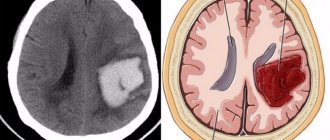
All types of stroke cause brain damage to one degree or another. In an ischemic stroke, an area of the brain suffers from a lack of oxygen and nutrients caused by a blood clot blocking a vessel; in a hemorrhagic stroke, the damage is usually more serious due to hemorrhage caused by a burst vessel.
A common consequence of strokes is paralysis, mainly of the limbs, the intensity and location of which is related to the affected area of the brain. Moreover, the most common consequence of the disease, which greatly annoys patients, is swelling of the limbs after a stroke. It usually develops in the first weeks after the stroke has occurred. In this case, swelling of the paralyzed part of the body can be caused by various reasons.
Swelling and damage to certain areas of the brain
After a stroke, all problems are, to one degree or another, associated with paralysis of parts of the body. With ischemic stroke, paralysis occurs less frequently than with hemorrhagic stroke. A stroke that occurs in the right hemisphere of the brain leads to paralysis in the left half of the body, and vice versa. It is believed that vascular ruptures that occur in the left hemisphere have less influence on the severity of the patient’s condition and on the intensity of paralysis, since the cells of the left hemisphere are destroyed more slowly under the influence of the disease.
Swelling of the arm after a stroke is a fairly common occurrence. Doctors say that the intensity of the lesions depends on the location of the stroke. If it is located in an area where there are no vital centers, the damage will be minimal.
The further to the periphery of the brain from its center a stroke occurs, the less consequences for the patient’s health, the less common are paralysis, the lower is its intensity and the area of the affected areas.
Many patients complain of swelling of the arms and legs after a stroke. In the presence of paralysis, this is a common occurrence. It is caused by a violation of trophism, that is, the circulation of fluids (blood and lymph) in the affected area of the body. The legs swell especially often and intensely in bedridden patients, and a completely or partially paralyzed limb may also swell. This condition is dangerous, and it is imperative to start fighting it as early as possible.
What to do
For swelling of the limbs after a stroke, the following will help:
- Proper patient care. A paralyzed arm should not always lie in one place. It needs to be regularly revised and developed. The limb should rest completely on the bed, without hanging from it. The arm is periodically raised, placed on a pillow or cushion and ensured a comfortable position.
- Performing special exercises. Exercises restore blood circulation and eliminate swelling of a paralyzed arm after a stroke. If the patient is able to move and is conscious, he should sit up, stand up, walk slowly and perform the exercises prescribed by the doctor. In case of complete paralysis, gymnastics is carried out with the help of relatives or medical workers.
- Massage. Improves blood flow, helps increase muscle tone. Must be performed daily. The first classes are supervised by an instructor. In the future, the patient’s relatives can perform the massage.
- Drug treatment. For ischemic stroke, antiplatelet agents (aspirin) are prescribed to restore vascular patency. Diuretics remove excess fluid, reducing the intensity of swelling.
The above methods are combined with the use of compression knitwear, which ensures uniform loads on tissues and blood vessels.
Causes of the problem
Patients are very confused and worried about why one arm swells after a stroke. This phenomenon can be caused by a number of reasons:
- Impaired blood circulation and lymph movement are observed if the paralyzed arm is motionless. This causes stagnation, leading to the formation of edema of varying sizes and intensity.
- Deep vein thrombosis. This is the most common reason why a partially or completely paralyzed leg becomes severely swollen after a stroke. Most often it is associated with ischemic stroke, that is, with an increased level of blood clots caused by high blood clotting.
- Edema caused by problems with the cardiovascular system. They can appear as consequences or complications of a stroke. They most often affect bedridden patients, start from the lower abdomen and sacral region, are characterized by increased density, and when pressing on the area of edema, a noticeable mark remains in it.
- Edema associated with impaired renal function appears on the face as a pasty appearance and usually has a loose structure.
