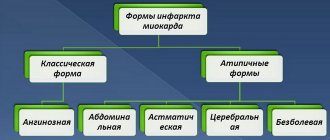
What is a heart attack and where does it come from?
Myocardial infarction is necrosis (death) of heart tissue.
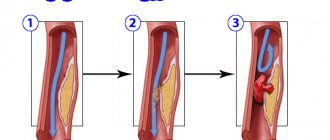
It appears Heart attack - Symptoms and cause, when for some reason blood stops flowing to the heart muscle (myocardium). Due to lack of oxygen, parts of the heart begin to die. The most common cause is a narrowing of the arteries supplying the heart, for example, due to cholesterol plaques. This condition is called coronary heart disease. For coronary artery disease to transform into a heart attack, sometimes no provoking factors are needed: it is enough to wake up and get out of bed for the plaque to rupture and the resulting blood clot to block the blood vessel. With stress or unusual physical activity, this risk increases.
Another, albeit less common, cause is a sudden spasm of the Heart attack of the coronary artery, which stops blood flow to the heart muscle.
Consequences
The consequences of a heart attack in men can be both physiological and psychological. The rehabilitation period after an illness can last from several weeks to several months. However, it is almost impossible to completely restore heart function.
The result of myocardial infarction is the formation of a scar on the tissue of the heart muscle. The functioning of the cardiovascular system in the post-infarction period depends on its size. If the size of the scar is insignificant, then the work of the heart is almost not affected. In the case when the scar is large enough, the contraction of the heart muscle does not occur in full, which means that the circulatory system does not work at full capacity.
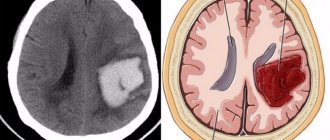
Disorders such as angina pectoris, shortness of breath, and chest pain during exercise occur in many men. More severe complications include heart failure, pericarditis, pulmonary edema, vascular thrombosis, ischemic stroke, and heart rupture. These problems often lead to death.
As a result of a heart attack, the human nervous system also suffers quite seriously. Often men become easily excitable, aggressive, and emotionally exhausted. They are dominated by depressed mood and negative feelings. Due to the fear of recurrence of the disease, men may be susceptible to other mental disorders.
If negative consequences occur, you should contact a cardiologist or psychologist as soon as possible, taking into account the nature of the disorders.
When you need to urgently call an ambulance
At the slightest suspicion of a heart attack, you should immediately call 103 or 112 or go to the nearest emergency department. If it is truly a heart attack, help should be provided within a maximum of 1-2 hours. Heart Attack: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, and Prevention. Otherwise, the consequences of a heart attack may become irreversible, and the risk of death will increase significantly.
Therefore, it is important to know what the symptoms of a heart attack look like.
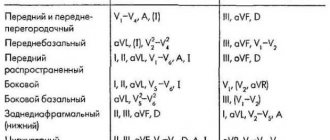
- Severe pain behind the sternum, which increases gradually and sometimes spreads to the left arm, shoulder, jaw, neck, under the left shoulder blade. The pain can be different: it presses behind the sternum, burns, bursts. This is the most common sign.
- Panic fear, which often comes along with pain. The man is worried, clutching his heart.
- Feeling of shortness of breath, like an asthma attack. Moreover, if a person is asthmatic and quickly takes a drug that makes breathing easier, it does not become easier for him.
- Shortness of breath despite no physical activity.
- Weakness, sudden dizziness, clouding of consciousness.
- Rapid, uneven heartbeat Heart Attack: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, and Prevention.
- Cold sweat.
- Nausea, heartburn, abdominal pain.
Signs of a heart attack can be different: some people have many of them and they are pronounced. Others, on the other hand, experience only minor chest pain and weakness. But the more symptoms you have, the higher the risk that it is actually a heart attack.
Secondary prevention of myocardial infarction
Secondary prevention is necessary for people who have already had a heart attack, it is aimed at preventing recurrent attacks. Carried out after a rehabilitation course. The same measures are applied as for primary prevention, but with minor deviations. In general, prevention after a heart attack lasts a lifetime, but is conditionally divided into two time periods:
- The first 1.5-2 years. The condition of the myocardium improves, the person recovers physically and psychoemotionally, coronary circulation and metabolism return to normal.
