What is thrombophilia? The process of blood clotting is a cascade of biochemical reactions leading to a change in the state of the blood. This process prevents blood loss from the damaged bleeding site and also prevents infection from entering it. There are conditions that can disrupt this response cascade, resulting in excessive bleeding - hemorrhage or increased blood clotting - thrombosis. Thrombophilia is a condition where a systemic disorder occurs during the process of hemostasis (clotting). This tends to increase thrombosis and, accordingly, thrombotic events, which can affect both the venous and arterial blood systems.
Causes of thrombophilia
Thrombophilia can be hereditary and acquired.
Hereditary forms of thrombophilia are caused by mutations in genes encoding the synthesis of blood clotting factors or key enzymes involved in this process.
Among the main genetic factors that cause the inherited form of tomophilia and mainly those that influence the course of pregnancy are:
Factor V Leiden
Factor V is a protein in the blood that plays a role in the blood clotting process. The mutant gene differs in only one amino acid in its composition, but this leads to significant imbalances in the blood clot. Factor V mutation is thought to be the most common form of inherited thrombophilia. Not all carriers of the mutant gene develop symptoms, but are prone to thrombotic events such as:
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT);
- Pulmonary embolism (PTE);
During pregnancy, this can cause early miscarriage, high blood pressure in the second half of pregnancy (most often after 20 weeks of pregnancy), placental abruption.
Factor II / Prothrombin 20210 (Prothrombin 20210)
Prothrombin is a protein that helps the blood clotting process. The G20210A mutation in the gene for this protein causes excessive blood clotting. This mutation, combined with a factor Leiden V mutation, increases the risk of thrombosis by 10-20 times.
Plasminogen Activation Inhibitor 1 Type 1 (PAI-1) 4G/5G
PAI-1 is a protein that inhibits fibrinolysis (breakdown) of blood clots. When the PAI-1 4G/5G mutation occurs in the gene for this protein, its production increases and this leads to increased clotting. A mutation of this protein most often causes thrombosis of various internal organs or early fetal loss during pregnancy due to thrombosis of the placental “nursing” vessels.
MTHFR mutation (C677T)
The MTHFR gene encodes the enzyme methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. This enzyme has many different functions in the human body, and its deficiency is associated with an increased risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, several types of cancer, etc. The C677T mutation in the MTHFR gene has been found to lead to an increased risk of cardiac thrombosis.
Symptoms
How does the disease manifest itself, how to determine the pathology?
Symptoms of the development of thrombophilia are:
- pain at the site of thrombus formation;
- discomfort when inhaling air;
- numbness of the limbs;
- increased heart rate;
- lethargy;
- fatigue and apathy;
- constant headaches.
The listed symptoms do not appear immediately, but gradually, so women do not pay attention to them. The expectant mother should be alerted by the appearance of swelling on the limb at the site of blood clot formation. Swelling is accompanied by pain. However, blood clots form not only on the extremities, but also on the internal organs.
Pathology is often indicated by a severe form of toxicosis with uncontrollable vomiting and pain.
Pathology can be suspected by the reaction of the fetus: it either increases the activity of movement, or freezes and does not move. This behavior should be a signal to seek advice from an obstetrician-gynecologist.
If a blood clot has formed in the lung, the following symptoms appear:
- difficulty breathing;
- discomfort in the sternum;
- cough with bloody discharge;
- the appearance of shortness of breath;
- feeling of fullness in the chest.
If a blood clot appears in the artery, the patient’s condition will deteriorate sharply:
- stroke;
- ischemia;
- miscarriage.
If a blood clot has formed in the veins, the following will appear:
- swelling;
- heaviness in the legs;
- pain syndrome in the calf muscles.
If a blood clot has formed in the intestines, the following will appear:
- nausea with vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- cutting pain.
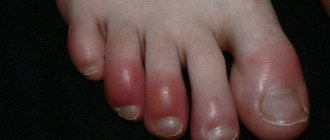
Visually, increased coagulability is noticeable in the subcutaneous vascular network and bruises under the nails. These signs indicate disturbances in blood circulation.
