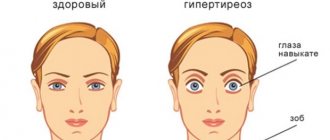
Does your child need an arrhythmologist?
Heart rhythm disturbances are found in 0.5% of young patients. In heart disease, this problem occurs in 15-20%. What is it? Sinus arrhythmia in children is in most cases a harmless condition that does not pose a threat to the health or life of the child. However, one cannot assume that this is the norm: such a symptom often accompanies serious cardiac pathologies. That is, in some cases it is a temporary functional disorder that does not require treatment, and in others it is a signal warning of cardiac disease.
If you need help right now
It happens that, for certain reasons, a VSD person is prohibited from long-term training of the heart muscle.
Or they are postponed for some time. What to do if your heart is beating strongly again and it’s difficult to breathe? As a rule, most often tachycardia occurs against the background of a panic attack with the release of adrenaline. Then your main task is to survive the adrenaline rush with dignity and wait for the body to come to its senses. You are well aware that if you fixate your thoughts on the current panic attack, the symptoms will intensify, and your heart will begin to beat like a rabbit, faster and faster. Try to help yourself in the following ways:
- Sit in a comfortable chair, wrap yourself warmly in a blanket, pick up crossword puzzles or turn on the TV. The warmth and distraction of the brain will help calm panic and palpitations.
- Drink 40 drops of Valocordin (Corvalol) and breathe deeply, slowly through your mouth. Try to exhale as much as possible to avoid hyperventilation.
- Drink a glass of water, this will thin the blood and ease the condition.
- Take a pillow and hit it a few times: activity burns adrenaline. Just don't overdo it.
- Get some fresh air or open a balcony. Breathe fresh air with the thought that after a few minutes the attack will pass. They always pass, and you know it very well.
- Call an ambulance. Some patients, as soon as they make a call, feel relaxation and a slowdown in heart rate. If you feel good, call back and cancel the call. You have every right to do this.
If you experience heart palpitations, you can simply go for a walk. Let it be a slow walk, but start small. The heart should not be weak and exhausted. Set aside time every day for a walk, going up and down the stairs on foot. If you don't have dumbbells at home, lift water bottles or move furniture. Dance. Do yoga, exercise, swimming. Don't become a sloth. Take a contrast shower every morning - this will help you combat your reaction to the weather.
Unpleasant, but not dangerous: physiological arrhythmia and the reasons for its occurrence
The safest type of arrhythmia is respiratory. When you exhale, the heart beats less often, and when you inhale, it beats faster. This condition does not affect the blood supply process in any way and does not require treatment, but observation. Interruptions in the functioning of the heart are caused by the following factors:
- conducting an ECG after physical activity. If, before performing the diagnosis, the child ran up the stairs or simply ran along the corridor, then the result of the cardiogram may show sinus arrhythmia. The same thing happens if the patient is placed on a couch covered with cold oilcloth. This will lead to an instinctive holding of breath, which will also affect the heart rate;
- severe physical or mental stress;
- rise in temperature;
- postnatal encephalopathy, high intracranial pressure in infants;
- premature birth (when a child is born with a weight below 2.5 kg and immature NA);
- rickets;
- obesity;
- rapid growth (for this reason, sinus arrhythmia often occurs in a 6-7 year old child and 9-10 year old schoolchildren).
As soon as the provoking factors are eliminated or the child outgrows the dangerous age, and his autonomic nervous system becomes more perfect, the phenomena of respiratory sinus arrhythmia will disappear.
Causes and symptoms of slow heartbeat
Past infectious diseases, fear or holding your breath can be causes of bradycardia in children.
Bradycardia is the opposite of tachycardia and means a slow heartbeat. This is a normal occurrence for a trained person who has been involved in sports for a long time. A child’s heart can slow down its rhythm slightly only at night, when he is at rest. In other cases, this is a deviation, which indicates a problem with the myocardium. You can recognize a slow pulse in children by their pale skin, lethargy, fatigue, shortness of breath, complaints of dizziness and jumping dark spots before the eyes. The reasons why the heart rate in children decreases may be as follows:
- thyroid disease;
- infectious diseases;
- low blood pressure;
- heart defects;
- taking certain types of medications;
- chest and brain injuries;
- hypothermia.
Pathological arrhythmia: what makes a child’s heart beat unevenly?
The second type of arrhythmia is non-respiratory. It can be associated both with the heart itself and with other diseases and pathological conditions. Attacks may occur several times a day or several times a year.
