Synonyms of the nosological group: Ischemic and post-stroke condition Residual effects of hemorrhagic stroke Residual effects of ischemic stroke Residual effects of cerebrovascular accident Residual effects of subarachnoid hemorrhage Residual effects of subarachnoid hemorrhage Post-ischemic stroke Post-thromboembolic stroke Consequence of cerebrovascular accident Consequence of insufficiency of cerebral blood supply Consequences of ischemic stroke Consequences of a stroke Post-apoplexy state Post-stroke period Post stroke syndrome Condition after stroke Condition after cerebrovascular accident Chronic cerebrovascular insufficiency. Preparations - ;Trade names - 59 ;Active ingredients - Active ingredients.
Classification
A psychiatrist's diagnosis of F70 is not a death sentence or even a reason to panic. Of course, the situation is extremely unpleasant, raising such a child is not easy, but this does not mean that the disease is guaranteed for life. Much is determined by the individual characteristics of the situation. In accordance with the ICD system, the indicated symbols code a mild degree of intellectual retardation.
The diagnosis is part of a large group of mental disorders and behavioral reactions (it includes diseases F00-F99), belongs to the subgroup “Mental retardation”, which includes diagnoses 70 to 79. Within the 70th diagnosis, a fairly large number of subtypes of intellectual impairment are distinguished; in the medical record they are coded by indicating numbers separated by a dot, for example F70.01. One of the options, say, diagnosis F70.19: a person has mild mental retardation, which is accompanied by tangible behavioral disorders, due to which the patient needs constant care. The reasons for the development of this pathology are unclear (if any are identified, the diagnosis will be changed, for example, to F70.11 or some other, depending on the identified aspects).
Classification of stroke, code according to ICD 10
According to the International Classification of Diseases (ICD 10), stroke is classified as cerebrovascular diseases, which are assigned codes from I60 to I69. Encrypted under these codes:
- blockage, stenosis of cerebral, precerebral vessels;
- bleeding in the brain;
- cerebral infarction;
- subrarachnoid hemorrhage;
- non-traumatic hemorrhage;
- unspecified stroke.
According to the classification, acute cerebrovascular accident is of two types: ischemic and hemorrhagic. A separate type of blood supply disorder is called transient stroke.
Ischemic type
It is characterized by impaired blood supply to the brain due to blockage of blood vessels by a blood clot, atherosclerotic plaque, or a sharp narrowing of the lumen. An obstacle in the vascular bed disrupts the full flow of blood, brain cells are in a state of oxygen and nutrient deficiency. Metabolic processes in the brain proceed intensively, and therefore nerve cells must receive oxygen and nutrients continuously. Even with the inclusion of compensatory mechanisms, irreversible changes are possible.
In the absence of oxygen, neuron cells stop transmitting nerve impulses and die. The risk group for the disease includes people suffering from cardiovascular pathology, diabetes mellitus, and atherosclerosis. Ischemic stroke, or cerebral infarction, can be triggered by physical activity and severe stress. It often develops at night and in the morning.
Hemorrhagic type
Associated with a violation of the integrity of the vascular wall. Effusion of blood from a vessel can fill the structures of the brain or form clots - hematomas. Unlike ischemic stroke, it occurs suddenly and is characterized by severe disorders in the brain. It can occur at any time of the day, most often triggered by stress and physical activity.
Transient cerebrovascular accident
Acute temporary disturbance of cerebral circulation in the form of transient attacks, which are accompanied by general or local lesions of the brain. The manifestations of the attacks are similar to ischemic stroke, only the symptoms persist for up to 24 hours and go away on their own. If neurological symptoms persist for more than 24 hours, the condition is regarded as an ischemic stroke.
Important! Transient disturbances of blood flow include the cerebral type of hypertensive crisis, which is associated with a sharp critical rise in blood pressure.
