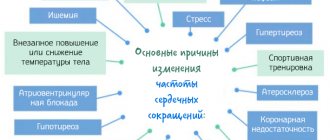
Causes of slow heartbeat
A rare and weak heartbeat can be caused by hormonal disorders, disruptions in the autonomic nervous system, and an imbalance of macroelements (potassium, sodium).
Bradycardia may be normal in athletes because their hearts are trained and work more efficiently. People who regularly engage in cycling sports may have a heart rate as low as 35 beats per minute. This is a consequence of vagotonia in athletes.
Physiological bradycardia is observed after eating, during sleep, and in the cold.
Types of pathological bradycardia:
- Neurogenic bradycardia. Heart function slows down during vegetative-vascular dystonia with vagoinsular crises. The vagus nerve and parasympathetic system, with the help of acetylcholine, have a negative chronotropic effect on the heart. As a result, the patient feels weakness, fear, lack of air, and cold sweat. Blood pressure decreases during such attacks. The person may become dizzy and lose consciousness. With constant bradycardia, the patient's weight increases due to edema. Neurogenic bradycardia can also be caused by bleeding under the meninges. The vagus nerve reacts during exacerbation of gastric ulcers, intestinal diseases, wearing a tie that compresses the carotid sinuses, and pressure on the eyeballs.
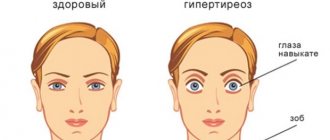
- Endocrine pathologies can affect the heart rate. For example, when the function of the thyroid gland decreases, bradycardia is observed. Adrenal insufficiency is manifested by a slowing of the heart. With adrenal insufficiency, sodium is quickly lost from the body, which leads to disruption of the depolarization process. Slow heart rate in neurocirculatory dystonia and hypothyroidism is functional in nature.
- Bradycardia accompanies infections (typhoid fever), intoxication with tobacco and heavy metals, bilirubin. Shifts in the work of the heart muscle are also observed with increased potassium content in the blood. Potassium relaxes the heart muscle, having a negative chronotropic effect, that is, it slows down the heart rate. Hyperkalemia occurs with an overdose of potassium preparations (potassium has a cumulative effect), the breakdown of muscle fibers, red blood cells in hemolytic anemia, as well as with citrated blood transfusion. Products of liver and kidney failure have a toxic effect on the myocardium and slow down the heart rhythm. This is toxic bradycardia.
- Dropsy of the brain and tumors can also cause the heart to slow down. This form of bradycardia is called neurogenic.
- Drug-induced bradycardia. Among the drugs that cause a slow heart rate are beta-blockers, sympatholytics and cholinomimetics. The heartbeat also slows down when using cardiotonics (Digitoxin), vasodilators (calcium blockers).
- Sometimes bradycardia is induced by inflammatory or sclerotic processes during post-infarction necrosis. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy also leads to a decrease in heart rate. This is an organic form of bradycardia. The heart function of weather-sensitive people can be affected by weather changes.
A slow heartbeat may indicate blockades of the conduction system of the heart: the sinus and atrioventricular nodes, the His bundle, and Purkinje fibers.
With severe bradycardia, a convulsive attack of Morgagni-Adams-Stokes develops, which is a consequence of oxygen starvation of the brain. This attack is dangerous due to the possibility of sudden death.
With a weak sinus node (SU), bradycardia alternates with tachycardia.
Weak SU syndrome:
- Heart rate is less than 40 beats.
- The appearance of ectopic foci after the failure of the sinus node.
- Sinoauricular block.
With a weak sinus node producing 60 pulses per minute or more, its role is taken over by the underlying levels of the conduction system of the heart. These are the atrioventricular node, the bundle of His and its legs.
There are three forms of joint weakness syndrome: latent, compensated and decompensated.
How to determine pulse deficit, what is the difference between
You can determine the pulse deficit, that is, the difference between heart contractions and pulse beats:
- place your palm on the heart area (in a thin person) or a phonendoscope;
- use a stopwatch to count the number of heart beats in one minute;
- Use your fingers to determine the location of the pulsation of the carotid or wrist artery and measure the pulse in a minute.
The difference between the heartbeat and pulse beats will be equal to the pulse deficit in atrial fibrillation. It is much less common to find it with extrasystole or tachycardia.
More complex rhythm disturbances are also possible when too many impulses are generated in the sinus node, and then they are partially delayed in the atrioventricular (atrioventricular) node. Then only every second or third, fourth passes, but there is also an unequal (non-rhythmic) passage in each cycle. In such a patient, the heart rate per minute is difficult to determine correctly.
Therefore, to identify pulse deficiency in atrial fibrillation and its causes, an examination is prescribed:
- ECG in normal mode;
- 24-hour Holter ECG monitoring;
- tests with physical activity (bicycle ergometry, treadmill with cardiogram recording);
- echocardiography to determine defects, the size of cavities, the presence of blood clots, as well as measure the filling of the ventricles and the ejection of blood;
- tomography – magnetic resonance, multislice computer for a detailed study of the myocardium.
