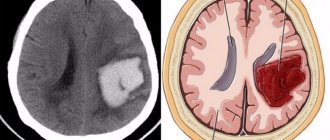
A stroke is an acute disorder of cerebral circulation, characterized by hemorrhage in the brain as a result of rupture of the vessel wall, the development of thrombosis or stenosis of cerebral vessels.
There are two types of damage:
- Hemorrhagic – has a rapid development. The basis of pathogenesis is cerebral hemorrhage. This is a common complication of arterial hypertension.
- Ischemic stroke - forms over a long period of time, often against the background of atherosclerotic narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels. The course and prognosis of ischemic stroke is much more favorable.
Caring for the sick at home
Treatment of a post-stroke patient after discharge continues at home. The rehabilitation period is quite long. With effective organization of care and activities with this group of patients, complete regression of clinical manifestations can be gradually achieved. Conversely, if care is absent or insufficient, the risk of irreversible neurological damage increases significantly.
Caring for a patient after a stroke requires patience and the acquisition of certain skills.
Medical staff should be trained in the principles of caring for a patient after a stroke
Nursing care for stroke
Many people mistakenly downplay the work of nurses, focusing solely on the importance of the work of a doctor.
Actually this is wrong. A lot depends on the qualifications of the nurse regarding the patient’s recovery. It is very important to pay attention to the skills of the person who will perform the functions of a caregiver. This is very hard work and will require some preparation. The factor is decisive in determining the patient's prognosis.
Types of nursing care
The possible range of actions a nurse can take is very wide. It all depends on her position, qualifications and assigned tasks. Conventionally, types of assistance can be divided into the following types:
- highly qualified assistance, we are talking about operating nurses who help during operations;
- personnel performing the necessary manipulations (injections, IVs);
- normal daily nursing care.
Often the last 2 functions are performed by the same person. However, it is not at all necessary that this be a full-time employee of the hospital. Often a caregiver is hired by a household to provide care at home.
Process steps
All stages and types of patient care can be divided into 3 groups:
- Dependent. These are those actions that are usually performed only strictly in accordance with the doctor's instructions.
- Independent. An ordinary set of procedures and manipulations that should be carried out with absolutely all patients. The nurse usually already knows about them and can decide on the appropriateness and nature of the procedure independently.
- Interdependent. They are prescribed by the doctor, but the nurse can begin to perform them only after other assigned tasks have been completed by another medical professional.
In each specific case, the list of stages and even their sequence will change depending on the condition and needs of the patient.
Recovery time
Depending on the condition of the patient, the time frame during which outside care will be required will depend. Often, an ischemic stroke requires that the patient require around-the-clock care for about a month, as he cannot perform even basic daily tasks.
In the future, for another 4-6 months the patient will need insurance and periodic assistance from a nurse. Often, loved ones strive to hire a specialist with specialized education, but in fact, at a late stage of recovery, simply a kind, responsible person or one of the family members will be able to cope with the tasks.
General rules of nursing care
It is customary to highlight a list of rules of nursing care that must be followed in any case. But do not forget about the individual approach to each patient. Each patient has different health conditions and personal needs that must be taken into account.
In this case, it is a mistake to follow only the doctor’s instructions. The doctor prescribes treatment, but in terms of care, everything depends on the nurse and the patient’s loved ones. That is why each issue should be given special attention.
Taking medications
A patient who has suffered a stroke may encounter a number of difficulties in taking medications. The person who will care for him during the rehabilitation period must ensure proper compliance with all the instructions of the attending physician.
The hospital organizes work in such a way that an appointment sheet is drawn up for each patient. It states:
- what drug should be taken;
- dosage;
- how many times a day and for what period of time should you take the medicine.
The peculiarity of the question is that it is first necessary to assess the patient’s condition. Sometimes the patient may well take medications on his own.
But situations are possible when the patient simply cannot do it himself (complete paralysis).
There are also frequent situations when, due to clouding of mind, the patient refuses to take pills, hides them, takes them not in accordance with the prescription list (in random order) or uses drugs excessively.
The nurse's task is to strictly control this process. It is necessary to leave only as much medication as needed for one dose. In addition, many products must be stored in the refrigerator or pre-prepared (diluted powders).
The nurse should also recheck the order sheet regularly. Sometimes the doctor, after the next examination, can adjust the list of necessary medications or their dosage. It's important to pay attention to this.
