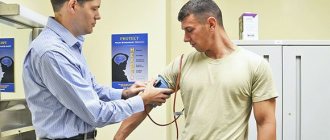
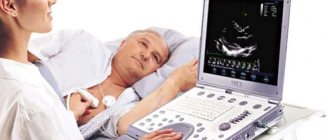
When I was in college, we had medical examinations twice a year. In September and May. Everything took place within one day at the medical center, which had an agreement with the institute for medical care for students. As a rule, for our faculty, it was Thursday, and then Friday (for the guys, examinations took place on this day, and Thursday was their day off), for us it was always a day off. And Saturday has always been considered a day of independent work. So then it turned out to be a little vacation. What was included in the inspection? In September: general blood test, dentist, ophthalmologist, fluorography, ECG, abdominal ultrasound, therapist, gynecologist, surgeon and general physical development test. In May everything is the same, but without fluorography. It all started with the fact that you had to choose which doctor would be first on your list and in what order you would then go to specialists. This method almost eliminated unnecessary waiting in lines. At most, I had to wait 40 minutes for my visit. I’ll tell you briefly about almost all the specialists. Everywhere everything was done with the utmost care for us. We even entered the fluorography room one at a time. But everything happened very quickly, the equipment did not break down, the film did not run out (or whatever was inside the device). I went in, undressed....take a deep breath and not breathe, got dressed and went out. All in less than five minutes. The therapist (female) asked me to undress to the waist, “listened” to my heart and lungs, measured my blood pressure and temperature at the time of the examination, asked about complaints….standard in general. The entire visit takes about 15 minutes. In the ECG room, you had to undress down to your underpants; you will lie down on the couch, and first they will “listen” to your heart, and then an ECG...also within 20 minutes. For an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, it was necessary to remove outer clothing and lower the trousers a little. They even let three people into this office. The surgeon (he was a gray-haired man about 60 years old) had to undress down to his underwear. He checked his posture (for this he asked to unfasten the bra), very carefully examined the navel, then the feet, for the presence of flat feet, knocked on the knees with a hammer, everything was also standard, the only not entirely pleasant moment was when the doctor asked to turn your back to him, bend over and pull your panties down to your knee, and that’s also standard. At the end of the examination, the surgeon examined the breast. (Usually the doctor uttered a cheerful phrase: “Prepare your breasts for examination,” (yes, you had to take off your bra). The breasts were examined in a standing position. The surgeon’s examination took about 25 minutes. The gynecologist examined in three stages: first, questions about sexual life, menstruation and complaints, then you undress from below... and onto a chair. Strange, but virgins were examined on the same chair with special small mirrors and also rectally, and then on the couch they were examined more... let's say, comprehensively and more thoroughly. The first two courses I was a virgin. I know exactly the differences. Although It would seem that it should be the other way around. They also did an ultrasound of the pelvis and a vaginal ultrasound. Then you dress from below, undress from above and they examine your breasts very carefully. In a standing, sitting and lying position. And they also do an ultrasound of the mammary glands. A routine examination with all the undressing and changing of clothes 35-40 minutes, and about 50 virgins. The only thing that was always a little embarrassing in all these offices was the lack of a screen. You had to undress, always practically looking “eye to eye with the doctor.” I won’t talk at all about the dentist, ophthalmologist and blood tests , everything is completely standard here.
But I would like to talk in more detail about this very Test of General Physical Development. I still cannot understand the purpose of this test. Let me start by saying that this examination took place in the nude.
Separately, we should talk about the entrance to the office. It was strictly forbidden to enter this office without a summons. Even people in white coats. If you're the first, then it's understandable. The “Sign In” sign lit up. She came in. There are two screen booths in front of you, you choose any one, you go in, undress and go to the doctor. If not, then as soon as the “Enter!” signal lights up for you. Come in. You choose a free screen booth. You undress, wait until your predecessor leaves the office, then go out to the doctor. At the end of your examination, as soon as you go into the booth to get dressed, they call the next one.