Clarification
Decoding the diagnosis of a child F70 is based on clarifying diagnoses. The absence of behavioral disorders or their presence in a weak form is indicated by F70.0; a unit after the dot will indicate significant impairments that require constant care for the patient. If there is an eight after the dot, this indicates behavioral disorders not included in the first two points (that is, any other). Finally, if there is no indication at all of behavioral disorders (presence, absence), the diagnosis will look like F70.9.
What is it about?
What is the interpretation of the diagnosis of the psychiatrist F70 - this question rightly worries parents on whose children the doctor made such a decision. The encoding denotes oligophrenia, that is, a condition when intellectual abilities develop much weaker than expected for a normal person. This condition imposes certain restrictions on capabilities: the brain develops incorrectly, the functioning of individual structures and physiological integrity are disrupted. This leads to a physical inability to overcome the established intellectual threshold. In fact, the coding indicates that in this particular case, biological aspects strictly limit the abilities of the intellect.

Mostly, a child is diagnosed with F70 at birth or shortly thereafter, since the causes of the pathology themselves are determined by factors that influenced him during the period of embryonic development. Science, however, knows several cases where backwardness was acquired. Such a development can be caused by serious brain injuries, disruption of the functionality of the vascular system of the brain and other similar factors, due to which tissue activity is disrupted and cognitive abilities are affected.
Treatment of stroke
Treatment of stroke will include first emergency care and subsequent therapy. Further therapy consists of a number of measures to normalize and support brain function. The doctor informs the patient about how to take nootropics for stroke and other medications, nutritional habits of patients with stroke, clinical recommendations for stroke.
The procedure for providing medical care for acute stroke
The scope of medical care for stroke or stroke will depend on the severity of the patient’s condition. It is important to get to the hospital as soon as possible. If the cause of the stroke is a blood clot, then it is necessary to take an antithrombotic drug within 3 hours after the onset of cerebrovascular accident to reduce the consequences.
Treatment of stroke occurs in a hospital, its duration is from two weeks (for mild damage). The patient is prescribed infusion therapy, medications to stabilize blood pressure, and medications to normalize the functioning of nerve cells. In the future, the patient will need a rehabilitation course to restore lost skills or adapt to new living conditions. Rehabilitation is a very important part of treatment. It is rehabilitation measures, when performed regularly, that contribute to the restoration of working capacity.
At the Yusupov Hospital you can undergo a full course of treatment for acute stroke and stroke, including emergency care and rehabilitation. The hospital employs the best neurologists, cardiologists, surgeons in Moscow, doctors of science, and doctors of the highest category who have extensive experience in successfully treating these conditions. The hospital is equipped with everything necessary for a speedy and high-quality recovery of patients.
Artificial ventilation for acute stroke
When a patient is admitted with stroke or stroke, the doctor assesses the adequacy of spontaneous breathing and the level of oxygen in the blood. If the patient has a low level of consciousness, there is a risk of aspiration, high rates of intracranial hypertension, he requires artificial ventilation (ALV).
Ventilation is also performed for:
- Violation of central regulation of breathing;
- Obstruction of the tracheobronchial tree;
- Pulmonary embolism.
ACVA: treatment with a dropper (infusion therapy)
Infusion therapy begins from the moment a patient is admitted with stroke or stroke. A 0.9% sodium chloride solution is prescribed. With stroke, hypovolemia (decreased blood volume) quite often occurs, which can be eliminated by infusion therapy. Infusion is also necessary to control the water balance in the body. Infusion therapy is canceled gradually, after confirmation of normalization of the level of electrolytes and other elements in a blood test.
Normalization of blood pressure
The first three days are critical after stroke. During this period, repeated violations or the development of a major stroke are possible. Now it is necessary to stabilize the patient's condition and respond to any changes. Some important indicators are intracranial pressure and blood pressure. Pressure level indicators should not exceed the permissible norm or be below the norm. Therefore, pressure monitoring is carried out constantly. To normalize the indicators, special drugs are first administered intravenously, and then switched to tablet form of drugs.
