To monitor the health of mother and baby during pregnancy and after childbirth, doctors prescribe a large number of tests and studies, the main one of which is a general blood test. The results of this study inform specialists about many indicators, the most important of which is the level of leukocytes. The number of leukocytes can tell the doctor about the presence of pathologies in the fetus at the stage of development, the presence of infectious ones. An increase in leukocytes in a woman’s blood after childbirth may be a sign of an inflammatory process that requires medical intervention.
Leukocytes, types and functions
Leukocytes, colorless cells in the circulatory system called white blood cells, represent the body's "front line of defense." When infectious agents and diseases enter the body, they surround the foreign body and begin to absorb it, dying in the process. In places of mass death of protective cells, swelling, redness or ulcers form, to which new immune cells rush. The process of absorption of foreign bodies by leukocytes is called phagocytosis.
The blood elements responsible for protecting the body are divided into two groups: granulocytes and agranulocytes, which differ in shape and structure.
Granulocytes are:
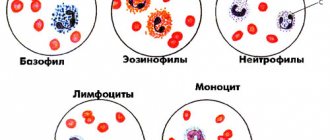
- neutrophils, which capture and digest hostile cells, and also stimulate cell growth and division
- eosinophils, fighting foreign protein and neutralizing their own dying cells
- basophils, which promote the penetration of blood cells through blood vessels and are responsible for blood clotting
Agranulocytes are:
- monocytes, which are produced by the bone marrow and enter the blood “immature”, which is why they have the greatest ability for phagocytosis
- b-lymphocytes that generate antibody proteins that resist bacteria and viruses
- t-lymphocytes, which allow them to resist fungi and viruses, as well as control b-lymphocytes and influence blood formation
For people of different genders and ages, the number of white blood cells should be different, which is caused by many factors.
Increased leukocytes in the blood after childbirth - the role of leukocytes, reasons for the increase, symptoms, norms
Childbirth is a natural process, but still stressful for a woman’s body. Weakness and some deterioration in well-being even after a normal birth are common occurrences.
Young mothers rarely pay attention to their health at this time - they are absorbed in communicating with the baby. However, if the analysis shows that leukocytes in the blood are elevated after childbirth, you will still have to pay attention to this.
This may be both a normal phenomenon and a signal of the beginning of the development of pathology.
Leukocytes - why is it so important to know about them?
Leukocytes are white blood cells that are the first to respond to microbes and infections entering the body. Their main function is protection. When foreign agents are detected, the body increases its production to detect and destroy them. If the level of white cells increases, this is a signal that there is an inflammatory process in the body.
A healthy adult has 1000 times fewer leukocytes than red blood cells. But their number is not constant - it varies slightly for various reasons. For example, their levels increase slightly in the evening or after eating.
A persistent or significant increase in cells signals a focus of inflammation, possible blood problems, or complications after childbirth or surgery.
Neutrophils are a type of leukocyte that is responsible specifically for neutralizing pathogenic pathogens. They absorb harmful cells and die in the process (actually, pus is destroyed neutrophils). Therefore, when assessing a blood test, you need to pay attention to this indicator.
Normal level in pregnant women
During the period of bearing a child, the following are considered normal BC indicators:
- 1-3 months: 4 – 7x109/l,
- 4-6: 7.6 – 10x109/l,
- 7-9: 10.4 - 12 x109/l.
It is customary to talk about physiological leukocytosis - a temporary increase in white blood cells, which is considered a medical norm, and pathological - constant and dynamic, which is a sign of inflammation.
Physiological leukocytosis
Nature has provided many mechanisms to protect the fetus. One of them is leukocytosis. By the second half of pregnancy, the mother’s body is already weakened. The consumption of vitamins and nutrients actually costs two.
And the body adapts - it produces a large number of leukocytes that react to the slightest deviations and suppress the infection before it has time to develop.
Thus, the norm of leukocytes in the body of a pregnant woman is higher than that of an ordinary adult.
