Category: Online analyzes
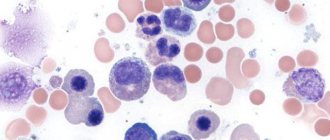
The smallest, slowest, but largest shaped structural unit of leukocytes is the basophil. Like all other leukocyte cells, they are formed in the hematopoietic organ (bone marrow), where, under the influence of special inducers, these primary cells are stimulated to divide.
After the four-day division process, a period (5 days) of special structure and formation begins, where the cells “acquire” functional specialization.
Basophils - what are they?
basophil photo
These amazing cells are represented in the body by three varieties - segmented basophilic granulocytes (basophilic leukocyte cells), mastocytes (tissue structure basophils) and pituitary basophils. In the last two species, the ripening process takes place in the bloodstream, and segmented basophilic leukocyte components enter it from the hematopoietic organ in the form of an already formed cell.
Although these three types of leukocytes have direct “related roots,” they differ in their structure and specific functional capabilities. All structural leukocyte components are characterized by immunocompetence with a very narrow “specialization”. Some are engaged in defense and building a protective barrier against the introduction of “alien enemies,” completely destroying everything. Others choose - selective phagocytosis.
But to use selective tactics, cells must have the ability to recognize “enemy agents.” This is precisely the property that segmented leukocytes have, taking on the functions of antiallergic responsibility.
The main responsibilities for which adult basophils are responsible are due to:
1) Immediate manifestation of hypersensitivity (immediate allergic reaction). When “enemies” are identified, the plasma cell membrane ruptures. Granulomatous release and secretion of various protective chemical agents occurs:
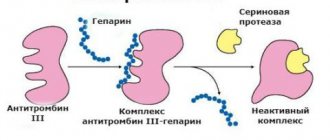
- The released heparin leads to activation of microcirculation, which improves blood flow in small vessels and tissue nutrition, and promotes new capillary growth. Its anti-coagulation property prevents the formation of blood clots and promotes the process of platelet aggregation (gluing), preventing hemorrhagic manifestations;
- The release of biogenic amines (histamine) causes an increase in vascular permeability, thereby promoting an increased flow of fluid into the area of inflammation;
- The isolated degranulated serotonin activates platelets and helps to increase vascular permeability in the capillaries, simultaneously expanding the vascular lumens;
- The formation of a significant amount of leukotriene “A4” by basophils attracts phagocytic cells (eosinophils) to places where they accumulate, promoting phagocytosis and protecting them from infections.
2) Delayed hypersensitivity caused by contact with tissue, or protein and allergen, due to:
- Extensive tissue damage from burns;
- Pathologies of a tumor or viral nature;
- Various insect bites.
All of these processes cause cellular infiltration that attracts phagocytic cells (monocytes, macrophages and neutrophils), each with its own specific phagocytic mission. The first sign of this type of reaction in adults is the formation of erythematous fields with the formation of a liquid infiltrate.
The combination of basophils and eosinophils present in the plasma is direct evidence of a hypersensitivity reaction.
3) Interaction of local immunity factors. Granulocytes and tissue leukocyte cells (mabocytes) play a dominant role in the local immune system, which is associated with the mechanism of protection of the mucous membranes and skin.
Basophils build a kind of shield against antigens, preventing their penetration into the blood. Which reduces the spread of infections and tissue inflammation reactions. As a result of this work, the protective factor in the form of an immune response is manifested by redness, swelling and blistering.
The normal level of basophils in the blood of adults is very low (ranges from 0.5 to 1%). In childhood, the indicator of these leukocyte components in the leukocytogram varies significantly.
In newborn children, basophils may be completely absent or reach 4%, gradually decreasing by one year of age to 1.2%. These indicators can easily change after the baby cries, with the start of complementary feeding, with illness and temperature changes. In the normal condition of the child, by the period of puberty the level of segmented granulocytes in the blood is compared with the adult standard.
Purpose of basophils 0 in an adult
Basophils are blood cells that are formed in the bone marrow, then they enter the blood, circulating in it for several hours, and then are sent to the tissues, where they remain for 8-12 days.
This is the smallest leukocyte group, which is mainly involved in immediate allergic reactions.