The patient cannot take some types of medications himself, even if he wants to. We are talking about injections and IVs. Then the nurse needs to have the appropriate skills so that she can carry out all this properly.
At this moment, it is important not to forget about hygiene. Needles, syringes and other accessories should only be used disposable. If tablets are being prepared, then there is no need to remove them from the blister in advance or leave them unattended. Suspensions, powders, solutions must be prepared immediately before use - this cannot be done for future use.
Nutrition
Nutrition is a separate and complex topic when it comes to stroke patients. The situation becomes more complicated if it is an elderly person. Often such patients have a number of concomitant pathologies, which should also be taken into account when choosing a menu.
Often, the doctor prescribes only the number of the dietary table and the nurse must, at her own discretion, compose the patient’s menu from the list of possible products.
It is important to take into account his individual characteristics of his condition, namely whether he can chew food on his own or needs to be served only in liquid form. Patients with this illness are often unable to care for themselves. Simply put, the nurse’s job is to feed and water a person.
The following important points should be taken into account:
- it is necessary to feed not too quickly; in stroke patients the act of swallowing is often slow;
- the food should be light, but the patient must receive a sufficient amount of nutrients;
- You will need 6-7 meals daily, but the portions will be small.
If the patient cannot hold a cup in his hands, then the nurse should make sure to give the patient something to drink more often.
Food and water should not be too hot or cold.
Prevention of complications
The hospital is responsible for each patient. At the same time, rehabilitation involves a difficult official approach to this issue, but also a human one. The nurse must show concern and concern for the patient.
To do this, it is important to take a responsible approach to each stage of care. There are no unimportant details here. Even a minor mistake can lead to serious complications.
To prevent this, it is important not to follow all the doctor’s instructions, but also to be observant. Typically, a nurse spends much more time with patients than a doctor, so it is easier for her to pay attention to any changes. It is important to inform your doctor about this, especially if the dynamics are negative. This will help avoid more serious consequences.
Bedsores
This is one of the most common problems faced by seriously ill patients. Previously, it was always said that such a process develops only if care is not carried out properly. In fact, this theory is only half true. Often, a serious illness can lead to bedsores even when the patient has a personal, experienced caregiver.
Bedsores are pathological changes in tissues that occur due to lack of physical activity, as a result of which normal blood supply is disrupted. That is why it is a mistake to believe that bedsores develop only due to lack of compliance with personal hygiene rules.
A bedridden patient often encounters such an unpleasant phenomenon after being in one position for a long time. A clear example: the condition may be so severe that the person cannot be turned over or moved.
Bedsores occur primarily on those parts of the body that have been in contact with the bed for a long time (buttocks, legs, back, back of the arms).
It is important to pay special attention to these points when conducting an inspection.
To prevent the occurrence of bedsores, it is necessary to perform the following manipulations:
- change the bed regularly (at least 2 times a week);
- even if the patient needs to lie down, you need to turn him to the other side at least 2 times a day;
- twice a day, the body should be wiped with a damp cloth, then wiped dry to avoid contamination;
- at the first opportunity, start massage sessions, gymnastics; during the massage, special attention is paid to the places most prone to bedsores;
- during hygiene procedures, it is necessary to use only special detergents and lotions to prevent the occurrence of allergic reactions;
- treat the body with special creams that prevent such damage to the skin and tissues; at the first symptoms, you must consult a doctor so that he can prescribe more potent ointments.
It is important to understand that bedsores are extremely difficult to treat. That is why it is much easier to prevent their occurrence than to then deal with an existing problem.
Room hygiene
It is important not to forget not only about the hygiene of the patient, but also the room in which he is located. This implies compliance with the following rules:
- The room must be ventilated 2 times a day, while avoiding hypothermia of the patient and drafts;
- You also need to wipe the floor and dust 2-3 times a day;
- Dishes and household items must be kept clean;
- It is best if there is nothing in the room that can cause allergies or other negative reactions of the body (flowers and air fresheners with a strong smell);
- The patient's towels and napkins must be changed daily.
It should be understood that at this time a person is most susceptible to various infections and diseases. That is why it is so important to provide him with the most neutral living environment without unnecessary provoking moments.
By the way, it is important to pay attention to the arrangement of things and furniture in the room where the patient is. Everything you need should be in a visible place so as not to waste a lot of time searching.
If the patient is already beginning to take care of himself (or initially the paralysis was partial), then things need to be arranged so that the person can reach them without risk to himself (not to accidentally turn anything over).