Elimination of convulsive syndrome
With stroke, there is a high risk of seizures. However, there is no prevention for this condition. Anticonvulsants are prescribed immediately when a seizure occurs. The drugs are administered orally or intravenously.
Use of neuroprotectors and nootropics
An important direction in the treatment of stroke and stroke is the restoration of damaged nerve tissue and the protection of healthy tissue from the spread of “vascular catastrophe”. Treatment is performed with the help of neuroreparants and neuroprotectors.
Features of nutrition in acute stroke
If swallowing is impaired, the patient is prescribed feeding through a tube. At the beginning of treatment, food contains the necessary elements to maintain the functioning of the body, combined with infusion therapy. The calorie content of food increases gradually. In the future, the method of eating will depend on the severity of the brain damage. The course of rehabilitation of patients after acute stroke and strokes includes the restoration of self-care skills, so with the proper effort and capabilities of the patient, he can feed himself again. Food should be varied, contain all the necessary microelements and vitamins, that is, comply with the principles of rational nutrition.
Common reasons
There is a high likelihood that a child born as a result of an incestuous relationship will be diagnosed with F70. The risk is also associated with severe infectious pathologies suffered by a pregnant woman in the first trimester of gestation.
Currently, the diagnosis of F70 for disability is a significant reason, since the treatment of such a health disorder is impossible with the current level of technology development. This has to do with the anatomy of the brain. If the disease proceeds in a moderate, complex form, psychopathic states aggravated by oligophrenia are additionally observed, which significantly complicates the work with the sick person.
Causes, symptoms of transient ischemic attacks
Transient attacks occur when the amount of blood flowing into the brain decreases. Short-term symptoms are associated with the opening of additional branches of the blood circulation, which temporarily provide blood to areas deprived of nutrition and oxygen. As the process progresses, collateral vessels are unable to supply the brain with blood, and ischemic stroke develops.
The reasons are the same as for ischemic stroke. In addition, transient attacks can provoke:
- osteochondrosis;
- spinal injuries;
- spondylosis of the cervical vertebrae;
- systemic vasculitis;
- collagenosis;
- nodular periarthritis.
Symptoms of attacks occur suddenly. General cerebral signs: headache, sweating, nausea or vomiting, confusion, blurred vision, feeling of a rush of blood, trembling in the body. Focal signs depend on the affected area, deprived of blood supply, they can manifest as:
- impairment, loss of sensation in certain areas of the skin or limbs;
- speech disorder;
- impaired perception of addressed speech;
- decrease, loss of motor activity in the limbs, parts of the body;
- decreased muscle tone;
- noise in ears;
- loss of visual fields;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- memory disorder;
- dizziness or loss of consciousness.
These symptoms disappear within 1 day.
Important! Transient attacks are considered harbingers of a stroke; according to statistics, 50% of people who suffered an ischemic stroke noted the appearance of neurological symptoms, which disappeared on their own within 24 hours.
It is important!
The diagnosis F70 indicates a static disease. This means that in the future, the situation will normally neither worsen nor improve. The exception is the mildest options, since as one gets older, the clinical signs smooth out significantly. This is due to life experience. If a person manages to adapt to the world around him, to occupy a suitable niche in human society, this helps to cope with the manifestations of mental disability and live a fairly normal life.
If a person is confident in his abilities and wants to get rid of the stamp of a person with mental retardation, he can undergo a special commission at the local branch of the PND. There are many cases where patients were previously diagnosed with F70. During the examination, mental abilities are tested, and based on the number of points scored, a decision is made on maintaining or changing status. If the patient does not agree with the results of the commission, he has the right to submit an application for review to the chief physician of the dispensary or contact the district or regional hospital. You can go to see a private psychiatrist.