Leukocytosis persists for another 1-2 weeks after birth. After this period of time, your white blood cell count should return to normal.
The following reasons can cause an increase in neutrophil levels:
- Physical activity or stressful situations.
- Breastfeeding also often keeps white blood cell levels above normal.
- The beginning of the menstrual cycle is 1-2 days before menstruation.
- Visiting a bathhouse or sauna the day before the test.
- Donate blood on a full stomach.
If the test shows elevated white blood cells, it is recommended to take it again after a few days. If the level has decreased or at least not increased, we are most likely talking about physiological leukocytosis.
Pathological leukocytosis
If leukocytes after childbirth are higher than normal, or their level continues to increase, it is customary to speak of pathological leukocytosis.
In women in the postpartum period, pathological leukocytosis occurs as a reaction to the following conditions:
- Inflammation of the genitourinary organs.
- Large blood loss.
- Mastitis.
- Endometritis.
- Pyelonephritis.
With pathological leukocytosis, there are accompanying symptoms characteristic of inflammatory processes: chills, fever, and often pain and weakness. Bloody or purulent discharge may occur. If you have these signs, you should immediately consult a doctor.
How to normalize indicators
With elevated BC, the expectant mother may be prescribed:
- antibiotics, if a violation of the norm is a consequence of an infectious disease,
- a special diet if white blood cells are impaired due to liver problems.
Patients with low BC need:
- eat buckwheat, raw vegetables, red fruits, oats,
- Avoid products with animal fat, meat and liver.
How to avoid complications
A young mother should be attentive to any signals from her body. After giving birth, she is greatly weakened, her immunity is reduced, and to this is added the happy excitement of communicating with the baby.
Fatigue and systematic lack of sleep themselves can cause an increase in white blood cells - the body activates additional protection in order to avoid diseases during a stressful period of life.
But if after childbirth your white blood cells are significantly elevated, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Scrupulous adherence to personal hygiene and doctor’s recommendations is the first thing that will prevent diseases. Any ailments, strange discharge or painful sensations should be the reason for immediate contact with a specialist. Especially if this is accompanied by fever, chills and weakness.
At this time, you should not hope that “it will go away on its own” and think that the cause of the illness is a mild cold or lack of sleep.
It is recommended to take regular blood tests to monitor changes in white blood cell levels after childbirth. Even if there are no symptoms of inflammation, it is worth visiting a doctor if they grow steadily, or if the level does not return to normal after two weeks after birth.
Paying attention to your health will help you avoid many problems. Timely consultation with a doctor can save lives.
Loading…
Source: https://dlja-pohudenija.ru/serdcze/prichiny-povysheniya-lejkoczitov-v-krovi-u-zhenshhin-posle-rodov-simptomy-normalnye-pokazateli-kto-vhodit-v-gruppu-riska
Leukocytosis, what it is and why it occurs
The content of leukocytes in the blood above normal is called leukocytosis, which can be physiological or pathological. Leukocytosis itself is not a disease - it is only a symptom of the disease, or a consequence of physiological third-party factors, such as a sharp change in ambient temperature, as well as psycho-emotional and physical stress.
Pathological leukocytosis
High white blood cells caused by pathological reasons are typical in the presence of health problems. Pathological leukocytosis occurs in the following cases:
- diseases of the hematopoietic system
- oncological diseases
- internal bleeding (or severe blood loss)
- burns
- infections
- non-microbial and microbial inflammatory processes
- heart attacks
- diabetes
Physiological leukocytosis
An increase in the level of leukocytes does not always indicate organ diseases; in many cases it indicates physiological reasons, such as:
- physical exercise
- stress or emotional distress
- PMS
- pregnancy and childbirth
- change in ambient temperature
- protein rich diet
There is no need to panic if you discover an increased level of white blood cells - just talk to your doctor about the reasons for this condition.
Why are leukocytes in the blood elevated after childbirth?