Treatment
To treat bradycardia, drugs are used that suppress the inhibitory effect of the vagus nerve on the heart. These are anticholinergics, drugs based on atropine and other belladonna alkaloids.
Adrenomimetics during blockades restore the physiological heart rate.
For slow heart contractions caused by vegetative-vascular dystonia, cardiac stimulants are prescribed, which have a positive chronotropic effect, i.e., increasing the heart rate. These are drinks that contain caffeine, Caffeine Sodium Benzoate Tablets.
Adaptogens prolong the action of catecholamines (adrenaline and norepinephrine). These include Rhodiola, Eleutherococcus, and ginseng. For mild bradycardia, you can limit yourself to caffeine.
For hypothyroidism with a rare heartbeat, hormonal replacement therapy with Bagotirox or Triiodothyronine is prescribed.
Metabolic agents are prescribed to support the heart: Carnitine, Mildronate, Coenzyme Q10, Solcoseryl. Trimetazidine (Mexidol) increases the body's resistance to hypoxia.
Patients need a diet without excess salt and fat, giving up bad habits, and physical therapy.
In cases of severe bradycardia, surgery is performed to implant a pacemaker. The indication for its implantation is a Morgagni-Adams-Stokes attack.
Bradycardia is a type of arrhythmia characterized by a weak heartbeat: less than 60 beats per minute. A low heart rate is considered normal in athletes and pregnant women. But more often, a decrease or increase in the frequency of heartbeats indicates disturbances in heart rhythm, and threatens with serious complications. Medications and traditional methods help normalize the heartbeat. For long-term bradycardia, surgical intervention is resorted to.
Tachycardia after eating
Some people feel that their heart begins to beat rapidly immediately after eating. A direct connection between increased heart rate and food intake can be observed in a number of cases:
- An individual characteristic, a variant of the norm that is not related to diseases;
- Overweight and overeating;
- Recovery period after anorexia;
- Old age;
- Poor nutrition (excess of “fast” carbohydrates);
- Chronic cholecystitis.
People suffering from cholecystitis experience the so-called cholecysto-cardiac syndrome - 10-20 minutes after eating, the heart begins to beat strongly, chest pain and even signs of myocardial ischemia on the ECG may appear.
To combat palpitations after eating, it is necessary to normalize your weight and eating style, and in the presence of cholecystitis and cholelithiasis, undergo cholecystectomy - an operation to remove the gallbladder. If the symptoms persist, palpitations after eating can be considered normal, but you need to regularly visit a doctor for timely diagnosis of possible complications.
***
Regardless of the reasons why the heart began to beat strongly and frequently, regardless of the severity of the clinical manifestations, this condition requires a visit to a qualified specialist for diagnosis and treatment. It must be remembered that diseases of the cardiovascular system occupy a leading place in the structure of mortality. Listen carefully to your heart!
General information
Causes of bradycardia
Changes in heart rate occur at any age because they depend on various factors. Rare heartbeat is aggravated by the following factors:
- Diseases of the endocrine system. Insufficiency of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands slow down the care of the heart.
- Arterial hypotension, which provokes weak blood flow to parts of the body and weak pressure on the walls of blood vessels.
- Heart diseases.
- Taking beta-blockers, sympatholytics and cholinomimetics.
- Drinking alcohol and smoking cigarettes.
- Hypothermia of the body.
- Poor nutrition.
In a child, the causes of the disease are hypoxia, rapid development of internal organs, and infectious diseases.
Low heart rate is not always a dangerous pathology. Athletes who engage in strength training for a long time strengthen their heart muscle well. When a long period of rest occurs, the muscle, accustomed to constant stress, relaxes and the pulse slows down. A slower heart rate in pregnant women is considered natural. The reason for this is the strong pressure of the uterus on the vena cava. Therefore, the expectant mother should constantly undergo examinations by a gynecologist. A decreased heart rate is dangerous due to the development of a Morgagni-Adams-Stokes attack, which occurs due to a lack of oxygen in the brain. The attack is fatal.
Return to contents
Symptoms of low heart rate
If weakness, fainting and low blood pressure occur, you should consult a cardiologist.
A deviation from the norm of a few strokes does not threaten the human body with serious consequences. But a large difference from the norm is dangerous due to cardiac arrest, fainting and injury when falling from loss of consciousness. There are times when the disease goes unnoticed. Severe bradycardia is accompanied by nausea, fatigue, “stars” before the eyes, and malaise. If at least one of the signs is present, you should definitely contact a cardiologist for timely help.