When basophils in the blood are low in an adult, this indicates the presence of a disease - basopenia. This condition can be diagnosed when the content of basophils in the peripheral blood is less than 0.01*109/l. It can be problematic even for specialists to draw specific conclusions right away, but often we are talking about the depletion of the leukocyte reserve in the body.
If basophils are low in an adult, the reasons can be very different, we will consider the most common of them in this article
When taking blood for a general blood test, the determination of basophils, as is known, is included in the calculation of a certain leukocyte formula.
Thus, the norm of basophils is indicated in the following indicators:
- Newborns - 0.75%
- Children aged 1 month - 0.5%
- One-year-old child - 0.6%
- Children aged 2 years - 0.7%
- Adults - from 0.5 to 1%
An increase in the number of basophil cells (when basophils are increased in the blood - more than 0.2 * 109 / l) is called basophilia. A decrease in the number of basophil cells in the peripheral blood (when it is low and the analysis shows less than 0.01*109/l) is called basopenia.
A regular condition in which the basophil level is below 0.01*109/l is called basopenia. It can occur due to the following diseases and conditions:
- under regular stressful conditions;
- for allergies with severe manifestations;
- for infectious diseases;
- with active thyroid function;
- for diseases of the adrenal glands;
- with pneumonia;
- when taking certain hormonal drugs.
It is worth noting that these indicators can also be observed during ovulation and pregnancy. Therefore, it is very important to do diagnostics in a comprehensive manner. It is worth saying that stressful situations can significantly reduce the content of basophils in the peripheral blood.
As in any other case, first of all, you should look for the root cause of this phenomenon. If such a disease is detected, the main therapy should be aimed at combating it, and after that the level of basophils will return to the required norm.
If there were no reasons for an increase in their level, then it is possible that this was due to a general weakening of the immune system, which means that all efforts should be directed towards strengthening it.
The name “blood scouts” clearly outlines the main functions of basophil 0 found in human blood. When their indicators do not exceed the norm, it means that everything is calm in the body and there is no need to worry about your condition, however, there are certain moments when these cells begin to become active.
This usually happens in cases where:
- The body encounters an allergen or other foreign particle penetrating into it from the outside world - they block their spread in the blood, thereby signaling to other cells that an “enemy” has appeared.
- The process of blood clotting is underway.
- It is necessary to increase blood flow in small vessels.
- It is extremely important to remove from the body the poisons that have accumulated in it or those that entered it some time ago.
It is very important to check whether these cells are absent from the human blood or are present in large quantities.
If you feel unwell or have (at first glance) causeless allergic reactions, it is better to consult a doctor.
Normal levels of basophil 0 in the blood of an adult are considered to be a percentage of one to five. If they are above the extreme limit of normal, they speak of a pathological condition such as basophilia.
Considering the fact that it is rare as an independent disease, an increased content of these cells may indicate conditions such as:
- chronic myeloid leukemia;
- acute leukemia;
- dysfunction of the pancreas;
- the presence of cancer related to the pulmonary system;
- diabetes;
- hepatitis accompanied by jaundice;
- viral infections;
- allergic reactions;
- disruption of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract);
- use of drugs containing estrogen;
- hemolytic type anemia;
- Hodgkin's disease.
In the case when the number of basophilic cells in the body of an adult is reduced or not observed at all, experts talk about such a pathological condition as basopenia. In this case, it is difficult even for an experienced doctor to correctly interpret the results of the analysis, but usually this condition is accompanied by acute leukocyte deficiency.
The main reasons for the decrease in the number of cells present in the adult body are:
- diseases that are infectious in nature and continue to develop over time;
- physical exhaustion;
- exposure to mental and moral stress, prolonged depression and stress;
- increased amount of hormones produced by the thyroid gland, disruption of its functioning;
- use of hormonal drugs;
- pulmonary infections in the acute stage;
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease.
Periodically, a reduced number of basophil cells can be observed in pregnant women in the early stages. This usually happens in cases where expectant mothers suffer from severe forms of toxicosis.
In any case, if a low level of “blood scouts” is detected (especially if these are 0 basophils in the blood), the specialist will prescribe adequate therapy to normalize the patient’s condition. Self-medication in such cases is strictly prohibited.
