Focusing on the norms of the fetal heartbeat by week, the doctor, during diagnosis, makes a medical conclusion about the health and development of the baby, and may also suspect the presence of pathological processes and take the necessary measures in a timely manner. Usually, the gynecologist conducts the first listening at the end of 1 month of pregnancy, when the child is in the embryonic stage. As it progresses, your heart rate (HR) will change. It is determined using hardware diagnostic methods and obstetric instruments.
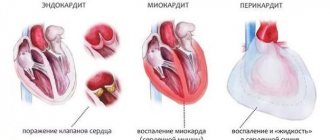
Fetal bradycardia
This complication is an abnormally low fetal heart rate, which is usually temporary.
Symptoms of bradycardia: a decrease in heart rate to 110 or lower, as well as a slowdown in fetal activity, which can be seen on CTG. Bradycardia is most often observed during childbirth, when a woman is taking analgesics, synthetic hormones, and drugs that are injected into the epidural space of the spinal cord to relieve pain.
Other causes of bradycardia include low blood pressure in a pregnant woman and umbilical cord compression. When the fetus does not receive enough oxygen, fetal distress occurs, resulting in a slow heart rate. When the expectant mother lies on her back, pressure is created that negatively affects a large blood vessel called the superior vena cava.
Also, fetal bradycardia can be caused by autoimmune diseases of the mother, gestosis, and anemia. In this case, treatment of the complication will lead to normalization of heart rate.
This complication can also be caused by congenital malformations. These may be structural abnormalities that can be refuted or confirmed by ECG.
Fetal bradycardia is a decrease in fetal heart rate below normal values.
Important advice from the editors!
If you are experiencing problems with the condition of your hair, you should pay special attention to the shampoos you use.
Frightening statistics - 97% of shampoos from well-known brands contain components that poison our body. The substances that cause all the troubles are designated in the composition as sodium lauryl/laureth sulfate, coco sulfate, PEG, DEA, MEA. These chemical components destroy the structure of the curls, the hair becomes brittle, loses elasticity and strength, and the color fades. Also, this nasty stuff gets into the liver, heart, lungs, accumulates in organs and can cause various diseases. We recommend that you avoid using products that contain this chemical. Recently, our experts conducted an analysis of shampoos, where products from the Mulsan Cosmetic company took first place.
The only manufacturer of completely natural cosmetics. All products are manufactured under strict quality control and certification systems. We recommend visiting the official online store mulsan.ru. If you doubt the naturalness of your cosmetics, check the expiration date; it should not exceed one year of storage.
The fetal heart, if we draw a parallel with other vital organs, develops much more slowly and more difficultly. It begins to form only in the fourth week from the moment of conception.
The entire cardiac embryo resembles an empty tube. And already in the fifth week the fetal heartbeat can be heard using an ultrasound machine.
Closer to the ninth week of pregnancy, the “motor” becomes similar to the organ of an adult. But it also has its differences, because the baby does not yet breathe on its own, but uses air from the mother’s body.
Based on the heart rate, we can talk about the well-being and development of the embryo. If, for example, the number of contractions per minute does not exceed one hundred beats, or slightly more than two hundred, then this is a serious reason for concern for the life of the fetus. Also, if the growth of the embryo is eight millimeters, and the heartbeat is inaudible, then conclusions can be drawn about a frozen pregnancy.
Expectant mothers should fear for the life of the child if the heart rate per minute does not exceed seventy times, since this may indicate fetal hypoxia, placental insufficiency, or that the baby is positioned head up.
Whether the development of the baby is normal is determined by the frequency of contractions of the small “motor”. The fetal heart rate table gives future parents an idea of the normal dynamics of the heart muscle.
| A week | Beats per minute |
| Fourth-sixth | 85 |
| Seventh | 100-130 |
| Eighth-ninth | 150-170 |
| Tenth-eleventh | 160-180 |
| Twelfth | 150-170 |
| Thirteenth | 150-170 |
| Fourteenth | 145-165 |
| Fifteenth-fortieth | 140-160 |
Unborn children are very sensitive to the amount of air and nutrients that reach them. An accelerated rhythm appears in the embryo if the mother is worried or too active. In order to obtain accurate research results, pregnant women should pay attention to the following points:
- There is no need to worry before the examination; you should get a good night's sleep.
- During the examination, you need to take a comfortable position.
- It should be remembered that an increased myocardial rhythm is visible with uterine tone or false contractions.
- If the study shows deviations in ri, you should find out the reason that led to such consequences as quickly as possible and begin treatment.