Sometimes a person may not be paralyzed at all and then he can even move around the ward. Then it is important to arrange the furniture in such a way that nothing poses a potential danger to him.
You must understand that in any case the person is very weak, coordination of movements is impaired, and he may simply fall or not see something from the objects.
Healing Fitness
Exercise is an integral part of the recovery process after a stroke. Typically, the patient begins classes after discharge from the hospital, when he begins to work with a rehabilitator. But an important condition is constant work, studying at home.
You can start doing basic exercises right in the hospital. It is important that the patient does not become overtired. That is why at the initial stage one lesson cannot exceed 5 minutes.
The nurse should explain to the patient what needs to be done at this stage in order to quickly return to normal. Demonstrating and sometimes doing exercises with the patient is her task.
The purpose of such classes:
- prevent the appearance of bedsores and muscle atrophy;
- restore motor skills;
- improve the general condition of the body;
- prevent congestion in the lungs and other parts of the body.
To do this, you need to start with the usual turns to the side, bending and straightening your legs. If paralysis occurs, then it is necessary to train at least the healthy side. For developing the hand, a rubber ball is ideal, which the patient can squeeze and unclench with his fingers. Gradually you can move on to bending your arm at the elbow and shoulder joints. It is important not to forget about breathing exercises.
Speech restoration
If a stroke provokes such a complex phenomenon as a violation of speech functions, then recovery will take more than one month. Often, initially a person can only pronounce individual sounds. Subsequently, the speech apparatus gradually returns to normal.
At home, loved ones can help solve this problem, but often at the initial stage the help of an experienced psychologist or speech therapist is required. For such patients, the same approach is needed as for small children - they are asked to name what picture it is. This develops not only speech functions, but also restores mental abilities after an impact.
While the patient is in the hospital, the nurse’s task is simply to talk to him more. While performing basic daily manipulations, you can simply communicate on abstract topics. At the same time, it is important to try in every possible way to understand the person. Even if speech is slurred, every effort should be made to communicate properly.
There is no need to focus on how bad the patient’s speech is at this stage - this can provoke depression and stress. That is why conversations should only be held in a positive way. Not only the topic itself, but also the voice of the medical worker should be positive.
Having first asked the patient if he is tired, you can turn on the TV or radio for a short time.
It is important not to give the patient too much time to communicate, even if he has a desire and certain positive dynamics. We must not forget that at this time even the most basic actions can tire him, which in this case is contraindicated.
Conclusion
Thus, stroke care does not necessarily need to be provided solely by a professional nurse. One of the patient’s loved ones can do this at home. The main thing is to initially approach this issue responsibly and clarify with doctors how to properly carry out this or that type of care.
While the patient is in the hospital, these responsibilities are assigned to the medical staff. Even if the patient’s relatives are ready to spend all the time at his bedside, they are unlikely to be able to perform all the necessary manipulations that require certain skills and abilities. This is why it is so important to ensure that you choose the right person to provide proper nursing care.
Stroke
Source: https://sosudoved.ru/lechenie/sestrinskij-uhod.html
Nutrition
- In the initial period of rehabilitation, it is important to observe the conditions of mechanical and chemical sparing in preparing food for a post-stroke patient. That is, the food should be warm, liquid or mushy, without the use of spices.
- Often patients are unable to eat on their own for some time, or there are various types of eating disorders. The caregiver, depending on the degree of loss of independent care functions by the patient, should help in eating: support cutlery, feed the patient if necessary.
- The diet should be enriched with fruits, vegetables and meat, which are so necessary for the restoration of damaged brain structures.
It is very important to improve the patient’s nutrition after a stroke.
Organizing nutrition for a patient after a stroke
When caring for people affected by a stroke at home, much attention is paid to nutrition and the digestive process.
The menu should not be the same; it should include antioxidants, essential minerals, and vitamins. In addition to the benefits, the wishes of the victim must be taken into account. Favorite dishes will brighten up difficult days after illness.
The basic principles of nutrition are:
- Limiting baked goods, animal fats, smoked and spicy foods on the menu.
- Refusal of alcoholic drinks.
- Inclusion of lean fish, meat, dairy products, cereals, berries, vegetables.
- All dishes must be boiled, stewed, steamed.
- If swallowing and chewing are impaired, food is served in liquid form or puree.
- In the absence of contraindications, it is recommended to drink up to 2 liters of water per day.