I always try to carefully analyze my blood tests, and my basophil levels have varied. Several years ago I had a severe allergy to laundry detergent and my basophils were elevated. And once they were below normal, the doctor then ordered a repeat blood test. At that time I was on a starvation diet and lost a lot of weight. When I returned to a normal diet, my basophil count returned to normal.
What if your general condition is not entirely good, but you don’t understand what’s wrong with you? In this case, what specific analysis should be taken? The therapist prescribes vitamins for vague complaints. He doesn’t even prescribe general blood. It’s like the season, and nothing hurts you.
Basophils are the smallest group of leukocytes, granulocytes. Basophils make up 0-1% of all leukocytes. Basophils are born in the granulocytic region of the bone marrow. The young enter the bloodstream and circulate in the human circulatory system and only then enter the tissues where they exist for about a week.
The cell contains a lot of histamine, prostaglandins, leukotrienes and serotonin. An “army” of basophils, together with other leukocytes, react to inflammatory phenomena in the body. In the place where there is inflammation, basafil releases substances histamine, heparin, and serotonin. These substances determine the function of these cells in the inflammatory process.
They manifest themselves most acutely during allergic reactions to the presence of an allergen in the body. By releasing numerous granules with substances contained in basophils, the body fights against unfavorable factors, which leads to an increase in basophils in the tissues and a decrease in them in the blood.
Increased basophils in tissues lead to a biological response, in particular redness, swelling of the tissue, and patients complain of itching.
The granularity of basophils is well stained with alkaline, or basic, paints. Alkalies are also called bases. And base in Latin is “basis,” which is why these cells are called basophils.
Basophils are normal in children and adults %
- at birth 0.75,
- up to a month 0.5,
- The norm of basophils in a child, infant is 0.6,
- 0.7 is for children under 12 years old,
- in adults 0.5-1.
Sometimes elevated basophils in a child are observed during an acute infection, especially if the disease lasts a long time with periods of recovery and the acute stage, chronic course of the disease. The child must be diagnosed for the presence of hidden, inflammatory processes. An increased number of basophils in a child is called basophilia in children.
Adult patients are assessed for basophil levels ranging from 1 percent to 5 percent. The laboratory recalculates their number in one liter of blood, which is normally considered 0.05 * 109/1 liter. With high basophils in the blood, the indicator increases to 0.2 * 109/1 l.
Basophils may be elevated in the blood due to the final recovery phase of acute inflammation. The level of basophils may be high, also due to the patient having chronic diseases. Often the reaction increases to a lack of iron in the body. The level is high in lung tumors, polycythemia, and also after splenectomy.
Basophil histamine dilates capillaries at the site of inflammation, and heparin prevents blood clotting; Thanks to this, blood circulation in this area improves, which promotes resorption and healing. It is thanks to their histamine that they cause the symptoms that occur with urticaria, bronchial asthma and other allergic diseases.
BASOPHILIA - from Greek means basis-foundation and philia-love. This is the quality possessed by cell bodies, inclusions of individual cells, as well as the ability of intercellular substances to perceive their main selective color from a mixture of basic dyes and acidic dyes.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o94ikVJc6L0
Basophils are higher than normal ({amp}gt;0.2109/l). Here are the diseases in which basophilia may be detected:
- lymphogranulomatosis
- chronic myelofibrosis, erythremia, myeloid leukemia,
- hypothyroidism
- allergic reactions to food and medications,
- introduction of a foreign protein into the body
- permanent ulcerative colitis
- use of estrogens
- anemia of unknown origin
- hemolytic anemias
The level of basophils can be normalized only by eliminating the cause that caused the increase. Basophils do not always increase due to illness or some other serious disease.
Sometimes they also increase in practically healthy people. The main reason is poor nutrition and, as a consequence, a decrease in iron levels in the body, iron deficiency.
What do elevated basophils in adults indicate?
obvious allergic reaction
What the indicator of elevated basophils in the blood in adults can indicate is, first of all, a signal about inflammatory and allergic reactions occurring in the body. The quantitative content of granulocytes in the blood is a kind of marker of the state of the immune system.
In principle, their number is not a diagnostic criterion, but often their functional activity allows a specialist to assess certain pathological conditions.
For example, the presence of chronic leukemia in combination with a basophilic crisis (a large number of basophilic cells) indicates the imminent approach of the terminal blast phase. Or their increase upon repeated encounter with an allergen (food, drug, or insect poison) can trigger the development of anaphylactic shock, which is deadly.