Return to contents
Tachycardia and alcohol
Many people notice that their heart beats strongly after drinking alcohol or having a hangover. At the same time, it is necessary to clearly distinguish between alcoholism, which has formed as a disease, with all its manifestations, and episodic alcohol consumption. That is, if a person has taken a certain dose of alcohol, not a toxic dose that causes ethyl alcohol poisoning, but one at which he usually feels normal and his heart begins to beat strongly, this is the usual effect of alcohol, which increases blood pressure and heart rate.
You need to understand the basics of the influence of alcohol on the activity of the cardiovascular system and the body as a whole, which with frequent alcohol consumption boils down to the following effects:
- Arrhythmogenic – the frequency of arrhythmias increases significantly;
- Cardiomyopathic – severe degeneration of the heart muscle, accompanied by fat deposition in the heart cells;
- Immediate direct toxic effect on the myocardium: contrary to the general opinion about the high calorie content of alcohol, it is an energetic intracellular poison that causes energy starvation of the myocardium;
- With frequent and long-term alcohol consumption, the risk of heart attack and sudden cardiac death increases significantly;
- Metabolism in the body is disrupted due to alcohol-induced pathology of the pancreas and liver, which leads to disruption of the heart.
And these are just the main effects of alcohol, which lead to the fact that the heart beats strongly and frequently. The most effective method of combating these manifestations is a complete abstinence from alcohol, and if the body has not yet been completely destroyed, it will certainly and quickly recover.
If the heart beats strongly with a hangover, you need to understand the reasons for this phenomenon, and then the methods of dealing with tachycardia and hangover in general will be clear:
- Intoxication caused by drinking alcohol and its breakdown products is treated by drinking fluids and increasing diuresis; gastric lavage is acceptable.
- Electrolyte imbalance is relieved by using saline solutions: Regidron (one of the best options), mineral water.
- The metabolism of alcohol in the body requires a large amount of B vitamins, which are also needed for the functioning of the heart; they can be replenished with vitamin complexes (Neurobeks Neo, Neuromultivit), foods rich in vitamins of this group (bread, tomatoes, meat), fermentation products - kvass.
- High blood pressure and pulse, which are a direct result of alcohol consumption and its breakdown, can be treated with appropriate medications (Captopril, Lisinopril, Atenolol and others).
- Excessive excitability, which also causes tachycardia, is treated with Motherwort, Valerian, and in severe cases, the doctor administers Diazepam, Realanium.
- Headache can be caused by various reasons, including the above, but only after all the above manipulations is it permissible to use painkillers - Aspirin, Citramon.
Alcohol has a destructive effect on the body, and while we often see chronic alcoholics, which exerts powerful psychological pressure in favor of giving up alcohol, cases of acute alcohol poisoning and death from it are rarely made public. It must be remembered that alcohol occupies a leading place in the structure of mortality from external causes; you should not get carried away with it, and if there are signs of alcohol poisoning and severe symptoms, when the heart beats strongly and frequently, and consciousness is confused or absent, you should seek medical help.
Diagnostic procedures
If your heartbeat is weak, your doctor will prescribe a number of procedures to help determine the cause of the problem. First, the cardiologist measures the number of heart beats per minute and intracranial pressure. A hormone test is performed to determine if there are problems in the thyroid gland. Ultrasound of the adrenal glands is recommended. A mandatory stage is an ECG and ultrasound of the heart. These measures will help determine how the heart muscle works. If the cardiologist sees a need, he refers you for consultation to doctors in other fields of medicine.
Return to contents
What to do if your heart rate is low?
Healthy sleep, proper rest and taking medications will help prevent the disease.
Treatment of the disease is possible with medication and surgery. Drug treatment is prescribed by a doctor and is selected strictly individually. The medications depend on the cause of the low heart rate. First of all, if your heartbeat is weak, it is recommended to drink strong coffee and black tea. Caffeine causes the heart muscle to contract. Ginseng, yarrow, belladonna have properties to increase heart rate.
Surgery is rarely performed. It is used for elderly patients who have suffered from bradycardia for several years. A person is given a pacemaker that regulates the rate and rhythm of the heart.
Traditional medicine offers recipes for treating bradycardia at home. Some of them are presented in the table:
| Ginseng | You need to add 25 g of finely chopped plant root to 1 liter of ethyl alcohol. Leave for 3 weeks. Take 10-12 drops before meals. The course of treatment is 3 months. |
| Honey and radish | Mix these 2 ingredients in equal proportions. Use 3 tsp. 3 times a day. |
| Pine branches | Pour 50-60 g of dry pine branches with 300 ml of alcohol, leave for 10 days and drink 15 drops before meals. |
If there is a slight deviation from the norm, it is not necessary to take pills right away. It is useful to steam the legs, then stick on mustard plasters. To achieve the desired result, mustard plasters are applied at least 2 times a day for 10 minutes. Light exercise or massage is recommended. The heart beats faster, the heart rate accelerates.
