When is it discovered?
It is impossible to determine the fetus on an ultrasound before the heartbeat begins, so it is important to understand what time the fetus’s heart begins to beat.
The formation of the heart muscle occurs in the 4th week of pregnancy; a week after this, the first tremors can be felt. Using ultrasound diagnostics, it is possible to detect pathology at 18-22 weeks of pregnancy, when a second ultrasound of the fetus is prescribed. There are cases when the pathology disappeared in the last trimester of pregnancy.
A hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle of the fetal heart is an ultrasound finding that is usually detected during a second routine ultrasound.
At the moment, its appearance is described in many fruits. Experts believe that it can be either a normal variant or, only against the background of identified markers of chromosomal abnormalities, indicate a serious pathology.
Using ultrasound diagnostics, it is possible to detect pathology during the week of pregnancy, when a second ultrasound of the fetus is prescribed. There are cases when the pathology disappeared in the last trimester of pregnancy.
What to do if GEF is detected?
As already mentioned, this deviation does not require specific treatment. In approximately 30-35% of cases, the lump disappears on its own by the end of pregnancy. In approximately 80% of newborns, it turns into an additional trabecula in the internal tissue of the ventricles of the heart. Such formations also do not affect health and do not require treatment. Based on the above, you should only worry about the presence of such a disorder after repeated screening if there are other syndromes that may indicate genetic diseases.
If the doctor detects several markers (signs) of such an anomaly at once, he prescribes an additional medical genetic consultation, as well as other studies to determine the diagnosis. After this, if necessary, treatment is prescribed or other further actions for the management of pregnancy and childbirth are discussed with the mother.
Remember that only a specialist can make a verdict on the advisability of additional examinations and drug therapy. Don't self-medicate!
Pregnant women often encounter unfamiliar terms during ultrasound examinations, which become causes of concern. Hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle of the fetal heart is one such term that requires explanation. What is a hyperechoic focus? How dangerous is this?
Reasons for education
We have found out what a hyperechoic focus is, but what are the reasons for its appearance? This:
- salt deposits;
- pathology in the chromosome set of the fetus;
- the presence of an additional chord in the heart, which is considered a normal variant and does not in any way affect the activity of the heart muscle.
If the appearance of compaction of myocardial structures was caused by salt deposition, then a pregnant woman has no reason to worry. Most often, such minor pathology goes away by the third trimester of pregnancy.
An additional chord in the heart is a structural feature that can create certain heart murmurs. At the age of 2-3 years, noises most often stop, but even if they remain, they do not pose a danger to the life and health of the child.
It’s another matter if the focus is caused by an incorrect set of chromosomes in the child. There is a risk of detecting Down syndrome in the fetus or other pathologies. If there is such a suspicion, additional tests are prescribed to clarify this information. However, most often the alarm turns out to be false.
The causes of a hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle of the fetal heart are individual and require examination to clarify them.
Diagnostic methods
It is easy to detect a hyperechoic inclusion in the LV or RV of the fetal heart in the second trimester during an ultrasound examination. To ensure the reliability of the preliminary diagnosis, the attending physician refers the expectant mother to fetal echocardioscopy. The reasons for prescribing this examination are:
- the age of the expectant mother is over 35 years;
- infection in a woman;
- the presence of heart disease, diabetes mellitus in relatives of the pregnant woman;
- identifying disorders in the heart muscle;
- fetus size is too small;
- detection of markers indicating the likelihood of chromosomal disorders.
What does a hyperechoic focus in the fetal heart mean?
A hyperechoic focus in the fetal heart means that in the place where it is found, compaction of the myocardial structures has occurred. It could be:
- salt deposits (usually calcium salts)
- accessory chordae or other developmental abnormality that does not usually interfere with the heart's ability to function normally
- a sign of chromosomal pathology.
If only such a phenomenon is detected, there is no need to worry: if it is a salt deposit, it usually resolves by the third trimester or by birth.
The additional chord (that is, the fibrous tissue that runs from the valves to the ventricles), according to most doctors, does not pose a danger to life and health and does not affect the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
This same extra chord may be the source of the heart murmur later discovered in your baby.
This does not affect your health, but you need to be constantly monitored by a cardiologist. This is necessary so that if other problems with blood circulation arise, which the constant noise may prevent the pediatrician from recognizing, they can still be detected.