Conditions in which the level of basophils in the blood of an adult is increased are called basophilia. Excessive quantitative increase is a rare phenomenon. Their absolute value is not constant and depends on many factors.
Basophils are increased
- viral infections (varicella, tuberculosis);
- inflammatory bowel processes;
- Crohn's disease;
- chronic dermatitis, sinusitis;
- suffocation, asthma;
- myeloproliferative diseases (polycythemia, myelofibrosis);
- Hodgkin's lymphoma;
- metabolic diseases (myxedema, hyperlipidemia);
- hemolytic anemia;
- endocrine pathologies (hypothyroidism, increased estrogen levels).
This problem is an indicator of various diseases. That is why it is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis and carry out effective therapy. Then the level of white cells will decrease. What treatment may the doctor prescribe:
- In severe cases, such as leukemia, a bone marrow transplant is required.
- For allergic reactions leading to respiratory diseases, antihistamines may be prescribed.
- Bacterial infections are treated with antibiotics.
If the doctor did not identify any pathology, but the analysis showed an increased content of basophils, the diet should be normalized, perhaps go on a diet, increase the intake of foods containing iron (animal liver, beans, seafood). In order for the microelement to be absorbed faster, it is better not to eat foods that interfere with the absorption of iron (for example, milk). Doctors often prescribe vitamin B12 injections. It promotes hematopoiesis, improves bone marrow function, and destroys “bad” cholesterol.
In such cases, your doctor may prescribe you medications containing iron. Sometimes taking vitamin B12 helps normalize the level; this vitamin is indispensable in the processes of hematopoiesis and brain function. Vitamin B12 is prescribed by injection. Eat food rich in B12: eggs, meat, milk.
Basophils may be elevated due to the use of certain medications, such as, for example, antithyroid and estrogen containing drugs and the like. Stop taking these medications and consult your doctor. During the menstrual cycle, especially at the beginning, women may experience a slight deviation from the norm in the level of basophils, as well as during pregnancy.
The doctor collects the patient’s medical history, including hereditary predisposition to individual intolerance to various substances. Diagnostics is facilitated by information about the specific reaction of the human body to contact with certain allergens. If it is impossible to determine the irritant based on an allergic history, a skin test or measurement of specific class E immunoglobulins in the blood is performed.
Currently, complex allergy chips have been developed. Thanks to which it is possible to simultaneously determine the patient’s sensitivity to 110 allergens from 50 sources. The disadvantage of the technique is its high cost.
One of the causes of this condition is ulcerative colitis, when inflammation of the mucous epithelium of the human colon occurs. Possible causes: hereditary predisposition, infection with pathogens, complications after taking oral contraceptives or smoking.
Basophils above normal are determined in test results in chronic hemolytic anemia. The incidence of the disease is extremely rare. It manifests itself in the form of uncontrolled destruction of red blood cells. As a result, the synthesis of red blood cells in the human body is activated and the concentration of their breakdown products increases significantly.
The prognosis for outcome is typically favorable. If the disease develops against the background of external factors, as a rule, their cancellation leads to recovery. The exception is the congenital form of the pathology, but even in this case, the methods of modern medicine provide a person with long-term remission.
The patient should also be checked for cancer of various locations. First of all, it is necessary to exclude malignant lesions of the circulatory system (leukemia). As a rule, these pathologies are accompanied by deviations from the norm in all parameters of a clinical blood test.
Despite the fact that phagocytosis is not the main function of basophilic granulocytes, their increase can be observed during infectious infections. For example, tuberculosis, chickenpox or viral flu. The human immune system is activated and the production of all protective blood cells is increased.
Also, the level of basophils can increase in chronic myeloid leukemia (eosinophilic-basophilic associations), myxedema (decreased synthesis of thyroid hormones), nephrosis, Hodgkin's disease, after splenectomy, as well as during therapy with estrogen and antithyroid drugs.
- the need to take medications. Especially if they contain components that cause an allergic reaction;
- introduction of foreign proteins;
- a latent inflammatory process that does not manifest itself in the form of clinical symptoms. In this case, it is recommended to undergo a comprehensive examination and exclude low-grade inflammation;
- a recent vaccination or insect bite, which can trigger an allergic response.