Pregnancy leads to a restructuring of the body to meet the needs of the developing baby.
And childbirth is very stressful for both mother and child. Nature has tried to do everything so that the human body quickly recovers from this stress. But sometimes leukocytes in the blood are elevated after childbirth. This situation can be caused by natural causes or pathology. In order to receive timely treatment if the disease develops, a woman should undergo regular tests and monitor her well-being.
Throughout human existence, the main defense mechanism for the body is the immune system.
To resist bacteria, viruses and other pathogens, the human bone marrow produces white blood cells and leukocytes.
Normally, their content in an adult, healthy person should be in the range of 4-9 × 109/l. An increase in this indicator means that the body needs support in maintaining health.
) a signal is transmitted to the bone marrow about the need to eliminate the problem. As a result, it begins to increase the production of white blood cells. Leukocytes are divided into types, each of which performs its own function.
Cells can absorb pathogenic microbes, neutralize the toxic effects of pathogens, promote rapid wound healing, etc.
Why does an increase in leukocytes in the blood occur? The reasons can be very different, but you definitely need to find out what led to the increased production of leukocytes by the body. During the process of childbirth, a woman’s body experiences stress; to maintain the health of the woman in labor, the body maximally activates all its resources and protective functions.
In the event of any disturbances, the first sign of a malfunction in the normal functioning of the body is increased leukocytes as a result of a blood test:
- The inflammatory process in the body increases the number of leukocytes.
- Surgical intervention during childbirth, the formation of cracks and tears in the body leads to tissue inflammation.
- If during childbirth, fragments of tissue from the placenta or amniotic membrane remain inside a woman’s body, the body will perceive them as foreign. To combat these tissues, additional white blood cells are produced. Other indicators are also increasing.
- Significant blood loss during childbirth will cause the concentration of leukocytes to increase. The bone marrow will produce white blood cells in order to quickly restore all functions and immunity of the mother's body.
- An increase in the concentration of white blood cells may be associated with a deficiency of vitamins and minerals, which are necessary for the normal functioning of all organs and tissues. As a treatment, it is necessary to raise to normal the content of all elements necessary for the body.
- Postpartum exacerbation of chronic diseases leads to an inflammatory process and an increase in the concentration of leukocytes.
- Diseases and inflammations of the genitourinary system occur during the postpartum period.
- Violation of hematopoietic function or blood clotting process.
- Cracked nipples, mastitis.
- Septic shock.
- Infection of cracks and tears resulting from the birth process.
It should also be taken into account that an increase in the concentration of white blood cells can be caused by physiological processes. Severe physical or mental fatigue leads to an increase in the indicator. Eating a heavy meal before donating blood for analysis will also distort the result.
After childbirth, leukocytes may be elevated simply because the body is under stress. This is a natural process and the white blood cell count quickly returns to normal. If this does not happen, you should immediately consult a qualified physician.
After the birth of a child, a woman's condition may be precarious.
Women in labor complain of fatigue, loss of strength, attacks of postpartum depression, etc. It happens that their body temperature rises or they suffer from pain.
You should immediately go to the hospital in the following cases:
- Increased body temperature for no apparent reason.
- Abdominal pain, nausea, dizziness, vomiting.
- The appearance of bloody discharge, which may be accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, fever and nausea.
- General weakness, increased sweating.
- Purulent discharge.
- Feeling of pain when urinating.
Due to the increase in the number of leukocytes in the blood after childbirth, there is no need to panic. However, you should definitely consult with your doctor about the causes of this condition and, if necessary, undergo additional examination. The condition of a new mother can be very vulnerable to infectious diseases and the development of pathologies.
It is no secret that in the postpartum period a woman may face various health problems.
In order to promptly detect and treat postpartum complications, it is necessary to carefully monitor your health and regularly submit biological materials for research.
One of the most common phenomena after childbirth is a jump in white blood cells. What does the biological analysis say, and why do leukocytes increase after childbirth?
