Pinchuk Elena Anatolyevna
Deputy chief physician for medical work, kmn, neurologist
Kritskaya Olga Pavlovna
Neurologist, highest category
Maltseva Marina Arnoldovna
Neurologist of the highest category, specialist in the field of extrapyramidal pathologies, doctor of the highest category
Shabunina Ekaterina Mikhailovna
Neurologist, category 2
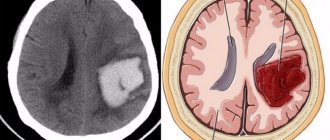
Stroke is a condition in which an acute disturbance of blood circulation occurs in the cerebral arteries, which ultimately leads to a persistent decrease or loss of function of the limbs and internal organs innervated by the affected area of the brain. Experts distinguish two forms of stroke: hemorrhagic and ischemic, while the ischemic form is observed 2.5 times more often than the hemorrhagic one. With an ischemic stroke, the lumen of the cerebral artery is blocked (occluded), due to which nutrients cease to flow to the neurons. In the hemorrhagic form, the mechanism of stroke development is different; a cerebral arterial vessel ruptures with blood spilling into the brain tissue and soaking it. As a result of a hemorrhagic stroke, displacement (dislocation) of the brain is possible with the development of severe complications, including death. Damage to the left hemisphere leads to dyslexia or complete loss of speech ability. Speech after a stroke can be restored, and in most cases, effective recovery depends on timely medical care.
Speech restoration
As mentioned above, the appearance of aphasia as a result of a stroke most often indicates the presence of aphasia. Hemorrhagic form of stroke in the left half of the cerebral cortex. The Clinical Brain Institute deals not only with speech impairment in hemorrhagic stroke, but also with speech impairment after ischemic stroke. It’s worth repeating once again - speech restoration after a stroke is most effective with qualified high-tech treatment, which can be obtained at the Clinical Institute of the Brain.
How to restore speech after a stroke if it is impaired or completely lost
Restoring speech after a stroke is one of the most important tasks in the rehabilitation of a patient. It is important not to postpone this process until later: the later you start, the less chance of success. And it’s better if you immediately approach the restoration of speech in a patient competently.
In this article we will look at the necessary stages of rehabilitation and all the possible ways to restore speech after a stroke.
If you suddenly have a stroke
What happens during a stroke? Blood circulation in various parts of the brain is damaged to varying degrees, the nervous system suffers, and communication with the brain is damaged. A person is deprived of many of the capabilities of his body, which he had never thought about before.
A stroke mercilessly divides a person’s life into “before” and “after”. At best, these are minor changes in memory, speech, and movement. And if treatment and rehabilitation are carried out on time and correctly, the person will quickly recover and return to normal life.
But there is also a complete loss of all these and some other functions of the body. And then the person will never be the same. This is a tragedy both for him and for his loved ones.
In this situation, panic should not be allowed. You need to be patient and take all possible measures to help the patient as much as possible. After all, he has to learn to live again.
What is necessary for a successful recovery of a patient after a stroke:
- Of course, drug treatment prescribed by a doctor. It stimulates impaired cerebral circulation. It is important to carry it out constantly.
- Restoration of motor functions. This requires exercise therapy, physiotherapy, and it is possible to use special simulators to restore sensitivity to paralyzed limbs.
- Work to restore speech, memory, ability to read and write, perception of reality. This cannot be done without the help of a speech therapist and a properly structured system of classes.
- A comfortable climate in the family, the psychological mood of the patient himself, as well as his relatives, a sea of patience and optimism.
Speech impairment due to stroke
Stroke can be hemorrhagic or ischemic. With a hemorrhagic stroke, too much blood flows to the brain, and arteries may rupture, but with an ischemic stroke, on the contrary, not enough blood flows to the brain.
Hemorrhagic stroke is less common, but causes more serious consequences for the patient. But in both cases, the areas of the brain responsible for speech may be damaged in a person.
If speech fails, then the disturbances occurred in the left hemisphere of the brain. With such a stroke, the right side is paralyzed and there is no speech.
Strokes with paralysis on the right side occur more often than on the left. And this is better for the patient, since in this case it is easier to make a diagnosis, since speech disorders are always manifested.
Such disorders are called aphasia. In this case, disturbances can occur in different parts of the brain. Depending on this, the consequences may be different. How to restore speech after an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke?
Let's look at the types of aphasia and their consequences:
- Amnestic . A person can communicate, but periodically forgets the names of the objects he is talking about.
- Semantic . In this case, you need to talk to the patient exclusively in simple sentences; he simply will not understand complex ones.