Therefore, if you receive results that deviate from the norm, you should not worry. It is recommended that the child be tested again 5-7 days after eliminating the influence of external factors.
If elevated values are repeatedly detected, a large-scale diagnostic examination of the small patient is carried out in order to establish a diagnosis. The reasons for the increase in the concentration of basophilic granulocytes are similar to adult patients.
Note: The norm of lymphocytes in the blood of a child by age is in the table
Reasons for increased basophils in the blood
The main reasons for the increase in basophils are due to:
- Acute and chronic pathologies in the respiratory, urinary and gastrointestinal systems;
- Maximema and hemolytic anemia;
- Chickenpox and the development of diabetes;
- Oncological neoplasms in bronchial and pulmonary tissues;
- Various types of intoxications;
- A consequence of taking hormonal drugs for endocrine pathologies;
- Taking corticosteroid and estrogen-containing drugs.
The manifestation of basophilia in women is typical in the initial period of menstruation and during the ovulation process. Another reason for a high level of granulocytes is a decrease in red blood cells and hemoglobin in the blood as a result of the development of hematological syndrome (anemia).
In a child, the level of elevated basophils indicates the possible development of acute or chronic processes in the body. They are caused by the same problems that are typical for adults. To these can be added exposure to toxic toxic substances and parasitic infestations. In addition to the registry are various benign (polycythemia) and cancer diseases of the blood and lymph system (acute or chronic leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis).
Pathologies caused by allergies or a wide group of diseases of the hematopoietic system are the most common causes of the development of basophilia in children. What can elevated basophils mean in a child? This is, first of all, the main symptom of a depleted and incompetent immune system.
Elevated
According to all standard indicators, during a blood test, the change in basophils should not be higher than one percent. Exceeding this mark indicates the presence of an infectious disease, a dysfunction of the immune system and a number of other problems:
- Hypothyroidism is a disease of the thyroid gland that occurs when there is a lack of iodine in the body.
- Diseases of the digestive system – ulcerative colitis, stomach ulcer.
- Myeloid leukemia, granulomatosis.
- Various types of allergies.
- Viral infections.
Increased basophils during viral infections
Also, increased basophils can serve as a diagnostic sign of iron deficiency, in some cases of lung cancer. Patients who have had their spleen removed have persistently elevated basophil counts.
Reasons for the decrease or absence of basophils
A decrease in the level of segmented granulocytes, or a complete absence of basophils in the structural composition of leukocytes is called basopenia. Such a manifestation may indicate a significant decrease in phagocytic functions and a violation of the body’s ability to adequately respond to the manifestation of allergy reactions. This is facilitated by:
- Presence of acute infectious diseases;
- Excessive hormonal activity of the thyroid gland and hyperactivity of the adrenal glands;
- Stressful situations and exhaustion of the body;
- Excessive activity and stress.
But not every condition with basopenia is a pathology and requires a drug response. Often the return to normal goes away on its own or is considered normal.
For example, at the beginning of pregnancy, basopenia is the norm, since its manifestation is due to an increase in the total blood volume, characteristic in this condition, against the background of which the number of segmented granulocytes, remaining within normal limits, is shown in the leukocyte analysis to be a reduced level per volume unit liquid fraction.
Basophil norm
The normal number of basophils varies depending on age and is calculated as a percentage of the total number of white blood cells in the blood:
- for an adult: 0.5-1%;
- newborn: 0.75%;
- 1 month: 0.5%;
- 1 year: 0.6%;
- 2 years: 0.7%
As you can see, the norm of basophils in the blood is from 0.5% to 1% of the total number of leukocytes. In absolute value, this comes out to approximately 0.3 nanoliters per liter of blood.
How to bring basophils back to normal?
If an increase in basophils is detected in the tests, it is the prerogative of the doctor to deal with the problem. Self-treatment will not give results and will only harm your health. The basis of therapeutic treatment is the relief of background pathology. The reason is due to prolonged use of hormonal therapy, which can be stopped by stopping the drugs or replacing them with similar ones, without side effects.
At the end of the drug course of treatment of infections and inflammation processes, auxiliary vitamin therapy is prescribed to restore the structural composition of the blood. These can be complex vitamin preparations, an individually selected diet, rich in foods containing group “B” vitamins, which helps improve hematopoietic processes.