What are leukocytes
Leukocytes are the colorless cells of the circulatory system, which are responsible for protecting the body from all kinds of infections. Defender cells move freely through the circulatory system and rid us of dead cells, infections, harmful substances and foreign bacteria.
These cells are popularly called white blood cells. The structure of leukocytes can differ from each other; they have an irregular shape and can be of different sizes.
An increase in the number of leukocytes in a person always indicates the presence of health problems. These can be inflammatory diseases of organs and tissues, blood diseases or postpartum, as well as postoperative complications.
Doctors call leukocytosis an excess of leukocytes in the blood above normal. After pregnancy, both false and pathological leukocytosis can occur. During pregnancy, normal blood test values are slightly changed.
During the period of gestation, a woman’s body works in extreme mode. All protective functions are activated to the maximum to ensure the safety of the baby. It is for this reason that a pregnant woman’s body produces more white blood cells.
After childbirth, the normal number of white cells should return to normal. However, there are often cases when, when taking a test, a young mother is diagnosed with leukocytosis. This does not always mean that a woman has some kind of disease. In most cases, this indicates the presence of physiological leukocytosis.
A harmless increase in the number of leukocytes in the blood may be due to the following factors:
- Regular physical activity.
- Second half of pregnancy.
- Stressful situations.
- Lactation.
- Food intake (to obtain adequate indicators, the analysis must be taken on an empty stomach).
- Visiting the bathhouse, bath, sauna.
- 2–3 days before menstruation.
With physiological leukocytosis, the young mother is not at risk of infection or disease. If, when taking a blood test, you were told about an increase in leukocytes, there is no need to worry.
In order to exclude the development of diseases and postpartum complications, the analysis must be repeated after a few days.
If your white blood cell count does not increase, it is safe to say that you have benign leukocytosis.
A pathological increase in white cells in the blood differs from a physiological one in that there is a constant increase in white cells. In this case, when repeated analysis, the content of bodies will be greater than in the previous study.
Pathological leukocytosis indicates the presence of diseases such as:
- Acute inflammatory diseases.
- Infarction of internal organs.
- Chronic kidney disease.
- Large blood loss.
- Coma due to diabetes.
- Burns.
- Brain hemorrhages.
- Purulent processes.
In women after the birth of a child, pathological leukocytosis can occur in the presence of complications such as:
- Pyelonephritis.
- Inflammatory processes in the uterus.
- Chest inflammation.
- Mastitis.
- Endometritis.
- Inflammation of the genitourinary system.
Associated symptoms of a pathological increase in leukocytes are pain, increased body temperature, general weakness, excessive sweating and other ailments.
It is necessary to understand that childbirth is a real test for the female body. After bearing a child and giving birth, a young mother’s body can be greatly weakened, which is the main impetus for the development of postpartum complications.
In order to avoid health problems, it is necessary to regularly take blood and urine tests, and also visit a gynecologist.
Source: https://moeserdce.net.ru/posle-rodov-povysheny-leykotsity-krovi-pochemu/
Why is it dangerous, what pathologies can there be?
In the postpartum period, a woman may experience an increase in the number of protective blood cells, which may not be a reason to visit a gynecologist. The physiological causes of postpartum leukocytosis are quite common - an abundance of proteins in the diet, taking water procedures at elevated temperatures, physical and emotional stress after the birth of the baby.
However, it is possible to develop pathologies such as:
- inflammatory processes in the uterus
- breast inflammation (nipple cracks, lactostasis, mastitis)
- postpartum ulcer, pyelonephritis, cystitis
- surgery during childbirth
- residue in the uterus of placental tissue or amniotic fluid
- anemia or blood loss
Leukocytosis that occurs for any of these reasons requires treatment, which can only be prescribed by the attending physician, and also requires observation by a gynecologist for 2-3 months after birth.
