Causes of paralysis of the right half of the body after a stroke
In acute cerebrovascular accident, a stroke occurs.
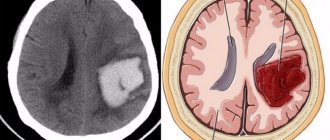
The right side can be paralyzed when ischemia or hemorrhage develops in the left hemisphere of the brain. If a stroke occurs, paralysis of the right side is manifested by impaired muscle function. Patients also experience changes in sensitivity on the right side. Patients with stroke are hospitalized at the neurology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital around the clock. In 85% of stroke cases, the cause of acute cerebral circulatory disorders is ischemia. Left-sided ischemic stroke develops due to spasm, narrowing and blockage of blood vessels in the left hemisphere of the brain. Necrosis of brain tissue occurs and the activity of the whole organism becomes unbalanced. Most often it occurs in patients suffering from arterial hypertension.
Hemorrhagic stroke occurs due to a violation of the integrity of the blood vessels of the brain. Its cause may be malignant arterial hypertension, congenital and acquired cerebral aneurysms, and blood diseases. The provoking factor is stress, physical strain, heat stroke.
With the development of left-sided strokes, in a third of patients, in addition to paralysis of the right half of the body, there are disorders of the muscle-joint sense, which significantly affects the restoration of range of motion in the paralyzed limbs and significantly complicates the restoration of walking and self-care. Some patients develop afferent paresis, which is manifested by a violation of the performance of targeted movements and sensitivity while maintaining strength and full range of movements in the limbs. Also, along with right-sided paralysis and decreased sensitivity, patients after strokes on the left side of the brain may develop pain and various uncomfortable sensations on the right side of the body:
- paresthesia (feelings of numbness, crawling, tingling sensations);
- dysesthesia (deviations in sensitivity to touch).
Poor circulation in the left hemisphere of the brain, in addition to paralysis of the right half of the body, is manifested by changes in speech, mental activity, memory loss, and misunderstanding of the meaning of words. Patients become withdrawn and depressed. The medical staff of the Yusupov Hospital treats patients with care and attention.
Upon admission of a patient with a stroke, an examination is performed using modern diagnostic equipment:
- computer and magnetic resonance imaging;
- duplex scanning;
- video electroencephalography;
- electromyography.
Neurologists establish an accurate diagnosis and begin treatment in a timely manner.
Classification of right-sided stroke
Stroke spares no one; people face the problem regardless of gender and age. But, more often, the disease is diagnosed in men and women who have crossed the age limit of 50 years. This feature is explained by medicine, the reason is that people do not follow the rules of a healthy lifestyle, are passive, do not eat properly, ignore the need for preventive examinations and do not strengthen blood vessels.
In the general classification, 3 types of cerebral vascular lesions are considered:
- Ischemic. A blockage occurs in one or more blood vessels, causing brain cells to experience oxygen starvation and subsequent cell death.
- Hemorrhagic. Characterized by hemorrhage in the brain tissue due to rupture of blood vessels.
- Mixed. Diagnosis is made if signs of both types of pathologies are present.
This division can be called incomplete, because each of the species is further divided into subspecies, depending on the provoking cause. It is important to identify such features in time, otherwise sane treatment may be ineffective. Ischemic stroke can be divided into:
- atherothrombic – arising due to progressive atherosclerosis;
- cardioembolic – occurs due to blockage of blood vessels in the brain;
- hemodynamic – predisposition is formed against the background of heart disease;
- lacunar - voids form in the body of the vessels, which are gradually filled with liquid, it accumulates, compresses the capillaries, causing the blood flow to change.
Hemorrhagic stroke is also usually distinguished by subtypes. By its nature, the disease is considered more dangerous, therefore the likelihood of a full recovery is somewhat lower. The prognosis noticeably worsens if the victim is elderly or the disorder does not appear for the first time.
There are such subspecies:
- epidural - blood enters the brain from the vessels located above its hard shell;
- subdural - the opposite of the epidural, the affected vessels are located under the dura mater of the brain;
- parenchymal - hemorrhage occurs in the soft tissue of the brain;
- subarachnoid - effusion occurs in the subarachnoid space;
- intraventricular – characterized by damage to the ventricles of the brain.
Attention! The main parameter on which the recovery prognosis depends is the speed of first aid and its correctness. The more time passes before the emergency team arrives, the less chance of recovery.
Features of the treatment of strokes manifested by paralysis of the right half of the body
When a patient is admitted to the Yusupov Hospital, doctors immediately begin to carry out emergency measures, using the “window of therapeutic opportunities.” This is 3-6 hours from the onset of the disease. During this period of time, it is possible to completely or partially restore the nerve cells of the brain. Even with deep destruction of neurons as a result of a stroke, they can partially regenerate lost functions. This ability is called neuroplasticity and helps in the patient's rehabilitation process. When a stroke occurs, the right side is paralyzed, the treatment regimen consists of the following points:
- general therapy;
- differentiated treatment;
- therapy and prevention of complications;
- early rehabilitation;
- secondary prevention.
General stroke therapy is aimed at restoring vital organs and systems. It includes:
- correction of breathing disorders;
- regulation of the cardiovascular system;
- normalization of water-electrolyte balance;
- control of glucose metabolism and body temperature.
Drug therapy depends on the type and symptoms of stroke. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital take an individual approach to choosing a treatment regimen, changing medications and their doses depending on the effectiveness of therapy and the course of the disease. Rehabilitators restore the motor function of the right arm and leg using local or general massage, perform passive exercises, and use biological control with the study of responses.
To the question whether recovery is possible in the presence of paralysis after a stroke, the answer is clear: the patient’s recovery depends on the restoration of blood supply to the brain. Recovery after a stroke with paralysis of the right side has its own characteristics. How quickly movements in paralyzed limbs will resume depends on the initial severity of the condition and the age of the patient, the size of the pathological focus and its location. When the pathological focus is located on the left side, movements are first restored. After a stroke, the right side of the body begins to function in the first 5-7 days of treatment. Impaired coordination of movements and speech disorder may remain forever.