- The second period lasts throughout a person’s life and includes preventive measures and monitoring by the attending physician.
Medications for the prevention of myocardial infarction:
- Aspirin. Indicated for people who have had a heart attack as a blood thinner. Helps reduce mortality from attacks.
- ACE inhibitors. They prevent the left ventricle from restructuring, which saves the patient from heart failure.
- Calcium antagonists. They are used for difficult-to-treat angina and contraindications to taking beta-blockers. Indicated for ischemia and tachycardia.
- Beta blockers. Relieves tension in the wall of the left ventricle. They reduce the risks by 20% after a person has had a heart attack. They are the most effective and should be prescribed for existing indications as early as possible; the course of treatment lasts a long time
Non-drug prevention after a heart attack:
- Exercise stress. After an attack, to prevent complications, physical activity should be regulated by a doctor and carried out in stages, depending on the patient’s condition.
- Psychological rehabilitation. For this purpose, psychologists and psychotherapists are involved.
In this case, the patient must inform his doctor about all the unpleasant effects and symptoms caused by one or another preventive method. Secrecy in this matter will not lead to anything good. It is also important to strictly follow the prescribed regimen, otherwise only the patient himself will be responsible for the consequences, and they can be very dire.
The first post-hospital period is best spent in a sanatorium that specializes in the treatment of cardiac pathologies, where effective preventive measures are carried out to restore patients in physical and psychological aspects.
After all treatment measures, an able-bodied person should get a job that does not involve huge physical or moral costs.
The sooner you pay attention to existing deviations in your health, the greater the chances of diagnosing the pathology on time and avoiding serious consequences. It is also important to undergo regular examinations for preventive purposes.
What to do before the ambulance arrives if someone else has a heart attack
- Lay the victim down. The position should be semi-sitting.
- Loosen your clothes if they are making it difficult to breathe.
- Open a window or otherwise provide fresh air.
- Give the victim nitroglycerin if previously prescribed by a doctor. Follow the instructions strictly.
- Give aspirin. Firstly, it relieves pain. Secondly, the drug thins the blood. This improves blood flow and may provide relief. Please note that aspirin should not be taken Chest Pain: First Aid if you are allergic to it or suffer from diseases associated with low blood clotting.
- Do everything to calm the person down.
- Tell the visiting doctors when the attack began, what symptoms were associated with it, and whether you took pills - which ones and in what quantity.
Diagnostics
First of all, you need to make it a rule after 40 years to visit a cardiologist twice a year and take an electrocardiogram in order to promptly identify possible heart problems and, if necessary, begin treatment immediately. For males, it is advisable to perform an ECG with exercise (bicycle ergometry). In addition, you should regularly monitor your blood pressure using a home blood pressure monitor. High blood pressure is dangerous, as it puts significant strain on the heart and can cause a heart attack.
Monitor your cholesterol levels and take blood lipid tests at least once a year, and also check your blood for clotting. If your readings differ from the norm, be sure to visit a cardiologist and follow his recommendations.
Eat regularly, 4 times a day. Remember that you should have dinner no later than three hours before going to bed. Try to limit the consumption of animal fats, sugar, sweets and baked goods, flour products, coffee and strong alcohol, as well as sausages, sausages, ham, canned food, salt and salty foods. Salt retains water in the body, which slows down metabolism and leads to cardiovascular diseases. The optimal amount of salt is no more than 5 grams per day. Do not overeat - the larger the amount of food, the higher the load on the heart. Avoid coconut, ghee and palm oil - they accelerate the aging of the heart and weaken its muscle tissue. Olive, flaxseed and sesame oil are much healthier for health.
Buy wholemeal bread - it contains a large amount of fiber, which collects harmful cholesterol and removes it from the body, slowing down the development of atherosclerosis. Fruits and vegetables are also rich in fiber - apples, bananas, oranges, grapes, avocados, pomegranates. They also contain heart-healthy vitamins. Prepare salads more often from fresh herbs, carrots, beets, and season them with vegetable oil. Add dried apricots and raisins to your dishes. Eat nuts and cereals - rice, buckwheat, rolled oats.