- Heart rate should also be monitored during labor. After all, children’s reaction to contractions and attempts should be natural. Expectant mothers should remember that if the obstetrician does not control the work of the main muscle of the baby’s body, you can ask him to do a CTG.
- The most common reason that causes deviations in the dynamics of the heart muscle is hypoxia. A small amount of air initially increases the functioning of the baby’s “motor,” and with a long stay without oxygen, the beats begin to slow down. Therefore, women in this position should be aware of such an important issue.
There is a widespread stereotype among the population that by the frequency of the heartbeat you can find out in advance who will be born: a boy or a girl. It is believed that boys' hearts beat a little slower than girls'. But can we rely on this data with confidence?
It is no secret that many factors influence the heartbeat, for example:
- Motor activity of the baby;
- Time of day (sleep or wakefulness);
- Individual characteristics of the innervation of the heart muscle and the conduction system of the heart;
- The influence of hormonal factors;
- Maternal and fetal hemoglobin levels;
- The presence or absence of certain pathological conditions during pregnancy (hypoxia, severe gestosis, bleeding, Rh conflict, etc.).
Given so many factors that change heart rate, is it possible to evaluate heart rate from only one perspective—sex determination? Certainly not. Moreover, a study was conducted in which the gender of the child was determined solely by the nature of the heartbeat, and the reliability of this technique was only 50%, which means that it is equated to the banal theory of probability: option one of two.
Thus, it is not possible to find out the sex of the child only by assessing cardiac activity.
Heart rate is an indicator of many processes occurring in the fetal body. The structure of the heart rhythm contains a large amount of information.
In fact, the heart rate reflects a complex of protective and adaptive reactions of the fetus to any influences and changes. Of course, assessment of cardiac activity in the prenatal period is extremely important. The presence of a large number of techniques, as well as their accessibility, greatly simplifies the process of monitoring the condition of the fetus.
Despite the development of complex, invasive techniques that make it possible to thoroughly study the condition of the fetus, their danger is sometimes very high and unjustified. For these reasons, all antenatal clinics, as well as maternity hospitals, are equipped with cardiac monitors, ultrasound machines, and all obstetricians practically do not part with a stethoscope, because this allows them to properly monitor the baby’s heartbeat without harming him.
How is fetal heart rate measured?
The fetal heart rate changes depending on the duration of pregnancy, that is, at different periods of the examination, different indicators have been established that are considered normal. They significantly exceed normal values in already born children and adults.
| Obstetric week of pregnancy | Heart rate, beats/min. |
| 6 | 92-150 |
| 7 | 122-161 |
| 8 | 150-185 |
| 9 | 159-190 |
| 10 | 158-190 |
| 11 | 153-187 |
| 12 | 150-182 |
| 13 | 147-171 |
| 14 | 146-168 |
Somewhere from 18-20 weeks until the end of pregnancy, the fetal heart rate is normally 120-160 beats/min.
Such changes are explained by the formation of the autonomic nervous system in the embryo.
In addition, the normal heartbeat of an embryo has the following characteristics:
- The contractions are rhythmic, that is, there is no acceleration or deceleration of the heartbeat.
- The beats of a small heart are regular, that is, they occur at approximately equal intervals.
To obtain accurate data regarding the fetal pulse rate, CTG, ECG, ultrasound and auscultation are used.
In the early stages of pregnancy, a specialist will determine the heartbeat using a transvaginal sensor. Already after the 7th week, the heart sound will be heard even when diagnosed with a transabdominal sensor (the doctor passes it over the woman’s abdomen).
A “four-chamber slice” of the fetal heart is used to identify developmental disorders. Often it is heart defects that cause a decrease or increase in heart rate. With this “cut”, the doctor clearly sees 2 atria and 2 ventricles of the fetus on an ultrasound.
If suspicions arise and the number of fetal heartbeats is not normal, additional research methods are prescribed.
This diagnostic method is carried out according to indications if an ultrasound revealed abnormalities: intrauterine growth retardation, heart function does not correspond to norms, pathology of the heart structure or fetal development. With its help, you can check in detail the structure of the heart, the performance of all functions and the presence of blood flow disorders in all parts of the heart.
For ECG, two- and one-dimensional images and Doppler measurements are used. The most informative period is 18-28 obstetric weeks due to the sufficient level of AFI.
In addition to a referral after an ultrasound, an echocardiogram will be prescribed for a woman if she is over 38 years old and has diseases of the endocrine (diabetes mellitus) or cardiovascular (congenital heart disease - CHD, for example) systems. The gynecologist may also decide to conduct an ECG if during pregnancy the expectant mother suffered from infectious diseases (especially severe ones) or she has children with congenital heart disease.