The prognosis for the recovery of motor disorders in strokes of the left hemisphere of the brain worsens in the case of delayed rehabilitation. This may be due to severe astheno-depressive state, severe cardiovascular diseases, age, late presentation or extensive lesions of brain tissue.
To rehabilitate patients with sensory disorders, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use special methods of kinesitherapy (physical therapy and therapeutic exercises), as well as selective massage. Neurologists prescribe treatment with tricyclic antidepressants, opioid analgesics (for severe pain in the extremities) and drugs that reduce paroxysmal brain activity (electrical activity of the cerebral cortex, in one of the areas of which excitation processes exceed inhibition processes).
Massage and kinesiotherapy are the main methods of rehabilitation treatment after strokes, which doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use against the background of qualified differentiated treatment. Selective massage has a mainly passive irritating effect on certain areas of the body or muscle groups, while classic massage has a general tonic effect. Under the influence of various massage techniques, irritation of receptor zones occurs, followed by a reflex response of the entire body. Kinesiotherapy preserves, restores and creates new conditions for the body’s adaptation to physical activity.
One of the leading centers for stroke treatment is the Yusupov Hospital. The neurology clinic has won this recognition thanks to the vast experience of its doctors, modern diagnostic methods, and the use of advanced technologies in the treatment of stroke. In the rehabilitation clinic, equipped with modern equipment, patients successfully restore lost functions. You can make an appointment with a doctor by phone.
Source: yusupovs.com
Symptoms characteristic of the pathology
All signs of ischemic stroke of the left hemisphere of the brain can be divided into 3 main groups:
- Focal neurological. They manifest themselves in the form of dysfunction of the sensory organs, memory loss, sensory disturbances on the right side, paresis, paralysis of the facial muscles on the right or limbs on the same side. The degree of their manifestation depends on the type of damaged vessel, the location of the lesion, its size and the condition of other neighboring arteries.
- General cerebral. The main part of them are causeless migraines, dizziness, confusion, nausea followed by vomiting, intolerance to bright light, loud sounds, touches, etc. Their manifestation is associated with increased intracranial pressure and irritation of the meninges. Symptoms will be pronounced only if there is an extensive stroke or contact of the source of the disease with the meninges. In all other cases, general cerebral signs may be weakly expressed or absent altogether.
- Vegetative. Each type of stroke, of any severity, is accompanied by symptoms such as: tachycardia, shortness of breath, sudden jumps in blood pressure, dry mouth, pale skin, intense sweating, fear of death.
Before the onset of an attack, there are several preceding signs, upon discovering which it is worth calling an ambulance so as not to waste time. The main ones are: severe headache, dizziness with loss of consciousness, deterioration in the mobility of limbs, a feeling of numbness, tingling on the right side of the body, often at night, speech impairment. The manifestation of two or more of the above symptoms indicates an approaching attack. If the malaise does not worsen and goes away on its own within the first 24 hours, then doctors diagnose a transient ischemic attack. When symptoms develop, become more intense and persist for more than 24 hours, an ischemic stroke is diagnosed.
To independently check a patient for acute cerebral infarction before the ambulance arrives, three exercises are enough:
- it is necessary to ask the patient to smile. If he cannot do this at all or only one corner of his mouth remains drooping, then a stroke is most likely to occur;
- the same can be said if a person cannot repeat a sentence spoken to him;
- and lastly, any healthy person can raise two arms up at the same time. In the presence of an ischemic stroke, this cannot be done.
The time within which assistance must be provided after the onset of an attack is from 3 to 6 hours. This is the so-called therapeutic window. Timely medical interventions will help slow down the destruction of the basic functions of the human body and reduce the likelihood of disability in the future.
Causes of ischemic stroke of the right hemisphere of the brain
An ischemic stroke on the right side of the brain develops as a result of a thrombus or embolus blocking the arteries supplying blood to the right hemisphere of the brain, as well as severe spasm of the vessels in this area. Acute circulatory disorders in the right hemisphere can be caused by hypertension with hypertensive crises and atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels. A right-sided stroke can be a consequence of pathological changes in the right carotid and vertebral arteries, through which oxygen flows with the blood to the right hemisphere of the brain. When small arteries are damaged, a lacunar stroke develops.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital diagnose the disease using computer and magnetic resonance imaging. Neurologists use individual treatment regimens depending on the subtype of ischemic stroke, the manifestations of the disease and the course of the disease. Rehabilitation clinic specialists restore impaired functions using innovative techniques.
Introduction
Stroke is included in the group of serious diseases. Every year thousands of people around the world die from it and become disabled. In general, 50–60% of patients manage to survive, and no more than 10% recover completely. This means that the consequences of the disease are really severe, and it is not always possible to influence them.
Click on photo to enlarge
The prognosis depends on several factors, which are described in the table:
| What are the consequences? | How factors influence the outcome |
| Form of the disease | The consequences of ischemic stroke are less dangerous than hemorrhagic stroke |
| Stroke dimensions | The larger the area of necrosis in the brain (massive stroke, or microstroke), the worse the prognosis for recovery |
| Involvement of vital brain centers in the process | Localization of a stroke in the brain stem is fatal |
| Age and general condition of the patient | The prognosis is worse for the elderly and people with severe underlying medical conditions |
| Time to provide assistance | The later the patient is brought to the hospital (more than 3–6 hours), the worse the consequences |
As for life expectancy after a stroke in the right hemisphere, it is in a wide range, as it depends on the factors described in the table, and ranges from several hours to tens of years.
A stroke on the right side of the brain differs in symptoms and consequences from the left side. This is due to the fact that each hemisphere is responsible for different brain functions.