Prevention of stroke
Prevention of pre-stroke and stroke conditions are measures to improve overall health and reduce the negative impact on the circulatory system. First of all, you need to quit smoking. Statistics for smokers are not favorable, and smoking negatively affects not only blood vessels, but also the condition of the lungs, heart muscle, liver, and skin.
You need to reconsider your diet. Eat more fruits and vegetables, foods with fiber (oatmeal, bran, beans, lentils). Reduce the amount of salt and salty foods you consume (salted fish, pickles, ready-made frozen meals, instant foods). Limit consumption of fatty foods (fatty meats, poultry skin, rendered pork and lamb fat, heavy cream and butter).
An effective way to prevent cerebrovascular accidents is moderate physical activity. Physical education should be done for at least 30 minutes three times a week. The intensity of exercise should correspond to the level of physical fitness and increase gradually, without overdoing it.
At the clinic you can get advice on individual methods of preventing strokes and strokes. Here they not only perform treatment, but also talk about measures to prevent pathology. You can make an appointment with a neurologist, cardiologist, or rehabilitation specialist by calling the Yusupov Hospital.
Bibliography
- ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases)
- Yusupov Hospital
- Badalyan L. O. Neuropathology. - M.: Education, 1982. - P.307-308.
- Bogolyubov, Medical rehabilitation (manual, in 3 volumes). // Moscow - Perm. — 1998.
- Popov S. N. Physical rehabilitation. 2005. - P.608.
Possible varieties
If F70 is diagnosed, we are talking about debility, that is, a mild form in which the symptoms are quite smoothed out. Making such a diagnosis often causes considerable problems due to the specific manifestations of the disease and the behavior of patients.
If the lag in the development of intelligence is moderate, imbecility is diagnosed. Finally, the third option, idiocy is the most severe form. A person’s intellectual capabilities are practically zero, and at the same time severe psychopathologies appear. You can contact the commission to remove the diagnosis only in the case of the mildest type of mental retardation.
Prices for services *
| Name of service | Price |
| Consultation with a rehabilitation specialist | Price: 3600 rubles |
| Comprehensive rehabilitation program after stroke | Price from 10,830 rubles per day |
| Comprehensive rehabilitation program after spinal injury | Price from 12163 rubles per day |
| Comprehensive rehabilitation program for Alzheimer's disease | Price from 11,497 rubles per day |
| comprehensive rehabilitation program for Parkinson's disease | Price from 10,300 rubles per day |
| comprehensive rehabilitation program for multiple sclerosis | Price from 10,497 rubles per day |
*The information on the site is for informational purposes only. All materials and prices posted on the site are not a public offer, defined by the provisions of Art. 437 Civil Code of the Russian Federation. For accurate information, please contact the clinic staff or visit our clinic.
Download price list for services
We work around the clock
Source: yusupovs.com
Alternative option
The diagnosis of F70 in accordance with ICD-10 obliges the patient to be examined using the Isaac test, which allows to identify the level of intellectual development. The testing results suggest the presence of the form:
- light;
- average;
- complex;
- deep.
Currently, this medical practice has not become widespread in our country. In addition, in severe cases, the use of testing is completely inappropriate. To assess intellectual retardation, the Wechsler technique is most often used, as well as scales (verbal, nonverbal). Using this approach, it is possible to identify and clarify the diagnosis of F70, and assess the intellectual level of a person with a small percentage of error.

Transportation Features
ACVA is an absolute indication for hospitalization in a specialized hospital. There are no contraindications for hospitalization in this case.
The patient is transported on a stretcher; his head should be elevated 30 degrees, regardless of the severity of the condition.
The ambulance team notifies the department in advance of the arrival of a patient with signs of acute stroke and indicates the approximate time of admission.
It is necessary to transport the patient within 4.5 hours to a specialized neurological department (department for patients with stroke) for the purpose of performing TLT.
Hospitalization in this case takes place without passing through the clinic’s emergency department.