So...and now about this inspection. There was always a male doctor here. You stand on the warm carpet naked in front of him. And he first asks about the underwear you are wearing, then the changes that have occurred since the previous examination. And we had to talk about everything: about changing the cycle, about changing the partner, about a casual relationship, if one took place, about the preferred position for sex, about what excites the most…. Even the gynecologist did not ask such questions. Then height and weight were measured. Then measurements began: the volume of the head, neck, waist, leg length from hip to floor, foot length, distance from one shoulder to the other, chest volume (measurements were carried out in three positions: standing, sitting, lying <on the couch>, then measured the "length" and "width" of each buttock, also in a standing and lying position. Then the "sides of the triangle" were measured. After that, the distance from nipple to nipple: in a standing, lying, sitting position, and also in the position, let's say " poses for push-ups." And the distance from nipple to nipple was measured, with the breasts brought together as much as possible. Then the distance from each nipple to the navel: this in a standing and lying position. Then the distance between the breasts was measured: here sitting, lying, standing. Then they measured each "side" of the breasts separately: in a standing and lying position. Then nipple halos... A device similar to a compass appeared in the doctor's hands. In general... the nipple was taken as , thus the "radius" and "diameter" were measured. Also in the position: standing, sitting and lying down The next measurement was taken only in the lying position. Devices similar to the membranes of a phonendoscope were placed on the nipples; they were terribly cold, trembling ran throughout the body, and the nipples became like “towers.” The time during which the nipples became “turrets” was immediately recorded, and the length of these “turrets” was measured. And then it will take time until the nipples return to their “normal” position. After this there was a series of completely strange exercises, which included the ability to hold on for as long as possible in a position on one leg, the other is bent at the knee and the heel rests on the knee of the straightened leg at an angle of 90 degrees, the back is straight, arms to the sides, eyes closed; just the time of “standing” on one leg, without these bells and whistles, running in place until exhaustion (the time of this run and the time of breathing returning to normal were counted), then just jumping in place, then with clapping, then just squats and pistols (and all this to your limit of exhaustion), then abdominal exercises (all according to the same scheme). After all this, they were sent back to the couch, asked to lie down and breathe calmly until the heartbeat and breathing were completely restored, then another series of tests: lie on your back calmly, hands “at your sides” and count to 11 in a whisper, then raise your right hand up and mark it outstretched behind head, again count to 11 and return to the position “at the seams”, then also with the left hand, then both hands were raised up and returned back to the count of 11, then the hands had to be pulled in front of you in the same way, and then the legs: the right one as high as possible , until 11 you count down, then the left, then both, in conclusion, first, as if with one breast, you stretch up, then the second, then both, then again until breathing is completely restored, and then you seem to “listen” to the doctor completely with a device similar to a phonendoscope, first lying on your back, and then lying on your stomach. Then you need to lie on your back again and pull in your stomach as much as possible, count to five, then “inflate” it as much as possible again to five, and again from the beginning. And so 27 times. A very difficult exercise, I tell you. You're almost out of breath by the end of it. And this is if, in general, you take care of yourself and play sports. Then he asked you to lie quietly on the couch for a while, and then you were allowed to go get dressed. All this took about an hour. The doctor behaved very delicately, no rudeness, no pushing... like “do it faster,” no caustic remarks. And by the fifth year the sequence was very well remembered. It’s strange, but visiting this particular office did not cause anyone a feeling of shame; for many it became the start of an intimate relationship. After my first visit to this office, I personally allowed my boyfriend to take off my bra. And it was after the next visit to this office that the “first time” happened. The doctor said that it was time for me to move on to heavier artillery than completely naked caresses. On the discharge sheet that was given to you after the examination, which contained the results of all examinations and recommendations, opposite the Test it always stated that the test of general physical development was passed at the proper level and that’s all.
What is an ECG?
Electrocardiography is a non-invasive technology for graphically recording the potential difference in the electric field generated during the work of the heart. It is carried out using an electrocardiograph.
The device has electrodes that are attached to certain points on the patient's body. They capture the electrical impulses of the heart, which, after amplification, are recorded by a galvanometer and recorded on paper using curved lines. The result is a cardiogram, which is subject to further interpretation by a cardiologist or therapist.
Goal and tasks
Taking an electrocardiogram is necessary for diagnosing disorders of the heart, and is also a mandatory element of the annual medical examination of the population. Cardiologists recommend an ECG every year for all people over 40 years of age.