In 30% of cases, non-respiratory sinus arrhythmia is caused by the following health problems:
- infectious diseases in which severe intoxication and dehydration occur. The accumulation of toxins has a negative effect on the water-electrolyte composition of the blood, which disrupts the conduction of nerve impulses (including those that regulate the frequency of CV);
- rheumatism. It is a complication of tonsillitis, scarlet fever and leads to damage to the heart valves and arrhythmia. Rheumatic disease often ends in myocarditis or endocarditis. Therefore, if the baby has suffered from such diseases, it is advisable to do an ECG;
- VSD. Arrhythmia in neurocircular dystonia is the result of the fact that the vessels supplying the heart are unable to correctly change their lumen in accordance with the tissue need for oxygen;
- anemia;
- myocarditis. If the heart muscle is inflamed, then not only arrhythmia will occur, but also other characteristic symptoms: chest pain, swelling, symptoms of heart failure;
- heart defects (congenital);
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract;
- neoplasms (extremely rare in children).
Parents who themselves suffer from sinus arrhythmia should be especially vigilant, because this increases the risk of the child developing similar problems.
Most often, sinus arrhythmia is diagnosed in a 7-year-old child. In addition to the reasons mentioned above, disrupted metabolism and hormonal changes may be provoking factors.
Treatment of heart failure
Non-drug approaches to the treatment of rhythm disturbances have not been developed. But the range of antiarrhythmic drugs is quite wide.
In the presence of arrhythmia against the background of an unchanged heart structure, according to ECHO-CS, any means can be used. This could be Propanorm, Allapinin, Sotalol, Sotalex or Betaloc. But in the presence of a defect, angina pectoris, or previous heart attack, the choice is limited to Cordarone or Amiodarone.
Tachyarrhythmias are accompanied by an increased risk of blood clots in the cavities of the heart. Therefore, for atrial fibrillation and paroxysmal forms of tachycardia, anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents are used. Usually the choice is made in favor of Warfarin. An alternative is Aspirin with Clopidogrel or new oral anticoagulants (Apixaban, Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban).
Atrioventricular blocks with Morgagni-Adams-Stokes attacks involve the implantation of an artificial pacemaker - a pacemaker. Serious preparation is required before surgery.
How to cope with interruptions before the ambulance arrives?
Reflexively, you can try to slow down the heart rate. To do this, you can lower your head face into cold water. The frequency is somewhat reduced if supraventricular tachycardia occurs.
The second technique is the Danini-Aschner method. The patient can apply light pressure to the eyeballs covered by the eyelids.
A more dangerous method is pressing on the area of the carotid arteries. This is the carotid sinus zone - a powerful reflexogenic zone. Sometimes it can cause a serious slowing of the heart rate.
About the classification of arrhythmia: what do the entries in the child’s card mean?
Arrhythmia in a baby can be congenital, hereditary or acquired. The doctor also determines the severity of its course:
- moderate. Symptoms of the disorder are mild or completely absent. Arrhythmia is detected accidentally during a routine examination or ECG;
- severe sinus arrhythmia in a child, which is characterized by the presence of specific symptoms. It usually occurs with cardiac anomalies and is found in 20% of preschool children and 20% of schoolchildren;
- sharply expressed. It is registered in 12% of children from 3 to 7 years old and in 13% of adolescents (13-14 years old). It develops as a result of disturbances in the functioning of the heart and other organs and requires competent treatment.
Types of outages
The arrhythmic process has many varieties. Some are more dangerous, others pose less of a threat to life and health.
Non-fatal forms
- Single extrasystoles. They feel like an extra heartbeat and represent functional impairments of a short-term nature. They develop as a result of extraordinary contractions of the heart muscle due to the generation of additional electrical impulses by the atrioventricular node, atria or ventricles. An important distinguishing feature of such interruptions in the heart is the singularity of changes. Moreover, this is not a regular problem. Up to 6-70% of all cores suffer from extrasystole, which makes this form the most common. There are no symptoms at all, so it is almost impossible to determine whether you have a problem. This is a variant of an incidental finding during an ECG.
- A mild form of atrial fibrillation (with a heart rate of up to 110 beats per minute). It is a disruption of the functioning of the entire muscular organ, when an electrical impulse is generated not only by the sinus node, but also by other cardiac structures. The process is noticeable, but does not pose any danger due to good control. Also called atrial fibrillation.
- Conduction disorder of the His bundles. Likewise, it is not characterized by manifestations. Since there are no symptoms, it is impossible to detect the process on your own; diagnostics are required. It is possible to cope with pathological changes using medicinal methods in a short time.
- 1st degree atrioventricular block. It is characterized by a violation of the passage of electrical impulses from the sinoatrial node to the atrioventricular node and further to the ventricles. At an early stage, changes are minimal, so quick correction is possible. There is almost no danger. In the future, there is a threat to life (over the next several weeks or months).
