicators:
- APTT shows the time it takes for blood clots to form. The norm is twenty seconds. If this indicator is lower, then the chances of blood clots are higher; if this indicator is higher, bleeding occurs.
- Fibrogen is a special protein involved in the formation of blood clots. At the end of pregnancy it is 6.5 g/l, it should not be more than this value.
- Platelets - synthesized by the bone marrow. The normal value is in the range of 131–402 thousand/µl.
- Lupus coagulant – shows antibodies. They shouldn't be normal at all. The presence of the indicator indicates the likelihood of miscarriage and thrombosis.
- Prothrombin is a plasma protein, the norm is from 78 to 142%.
All indicators are related to the duration of pregnancy and vary depending on the trimester and some other factors. If you receive the results of a bad test for blood clotting during pregnancy, you should not worry. It is deciphered by a doctor, and only he is able to correctly interpret the results.
Any analysis requires some preparation so that the results are as informative as possible. It is also recommended to comply with certain requirements before the coagulogram. Firstly, you will have to refuse food approximately 10-11 hours before the diagnosis, and you cannot even drink tea or juice, only drinking water is allowed. Biomaterial is taken from a vein in the morning.
Secondly, research has proven that psycho-emotional experiences can distort the true diagnostic results. Therefore, it is recommended that mommy sit down and calm down, only then can she go into the room for a blood draw. Don’t forget about medications; if you are taking anything, you need to warn a specialist about it.
We suggest you read: Pain after urination during pregnancy: what is the symptom, causes, what diseases does it occur with?
Blood clotting during pregnancy has many indicators and clotting factors, but there are also basic ones by which the course of pregnancy and the likely risks can be assessed. Typically, an abbreviated coagulogram indicates the values of aPTT, fibrinogen and prothrombin; with a detailed study, additional values are indicated.
The APTT component represents the period during which partial blood clotting occurs. In non-pregnant patients, this value is about 24-35 seconds. Any injury to the body can affect this value. In pregnant women, the aPTT may be lower, up to 18-20 seconds.
This phenomenon is explained by the preparation of the mother’s body for the upcoming blood loss during childbirth. If the aPTT is significantly lower than 18, then this may warn of the threat of disseminated intravascular coagulation. With elevated levels, hypocoagulation is diagnosed, which develops for many reasons.
Fibrinogen
This substance of protein origin, from which fibrin is subsequently formed, is produced by the liver. This is the main thrombus-forming element. Due to the formation of the uteroplacental vascular network, indicators increase closer to childbirth. If fibrinogen abnormalities are observed, this indicates probable inflammation in the maternal body and even necrotic processes. During pregnancy, fibrinogen levels change noticeably:
- If there is no pregnancy – 2.3-5 g/l;
- In the first trimester – 2.4-5.1 g/l;
- In the second – 2.9-5.4 g/l;
- During the third trimester – 3.7-6.2 g/l.
When fibrinogen is normal, then at the slightest vascular damage, the protein accumulates in this area, forming an insoluble clot that clogs the wound and stops bleeding. Any deviations from the norm require closer attention from specialists. An increased fibrinogen content is observed with influenza infections and inflammations, extensive burns and increased estrogen levels, with recent surgical interventions, protein metabolism disorders, etc. Fibrinogen deficiency is observed with preeclampsia and disseminated intravascular coagulation, deficiency of ascorbic acid and B12, myocardial insufficiency, etc.
Prothrombin
One of the most important indicators of blood clotting in pregnant women. It shows the performance and functionality of hemostasis. Normally, the prothrombin content should be about 80-140%. Using this indicator, specialists will promptly identify signs of thrombotic processes, which will save the baby and the mother herself.
If deviations of this indicator are detected below the norm, an extended coagulogram, a study of enzymatic liver substances, etc. are performed. If prothrombin is exceeded, the causes may be factors such as a tendency to thrombosis or taking medications that interfere with the absorption of vitamin K.
Platelets
These are cellular structures of the blood that are actively involved in blood clotting processes and are responsible for the state of the hemostatic system. In pregnant women, their indicators decrease slightly, but if the decrease is quite significant, this indicates the presence of pathological factors.
Platelets are formed in bone marrow structures and are actually the main part of the blood clot that forms when the vessel wall is damaged. In case of acute platelet deficiency, the blood is said to be too thin, which is dangerous due to heavy bleeding and internal hemorrhages.