But if you have previously had markers of chromosomal abnormalities (determined by a blood test, which is usually prescribed by a geneticist), then a hyperechoic focus may not be such a simple anomaly.
This may be evidence of severe chromosomal diseases, in particular Down syndrome.
If all these studies do not give an unambiguous, comforting result, you need to contact a geneticist. Only as a last resort:
- if dangerous markers are found in the blood,
- there are other ultrasound signs of pathology,
According to his proposal, it is worth carrying out the invasive procedures listed above.
The heart is formed at 4 weeks. The first fetal heartbeat can be detected by ultrasound as early as 5 weeks of pregnancy. This can be done transvaginally. With an abdominal sensor, heart contractions can be recorded a week or two later.
The number of contractions of the heart muscle in the earliest period should be per minute. At 8 weeks they should already be there for about a minute. On an ultrasound performed at week 11, the fetal heartbeat is heard at a frequency of one minute. This frequency persists until the time of birth.
Such early detection of the fetal heartbeat can only be heard on ultrasound. Even the most experienced doctor can do this with a stethoscope. Your family members can listen to how it beats only from the 30th week.
It is carried out according to the following indications:
- the expectant mother is over 35 years old
- she suffers from diabetes
- the woman had some kind of infectious disease in the early stages
- A routine ultrasound revealed pathology of the heart
- according to fetometry, fetal size lags behind gestational age
- the pregnant woman herself, her relatives or older children were diagnosed with a heart defect
- when markers of chromosomal diseases are detected.
At what time should an ultrasound of the fetal heart be performed? This is done only starting from the 18th week of pregnancy.
After 28 weeks, the study is not very informative, since assessing the results of the study is difficult due to the small amount of amniotic fluid and the large size of the child.
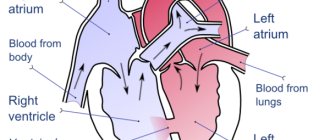
Echocardioscopy evaluates the various sizes of the heart cavities and valves, its filling and contractility. They differ from the measurements of this organ in an adult, since the fetus has a completely different body area.
So, such an ultrasound at 22 weeks of pregnancy is represented by the following standards (in centimeters):
- right ventricle (RV) width: 0.4-1.10
- left ventricular (LV) width: 0.45-0.9
- LV/RV width ratio: 0.9-1.15
- LV length: 0.9-1.8
- pancreas length:0.5-1.75
- aortic mouth: 0.3-0.52
- tricuspid foramen diameter: 0.32-0.65
- Mitral orifice diameter: 0.36-0.63
- pulmonary artery mouth: 0.28-0.5
- heart rate: per minute.
The price of such a study: 1900 – 2600 rubles.
So, a hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle of the fetal heart is an ultrasound phenomenon that most often does not mean pathology. Detection of such an acoustic shadow requires further further examination as planned.
This term has another definition among doctors. They call this phenomenon "golfball" (golf ball). A hyperechoic focus in the fetal heart means that compactions of myocardial structures have appeared at the site of its detection.
- salt deposits (most often we are talking about calcium salts);
- accessory chord - fibrous tissue passing from the valves to the ventricles;
- pathologies of chromosomal type;
- another abnormality of formation, which normally does not prevent the heart muscle from working normally.
If only one such phenomenon has been diagnosed, then there is no need to worry. So, for example, if we are talking about the deposition of calcium salts, then in 80% of cases it resolves by the last trimester or by the birth of the child.
The additional chord does not pose any danger to life and health. In addition, it does not affect the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
It should be noted that an extra chord is a factor in the development of heart murmurs, which are likely to occur in the child in the future.
What needs to be done with such a diagnosis?
First of all, you should undergo additional diagnostics to exclude the presence of chromosomal causes. If there are any, the expectant mother needs to consult a geneticist.
If the examination is carried out later than the 25th week, it will not give accurate results, because the fetus will increase in size, and it will be extremely difficult to examine the signs of a cardiac phenomenon. To maximize the likelihood of developing complications, the doctor prescribes the following additional examination measures:
- A blood test to detect the presence of chromosomal abnormalities in the embryo. Based on the results, the specialist determines the likelihood that the child will be born with chromosomal abnormalities.
- Fetal fetoscopy allows you to examine the fetus for the presence of pathologies and hereditary diseases. To do this, a thin tube is inserted through the wall of the reproductive organ into the amniotic sac. The method is quite dangerous as it can cause spontaneous abortion. Fetoscopy is used only when other diagnostic measures do not provide certainty.