Bradycardia, like any other disease, is better to prevent than to treat later. To prevent the appearance of a low heartbeat, the body needs proper rest, at least 8 hours of sleep at night. It is worth giving up alcohol, cigarettes, and drugs. Take healthy food intake and vitamins. Walking in the fresh air strengthens the body and has a positive effect on the functioning of the heart.
It is important to know! An effective remedy for normalizing heart function and cleaning blood vessels exists! ...
There are various reasons for a weak heartbeat: from occupational diseases to hormonal imbalances. Since the heart is one of the most important human organs, the slightest malfunction in its functioning can cause serious consequences. If a decreased heartbeat is noticed, then you need to start looking for the cause and treating the disease as soon as possible.
As a preventive measure
In order to prevent attacks of tachycardia, it is recommended:
- Avoid stress and high physical activity.
- Avoid drinking black tea and coffee or limit their consumption and give preference to green tea.
- Instead of tea, you can drink an infusion of hawthorn and rose hips, which helps normalize heart rate. To prepare it, mix the fruits of these plants in equal proportions, add boiling water and infuse.
- If tachycardia develops against the background of hypertension, green oat juice (drink 50 g three times a day) or infusion of blue cornflower flowers (take ½ glass three times a day) helps well. If you are prone to heart attacks with high blood pressure, it is recommended to take a tablespoon a day of Adonis infusion and drink green tea with mint or lemon balm leaves.
Description of the disease
A disorder associated with a slow beating heart is called bradycardia.
The normal heart rate for humans is 60 to 90 beats per minute. Any deviation from this interval is considered unhealthy. However, this rule does not apply in all cases. The individual characteristics of each human body should be taken into account. The fact is that for some people this is the norm. In addition, low heart rate is not a problem for some athletes, as their heart works more efficiently.
Symptoms of the disease depend on its severity. With a slight deviation from the norm, they may remain invisible. Symptoms of bradycardia include: dizziness, fainting, weakness, increased fatigue, tinnitus, increased sweating, shortness of breath. An insufficient number of heart contractions leads to oxygen starvation of the brain and other organs. For an accurate diagnosis of bradycardia, it is necessary to consult a cardiologist. As part of the examination, the cardiologist will most likely order an electrocardiogram, with the help of which it will be possible to find out exactly what the problem is. Your doctor may also order a chest assessment or basic heart monitoring.
Tachycardia during pregnancy
If the heart begins to beat strongly during pregnancy, it is necessary to take into account the special state of the female body, because in addition to the general reasons for the development of increased heartbeat, pregnancy itself also has an impact. Science knows that tachycardia in pregnant women is more common, which is due to the following factors that occur during pregnancy:
- High levels of estrogen and human chorionic gonadotropin;
- High concentration of catecholamines;
- Increased sensitivity of adrenergic receptors;
- Emotional lability.
In the vast majority of cases, if the heart beats strongly and frequently during pregnancy, this is not accompanied by any significant disorders of the cardiovascular system and does not in any way threaten the health of the mother and child. It should also be taken into account that during pregnancy, weakness, dizziness, and fainting are often encountered, which are caused by the pregnancy itself and do not indicate illness.
When a pregnant woman experiences a feeling of palpitations for the first time, especially if there are other complaints, it is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible in order to diagnose this condition and possible treatment, because at this period of life a woman has a double responsibility for her own and her child’s health. Before seeking medical help, you can independently perform a number of non-drug actions that can calm your heart:
- Massage of the carotid artery in the area of the carotid sinus (approximately in the middle third of the anterolateral surface of the neck), should be applied alternately on each side, which leads to a decrease in the pulse rate;
- Putting your face in a container of very cold water (diver's reflex) also slows down the heart;
- Close the glottis and try to inhale strongly - this reflexively makes the heart beat slower (Valsava maneuver);
- Press your finger on the root of your tongue as if you are going to induce vomiting;
- Pressing the fingers on the eyeballs through closed eyelids until a slight pain is felt for 15-20 seconds, then the fingers are sharply removed from the eyes.
These manipulations are called “vagal techniques”, are safe, and can be used by everyone, not only pregnant women.
During pregnancy, self-administration of any medications is prohibited. Medicines are prescribed only by a doctor and only long-known, proven and safe drugs.
Video: example of vagal action to relieve palpitations
Etiology of the disease
Treatment for low heartbeat depends entirely on the cause, so finding it is important. The most common cause of slow heartbeat is aging, because towards the end of life the heart stops working at full capacity. If the individual characteristics of the body do not provide for a low heart rate, then this indicates certain health problems, such as:
1. Various injuries to the chest or other organs. 2. Stomach diseases. 3. Endocrine disorders. 4. Brain diseases. 5. Lack of nutrients. 6. Typhoid fever, jaundice. 7. Poisoning. 8. Neuroses. 9. Dropsy of the brain.