A stroke is usually accompanied by the first form of edema, caused by disturbances in the movement of fluids in the body and lack of mobility in the paralyzed limb. The intensity of the swelling depends on how deeply the part of the body is paralyzed. With partial motor impairment, only slight swelling may be noted in the affected areas, and with complete paralysis, the leg may be swollen to the very feet.
Knowing these features of the consequences of a stroke, it is important to begin treatment as quickly as possible, as well as to use methods to prevent the formation of edema in stroke patients.
Causes of pathology
The occurrence of a pathological condition is diagnosed several hours after the attack. This is explained by the fact that the water and electrolyte balance in the patient’s body is disturbed. The development of leg swelling after a stroke is observed with other diseases in the patient’s body:
Chronic heart failure . With unstable heart function and lack of appropriate physical activity, insufficient blood supply is observed in the legs. When the right hemisphere of the brain is damaged, the veins become overflowing with blood, which can lead to swelling of the leg or arm.
Acute deep vein thrombosis . After an acute attack of stroke, acute thrombosis occurs, which damages small and deep veins and capillaries. Due to the lack of normal blood circulation and accumulation of blood in the leg, it may swell.
Varicose veins . If the circulatory and cardiac systems are characterized by unstable operation and there is an overflow of blood in the vessels and capillaries, this leads to an increase in the legs and loss of physical activity. Varicose veins are observed in older people, especially with spinal deformity.
Kidney diseases. Stroke affects brain tissue and the central nervous system. Also, with pathology, disturbances in the functioning of other organs and systems are observed. Against the background of a stroke, blood circulation, water and electrolyte balance are disrupted, which can lead to dehydration or the accumulation of excessive amounts of fluid. If kidney disease is not treated promptly after a stroke, the leg may swell.
Recommended Treatment
After a stroke has occurred, treatment and rehabilitation begins a few weeks after the main attack has stopped, when the prognosis and degree of damage to the patient’s body becomes clear. But time cannot be wasted, so the patient’s relatives and friends should know what to do to prevent the development of edema, and what treatment helps against it.
To prevent swelling caused by paralysis, the following measures are taken:
- Regularly changing the position of the paralyzed limb.
- The painful part of the body must have stable support.
- The fingers of the hand should be kept in an open position, in an extended state.
- If the patient is sitting, his back should rest firmly against the backrest or a large pillow.
- When sitting, a stool should be placed under the patient's feet for support.
- If the patient's arms or legs are partially paralyzed, treatment of edema involves maximizing the preservation of mobility in the limb. To do this, the patient must be forced to constantly move the affected parts of the body in order to enhance trophism in every possible way.
- Perform therapeutic massages with the patient. With their help, it is possible to “accelerate” blood and lymph, enhance trophic processes and reduce the risk of swelling and stagnation, which can cause the development of bedsores.
- When the attending physician allows it, proceed to restorative exercises.
Read also: Causes of stroke in young people
Treatment of edema, paralysis and other consequences of a stroke is a long and troublesome task, requiring a lot of effort and patience. But every person has a chance to recover and return to normal life.
Why do my legs swell after a stroke?
During the rehabilitation period after acute cerebrovascular accident (ACVA), the patient may develop complications and side effects of therapy of varying degrees of complexity. If the leg swells after a stroke, this may indicate a violation of the rules of patient care or the development of a pathological process. Before taking any action, you should discuss the problem with your doctor. The specialist will carry out the necessary diagnostic procedures and prescribe the optimal treatment option.
Swelling of the limbs as a consequence of a stroke
If, after suffering a blow, one side of a person’s body is paralyzed, then it will require enhanced care. Lack of physical activity after just a few weeks can lead to disruption of physiological processes in the limbs. One of the symptoms of such failures is the appearance of edema.
In order for a paralyzed arm or leg to respond adequately to rehabilitation therapy and ultimately work, it is necessary to monitor its condition, combat negative manifestations and prevent them.