Long-term manifestation of signs of basophilia is a clear presence of a course of chronic pathologies that need to be urgently diagnosed and eliminated.
The prognosis of basophilia and basopenia depends on successful treatment of the underlying cause that caused the quantitative structural instability of leukocyte cells, and on the level of viability of immune functions.
- Timely treatment of pathological conditions and regular monitoring of basophil levels can protect against many diseases.
Tags: analysis
- Low hemoglobin: causes and consequences in adults and children
- Urticaria in adults: photos, symptoms and treatment,…
- Rhinopharyngitis - symptoms and treatment in children and adults
- Vasomotor rhinitis - symptoms and treatment in adults...
- Vitamin deficiency - symptoms, photos on the skin, treatment for children and...
- Glaucoma - causes, symptoms and treatment, disease prevention
What to do if basophils in the blood are elevated
In most cases, basophilia can be cured if the immediate cause of its occurrence is eliminated, in particular, the underlying disease is cured. But in some cases, a high level of basophils can be observed in relatively healthy people, then you need to use these recommendations:
- Increase the body's saturation with vitamin B12, because it is actively involved in the formation of blood cells and brain function. This can be done by taking special medications or adding meat, kidney, eggs and milk to your diet.
- Include iron-containing vitamins and foods in your diet: liver (especially chicken), buckwheat, fish and other seafood.
If basophils in the blood are elevated, in some cases, it is enough to stop taking medications: antithyroid, estrogen-containing and the like. In women, basophilia can be observed during ovulation, in the first days of the menstrual cycle, and also during pregnancy. This is due to a direct relationship between the level of estrogen and progesterone in the blood and the number of basophils.
(Visited 26,048 times, 8 visits today)
Functions of basophils
Basophils are carriers of many substances that the body needs. They are involved in the transport of stimulating factors, which are aimed at the production of compliment, immunoglobulin E, and cytokines. These cells are responsible for immediate reactions; they take part in the development of anaphylactic shock. In just a few seconds, a person may require emergency medical assistance.
Basophils are responsible for the production of serotonin, heparin, histamine, proteolytic enzymes, prostaglandins and other biologically active substances. When pathogens enter the body, basophils quickly go to the right place and force all of the above substances to come out of their membranes and “save” the human body (capillaries expand, tissue regenerates, eliminates inflammation, etc.).
Basophils are responsible for the production of heparin, which prevents blood clotting and the formation of blood clots.
What to do if the level of basophils increases and what could this mean?
If the results of a blood test reveal that basophils are elevated, there is serious reason to worry. The number of these blood cells is insignificant, but their role in the body is enormous. That is why any deviations should not be ignored.
Basophils under a microscope
What are basophils?
First, let's look at what kind of cells these are - basophils. They belong to the category of leukocytes, that is, white blood cells. This is a special form of so-called granulocytes. They indirectly take part in protecting the body from infections and irritants.
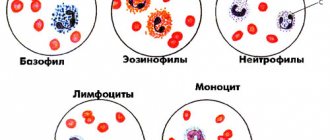
Types of granulocytic leukocytes
Nature of education and standard of maintenance
Basophils are formed in the bone marrow, namely in the granulocytic process. They enter the peripheral bloodstream, thus being distributed throughout the tissues. There they perform their functions, remaining in the body for up to twelve days.
The human body produces basophils in small quantities. The norm for the general lymphocyte formula ranges from 0.5-1%. This amount is quite enough for healthy activity, and any deviations often indicate pathological processes. The absolute value of the norm is 0.01-0.065*109 units per liter of blood.
| White blood cell shapes | Leukocyte content | |
| % | absolute values (X 109/l) | |
| Band neutrophils | 1-6 | 0,04-0,3 |
| Segmented neutrophils | 47-72 | 2,0-5,5 |
| Eosinophils | 0,5-5 | 0,02-0,3 |
| Basophils | 0-1 | 0,0-0,065 |
| Lymphocytes | 19-37 | 1,2-3,0 |
| Monocytes | 3-11 | 0,09-0,6 |
Table: Norms for the content of basophils and other forms of leukocytes
If basophils are elevated in an adult, the condition is called basophilia. Minor fluctuations are allowed in some categories of people, for example, women, which is associated with the menstrual cycle and hormones.