Click on photo to enlarge
Ischemic stroke on the right side of the brain. Features of the clinical picture
In the right hemisphere of the brain there are clusters of nerve cells that provide the sensation of the body in space, sensitive perception of the surrounding world, and analysis of incoming information. In left-handed people, the speech center is located in the right hemisphere of the brain. During the acute period of right-sided ischemic stroke, the following symptoms are observed:
- complete or partial paralysis of the left half of the body;
- changes in the face (smoothness of the nasolabial fold on the right, “sailing” movement of the lips when breathing, lowering of the corner of the mouth downwards;
- inability to assess the position of your body; determine the size of objects;
- loss of memory for recent events while maintaining the ability to remember the past;
- lack of ability to concentrate.
The consequence of an ischemic stroke on the right side in left-handers is speech impairment.
Occlusion of the right carotid artery (stenosis, thrombosis, embolism) is often asymptomatic. Neurological disorders are associated mainly with insufficiency of blood supply in the middle cerebral, and sometimes in the anterior and posterior cerebral arteries on the right. Usually, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital observe the so-called “flickering” of symptoms. Developing partial or complete left-sided paralysis with impaired speech function and the alternating blindness combined with them disappear after a few minutes or hours. Increased pulsation in the arteries of the face, low pressure in the retinal arteries of the right eye indicate narrowing or blockage of the internal carotid artery on the right. A blood clot in a major vessel in the neck can be palpated by a neurologist, identified by angiography and urgently removed by a surgeon at partner clinics of the Yusupov Hospital.
During the recovery period after an ischemic stroke on the right side, neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital note in patients, in addition to impaired motor functions, emotional manifestations of the disease: a depressive state is replaced by gaiety, “foolish” behavior, lack of tact and a sense of proportion. When a large cerebral artery is blocked and there is extensive damage to the right hemisphere of the brain, focal clinical manifestations rapidly increase against the background of severe headache. A characteristic change in the face appears, and immobility of the left half of the body increases. Swallowing may be impaired and speech difficulties may increase.
Right-sided lacunar ischemic stroke develops gradually in patients suffering from diabetes mellitus and hypertension. General cerebral manifestations are weakly expressed. Half of the patients develop weakness in the left arm and leg, and there is a loss of sensation in the left side of the face. In 1/3 of patients, there is a loss of pain sensitivity and the ability to distinguish the shape and temperature of an object by touch. In every tenth patient, lacunar stroke is manifested by severe dizziness and the inability to move independently.
Stroke on the left side - consequences and how long they live
Attack, blow, onslaught - this is how the Latin word insultus is translated, meaning severe brain damage. How long do patients live after a stroke on the left side - the answer is given by medical practice. How the signs and symptoms differ depending on the location of the disease are questions that concern everyone who has encountered this insidious disease.
Causes of stroke
A crisis that suddenly befalls a person usually matures in his body for several years. The long destructive work is evidenced by statistics according to which older people are most often susceptible to the disease. Based on the location of the damage, right-sided and left-sided strokes are distinguished.
Stroke on the left side, consequences and treatment, rehabilitation makes sense if loved ones help the patient overcome psychological difficulties and get rid of bad habits.
What to expect after a left-sided stroke is a problem facing loved ones caring for the patient at home. The answer depends to a large extent on eliminating the causes that provoked the attack.
The reasons for the defeat are:
- hypertensive crisis;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- excess cholesterol;
- excess sugar;
- aneurysms;
- poor blood clotting.
The list of reasons continues with bad habits that aggravate natural deviations or contribute to their appearance.
Recovery after a stroke on the left side can be accomplished at home if you follow the doctor’s recommendations, conduct physical therapy sessions, breathing exercises, massage and other rehabilitation measures.
Bad habits leading to a stroke on the left side.
- alcohol;
- smoking;
- obesity.
Areas of the brain that have difficulty accessing blood and oxygen when they are affected by a left-sided ischemic stroke lose the ability to perform their functions normally. Damaged areas of the left hemisphere in the hemorrhagic type of the disease also stop transmitting impulses to the organs for proper functioning.
Functional features of the left hemisphere
The consequences of a left-sided stroke in men adversely affect all areas of life: the ability to clearly pronounce words, read, write, understand speech, concentrate, and navigate in space is lost. The impact manifests itself in numbness or paralysis of the right arm or leg.
Doctors find it difficult to definitively answer the question: “Which stroke is more dangerous: left-sided or right-sided?” , because the body’s performance of psychophysical tasks depends on the interaction of the left and right sides.
The left hemisphere helps to recognize numbers, signs, and symbols. The consequences of a stroke on the left side of the brain result in impaired speech and cognitive functions; the victim loses the ability to adequately perceive reality, finds it difficult to connect disparate facts into a single whole, and is unable to draw the simplest conclusions.
You can find out in which side of the brain the rupture occurred and on which hemisphere the pressure was applied by external signs. If the blow hits the left side, the right side of the body is taken away and vice versa.
Types of diseases of the left hemisphere of the brain
A circulatory disorder caused by the formation of a blood clot is called an ischemic stroke.
If the attack is caused by a rupture of a blood artery and hemorrhage occurs, they speak of a hemorrhagic stroke on the left or right side of the brain.
Depending on the degree of damage, both types of disease manifest themselves in numbness of the tongue, limbs and can paralyze half the body.
Ischemic
The cessation or obstruction of access of blood and oxygen to the brain causes dysfunction of all human life-support systems. An ischemic stroke of the left side occurs when an obstacle gets in the way of the blood-carrying vessels.
The barrier in this case is a blood clot or thrombus caused by high lipid content. Fat deposits in the vessels narrow or close the lumen of the artery, as a result of which the patient feels as if he is losing his tongue, arms and legs.
Hemorrhagic
The diagnosis means a ruptured blood vessel with associated bleeding. A large outpouring of blood occurs, flooding the brain tissue. Its influx puts pressure on them, as a result of which they become incapacitated.