- Placentocentesis is similar in principle to a biopsy. Cells from the placenta are removed to analyze the genetic makeup of the embryo. This study allows you to quickly confirm or refute the presence of hereditary anomalies.
- Amniocentesis (analysis of amniotic fluid). After analyzing the totality of indicators, you can consider the degree of risk of having a child with chromosomal abnormalities.
- Echocardioscopy is the most accurate diagnostic method for GEF. In combination with ultrasound, it allows you to track the main indicators of heart function. However, echocardioscopy cannot be used after 25 weeks of pregnancy.
If the “golf ball” is not accompanied by other pathological manifestations, the fetus is considered healthy. However, to ensure that there are no abnormalities, the child needs to undergo a control echocardiogram in the first months of life.
What needs to be done?
In most cases, the causes of a hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle of the fetal heart are clarified. If no chromosomal changes were detected, then there is no need to worry. In such situations, no additional measures are taken until the birth of the child.
In most cases, the causes of a hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle of the fetal heart are clarified. If no chromosomal changes were detected, then there is no need to worry. In such situations, no additional measures are taken until the birth of the child.
Possible complications and consequences
Most often, the accessory chord in the left ventricle of a baby disappears by the time of birth, but can be present in the heart until 2-3 years of age, and can persist for life.
Reference! This condition does not pose a threat to the baby’s well-being, but you need to be aware of it and not ignore preventive visits to the cardiologist.
The local pediatrician should also be warned about the child’s health characteristics in order to exclude erroneous diagnoses when listening with a stethoscope.
Hyperechoic focus in the right ventricle of the fetal heart
What is a hyperechoic focus in the fetal heart?
Hyperechoic focus is a term that refers to increased echogenicity (brightness) of a small area of the heart muscle on an ultrasound image. Identification of a hyperechoic focus in the heart is NOT a cardiac malformation, but simply reflects the nature of its ultrasound image.
Why can a fetus have a hyperechoic focus in the heart?
— Sometimes a hyperechoic focus in the heart is detected in absolutely normal fetuses, and this sign may disappear with dynamic ultrasound.
— The presence of a hyperechoic focus in the fetal heart may be a manifestation of chromosomal diseases of the fetus, in particular Down syndrome. In this regard, when a hyperechoic focus is detected, a careful assessment of the fetal anatomy is carried out.
However, this marker refers to the “small” markers of Down syndrome, therefore, identifying only a hyperechoic focus in the heart does not increase the risk of having Down syndrome and is not an indication for other diagnostic procedures.
What to do if a hyperechoic focus is detected in the fetal heart?
- if the fetus has ONLY a hyperechoic focus in the heart, then no additional examinations are required; the risk of Down's disease does not increase.
— during a planned ultrasound in a week, the fetal heart will be examined again. In most cases, the hyperechoic focus in the heart disappears by this stage of pregnancy, but even if it continues to remain in the heart, this does not in any way affect the health of the fetus and the management of pregnancy.
Chief Physician of the Fetal Medicine Center
obstetrician-gynecologist, ultrasound diagnostics doctor
During a second routine ultrasound, a pregnant woman may be informed that a hyperechoic focus has been detected in the left ventricle of the fetal heart. Of course, any woman will be scared after hearing such a long diagnosis, but is it really that dangerous?
exactly 15 weeks
At an early stage of pregnancy, during a repeated ultrasound examination, the expectant mother may be puzzled by the news of the presence of such a diagnosis as a hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle of the fetal heart.
Such an incomprehensible combination of words, undoubtedly, can plunge one into a state of shock and cause the most sincere worry and anxiety in any woman who is not experienced in the subtleties and specifics of medical terminology.
A similar diagnosis is currently found in almost every fourth fetus. It is worth highlighting that there is no unanimous opinion among scientists and doctors regarding this formation in the heart of the fetus.
If all of the above is translated into simple language, the conclusion will be quite optimistic. Diagnosing a hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle of the heart in a fetus does not pose any danger to the child’s health; the only exceptions are those cases when there are abnormalities in the chromosomes.
You will soon become parents! Many are awaiting this news with special trepidation and a feeling of slight excitement. First examinations, first ultrasound. Sometimes the hearing of parents can be alarmed by the conclusion about a hyperechoic inclusion in the fetal heart. What does this mean?