Looking at the cardiogram, the doctor will evaluate:
- Frequency (pulse), rhythm and regularity of heart contractions.
- Physical condition of the heart.
- The presence of disturbances in electrolyte metabolism (potassium, calcium, magnesium and others).
- Conducting system of the heart (various blockades and arrhythmias).
- The effectiveness of treatment in acute and chronic diseases.
- Localization, size and degree of damage during ischemia and myocardial infarction.
- The presence of cardiac complications in diseases of other organs and systems (pulmonary embolism).
Reasons to get tested
A cardiogram is done at the slightest complaint:
- for interruptions in heart function;
- shortness of breath;
- heaviness and pain in the chest;
- weakness, dizziness;
- high blood pressure;
- pain in the back, chest and neck.
- before operations;
- at medical examinations;
- during pregnancy;
- if there is a risk of developing heart disease;
- to obtain a medical record when applying for a job.
For a complete diagnosis, one cardiogram is not enough. The doctor will be able to draw conclusions about your health based on a comprehensive examination, taking into account the results of other examinations, tests, your complaints and medical history.
What kind of doctor does it?
At the clinic, a referral for cardiography is given by a therapist. And the doctor who deciphers it is called a cardiologist.
The following can also be concluded:
- functional diagnostics doctor;
- emergency doctor;
- Family doctor;
- pediatrician.
The procedure itself is carried out by nurses in a specially equipped room.
After receiving the test results, you must make an appointment with the doctor who prescribed the ECG to receive recommendations or treatment prescriptions.
How to choose a bra for a nursing mother
During breastfeeding, choose underwear made from natural hypoallergenic, breathable and smooth fabric, without seams and preferably without pits. It is important that the material does not rub the skin and nipples, does not sting or squeeze the mammary glands. And to prevent milk from leaking through underwear or clothes, you can use special breast pads or pads.
If you prefer synthetic items with ruffles or lace, choose models with cotton inserts inside. They should completely cover the nipple and areola. When choosing a model with underwires, do not forget that the latter must be made of plastic. And do not wear such products for too long.
For nursing mothers, they produce models with cups with valves, where you only need to unfasten the top part. This way, you can quickly empty your breasts and feed your baby. When choosing lingerie, be sure to try on the item and leave it on for a few minutes. Pay attention to the skin; there should be no traces of the straps left after the laundry.
Wash your bra regularly, as it is in constant and close contact with the skin. By the way, experts do not recommend wearing a bra for two days in a row, since during this time it does not have time to restore its cup shape and elasticity. Be sure to choose the model by size. It should not be too tight or close to the body.
Choose a product with wide straps so that it properly supports the breasts and does not put pressure on the mammary glands.
It is important that the material is safe, does not scratch or injure the skin, and does not cause an allergic reaction. For more information about the types and selection of underwear for breastfeeding, read the link. Subscribe to our VKontakte group
Preparing for the examination
Rules for preparing for an ECG:
- On the day of the procedure, you should refrain from drinking coffee, tea and energy drinks.
- Do not eat heavy food 2 hours before the test.
- Do not take sedative medications. If you regularly take cardiac medications (antiarrhythmics, beta blockers, cardiac glycosides), be sure to inform your doctor about this.
- Smokers should stop smoking an hour before the ECG.
- Do not expose yourself to physical stress. It is advisable to arrive 10–15 minutes before the examination and relax on the couch.
- Do not use greasy cream or lotion in the chest area.
- Clothing should be comfortable so that you can quickly expose your wrists, legs and chest. You will also have to remove all metal jewelry and watches.
- Be sure to take your previous cardiograms and test results with you.
Standard research design
The doctor does an ECG as follows:
- Before installing the sensors, make sure that there are no metal jewelry on the patient’s body. The patient's body is freed from excess clothing, the upper torso, wrists and shins are exposed.
- The electrode attachment points are treated with special compounds to better attach the sensors to the skin surface.
- The person takes a horizontal position, lying on his back. Before doing an ECG, the doctor writes down all the information about the patient.