Hemorrhagic stroke of the left half is difficult to diagnose, which makes it difficult to provide emergency care to the victim. Therefore, the consequences of this form of the disease are the most severe and difficult to recover.
The extensiveness of the source of damage causes swelling, leading to disability or death.
Symptoms
Symptoms have cerebral, focal and vegetative manifestations. The first manifest themselves in a violation of general vital functions. Focal ones show the localization of the lesion. Vegetative symptoms manifest themselves in changes in sensitivity.
General cerebral
Patients who have suffered a stroke on the left side have difficulty maintaining balance, have impaired coordination of movement, and complain of dizziness. In particularly difficult cases, the ability to get out of bed and walk is impaired.
Focal
If the frontal lobes are affected, the patient complains of blurred images, double vision, partial or complete loss of vision.
Vegetative
After a stroke on the left side, the right side of the face becomes distorted. The mouth curves when smiling. The arms become numb, and complete or partial paralysis of the entire arm, hand, or leg is possible.
Which side recovers faster during a stroke: the right or the left?
If it is possible to stop the spread of a blood clot during an ischemic stroke on the left side in the first four and a half hours, we can talk about the speed of the patient’s recovery. In the case of a hemorrhagic stroke of the left hemisphere, center or right hemisphere, this is more difficult to do, so all further actions to rehabilitate the patient become long and complex.
Providing qualified medical care in the first hours after a left-sided stroke is of primary importance to stop the spread of tissue death and speedy recovery of the patient.
The restoration of the right side, as well as the left, largely depends on the individual characteristics of the body. If the patient is young, we can talk about recovery from a left-sided stroke in two weeks. In patients with weakened vitality, the duration of the first stage of treatment for left-sided stroke is up to six months.
Diagnostics
A patient with a suspected stroke is asked to smile. If this simplest movement is difficult for him, the first sign of the disease is noted. Asymmetry in the face on the right side is another sign of a left-sided stroke.
The patient is asked to pronounce a phrase that requires mastery of the articulatory mechanism. For example: “thirty-three heroes with scales like the heat of grief” or another tongue twister. If difficulties in pronunciation are noticeable, then we can talk about a left-sided stroke.
The third command that the patient is asked to perform concerns movement. He must raise both arms simultaneously at the level of the elbow joint or above. If a person is unable to raise or hold his arms up for one to two seconds, they speak of brain damage.
Treatment
After confirmation of the diagnosis, the patient is immediately assigned to treatment in the neurological department.
In the hospital, the patient is connected to a ventilator and is provided with the necessary functions for life. Eliminate the causes contributing to the development of the disease: stop the outpouring of blood, carry out procedures to dissolve blood clots. If possible, the blood clot is removed surgically.
Drug treatment
For hemorrhagic stroke on the left side, drugs are prescribed that strengthen blood vessels and prevent the spread of hemorrhage (Gordox, Contrical), and preventive drugs against vasospasm are given, and drugs that protect the central nervous system.
For ischemic stroke on the left side, the following is prescribed:
- thrombolytics;
- anticoagulants;
- vasoactive drugs;
- anticonvulsants.
Hemorrhagic stroke on the left side most often requires surgical intervention. Practice shows that sometimes this is the only way to return the patient to normal life.
For both types of stroke on the left side, general remedies are prescribed:
- strengthening;
- sedatives;
- diuretics;
- decongestants.
Medicines that relieve headaches are indicated.
Physiotherapeutic methods
These methods are used to improve blood circulation, eliminate residual effects and cope with the dangerous consequences of a stroke on the left side. Usually used:
- magnetic therapy;
- vibroacoustic therapy;
- acupressure massage;
- acupuncture.
The technique is suitable for the period after the main painful symptoms of a stroke on the left side have been relieved and is more rehabilitative than therapeutic.
Consequences of a stroke
Regardless of the type of brain damage, loved ones need to prepare for the most severe complications. Everyone agrees that a stroke on the left side is a catastrophe that takes a person out of his normal rut for a long time.
If you miss the first hours (4, 5 hours) to stop the development of a blood clot or hemorrhage, in most cases the consequences will be irreversible.
This:
- complete or partial paralysis;
- disturbance of mental activity;
- loss of independent control of basic life functions.
- inadequacy of perception of reality.
- death.
Depression often accompanies a person who has had a stroke on the left side. Women and men affected by this disease need to create a special psychological mood, support from staff and loved ones.
Forecast
If the victim received medical care on time, if doctors managed to neutralize or remove the blood clot that caused brain damage, there is hope for recovery even in the most severe cases.
The prognosis for recovery after a stroke on the left side also depends on the extent of the focus of the disease, the psychological mood of the patient, the equipment of the medical institution and the help of loved ones.
Rehabilitation
After the first acute symptoms of a stroke on the left side have been relieved and the therapeutic period has ended, they move on to restorative procedures.
A person’s return to a full life largely depends on successfully completed rehabilitation measures.
Physiotherapy
Performing feasible exercises is a mandatory part of the recovery period after a stroke on the left side. The use of simulators with biofeedback is a serious help for patients and their loved ones. Recommendations for exercise therapy are received from a specialist who demonstrates the correctness of their implementation.
Breathing exercises
Proper breathing is an essential component of the healthy functioning of all organs of the body. Breathing exercises help enrich the body with oxygen and saturate the cells with the energy necessary for rehabilitation after a stroke on the left side. Control of the respiratory system normalizes the patient’s neuropsychic state, which determines the quality of life after a stroke.
Speech restoration
Work to restore speech includes the complete psychological adjustment of the body to normal functioning after a stroke on the left side. A speech therapist works to recreate the patient's contact with the outside world through perception, hearing, vision and verbal communication.