Why are there elevated leukocytes in the blood after childbirth: causes and treatment
Elevated leukocytes in the blood after childbirth is a very common problem. Similar cases are often recorded in modern medical practice. It is quite natural that new mothers are interested in how dangerous such a condition can be.
Why does the number of white blood cells increase? What do elevated leukocytes in the blood after childbirth indicate? What symptoms should you look out for? The answers to these questions are worth exploring.
What are leukocytes needed for? General description and main functions
Leukocytes, called white cells, are a whole group of human blood cells. By the way, it is not by chance that they are called white - they do not have their own coloring.
The main function of these structures is protection. Leukocytes are capable of movement and can penetrate into the intercellular space through the capillary wall. These cells absorb foreign particles (including pathogenic structures), neutralizing and digesting them.
Normally, the level of leukocytes in the blood of an adult woman ranges from 4-9·109/l. If after childbirth this indicator changes, this may indicate an inflammatory process.
Why are leukocytes in the blood elevated after childbirth? List of physiological reasons
Elevated leukocytes in the blood after childbirth do not always indicate the presence of some kind of pathology. The reasons may be completely natural, physiological in nature.
In order to bear and give birth to a child, a woman’s body adapts: changes in hormonal levels are observed, an increase in blood volume, etc. Immediately before childbirth, leukocytes begin to accumulate in the area of the uterus, stimulating the contraction of its muscles and preventing the penetration of infection. This is why the number of white blood cells increases by about 20-30%.
Childbirth is associated with tissue damage to one degree or another. That is why elevated leukocytes in the blood after childbirth (especially if the child was born via cesarean section) are considered quite normal.
This helps speed up the tissue healing process, prevent infection and the development of further complications.
In most cases, the number of white blood cells in the mother's body returns to normal 3-6 days after the birth of the baby.
Elevated leukocytes in the blood after childbirth
The reasons for this phenomenon, as already mentioned, may be different.
If changes in the blood count are observed a week after the birth of the child, then this is no longer considered normal and requires additional diagnostic measures.
Why are leukocytes in the blood elevated after childbirth? The cause in this case is an inflammatory process, the focus of which can be located in any part of the woman’s body.
If the number of white blood cells exceeds 4-9·109/l, then this may indicate the presence of problems such as:
- inflammation of the endometrium lining the uterine cavity (endometritis is considered a very common postpartum complication);
- mastitis (inflammation of breast tissue) is also a very common complication after childbirth;
- postpartum ulcers that develop in the presence of tears and cracks;
- lactostasis (stagnation of milk in the mammary glands leads to inflammation if it is not eliminated in time);
- inflammation of the bladder (cases of postpartum cystitis are often recorded in medical practice).
In the most severe cases, an increase in white blood cell levels indicates the development of sepsis. This is a very serious, rapidly progressing disease that often leads to death.
Risk factors
As you know, inflammation is the result of the activity of bacterial microorganisms.
As a rule, these are opportunistic bacteria, in particular staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli, etc.
They are always present in the body, but their reproduction processes are activated against the background of stress, which is the birth process, as well as when the immune system is weakened. Risk factors include:
- loss of blood, which, alas, is inevitable during childbirth;
- vitamin deficiencies;
- anemia (decreased number of red blood cells);
- disturbances in blood clotting processes (fraught with additional blood loss);
- the presence of remnants of membranes and/or placental tissue in the uterus;
- cracks in the nipple area;
- surgical interventions during childbirth;
- severe pregnancy;
- birth process with complications;
- Constant stress, overwork and lack of sleep also affect hormonal levels and the immune system, weakening the body.
What symptoms should you pay attention to?
Many mothers face the problem of elevated leukocytes in the blood after childbirth. Reviews from doctors indicate that in most cases, such changes in the blood count are associated with stagnation of milk or infection of the ruptures.
In itself, an increase in the number of white cells in the blood only indicates inflammation. But the accompanying symptoms can clarify the picture:
- The inflammatory process is inevitably accompanied by an increase in body temperature, sometimes up to 40 degrees or more.