The possibility of feeding a patient at home without the use of additional equipment is determined by the doctor, based on the condition of the masticatory muscles responsible for swallowing and peristalsis of muscle groups. If nutrition in the usual way is not possible, it is provided through a nasogastric catheter, or parenterally (intravenously).
If the patient is able to chew and swallow, mechanical processing of food is still required, since chewing large pieces, hard and dry food is difficult. In the early post-stroke period, food is prepared with a mushy, liquid consistency.
Sometimes patients experience excessive salivation. It is necessary to keep the patient's face dry and clean, and wipe off excess saliva and food. To prevent aspiration, food is served from the side so that it flows down the cheek into the throat. In this case, you should try to put food on the healthy side of the mouth. At the end of feeding the patient, you should make sure that there are no food residues in the oral cavity.
The diet is prepared by the attending physician, but the basic principles of nutrition are as follows:
- Plenty of fluids (about 50% of the diet).
- Heat treatment and maximum grinding of food.
- Gentle composition - minimum salt, no spices, hot seasonings, fatty foods.
- Mono-component soups, stews, porridges, i.e., consisting of one product (one vegetable, cereal, etc.), since such dishes are easily digestible.
- Mandatory inclusion in the diet of vegetables and fruits, i.e. foods containing fiber. It is necessary for intestinal motility during a long static position.
Prevention of infections
A weakened body is predisposed to the development of infectious processes. The condition is aggravated by the forced lying position of the patient. Stagnation of lymph and blood occurs, chest excursion decreases, which often leads to bronchopulmonary diseases. Infections can be prevented by following these recommendations:
- Carrying out daily chest drainage massage. Its correct implementation involves rubbing and tapping movements along the projection area of the lungs in the direction from bottom to top. The massage is carried out from all sides: chest, back and sides.
- It is important to exclude the patient from hypothermia and drafts.
- If the risk of infection is high, the doctor may prescribe antibiotic therapy for preventive purposes.
- During an influenza epidemic, vaccination is recommended for such patients, as they are at risk.
To prevent pneumonia, you need to regularly do breathing exercises
Bedsores
In bedridden or inactive patients, bedsores may develop over time if there is insufficient care. These areas of inflammation and necrosis occur in places of greatest pressure: lower back, buttocks, subscapular region. The pathological process begins with the skin and gradually deepens, reaching bone tissue. Stage 3 and 4 pressure ulcers require surgery to remove dead tissue.
Preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of pressure ulcers in patients who have had a stroke:
- A general massage tones the muscles of the body and increases blood circulation, preventing blood stagnation.
- Timely hygiene procedures. If using a bath or shower is difficult, it is necessary to dry the patient several times a day.
- Experts recommend placing soft or inflatable cushions under areas of the body that experience maximum pressure. They reduce tension and prevent tissue compression.
- A special functional bed designed for bedridden patients perfectly relieves muscles.
To prevent bedsores, you need to purchase a special mattress
General treatments for stroke and its complications
Stroke is an acute disorder of cerebral circulation, the treatment of which cannot be carried out according to ready-made schemes.
There are two types of disorders - hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke. The answer to the question “how to treat a stroke” can only be obtained from specialists - neurologists, neurosurgeons. The tactics of therapy completely depend on the type, initial state of health, the causes of the disorder and the consequences of the pathology. The main methods of treatment are medication and surgery, however, relief of the acute condition and stabilization of indicators is not all that can be done to restore the function of the nervous system to the maximum possible extent. Further rehabilitation also applies to the treatment of the consequences of a stroke. They can be overcome completely, but this depends on the degree of damage to brain structures.
This article discusses in detail the features of the course of both types of disease, as well as each of the treatment methods and subsequent rehabilitation measures.
Main directions of stroke treatment
Depending on the nature of the circulatory disorder in the brain, the doctor selects special treatment methods, as well as additional general therapeutic and preventive measures.
The latter are procedures and methods of drug correction to prevent possible complications of a stroke. First of all, this is control of important functions - breathing, urination, blood circulation (including peripheral), as well as daily care. It plays an important role in rehabilitation treatment, since the patient remains in bed for some time, which is fraught with certain consequences.
Special treatments for ischemic stroke
Thrombolytics. Medicines that dissolve formed blood clots can restore blood circulation and prevent damage to brain neurons - reducing the size of the damaged area. The use of this group of drugs is carried out by a doctor with caution, since one of the possible complications may be a hemorrhagic stroke - a secondary acute disorder of cerebral circulation in a previously damaged area of tissue.