Hirudotherapy
The use of medicinal leeches for the prevention, treatment and recovery after a stroke of the left side is an ancient and proven method. Leeches bite through the skin and suck out blood, releasing natural anticoagulants into the wound. In this way, blood clots are resolved, blood supply is improved, and the risk of a recurrence of a stroke on the left side is eliminated.
Massotherapy
Therapeutic massage is carried out by the hands of a professional massage therapist or with the help of special massage devices. If you follow your doctor's recommendations, massage is very effective in recovering from a stroke.
Special diet
A patient’s diet after a stroke should be varied and nutritious. A separate menu is drawn up for him with a limitation of fats and carbohydrates. It is not recommended to completely exclude protein foods from your diet. But it is necessary to diversify it with the consumption of fresh vegetables, fruits and herbs.
Getting rid of bad habits
After suffering a blow to the left or right hemisphere of the brain, it is necessary to cleanse the body of toxins accumulated in it. For this purpose, it is recommended to stop drinking alcohol and smoking. Physical therapy exercises, massage, breathing exercises, and the mindset of complete recovery help in getting rid of bad habits.
A stroke on the left side is a difficult ordeal for every person. The help of others and loved ones is necessary here. Life after a stroke is possible. Experience shows that people who have suffered this terrible disease live five to ten years with good care.
Source: https://prodavlenie.online/insult/levoj-storony.html
Diagnosis of right-sided ischemic stroke
In order to promptly detect an ischemic stroke in the right half of the body, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use high-tech equipment that allows them to obtain accurate information about the state of blood flow in the vessels of the right hemisphere and the degree of damage to brain tissue. Neuroimaging methods (computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging) allow not only to determine the type and location of stroke, but also to establish the pathogenetic subtype of cerebral infarction, identify the pathology of the vessel that led to acute cerebrovascular accident, and determine treatment tactics.
With perfusion computed tomography, neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital are able to identify the so-called “mismatch” phenomenon - a difference in the volume of brain matter, where the speed of blood flow and blood volume are reduced. This area is the ischemic penumbra zone, that is, a region of the brain that, with timely intervention, can potentially be saved from death.
At the Yusupov Hospital, doctors also use the following innovative methods for diagnosing ischemic stroke of the right hemisphere:
- transcranial Doppler sonography, which allows assessing the state of cerebral blood flow;
- cerebral angiography, which is indispensable when planning surgery;
- electroencephalography, which helps identify areas of cortical and subcortical damage;
- scintigraphy and positron emission tomography are research methods that allow you to assess cerebral metabolism (metabolism) and are important in the stage of transient cerebrovascular accidents, as well as at the very beginning of ischemic right-sided stroke.
Forecast
After a right-sided ischemic stroke, the prognosis depends on the extent of brain damage. A chance for complete recovery is possible with timely relief of the attack and small amounts of cerebral tissue ischemia. In more severe cases, it is not possible to be completely rehabilitated, but patients have the opportunity to at least partially regain impaired abilities and live a normal life.
With hemorrhagic stroke of the right hemisphere, the prognosis is generally unfavorable. Patients often die immediately after the stroke or within a few days later. If a person manages to survive, he still remains disabled; many functions cannot be restored at all.
Thus, right-sided stroke is a dangerous pathology that entails many serious complications. To reduce the risk of developing this disease, you should be more attentive to your health, starting from childhood.
Treatment of ischemic stroke of the right hemisphere of the brain
At the Yusupov Hospital, doctors individually approach the treatment of each patient with acute cerebrovascular accident. Basic therapy begins with the organization of proper care for the patient. For several days, a patient with a right-sided ischemic stroke should be in a horizontal position with his legs elevated.
From the very beginning, prevention of bedsores, purulent corneal ulcers, hypostatic pneumonia, and early contractures is carried out. Within 24-48 hours after the patient’s admission to the neurology clinic, passive movements in the joints begin, turn the patient in bed, and clear his airways. In case of persistent vomiting, a nasogastric tube is inserted into the stomach, and if swallowing is impaired, parenteral nutrition is provided, in which nutrients are administered intravenously. Doctors monitor the function of the excretory organs, if necessary, catheterize the bladder and prescribe cleansing enemas.
Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital use effective medications and non-drug agents to treat strokes of the right half of the brain. They are prescribed strictly according to indications with the participation of cardiologists, and, if necessary, resuscitators and neurosurgeons, taking into account the results of laboratory tests. Doctors monitor blood pressure and prescribe antihypertensive drugs if it increases.
Regulation of water-salt metabolism is carried out by infusion therapy under the control of pH measurements, electrolyte levels, urine and blood osmolarity, and biochemical blood tests. To combat cerebral edema and to prevent increased intracranial pressure, dexazone or osmotic diuretics are used. Cardiologists and resuscitators at the Yusupov Hospital are involved in basic therapy.
Anticoagulants are prescribed by monitoring blood clotting parameters and in the absence of exacerbation of peptic ulcer disease, hemorrhagic diathesis, severe liver and kidney damage. Patients are first given intravenous and then subcutaneous heparin. 1-2 days after stopping heparin, switch to indirect anticoagulants. At this time, prothrombin time is monitored daily.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe antiplatelet drugs from the 3rd to 5th day of right-sided ischemic stroke. Individual therapy is carried out with vascular drugs that have antiplatelet activity: trental, beta blockers, calcium antagonists, stugeron, cavinton, aminophylline.
In the acute period, patients with right-sided ischemic stroke are administered gordox and contrical. Even with initial manifestations of insufficient blood supply to the brain, antiplatelet agents containing nicotinic acid, polyunsaturated fatty acids or iodine are prescribed. To restore brain nerve cells, drugs that have a neuroprotective effect are prescribed. To dissolve blood clots and restore blood flow through the arteries of the right hemisphere of the brain, thrombolytic agents are prescribed. Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital carry out thrombolysis with the most effective drug to date - recombinant tissue plasminogen activator.