- Bloody and sometimes purulent discharge from the vagina may appear. Sometimes they turn into full-blown bleeding.
- The presence of pain and burning during urination, as well as nagging pain in the lower back. All this is typical for various diseases of the excretory system (in particular, the bladder and kidneys).
- Headaches, severe weakness, chills, body aches, nausea, and vomiting may occur.
If you notice such symptoms, you need to contact your gynecologist as soon as possible.
What to do if the level of leukocytes increases?
Under no circumstances should such a problem be ignored. If you notice the symptoms described above, you should definitely consult a doctor. The success of therapy largely depends on how quickly the disease is diagnosed.
The treatment regimen depends on the type and location of the inflammatory process and the nature of the pathogen. Treatment almost always involves taking antibiotics.
During laboratory tests, it is possible to determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to a particular drug.
In addition, patients are prescribed anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, antihistamine medications, vitamins, and other drugs.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/413150/pochemu-povyishennyie-leykotsityi-v-krovi-posle-rodov-prichinyi-i-lechenie
Symptoms of elevated white blood cells
Despite the fact that leukocytosis is not a separate disease, it can be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- constant malaise and fatigue
- weakness and lethargy
- dizziness
- fainting
- lack of appetite
- enlarged lymph nodes
- nosebleeds
- vision problems
If one or more symptoms are detected, it is necessary to be thoroughly examined to identify the reasons why the number of leukocytes is increasing.
Associated symptoms
An increase in the number of white blood cells after childbirth is indicated by symptoms such as dizziness, fatigue, decreased appetite and general weakness. In severe cases, vision problems and nosebleeds may occur. These symptoms are characteristic of all forms of leukocytosis, regardless of its cause.
If the disorder is caused by inflammation, the patient also notes:
- pain in the lower abdomen and lower back,
- low-grade fever accompanied by chills,
- redness and pain in the chest,
- compactions when palpating the mammary glands,
- frequent and painful urination,
- darkening and cloudiness of urine, the appearance of pus and blood clots,
- yellow, green and brown vaginal discharge with a strong odor.
Normal white blood cell count for pregnant women
The leukocyte norm for pregnant women is higher than for other women. This is due to the fact that the pregnant woman’s body is preparing for childbirth, the process of hematopoiesis is intensified, and the immune system increases the concentration of protective blood cells. By the time of birth, a 5-fold increase in the number of white blood cells may be normal.
The reasons for the increase in white blood cells in pregnant women are mainly physiological, they are caused by the fact that the body is actively preparing for the upcoming birth, and also performs the functions of the fetal immune system.
There is no need to try to determine your leukocyte count yourself - only a doctor can do this. It is important for a pregnant woman to be under constant supervision of a specialist, so listen to yourself and report any causes of concern to the leading gynecologist.
Pathological leukocytosis
In practice, leukocytosis after childbirth of a more serious nature, called pathological in medicine, is often recorded. It differs from the physiological one by the constant growth of white blood cells, confirming, most often, the presence of a number of characteristic diseases. Among them are:
- Acute inflammation.
- Heart attacks of one or another internal organ.
- Blood deficiency caused by bleeding.
- Deviations in the functioning of the renal and other body systems.
In women after childbirth, it can also begin due to inflammation of the uterus or breasts, mastitis, and inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system.
How to normalize
Compliance with the following recommendations helps to normalize indicators for physiological leukocytosis:
- organizing a proper work and rest regime (after childbirth, a woman should rest as much as possible, which is necessary to restore normal immune function);
- proper nutrition (fatty, fried and spicy foods are excluded from the diet, fresh vegetables and fruits, dietary meats, and dairy products are healthy);
- taking vitamin supplements prescribed by a doctor;
- exclusion of heavy physical activity (some of the housework should be entrusted to relatives);
- adherence to a breastfeeding regimen that does not allow stagnation of milk.