Upon admission, the patient is examined by an on-duty neurologist who:
- assesses the state of vital functions of the body, the general condition of the patient, and his neurological status;
- takes measures to restore impaired body functions of a patient with signs of a stroke;
- organizes an ECG, blood sampling to determine the level of platelets, glucose, international normalized ratio, activated partial thromboplastin time.
Blood is drawn no later than 20 minutes from the moment the patient is admitted to the neurological department. The result is transmitted to the neurologist on duty.
After this, to clarify the diagnosis, the patient is sent to a CT or MRI, the conclusion is also transferred to the doctor on duty in the neurological department.
Pevzner classification
The features of dividing the F70 diagnosis into groups were developed in 1979 by specialist Pevzner. This system, which has made it possible to improve pedagogical work with children with intellectual disabilities, is currently widely used to assess the degree of oligophrenia. The pathogenesis of the problem and etiology are taken into account.
The system is as follows:
- oligophrenia without pathologies;
- retardation accompanied by neurodynamic problems (inhibition, excitation);
- retardation, in which there is a weakening or absence of functioning of the analyzers of hearing, vision, and tactile sensations;
- mental retardation, accompanied by psychopathology affecting behavioral reactions;
- a disease caused by frontal insufficiency.
Oligophrenia: what happens
Explanation of the diagnosis F70 - mild retardation, revealed by the use of a specialized test aimed at assessing the intellectual abilities of the person being examined. The clinical manifestations of the disease are weak, the symptoms are more pronounced in childhood, while the mechanical memory is quite strong, and the sphere of will and emotions is preserved. A distinctive feature of mental retardation is the difficulty of perceiving new information and consolidating knowledge. This requires a lot of time and effort, impressive volumes fall out of memory, so you have to learn them again over and over again.

Decoding the F70 diagnosis requires understanding that the sick person has no abstract thinking at all. But descriptive processes are very developed. There are difficulties connecting the logic of different subjects. Mostly with mild retardation, patients are completely unaware of the essence of space and time as concepts.
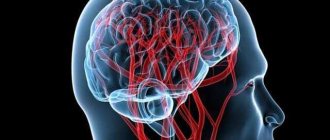
Acute cerebrovascular accidents (ACI)
4. Thrombosis of the venous sinuses.Risk factors for stroke are arterial hypertension, obesity, smoking, and old age. In addition, each type of stroke has its own specific development factors: - Transient ischemic attack occurs due to local cerebral ischemia, and no infarction is formed. TIA occurs as a result of cardiogenic or arterial embolism. Less commonly, it occurs with stenosis of large (carotid or vertebral) arteries, which leads to hemodynamic cerebral insufficiency. - Ischemic stroke. They cause diseases that lead to a decrease in the lumen of the cerebral arteries (thrombosis, embolism, stenosis, compression of the vessel by a tumor or hematoma). In the area supplied by this artery, local ischemia occurs. This leads to necrosis of brain tissue and the formation of a cerebral infarction. - Intracerebral hemorrhage. For its development, a combination of high blood pressure and damage to the artery wall is necessary, which can lead to its rupture. As a result, a hemorrhage is formed like a hematoma or hemorrhagic impregnation. - Subarachnoid hemorrhage. It is most often caused by a rupture of an arterial aneurysm with blood leaking into the subarachnoid space.
II. Prevalence of stroke
Currently, more than 400,000 strokes are registered in Russia per year. The incidence of stroke is approximately 3.2 cases per 1000 population per year. ACVAs are more common in the urban population; recently there has been a tendency towards rejuvenation of this nosology.
III. Classification of ONMC
1. Transient cerebrovascular accident (transient ischemic attack) 2. Stroke. Divided into: - Ischemic stroke or stroke of ischemic type. — Hemorrhagic stroke or stroke of hemorrhagic type. Includes: a. Intracerebral or parenchymal hemorrhage. b. Spontaneous (non-traumatic) subarachnoid hemorrhage. V. Spontaneous (non-traumatic) subdural and extradural hemorrhage.