In 70 percent of cases everything passes without a trace
Should we be afraid of such a conclusion? Statistics say that in 20 percent of cases of detected hyperechoic focus in the heart, children are born with chromosomal pathologies. In 70 percent of cases everything goes away without a trace.
Children with right-sided localization of a hyperechoic inclusion are often born with pathology of the cardiovascular system (CVS), which can carry adverse risks for the life and health of the fetus. Therefore, in any case, such a child must be monitored by a cardiologist.
Children born with a hyperechoic focus in the heart cavity may have symptoms of a malfunction of the cardiovascular system in the first years of life: increased fatigue and drowsiness, attacks of pain in the heart area, shortness of breath (lack of air) when performing physical activity (PE), rapid palpitations, swelling of the lower extremities in the evening, pallor or bluish tint of the skin, cold hands and feet in a warm room or in hot weather.
Such a conclusion - the focus of increased echogenicity in the fetal heart can be both a variant of the norm and a sign of possible pathology or abnormalities. Therefore, when planning a pregnancy, a woman with a history of cardiovascular diseases should contact a antenatal clinic physician or cardiologist to undergo the necessary list of examinations.
There is no need to panic in advance and without reason. It is important for a pregnant woman to take care of her health and follow her doctor’s recommendations, because in such a difficult period she is responsible for two!
GEF in pregnant women and newborns. What should parents do?
Most often, a hyperechoic focus is harmless. A dense area of the myocardium may be associated with an abnormal chord; a newborn baby with a similar problem should be under medical supervision to avoid problems with impaired blood flow and arrhythmia. The short accessory chord also requires attention, as it interferes with the functioning of the ventricle.
An extra chord in the right ventricle is considered more dangerous; in some cases, parents are informed that surgical intervention may be required.
To prevent problems, parents who have hereditary problems in the family are referred to a geneticist for consultation. A geneticist collects a family history to confirm or exclude genetic, occupational and household risk factors. In addition, the geneticist evaluates the level of health of the parents, spermatogenesis, data on andrological and genealogical hereditary burden.
A geneticist, having identified a pathology in a married couple planning parenthood, takes measures aimed at eliminating mutagenic factors that can lead to GEF. The greatest effect is achieved by measures taken two or three months before pregnancy.
If an echogenic focus is nevertheless detected, then the reasons may be:
- mineralization of blood vessels in the myocardium;
- additional septum in the heart;
- chromosome pathology.
The detection of a chromosomal pathology most often confronts a woman with the possibility of terminating her pregnancy. In other cases, GEF is considered normal, and its signs completely disappear by the age of four years of the child’s life. Before this period, the child should be observed by a cardiologist.
Like any procedure associated with interference with the body, aspiration carries the risk of miscarriage. But in the case of diagnosing genetic abnormalities, such interventions are necessary, as they help exclude Down syndrome and other severe hereditary diseases.
It is important for every expectant mother that her child is born healthy. For this purpose, there is a system of monitoring pregnant women by specialists: obstetricians-gynecologists, geneticists, prenatal diagnostic doctors.
Any detected deviations from the statistically normal development of the fetus often cause great anxiety in the expectant mother. But not all “findings” of both a functional and anatomical nature mean an inevitable disease in the baby. Thus, in the case of ultrasound examination, ultrasound diagnostic specialists can detect such abnormalities in the fetus in the first half of pregnancy as cysts of the choroid plexus of the brain, hyperechoic inclusions (foci) in the heart, pyeloectasia in the kidneys are small markers of chromosomal abnormalities. Why small?
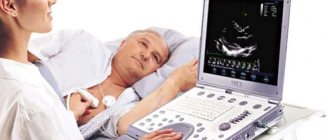
Echocardioscopy
An ultrasound of the fetal heart is prescribed to a woman if there are the following indications:
- age over 35 years;
- diabetes mellitus of any type;
- infectious diseases suffered in early pregnancy;
- routine ultrasound revealed pathology of the fetal heart muscle;
- the child in the womb lags behind in terms of development;
- the pregnant woman or one of her close relatives has a heart defect.
The opportunity to perform an echocardioscopy procedure appears from the 18th week of pregnancy, when you can listen to the baby’s heartbeat using ultrasound. If echocardioscopy was not performed before 28 weeks, then its information content is minimal due to the large amount of amniotic fluid and the large size of the fetus.
The procedure is designed to evaluate the functioning of the heart muscle, valves, cavity sizes, their filling and contractility. The data obtained is then compared with the norm, according to the woman’s gestational age:
- width of the right ventricle - 0.4-1.10 cm;
- width of the left ventricle - 0.4-0.9 cm;
- length of the left ventricle - 0.9-1.15 cm;
- length of the right ventricle - 0.7-1.75 cm;
- size of the aortic mouth - 0.3-0.5 cm;
- diameter of the tricuspid foramen - 0.3-0.6 cm;
- pulmonary artery mouth - 0.2-0.5 cm;
- Heart rate varies from 140 to 160 beats per minute.
For any deviations from the norm, pathology is diagnosed. In such cases, the diagnosis of a hyperechoic focus of the left ventricle of the fetal heart continues by using other research methods.
- width of the right ventricle - 0.4-1.10 cm;
- width of the left ventricle - 0.4-0.9 cm;
- length of the left ventricle - 0.9-1.15 cm;
- length of the right ventricle - 0.7-1.75 cm;
- size of the aortic mouth - 0.3-0.5 cm;
- diameter of the tricuspid foramen - 0.3-0.6 cm;
- pulmonary artery mouth - 0.2-0.5 cm;
- Heart rate varies from 140 to 160 beats per minute.
When diagnosing a focus of increased echogenicity of the left ventricle in a fetus, the use of echocardioscopy for detailed monitoring of the functioning of the heart muscle will be an effective step.
This procedure allows you to monitor the main parameters of the fetal heart (atrial filling, ventricular contraction, etc.) in real time using ultrasound and detect possible deviations from the norm.
Cardiac echocardioscopy is the study of the structure of the heart and its functioning using ultrasound.
The main indications for examination using echocardioscopy are:
- the age of the pregnant woman exceeds 36 years;
- the presence of diabetes mellitus in the expectant mother or immediate relatives;
- recent infectious or viral disease in the early stages of pregnancy;
- the woman has a congenital heart defect, taking into account immediate relatives;
- the presence of markers of hereditary pathology in the blood of the expectant mother.
Decoding and norms
When examining the fetus, all cavities of its heart are measured and the doctor compares the results with special standards:
- length of the right ventricle – from 0.5 to 1.75 cm;
- width of the right ventricle – from 0.4 to 1.1 cm;
- length of the left ventricle – from 0.9 to 1.8 cm;
- left ventricular width – from 0.44 to 0.89 cm;
- ratio of the width of the left ventricle to the right – from 0.45 to 0.9 cm;
- aortic mouth – from 0.3 to 0.52 cm;
- the mouth of the pulmonary artery – from 0.3 to 0.5 cm;
- mitral orifice – from 0.35 to 0.6 cm;
- tricuspid foramen – from 0.3 to 0.63 cm;
- the mouth of the pulmonary artery – from 0.3 to 0.5 cm;
- mitral orifice – from 0.35 to 0.6 cm;
- tricuspid foramen – from 0.3 to 0.63 cm;
- the number of heart contractions is from 140 to 160 beats/minute.
It should be taken into account that the size of a child’s heart and its individual components differs significantly from the corresponding sizes in an adult, because the size of the organs depends on the size of the body. Ultrasound in this case is very informative, and if there is a pathology, it will always be detected .
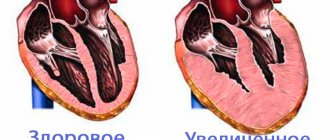
Photo 1. Hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle of the fetal heart.
Sources
- https://babytwins.ru/golfnyj-myach-u-ploda/
- https://profuzi.ru/grudnaya-kletka/giperehogennyj-fokus-v-serdtse.html
- https://VseProRebenka.ru/beremennost/plod/giperehogennyj-fokus-v-levom-zheludochke-serdca-ploda.html
- https://MediGid.com/uzi/organy/grudnaya-kletka/rebyonku-grudnaya-kletka/giperehogennyi-fokus.html
[collapse]
What to do in case of pathology?
The prognosis for a hyperechoic focus of the left ventricle of the fetal heart is in most cases favorable, since the cause of this is most often a slight deposition of salts, which resolve by the end of pregnancy.
It is also recommended to be periodically examined by a cardiologist to diagnose this pathology and monitor its development. In most cases, the heart murmur created by the additional membrane goes away without a trace before the age of three. Then the cardiologist gives a conclusion that the child is completely healthy.
If hyperechoic foci in the fetal heart are still recognized as a pathology, a thorough medical examination, constant monitoring of the health status of the mother and child, as well as taking vitamins and other complexes are necessary. This will help to maximally correct the problem of fetal heart development.
At the initial stage, dysfunction of the left ventricle does not have clearly defined symptoms.
The first signs of cardiac dysfunction appear closer to childbirth and are due to the fact that the fetal heart is anatomically formed and begins to operate independently.
The presence of a seal (a string stretched between the right atrium and the right ventricle) leads to increased pressure in the cavity of the left atrium. This condition occurs due to insufficient blood flow from the left atrium to the right ventricle.
The atrium is not completely emptied, and the ventricle does not receive blood in the required quantity. A natural consequence of such dysfunction is that the fetal organs receive insufficient oxygen and nutrients.
The occurrence of golf ball syndrome in utero often has negative consequences for both the newborn and the child during the first years of his life.
In this case, the most striking symptoms characteristic of this pathology are:
- increased fatigue;
- apathy;
- attacks of pain in the heart area;
- dyspnea;
- cardiopalmus;
- swelling of the limbs;
- characteristic pallor of the skin with a tendency to subsequent blue discoloration.
Attacks of tachycardia (due to rapid contraction of the heart muscle) are often observed; as a result, the pulse can exceed 200 beats per minute. Timely symptomatic therapy in most cases helps to cope with the consequences of intrauterine additional education.
Should I worry about this diagnosis?
As a rule, a hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle of the fetal heart does not pose a danger to the child. After birth and a routine examination by a doctor, no deviations from the norm are detected in children; only minor noises are possible in the presence of an additional chord.
When the child reaches the age of 2-3 months, for greater peace of mind for the parents, an ultrasound of the heart can be done, which will detail all the sizes of the cavities and valve openings, the number of additional chords and the general condition of the cardiovascular system. In conclusion, a diagnosis will be written about the health of the heart and full compliance with age characteristics (usually, before the age of one year, children are diagnosed with an open foramen ovale).
Only in a small percentage of cases, an additional chord of the left ventricle in a child can lead to heart disease or other pathologies. But for this, the mere presence of “golf ball” syndrome is not enough; precise confirmation of the danger is necessary through sampling of amniotic fluid or blood from the umbilical cord and the presence, after diagnosing the blood, of pathological markers indicating the presence of chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus.
The prognosis for a hyperechoic focus of the left ventricle of the fetal heart is in most cases favorable, since the cause of this is most often a slight deposition of salts, which resolve by the end of pregnancy. After the birth of the child, an additional examination is carried out, the results of which are transferred to the local pediatrician.
It is also recommended to be periodically examined by a cardiologist to diagnose this pathology and monitor its development. In most cases, the heart murmur created by the additional membrane goes away without a trace before the age of three. Then the cardiologist gives a conclusion that the child is completely healthy.
Greatest danger
In rare cases, a hyperechoic focus may persist after birth. In such a situation, blood pressure in the left atrium increases, due to which an insufficient amount of physiological fluid enters the right atrium.
A child born with this pathology may experience the following symptoms during the first years of life:
- Increased fatigue, which is expressed in drowsiness and reluctance to play for a long time.
- Apathy.
- Attacks of acute pain in the heart area, which arise due to disturbances in its functioning.
- Shortness of breath, especially during light physical exertion, such as climbing stairs or active games.
- Cardiopalmus. This symptom can be either constant or periodic.
- Swelling of the limbs, which is most noticeable in the evening, as well as in the morning if the child drank water at night.
- Paleness of the skin, sometimes cyanosis.
- Cool hands even in hot weather.
In addition, attacks of tachycardia and rapid breathing are sometimes observed. In such cases, it is necessary to register the child with a cardiologist. He will prescribe appropriate treatment that will help relieve symptoms in a sick child.
In rare cases, a hyperechoic focus may persist after birth. In such a situation, blood pressure in the left atrium increases, due to which an insufficient amount of physiological fluid enters the right atrium.
In addition, attacks of tachycardia and rapid breathing are sometimes observed. In such cases, it is necessary to register the child with a cardiologist. He will prescribe appropriate treatment that will help relieve symptoms in a sick child.
Action tactics
In most cases, if a hyperechoic inclusion is detected, additional research is indicated. In this case, they can assign:
- repeat ultrasound to clarify the diagnosis;
- echocardioscopy (performed only until the 25th week);
- blood chemistry;
- karyotyping.
Invasive diagnostic procedures are used quite rarely:
- amniocentesis (taking a sample of amniotic fluid through the abdominal wall);
- placentocentesis (biopsy of placental cells);
- fetoscopy (examination of the fetus using a video probe).
First of all, of course, genetic causes of hyperechoic inclusion should be excluded. To do this, the diagnostician searches for other small markers of chromosomal pathologies. These include congenital heart defects, thickening of the cervical fold, developmental disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and skeletal system. They are usually detected during ultrasound examination. If they are detected, consultation with a geneticist is necessary.
Are the worries justified?
Despite the fact that doctors advise not to worry ahead of time, many pregnant women are unable to cope with their emotions. As a rule, even with such a minor feature, the heart beats normally, without causing any discomfort to the child.
In the presence of a hyperechoic focus of the left ventricle of the fetal heart after the birth of a child, slight heart murmurs are detected, which are created by the peculiarity of the myocardial structure.
When the child reaches 2-3 months of age, an ultrasound diagnosis of the heart is prescribed, after which a conclusion is issued with a detailed description of the structures of the heart, its function, and size. Rarely, such a diagnosis may reveal an oval window - a small hole between the atria.
When the child reaches 2-3 months of age, an ultrasound diagnosis of the heart is prescribed, after which a conclusion is issued with a detailed description of the structures of the heart, its function, and size. Rarely, such a diagnosis may reveal an oval window - a small hole between the atria.
Mitral heart disease
In very rare cases, in approximately 1 in 5000, a hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle of the fetal heart is a sign of mitral heart disease. Of course, the compaction itself cannot lead to such a serious pathology, but it can be one of the many symptoms.
This pathology is characterized by fusion of the mitral valve of the heart with the left ventricle, which can result in heart failure.
Excessive impregnation with calcium salts
Yes, yes, this is exactly the reaction that a similar conclusion from an ultrasound diagnostic doctor can cause in parents. In fact, neither one nor the other is true. A hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle of the fetal heart is not a malformation or an anomaly.
Many parents are afraid that this kind of finding in the child’s heart is a sign of severe chromosomal pathology, for example, the presence of Down syndrome. To date, there is no scientific evidence that the presence of a hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle of the fetal heart is a reliable sign of chromosomal pathology in the absence of other signs.
Why does such a focus of increased density occur in the prenatal period? There are several possible reasons.
- Excessive impregnation of calcium salts (calcification) of a certain area of the heart muscle. Most often, such changes are localized in the area of the papillary (papillary) muscles. The second trimester of pregnancy, during which such changes are most often detected, is characterized by active mineralization of the child’s musculoskeletal system.
- The presence of an additional or false chord in the ventricle of the child’s heart. Such a false or additional chord does not carry a functional load, and is not a pathology, but refers to minor anomalies of cardiac development (MADC). This phenomenon is a common finding during ultrasound examination.
The chords themselves in the prenatal period can provoke the deposition of calcium salts, as well as increase the brightness of the hyperechoic focus.
- One of the signs indicating chromosomal pathology. Let us remind you once again that in the absence of other reliable signs of chromosomal pathologies, the presence of a compaction or hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle of the fetal heart does not indicate genetic disorders.
Features of the functioning of the fetal heart on ultrasound
The formation of the heart muscle occurs in the 4th week of gestation. At this stage of development, the organ looks more like a hollow tube. In the middle of the 5th week, the activity of the heart begins and its first contractions occur. By the 9th week, this muscle already has 4 chambers and can be called a full-fledged organ, since ventricles and atria are observed.
If an ultrasound is performed correctly, the baby’s heartbeat can be heard already at 5-6 weeks of gestation. When using a transabdominal type sensor, it allows you to recognize the organ’s beating a little later, by about 1 week. A hyperechoic focus in the area of the left ventricle of the fetal heart (LV) has not yet appeared, so there is no need to worry about its possible formation.
At this stage of pregnancy, the doctor records the intensity of the organ’s work, the speed of its beating and other parameters. If heart activity is not observed, then one can suspect that pregnancy has been interrupted. In this case, the specialist recommends repeating the diagnosis after a few days to refute fetal freezing or confirm it.