To understand what basophils are in a blood test, it is necessary to take a closer look at their functions.
Cell functions
Basophilia indicates malfunctions in certain areas of the body, for which the corresponding cells are responsible.
Important! Basophils are not directly involved in maintaining immunity. Other groups of lymphocytes play an active role.
Basophils synthesize substances such as serotonin, heparin, histamine, leukotrienes, prostaglandins, that is, highly active compounds that can affect a person’s condition when faced with a foreign irritant.
The function of cells of this type is as follows:
- participation in allergic reactions;
- identification of foci of inflammation and infections;
- provoke contraction of smooth muscles, accelerating blood flow;
- promote the formation of new capillaries;
- phagocytosis;
- regulate blood clotting.
If basophils in the blood of an adult are elevated, it means that in one or more directions there is a need to increase the number of these cells due to a disruption in normal life.
Main functions of basophils
Important! The main task is to recognize and respond to allergens. In this case, the reaction can occur rapidly in the form of anaphylactic shock, when only basophils take part. When lymphocytes join, a delayed-type allergy occurs, which is less dangerous for humans.
Symptoms and causes of increase
Specific symptoms that basophils in the blood are elevated are quite difficult to identify. It all depends on the reason that provoked the deviations. In general, the following conditions may occur:
- weakness;
- slight increase in temperature;
- skin rash, itching, redness;
- cough;
- lacrimation, swelling;
- joint pain;
- bowel dysfunction;
- spontaneous weight changes;
- enlarged spleen;
- liver problems.
Also study the article on why lymphocytes may be low in adults on our website.
Allergic symptoms may indicate basophilia
When the level of basophils rises above normal, certain signs of pathology make themselves felt. It is extremely rare that nothing indicates hesitation. The absence of symptoms may be due to changes in the body in women (menstruation, ovulation, pregnancy).
It also often happens that segmented neutrophils are elevated in the blood. In this case, you should become more familiar with the causes of this pathology.
In pregnant women, mild basophilia is normal
The main causes of basophilia are as follows:
- reaction to an allergen;
- chronic sinusitis;
- helminthiasis;
- early stage of infectious diseases;
- immune depletion;
- diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- anemia;
- Hodgkin's lymphoma;
- thyroid dysfunction, diabetes;
- hepatitis;
- removed spleen;
- pulmonary oncology;
- chronic gastrointestinal diseases;
- carrying out radiation therapy;
- taking hormonal drugs.
To find out the exact picture and causes of the disorders, it is necessary to conduct a detailed blood test, as well as a number of additional studies. This is especially true for those patients who are suspected of having serious pathologies.
Solution
The basophil count can be brought back to normal only through high-quality treatment of the underlying disease that caused its increase. Only after eliminating the irritant are positive changes possible.
If we are talking about allergies, in order to find out which substances cause an undesirable reaction, a basophil activation test is performed. For this purpose, cells obtained from the patient's blood are used. The in vitro method is used so as not to put human health at risk or cause discomfort during the experiment.
Note: the body's reaction to the substances used allows us to identify previously unknown potential sources of allergens. This test is especially relevant in the presence of atopic dermatitis.
You can partially normalize basophils in the blood when they are elevated in the following ways:
- stop using medications that can provoke increased synthesis of these cells;
- enrich the menu with iron-containing products;
- eliminate vitamin B12 deficiency.
It is recommended to compensate for vitamin B12 and iron deficiency
If you have basophilia, you should definitely check with your doctor about the cause of its development and take measures to eliminate it. Although there are not as many of these cells in the human body as other lymphocytes, an increase in their concentration, even a small percentage, can negatively affect health, and sometimes even threaten life, as in the case of the development of a rapid allergic reaction.
We recommend studying similar materials:
- 1. Causes and dangers of increased basophil levels in children
- 2. The level of basophils in adults has decreased: how to treat basophilia
- 3. Reasons for an increase or decrease in neutrophils in a blood test in children?
- 4. Functions and possible causes of pathologies of segmented neutrophils
- 5. What does a high level of neutrophils mean and is it dangerous?
- 6. What do elevated eosinophils mean in a blood test in adults?
- 7. Proper nutrition for high levels of bilirubin in the blood
moyakrov.ru