Be sure to include calcium-rich fermented milk products in your diet: kefir, milk, cottage cheese, yogurt, cream, sour cream.
Regularly eat seafood and fish: salmon, hake, trout, pollock, salmon. Fish is best baked, steamed or stewed.
Meat is also healthy to eat baked. Pork should be preferred to lean veal, chicken, turkey, and rabbit.
For drinks, green tea is recommended, as well as viburnum tea with honey. You can allow yourself one or two glasses of dry red wine a week. Stay hydrated - drink at least two liters of water per day. Water thins the blood and prevents the formation of blood clots. Never quench your thirst with carbonated drinks - they increase triglyceride levels and several times increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases, and also provoke obesity. Instead of sweet fizzy drinks, it is better to drink a glass of mineral water.
How to reduce the risk of a heart attack, including a recurrent one
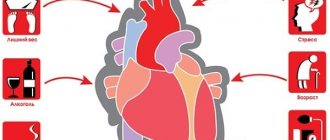
Heart attacks are more common in men over 45 and women over 55. Those who have already had a heart attack in their family are also at risk. Unfortunately, it is impossible to combat these risk factors. But there are others that are entirely within your power to defeat.
Here's what to do to reduce your chance of having a heart attack.
- Try to quit smoking and give up alcohol.
- Move more. According to 5 Heart Facts That May Surprise You from Johns Hopkins University experts, physical inactivity is even more dangerous than smoking.
- Spend as little time as possible sitting. A sedentary lifestyle is another powerful risk factor.
- Watch your blood pressure. High blood pressure can damage the arteries that supply the heart. If you experience attacks of hypertension, be sure to consult with a therapist or cardiologist and learn how to return your blood pressure to normal.
- Control your cholesterol levels.
- Watch your weight. Try not to lead the situation to obesity.
- Learn to deal with stress.
Yes, these are boring prevention recipes. But others don’t work, and there is no magic pill for a heart attack. Everything is in your hands, and this also applies to your heart.
How to live for men after a heart attack
After myocardial necrosis, it is extremely important to change your previous lifestyle. It is necessary to control sugar levels, blood pressure, body weight, cholesterol levels, avoid stressful situations, and prevent fatigue. You cannot abruptly resume physical activity, so after an attack, exercise therapy classes are prescribed to enrich the heart muscle with oxygen and increase its endurance. Among sports, experts recommend cycling, walking, and swimming. A specialized diet is of great importance after a heart attack. Experts recommend following a low-calorie, but nutritious and balanced diet. Such a diet has the goal of safely and quickly restoring the myocardium after necrosis.
It is vitally important to give up tobacco addiction, which can cause myocardial necrosis or cause a recurrent attack in it.
The diet requires the patient to eat more frequently in the first week, up to 6 times a day. You must include lean beef, boiled or stewed fish, and crackers in your daily diet. Also, the diet recommended after a heart attack involves the consumption of vegetable puree soups and cereals, and fermented milk products. But products like smoked meats and cheeses, baked goods and alcoholic beverages, salt and coffee, chocolate should be completely removed after a heart attack.
The post-infarction diet involves split meals in the first month; after a week, you can start eating unsalted, unprocessed foods. Seafood and prunes, dried apricots and raisins are considered very beneficial for the body during this period. Practice shows that such a diet improves the condition of patients.
Drug prophylaxis
It is used as an additional mechanism to prevent myocardial infarction mainly in patients at risk and already having cardiac pathology.
Drug support includes a number of drugs:
| Secondary | Aimed at preventing the re-development of the pathological condition (relapse) |
| Non-drug | Effect on controllable disease risk factors |
| Medicinal | Addressing existing health problems that may worsen or even cause cardiac disease |
| Drugs | When is it prescribed? |
| Statins | High numbers of cholesterol fractions and low response to non-drug types of exposure |
Atherosclerotic changes in vascular walls
Previous disturbance of blood flow in cardiac tissue
Tendency to form vascular clots or history of thrombosis
Pathology of the heart valve apparatus
High risk of developing heart disease