Treatment of a pathological phenomenon
To understand why an arm or leg swells after a stroke, you need to see a doctor. Most often this is the result of slower circulation in the tissues of blood and lymph. Swelling is often accompanied by the appearance of purple spots and a decrease in skin temperature.
Here are a few techniques that allow you to quickly get rid of swelling in this case:
- daily fluid volume is reduced to 1 liter;
- the daily amount of salt is reduced to 1-1.5 g;
- the volume of urine excreted is monitored, which should be at least 75% of the volume of fluid consumed;
- taking diuretics, but only with the permission of the doctor and within the dosages prescribed by him.
Sometimes the arms and legs swell after a stroke due to increased capillary permeability, inflammatory damage to the lymph nodes, excessive increases in ambient temperature, or medications. In some cases, it is enough to eliminate the effect of the irritant, in others it will be necessary to carry out additional therapy.
Prevention of swelling of the limbs
To prevent swelling of the arms and legs after a stroke, a bedridden or inactive patient should be provided with appropriate care. Performing a number of simple manipulations will reduce the likelihood of a problem arising as a result of metabolic disturbances to a minimum.
Swelling in the extremities will not occur if:
- regularly change the position of the patient’s limbs, at least once every two hours during the daytime and once every 4-6 hours at night;
- do not allow the victim’s immobile limbs to hang down;
- when a person is sitting, place his paralyzed hand on a thick pillow, slightly bent, palm down and with fingers apart;
- In a sitting position, place your legs on a stand or bench, and support your calves with a pillow;
- encourage the patient to move his limbs or perform passive movements with him;
- Massage your limbs daily using natural oils with a mild irritating effect.
Your doctor will tell you in detail how and what to do to prevent edema after a stroke. He will select the optimal set of exercises and tell you about the nuances of conducting a specialized massage.
Read also: Stroke and epilepsy
Some more probable causes of the symptom
In some cases, a paralyzed leg after a stroke swells due to functional failures in the functioning of internal organs. Often the pathological process spreads to a healthy limb. Treatment of the symptom here is directly related to the elimination of the provoking factor. The approaches listed above will not give a lasting effect. Only after the cause of the condition has been eliminated or specialized therapy has begun, the clinical picture begins to change for the better.
Chronic heart failure
If the patient had this condition initially, then after the stroke it will progress due to lack of physical activity. The heart is no longer able to cope with processing the entire volume of blood in the usual rhythm, so fluid stagnates in the lower extremities and they swell. The capillaries are subject to increased stress, which causes the blood plasma to peel off and enter the intercellular space.
The following techniques are used to combat the condition:
- the load on the heart decreases;
- the endurance of the heart muscle increases;
- tissue swelling is eliminated.
Swelling is eliminated by taking diuretics. Furasemide, Torasemide, and Hypothiazide are used for medicinal purposes. They come in combination with anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents. If your legs swell, be sure to monitor your pulse and blood pressure.
Varicose veins
This condition is characterized by a characteristic clinical picture, thanks to which an experienced doctor, after examination, will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment. Drug therapy is aimed at normalizing blood flow in the legs, increasing the tone of the vascular walls and preventing the formation of blood clots. The main task falls on venotonics. Preparations with diosmin – “Detralex”, “Phlebodia” - have a high degree of effectiveness.
Sometimes physiotherapeutic treatment of the swollen area and the use of compression garments are allowed. Treatment should begin at the first symptoms of the disease. Against this background, thrombophlebitis can quickly develop, which in this situation is extremely dangerous and does not respond well to therapy.
Acute deep vein thrombosis
In this case, the swelling of the limb is one-sided, accompanied by cyanosis of the skin and severe pain. If the lumen of the inferior vena cava is blocked, both legs swell at once. In the initial stages of the disease, it is usually possible to manage with conservative therapy - taking anticoagulants, for example, Heparin. In advanced cases, removal of the blood clot by surgery or installation of a vena cava filter is required.