- The sensors are fixed on the body using special clamps. The devices are placed in the lower part of the forearms, the outer and inner areas of the legs.
- The chest leads are attached to the skin of the chest in 6 zones using adhesive tape.
- The sensors are connected to the device according to a certain scheme: the red wire is attached to the right hand; yellow – to the left upper limb; green - to the lower left, white - to the chest.
- Leads are registered. According to the standard scheme, sensors are registered through alternate connections: 1 lead - the sensor from the left upper limb is connected to the electrode of the right hand; Lead 2 – the sensor from the right upper limb is combined with the electrode of the left leg; Lead 3 – combines the sensors of the limbs located on the left side.
Standard ECG scheme
Important! During the procedure, the person must not move and remain in a calm psycho-emotional state.
To register an electrocardiogram, the patient is recommended to follow some rules:
- during the diagnostic procedure, breathe evenly and avoid emotional overload;
- do not eat 2-3 hours before the procedure;
- patients with severe shortness of breath are recommended to perform the procedure in a sitting position;
- Women should remove their bra.
Patients who have never had an ECG often ask: how long does the study take? Answer: about 3-5 minutes. Another question that interests women is whether it is necessary to take off their bra before an ECG? Answer: when recording an ECG, suction cups are placed on the surface of the skin of the chest, and any materials, including a bra, create interference.
To examine heart rhythms that occur only during physical activity, non-standard ECG schemes are used, for example, a stress test. Heart rate measurements are taken after exercise on a treadmill or bicycle. If the patient has contraindications to physical activity, then to conduct a stress test, he is injected intramuscularly with drugs that stimulate the heart.
Stress tests are prescribed to diagnose a patient with coronary heart disease in the early stages of development, which does not manifest itself with characteristic symptoms.
Several hours before the procedure, alcoholic and caffeine-containing drinks are excluded from the diet.
Performing a stress test
You should know! An ECG of the heart according to the standard scheme is performed in a supine position. But if it is necessary to confirm disturbances in heart rhythm or conduction of the cardiac arteries, the procedure is performed in a standing position. Before the ECG, women will only need to remove their bra, and men should preferably shave their chest hair so that the ECG recording goes as smoothly as possible.
If stress tests record abnormal values, then the diagnosis is carried out with hyperventilation. What is this technique used for? Nonspecific changes in the cardiogram can appear for two reasons - due to increased physical activity or as a result of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
To understand the cause of the anomaly, the doctor asks the patient to breathe evenly and deeply. During this time, adaptive changes occur in the body, and the line on the ECG takes on a normal physiological appearance. If after hyperventilation the heart rate increases two or more times relative to the control result, then the test is considered positive. This indicates that the patient has neurocircular dystonia.
A stress test with hyperventilation is not performed on children and patients suffering from problems with cerebral circulation, since the test may provoke vasospasm.
If the patient has a predisposition to an irregular rhythm, then he is prescribed Holter monitoring. In this case, using a standard scheme it will not be possible to detect the deviation in a few minutes. The device for Holter monitoring has 2, 3 or 12 valves. It is worn for 24-48 hours.
Holter monitoring device
How to wear the device correctly? Self-adhesive sensors are attached to the treated areas of skin. The wires coming from the electrodes go to the recording apparatus. During research, a person can lead a normal lifestyle.
The main condition during the study is to avoid getting the device wet. In parallel with Holter monitoring, the patient must record the moments when unpleasant signs appear in the heart area. The doctor will compare the notes taken with the readings from the device.
ECG, as a simple and at the same time reliable way to determine heart disease, has been used since 1873. The activity of the circulatory organ is affected not only by cardiovascular pathologies, but also by other disorders in the body. If unpleasant cardiac symptoms occur, do an ECG so that the doctor can track abnormalities in the functioning of the organ and prescribe a timely treatment regimen.
Source: lechiserdce.ru
General algorithm of actions when taking an ECG
- The health worker writes down all the patient's data in a journal.
- The wrists, legs and chest are exposed.
- Electrodes are attached while lying down. Before this, the skin is degreased with alcohol, and for better contact with the sensors, a special gel is applied, or wet gauze wipes are used.
- The indicators are recorded on paper, after which the terminals are removed and the skin is wiped dry.