People who are weather-sensitive may experience heart failure due to sudden weather changes. Being overweight, smoking, drinking alcohol and using drugs can cause serious problems in your heart rate. Slow heartbeat can also be caused by taking certain medications, such as:
1. Cardiac glycosides. 2. Cholinomimetics. 3. Sympatholytics. 4. Verapomil. 5. Quinidine. 6. Morphine.
First aid
It is very important not to panic at this moment. If you have experienced such situations before, then immediately take the medicine that was prescribed by your doctor just for this case. Self-prescribing medications is fraught with dire consequences.
To drink coffee
The following drinks are very good for raising your heart rate:
- coffee
- various energy drinks
- hard-brewed tea
Mustard plaster, which should be placed on the chest, helps to normalize the pulse perfectly.
All of the above measures can be taken if such a phenomenon was not associated with heart disease.
Treatment and prevention of bradycardia
Treatment of low heart rate involves treating the underlying disease and compensating the heart rate. Patients are prescribed various diets, special massages, physical exercises, and giving up bad habits. The cardiologist prescribes medication or pacemaker implantation if the disease is severe. That is why you should not delay visiting a doctor, since in case of serious problems the situation can be fatal. Self-medication is strictly not recommended. Statistics speak about the seriousness of cardiovascular diseases: they are the most common cause of death in the world.
In order to avoid serious health problems, it is recommended to check your heartbeat from time to time. If deviations are noticed, it is necessary to see a cardiologist as soon as possible. It is worth remembering that the heart is the main mechanism in the human body that must be protected to maintain health.
The most dangerous diseases
- Life-threatening arrhythmias:
- ventricular tachycardia;
- sick sinus syndrome;
- complete atrioventricular block.
- Coronary heart disease and myocardial infarction. Sometimes palpitations are a manifestation of myocardial infarction or unstable angina. It must be remembered that myocardial infarction can occur in a painless form, manifesting itself, in particular, as rhythm disturbances.
- Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome (WPW syndrome).
- Electrolyte disturbances:
- hypokalemia (lack of potassium in the blood);
- hypomagnesemia (lack of magnesium in the blood).
And a little about secrets...
Have you ever suffered from HEART PAIN? Judging by the fact that you are reading this article, victory was not on your side. And of course you are still looking for a good way to get your heart functioning back to normal.
Then read what the experienced cardiologist E.V. Tolbuzina says about this. in his interview about natural ways to treat the heart and cleanse blood vessels.
Read an interview with a cardiologist >>
A slow heart rate is called bradycardia. This is a condition when the heart rate is less than 60 beats per minute. With moderate bradycardia, the patient may not feel the heart rate slowing, but the electrocardiogram will show this. With a strong deceleration, a person may feel weak. There are extracardial, organic, toxic forms of heart rate slowing.
Tachycardia with excitement
When the heart beats strongly during excitement, this is considered a natural response of the cardiovascular system to emotional overexcitation. Sometimes it happens that for some reason a person needs to avoid rapid heartbeat and psycho-emotional arousal in such a situation, “vagal techniques” will help, as well as sedatives: Valocardin, Corvalol, Valerian tincture, Peony tincture, Motherwort tincture, Validol and many others, the choice of a particular one is determined by personal preference.
Causes of slow heartbeat
A rare and weak heartbeat can be caused by hormonal disorders, disruptions in the autonomic nervous system, and an imbalance of macroelements (potassium, sodium).
Bradycardia may be normal in athletes because their hearts are trained and work more efficiently. People who regularly engage in cycling sports may have a heart rate as low as 35 beats per minute. This is a consequence of vagotonia in athletes.
Physiological bradycardia is observed after eating, during sleep, and in the cold.
Types of pathological bradycardia:
Neurogenic bradycardia. Heart function slows down during vegetative-vascular dystonia with vagoinsular crises. The vagus nerve and parasympathetic system, with the help of acetylcholine, have a negative chronotropic effect on the heart. As a result, the patient feels weakness, fear, lack of air, and cold sweat. Blood pressure decreases during such attacks. The person may become dizzy and lose consciousness. With constant bradycardia, the patient's weight increases due to edema. Neurogenic bradycardia can also be caused by bleeding under the meninges. The vagus nerve reacts during exacerbation of gastric ulcers, intestinal diseases, wearing a tie that compresses the carotid sinuses, and pressure on the eyeballs.
Endocrine pathologies can affect the heart rate. For example, when the function of the thyroid gland decreases, bradycardia is observed. Adrenal insufficiency is manifested by a slowing of the heart. With adrenal insufficiency, sodium is quickly lost from the body, which leads to disruption of the depolarization process. Slow heart rate in neurocirculatory dystonia and hypothyroidism is functional in nature.
Bradycardia accompanies infections (typhoid fever), intoxication with tobacco and heavy metals, bilirubin. Shifts in the work of the heart muscle are also observed with increased potassium content in the blood. Potassium relaxes the heart muscle, having a negative chronotropic effect, that is, it slows down the heart rate. Hyperkalemia occurs with an overdose of potassium preparations (potassium has a cumulative effect), the breakdown of muscle fibers, red blood cells in hemolytic anemia, as well as with citrated blood transfusion. Products of liver and kidney failure have a toxic effect on the myocardium and slow down the heart rhythm. This is toxic bradycardia.