In the early stages, this method is not used due to its ineffectiveness. But after 20 weeks, the gynecologist will definitely listen to the fetal heartbeat with a special tube (wooden, plastic or aluminum) during each examination. During the procedure, the expectant mother should lie on her back on the couch.
Every week the doctor will hear the fetal heartbeat more clearly among the sounds of the intestines or uterine vessels. Often the doctor has to look for the most favorable point for using auscultation, because the clarity of tones depends on the position of the fetus, its movements and placenta previa.
With the help of auscultation, you can guess how the baby is located in the womb. If the heartbeat is best heard at the level of the woman’s navel, then the baby is in a transverse position. If below the navel or on the left, then the baby is in a cephalic presentation. If above the navel - in the pelvic.
It is important that the gynecologist hears the rhythm of the knocking. If the heart rate is without rhythm, then one can suspect hypoxia (in this case, the beat still becomes muffled) or congenital heart disease.
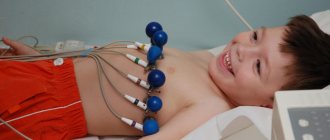
From about 32 obstetric weeks, a fairly effective method for diagnosing heart function - CTG - comes to the fore. This method is good because it simultaneously records the functioning of the vessels of the uterus and the fetus. If the pregnancy is completely healthy and the doctor does not suspect any abnormalities, then CTG may not be performed on the pregnant woman.
Procedure: 2 sensors are attached to the expectant mother’s stomach, with which she should remain for about an hour (sometimes 30 minutes is enough). CTG does not affect the health of the fetus or the woman’s condition in any way.
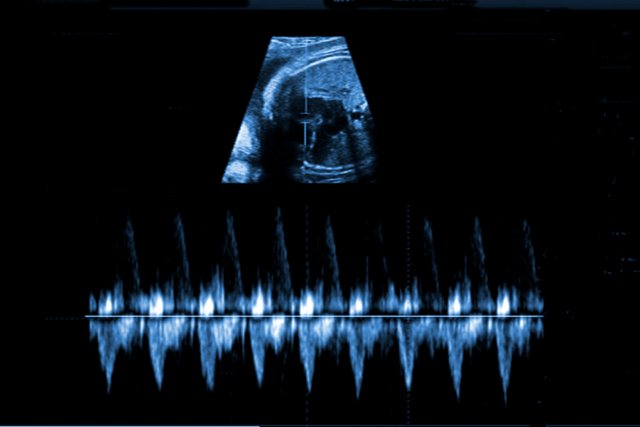
Cases when cardiotocography is mandatory:
- increased maternal body temperature (above 38-38.5 degrees);
- there is a scar on the uterus after surgery;
- a pregnant woman suffers from chronic endocrine or cardiovascular diseases (sinus tachycardia);
- gestosis (late toxicosis with the presence of protein in the urine);
- premature birth or post-term pregnancy;
- during childbirth, used when stimulation of labor is prescribed;
- oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios;
- IUGR fetus (intrauterine growth retardation);
- Dopplerometry revealed disturbances in blood flow in the arteries;
- early maturation of the placenta;
- During auscultation, the gynecologist observes a slowdown, acceleration of the rhythm, and other disturbances.
If the fetal heart rate in response to uterine contractions becomes less frequent, this may indicate disturbances in the uteroplacental blood flow and fetal hypoxia. It is especially dangerous to reduce the frequency of contractions to 70 or less within 1 minute.
Causes of abnormalities in contraction frequency
There are several cases when the baby's heartbeat cannot be heard. Such an unpleasant diagnosis is possible if the expectant mother:
- large or small amount of amniotic fluid;
- too large abdominal wall (often found in obese women);
- two or more embryos.
Also, if the baby is too active in the mother’s tummy, this may be the reason why the frequency of contractions is not visible. Everyone needs to take into account that by nine weeks of pregnancy, the dynamics of the main muscle of the body is already determined by ultrasound.
If this cannot be done, then we can say that the embryo has frozen. In this case, the first thing the ultrasound doctor needs to do is perform a repeat ultrasound to make an accurate diagnosis.
Medical doctrine identifies the reasons why accelerated ri appears. If a pregnant woman suffers from the following ailments, then the cardiac dynamics of the embryo can sometimes exceed two hundred beats per minute:
- anemia;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- diabetes;
- kidney disease;
- drug and alcohol addiction.
Such deviations from the norm can affect blood circulation in the “mother-placenta-fetus” system, and they will also lead to post-term pregnancy and complications during labor.
Sometimes after a study it turns out that the heartbeat does not correspond to accepted standards. This situation must be treated with due attention and find out why this happened.