In order to prevent the development of existing blood clots and the appearance of new ones, anticoagulants are more often used. They lead to a decrease in the number of platelets, and, accordingly, blood clotting indicators. This can be fraught with internal bleeding in cases where the patient suffers from a stomach or duodenal ulcer, so in these cases anticoagulants are also prescribed with caution.
atherosclerosis;
blood diseases accompanied by a tendency to thrombosis.
In addition, antiplatelet agents are prophylactic drugs that can prevent the development of a recurrent stroke.
All of these medications restore and improve cerebral blood flow. The course of treatment is individual - in each specific case, the specialist calculates the dosage and combination of drugs, taking into account the initial condition, indications, contraindications, and the severity of the disorder.
A stroke causes the death of nerve cells because they no longer receive nutrients and oxygen. In order to stop pathological biochemical reactions, neuroprotectors can be used. They allow you to reduce the focus of damage to brain tissue. Neuroprotectors also help surviving cells become involved in performing the tasks of those that are unable to function.
The surgical method of treating ischemic stroke - carotid endarterectomy - is used only for certain indications - sudden stenosis (narrowing) of the carotid artery or its blockage with an atherosclerotic plaque. Despite the seriousness of the surgical intervention, this method is in some cases used as a prophylactic method - to prevent a possible first stroke and the development of a recurrent cerebrovascular accident.
The main tasks in hemorrhagic stroke are to stop bleeding and constant control of blood pressure.
Reducing blood pressure is the main condition for reducing blood pressure on the walls of blood vessels. This allows you to stop bleeding faster. For this purpose, a group of antihypertensive drugs is used. The patient takes them orally or receives them intravenously - it depends on his general condition and indications.
Performing surgery allows you to restore the integrity of the vessel, but this is not always possible.
Bleeding can be stopped with medication, in which case surgery is not advisable. There are also inoperable cases - hemorrhage occurring deep in the brain tissue cannot be corrected by intervention due to the high risk of complications.
Open method Closed method
Opening the patient's skull (trepanation) and removing the hematoma. Inserting a cannula through a small hole into the center of the hemorrhage and removing blood through it.
In cases where the hemorrhage occurred from a ruptured aneurysm (protrusion of the wall of a vessel or artery), it is excluded from the general blood flow - “closed” with metal clips. This is called aneurysm clipping.
If an aneurysm is located on the surface of the brain, its rupture leads to subarachnoid hemorrhage - blood spreads throughout the space surrounding the brain. Healthy vessels narrow, which can lead to ischemic events. To prevent these complications, the doctor administers special drugs intravenously.
In cases where hemorrhage affects the cerebral ventricles, blockage of the openings for the outflow of fluid from the skull may occur. This leads to expansion of the ventricles and compression of tissues - the development of obstructive hydrocephalus. In this case, emergency surgical intervention is indicated - installation of drainage in the ventricles to ensure fluid outflow.
One of the most dangerous complications of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke is cerebral edema. This is an excessive accumulation of fluid in the tissues, which results in an increase in volume. Edema leads to displacement of brain structures and their compression, and can also lead to death.
The main tactic for correcting complications in this case is the administration of osmotic diuretics. They are designed to create high osmotic blood pressure and provoke the removal of excess fluid into the blood. In cases where the patient is on mechanical ventilation, the doctor selects a ventilation mode to reduce intracranial pressure.
sedatives – in the presence of severe agitation;
anticonvulsants - in cases where seizures are observed or there is a risk of their development (for example, a history of epilepsy);
pain relief, etc.
In some cases, other measures may be needed to maintain the vital functions or general condition of a person who has had a stroke.
The primary task after performing first aid after a stroke is to prevent possible complications or their timely correction.
Complication Correction/prevention
Pneumonia Breathing exercises if the patient is conscious. Daily ventilation of the room.
Bedsores Turn the patient in bed. Plant with the permission of a doctor. Daily treatment using special products, use of disposable hygiene products.
Violation of water balance. Installation of a probe in the absence of swallowing.
Thrombosis of the veins of the legs Performing leg exercises, flexion-extension in the joints, passive exercises - with the help of a caregiver. Massage from foot to thigh in consultation with your doctor. In the presence of thrombosis, bandage the limbs with an elastic bandage.