Unspecified stroke, non-purulent thrombosis of the intracranial venous system is also distinguished. In Russia, acute hypertensive encephalopathy is classified as acute hypertensive encephalopathy.
IV. Clinical manifestations of stroke (symptoms of stroke)
Stroke is characterized by both focal and cerebral symptoms. Focal symptoms are determined by disruption or loss of certain neurological functions, depending on the location of the lesion. This may include paralysis and paresis, loss of sensitivity, speech impairment, etc.
General cerebral symptoms include headache, convulsions, depression of consciousness, nausea, and vomiting. When the meninges are irritated, meningeal signs appear (stiff neck, Kernig's sign). The severity of neurological disorders depends on the location and type of stroke, the depth and extent of damage to brain tissue. With a transient ischemic attack, focal symptoms develop suddenly, but within 10 to 20 minutes from the onset they completely regress. In ischemic strokes, cerebral symptoms are mild or may be absent. In hemorrhagic stroke, general cerebral symptoms (headache, vomiting, seizures) are very typical. Moreover, focal symptoms quickly increase and subsequently a severe neurological defect is formed.
If stroke occurs in the carotid arteries, and the cerebral hemispheres are affected, this is manifested by the following clinical picture. Hemiparesis and hemiplegia (on one side of the body) are characteristic. Sensory disturbances are also observed there. There may be loss of vision in one eye or narrowing of the peripheral visual fields. Aphasia, apraxia (violation of purposeful movements), and disturbance of the body diagram are common.
If stroke occurs in the vertebrobasilar region, the patient experiences dizziness, impaired coordination of movements and balance. There may be motor and sensory disturbances that are bilateral. There is also a narrowing and loss of peripheral vision fields, and there may be diplopia. Pseudobulbar disorders (impaired swallowing) occur. With spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhage, a sharp, inexplicable, painful headache occurs, which is accompanied by symptoms of irritation of the meninges.
Features of the disease
Oligophrenia is accompanied by speech problems. Typically, such patients have a poor vocabulary, use few words, are not inclined to talk, and use narrow forms. It is extremely difficult for them to learn a certain text by heart and retell what they heard, read, or saw. Permanent memory is characterized by very weak functioning, so what has been learned is soon completely erased.
A mild form of intellectual retardation is often accompanied by talent in a narrow field or area. It is known that some children can easily cope with complex mathematical calculations in their heads, while others are able to create unique pictures. At the same time, there are difficulties in integrating into the social system, including those associated with emotional manifestations controlled by the external conditions of a particular situation. In most cases, the activities of mentally retarded people are such that long-term achievement of the goal is simply impossible. If you analyze the reasoning of sick people, they will be predominantly negative.
Doctor, what's wrong with me?
Let's look at several common diagnosis options. Decoding F70.09 means that the child has a mild form of intellectual retardation, accompanied by subtle behavioral problems. The reasons for this condition are unknown - at least at the time of formulating the diagnosis, doctors cannot say exactly why oligophrenia developed. The diagnosis F70.09 occurs much more often than the parents of such children would like. However, there is always hope, especially if the problem was identified at an early age. Usually, with such a conclusion, they are sent to study at a school with a special profile.
Another fairly common situation is the diagnosis of F70.08. This is also a mild form of impaired brain activity, for which doctors know exactly the causes, but they do not fit into the strict categories of other groups (infection, intoxication, phenylketonuria). With this diagnosis, slight deviations in behavior are observed or none at all. If a problem is discovered in early childhood, a certificate is usually issued to visit a number of doctors (speech therapists, speech pathologists) in order to improve the child’s condition and give him a chance to fully function in society.
The diagnosis of F70.02 is similar to F70.08 discussed above, but in this case doctors know exactly what caused the problem: injury, physical agent. Behavioral disorders are either mild or absent altogether.