- Sensory . A complex type of aphasia in which the patient does not understand speech at all. For him it comes down to a set of sounds. At the same time, he practically cannot understand the meaning of what was said.
- Motor . A person understands everything, but cannot say anything coherently, confuses sounds and words, or gets stuck on one sound combination.
- Total . The patient does not understand anything, does not recognize anyone, cannot say anything. Most often, this phase occurs immediately after a stroke. After some time, it can turn into motor.
Can speech be restored after a stroke and how quickly will this happen?
No one can give a 100% guarantee that the patient will be able to speak at all. But if you act quickly, correctly, follow all the recommendations of specialists, create an atmosphere of patience, love and care around a sick relative, support him as much as possible in his desire to recover, then he has a much better chance of quickly recovering his speech loss.
Simple speech problems can be solved in 2–6 months with special regular training and exercises. If the degree of violation is greater, then more time will be required.
Sometimes this can last up to several years. A forecast of 5-10 years is considered a period after which changes for the better are hardly possible. However, miracles of recovery happen, but they most often lie in the realm of intangible reality.
People say, “Houses and family walls heal.” This relates to the question of how relatives of a stroke patient should behave.
The first questions they ask the doctor are: “Is speech restored after a stroke? Is it even possible to restore speech after a stroke? How long does it take for speech to be restored after a stroke? Relatives can be understood. But a lot depends on their behavior, on their actions.
Here are the usual recommendations from doctors to the patient’s relatives:
- The patient must feel that his family needs him, that he is valuable to her, that his relatives believe in him, love him, sincerely wish for his recovery and do not doubt it at all. In this case, he will have additional motivation to get back on his feet as quickly as possible. This means there will be energy for this.
- You need to constantly talk with the patient and in his presence. Then he will feel involved in the family. But the most important thing: if the topic is important to him, he will try to talk.
- It’s good if his favorite music, the songs he used to sing, are played in the house. The inner desire to sing along can well stimulate the awakening of his speech impulses.
- But it is better to remove excess noise, variety and volume of sounds so as not to overload the patient. You need to talk to him quietly, calmly, without explosive emotions. Surround him with your kindness. At the same time, there is no need to emphasize every time that he is terminally ill.
- Relatives need to have maximum patience, since they are the ones who must become constant assistants for the patient when performing the exercises that the speech therapist will show. And under no circumstances should you react with irritation if you can’t do the exercise.
What to do if a stroke causes loss of speech
How to regain speech after a stroke? Immediately after the first necessary assistance to the patient, it is important to contact a speech therapist.
Only this specialist will be able to correctly assess the degree of speech damage and draw up an effective set of measures for its restoration. the task of such a complex is to restore speech breathing, voice, articulation, intonation, timbre.
How to restore speech after a stroke at home? You should not self-medicate in this case. Only after the exercises and massages shown by the speech therapist will it be possible to regularly perform them independently at home with the help of relatives.
Speech therapy exercises to restore speech after a stroke at home
Let us now consider what methods a specialist can offer to restore a patient’s speech, and how they should be applied.
Articulation and breathing exercises
First, the person is asked to simply breathe, then, as he exhales, pronounce certain consonant sounds, one sound per exhalation. After this, while exhaling, all these sounds are pronounced in a row. There are no more than four of them. Sounds can be pronounced while exhaling, also with the chin raised.
Articulation gymnastics after a stroke
It includes exercises for the tongue, lips, voice, and facial muscles.
Exercises for the tongue and soft palate
- Stick your tongue out of your mouth and hold it there for a few seconds.
- Pull it down again and bend it up, hold it for a while.
- Pull it down and direct it first to the right corner of the mouth, then to the left.
- Move the tip of your tongue back and forth across the roof of your mouth.
- Direct your tongue to the right and left cheek.
- Click your tongue, first once, then twice, then three.
- Relax your tongue and, moving it back and forth, lightly bite with your teeth.
- Lick your lips first in one direction, then in the other.
Lip exercises
- Move your lips forward.
- Make a smile with your mouth closed.
- Bare your teeth and raise your upper lip, hold this for a couple of seconds.
- Puff out your cheeks and pump the air from side to side, rolling the air around your mouth.
- Relax your lips and blow through the gap in them.
Voice exercises
Speech gymnastics is performed for ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke.
- We pronounce all the vowel sounds separately, first long, then short, while exhaling. After this, as you exhale, we pronounce all the sounds in a row.
- We say the sound Y only articulatory, without sound, and feel the tension under the chin.
- We pronounce all the vowel sounds in a row, flowing into one another, alternately emphasizing different sounds.