There is no need to be nervous or talk during the ECG. The recording technology is absolutely safe and painless. The duration of the examination is 10–15 minutes.
Breathing should be smooth and calm. It may be necessary to record inspiratory readings. In this case, the nurse will instruct you to take a deep breath and hold your breath.
ECG manipulation is carried out in the functional diagnostics room. The room should be warm and isolated from possible sources of electrical interference. It is also recommended to turn off your mobile phone.
How is cardiac cardiography done?
An electrocardiogram records electrical signals in the heart.
This is a general test used to identify problems and monitor the condition of the heart in various situations, as an ECG is done in the functional diagnostic room, in ambulances, and at the patient’s home. Electrocardiographic examination is non-invasive, painless and gives quick results. During the test, sensors (electrodes) are attached to the limbs and chest and remain for a few minutes, which usually does not cause discomfort.
What is electrocardiography (ECG)
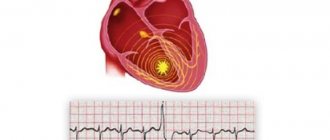
Each heartbeat is triggered by an electrical impulse, and an electrocardiogram records the timing and strength of these signals as they travel through the myocardium.
The device for recording electrical impulses is called a cardiograph, it has several terminals and electrodes that collect information from 12 different areas on the skin of the chest and limbs.
Electrical activity is recorded as waves on a graph, with different patterns corresponding to each electrical phase of the heart rhythm.
An ECG graph is a graphical representation of changes in the electrical potential of the heart.
Standard procedure
Typically, cardiac cardiography is performed on a stationary cardiograph in a functional diagnostics room. The room should be warm so as not to cause muscle tremors and discomfort. The subject is placed on the couch face up, with his arms placed freely along the body.
Clips are placed on the exposed areas of the limbs above the wrist and ankle. Before this, the skin is wiped with a degreasing compound (most often ethanol). The terminal may look like a clothespin, or it may be a plate on a wire that the nurse will secure with a rubber band. First, conductive gel is applied to the electrodes or conductive pads are placed under them.
Electrode sensors are also placed on the bare chest at certain points. For ease of use, they have the form of suction cups, which can be easily removed and moved to the desired points. The skin of the chest, before taking an ECG, is also wiped for better contact between the electrodes and the skin.
The usual position of the patient when recording an electrocardiogram You can also read: ECG for angina pectoris
When recording an electrocardiogram, breathing should be calm and uniform, unless there is a command from the medical staff to hold it. While the reading is being recorded, the nurse will switch the knob on the device several times. This corresponds to recording readings from various leads.
After recording is completed, the electrodes are disconnected and the body areas are wiped dry. As a rule, the entire procedure takes no more than 10 minutes.
Women should note that wearing tights for the procedure is not very convenient, since you will need to completely expose your ankles. You should also not use creams or lotions on the body and chest, as they interfere with the conductivity of the current on the skin.
Underwear also needs to be removed, since a tight bodice can disrupt the movement of the chest, and the so-called metal “bones” can interfere with the readings of the device; in addition, this wardrobe item will not allow you to install electrodes at the right points around the chest.
Stress test
Often, some heart symptoms only appear during physical activity.
Therefore, in such patients it is necessary to conduct an ECG of the heart after light physical activity (walking on a treadmill, riding an exercise bike, squats), which is called a stress test.
If at the same time the patient has a disease that prevents him from performing physical work, then a drug that stimulates the heart (beta blockers or potassium supplements) is administered for a stress test.
Scheme of stress test under load
This type of study is used when there is a suspicion of coronary heart disease in its initial asymptomatic stage.
Features of preparing for the test - avoid smoking, caffeinated drinks and food, alcohol and taking medications several hours before the examination.
Orthostatic test
Typically, the electrocardiogram is taken with the patient lying down. But if there is a need to confirm rhythm and conduction disturbances in the heart of a vago- or sympatho-dependent nature, then the recording procedure is carried out while standing.
Women do not require special preparation, but for men it is advisable to shave their chest hair for better contact between the electrodes and skin and high-quality recording.