- Sinus tachycardia. Acceleration of cardiac activity due to excessive stimulation of the pacemaker. Develops as a response to internal or external controllable factors. In the early stages it does not require correction at all. It appears brightly, but does not pose a danger to health or life.
- Bradycardia. Reverse process. It also develops due to dysfunction of the sinus node. In 40-50% of cases it is of physiological origin, not associated with pathogenic processes.
Dangerous species
Requires urgent medical attention. It is impossible to predict in advance when a fatal complication will occur. Immediately after identifying the problem, treatment should be prescribed, preferably in an inpatient setting or under the constant supervision of a cardiologist as part of outpatient diagnostics.
- Multiple extrasystoles. Unlike single ones, they are repeated many times, repeatedly. As a result, cardiac structures work chaotically and cannot be coordinated. Possible cardiac arrest. It happens suddenly. Since this type of pathological process almost never makes itself known, it is difficult to identify the problem.
- Ventricular flutter.
- Advanced atrioventricular blockade, complete or 2 degrees. The conductivity of cardiac structures is impaired. In this case, the ventricles are “switched off”, which is fraught with sudden cardiac arrest. It is impossible to restore functional activity even within the framework of emergency resuscitation.
- Paroxysmal tachycardia. It is characterized by an acceleration of the frequency of contractions of the muscular organ, the number of “movements” can reach 150-180 or more, these are full-fledged beats that the patient feels as if the heart is turning over and jumping out of the chest.
Heart rhythm disturbances are the result of a process of cardiac, endocrine or neurological origin. Less commonly, a natural phenomenon occurs that is not related to organic changes.
External manifestations of pathology. What is the child complaining about?
Parents can suspect sinus arrhythmia in an infant under one year old based on the following symptoms:
- pale or bluish skin;
- decreased appetite;
- breast refusal;
- interrupted, restless sleep;
- frequent crying for no reason;
- suffocation.
With sinus arrhythmia, there are no pronounced specific symptoms. Older children can only complain about a rapid heartbeat, which is replaced by the fact that the heart “freezes” for a while, pain in the chest, and fatigue. During an attack, they may faint. The condition worsens sharply with physical activity.
Is VSD a danger to the heart?
To understand how rapid heartbeat is triggered during VSD, and why the patient feels the heartbeat so clearly, it is necessary to know some points of anatomy.
In a certain area of the heart muscle there is a special reflexogenic area that responds to any stimulation by increasing heart contractions. And no matter how the VSDers scold the natural structure of the human body, nothing can be done about it. Yes, we have a heart, and it beats – and periodically beats harder than it should. Not because nature wants to make fun of our phobias. But because that’s how the body works. Sometimes the heart must beat as hard as it can, supplying our organs with healing blood and helping us overcome dangers. In some situations, due to increased heartbeat, the body warms up, the brain solves complex problems, and the organs receive the necessary amount of nutrients. There is no need to think that if your heart is beating strongly, then this is definitely a dying sign, and it’s time to call “03”.
The heart is a muscle that becomes stronger and more resilient the harder it is trained. The reflexogenic zone regulates proper blood pressure and blood flow by controlling heart rate. With VSD, this zone often comes into a state of excitement due to the above factors; sometimes the body simply does not have time to figure out what happened - and the heart has already jumped into a dance. Naturally, this mortally frightens the VSD student, who immediately strives for complete peace. Any physical activity that causes a person to feel a strong heartbeat is immediately written off the agenda - the VSD student prefers not to “risk” his life and goes to the bottom. And completely in vain!
How to cure “uneven pulse”?
If such problems are associated with disorders of the cardiovascular system, then medications are prescribed that reduce or enhance cardiac conduction, vitamin-mineral complexes, and painkillers. They can only be taken with the permission of a cardiologist. If the arrhythmia lasts a long time and causes suffering to the child, then atropine is used intravenously, in especially severe cases - hindine and novocainamide.
For respiratory arrhythmia, the goal of therapy is to eliminate factors that lead to abnormal heart rhythm. It is better for the child to refrain from high physical activity, but moderate activity will only benefit him. It is necessary to properly organize his nutrition - exclude fatty foods from the diet, replace them with raw fruits and vegetables. It is useful to eat foods that support the heart: walnuts, honey, pumpkin, dried apricots. The daily routine is of great importance: daytime sleep, night rest from 8 to 10 hours. To reduce the likelihood of a night attack, it is better not to have a heavy dinner. The child's weight should be maintained at a normal level. It is advisable to protect such children from stress.
Treatment for palpitations
It is necessary to discontinue medications and substances that provoke arrhythmia. If potentially dangerous arrhythmias are caused by medications that need to be taken, other medications should be tried.