Thrombin time
Thrombin time is the period during which a blood clot forms. In pregnant patients, the thrombin time is about 9.5-25 seconds. If the indicators are higher, this may indicate the presence of increased bilirubin, decreased fibrinogen and liver pathologies. When thrombin time is less than 9.5 seconds, the development of disseminated intravascular coagulation and increased fibrinogen levels are suspected.
Thrombin time shows plasma blood clotting ability. This indicator is very important during pregnancy, since its abnormal level indicates the development of pathological conditions such as hemophilia, liver pathologies and other coagulation disorders. Normally, in the absence of pregnancy, a woman’s thrombin time is about 12.7-15.4 seconds, but upon conception its indicators change:
- In the first trimester, thrombin time is 9.7-13.5 seconds;
- In the second trimester – 9.5-13.4 seconds;
- In the third – 9.6-12.9 seconds.
In some laboratories, thrombin time values in pregnant women are considered normal: 11-18 seconds. An increase in the indicator may indicate a threat of bleeding and heavy blood loss, the formation of hematomas, etc.
Antithrombin III
This substance belongs to complex proteins, its task is to inhibit blood clotting. Antithrombin is necessary to prevent the accumulation of large numbers of blood clots in the vascular passages. Normally, the level of antithrombin in pregnant women reaches 70-120%. An increase in antithrombin may be a sign of acute hepatitis or any inflammatory process, bile stasis and vitamin K deficiency, taking anticoagulants, or acute pancreatitis.
Reduced antithrombin levels may indicate chronic kidney failure, vascular occlusion or atherosclerosis, and is also observed during treatment with Heparin and acute disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome.
These antibodies, when formed in the body, stop the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. In healthy patients, this component is absent in the blood. This indicator refers to the most dangerous manifestations. If it is detected, then the pregnant woman develops a systemic autoimmune pathology like lupus erythematosus, during which her own cellular structures are perceived as foreign, and therefore antibodies begin to be produced against them.
In pregnant women, lupus anticoagulant can also be detected with the development of preeclampsia, in which extensive vascular thrombosis develops. If pregnancy occurs with such a pathological disorder, then most often it ends with a heart attack, spontaneous abortion, intrauterine fetal death or placental abruption.
As gestation progresses, the indicators change, coagulability increases, which is associated with preparation for childbirth. The results of a coagulogram should only be assessed by a specialist, since the patient will not be able to correctly decipher them on her own, unless, of course, she is a qualified doctor.
A hemostasiogram or coagulogram is a test of blood for its ability to clot (thicken). This analysis shows doctors whether the patient’s body maintains a balance of hemostasis (the processes of blood clotting and thinning). The nervous and endocrine systems are responsible for the proper functioning of hemostasis processes in our body.
For women, this test is usually prescribed during pregnancy or before surgery - that is, when blood loss is possible or when varicose veins, cardiovascular or autoimmune diseases, and liver disease are diagnosed.
High blood clotting (hypercoagulation) can be dangerous due to too rapid formation of blood clots, and this is the main cause of all thrombosis of blood vessels, brain and internal organs. Reduced clotting (hypocoagulation) leads to the risk of various serious bleedings. Timely research and correct interpretation of data make it possible to timely determine the degree of risk and control the dosage and effectiveness of blood thinning medications.
In a laboratory analysis of blood coagulation according to Sukharev, capillary blood (from a finger) is examined; in a study using the Lee-White method, venous blood is examined.
- This analysis is carried out only on an empty stomach. It is important that you do not eat for at least 8 hours before the diagnosis.
- In order for the coagulogram to be as reliable as possible, you should not drink alcohol the day before; you need to avoid tobacco 2-3 hours before taking blood.
- Before donating blood, you can drink, but not more than a glass of plain, ordinary water.
- During blood sampling, it is advisable to be relaxed and balanced: if the sight of blood makes you dizzy or other unpleasant symptoms, do not be lazy to tell the laboratory assistant about it.
Increased blood clotting
This property of blood, such as coagulation, does not allow a person to bleed it out in the event of a cut or any other injury.
However, increased blood clotting is life-threatening, as it is the cause of the development of many diseases. Normal blood moves freely through arteries and veins, supplying tissues with oxygen. In thick conditions, clots and blood clots often form, and an insufficient amount of oxygen reaches the tissues of organs, which leads to a deterioration in well-being and a decrease in a person’s performance.