Initially, the cardiogram is taken as usual, then a short rest follows, after several minutes of being in an upright position, they begin to record the second stage of the cardiogram - standing.
In children, ECG is performed in the same way as in adult patients, including orthostatic tests in a standing position
Hyperventilation test
An electrocardiogram during a stress test may show nonspecific changes. Alternatively, this could either be a consequence of physical activity, which is normal, or a manifestation of respiratory alkalosis and hyperventilation.
The patient is asked to breathe deeply and rhythmically for about three minutes. During this time, a whole cascade of adaptive changes occurs in the body and the ECG curve takes on a characteristic appearance. The test is considered positive when the heart rate increases by 2 times from the control ECG. This is how neurocirculatory dystonia is defined.
Hyperventilation can cause spasm of coronary and cerebral vessels, so it is not performed on young children and patients with cerebrovascular accidents.
Holter monitoring
This is what a connected Holter monitor looks like
A patient's tendency to have an irregular rhythm, which may come and go and cannot be “caught” in a few minutes, is an indication for the use of a Holter heart rate monitor.
A small device is usually equipped with two or three or twelve channels; it must be worn for a day or two. Electrodes, usually self-adhesive, are installed on areas of suitably prepared skin. Men are offered to shave their chests. For what? To ensure reliable contact of the electrodes with the skin.
Wires from the electrodes on the chest go to a self-powered recording device that is located in a pocket or on a shoulder strap. While readings are being taken, you can go about your daily activities, just do not get the electrodes wet. At the same time, you need to record all the moments when unpleasant cardiac symptoms appeared and the time of their occurrence.
Subsequently, the doctor will compare such records with the device’s reading to determine the cause of the symptoms.
As you can see, the method is quite simple, but it helps to solve many issues of functional diagnostics of the heart and notice pathological changes in time. Moreover, the activity of the heart can reflect not only diseases specific to it, but also any disorders in the body. So periodic examination with an ECG should become your good habit.
Source: https://icvtormet.ru/diagnostika/kak-delayut-kardiografiyu-serdca
Features of ECG according to Slopak
In medicine, there is another way to conduct electrocardiography - ECG according to Slopak. It differs from the standard procedure. Used to diagnose posterobasal myocardial infarction.
- Green - left leg.
- Black - right leg.
- The yellow electrode is placed on the fifth intercostal space on the left along the posterior axillary line (at the level of thoracic V6).
- Red is moved sequentially and used to remove the chest leads.
The marking looks like this:
- S1 - at the left edge of the sternum;
- S2 - in the middle of the distance between leads S1 and S3;
- S3 - second intercostal space on the left along the midclavicular line;
- S4 - second intercostal space on the left along the anterior axillary line.
In this case, the contact switch must remain in position I.
Procedure
How is an ECG performed?,
what if the appointed time has come?
You will be asked to remove your outer clothing so that nothing obstructs access to the chest, and free your lower legs. The places where the electrodes will be attached will be treated with alcohol, and a special gel will be applied to them.
The next stage comes down to attaching the cuffs and suction cups. They are fixed on the arms, ankles and chest. Ten electrodes will track the heart rhythm and give an encrypted result.
Interpretation of the results will be effective if the patient has followed all instructions for preparing for the ECG
The heart plays the role of an electrical generator. Body tissues have a high degree of electrical conductivity, which makes it possible to detect the electrical impulses of the heart by applying electrodes to areas of the body. The readings of biopotentials are processed by an electrocardiograph and provides data in the form of a summary picture - the distribution of excitation signals throughout the muscle in a graphic image. More specifically, the difference in electrical voltage.
The spread of the impulse throughout the heart is facilitated by the depolarization of myocardial cells
, during which some of the cells acquire a positive charge, the other part - a negative one. This is how a potential difference arises. In the case of complete depolarization (contraction) or repolarization (relaxation) of the cell, no voltage difference is noted. The device records EMF—electromotive force of the heart.
After an ECG is performed, the doctor gets an idea of the functioning of the organ and any abnormalities.
An electrocardiogram can reveal:
- arrhythmia
- ischemia
- myocardial infarction
How to do an ECG for women
ECGs are done for women in the same way as for men. The only peculiarity is that the girls take off their bra, since the impulse does not pass through the fabric of the bra. For the same reason, it is not advisable to wear tights or stockings.