In cases of single atrial or ventricular estracystoles in the absence of structural pathology of the heart, one can limit oneself to just a conversation with the patient. If the arrhythmia leads to disruption of lifestyle, 5-blockers may be prescribed in otherwise healthy patients, and efforts are made to reduce the acuity of patients with increased anxiety and reassure them that there is no serious pathology.
Treatment of identified rhythm disturbances and underlying diseases is carried out.
Features of diseases in the elderly
Elderly patients are especially at risk for side effects from antiarrhythmic drugs; reasons for this include decreased GFR and concomitant use of other drugs. If it is necessary to prescribe medications, minimal doses should be used at the beginning of treatment. There may be conduction disturbances that do not have clinical manifestations (as detected by electrocardiography or other studies), which may be aggravated by the use of antiarrhythmic drugs; such patients may require pacemaker implantation before antiarrhythmic drugs are prescribed.
Some treatments for arrhythmias
Narrow complex tachycardias:
| Disease | Treatment |
| Multifocal atrial extrasystoles | Psychotherapy or β-blockers |
| Atrial fibrillation | Aspirin, warfarin, enoxaparin, unfractionated heparin, EIT, flecainide, β-blockers, digoxin, verapamil, diltiazem, ibutilide, amiodarone, radiofrequency ablation or maze surgery depending on the clinical situation. |
| Atrial flutter | EIT, digoxin, β-blockers, verapamil, anticoagulants or radiofrequency ablation |
| Supraventricular tachycardia | Vagal tests, adenosine, EIT, β-blockers, verapamil, flecainide, amiodarone, digoxin, or radiofrequency ablation |
| Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia | β-blockers, verapamil, or radiofrequency ablation |
Wide complex tachycardias:
| Disease | Treatment |
| Ventricular tachycardia | EIT, amiodarone, sotalol, lidocaine, mexiletine, flecainide, radiofrequency ablation or defibrillator implantation |
| Torsade de pointes ("pirouette") | Mg, K, EIT, β-blockers, pacemaker or defibrillator implantation |
| Ventricular fibrillation | EIT, amiodarone, lidocaine or defibrillator implantation |
| Brugada syndrome | EIT or defibrillator implantation |
Source: www.sweli.ru
How is the cause of tachycardia diagnosed in children?
When contacting a highly specialized specialist - a cardiologist - it is necessary to tell about all the symptoms that worry the child. Diagnostic measures begin with a study of the medical history and physical examination of the patient. The doctor performs thermometry, anthropometry, auscultation and palpation of the child. You will also need to undergo a number of examinations to exclude some cardiovascular pathologies:
- electrocardiography of the heart,
- stress test,
- biochemical and clinical blood tests,
- analysis of urine and feces (if inflammatory diseases of the myocardium are suspected, bacterial culture is done).
Collecting reliable information will allow a specialist to conduct a differential diagnosis and identify the cause of the disorder. A correct diagnosis will allow you to prescribe the correct treatment and ultimately lead to the child’s recovery.
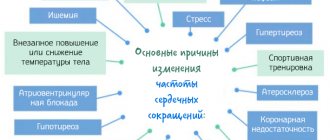
What can lead to rhythm disturbance?
Not every disease can disrupt the smooth functioning of the heart rhythm. The heart beats intermittently due to chronic effects on the body, since it is difficult for viruses, bacteria, and prions to disrupt the nerve innervation. This can only be caused by certain factors:
- previous myocardial infarction;
- side effects of medications;
- disruption of the endocrine glands: pituitary gland, adrenal glands, thyroid and parathyroid glands, hypothalamus;
- central paralysis, paresis, decompensation of the nervous system;
- stressful situations;
- uncontrolled intake of nicotine, ethyl alcohol, narcotic compounds (hemp, cocaine, heroin, spice);
- menopause in women;
- anomalies of intrauterine development (Fallot's disease, heart defects - open Batal duct, or foramen ovale);
- excessive food consumption, obesity;
- inflammatory processes of the heart: endocarditis, pericarditis, myocarditis;
- chemical poisoning;
- high blood pressure.
The above factors are most often encountered in medical practice and the etiology of cardiac arrhythmias. Missed heartbeats are observed after a myocardial infarction. The necrotic area heals under the scab, and connective tissue in the form of a scar forms in place. Local coronary blood flow is disrupted when the moment of systole (heartbeat) occurs, a certain section of the myocardium falls out.
Nervous system disorders operate on a slightly different principle. Stressful situations activate the sympathetic part of the autonomic system, resulting in the release of catecholamines (adrenaline, dopamine), stress hormones (cortisol), and antidiuretic hormone. The substances begin to act on the cerebral cortex, the sinoatrial node (which controls the rhythm of heart contractions), and the medulla oblongata, where the center of the heartbeat is located. An increased heart rate (tachycardia) occurs, and when everything subsides, missed heartbeats begin.
Source: vashflebolog.com