Dropsy of the brain and tumors can also cause the heart to slow down. This form of bradycardia is called neurogenic.
Drug-induced bradycardia. Among the drugs that cause a slow heart rate are beta-blockers, sympatholytics and cholinomimetics. The heartbeat also slows down when using cardiotonics (Digitoxin), vasodilators (calcium blockers).
Sometimes bradycardia is induced by inflammatory or sclerotic processes during post-infarction necrosis. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy also leads to a decrease in heart rate. This is an organic form of bradycardia. The heart function of weather-sensitive people can be affected by weather changes.
A slow heartbeat may indicate blockades of the conduction system of the heart: the sinus and atrioventricular nodes, the His bundle, and Purkinje fibers.
With severe bradycardia, a convulsive attack of Morgagni-Adams-Stokes develops, which is a consequence of oxygen starvation of the brain. This attack is dangerous due to the possibility of sudden death.
With a weak sinus node (SU), bradycardia alternates with tachycardia.
Weak SU syndrome:
Heart rate is less than 40 beats. The appearance of ectopic foci after the failure of the sinus node. Sinoauricular block.
With a weak sinus node producing 60 pulses per minute or more, its role is taken over by the underlying levels of the conduction system of the heart. These are the atrioventricular node, the bundle of His and its legs.
There are three forms of joint weakness syndrome: latent, compensated and decompensated.
Low pulse: causes, symptoms and treatment
A slow heartbeat that occurs when the pulse rate (i.e., heart rate) is low is called bradycardia, arrhythmia, or cardiac arrhythmia. Every day, a healthy heart beats about 100,000 times, at a rate of about 60 to 100 times per minute. What to do if your heart rate is below 50 beats per minute, and how to increase your low heart rate - let's try to figure it out.
Changes in heart rate caused by activity, diet, medications and age are normal and common, but if the heart rate decreases without the above-mentioned causes being present, it may indicate a health problem that requires emergency care or a visit to a specialist.
What pulse is considered slow?
An abnormally slow heart rate, usually below 60 beats per minute, can be harmless or life-threatening. For example, at certain times, such as during sleep, your heart rate will be slow, and this is normal. What is considered an abnormally low heart rate for one person may be normal for another. For example, a young, strong, healthy athlete may have a resting heart rate of 30-40 beats per minute, but can easily increase their heart rate to 180 beats per minute during exercise. This increased heart rate is normal—but only for those who exercise regularly. Another person may have a heart rate of 30-40 beats per minute while walking up stairs, but they feel weak and tired. It is not normal.
What Causes a Slow Heartbeat?
The heartbeat is controlled by an electrical system that signals the heart muscle when to contract to pump blood to the rest of the body. Bradycardia occurs when the system slows down or blocks these signals.
Types of Slow Heart Rate
- Sinus node dysfunction is an abnormally slow natural “pacemaker” in the heart. The heart has a group of cells in the upper chamber (right atrium) called the sinus node, which causes an electrical signal, or impulse, in the lower chambers (left and right ventricles) to produce compression, causing the heart to beat at a rate of approximately once per second. state of rest. The sinus node can increase its speed depending on the body's needs. This machine can wear out and work too slowly or sometimes fail to work, resulting in a slow heart rate (sinus bradycardia).
- Heart block is a breakdown of the “wires” that carry electrical signals from the sinus node to the heart muscle. The heart muscle contracts, causing the heart to beat, only when it receives these impulses. In this case, the sinus node works normally, but the signal does not reach the muscle. There are three types of heart block:
- First degree - the impulse from the upper chambers of the heart reaches the lower chamber, but more slowly than usual. The heart rate is normal and it usually does not cause symptoms.
- Second degree - some, but not all, impulses are transferred from the upper chambers of the heart to the lower ones. This may cause some symptoms.
- Third degree - impulses from the upper chambers are “blocked” and do not reach the lower chambers. This can lead to a very slow heart rate, fainting, and other symptoms.
- Tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome. It is possible that the same person may have a slow heartbeat when the heart is in a normal rhythm and periods of fast, irregular heartbeats (supraventricular tachycardia) at other times. Sometimes medications are needed to control a fast heart rate, which can worsen an already slow heart rate. People with this syndrome often complain of rapid heartbeat, dizziness, and fainting. This heart rhythm problem can also cause shortness of breath or chest pain. Treatment for tachybradycardia syndrome usually requires a pacemaker to keep the heart from beating too slowly and medications to keep the heart from beating too quickly.
Symptoms of a slow heart rate
A slow heart rate, or bradycardia, can cause the following symptoms:
- Weakness
- Difficulty walking, climbing stairs, or exercising
- Fatigue
- Irregular breathing
- Dizziness
- Fainting
How to increase your heart rate naturally?
