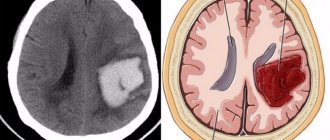
Eyes are one of the most important human organs; 80 percent of information about the world around us is perceived visually. Therefore, visual impairment directly affects the quality of life of patients. In this case, impaired visual acuity can occur not only due to congenital anomalies, but also as a result of eye diseases. People who have had an ocular stroke fall into this risk group. In medical practice, the concept of “ocular stroke” is deciphered as blockage of blood vessels in the retina of the eye, followed by their blockage or rupture.
Why does vision loss occur?
In case of vascular diseases, there is a disturbance in the activity of the brain, because
The blood supply to this organ is not complete, which leads to damage to brain tissue. Some cells responsible for visual function die. Restoring vision is a long process. It is impossible to regenerate dead cells, so other healthy neurocells must begin to perform their tasks. Visual impairment due to stroke can vary in severity. It depends on how badly the brain cells were damaged and which areas were affected by the devastating effects of the disease.
Loss of vision due to stroke is common. In this case, the pathology is often expressed in different ways. There may be loss of vision in both eyes or just one, and sometimes visual hallucinations or oculomotor disorders occur. However, with properly organized treatment, which is prescribed only by a specialist, there is a high probability of restoring visual function partially or even completely.
This disease provokes hemorrhage that spreads to the brain tissue. In turn, this leads to negative effects on the optic nerve because it is located very close to many parts of the head. Namely, it starts from the retina and reaches the visual center, which is located in the occipital region.
- Diplopia - double vision occurs, which cannot be focused on one point. Pathology develops due to deviation of the eye axis from the correct position. The patient feels severe dizziness and cannot concentrate when moving the body. Therefore, he walks with his eyes closed until he fully recovers.
- Exophthalmos is a characteristic sign of oculomotor nerve atrophy. One or both eyeballs move forward. As a result, the motor function of the organ is disrupted, the eyelids do not close and the cornea dries out, which aggravates the disease with inflammatory processes. In this case, the upper and lower eyelids are partially or completely stitched together for a certain period of time to prevent serious complications.
- Optic nerve atrophy is the partial or complete destruction of the structure of the nerve fibers that transmit visual stimuli from the retina to the brain. The pathology leads to impaired color rendering, narrowing of visibility, decreased or complete loss of vision. And if a muscle disorder occurs, then drooping eyelids and trembling of the apples occur. The prognosis in most cases is unfavorable, and the patient is assigned a disability group.
How to restore vision after a stroke
Restoring vision after a stroke is not an easy task; it all depends on the volume and location of the lesion. The result of recovery is also influenced by the patient’s age and lifestyle. It becomes impossible to restore vision after a stroke in cases where the system of organs that perceive and transmit visual information into images is damaged, and the nerve impulse is not transmitted from the retina to the brain, as well as in the case of hemorrhage in the area of the optic nerve.
So is vision restored after a stroke? The answer may be positive if a person seeks qualified medical help in a timely manner. The doctor must analyze the damage and prescribe appropriate treatment. During the first 90 days after a stroke, the possibility of vision restoration is maximum.
First of all, a person who has had an eye stroke should contact an ophthalmologist or neurologist. After the doctor has drawn up a clear treatment plan, the patient must undergo a rehabilitation course of therapy. It may include physical therapy, but only for those patients who do not have complete or partial loss of vision. Physical activity reduces the risk of recurrent ocular strokes.
A course of medication and restorative therapy will help significantly speed up the restoration of visual functions.
What is an ocular stroke?
This is a vascular pathology of the retina and nerve, which is provoked by poor circulation in the visual center. Occurs due to blockage of an artery. The main danger is that the course of the disease is asymptomatic. The absence of clinical manifestations does not allow timely detection and elimination of the problem. Depending on the type of ischemic lesion, several deviations are distinguished:
- Central artery occlusion - the disease develops suddenly and very sharply, causing unilateral loss of vision. Color rendering changes. In rare cases, with timely treatment, a weak lateral viewing angle remains in the form of complications.
- Separation of the retinal veins - the picture of perception is distorted, white spots flash. Usually one eye is affected. The cause is a venous thrombus.
- Artery occlusion and retinal detachment are the most dangerous painless form of the disease. A characteristic symptom is loss of peripheral vision, and then central vision. Against the background of this disease, changes in blood pressure and heart function develop.