Rehabilitation
After a stroke, all measures are aimed at restoring impaired functions, which may include disturbances in motor, speech, visual functions, orientation in space, and time. During the rehabilitation period, physiotherapy, massage, therapeutic exercises, and classes with a speech therapist are prescribed. Massage relieves spasms and normalizes muscle tone.
Physiotherapy procedures, such as magnetic therapy, electrical stimulation, ozokerite applications, improve the performance of healthy brain cells, and in combination with exercise therapy have a positive effect on spasmodic muscles. A speech therapist helps restore speech impairment. The brain is neuroplastic; with properly selected treatment, new connections are formed between nerve cells, making it possible to restore speech and movement.
In rehabilitation after a stroke, the main thing is regularity; all prescribed exercises must be done every day to achieve results. They can be supplemented with reflexology, intellectual exercises, and various exercise machines. Drug therapy includes taking neuroprotectors, blood pressure stabilizing drugs, anticoagulants and other drugs that are selected depending on the patient’s condition.
Practice of foreign colleagues
Just as in our country the term “moron” was used in medical practice in the past, so in English-speaking countries patients were called moron. The essence of this word is the same - disability associated with intellectual retardation, expressed in a mild form. Currently, the English term is recommended not to be used in the practice of doctors, since (along with the change in our language) it has become widespread among healthy people as an insult. Based on this, it is preferable to use more complex but correct names for deviations in the development of the body, so that there are no unnecessary associations with everyday negative statements (often completely groundless).
Mild retardation: features of the situation
You can suspect such a diagnosis in a child if the child has difficulty acquiring speech skills, falling behind (often noticeably) behind his peers. Moreover, in the vast majority of cases, sick people eventually develop the skills to maintain a conversation, can use speech to solve everyday problems, and easily answer during clinical interviews. Mostly people diagnosed with a mild form of oligophrenia take care of themselves, they are independent in everyday life, they are able to cook, eat, wash, and go to the toilet. Practical skills at home do not pose a serious problem for them; the only peculiarity is the slow development of opportunities to apply skills in practice.
Most often, the greatest difficulties are associated with the educational school program, since the academic performance of persons with impaired intellectual capabilities is very low. The most difficult aspects are reading and writing. If the deviations are mild, education, no matter how complex it may be, brings tangible benefits. You need to resort not only to the classical program, but also to special subjects that help develop various skills and activate compensatory capabilities.

Clinical picture
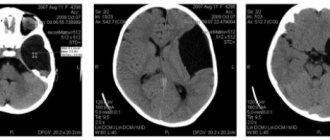
Computed tomography of the brain.
Hypertensive subcortical hematoma in the right frontal lobe Computed tomography of the brain of the same patient 4 days after surgery - removal of an intracerebral hematoma of the right frontal lobe If symptoms of acute cerebrovascular accident appear, you should immediately call emergency help in order to begin treatment as early as possible[32].
Symptoms
Stroke may manifest as cerebral
and
focal
neurological symptoms[33].
General cerebral symptoms
strokes are different. This symptom may occur in the form of impaired consciousness, stupor, drowsiness, or, conversely, agitation; a short-term loss of consciousness may also occur for several minutes. A severe headache may be accompanied by nausea or vomiting. Sometimes dizziness occurs. A person may feel a loss of orientation in time and space. Possible vegetative symptoms: feeling of heat, sweating, palpitations, dry mouth[33].
focal symptoms appear
brain damage. The clinical picture is determined by which part of the brain is affected due to damage to the blood vessel supplying it[33].