When the patient’s condition improves, speech therapists from the Yusupov Hospital work with him. Rehabilitators provide classic and relaxing massages and physiotherapeutic procedures. To restore motor function, kinesitherapy and modern methods of physical therapy are used.
Thanks to the use of innovative treatment methods, only 5-6% of patients with right-sided ischemic stroke who are discharged from the neurology clinic after rehabilitation require outside care. If you have the first signs of an ischemic stroke of the right hemisphere of the brain, call. At the Yusupov Hospital, they successfully restore impaired neurological functions even to those patients who were abandoned in other rehabilitation centers.
Source: yusupovs.com
Diseases associated with impaired cerebral circulatory function. - the second most common cause of death both in our country and around the globe. According to the All-Russian Center for Preventive Medicine, in our country 25% of men and 39% of women die from cerebrovascular diseases.
Diseases associated with impaired cerebral circulatory function. - the second most common cause of death both in our country and around the globe. According to the All-Russian Center for Preventive Medicine, in our country 25% of men and 39% of women die from cerebrovascular diseases.
This sad statistics is also due to the fact that not all victims receive timely medical care and subsequent treatment. Many patients, as a result of a stroke, remain disabled with varying degrees of physiological and psycho-emotional disorders. Perhaps the most common and frightening consequence is that the right side of the body is paralyzed with a stroke of the left hemisphere of the brain and the left side with a stroke of the right.
We will consider the features of the manifestation and treatment of strokes of the left hemisphere (hemisphere) of the brain.
A stroke is damage to the blood vessels that supply blood to the brain. These vessels can be both superficial and deep, and their rupture or blockage can lead to necrosis of certain areas of the brain. If small capillaries are damaged, a micro-stroke occurs; if large arteries are damaged, necrosis can be extensive, affecting almost all areas of the hemisphere. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic (up to 85%), resulting from blockage of a vessel or critical narrowing of the passage, and hemorrhagic (up to 15%) - due to rupture of the vessel wall. A small percentage of cases are subarachnoid hemorrhages (less than 5%).
It is important. The causes of stroke can be different: ischemia occurs due to the adhesion of atherosclerotic plaques to the walls of blood vessels or hemodynamics (decrease in pressure) of blood vessels, hemorrhage is almost always caused by hypertension (persistent increase in blood pressure).
To protect yourself and your loved ones from serious consequences due to late treatment at the clinic, remember the first signs of a stroke:
- General: disturbances of consciousness, headache and dizziness, nausea, visual and hearing disturbances, impaired coordination of movements.
- Symptoms of a stroke on the left side: partial or complete paralysis of the right side of the body and face, speech disorders (in a mild degree, a person expresses himself in fragmentary sentences-nouns, in a severe case, he cannot speak clearly, he mumbles), mental disorders, disturbances in the logic of thinking.
Consequences of a stroke, how long do they live?
Stroke is one of the most dangerous vascular diseases, because it is an acute disturbance of blood circulation in the brain. The consequences of a hemorrhagic stroke are especially severe; with this pathology, a person can quickly die or become paralyzed.
How long do they live after pathology?
The least life-threatening is the so-called micro-stroke - during it, the patient’s blood supply to the basin of a small cerebral artery is disrupted, which can recover on its own.
In acute ischemic stroke, oxygen starvation occurs in a larger area of the left or right hemisphere, therefore, the consequences will be more serious.
The most severe is a hemorrhagic stroke - in it, blood permeates the brain matter with the appearance of a hematoma.
Stroke has become “younger” - it often occurs in people aged 35-45.
The prognosis for survival after a stroke is highly dependent on the age of the patient and the severity of the pathology.
Up to 45 years of age, mortality does not exceed 25%; most patients die due to extensive cerebral hemorrhages due to trauma and rupture of aneurysms. After 50 years of age, mortality exceeds 40-45%; in women, the disease often ends in failure.
After 70-80 years, only 20% of people survive, but full recovery is impossible, the consequences are as follows:
- paralysis;
- change in mental abilities;
- worsening of chronic diseases;
- recurrent stroke.
After an attack, many live 10 years or more; at a young age, with quality treatment, life expectancy is common among their peers.
But negative prognoses are also not uncommon - in 30% of survivors, death occurs in the first year after the initial attack.
After repeated attacks, the average life expectancy is usually no more than 2-4 years, this is due to the persistence of risk factors - a tendency to blood clots, atherosclerosis, hypertension.
What influences the consequences of the disease?
Complications are most serious in elderly patients. There are many reasons, besides natural wear and tear of tissues and organs:
- hypertension that responds poorly to treatment;
- the presence of arrhythmia and coronary heart disease;
- high cholesterol;
- chronic kidney diseases, etc.
That is why in people over 60-70 years of age, a stroke often ends in coma and death, the disease progresses aggressively, affects brain tissue faster and covers large areas. At a young age, the ability to recover is higher, but a number of factors worsen the prognosis:
- hypertension;
- diabetes;
- obesity;
- vascular and heart diseases;
- prolonged stress;
- pregnancy;
- taking hormonal contraceptives.
With extensive hemorrhage or ischemia, the cells suffer so much that even after a year they cannot recover. Due to improper functioning of the brain, there is a predisposition to a repeated attack.
The larger the affected area, the higher the risk of paralysis, mental disorders, and edema.
Paralysis and immobile position of the body also aggravate the consequences - bedsores, kidney and lung diseases, and infections occur.
Early complications of stroke
The most serious consequences are caused by a stroke on the left side of the brain, since in most people it is more developed. Depending on the affected hemisphere, the opposite side of the body suffers - with a stroke on the right side of the brain, the consequences affect the left side of the body, and vice versa.
Most often, an attack occurs in the first half of the day or before waking up.