Any physical movement makes the heart beat faster, but among the simplest in terms of execution and load, you can try these:
- Aerobic exercise : Aerobic exercise safely increases your heart rate. These include walking, water aerobics, cycling, swimming, running, kickboxing and dancing. Choosing the right aerobic exercise should be based on your personal needs, abilities and preferences. If you're just starting to exercise, it's best to start with lower-impact, gentle-movement activities like walking and swimming. Once your heart starts to get stronger, you can move up a level to longer activities like dancing or cycling.
- Strength exercises : These involve the use of kettlebells or any other mechanism that adds weight. When muscles meet resistance, they demand more oxygenated blood, which in turn increases your heart rate. At first you can use your own body as a weight by doing push-ups or squats, but over time you can add additional weight.
- Stretching : What many people don't know is that stretching can get your heart pumping and it certainly can and should be done for good heart health. Stretching increases flexibility and improves blood flow, and is not very difficult to do.
Two things to consider before starting a workout are your health and ability. It is always important to get clearance from your doctor and even guidance before you begin. It's also important to know your limits. While you may be looking for immediate results, exhausting yourself will only lead to injury and inability to perform. Take your time, start slowly and gradually make things more difficult for yourself.
Not only does exercise help get your adrenaline flowing, but it can also reduce your risk of many common heart-related diseases by making your heart much stronger.
First aid for slow heartbeat
If your heart rate is below 50 beats per minute, what should you do in this situation? Depending on your blood pressure readings, there are three types of emergency care for low heart rate:
- Normal pressure. In this case, it is necessary to administer antiarrhythmic drugs intravenously: novocainamide, panangin with glucose or lidocaine.
- High blood pressure (140/90). Groups of alpha-blockers, inhibitors and ACE are used, but after this you should immediately consult a doctor.
- Low pressure. In this case, strong tea or coffee will help.
In any case, if the causes of low heart rate are unknown, and symptoms appear frequently or systematically, you should not self-medicate - consult a doctor without delay. Only a specialist, through diagnosis and analysis, will be able to accurately determine the cause of the low pulse and prescribe the correct treatment.
We also invite you to watch a fragment of the program “About the Most Important Thing!” - causes of low heart rate:
Treatment
To treat bradycardia, drugs are used that suppress the inhibitory effect of the vagus nerve on the heart. These are anticholinergics, drugs based on atropine and other belladonna alkaloids.
Adrenomimetics during blockades restore the physiological heart rate.
For slow heart contractions caused by vegetative-vascular dystonia, cardiac stimulants are prescribed, which have a positive chronotropic effect, i.e., increasing the heart rate. These are drinks that contain caffeine, Caffeine Sodium Benzoate Tablets.
Adaptogens prolong the action of catecholamines (adrenaline and norepinephrine). These include Rhodiola, Eleutherococcus, and ginseng. For mild bradycardia, you can limit yourself to caffeine.
For hypothyroidism with a rare heartbeat, hormonal replacement therapy with Bagotirox or Triiodothyronine is prescribed.
Metabolic agents are prescribed to support the heart: Carnitine, Mildronate, Coenzyme Q10, Solcoseryl. Trimetazidine (Mexidol) increases the body's resistance to hypoxia.
Patients need a diet without excess salt and fat, giving up bad habits, and physical therapy.
In cases of severe bradycardia, surgery is performed to implant a pacemaker. The indication for its implantation is a Morgagni-Adams-Stokes attack.
The heart is the most important internal organ of a person. Every day it pumps about 8 thousand liters of blood, making more than 100 thousand contractions. The heart rate can fluctuate depending on the condition: during sleep it slows down somewhat, and during physical activity, emotional outbursts or after a heavy meal it increases. On average, the heart of a healthy person beats at a frequency of 60-80 beats per minute.
Human life and health depend on the coordinated and uninterrupted functioning of the heart. Insufficient supply of body tissues with oxygen and nutrients can lead to disruptions in the functioning of internal organs.
How to increase your heart rate?
There are two methods of treating bradycardia: taking medications and performing a minimally invasive operation to install a pacemaker - this is a device that sets the heart the necessary frequency and rhythm of contractions. The second method is usually used for significant and prolonged bradycardia that has developed in an elderly person.
The need for drug therapy for a low heart rate is determined only by a doctor, depending on the cause of the disease. It is not recommended to take any medications on your own, as this can only worsen the condition. If no pathology is identified, the patient feels well, and special treatment is not required, the following methods will help raise a low pulse:
- complete rest;
- a cup of green tea;
- various herbal remedies - tincture of ginseng, eleutherococcus, aralia, etc.;
- taking special vitamin preparations, for example, doppelhertz ginseng active;
- physical exercise (for example, gymnastics that strengthens blood vessels and the heart).