Computer rehabilitation after stroke
There are also modern methods of rehabilitation - these are specialized computer programs aimed at expanding the field of vision and making the image clearer. This is a kind of eye simulator that, with the help of lighting effects, helps restore visual perception. The whole process takes no more than 20 minutes. The main task of such programs is to increase visual eye movement and reboot the brain’s ability to visually perceive the left and right sides. Such programs are divided into two types - vision restoration and vision compensation. The recovery program improves the visualization of sensitivity, which makes it possible for the patient to distinguish objects in the blind area. The compensation program teaches you to direct your gaze towards the damaged area and an invisible object. The disadvantages of computer-assisted rehabilitation are that such therapy is not suitable for patients with epileptic conditions that occur with light stimulation and patients with significant impairment of ocular function.
In conclusion, we can conclude that vision is restored after a stroke, but it is impossible to give 100% guarantees. The most important thing is timely identification of the disease, immediate contact with specialists and systematic implementation of all recommendations. It is necessary to understand that the rehabilitation process will not be quick and you will have to get used to a new daily routine with daily exercises and proper nutrition. General recovery methods will allow you to achieve positive results in the future
What to do and how to treat?
Timely seeking help from a specialist will make it possible to stop the process of vision deterioration.
| Group | Name |
| Pharmaceuticals that stabilize blood flow | "Kavinton" |
| "Cebrolysin" | |
| "Piracetam" | |
| "Nootropil" | |
| Medicines that improve cellular metabolism | "Colcoseryl" |
| "Cortexin" | |
| Anticoagulants | "Heparin" |
To improve the patient's condition, you can use traditional medicine, namely decoctions and infusions.
Restoring vision after a stroke is a long process, during which it is possible to use non-traditional therapeutic measures. It is possible to partially restore visual function using the following recipes that are prepared at home:
- Fir and pine cones. The components are aimed at restoring blood circulation in the brain. The ingredients are used to prepare a decoction, tinctures, and jams intended for internal and external use.
- Mountain arnica. For 1 tbsp. l. substances are used in 500 ml of water. Boil the medicine over low heat for a quarter of an hour, allow to cool, filter and use to restore peripheral vision.
- Lemon and garlic. The drugs help eliminate double vision that occurs after a stroke.
A special exercise for the eyes, which is recommended to be performed several times a day, helps the patient recover. This technique, when used systematically, is sometimes more effective than medications. When charging, perform the following eye exercises:
- Lightly press on different edges of the eye socket with the fingers of both hands.
- Slowly and carefully press on the eyes.
- Massage the area of the bridge of the nose.
- They try to blink as often as possible.
- Move the eyeballs as far as possible to the sides, then down.
- They try to alternately concentrate attention on objects that are far and close.
Surgical intervention is necessary in cases where medications and alternative medicine are powerless.
If significant visual impairment occurs during a stroke and conservative methods are powerless, then surgical intervention is prescribed. Radical therapy is often used for double vision or a shift in the visual organ. Laser treatment is the most popular. An ophthalmologist or neurologist can prescribe an operation after a comprehensive examination. After surgery, you are required to take a course of medication to prevent complications.
Types of disease and its manifestations
Patients who have significant visual field loss may collide with or even fall into obstacles. They are surprised by people or objects that suddenly appear out of nowhere (from their blind spot). They quickly become disorientated in traffic jams and crowded places and can no longer find their way.
Many people are afraid to leave the house or be in public out of fear. Searching for items on a supermarket shelf is a nightmare for affected people. While eating, it may happen that a glass or cutlery falls in a limited visibility area. Therefore, many people are reluctant to accept an invitation to eat or go to a restaurant.
If reading a newspaper becomes tiring, this is a symptom of visual impairment after a stroke.
Often reading a newspaper or book becomes very tiring. The patient does not find the beginning of the line or loses its end. Even if visual field loss after a stroke cannot be prevented, there are things you can do to help you recover quickly.
A stroke can result in complete or partial loss of vision. This is a fairly common phenomenon and is observed in 30% of patients who have had the disease. In cases where small areas of the brain are damaged, visual function is gradually restored. With extensive necrotic changes in the brain, various problems with vision arise, up to its complete loss. Such patients require drug treatment and long-term rehabilitation.
The main signs of occlusion are decreased visual acuity and distortion. But there are other manifestations of pathology that should concern a person and cause an immediate visit to an ophthalmologist. Ignoring them is imprudent and dangerous. These include:
- the organs of vision periodically hurt;
- from time to time double vision appears before the eyes, bright spots, flashes and lightning;
- narrowing of the central and peripheral field of vision;
- disturbance of color perception.