At an early stage, headaches, numbness of the face and limbs, and speech disorders may be noted. Vision deteriorates, an arm or leg or both limbs do not work. The consequences for the patient at first are as follows:
| Sign | Meaning |
| High blood pressure | The body's attempt to restore blood circulation can lead to brain swelling and recurrent stroke. |
| Temperature rise | Bad symptom, increases risk of death by 1/3 |
| Inhibition of reactions | Damage to the corresponding brain centers on the right or left side |
| Convulsions | More typical for hemorrhagic stroke |
| Rapid paralysis | The larger the affected area, the higher the risk of loss of motor functions |
Already in the first hours after the attack, a person often becomes deaf, loses vision, and an arm or leg becomes paralyzed. Memory is lost completely or partially. Speech impairments are more typical for left-sided lesions.
If a large part of the brain is attacked, coma occurs. The best prognosis for emerging from a coma is for people with preserved reflexes, including swallowing, who remain in this state for no more than an hour.
Also, at an early stage, a serious consequence is cerebral edema - swelling of its glial tissue due to soaking in fluid.
Late consequences of the disease
The timeliness of assistance plays a big role in the quality of subsequent rehabilitation, but adverse consequences are observed after almost every case of the disease. Only 10% of people recover completely; the rest experience varying degrees of disability.
Hemorrhagic stroke always has the most serious complications.
Brain hemorrhage in the future threatens complete or partial paralysis and severe mental disorders.
A person may lose vision, speech becomes slow, there are difficulties with pronunciation, perception, and adequate assessment of the situation. Many people lose their memory, become depressed or become aggressive.
A person's mental abilities decline. Often occur:
- epileptic seizures;
- pain in different areas of the body;
- mood changes;
- uncontrolled excretion of urine and feces.
An ischemic stroke causes the death of neurons in the right or left side of the brain. This provokes weakness of the legs and arms, unsteadiness of gait or paralysis, deterioration of motor skills and movements of the facial muscles.
Patients forget the past, have poor orientation in time and space, and cannot clearly pronounce words.
In severe cases, reflexes are disrupted - for example, the act of swallowing, and a person can choke even on water.
Repeated stroke
One of the most serious consequences is the tendency to have another stroke. The second and subsequent attacks determine the prognosis, because it is even more difficult to recover from them. How long the life expectancy will be depends on the effectiveness of preventing a second attack within a month of the first. The statistics are as follows:
- in the first year the pathology recurs in 5-20%;
- in the first three years, recurrent stroke occurs in 40%.
Relapse is more often observed in old age, with untimely hospitalization, poor care, and stress. The disease also recurs in people with serious chronic diseases - diabetes, hypertension and others. In the long-term stage, the attack may occur again if the patient continues to smoke, forgets to take medications for thrombosis, to lower cholesterol and blood pressure.
Rehabilitation after illness
After a mini-stroke, recovery may take 2-3 months, but after extensive brain damage, rehabilitation will be lifelong. It can be done at home or in a medical facility, with the involvement of specialists or loved ones.
The initial stage requires the use of drugs:
- thrombolytics to dissolve blood clots;
- drugs to improve microcirculation and tissue trophism;
- sedatives to relieve anxiety;
- muscle relaxants to eliminate muscle spasms;
- antihypoxants against oxygen starvation;
- medications to lower blood pressure.
In the future, massage specialists and speech therapists are involved in rehabilitation; physical therapy is required - electrical stimulation of muscles, ozokerite, paraffin, magnetic therapy, acupuncture.
Diet and other recovery methods
Dietary nutrition is aimed at normalizing cholesterol levels and preventing the progression of atherosclerosis.
The amount of meat, eggs, and animal fat should be reduced; it is allowed to eat fish, lean veal, and poultry. Additionally, you can take Omega-3, which stabilizes cholesterol and blood pressure.
In the absence of hypertension, natural coffee will also be useful, but no more than 2 cups per day. You need to eat more often:
- apples;
- pears;
- bran;
- greenery;
- other plant foods.
Exercise, even passive exercise, is important to prevent bedsores and helps fight paralysis. To eliminate stress, many patients are advised to take antidepressants and work with a psychologist. It is recommended to visit special resorts, sanatoriums, and water treatments.
i
Please rate the article, we tried:
Source: https://netbolezni.net/nevrologiya/483-posledstviya-insulta-skolko-zhivut.html
Possible consequences of a stroke on the right side and its treatment
It is very important that the victim receive medical assistance as soon as possible, because the longer the cause of the stroke remains untreated, the larger the area of brain tissue necrosis and the more severe the consequences.
With a mild ischemic stroke, the patient may experience partially reversible speech dysfunction, paresis of the muscles on the right side of the body, dyslexia and dysgraphia, loss of adequate perception of reality, memory, understanding of spoken speech, and severe depression. In more severe cases (with an extensive hemorrhagic stroke, for example), the above disorders may remain irreversible and even worsen.
According to medical statistics, left-sided stroke occurs more often than right-sided stroke (up to 57% of cases), but it is more easily tolerated by patients. Treatment of the consequences of a stroke should begin immediately upon the patient’s arrival at the hospital. After identifying the lesion, doctors surgically try to eliminate the cause of the stroke (they remove the blood clot that has blocked the vessel during ischemia or, on the contrary, during hemorrhage - they inject a coagulant to close the gap in the vessel wall, drain the hematoma to avoid compression). In the first days after a critical illness, drug therapy includes the administration of decongestants and anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as drugs that stimulate cerebral circulation. Then the possibilities of physiotherapy (from electrophoresis to mud therapy), therapeutic exercises, speech therapy, defectology and psychotherapy are connected. Restoration of motor functions after paralysis usually takes from 2 to 4 months (for ischemic stroke) and from a year to several years (for hemorrhagic stroke).
The rehabilitation period after a stroke is no less important than active treatment, because it is then that the final and maximum (as far as possible) restoration of lost functions of the brain and the entire body as a whole occurs and complications are prevented.