- We pronounce consonant sounds, first unvoiced, separately, then one after another on one exhalation. After this, we pronounce voiced sounds in the same way. We add consonant sounds with vowels into certain syllables, while alternating paired unvoiced and voiced consonants.
All combinations of sounds, their permutations and combinations are determined by the speech therapist.
Tongue twister exercises after a stroke
First, we ask the patient to finish the tongue twister he knows, gradually increasing the number of words he says. If possible, we bring the exercise to perfection.
Exercises for facial muscles
- Raise your eyebrows, lower them, frown, relax.
- Open your mouth wide, try to stretch it, then relax it.
- Smile without opening your mouth.
- Inflate and deflate your cheeks.
- Pull your lips out as if for a kiss.
- Extend your tongue as far as possible in different directions from your mouth.
- Move your lower jaw carefully, first to the left, then to the right, then in a circle.
Speech therapy massage after stroke
After completing a set of exercises, it is necessary to apply a facial massage to each area of the face.
It is important that massage movements are selected only by a specialist. Some areas of the face will need to be relaxed, while others will need to be toned. If you approach this on your own, you can cause irreparable harm.
In addition to massaging the facial muscles directly, they massage the tongue, lips, inner surface of the cheeks, ears, scalp, and hands. All this relieves muscle stiffness and thus liberates speech.
Features of the doctor’s work with the patient
- The task of all specialist actions is to disinhibit speech. And for this they use all the capabilities of the patient that he has at the moment. Exercises should not tire the patient. They start with simple elements and last 10-15 minutes. Afterwards the program becomes more complicated and the lesson time increases.
- You need to talk to the patient calmly and slowly so that he understands the speech. If he cannot say anything, then we ask him to nod in response, showing that he understands.
- If the patient has difficulty speaking, you should ask him to make any onomatopoeia that he can make. If he can only pronounce one syllable, then you should choose words that begin with this syllable and let him try to finish them gradually.
- The same is with proverbs and sayings, names of famous films. You need to start a phrase and ask the patient to complete it, either with a word or with a syllable, as best he can. All the words that we usually pronounce automatically should be offered to him to say. These could be days of the week, months, a regular count to ten.
- It’s good to include cards with pictures in your work. You can ask simple questions: “What is this? What is he doing? What is he like? At the same time, it is important to move in these tasks gradually. The nouns are called first. After a while, when this stage has been completed, verbs are added, and only then adjectives.
- Gradually, rehabilitation activities include drawing and writing exercises. First, the person is asked to simply insert the missing letters in the word, then copy the entire word. The tasks gradually become more difficult.
- Exercises based on questions asked to the patient will be good. First, simple questions are asked with an option to answer “yes” or “no.” Afterwards, the questions are complicated so that the question itself contains a monosyllabic answer. And this word is what the patient should say as an answer.
Music therapy
It often happens that a person who has had a stroke has difficulty speaking, but can sing. Then all speech therapy exercises with sounds, syllables, and words are performed like a song.
Facial reflexology
Biologically active points on the face are affected in a certain way.
Acupuncture
This method is used mainly for motor aphasia. In this way, a person’s speech activity is corrected.
Conclusion and conclusions
And in conclusion, I would like to emphasize the most important points that should not be forgotten when restoring speech in a patient after a stroke:
- This is a quick response to the problem and not postponing rehabilitation measures for later,
- moderation in everything
- gradual increase in loads during exercise,
- mandatory contact with a speech therapist, and possibly with a defectologist,
- strict compliance with all their instructions,
- great patience and creating the most friendly atmosphere in the house.
Stroke is a serious disease, but with this approach it is much easier to overcome.
How to restore speech after a stroke if it is impaired or completely lost Link to main publication
Source: https://KakGovorit.ru/vosstanovlenie-rechi-posle-insulta
Mental gymnastics after a stroke
It is used to restore the functions of the nervous structures of the brain. Its essence lies in self-hypnosis and the idea of how a person performs exercises to recover from a stroke, which helps to implement this faster. Commands must be given out loud. This can be done by the patient himself or by the methodologist who is caring for him.
Rehabilitation of a patient after a stroke is a complex process that requires full commitment from the victim and his relatives. Regular exercise will help restore lost functions and return the patient to a full life.
Additional Methods
Working on the perception and pronunciation of speech is the most important, but not the only part of speech restoration. If necessary, the following must be used:
- Drug therapy - drugs that restore blood circulation and the functioning of brain cells (Ceraxon, Trental, Piracetam, Cerebrolysin).
- Physiotherapy – electrical pulse therapy, myostimulation, acupuncture, massage of the tongue and facial muscles and other techniques.
- Surgical operations are vascular and neurosurgical interventions that improve blood circulation and the functioning of brain cells.