The method of treating pathological leukocytosis is selected depending on the type of underlying disease. There is no remedy that reduces elevated white blood cells. The treatment regimen may include the following drugs:
- Antibiotics (Cefazolin, Amoxiclav). Most often, the number of white blood cells increases due to infections. Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs help eliminate the cause of leukocytosis and normalize blood composition.
- Hormonal agents (Dexamethasone). Used in the treatment of allergic reactions accompanied by an increase in the number of white blood cells. Therapy is supplemented with non-hormonal antihistamines (Suprastin). Breastfeeding is stopped during treatment.
- Chemotherapeutic agents. Such drugs are prescribed for leukocytosis caused by cancer of the hematopoietic system. Cytostatics suppress the division of cancer cells, slowing tumor growth.
Physiological causes of postpartum leukocytosis
Labor is a natural process. The body prepares for it in advance. To prepare for significant blood loss, the process of hematopoiesis is enhanced. In addition, white blood cells accumulate in the uterine area to prevent infection and stimulate uterine contractions. Therefore, at the time of birth, leukocyte counts can exceed the norm by 20% and reach up to 12x10^9 particles per liter.
Already at the beginning of labor, the level of leukocytes increases rapidly and amounts to 30x10^9 per liter.
The process of childbirth itself is a huge stress, having both physical and psychological origins. This factor also provokes a physiological increase in white cells.
After childbirth, the recovery period is accompanied by increased formation of blood particles and healing of damaged tissue, which explains the increase in the level of leukocytes.
Leukocytosis against the background of active hematopoiesis is observed in women who have lost a lot of blood during childbirth, as well as as a result of cesarean section. Blood counts are restored 3–5 days after delivery.
What are leukocytes needed for? General description and main functions
Leukocytes, called white cells, are a whole group of human blood cells. By the way, it is not by chance that they are called white - they do not have their own coloring.
The main function of these structures is protection. Leukocytes are capable of movement and can penetrate into the intercellular space through the capillary wall. These cells absorb foreign particles (including pathogenic structures), neutralizing and digesting them.
Normally, the level of leukocytes in the blood of an adult woman ranges from 4-9·10 9 /l. If after childbirth this indicator changes, this may indicate an inflammatory process.
Increased leukocytes in the blood after childbirth: what does this mean, what is the reason for exceeding the norm, what to do?
The significant stress that a woman’s body experiences during pregnancy and the postpartum period often leads to diseases of varying severity.
At this time, the patient's condition is complicated by insufficient rest due to caring for the child.
One of the most effective methods for diagnosing postpartum pathologies, especially inflammation, is the study of blood and urine for the level of leukocytes.
Leukocytes: types and functions
Leukocytes or white blood cells are colorless cells that move through the circulatory system and cleanse the body of infections and harmful substances. During illness, the number of foreign agents increases many times, which does not allow leukocytes to fully absorb them. This leads to the formation of swelling, increased body temperature and redness of the affected areas.
Leukocytes differ in structure and size and are divided into 2 large groups: granulocytes and agranulocytes. Granulocytes are characterized by a granular structure and the presence of a segmented nucleus. Cells of this group make up about 80% of all leukocytes.
In turn, these cellular formations are divided into the following types:
- neutrophils - destroy bacteria and fungi, stimulate cell division;
- eosinophils – absorb foreign protein formations and the body’s own dead cells;
- basophils - increase vascular permeability and regulate blood clotting, trigger allergic reactions.
Agranulocytes have larger oval-shaped nuclei. These cells are able to penetrate from the bloodstream into the connective tissue to carry out phagocytosis. The functions of agranulocytes depend directly on the cell type:
- monocytes - absorb large foreign particles, over time they turn into macrophages, which participate in cellular and humoral immunity;
- B lymphocytes - produce antibodies against foreign proteins;
- T-lymphocytes – destroy foreign microorganisms, enhance the immune response;
- NK lymphocytes - recognize their own altered and foreign cells, destroy cancerous formations.