Are there any special features during pregnancy?
There are no contraindications for ECG during pregnancy. This is the same stage of monitoring the health of the expectant mother as an ultrasound. That is why women should not refuse to perform such a study.
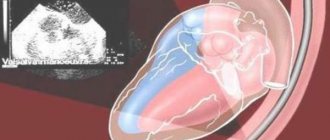
During pregnancy, the heart experiences increased stress. During pregnancy, an ECG is prescribed 2 times. In addition, an electrocardiogram is performed not only on the woman, but also on the fetus - this study is called CTG (cardiotocography).
During pregnancy, the following changes appear on the cardiogram:
- displacement of the electrical axis of the heart to the left;
- increased heart rate, single extrasystoles;
- negative T wave in the third and fourth leads;
- shortened PR interval;
- pathological Q wave in the third lead and aVF (right arm lead).
Bra for breastfeeding: pros and cons
If the bra is chosen incorrectly, it can actually cause harm. Such underwear impedes the flow and movement of milk through the ducts, which impairs lactation and injures the nipples and breasts. It provokes the appearance of lumps and nodules in the mammary glands, forms stagnation of milk and causes lactostasis. Without timely intervention, it develops into mastopathy and other complex diseases.
If a nursing mother is comfortable without a bra, then wearing underwear during lactation is not necessary. However, many women have a difficult time, as the breasts become larger and heavier due to milk. In this case, support and fixation are needed. Then it is important to choose the right bra model. By the way, today they make special underwear for nursing mothers.
Decoding indicators
ECG is assessed according to several criteria:
- The rhythm is correct and regular. No extraordinary contractions (extrasystoles).
- Heart rate. Normally - 60–80 beats/min.
- Electrical axis - normally R exceeds S in all leads except aVR, V1 - V2, sometimes V3.
- Width of the ventricular QRS complex. Normally no more than 120 ms.
- QRST - complex.
QRST - normal complex
Brief designation of the main elements of the film:
- P wave - shows atrial contraction;
- PQ interval is the time the impulse reaches the atrioventricular node;
- QRS complex - shows ventricular excitation;
- T wave - indicates depolarization (restoration of electrical potential).
Video about ECG norms from the Mass Medika channel.
Terminology and interpretation of results
The research will take a few minutes, and the same amount will be required to decipher the result.
The results are recorded on a form or directly on a graph in the form of a special abbreviation, which can be deciphered not only by the doctor, but also by the person being examined.
Heart rate is the rate at which the heart beats. The norm for an adult is considered to be 60–90 contractions per minute. The numbers indicate more or less bradycardia or tachycardia.
EOS is the name of the electrical axis of the heart, which shows the position of this organ relative to the chest. The axis can be vertical or deviated from the vertical at any degree.
Hypertension is often accompanied by left-sided deviation or horizontal axis position. In overweight people, the EOS is often horizontal, in thin people it is vertical.
Changes in EOS are always alarming: if this occurs, a more thorough examination is required after an ECG.
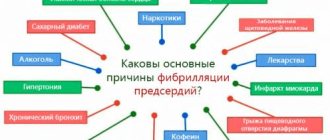
Flickering occurs in most people over 60 years of age. This is a heart rhythm disorder, it has no symptoms, but without treatment it can result in a stroke, as it leads to blood clots.
If the ECG reveals atrial fibrillation, the patient is prescribed antithrombotic therapy, even if the patient has not received any complaints up to this point.
Sinus arrhythmia is a violation of the rhythm of contractions. There are two types of sinus arrhythmia: respiratory, which does not require treatment, and non-respiratory, which requires deeper study.
It is in order to identify non-respiratory arrhythmia that when undergoing an ECG, the doctor asks the patient to hold his breath.
Extrasystole is the name given to a painful voluntary contraction of the heart that causes an abnormal electrical signal.
This is the most common abnormality in the functioning of the heart, which is detected as a result of an ECG. Not all systoles are a sign of illness, although patients actively complain about them.
In most cases, they indicate physical overexertion, vegetative-vascular dystonia, and stress. Video: