Diagnostics
If there is an assumption regarding sinus tachycardia, the woman must undergo a series of diagnostic measures.
Thanks to this, it will be possible to detect possible pathologies and prevent the development of consequences. First of all, a pregnant woman should visit a gynecologist. You will also need to donate blood and urine. Their analysis will allow you to estimate hemoglobin and the number of red blood cells. In addition, laboratory test results will show whether the thyroid gland is normal. Very often, anemia in combination with disorders in the endocrine system leads to an increase in heart rate.
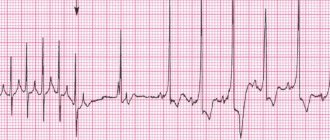
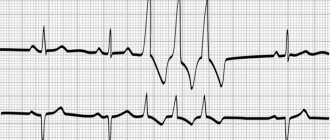
The patient still has to undergo an ECG, which will give an idea of the work of the heart muscle. The conclusion of this study contains the position of the EOS (electrical axis of the heart), which can be vertical, horizontal, normal, deviated to the right or left side.
If necessary, Dopplerography or echocardiography will be prescribed, after which it will be possible to find out what kind of tachycardia we are talking about, and whether there are organic lesions in the heart and vascular system. The final stage will be a visit to a cardiologist, endocrinologist and neurologist.
Symptoms of fetal tachycardia
Pathology can be suspected based on several symptoms. One of them is an increased heart rate in the mother. It can reach 120 beats/min. and higher.
A woman may also exhibit other signs:
- dizziness;
- attacks of nausea;
- heartache;
- general weakness;
- numbness of different parts of the body;
- increased irritability;
- sleep problems.
Problems with blood flow can interfere with the normal functioning of the immune system. This leads to frequent illnesses.
Causes of failures in pregnant women, risk factors
The development of cardiac tachycardia during pregnancy is promoted by:
- an increase in blood volume, which causes a compensatory increase in heart rate;
- hormonal levels change (estrogen production is activated), which causes myocardial excitability;
- The uterus increases in size, limiting the mobility of the diaphragm, abdominal pressure increases and the position of the heart changes.
The condition is considered normal if there are no cardiovascular pathologies. But if they are present, such a condition can be dangerous to the health of both the expectant mother and the child.
Risk factors also include:
- excess weight;
- anemia (anemia);
- allergic reactions of the body to medications and vitamin preparations;
- excessive thyroid function;
- bronchial asthma;
- drinking coffee, tea;
- infections and inflammations of the respiratory system;
- bleeding due to ectopic pregnancy, trauma, early placental abruption;
- toxicosis, in which dehydration and exhaustion of the body occur;
- a sharp increase in body temperature (one degree increases the frequency of contractions by 10–12 units);
- frequent stress, excitability, anxiety;
- infections, sepsis;
- bad habits - alcoholism, drug addiction, nicotine addiction.
Etiology
Normally, the heart rate is 60–80 beats per minute, a pulse above 80 beats is tachycardia, below 60 beats is bradycardia. In pregnant women, heart rate does not deviate from the norm; it may increase slightly only after exercise. Why does tachycardia occur, and is it always necessary to treat it? First, let's look at the reasons, there are quite a lot of them:
- weight gain and its rapid accumulation during pregnancy;
- as a result of the growth of the uterus, pressure is exerted on the blood vessels and diaphragm;
- anemia;
- thyroid diseases;
- increase in body temperature (with an increase of 1 degree, the pulse accelerates by 10 beats);
- with toxicosis as a result of dehydration;
- increase in circulating blood volume;
- changes in hormonal levels.
How to treat tachycardia
Tachycardia should be treated by a cardiologist who coordinates his actions with a gynecologist. The woman is prescribed sleep, lack of stress, and relaxation in a calm environment, for example, in a sanatorium near her home. If this does not help, then drug therapy cannot be avoided.
A violation is considered to be a rapid heartbeat that occurs on its own, for no apparent reason. The first step is to eliminate the cause of the tachycardia, which should lead to an improvement in the patient’s health. In the future, doctors’ recommendations are reduced to stopping attacks and relapses.
General treatment looks like this:
- In the first trimester, a pregnant woman is advised to rest, which can be provided by mild sedatives: Valerian, Motherwort. To maintain the heart muscle and strengthen the immune system, it is advisable to drink decoctions with hawthorn and rose hips.
- Pathology that worries the patient during the 2nd trimester is treated in the same way as in the 1st trimester.
- In the 3rd trimester, the doctor prescribes more intense sedatives, taking into account the developmental characteristics of the baby and the woman’s age. Vitamins and minerals are also shown.
Treatment of tachycardia
During an attack of tachycardia, a woman should first of all calm down, relax and rest (read more about relieving an attack of tachycardia at home here). Most often, the heartbeat is restored. In cases where it does not disappear, you need to contact a gynecologist. The doctor will diagnose and prescribe treatment depending on the cause.
A slight deviation from the norm is considered acceptable. This is due to the fact that the mother’s body works for two. There is no need to worry about this condition. Nervousness and anxiety can only make the situation worse.
There is no need to worry especially when tachycardia or arrhythmia occurs during physical activity. This is a normal reaction of the body to changes occurring. After a short rest, your heart rate will return to normal.
When tachycardia is established, when the attacks are prolonged and quite strong, sedatives and vitamin complexes are prescribed. All medications are prescribed only by a doctor. Taking medications on your own or conducting therapy at home is strictly prohibited.
Treatment of tachycardia in the fetus and mother
If the mother's episodes of heart palpitations occur irregularly, such conditions may not require medication adjustment. In any case, additional research is needed to help determine whether these cases are simply a deviation from the norm or indicate the development of tachycardia and other abnormalities in the development of the fetal cardiovascular system.
It is desirable that every pregnant woman has in her arsenal a household Doppler monitor that allows her to independently measure her heart rate. It is recommended to repeat this procedure at least twice a day.
If attacks of increased heart rate are regular, it is recommended to take the following measures to independently relieve such conditions:
- eliminate physical inactivity (long sitting at the computer/TV), walk more in the fresh air;
- adjust your diet (include in the menu foods containing “heart vitamins” - magnesium and potassium - these are dried fruits, fresh vegetables/fruits, beans, side dishes from whole grains);
- include herbal tea with a calming effect in the menu (melissa and mint have this effect).
If an attack of tachycardia has begun, you should take a lying/sitting position and try to relax, abstracting from everyday problems, which is facilitated by breathing exercises
Is sinus tachycardia dangerous during pregnancy?
By understanding what sinus tachycardia can cause in pregnant women, what it is, and how to treat it, it will be possible to prevent serious consequences. A strong heartbeat is considered dangerous, which is accompanied by an increase in heart rate (HR) over 100 beats per minute. At such a moment, a woman may complain of discomfort in the chest area and heart pain.
A jump in heart rate to 140-200 beats/minute is extremely dangerous. In this case, the duration of the attack can be several hours or days. This condition may be associated with a focus of excitation within the conduction system, where impulses are regenerated. It often originates in the ventricles and atrium cells. In this regard, ventricular and atrial tachycardia are distinguished.
If a pregnant woman experiences palpitations, a drop in blood pressure, dizziness, increased sweating, nausea or a feeling of tightness in the heart area, then the help of medical specialists is required. Without adequate treatment, there is a high risk of serious consequences.
With increased heartbeat, the birth process may occur with complications. In addition, against the background of a persistent increase in heart rate, a woman may begin to give birth earlier than expected.
Main symptoms
Regardless of the causes of sinus tachycardia in pregnant women, it manifests itself in the same way. The main clinical sign is an increase in heart rate to 100–120 beats per minute. For a pregnant woman, such a condition is a completely physiological process while maintaining a normal heart rate. In this way, the body creates favorable conditions for the development of the baby, since providing the placenta with the proper amount of nutrients and oxygen requires a lot of effort. All this makes sinus tachycardia an adaptive mechanism. However, there are a number of symptoms that accompany palpitations that are worth paying special attention to:
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Dizziness and loss of consciousness.
- Pain in the heart area.
- Numbness of various parts of the body.
Such clinical signs indicate the possibility of serious complications. If they occur, you should immediately consult a doctor.
In addition to sinus, the development of paroxysmal tachycardia is possible. Such a change in heart rate is characterized by a violation of the normal rhythm of heart contractions and is pathological. The pulse can increase to 180–200 beats per minute. If such tachycardia is combined with pain or general weakness, you should seek medical help.
Treatment
An attack of tachycardia may appear suddenly. At the same time, the expectant mother is able to help herself on her own. To do this you need:
- Open a window or go outside to get some air.
- Slowly take a few as deep breaths as possible.
- Take an approved sedative during this period, for example “Valerian extract”.
- Wash with cold water or apply a cool compress to your face.
As soon as the condition returns to normal, you need to rest, lie down, read a book, relax.
If such attacks occur frequently, the woman needs to be examined. After this, taking into account the duration of pregnancy, the doctor will prescribe the necessary therapy.
In the first half of pregnancy, the cause of tachycardia is mainly hormonal changes. In this case, it is recommended to use medications that strengthen blood vessels and the immune system, as well as sedatives based on herbal components. In the second half of pregnancy, additional vitamin and mineral complexes may be prescribed.
Any medicine can be taken only on the recommendation of a doctor. In this case, the following may be prescribed:
- Sedatives. During this period, preference is given to products based on herbal components (Valerian, Novo-Pasit, Magnesium B6, etc.).
- Antiarrhythmic drugs (Adenozyme, Propranolol).
Impact on childbirth
A special question is how to give birth with sinus tachycardia. It all depends on two factors:
- degree of tachycardia severity;
- reasons for heart rate acceleration.
The doctor will evaluate these factors and offer different options.
Moderate tachycardia, which developed during pregnancy, is not considered an indicator for cesarean section. It occurs in many pregnant women, and only one in ten cases requires medical intervention during childbirth.
If the acceleration of the pulse is associated with cardiovascular diseases, but the general condition of the woman in labor is good, she is offered the option of giving birth in a special maternity hospital, under the supervision of cardiologists.
In case of paroxysmal tachycardia and unfavorable accompanying factors, the patient is offered elective surgery. Most women have a favorable outcome from this surgical procedure.
Reviews from obstetricians and gynecologists about most cases of accelerated heart rate in expectant mothers are encouraging: usually tachycardia does not harm the baby, and only creates some discomfort for the mother during pregnancy. The situation can be controlled and the forecasts are positive. Complications usually occur only in women with a history of complications.
The danger of tachycardia attacks during pregnancy
A slight increase in heart rate does not threaten the health of the pregnant woman and is even considered normal. With an increased heart rate, the heart pumps a large volume of blood, which contributes to normal oxygen exchange for the child and saturation of his body with nutrients. The fetus, receiving all vital elements, develops and grows normally.
But in the case of frequent and prolonged tachycardia, serious complications can arise:
- If the heartbeat increases due to diseases of the heart or circulatory system, then there is a risk of developing a stroke and even a heart attack. Accordingly, this can result in death for the fetus or mother.
- With increased heart rate, the heart works hard.
- Problems may arise with a woman’s well-being during labor.
Treatment of tachycardia during pregnancy
To get rid of minor attacks of increased heart rate in the initial stages of pregnancy, you should take the most relaxed position (lie down on the bed or sit on a chair), restore your breathing, taking slow deep breaths and exhalations, and close your eyes for a while.
Tachycardia requires medical treatment when:
- deterioration of health, pain and anxiety during an attack;
- sudden onset of an attack and immediate weakening (paroxysmal form);
- the appearance of nausea and gag reflexes.
If the cause of tachycardia is known, then treatment is aimed at eliminating it. When the etiology remains unknown, therapy relieves symptoms, restores heart rhythm and prevents the development of complications.
Medication methods are often used, and the drugs are selected taking into account the absence of contraindications during pregnancy:
- Sedatives created on the basis of components of natural origin, that is, herbs. Safe medications: liquid or tablet valerian, motherwort, Concor, Magne B6, Etatsizin, Persen, Novo-Passit, Magneorot. The drugs are aimed at calming the nervous system and reducing the frequency of tachycardic attacks.
- Antiarrhythmic drugs help restore heart rate. The presented group is prescribed exclusively by a specialist, since many drugs are contraindicated during pregnancy and have various adverse reactions. The most commonly used are Verapamil, Adenosine, Flecanil or Propronolol.
Features of treatment depending on the etiology of the origin of tachycardia:
- If a pregnant woman has a rapid heartbeat due to chronic diseases, then urgent therapeutic measures are prescribed.
- For non-pathological factors of tachycardia (bad habits, physical activity, stress, etc.), medications should not be taken. The only acceptable drugs are sedatives. To maintain the heart in normal condition, the doctor will prescribe magnesium supplements. A pregnant woman is recommended to relax, get enough sleep and take a walk in the fresh air.
Treatment based on trimester:
- In the first trimester of pregnancy, therapeutic measures are necessary, since tachycardia attacks are a pathological disorder, even if their causes are physiological. Medications are required. Additionally, it is recommended to take products based on herbal components to strengthen the immune system.
- In the second trimester, treatment is often not required, since tachycardia of pregnant women may appear from the 12th week. But if tachycardia brings discomfort to the pregnant woman and worsens her well-being, then treatment is still prescribed.
- In the third trimester (especially from 32 weeks), tachycardia is most often the norm, so there is no specific therapy. The expectant mother is recommended to consume more vitamin and mineral complexes. If necessary, you can use sedatives prescribed by your doctor.
Is treatment required and what should it be?
Treatment of tachycardia in pregnant women is prescribed based on the diagnostic results of ECG, echocardiography, and hormonal balance tests. Heart failure requires treatment without delay.
The therapy is based on blocking adrenaline, a hormone that provokes the frequency of contractions of the heart muscle. The difficulty is that most cardiovascular drugs affect the development of the fetus - hence the selective and careful prescription.
The priority is therapy of plant origin: collections of motherwort, valerian, anise and yarrow, lemon balm.
Physical therapy is prescribed so that in the future the mother’s body can cope with the increasing load. In the extreme, it is recommended to eat small and often meals. Tachycardia after eating during pregnancy is a common occurrence. A full stomach puts pressure on the heart, which makes you feel worse and intensifies attacks.
Is sinus tachycardia dangerous during pregnancy?
If sinus tachycardia in pregnant women is not caused by serious disorders in the functioning of the heart, then it can be successfully treated with the help of sedatives and agents that are designed to saturate the expectant mother’s body with catalytic ions of calcium, phosphorus and potassium. If therapy is not carried out, a pregnant woman may experience a feeling of anxiety, sleep disturbance, and the defenses of an already weakened body may also decrease. Persistent arrhythmia can provoke pressure changes, which, in due course, can cause problems in the functioning of the heart.
If the symptoms of sinus tachycardia are associated with heart disease, then failure to consult a doctor in a timely manner can lead to a deterioration in the general condition of the expectant mother. The risk of losing the baby and complications during childbirth may also increase.
Especially for beremennost.net Anna Zhirko
What are the reasons
The causes of the disease in a pregnant woman are the following factors:
- Fetal growth and development;
- Increased load on the heart muscle due to the common circulatory system in the woman and fetus;
- The mother's heart feels compressed;
- Acceleration of metabolism;
- Various pathologies of heart development in the fetus.
We note the fact that the causes of tachycardia during early pregnancy must be identified and monitored with special attention. After all, the fate of the pregnancy itself, the fetus and the expectant mother in particular largely depends on the correct diagnosis of a woman.
After all, a mild degree of sinus tachycardia in pregnant women is considered normal and does not require virtually any treatment. Attacks of too fast heart rate occur and disappear suddenly. What to do?
At this time, you just need to try to calm down and stop yourself from being nervous. After all, the heart of the expectant mother works “for two”, so it contracts somewhat more intensely than usual. This is why sinus tachycardia is so common in women in the last trimester.
But if a patient is diagnosed with a pathological form of the disease during pregnancy, then this condition requires attention from doctors.
Fetal heartbeat
It turns out that tachycardia can also develop in the fetus. Let's consider the factors that provoke it:
- heavy blood loss in the mother;
- diseases of the endocrine, circulatory, respiratory systems;
- fetal infection;
- circulatory disorders in the umbilical cord;
- fetal hypoxia;
- airway obstruction;
- pathologies in child development.
If even the slightest signs of tachycardia are detected in the fetus, the woman is prescribed a number of additional examinations:
- echocardiography;
- Ultrasound;
- Dopplerography.
Based on the research results, a decision is made on the treatment of tachycardia in the fetus during pregnancy.
Why is tachycardia dangerous for pregnant women?
As a rule, tachycardia is extremely rarely diagnosed in early pregnancy. Basically, rapid heartbeat is associated with physical exertion or stressful situations, as well as hormonal instability. Such manifestations are considered normal and can be easily eliminated. However, they should not be neglected. Negligent attitude towards your health can cause:
- sleep disorders;
- anxiety;
- diseases of the circulatory system;
- serious decrease in immunity.
Tachycardia in the later stages, both in the fetus and in the mother, can lead to serious bleeding and the onset of labor before the period of pregnancy.
Prevention
The most important measure to prevent tachycardia in the fetus is careful pregnancy planning. All chronic diseases should be treated and your diet and lifestyle should be changed in advance.
During pregnancy, you need to control your diet and walk in the fresh air more often. You should not skip visits to the doctor - various pathologies may be identified at the appointment, even if the woman herself does not feel any changes.
During pregnancy, it is important to avoid stressful situations, worries, and panic. If a strong surge of emotions does occur, then you should try to relax as much as possible. It is useful to practice breathing exercises.
Tachycardia in the fetus is common. In most cases, this problem can be solved without unpleasant consequences, provided that it is identified in a timely manner and treated correctly under the constant supervision of the attending physician.
Treatment with traditional methods
In any trimester of pregnancy, the treatment regimen is the same:
- a woman should rest and sleep more;
- it is necessary to exclude stressful situations, that is, to provide her with a normal psycho-emotional state;
- It is necessary to eat only healthy foods and avoid harmful ones.
Drug therapy allowed during pregnancy:
- Novo-Passit.
- Valerian.
- Persen.
- Motherwort.
- Ethacizin.
- Magne B6.
- Magnerot.
- Hawthorn forte.
- Phenobarbital.
- Concor.
- Diazepam.
Reasons for the development of pathology
If a pregnant woman experiences frequent heart palpitations, this may negatively affect the development of her baby.
One type of tachycardia is the sinus form. In this condition, electrical impulses very often occur in the sinus node, which leads to contraction of the atrium on the right side up to 120 beats per minute. Such a violation occurs due to metabolic changes, heart pathologies, intoxication of the body, and pregnancy. According to the international classification of diseases, sinus tachycardia is assigned an ICD-10 code.
There are physiological and pathological forms. The first is a reaction to external stimuli, and the second occurs against the background of sinus node dysfunction. As for pregnancy, in this condition a woman may experience tachycardia for the following reasons:
- excessive stress on the heart and central nervous system;
- hormonal changes;
- increased work of internal organs;
- increased tissue metabolism;
- change in the location of organs due to an enlarged uterus.
The mechanism of development of tachycardia can also be triggered by physical activity in the presence of organic heart damage. This attack can occur as a result of an allergic reaction, infection of the body, bradycardia, fever, toxicosis, dehydration, stress, or drug overdose.
Causes
Common causes of abnormal heart palpitations are:
Tachycardia can be diagnosed long before the onset of an “interesting” situation and not cause discomfort. In this case, we are talking about the physiological individuality of the body and manifests itself as a symptom of heart failure.
Pregnant women with tachycardia need an individual approach with the complete exclusion of stressful conditions.
Atrial view - beats reach 250 per minute. The cause is located in the atrium. There are supraventricular and supraventricular.
Paroxysmal type - heart rate accelerates and reaches from 140 to 250 per minute. The focus is located in the ventricle of the heart.
The danger of this type lies in the possibility of death due to disruption of cardiac activity and blood supply to the organ.
Signs and diagnosis of tachycardia during pregnancy
Speaking about the diagnosis of tachycardia, one should take into account the individual characteristics of the body of each expectant mother. Some feel great even if they are overweight, while others feel their heart jump out at the slightest excitement. However, there are symptoms that indicate a possible threat to the health of mother and baby. It is necessary to “sound the alarm” if:
- there is an increase in heart rate without physical activity (more than 90 beats per minute);
- loss of strength and drowsiness often occur;
- the head is spinning, parts of the body are numb, noise is heard in the ears;
- there are fainting states with nausea, bouts of sweating and digestive disorders;
- pain spreads to the heart area;
- the condition is aggravated by increased anxiety and irritability.
An increased heart rate is a normal “companion” of pregnancy, and such attacks in themselves should not cause panic in the expectant mother.
However, if any of the listed symptoms are added to them, and even for a long time, consultation with a doctor is necessary as soon as possible in order to exclude serious complications of pregnancy. Diagnosis of tachycardia consists of:
- consultations with doctors (gynecologist, cardiologist, endocrinologist, etc.);
- conducting an electrocardiogram and Doppler ultrasound to monitor the heart rhythm;
- behavior of echocardiogram and ultrasound to determine the functioning of the heart, blood vessels and identify pathologies.
A comprehensive examination will help the doctor identify the root causes of tachycardia and give the necessary recommendations to alleviate the condition of the pregnant woman.
Review of reviews from pregnant women about the problem
Tachycardia during pregnancy has received conflicting reviews from cardiologists and patients. As experts assure, in practice the permissible rate of beats per minute exceeds 100 and is purely individual. Depends on body weight, blood volume and overall health. Often, patients at rest have a pulse of 120-135 beats, without experiencing any particular discomfort.
It has also been noted that in most cases, the second and subsequent gestations are easier from the point of view of cardiac work.
Complex treatment
Treatment tactics are selected based on the reason why the heart rate increases. The essence of therapy is to eliminate the pathology that caused the tachycardia. This will improve the condition of the pregnant woman and eliminate relapses. To stabilize the heart rate, an integrated approach is used:
It is extremely important to ensure complete rest for the woman in the first trimester of pregnancy. An increase in heart rate is often associated with hormonal changes in the body
Natural sedatives may be prescribed as treatment. These include valerian and motherwort. At the same time, it is recommended to take medications that help strengthen the heart and the body’s protective functions. Rosehip and hawthorn have similar properties. If tachycardia accompanies a pregnant woman throughout the second trimester, treatment is the same as in the early stages. The third trimester is very often characterized by a rapid heartbeat, because the growing fetus puts serious pressure on all the organs of a pregnant woman. Sedatives, vitamins, and minerals can be used for therapeutic purposes.
Any pills during pregnancy should be taken with extreme caution and be sure to consult a doctor. If more serious treatment is required, the patient may be prescribed the following drugs:
- Sedatives. This group of medicines is made using medicinal plants. But at the same time they can be synthetic, such as Phenobatbital and Diazepam. They are prescribed for palpitations and VSD. The most popular of them are represented by such drugs as Novo-Passit, Magne B6, Persen, Concor. Thanks to the action of sedatives, it is possible to put the nervous system in order and reduce the number of attacks of tachycardia.
- Antiarrhythmic. Prescribed only as prescribed by the attending physician. It is very dangerous to self-medicate at home, especially during pregnancy. Uncontrolled use of these drugs can cause adverse reactions. The most effective drugs in this group include Adenosine, Propranolol and Flecanil. Their action ensures normalization of heart rate.
- Beta blockers. Suppress adrenaline-sensitive receptors. Most of them involve long-term use. Of this group of drugs, Timolol, Esmolol, and Atenolol are most often prescribed.
- Calcium channel blockers. Provide blocking of channels involved in the mechanisms of heart contraction.
Ventricular tachycardia requires immediate treatment. To cope with a sudden attack, a woman should try to calm down and get some fresh air. The Validol tablet will help muffle the attack. When the patient is admitted to the hospital, she may be given the drugs Quinidine and Novocainomide. If a paroxysmal form of tachycardia is detected, intravenous administration of antiarrhythmic drugs is prescribed.
Tachycardia in the fetus during early and late pregnancy: causes, diagnosis and treatment
During pregnancy, the condition of the fetus is regularly monitored. Particular attention is paid to the work of the heart. Often, children are diagnosed with a rapid heartbeat during antenatal development.
This happens both in the early stages of gestation and in later stages.
How is tachycardia manifested and diagnosed in the fetus? What are the reasons for this phenomenon? How dangerous is it? What therapeutic measures are taken to eliminate it?
What is tachycardia?
In medicine, this term means an increase in heart rate to 90 beats per minute or more. In this case, tachycardia can be understood as both a pathological condition and a normal physiological phenomenon.
In the first case, there is intense heartbeat at rest, which is regarded as a painful symptom. In the second case, an increased heart rate is caused by physical exertion, anxiety or fear. This phenomenon is short-term and does not pose a threat to health. Tachycardia is not a disease; it is regarded by doctors as a manifestation of various pathologies.
Diagnostic tests for fetal heartbeat
The decision on the need for diagnosis is made by the doctor based on the complaints of the pregnant patient. After analyzing them, the specialist prescribes a series of diagnostic procedures for the expectant mother in labor. Information about the methods used to study the work of a child’s heart is presented in the table.
| Diagnostic methods | abbreviated name | Description | At what stage of gestation is it performed? |
| Ultrasound examination of the heart | Ultrasound | Diagnosis of tachycardia and identification of associated pathological processes | After 6 weeks |
| Echocardiography | ECG | Diagnosis of heart defects | From 5-6 weeks |
| Cardiotocography | CTG | Analysis of the contractile activity of the uterus and the frequency of contractions of the fetal heart muscle | From 30 weeks |
| Auscultation | Absent | A study of the heart, which consists of listening to the patient’s abdomen using a stethoscope | After 18-20 weeks |
| Doppler study | Doppler | Assessment of the nature of atrial contractions in the fetus, as well as the state of blood circulation in the myocardium | Starting from 21-22 weeks |
Symptoms of fetal tachycardia in pregnant women
With this disruption of the heart in the fetus, a pregnant woman feels a strong heartbeat of up to 120 beats per minute and above. Against this background, she experiences attacks of nausea and dizziness. In addition, fetal tachycardia may be accompanied by:
- painful sensations in the chest;
- general weakness;
- rapid fatigue;
- disturbances in sleep and wakefulness;
- loss of sensitivity in various parts of the body;
- disturbance of psycho-emotional state.
If these symptoms appear, you should immediately seek medical help. Ignoring these manifestations is fraught with the development of severe complications, including the death of the child.
Causes of pathology
The causes of this pathological phenomenon are external and internal. The first type is associated with heart disease of the woman, the second is caused by disturbances in the functioning of the heart of the fetus itself.
Factors provoking the development of fetal tachycardia:
- use of certain medications during pregnancy;
- insufficient oxygen supply to the fetus;
- infection of the child in the womb;
- anemia;
- genetic abnormalities caused by chromosomal abnormalities;
- pathologies of the endocrine, respiratory, cardiovascular systems;
- disturbance of water-salt balance as a result of prolonged toxicosis;
- errors in nutrition that provoked insufficient intake of vitamins and essential microelements into the body.
Along with this, it is important to promptly identify other defects (anemia, oxygen starvation, intrauterine infections), because Prompt elimination of their signs will help prevent the occurrence of many complications.
Treatment tactics
If attacks of rapid fetal heart rate are regular, treatment of this pathological phenomenon is carried out in a hospital setting. In episodic cases of increased heart rate, normalization of the functioning of this organ is carried out on an outpatient basis. The table provides information on what methods are used to treat this pathological condition.
| Diagnosis | Medicinal treatments | Actions aimed at alleviating the condition during attacks of tachycardia |
| Polymorphic gastric tachycardia | Magnesium preparations are prescribed together with Propranolol and Lidocaine | If signs of this phenomenon appear, it is recommended to take a lying or sitting position, completely relax, and do breathing exercises. If there is no improvement, you should consult a doctor. |
| Heart rate exceeding 220 beats per minute | Antiarrhythmic drugs used: Amiodarone, Sotalol | |
| Intrauterine myocarditis | Dexamethasone indicated |
Until the 32nd week of gestation, antiarrhythmic medications are prescribed in extreme cases, because drugs in this group can do more harm to the fetal heart than help.
From the 36th week of pregnancy, in most cases they resort to drug treatment.
This is explained by the fact that in the later stages of the gestational process, when comparing the likely risk to the child’s health with the possible harm caused by drugs, the decision is most often made in favor of the first factor.
Consequences of tachycardia during intrauterine development
A regular increase in heart rate in the fetus is fraught with the following consequences:
- intrauterine death;
- stillbirth;
- birth earlier than expected;
- insufficient oxygen supply;
- genetic abnormalities;
- heart defects;
- delayed physical and mental development.
Preventive actions
To help avoid this problem:
- giving up bad habits at least 3 months before pregnancy;
- exclusion of excessive physical and emotional stress;
- good nutrition;
- taking vitamin complexes, previously agreed upon with the attending physician;
- daily long walks in the fresh air;
- a complete examination of the body at the stage of planning a child and elimination of identified pathologies.
Source: https://www.OldLekar.ru/beremennost/plod/tahikardiya-u-ploda.html
Tachycardia During Pregnancy - Causes and What to Do
Pregnancy is a happy, but difficult period in a woman’s life. Waiting for a child in itself is wonderful, but it becomes a real test for the body.
During pregnancy, a number of serious changes occur inside, and the load on it increases significantly. Therefore, during pregnancy, various diseases often “come to light”, the presence of which the expectant mother had not had the slightest suspicion before.
Tachycardia in pregnant women: what is it?
Normal heart rate ranges from 60 to 80 beats per minute. If this figure exceeds 100, then in this case it is customary to talk about the presence of tachycardia. A pulse in the range of 80 to 100 can also be considered a rapid heartbeat, but such an increase is not considered significant.
During pregnancy, a restructuring of the cardiovascular system occurs, which is primarily due to an increase in the volume of circulating blood.
What is tachycardia
Tachycardia is an increase in heart rate above 85 beats per minute.
The disease relates to the cardiovascular system. There are physiological and pathological. Pregnant women have both types.
Causes of physiological tachycardia in pregnant women:
- stress;
- feeling of fear;
- constant anxiety;
- physical activities;
- bad habits (alcohol, smoking);
- excess caffeine consumption;
- increase in the quantitative content of sex hormones;
- enlarged uterus.
Sinus tachycardia during pregnancy
During pregnancy, alarming pathological manifestations are often observed, indicating possible health problems. All these clinical manifestations must be carefully monitored, and their very appearance can be caused by a restructuring of the systems and organs of the pregnant woman’s body, an increase in the load on the nervous system, an increase in the intensity of the work of vital organs during pregnancy, compression of some organs and areas as a result of fetal development, and also changes in hormonal levels in the body.
In particular, an important symptom that you should definitely pay attention to is sinus tachycardia. An increase in heart rate in a calm state of rest is a possible indication of a disorder in the sinus region, which is responsible for the formation of conductive impulses
In other words, a woman should definitely be concerned if she experiences more than ninety beats per minute.
Consequences of fetal tachycardia and prevention
Of course, treatment of fetal tachycardia with medications during pregnancy does not always go without leaving a trace. But in any case, it is much safer than letting everything take its course with the hope that the problem will solve itself.
Recovery occurs in 90% of cases, but there is still a fairly high risk that the drugs will kill the fetus. Tachycardia itself, in combination with other pathologies, does not provide such a high guarantee that the child will be born alive and healthy.
The most important prevention, which should be mandatory for any woman planning to become a mother, is maintaining a correct lifestyle. This applies not only to the period of pregnancy, but also to the several months of preparation for it. A couple of months before the planned conception, a representative of the fair sex needs to undergo examination for the presence of diseases and infections. If anything like this is detected, treatment should be started immediately. It is better to exclude pregnancy at this time.
There is no special prophylaxis to reduce the risk of tachycardia in the fetus. Hereditary factors, poor ecology, and many other reasons can play a role here. But those women who do not have bad habits, eat right and lead an active lifestyle are more likely to give birth to a healthy child.
Carrying out CTG during pregnancy can show a condition such as tachycardia in the fetus - a pathologically increased heart rate. A deviation is considered to be an increase in frequency to 170 or more beats per minute.
The cause of tachycardia during pregnancy can be diseases of the mother or intrauterine anomalies of the child itself. In any case, this condition requires careful handling of the pregnant woman and constant monitoring of the woman.