There are three main types of eye occlusion - occlusion of a vein, artery and centralized - any of them is dangerous due to complete blindness in the absence of immediate medical help
In severe cases of the disease, pinpoint hemorrhages – hemorrhages – are visible on the whites of the eyes. The vascular network is dark red in color, clearly expressed; with extensive hemorrhages and weakened vessels, the entire protein may turn red. Sometimes there is an increase in intraocular and intracranial pressure.
The pathology is classified depending on which vessel is damaged and how badly the retina is damaged. The most dangerous form of the disease is the combination of blood clot formation in the central artery with retinal detachment. The symptoms of the pathology are severe. There is usually no pain. But the following symptoms are noted:
- loss of peripheral vision;
- partial loss of the central one;
- narrowing of the carotid artery, which is the most dangerous.
Complete restoration of vision after an ocular stroke of this type is currently impossible; white spots and narrowing of visual fields will still bother you for the rest of your life.
When a blood clot forms in the central retinal vein, accompanied by a detachment, a narrowing of central and peripheral vision also occurs, and light spots appear, reminiscent of bright glare of light. There is a feeling of a veil before the eyes, objects are not clearly visible, and pain rarely occurs. The pupils of the patient with this form of pathology are narrowed.
Impaired movements of the eyeball, strabismus, blindness of the eye - one of the signs of centralized blockage of the artery of the eye
With centralized blockage of the artery, all of the above symptoms appear sharply and pronouncedly. Characteristic signs of this form of pathology:
- loss of central vision;
- distortion of the visual picture;
- severe pain;
- various oculomotor disorders - one eye squints or the eye does not open;
- constriction of the pupil.
This form is often accompanied by partial paralysis and impaired movement of the opposite arm and leg; in addition, other symptoms may be observed.
Regardless of the type of pathology, only surgery or laser treatment can help restore vision.
The disorder is associated with damage to the brain and manifests itself in the form of hallucinations, blindness or strabismus.
- rapid decrease in visual acuity in one or both eyes;
- complete blindness;
- visual hallucinations;
- oculomotor type disorders;
- strabismus.
Visual deviations can be permanent or transient. In the first case, loss of specific visual fields or unilateral blindness is recorded. The transient form is mainly observed after an ischemic stroke, as a result of which vision is lost partially or completely.
Classification of visual impairments
The pathological processes occurring during this disease cause the following changes:
- Double vision.
- Hallucinations.
- Decreased visual acuity.
- Blindness in one or both eyes.
- Oculomotor disorders.
Based on the symptoms, you can determine how severe the damage has occurred and which part of the brain is affected:
- Loss of fields is a violation of the coverage of the amount of space with a strictly fixed look forward. This pathology is called “blind spot”. When a person looks at a specific target, there is a small area due to which nothing can be seen. At the same time, the eyes hurt a lot. This means that the lesion is small, and with treatment all changes will be restored.
- Lack of peripheral vision - lateral vision disappears. In this case, the patient sees all objects as if through a pipe. This indicates damage to brain tissue, since 2 lobes are responsible for this function. Intensive therapy with long-term rehabilitation is required.
- Oculomotor nerve palsy is an eye condition resulting from injury to the nerve itself or its branch. Muscle fibers atrophy. Thus, there is a restriction in movement and normal alignment of the organ when looking forward, resulting in strabismus and exophthalmos.
Important! Most pathological disorders with the visual analyzer are treatable. But only with timely diagnosis and strict adherence to doctor’s orders.
How to recognize the symptoms?
Sometimes a patient after a stroke does not pay attention to the deterioration of vision for a long time and does not consult a doctor in a timely manner until visual function disappears completely. It is possible to recognize a disorder after an attack by the following manifestations:
- spasms of the eyelids;
- double vision;
- pain;
- feeling of a foreign body in the eyeball;
- exophthalmos, characterized by bulging eyes;
- decreased visual acuity;
- redness and swelling;
- eye trembling;
- corneal clouding.
Eye stroke and its symptoms
The main “bells” when detecting an ocular stroke:
- increasing weakening of vision or its temporary loss;
- deterioration of peripheral vision;
- violation of color perception;
- “glares” in the eye, white spots, hemorrhages;
- Dropping areas appear in the field of view.