Factors leading to rapid heartbeat (tachycardia):
- Disturbances of uteroplacental blood flow.
- Anemia in the mother.
- A decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the fetus (for example, with hemolytic disease) causes an acceleration of blood flow, as well as a compensatory reaction in the form of tachycardia.
- Placental insufficiency.
- Bleeding in the mother (for example, due to placental abruption).
- Malformations of the heart.
- Increased temperature in a pregnant woman (febrile state).
- Inflammatory process in the membranes (amnionitis).
- Taking certain medications. For example, a frequently used drug in obstetrics, Ginipral, can cause tachycardia not only in the mother, but also in the fetus. In addition, drugs that block the influence of the parasympathetic nervous system (for example, Atropine) can also cause increased heart rate.
- Pathology of the umbilical cord (two vessels in the umbilical cord, entanglement, etc.).
- Acute intrauterine hypoxia can cause a sharp increase in the fetal heart rate to 200-220 per minute.
- Loss of umbilical cord loops.
- Increased fetal intracranial pressure.
Reasons that cause a slow fetal heart rate (bradycardia):
- Prolonged stay of a woman in a supine position, in which compression of the inferior vena cava occurs.
- Taking medications that block the sympathetic nervous system, such as Propranolol.
- Severe disturbances of the acid-base balance in the fetal blood with serious metabolic disorders.
- Some anomalies in the development of the conduction system of the fetal heart.
- An increase in the concentration of potassium in the blood of the mother and child, which leads to heart rhythm disturbances and the appearance of bradycardia.
- Prolonged compression or knot of the umbilical cord.
Each of these reasons is very serious and often requires treatment, and in some cases even emergency delivery in the form of a cesarean section.
What are the research methods?
Assessing the heart function of an unborn child using ultrasound diagnostics is the most popular method.
In pregnant women, it is carried out in two ways:
- transabdominal method - gives a general picture of the course of pregnancy;
- transvaginal examination - provides more complete information about the state of development of the embryo, the woman’s internal organs and blood vessels.
An ultrasound scan makes it possible to evaluate the following indicators:
- The rhythm of the heartbeat. Like an adult, an unborn baby's heart should beat at regular intervals, but changes in the rate of contraction are possible. The specialist is able to assess the nature of the work of the heart muscles, and if there is arrhythmia, draw a conclusion about whether this is normal or not.
- Peculiarities of tone - a healthy heart beats clearly and clearly. In the presence of pathology, the tones are blurred and sometimes difficult to hear.
- Heart rate. This indicator indicates not only the correct functioning of the main organ in ensuring blood supply, but also the correct development of the entire organism as a whole.
- During childbirth, monitoring the baby’s heart is very important; this makes it possible to monitor the baby’s condition and take action in case of emergency situations.
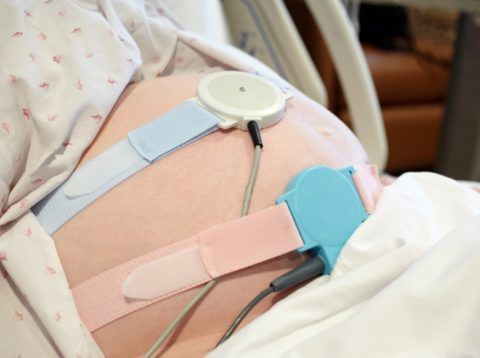
Monitoring your heart rate during contractions is extremely important.
Heart rate and heart rhythm are one of the most important indicators, the values of which can say a lot about the health of the unborn child. Therefore, they are monitored regularly throughout the gestational period. For this purpose, various hardware research techniques are used:
- Ultrasound. This is the first method used to determine heart rate. Already from the 7th week of pregnancy, the sound of the baby’s heart can be heard using an ultrasound sensor, which a specialist moves over the woman’s abdomen or inserts into the vagina.
If the results of the study raise any questions for the doctor or not all indicators correspond to the norm, he will refer the pregnant woman for additional examination.
- Auscultation. This is listening to a small heart using a stethoscope - a special plastic, wooden or aluminum tube. The procedure is carried out during each scheduled visit of a pregnant woman to a gynecologist.
The woman lies down on the couch on her back. The doctor applies the wide funnel of the stethoscope to her bare stomach and the other side to his ear.
The procedure begins at 18-20 weeks. Previously, this does not make sense, since it is not possible to hear the heartbeat in this way.
An experienced specialist, through auscultation, can determine the clarity of tones, the place of best listening, the approximate heart rate, and the position of the fetus. Although a person without medical education, for example, a mother, husband, girlfriend, etc., can listen to the heart rhythm at home.