Kidney diseases
Acute or chronic glomerulonephritis, as well as renal failure, often cause pathological processes that result in stroke. It turns out that the diseases are closely related to each other. This is confirmed by the fact that after suffering a blow, the severity of problems with the urinary system only intensifies.
In this case, swelling affects not only the legs, but also the arms, and a pasty appearance of the face is observed. The affected areas are pale, warm and soft. The treatment process is based on the fight against the underlying disease and its causes. With the development of renal failure, diuretics are used, often in large doses.
If the symptom is not dealt with, swelling can spread to the patient’s back, which can lead to interruptions in the functioning of the heart.
If your legs swell after a stroke, you must immediately respond to the unpleasant process. Lack of treatment can lead to the development of even more serious complications, for example, tissue suppuration or the development of bedsores. These conditions not only require more aggressive treatment, but also slow down the process of restoration of functionality and motor activity of the limbs.
Features of therapy
If a pathological process occurs, it is recommended to seek help from a doctor. The specialist will prescribe a comprehensive diagnosis to the patient, which will help determine the cause of the pathology. This will enable the specialist to determine what to do in a particular case.
Heart failure
If the pathological process is observed against the background of heart failure, then the patient is prescribed treatment aimed at relieving swelling of the legs, normalizing heart function, and increasing myocardial endurance. Removal of edema is carried out using:
- Torasemide. The drug has a mild effect and removes potassium from the body in minimal quantities. If a person is diagnosed with severe heart failure, it is recommended to take 20-200 mg of medication per day.
- Furosemide. It is produced in the form of tablets or injections for intravenous and intramuscular administration, which allows you to choose the most appropriate option for the patient. The dosage of the medication is selected individually in accordance with the severity of swelling. The patient is allowed to take up to 10 mg of medication. After achieving a positive therapeutic effect, the dosage may be reduced.
- Hypothiazide . This diuretic is characterized by a minimal number of unwanted effects. To ensure the effectiveness of the drug, it is recommended to use other diuretics simultaneously.
Varicose veins
Varicose veins are characterized by a specific clinical picture. After a stroke, treatment of varicose veins requires the use of drugs that increase the tone of the venous wall. Treatment is aimed at improving blood flow in the affected area. Patients are prescribed medications that eliminate the possibility of blood clots.
Treatment of varicose veins is carried out with venotonics - Phlebodia, Detralex. If a person is diagnosed with limited mobility, he is recommended to wear compression garments.
Acute thrombosis
In pathology, swelling of one leg is observed. Patients complain of pain. The skin of the affected limb turns blue. If thrombosis of the lower half of the vein is observed, then swelling of both legs is diagnosed.
During the course of the pathological process, thrombectomy is recommended. This is a surgical procedure that removes a blood clot. If the patient has contraindications to surgery, a vena cava filter is installed. This is a special installation that is used to catch separated clots.
For minor damage, it is recommended to use anticoagulants. Heparin is most often prescribed to patients. During its use, it is necessary to monitor the level of blood clotting. At the next stage, the use of Warfarin is recommended.
Kidney diseases
Swelling of the legs in patients after a stroke is diagnosed against the background of chronic renal failure, chronic or acute glomerulonephritis. Diseases develop during a chronic inflammatory process in the body. The cause of diseases is pathological changes in blood vessels . During the pathological process, patients experience swelling of the legs, face, and arms.
To combat swelling, treatment is prescribed, which is aimed at eliminating its cause. If a patient is diagnosed with renal failure, the use of diuretic drugs in large quantities is recommended.
For swelling of the legs, regardless of the cause of its appearance, the use of gymnastics is recommended, with the help of which a uniform flow of blood to the limbs is ensured. Patients are recommended to do gymnastics and swim in the pool every morning. Daily walks in the fresh air will improve your condition.
During the rehabilitation period, massage of the lower extremities is recommended. They are recommended to be carried out by a highly qualified specialist, which will have a positive effect on the result. The duration of the massage should be at least 30 minutes. The duration of treatment should be at least 2 weeks.