The first ultrasound examination is carried out at three months to identify any pathologies. Down syndrome occurs frequently and it is necessary to undergo diagnostics during this period in order to exclude such a deviation. The work of the heart is also being studied for the first time at this stage of the baby’s formation. There are certain standards by which you can understand whether the fetus is healthy or not.
| Term | Number of organ beats in 1 minute |
| 6-8 weeks of fetal formation | 110-131 beats/min |
| 9-10 weeks of child development | 170-191 beats/min |
| From 11 weeks until birth | 140-162 beats/min |
Such changes in the rate of organ contractions are due to the formation and further development of the autonomic system. It is this area that is responsible for the correct and coordinated functioning of any of the internal organs, as well as systems. There are certain indicators that the doctor needs to pay attention to. Due to such factors, the baby in the womb experiences some disturbances in the form of a hyperechoic, hypogenic focus.67
What you need to pay attention to:
- in the anamnesis of children born earlier, there are records of a similar condition;
- the presence of congenital heart defects in either parent;
- pregnancy in a woman over 38 years of age;
- diseases of an infectious nature in the expectant mother;
- delayed fetal formation;
- diabetes mellitus in a pregnant woman;
- the presence of defects of other organs in the child in the womb.
Despite the fact that hyperechoic inclusion in the left ventricle of the fetal heart is not considered a dangerous pathology, there is a certain risk. In simple terms, the presence of hyperechogenicity in an organ can be a consequence of a disease, but only if the baby has problems at the genetic level, chromosome mutations and others. During the examination, the doctor examines the structure of the child. When such deviations from the norm appear as shortening of the neck and changes in the area of the nasolabial triangle, it means that we can talk about Down syndrome. Such a diagnosis is established only in 20% of children with increased echogenicity in the heart. Additionally, geneticists identify a chromosomal defect that confirms this pathology.
Prevention measures
To prevent a hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle of the fetal heart, a woman should adhere to the following recommendations:
- If there is a genetic predisposition, for example, when close relatives have had this diagnosis, the woman must undergo a full examination before pregnancy and only after that plan to add to the family. With timely examination, hidden infections can be identified that can harm the child at the time of formation of the heart and other vital organs.
- If possible, a woman should protect herself from pathogenic viruses and microorganisms, for example, avoid contact with animals, even domestic ones.
- A child's heart beats starting from the 5th week of intrauterine development. It is very important not to miss this moment and undergo a transvaginal ultrasound examination to exclude possible pathologies or fetal fading.
- Subsequently, it is recommended to monitor the frequency and strength of the baby’s heartbeat before birth. This is done during routine ultrasounds.
Unfortunately, even with every effort, it is impossible to completely protect yourself and your child from possible developmental pathologies. However, it is important to diagnose them in time and take appropriate measures.
A set of measures aimed at ensuring that pregnancy and subsequent births occur without complications (if the above syndrome is detected in the fetus) should include the need for treatment and monitoring of the expectant mother.
The primary task of doctors is the timely implementation of preventive measures aimed at preventing complications in women
It is extremely important to protect the expectant mother from contact with a possible source of pathogenic viruses or microorganisms. It is women who have suffered from various diseases of an infectious nature who form the main risk group in the early stages of pregnancy.
Why register with a doctor?
Most scientific experiments conducted to study in more detail the hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle of the fetal heart have shown that the appearance of an additional string is a consequence (in most cases) of chromosomal pathology. This pathology is mainly inherited through the female line.
The need for a child with golf ball syndrome to be under constant medical supervision is primarily due to the fact that such structural compaction in the heart cavity often leads to disruption of the rhythm of the myocardium (heart muscle). Due to the fact that the string is short, the volume of the ventricular cavity decreases, and this leads to its incomplete relaxation and, accordingly, poor filling with blood. The result of this anatomical pathology is a violation of the blood circulation of the fetus itself.
The main function of blood in the body is to deliver oxygen and various nutrients to cells, tissues and organs. Weakening of blood flow can then cause oxygen starvation of the fetus or damage to the inner lining of the heart muscle, with a high probability of subsequent miscarriage.
But still, according to most experts, the presence of a compacted string in the left ventricle of the fetus is not such a serious pathology compared to the compaction that can occur in the right ventricle of the heart.
Diagnosing a focus of increased echogenicity of the right ventricle of the fetal heart inevitably leads to complications and often incompatible with life. In such circumstances, the best option is surgical correction of the defect.
All of the above is clear evidence that in order to timely identify problems with blood circulation, the child will definitely need to be registered with a cardiologist.