Consequences
If the left hemisphere is affected, the consequences may be as follows:
- paralysis of the right side of the body;
- speech impairment - the change can be observed in several variations:
- slurred speech due to paralysis of the facial muscles;
- the patient speaks clearly but incoherently;
- primitive speech;
- deterioration of visual function;
- memory loss - complete or partial.
How quickly a person recovers from a stroke and how long he will live after the attack depends on many factors:
- degree of damage;
- localization of the affected area;
- how timely assistance was provided;
- age;
- how competently the rehabilitation measures were carried out, and so on.
In severe forms of stroke, the risk of recurrence increases greatly, so it is necessary to strictly follow all doctor’s prescriptions.
Prognosis for recovery after left hemisphere stroke
It is not always possible to provide the patient with all the necessary conditions for full recovery at home or in an outpatient setting and at the same time, constant monitoring by a neurologist. In such cases, a reasonable solution would be to contact an organization specializing in rehabilitation.
For many years, ours has been providing services to restore the health of patients after various serious illnesses and conditions: strokes, heart attacks, injuries. We practice a multidisciplinary approach: motor, psycho-emotional and social rehabilitation of the patient. For each patient, our experienced doctors develop an individual recovery program, which is then adjusted as it progresses. The combination of classical approaches to treatment with proprietary techniques allows you to achieve the best results in the shortest possible time, and fresh air and the comfort of living in a well-equipped hotel of the center only contribute to the patient’s recovery.
If you want your loved one to forget about the consequences of a stroke as soon as possible, a rehabilitation specialist is always ready to help.
Source: www.three-sisters.ru
Stroke on the left side: consequences and features of recovery. How long do people live with this diagnosis?
A person's life is at risk if he has a stroke on the left side. The consequences of such a pathological condition are very destructive to health. The patient’s relatives must take note of the information about recovery and prognosis for such a diagnosis. Preparedness for what is happening is necessary for everyone who is struggling with this serious illness.
Left-sided stroke: two sides of the same disease
What awaits a person after a stroke on the left side cannot be said with one hundred percent accuracy, because each organism is purely individual, in addition, there are quite a lot of factors that aggravate or alleviate the consequences of the disease. Let's try to create an approximate “risk map” by familiarizing ourselves with the types of stroke and their effect on the body.
The walls of the vessels did not “withstand” - what next?
If the vascular walls of the brain are damaged and blood enters the medulla, doctors will characterize the incident as a hemorrhagic stroke. When the left side of the brain is damaged, it negatively affects the entire right side of the body. Left-sided cerebral hemorrhage is often diagnosed late, so the time needed for effective care is often lost.
Consequences of left-sided hemorrhagic stroke
The pathological changes caused by a stroke depend on how large the size of the affected area of the brain is and what the general condition of the patient's body is. A hemorrhagic stroke that damages the left hemisphere of the brain can cause various health problems.
Possible consequences of the “blow”:
- muscle paresis;
- paralysis of the body on the right;
- lack of normal coordination of movements;
- difficulty swallowing, pronunciation, reading words;
- disruptions in the functioning of the intestines and bladder;
- inappropriate behavior and assessment of what is happening;
- disturbances in mental operations and memory;
- irritability and depressed mood;
- attacks of pain.
As a result of such disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system, which affects the entire body, a person becomes unable to serve himself and evaluate his actions, and inadequately perceives the people around him. He cannot do without the support of his loving family.
Recovery and prognosis
The rehabilitation period after such an attack lasts quite a long time - up to 2 years. During this time, you need to undergo a course of therapy and massage prescribed by the doctor, do therapeutic exercises, speech therapy, use reflex-stress systems and other rehabilitation methods.
Whether these efforts are successful depends on the correct treatment, the ability to move, the condition of the person's vital organs and his personal desire to survive. 80% of people become disabled after a cerebral hemorrhage.
As for life expectancy, domestic statistics are disappointing - 50% of patients with this pathology die, but we cannot forget that stroke survivors have a chance of ending up in the other half.
Ischemic stroke: left side
An ischemic stroke is an acute cerebrovascular accident that deprives part of the brain of blood supply for a period of time. Such a violation cannot pass without leaving a trace on the central nervous system. If a problem with blood circulation occurs on the left side, the functions that the left hemisphere of the brain regulates will be disrupted.
“Traces” of a left-sided ischemic stroke:
- speech disorders, up to complete loss of the ability to speak;
- impaired sensitivity, as well as paralysis of the right side of the body;
- problems with vision, hearing, smell;
- arrhythmia, sweating, muscle tremors;
- change in skin tone;
- panic attacks;
- loss of balance when moving.
Chances of recovery: what are they?
After an ischemic stroke that affects the left hemisphere of the brain, it will take up to 3 years to recover. In order for the patient to return to normal life, the same therapeutic methods are used as for the hemorrhagic type of the disease.
Advanced age, concomitant diseases, complications, immobility are “enemies” that prevent a person from surviving and at least partially recovering.
Doctors say that if an ischemic stroke occurs that affects the left side of the brain, the consequences determine how long the patients live.
25% of patients die within the first month after such a stroke due to complications. 60% remain with severe neurological disorders.
70% of people manage to live a year after this pathological condition, half – 5 years, and 25% – 10 years. The most serious risk factor is a second blow. A second attack occurs in approximately 30% of patients. After a second stroke, the life expectancy of almost half of the patients is reduced to 2-3 years.
What should you definitely ask your doctor?
Of course, treatment and rehabilitation of the patient must take place under the guidance and supervision of a doctor. The doctor can also make an individual prognosis for your loved one based on medical history data that is fully available to him.
If your conversation with the doctor was not so thorough, you can draw conclusions from the following facts - how damaged the brain is, whether cerebral edema was overcome, whether the patient is in a coma.
Source: https://medictimes.ru/insult-levoy-storonyi-posledstviya-i-osobennosti-vosstanovleniya-skolko-zhivut-s-takim-diagnozom