Drawing conclusions
Strokes are the cause of almost 70% of all deaths in the world. Seven out of ten people die due to blocked arteries in the brain. And the very first and main sign of vascular blockage is a headache!
Blockage of blood vessels results in a disease under the well-known name “hypertension”, here are just some of its symptoms:
- Headache
- Increased heart rate
- Black dots before the eyes (floaters)
- Apathy, irritability, drowsiness
- Blurred vision
- Sweating
- Chronic fatigue
- Swelling of the face
- Numbness and chills in fingers
- Pressure surges
Attention! If you notice at least 2 symptoms, this is a serious reason to think about it!
The only remedy that gave significant results. READ MORE. >>>
Read also: 4th degree stroke
Why does the hand swell after a stroke?
Kabardino-Balkarian State University named after. HM. Berbekova, Faculty of Medicine (KBSU)
Level of education – Specialist
State educational institution "Institute for Advanced Medical Studies" of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Chuvashia
Many people who have had a stroke experience swelling in their limbs. Swelling occurs in people regardless of gender, body characteristics and age. Also, swelling of the leg after a stroke is typical after the development of pathologies and warns of changes in the body. Let's take a closer look at why the hand swells after a stroke?
Why does swelling of the legs appear after a stroke and what to do? Leg pain after stroke
Stroke – translated means “strike, attack”, “paralysis” – an acute disturbance of blood circulation in the brain. The disease develops suddenly (from a few minutes to 1-2 days), manifests itself against the background of overexertion.
Reference. The first descriptions of the disease were made by Hippocrates back in 460 BC.
There are three types of disease:
- Ischemic stroke (up to 75–85% of cases), affects people over 60 years of age;
- Hemorrhagic stroke (up to 20%) occurs in people with hypertension aged 40–60 years;
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage (up to 5%) – rupture of an aneurysm, brain injury.
Important! Every 1-2 minutes, someone in Russia develops a stroke. Up to 80% of stroke survivors become disabled, 20–30% of them require constant care.
Why is swelling of the limbs dangerous after a stroke?
Swelling of the arm after a stroke or swelling of the leg after a stroke can cause serious consequences if the problem is ignored. The fact is that prolonged stagnation in swollen and paralyzed limbs will sooner or later lead to the formation of trophic ulcers.
And this is a pathology that is difficult to treat if blood flow is impaired. That is, it will be a vicious circle. In turn, trophic ulcers gradually develop into gangrene and then into sepsis.
In addition, impaired blood flow leads to excessive dryness of the skin, brittle nails and hair on paralyzed arms and legs.
Peripheral pain
This type of pain in a paralyzed arm occurs during the period of restoration of its function. Since during a stroke the transmission of impulses from the brain to the muscles and ligaments is disrupted, they reduce their tone and stop working.
During the restoration of flexion and extension function, which occurs two weeks after the stroke, impulses from the brain begin to flow to the muscles, causing them to contract. Increased muscle tone is felt as a sharp, severe pain.
This is a good sign to activate the restorative functions of a paralyzed arm. Pain occurs when trying to move the arm, which becomes a big problem for the patient.
Folk remedies to combat edema
It is no less popular and effective to treat swelling of the legs with folk remedies, which include tinctures, decoctions, jams, poultices, compresses and baths with the addition of herbs.
So, a good diuretic composition is the juice of carrots, cucumbers and lemon, which should be drunk three times a day before meals. Three grams of milkweed juice and egg yolk, mixed and taken three times a day, will not only increase the tone of the body, but also relieve excess swelling.
Tinctures of mint and flax in water or alcohol have the same effect and help relieve swelling after three to five days.
Baths of mint, sea salt, juniper and mustard also help well with swelling. Do them every evening before bed for a week. If you combine it with medication and massage, you will be able to relieve swelling in just three days.