It should be understood that if at least one of these symptoms appears, you should immediately make an appointment with an ophthalmologist - diagnosing a possible circulatory disorder and its timely treatment will help save or minimize the consequences of an eye stroke.
Treatment
To improve visual function after experiencing an illness, you can perform various exercises:
- Working with drawings. You need to draw several well-known objects, and then ask the sick person to finish the pictures;
- Exercises using a pencil. The pencil is held at the patient's eye level, at a distance of several centimeters. After which the pencil moves up and down, left and right, the patient must follow it with his eyes alone;
- Eyelid exercise. You need to hold the upper eyelid with your fingers and try to close it. Such actions help strengthen the eye muscles.
A stroke affects many important functions, including vision. The patient definitely needs recovery. It is possible to restore vision completely or at least partially with an integrated approach to solving the problem. In some cases, it is necessary to resort to surgical intervention.
During a stroke, brain activity is disrupted, and the process occurs in the acute phase. Vision problems arise due to a blockage in the part of the brain that receives and analyzes information transmitted by the visual organs. In addition, the vessels lose their integrity or become clogged, causing necrotic and atrophic changes. As a result, half of the field of vision may fall out and double vision may begin. It is possible not only to deteriorate vision, but also to completely lose it.
Based on the characteristics of the disorders, one can understand which part of the brain has undergone changes. If part of the field of vision falls out, then a small area is affected. In this case, vision can be restored even on its own or with a minimum of effort.
Loss of peripheral vision indicates serious damage to brain tissue. Recovery requires intensive therapy. If the oculomotor nerve is paralyzed, then atrophy affects the muscles and fibers responsible for motor function.
After a stroke, the following vision problems are possible:
- Bifurcation. The patient cannot control the direction, which is why the eyeballs protrude and turn in different directions. As a result, visual perception is disrupted.
- Spasm of the eyelid and trembling of the eyeballs. This phenomenon occurs after a stroke due to atrophy of the optic nerve. The violations that occur are very serious and therefore often irreversible. In this case, visual impairment is possible.
- Protruding eyes. This also occurs due to atrophy of the optic nerve. Paralysis affects not only the body, but also the eyes, causing impairment of basic functions. The eyeball undergoes constant tension, which is why constant tearing occurs. It indicates dryness of the cornea. In this case, it is important to start treatment in a timely manner, otherwise vision will deteriorate and it will be impossible to reverse the changes.
- Presbyopia. This condition means problems with the normal perception of objects or text at close range.
Vision problems can cause panic attacks in the patient. The possibility of recovery and its speed directly depend on the timeliness and correctness of the measures taken.
If a stroke causes vision loss, then the general rehabilitation program includes restoration of visual function. All its stages must be established and monitored by an ophthalmologist.
The general principles of the recovery period are as follows:
- moisturize eyes;
- restore visual functions through drug therapy;
- to do exercises;
- take nutritional supplements;
- adhere to a diet with the required amount of vitamin D and A.
Therapy and the likely consequences of the pathology largely depend on the degree of damage to the organ, the duration of the disease and how timely premedical care was provided to the person. Early diagnosis of the phenomenon allows us to talk about good treatment effectiveness and complete restoration of visual function.
In certain cases, the symptoms and causes of ocular stroke require specific therapeutic treatment. In such circumstances, the patient is prescribed hyperbaric oxygen therapy. During this procedure, the patient is in a hermetic pressure chamber. Treatment is carried out in it using oxygen, which is under pressure.
Drug therapy for ocular stroke
Drug treatment for ocular stroke involves taking medications aimed at eliminating a blood clot, eliminating spasms, and normalizing blood circulation and blood pressure. The following may also be prescribed:
- angioprotectors;
- antibiotics (in case of infection);
- agents that prevent the formation of blood clots;
- medications to eliminate concomitant ailments that can aggravate the pathology.
All medications are selected by a specialist, taking into account the characteristics of the patient and the symptoms of the disease.
Operation
Methods of surgical correction of ocular stroke
At the moment, the use of laser coagulation is the most effective and widespread method of treating pathology. This procedure contributes to the complete destruction and removal of the blood clot, as a result of which blood circulation in the problem area is normalized again. In addition, laser correction is also recommended in cases of retinal detachment or to correct degenerative changes in the fundus of the eyeball.
If your eye health deteriorates, you should consult an ophthalmologist to prescribe an individual course of therapy. There are several methods to combat pathology:
- Gymnastics.
- Application of computer programs.
- Drug treatment.
- Ethnoscience.
- Surgical intervention.