In addition, it is recommended to give up bad habits (alcohol, smoking), switch to a healthy diet (especially consume less animal fats) and undergo an annual cardiac examination.
www.infmedserv.ru
Signs of a weak heartbeat
A heartbeat is one beat of the heart, i.e. the compression and expulsion of blood. Palpitations are not a specific symptom or a syndrome of any disease identified by objective research methods, it is the feeling of your heart beating. When complaining about palpitations, each person refers to various changes in the heart rhythm.
A weak heartbeat is considered to be a pulse less than 50 beats per minute. A decrease in heart rate leads to disruption of the normal functioning of the entire body, a person experiences weakness and dizziness. gets tired quickly and may lose consciousness; increased sweating and shortness of breath may occur. weight gain.
What is heart rate deficiency?
The term pulse deficiency means that not every contraction of the heart is accompanied by a pulse beat, that is, not all blood emissions are effective and reach the arteries. This is only a symptom and not an independent disease, since it requires an underlying cardiac disorder to occur.
We can talk about a pulse deficiency if a difference is found between the frequency of the heart rate measured per minute and the pulsation on the radial, carotid or femoral artery. In this case, the rhythm of contractions or pulsation itself does not matter; it can be normal (60-90 beats/min), slow (up to 60) or frequent (more than 90). For example, with a heart rate of 93 beats per minute, the pulse may be in the same time. Then the heart rate deficit will be 33.
Causes of weak heartbeat
There can be many reasons for a weak heartbeat. It must be remembered that in this way the cardiovascular system can respond to numerous disorders in the body. These include neuroses, diseases of the endocrine or digestive system, increased levels of potassium in the blood, and psychological stress. Thyroid disease may be indicated by a weak pulse, accompanied by fatigue, constipation, hair loss, and weight gain.
Taking certain medications, such as beta blockers or hormones, can also cause your heart to slow down. It is possible that a weak heartbeat may indicate a malfunction of the cardiovascular system - heart failure. In such cases, the pulse becomes frequent and weak.
A weak heartbeat may occur in people with low blood pressure who suffer from bradycardia. In this case, the heart beats at a frequency of no more than 40-50 beats per minute. With bradycardia, a person may not pay attention to a weak heartbeat for a long time until other, more severe symptoms appear. Bradycardia requires mandatory drug treatment.
With varying degrees of heart block, the heartbeat becomes especially weak. This is due to the fact that the impulse cannot pass through certain areas of the heart muscle, which threatens complete cardiac arrest. Such manifestations may be a consequence of the inflammatory process of the heart muscle or various diseases. During the blockade, decreased performance and fainting may occur due to a lack of sufficient oxygen to all organs.
A weak heartbeat may be associated with large blood loss and vomiting. dehydration, overdose of certain drugs. Also, a weak heartbeat may also depend on physiological reasons: for example, during sleep, when staying in a cold room for a long time, when climatic conditions change.
In cases where a weak heartbeat is not associated with physiological causes, only a cardiologist can make a correct diagnosis based on various examinations.
Possible complications caused by heart palpitations
Symptoms of tachycardia may include fatigue and discomfort. They also lead to heart failure and muscle wear. Conduction and rhythms are disrupted. The following complications are observed:
- heart asthma;
- arrhythmia, shock;
- pulmonary edema;
- vascular thromboembolism;
- insufficiency of blood supply to the brain in acute form.
A heart attack with ventricular tachycardia is sometimes fatal.
If the pain is not related to illness, complications are unlikely to arise. If they are caused by heart disease, the following complications may occur:
- Periodic fainting caused by sudden changes in pressure. This often occurs in people suffering from congenital heart defects or malfunctioning heart valves.
- Arrhythmia (decreased efficiency of cardiac function).
- Stroke. The rapid beating of the heart causes a deviation in the functioning of the upper chambers of the heart, as a result of which the blood stagnates, forming blood clots.
- Heart failure. It is expressed in prolonged atrial fibrillation caused by arrhythmia.
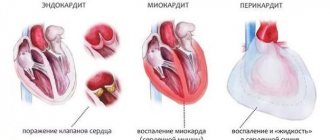
- Myocarditis. Inflammation of the heart muscles. Diagnosing this disease is difficult, so to detect it in a person who has not previously consumed alcohol, it is necessary to collect an anamnesis. If the disease is long-term, swelling may appear.
- Heart attack. Stress often causes an influx of adrenaline and, as a result, vascular spasms, due to which the access of oxygen and blood to the heart is blocked. If, after prolonged stress, the body loses the ability to quickly adapt, sooner or later a heart attack may occur.
In advanced cases, the presence of any type of arrhythmia can be complicated by flutter and ventricular fibrillation, which can become a source of circulatory arrest and lead to death. In the first seconds, the patient experiences dizziness and weakness, fainting, convulsions and even involuntary urination. Symptoms of clinical death occur - pulse and pressure cannot be determined, pupils dilate and breathing stops.