Burning sensation in the hand after a stroke
Stroke is a terrible disease because it affects the brain, the main organ that can make an individual out of a thinking person.
Not everyone survives a stroke, but if a person is lucky enough to live for many years after a stroke, he sometimes feels pain, such as a burning sensation in the arm, tingling. This pain is called neuropathic.
Everyone is familiar with pain of one kind or another after a stroke, but neuropathic pain is associated with nerve damage. Often, the burning sensation in the hand is quite painful for a long time, which disrupts the normal course of human life.
These burning sensations make performing the most basic actions impossible. Very often, patients are unable to explain the nature of the pain they experience to their doctor, so such patients may not receive adequate help and the necessary treatment.
Causes of pain and burning in the arm after a stroke
Source: https://probol.info/sustavy/pochemu-poyavlyaetsya-otek-nog-posle-insulta-i-chto-delat-bolit-noga-posle-insulta.html
Causes of swelling in the arm after a stroke
Swelling and pain appear over several weeks in the arm that was previously affected by the stroke. This often impairs the motor abilities of the limbs and leads to partial numbness. Why do limbs swell? The following diseases usually contribute to hand swelling, which we will discuss below:
- Pathologies and disorders in the nervous system. After a stroke, an increase in capillary permeability is observed. Swelling, edema, and tissue suppuration are diagnosed;
- Thrombosis. The occurrence of thrombosis in the subclavian vein is the most common cause of swelling;
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes. Damage to the lymph nodes is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, swelling occurs, weakness appears in the body, as well as unpleasant, painful sensations in the area of the affected limbs;
- Swelling can also occur during pregnancy;
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system, kidneys and endocrine system;
- Taking certain medications can also affect the occurrence of swelling of the extremities. Carefully study the side effects of drugs before using them;
- An increase or decrease in temperature in certain seasons of the year also affects the appearance of swelling;
- Heavy physical labor, long walking, poor diet and insufficient water intake also provoke the appearance of swelling.
Most often, legs swell due to problems with the body, as well as due to complications of the disease. The appearance of puffiness extremely rarely occurs due to exposure to certain environmental factors or due to human activity. If the above reasons for swelling apply to any part of the body.
Undoubtedly, swelling of the arm after a stroke is an extremely unpleasant consequence, but thanks to several recommendations from doctors, you can quickly and easily get rid of this symptom. If the swelling is caused by any disease, then it is necessary to do an examination of the body, take the necessary tests and consult a doctor about prescribing treatment.
Forecast
Despite the fact that swelling of the legs is considered a minor consequence after a stroke, almost 80% of patients experience it , if only because of a sedentary lifestyle and a state of rest. You can completely get rid of swelling in three to eight days, although older people can suffer from it for up to two weeks. In the future, symptoms may appear even after recovery if prevention is not carried out or the course of treatment is not completed. In 30% of cases, swelling of the legs can lead to more serious illnesses, kidney failure or a recurrence of stroke due to thrombosis, the accumulation of fluids.
To prevent all this from happening, you just need to follow the doctors’ orders, follow the recommendations and not refuse hospitalization. If you notice the first symptoms of a stroke or prolonged swelling, go to the hospital. After all, mortality and serious consequences arise only due to late seeking of help.
Partial or complete paralysis is one of the most common consequences of a stroke. This is why a bedridden patient develops swelling of the extremities after a stroke due to prolonged immobility. What this condition threatens and how to deal with it is discussed below.
How to determine the appearance of swelling?
Visually, the swelling is practically invisible and it is quite problematic for an inexperienced person to identify it. Especially when a person who has recently suffered a stroke cannot yet accurately describe his feelings. So how can you still determine the appearance of swelling?
Apply pressure to the patient's soft tissue so that it presses against the bone. If, after pressing, a whitish dimple remains, which slowly disappears, then there is swelling. Also, swollen parts of the body are larger than healthy ones. Such measurements should be taken with similar but healthy areas of the body.