What indicators are considered normal and deviation?
In 1% of cases, leukocytes are completely absent in the blood and urine. The following number of leukocytes is not considered a deviation:
- in the blood – up to 4-9 x 10⁹/l;
- in urine – no more than 10 units;
- in a smear – no more than 20 units.
Why does the level of leukocytes increase after childbirth?
It is important to understand that elevated white blood cell levels in and of themselves are not a disease. After childbirth, the number of white blood cells in the blood and urine is always increased, which is due to the effect of physiological and external factors on a weakened body. To identify pathology, tests are done several times.
Inflammatory processes
Leukocytes after childbirth, formed as a result of inflammation, signal the need for complex treatment of the pathology. Having cured the underlying disease, you need to undergo a re-examination by a gynecologist after 3 months. If the patient’s leukocytes are elevated, it means that the following inflammatory processes are developing in the body:
- postpartum endometritis after cesarean section;
- inflammation due to the remainder of the placenta in the uterus or careless suturing after natural childbirth;
- lactostasis and mastitis;
- cystitis and pyelonephritis;
- allergy.
Physiological reasons
Physiological causes of leukocytosis lead to a slight increase in indicators, which return to normal within 5 days after delivery. The reasons why the level of leukocytes in the blood and urine is increased are:
- excessive blood loss during childbirth;
- significant emotional stress;
- high ambient temperature;
- eating predominantly protein foods, especially legumes;
- intense physical activity.
Associated symptoms
An increase in the number of white blood cells after childbirth is indicated by symptoms such as dizziness, fatigue, decreased appetite and general weakness. In severe cases, vision problems and nosebleeds may occur. These symptoms are characteristic of all forms of leukocytosis, regardless of its cause.
If the disorder is caused by inflammation, the patient also notes:
- pain in the lower abdomen and lower back;
- low-grade fever accompanied by chills;
- redness and pain in the chest;
- compactions when palpating the mammary glands;
- frequent and painful urination;
- darkening and cloudiness of urine, the appearance of pus and blood clots;
- yellow, green and brown vaginal discharge with a strong odor.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of postpartum leukocytosis includes a general analysis of blood, urine and vaginal smear. To get accurate results, you need to follow the recommendations:
- good rest the day before the test;
- donating blood on an empty stomach;
- notifying the doctor about antibiotics taken;
- taking a smear after the cessation of postpartum discharge;
- avoid douching on the eve of taking a smear, use warm water and baby soap for washing.
Treatment regimen
To treat leukocytosis in women who have recently given birth, it is prohibited to use potent drugs. If the increase in the level of leukocytes is caused by physiological reasons, it is enough to follow a daily routine that includes proper rest, a balanced diet and walks in the fresh air.
To bring the level of leukocytes back to normal, they also drink juices from lingonberries and currants, decoctions of chamomile, dandelion and hawthorn, and green tea. If the growth of leukocytes is associated with drug therapy, it is necessary to replace the drugs with analogues. For example, one of the safe medications against inflammation of the genitourinary system, which can be taken by women after childbirth, is Canephron.
Why deviations occur
Leukocytosis after childbirth does not always indicate the presence of a dangerous disease. In most cases, the phenomenon is temporary and caused by physiological reasons. Non-hazardous provoking factors include:
- increased physical activity (the body weakens after childbirth, which is why even usual household chores can negatively affect a woman’s condition);
- stress (an increase in the number of leukocytes can be facilitated by lack of night sleep, changes in the rhythm of life, psycho-emotional overload);
- breastfeeding (lactation can cause a temporary change in blood composition);
- eating before donating blood for analysis (the procedure must be carried out on an empty stomach);
- visiting a sauna or bathhouse, taking a hot bath;
- the upcoming onset of menstruation (leukocytosis is caused by a sharp change in hormonal levels observed when breastfeeding is stopped).