Physical exercises for the eyes are simple, and after the rehabilitator once demonstrates correct execution, the patient will be able to independently perform them at home.
Before the procedure, you need to moisten the cornea. To do this, pour warm water into a bowl and lean over it. Look directly and spray a little on your face with wet hands. Perform the manipulation 10 times. Dry with a dry towel.
List of exercises:
- Close your eyes and shield your face with your hands. Take several deep breaths and exhalations. Place your index, middle and ring fingers on the upper edge of the eye socket and press lightly. Gradually descending to the bottom. This improves blood flow. Repeat these steps 3 times in one session, then gradually increase the amount.
- Gently, with your fingers, press on the indentation that is located above the eyeballs. Apply the pressure in the form of vibration and then release it sharply. Perform no more than 5 times.
- Gradually apply pressure to the eyeballs, and then quickly remove your hands. 5 pressures on each eye at the same time.
- Close your eyes tightly and hold in this position for 5 seconds. Then completely relax the muscles. Repeat several times.
- Use your index phalanx to fix the eyelid in the open position and try to close your eyes in this way. Then carry out the procedure with the lower eyelid.
- Using two fingertips, lightly pinch the bridge of your nose near the corners of your eyes and hold for 5 seconds. Let go quickly. Repeat 5 times.
- Open your eyes wide and blink quickly. Then close them.
- Lightly pressing on the eyeballs, move your fingers from the temple to the bridge of the nose and vice versa. Continue for about a minute.
- Take a pencil in your hand and place it at a distance in front of your face. It is impossible to concentrate your gaze directly. Gradually start moving it up and down, on the sides, diagonally, in a circular motion, bringing it closer and further away. Do not twist your head, just stretch the oculomotor muscles.
Regular therapeutic physical training will bring a positive effect only in combination with taking vitamins and medications.
After a brain stroke, the quality of vision very often deteriorates and, to prevent it from completely disappearing, it is recommended to carry out training with special programs. The most common is “Eye corrector”. Its purpose is based on restoring and improving the ability to see, eliminating fatigue and preventing deterioration of health.
The principle of operation is aimed at processing stereo images by a visual analyzer. This program uses SIRDS pictures, which are illegible patterns, but if you relax your eyes and look through it, a three-dimensional encrypted image appears. This procedure improves blood circulation and relieves muscle tension.
You need to exercise 2 times a day until complete recovery. Periodically visit a doctor to record the dynamics and correct tasks.
Medicines are selected depending on the clinical manifestations of the stroke. If brain tissue is damaged, it is necessary to take complex therapy, which includes the following groups of drugs:
- Agents that restore blood circulation in the eyes - Cavinton, Cerebrolysin.
- Thrombolytics - their action is aimed at dissolving blood clots. Ticlopidine.
- Anticoagulants - reduce the activity of the blood coagulation system. Heparin.
- Medicines that help improve tissue metabolism and accelerate regeneration processes - Solcoseryl.
- Vitamin complexes.
- Moisturizing drops.
Important! The wrong combination of drugs can lead to the development of severe complications. Self-medication is strictly prohibited.
First you need to change your diet: balance it, eat more vegetables and fruits, meat, fish, dairy products, greens, nuts, seeds. Many ingredients contain a huge amount of beneficial substances that affect the circulatory system, vascular membranes, and also have an antioxidant effect. To improve the result, it is recommended to take infusions and decoctions of herbs. But only after consulting a doctor.
The most popular folk remedies for improving vision:
- Mountain arnica is a real savior for strokes. To do this, add 1 teaspoon of dry plant to a glass of boiling water and leave to infuse for 60 minutes in a dark place. Take a tablespoon before meals. It has anticonvulsant, sedative, hemostatic, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory effects. A decoction of it helps improve the functioning of the heart muscle and expands the coronary canals.
- Lemon and garlic - the combination of these products brings more benefits. The main therapeutic effect is to strengthen and cleanse blood vessels, increasing their elasticity. To prepare the infusion, you need to take the lemon and wash it under running water. Cut into pieces along with the peel and place in a blender. Next, peel the head of garlic and add to the lemon. Grind both products. Transfer the resulting mixture into a glass jar and add a liter of warm water. Cover with a lid and leave in a dark place for 3 days. Stir occasionally. After time, strain the tincture. Take 50 ml 3 times a day.