If a part of the brain provides the function of movement, then weakness in the arm or leg develops, including paralysis. Loss of strength in the limbs may be accompanied by a decrease in sensitivity in them, impaired speech, and vision. These focal stroke symptoms are mainly associated with damage to the area of the brain supplied by the carotid artery. Muscle weakness (hemiparesis), speech and pronunciation problems, decreased vision in one eye and pulsation of the carotid artery in the neck on the affected side are characteristic. Sometimes there is unsteadiness of gait, loss of balance, uncontrollable vomiting, dizziness, especially in cases where the blood vessels supplying the areas of the brain responsible for coordinating movements and a sense of body position in space are affected. “Spotty ischemia” occurs in the cerebellum, occipital lobes and deep structures and brain stem. Attacks of dizziness in any direction are observed when objects rotate around a person. Against this background, there may be visual and oculomotor disturbances (strabismus, double vision, decreased visual fields), unsteadiness and instability, deterioration in speech, movements and sensitivity [33].
What's next?
A person suffering from a mild form of mental retardation can work on an equal basis with others in the future if he can choose a suitable field of activity. Jobs that force abstract thinking are not suitable for such people, but practical employment is not only possible, but also brings real pleasure to many. People diagnosed with a mild form of mental retardation can work in both unskilled and semi-skilled jobs, performing a variety of tasks, working with their own hands.
Finding themselves in a social and cultural space where abstract reasoning and a tendency to theorize are not required from a person, patients do not at all show their differences from others around them, so there will actually be no problem. However, many note immaturity in terms of social behavior and emotional aspects, which leads to some restrictions. It is very difficult for a person with mental retardation to create his own family, since the difficulties are associated with the requirements imposed by the obligations of marriage. Raising children can be no less a problem. It is known that people with such diagnoses have great difficulty adapting to the requirements of culture, traditions, and generally accepted norms.
Are the differences that significant?
As psychiatrists note, a mild form of oligophrenia is much closer to the healthy state of an ordinary person than to a moderate or severe form of the disease. All disorders associated with deviations in behavior, emotional state, and the ability to adapt in society are in many ways close to those that are characteristic of completely healthy individuals. Of course, violations of this type require adjustment, support, and a therapeutic course, but its features are close to those recommended for many people whose intellectual level is normal.
Recently, the predominant percentage of patients are people in whom an organic etiology of the problem has been discovered. Of course, this is far from 100% of all cases, but the percentage of such causes of deviations from normal intellectual development is steadily increasing.
Diagnostic features
Detection of deviations is based on the use of standard tests, through which the intelligence quotient is determined. If the parameter varies between 50-69, they speak of a mild form. When observing patients, there is a slight delay in understanding and speech perception. There are cases where certain speech problems persist into adulthood
In some cases, oligophrenia is accompanied by other diseases: mental, intellectual. Medicine knows quite a lot of cases of diagnosing mild mental retardation in patients suffering from autism and epilepsy. The International System of Classification of Medical Diagnoses requires independent coding of mental retardation and other pathologies found in a patient.
Mental retardation and childhood
Among other developmental disorders, this is, unfortunately, quite common in our time. Such a diagnosis is obvious evidence that in the future the child will face serious difficulties when trying to adapt to society. In most cases, oligophrenia is diagnosed before the age of three. You can suspect a disease in your child and notice the need to contact a specialist for the following problems:
- cognitive impairment;
- persistent mental disorders that cannot be reversed to a normal state;
- mental problems have organic causes.

Where did the trouble come from?
There are several main risk factors that provoke this pathology:
- pathologies suffered during gestation;
- toxicoses that bother you in the third trimester;
- intoxication of the maternal body with various toxic components;
- metabolic problems of the maternal body;
- pathologies of the immune system;
- too fast or very long labor;
- incorrect presentation of the baby;
- influence during pregnancy of chemical compounds, radioactive radiation;
- rubella;
- toxoplasmosis;
- infection of the fetus during pregnancy;
- genetic background;
- bad habits of parents.
There is a possibility of mental retardation in children whose mothers had a very narrow pelvis, the fetus was entwined with the umbilical cord, and the Rh factors of the mother and child are incompatible. Intellectual abilities can be impaired due to trauma received during childbirth or pathologies that the baby suffered before reaching the age of three. The problem is often caused by polio, influenza, measles and a number of other infectious pathologies.