In an advanced state, thrombophilia leads to the formation of gangrene and necrosis of soft tissues.
How does pathology manifest during pregnancy? A woman cannot bear a fetus after conception, since the hematopoietic system is not able to provide it with nutrients. That is, this manifests itself in constant miscarriages. Often miscarriages occur in the very early stages: it seems that the woman cannot become pregnant.
Thrombophilia and pregnancy
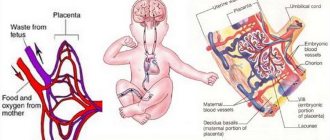
Pregnancy is considered a physiological hypercoagulable state, resulting in a significantly increased tendency for thrombosis, especially venous thrombosis. This trend is associated with an increase in the concentration of cascade factor V coagulation factors and others synthesized in the liver under the influence of pregnant sex hormones - estrogens and progesterones. The presence of congenital or acquired thrombophilia factors further increases the tendency to clot. This can lead to vascular thrombosis in the placental space of the placenta, disrupting the exchange between maternal and fetal blood flow, and consequently causing the fetus to die in the womb.
In what case is it advisable to screen for inherited forms of thrombophilia?
- All patients with a history of venous thromboembolism (VTE), regardless of age of initial stroke (before or after 45 years);
- All women with obstetric complications (except VTE) in previous and/or current pregnancies;
- Preeclampsia, eclampsia, HELLP syndrome;
- Intrauterine fetal retardation (IUDP);
- Premature placental abruption
- History of embryonic (>2 in the first trimester) and fetal loss (>1 second or third trimester);
- Asymptomatic patients with a family history of VTE requiring oral contraception and hormone replacement therapy.
Approach to pregnant women with a hereditary form of thrombophilia
- Before pregnancy and the first trimester, education should be made about the potential risk of vascular thrombotic events during pregnancy and in the perioperative period, as well as the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes.
- Early initiation of prophylaxis with low-dose aspirin -100 mg/day is recommended as soon as the pregnancy test is positive.
- Take folic acid before conception until the 19th week of pregnancy to prevent neural tube defects. In MTHFRD, the dose of folic acid is double or sometimes triple the usual dose. Taking two folic acid tablets daily reduces the risk of fetal cardiovascular abnormalities, according to new research.
- Patients with inherited thrombophilia who are on long-term therapy with indirect anticoagulants (warfarin) should be treated with low molecular weight heparin - Fraxiparin, Clexan 0.40 sc before a planned pregnancy or immediately after its establishment.
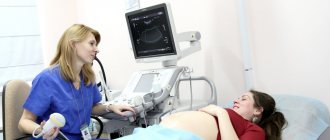
- Ultrasound examination in the first trimester is necessary to accurately determine gestational age and due to advanced obstetric history, every two weeks until 12 weeks
- An ultrasound examination is required for 11 to 14 weeks to measure nodular fissures, the presence or absence of nasal bone, look for abnormal blood flow in the ductus venosus, or the presence of tricuspid regurgitation. These markers, like others, are used for biochemical screening in the 1st trimester for Down syndrome. It is also important to interpret hormone values for potential risk of obstetric complications.
- If necessary, biochemical screening is carried out in the 2nd trimester.
Antenatal period
- In patients with an inherited form of thrombophilia, it is recommended to conduct a Doppler blood test in aa. uterus at 14-16 and 20-22 weeks, and after 28-32 weeks. The presence of increased pulsatility with or without prostatic incisions identifies patients at high risk for developing preeclampsia, eclampsia, intrauterine retention, and other complications. In these, fetal growth rate and Doppler monitoring were assessed by more frequent ultrasound examinations over a 2-week period. In patients with normal blood flow in the aa. The growth rate of the fetal uterus and Doppler is estimated at 3-4 weeks.
- If fetal growth is abnormal and abnormal Doppler is present, the pregnancy is considered high risk. This requires intensive fetal monitoring and, if necessary, hospitalization in specialized clinics.