- Young pine cones contain phytoncides, which have a strong antimicrobial and tonic effect. The very cones contain medicinal substances - tannins. They are able to stop the necrosis of brain cells during a stroke. To prepare the decoction, you need to take 5 cones, wash, cut, place in a pan and pour 500 ml of water. Place on fire and bring to a boil. Wait 5 minutes. Then remove and cool. Take 50 ml in the morning after meals.
- Working with drawings. You need to draw several well-known objects, and then ask the sick person to finish the pictures;
- Exercises using a pencil. The pencil is held at the patient's eye level, at a distance of several centimeters. After which the pencil moves down, left and right, the patient must follow it with his eyes alone;
- Eyelid exercise. You need to hold the upper eyelid with your fingers and try to close it. Such actions help strengthen the eye muscles.
Medications
One of the most important components of a set of measures to restore vision after a stroke is drug therapy. The doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- Drops or gels for moisturizing. Such remedies are especially important if the patient is in a coma.
- Capilar. This drug is used in combination with other drugs. It improves vision and activates the resorption of hemorrhage.
- Emoxipin. This drug is prescribed to reduce the permeability of the vascular wall, resolve intraocular hemorrhages and improve microcirculation.
- Semax. These drops are a nootropic agent. The drug is nasal, but in ophthalmology it is used for optic nerve atrophy.
- Heparin. This anticoagulant provides vasodilating, anti-inflammatory and hyposensitizing effects.
- Trental (Pentoxifylline). This drug improves brain microcirculation and is indicated for acute circulatory disorders of the retina and choroid.
- Cerebrolysin or Cavinton. These drugs are not ophthalmic, but have a positive effect on vision restoration, as they normalize blood circulation.
A vitamin complex should also be included in drug therapy. Vitamin C strengthens blood vessels, B1 is necessary for the proper functioning of the nerve pathways of the eyes, and B12 helps restore normal blood circulation to eye tissue. Vitamins D and A are also useful.
Only an ophthalmologist has the right to prescribe medications to restore vision. He will select the necessary drugs, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient and compatibility with other drugs of the complex prescribed after a stroke.
Causes
Often, partial or complete occlusion is caused by blockage of blood vessels with blood plaques (emboli). In one hundred percent of cases, occlusion of the central retinal artery manifests itself as a consequence of acute hypertensive abnormalities. The underlying causes of occlusion of the central artery or retinal veins are diseases such as arrhythmia, diabetes mellitus, and antiphospholipid syndrome. Also provoking factors are hematomas and drusen of the optic disc, as well as the consequences of possible eye injuries.
Symptoms of ocular stroke due to occlusion of the central retinal artery:
- Partial or complete loss of peripheral vision, gradually developing into partial or complete blindness.
- Distorted image perception or the appearance of blind spots.
Such a deviation from the norm is considered one of the most dangerous, as it develops against the background of other spasmodic processes in the body - heart defects, hypertensive complications, defects of the spinal arteries. Often this disease is not accompanied by pain, and therefore a person does not pay attention to the symptoms that appear; however, prolonged occlusion of the central retinal artery (CRA) entails irreparable visual impairment.
Folk remedies
The following recipes are effective for restoring vision after a stroke:
- Take young pine cones and pour warm water (half a glass per cone). Boil for 10 minutes, strain after cooling. Take the product three times a day, 50 ml.
- Grind the parsley roots, add honey and lemon juice. You should take the product one teaspoon one and a half hours before meals.
- Pour mountain arnica with water (2 cups of liquid per 1 tablespoon of raw material). Boil for 15 minutes over low heat. When the broth has cooled, strain it. Drink 1 tbsp. l. three times a day.
- Pour 3 tbsp. l. creeping wheatgrass with a liter of water, cook for an hour. Take the product 5-6 times a day, 1 tbsp. l.
- Take cornflower petals and medicinal eyebright, 1 tbsp. l., pour half a liter of water and cook until the volume is halved. When the broth has cooled, strain it. Drink in 3 doses before meals.
- Grind the elderberries in a meat grinder, place the resulting mass in a jar and keep in the sun for 2 days. The juice should be squeezed out and taken a teaspoon half an hour before meals three times a day.
It is important to enrich your diet. The following products are useful for restoring vision:
- carrots and fresh juice from them;
- blueberry;
- black currant;
- spinach;
- apricots, fresh juice from them, dried apricots;
- cottage cheese;
- fish and fish oil;
- sprouted wheat;
- onion.
You should not rely only on traditional methods. A stroke greatly affects the entire body, therefore, without drug therapy and proper exercises, it is difficult to achieve a positive effect.