Stomatitis: Daily brushing of teeth and rinsing mouth after meals. Wiping the mouth with a cotton ball soaked in a special solution.
Caring for a bedridden patient who has suffered a stroke should also include fulfilling hygienic requirements - timely washing, using special containers to ensure cleanliness of linen during bowel and bladder emptying.
In many cases, after some time, the functions partially return, and the patient is allowed to move independently and not have to adhere to such strict bed rest. However, the restoration does not end there.
The recovery period is no less important than the first therapeutic and surgical measures in the treatment of stroke.
Its main goal is the stabilization of neurological symptoms and their gradual regression. This is achieved through a kind of “retraining” of brain cells - the preserved tissue areas take on the functions of those parts that were damaged as a result of circulatory disorders.
vasoactive agents - drugs that improve blood circulation;
amino acids;
nootropic drugs.
In addition, rehabilitation consists of massage sessions, electrical stimulation and physical therapy. They reduce the likelihood of developing contractures, thrombosis and other possible consequences and restore motor functions.
Room hygiene
Similar article: Exercise therapy after a stroke at home
A person caring for a post-stroke patient must know the rules of hygiene of the room in which the patient is located.
- It is necessary to periodically ventilate the room, providing an influx of fresh air. But, as mentioned above, beware of the formation of drafts.
- It is recommended to carry out wet cleaning daily, especially carefully in the room where the patient is.
- Frequent change of bed linen is encouraged. Crumbs left in the bed after eating and wrinkles that have formed are additional risk factors for bedsores.
Exercise therapy
Nursing care of a patient after a stroke requires knowledge of physical therapy. For a faster recovery, the patient should perform individually selected exercises daily to help restore motor functions.
- If the pathological process affects the functions of the upper extremities, then first the patient will be taught to pick up and hold various objects. Then fine motor skills are restored: sorting out cereals and beads, folding puzzles, tying shoelaces and unfastening buttons.
- If the lower extremities are affected, the patient first masters the exercises while lying in bed. The “bicycle” is effective. The patient, in a supine position, rests his feet on the palms of the assistant and alternately bends and straightens his legs at the knee joints. Then the training moves to a horizontal position. The patient learns to walk, first with support and gradually moving to independent walking.
- Joint activities in the pool help a lot. Such workouts are gentle on a fragile body, but at the same time they are very effective.
Physical therapy will allow you to quickly restore functions lost due to a stroke
Psycho-emotional disorders
The illness suffered greatly affects the emotional state of the patient. Temporary loss of full social activity can lead the patient into a state of despondency and depression. In addition to the professional help of a psychotherapist, which may be needed, communication with relatives and loved ones is important.
The manifestation of love and participation on their part, warm conversations with the patient will help him accept his weak state and survive it. In addition, a positive emotional attitude increases the desire to be treated and increases the effectiveness of the therapy.
Restoring functions lost after a stroke is not always fully achievable. However, it is important to remember that a conscientious and timely rehabilitation process is the key to a speedy and maximum possible recovery.
How to Avoid Depression
A common mistake made by relatives is that by the concept of “how to care” they only mean maintaining cleanliness, timely administration of medications and preventing complications, but at the same time they do not pay attention to the psychological problems of the patient.
Depression after a stroke develops if a person feels superfluous and unnecessary due to illness. A depressive state negatively affects the quality of rehabilitation. Here are some tips to beat depression:
- Communication. The patient must communicate. There is no need to interfere with the visits of colleagues and friends.
Hobby. This could be knitting, embroidery, gluing models from matches, etc. similar hobbies are not only good psychological rehabilitation, but also a way to improve finger motor skills.
- Encouraging independence. If a person wants to eat or wash himself, then there is no need to prevent this, even if the bed gets dirty. Believing in your independence speeds up psychological recovery.
- Communication as equals. Despite the fact that a stroke patient is limited in movement, this condition cannot be emphasized with unnecessary pity - this makes patients moody and increases the tendency to depression. It is worth listening to the patient’s wishes and talking about their problems. Such communication will help to find a compromise and will not allow a person to feel inferior.
- Newspapers and TV. Lack of information has a negative impact on the psychological state. Let him read books, newspapers and watch TV - this will help him recover faster.
Well, if a depressive state has set in and a person refuses to eat and does not want to do gymnastics, then you need to consult a doctor about how to get out of depression. Psychologists have psychocorrectional programs that will help cope with depression.