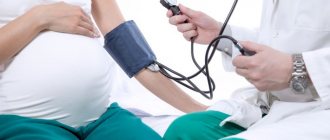
- Due to the increased risk of early preeclampsia (<32–34 weeks), regular blood pressure monitoring and urine testing for proteinuria are necessary.
Timely and accurate diagnosis of hereditary forms of thrombophilia is of great clinical importance due to:
- High risk of vascular thrombotic events during pregnancy and the perioperative period.
- Prophylactic antithrombotic therapy should be included.
- The need for intensive prenatal monitoring of the fetus.
Due to the risk of developing respiratory disorders in newborns, mothers with hereditary forms of thrombophilia are recommended to stop anticoagulant treatment within 30 days before the due date. Suspension of anticoagulant therapy should be combined with fetal monitoring with cardiotography, monitoring of maternal blood flow, as well as fetal and development of fetal birth with the least abnormalities.
Carrying out one of the forms of thrombophilia is an absolute contraindication for the use of oral contraception and hormone replacement therapy!
Acceptance of one of the forms of thrombophilia is associated with a high risk of developing myocardial infarction, coronary heart disease and cerebrovascular accidents!
Treatment
Women are prescribed pharmaceuticals such as Utrozhestan or Femibion (the dosage is calculated by the gynecologist). To strengthen the body, you need to take magnesium pharmaceuticals, as prescribed by your doctor.
However, treatment will not be successful if the woman has low mobility. Blood stagnation is often caused by physical inactivity, so it is recommended to take more frequent walks in the fresh air in good weather. It's not worth getting too cold for the sake of movement.
Doctors recommend performing gymnastic exercises for pregnant women right up to childbirth. These exercises will not harm the fetus, but will strengthen the muscles and get the blood flowing. Therefore, do not neglect the recommendations of gynecologists.
Swimming plays a special place in physical development. Regular visits to the pool strengthens muscles, relieves tension and prepares the body for childbirth.
Diet food
A special diet includes foods that thin the blood. These include:
- ginger;
- fresh herbs;
- seafood;
- raw vegetables;
- red berries - cranberries, lingonberries, viburnum;
- fruits in raw and dried form.
Women are prohibited from eating fried and smoked foods, as well as pickles. Products with preservatives (convenience foods) and cholesterol should be excluded from the menu. Food should be prepared from fresh ingredients with minimal heat treatment. Instead of frying - steam, simmer, simmer. Fried cutlets are replaced with steamed ones; instead of cutlets, it is better to eat dumplings or manti made from lean meat.
If you have viscous blood, you should not eat lard or fatty meat. Beef liver is also contraindicated.
Exclude from the diet:
- fatty broth;
- refined products;
- chocolate, sweets;
- all types of nuts;
- whole fat milk;
- cream;
- hard cheeses;
- coffee, cocoa;
- green tea.
You should categorically refuse such delicacies as chicken skin, which contains a lot of fat, industrial dumplings or pates. It is better to replace meat products with low-fat fish and seafood. For satiety (if you are hungry), you can prepare dishes from beans, lentils, and soy.
Sea kale is a storehouse of vitamins and minerals for a pregnant woman; it helps thin the blood.
Decoctions (compotes) of dried fruits are of great benefit. They contain a lot of minerals, vitamins, and microelements. In dissolved form, they are absorbed much better and do not overload the body with additional work of digestion. Dried fruits need to be kept in the broth until they cool completely, then you can eat them or make a pie filling from them.
Blood clots can become fixed on the walls of blood vessels if cholesterol plaques are deposited on them. Therefore, one of the urgent tasks for the prevention of thrombophilia is the removal of “bad” cholesterol from the body. Cereal porridge with water, fresh fruits and raw vegetables can cope with this: you need to increase their consumption.
Plasma transfusion
For mild forms of pathology, injections with lyophilized plasma are given. Instead of plasma, donor blood is administered. In severe cases of pathology, pharmaceuticals are added to the plasma. Injections are given into a vein or into the place where a blood clot has formed.