It is impossible to hear the baby's heartbeat in the following situations:
- polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios;
- multiple births;
- the child has high motor activity;
- the placenta is located on the anterior wall of the uterus;
- The pregnant woman is overweight.
- Echocardiography (EchoCG). It is usually prescribed at 18-28 weeks of pregnancy. Of course, the procedure can be done later, but then the fetus is much larger and the amount of amniotic fluid is less, so visualization becomes more difficult.
Indications for its implementation are:
- the pregnant woman herself has myocardial defects;
- the woman has already given birth to children with disorders in the functioning of the heart;
- intrauterine growth retardation;
- pathologies of other organs were detected through ultrasound;
- diseases of infectious origin suffered by a pregnant woman (especially in the first trimester);
- a woman has diabetes;
- detection of heart enlargement, heart rhythm disturbances, and heart rate abnormalities during ultrasound examination;
- detection of genetic diseases that can provoke disturbances in the functioning of the heart muscle;
- The pregnant woman is over 38 years old.
EchoCG is a special type of ultrasound examination that exclusively analyzes the functionality of the myocardium. In addition to two-dimensional ultrasound, one-dimensional ultrasound (M-mode) is used here to examine the cardiovascular system and Doppler mode to examine blood flow in different parts of the heart.
Echocardiography allows you to study the functions of the myocardium, its structure, as well as the structure and functionality of large vessels.
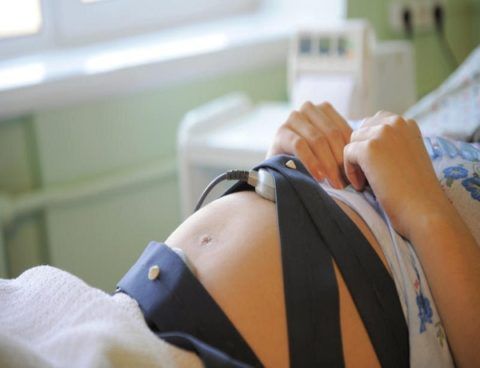
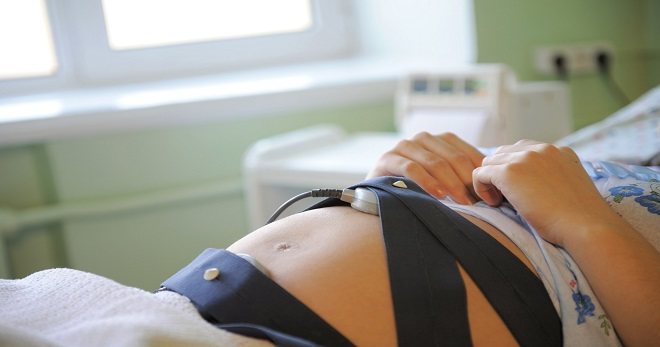
- Cardiotocography (CTG). The device used is an ultrasonic sensor, the main task of which is to send and capture signals from the child’s heart. CTG is used from the 32nd week of gestation and allows you to adequately assess not only the heartbeat, but also uterine contractions.
To record CTG on film, the pregnant woman takes a sitting or lying position on her side or back. The sensor is attached to her abdomen in the place where heart sounds can best be heard. The procedure lasts no more than an hour (usually from 10 to 50 minutes), after which specialists assess the heartbeat of the unborn child, according to the recorded results.
It is advisable to carry out cardiotocography for all registered pregnant women, but special attention should be paid to the procedure in the following situations:
- intrauterine developmental delay;
- disruptions in the frequency and nature of heart contractions, which were identified through auscultation;
- arterial blood flow disorders;
- oligohydramnios, polyhydramnios;
- premature aging of the placenta;
- weak labor activity, which will require inducing labor;
- presence of scars on the uterus;
- childbirth during premature or post-term pregnancy;
- febrile state with a temperature rise above 38 degrees;
- severe gestosis;
- arterial hypertension;
- diabetes.
You can see how cardiotography is performed and what it shows in the picture below.
All methods for measuring the frequency of myocardial contractions are usually carried out plannedly or on the direction of a doctor. But if a pregnant woman is too worried about the condition of her child, she can undergo the considered diagnostic measures on her own initiative in any medical institution where they are carried out.
Preventing heart problems in babies
There are several popular methods for determining the sex of a child by the fetal heartbeat, but doctors refute them.
One such method involves listening to the fetal heart rate. In boys, according to adherents of this technique, the heart beats more rhythmically and clearly, while in girls it is more chaotic, and the heartbeat rhythm does not coincide with the mother’s.
According to the second similar folk method, the location of the heartbeat can indicate the sex of the baby. Listening to the tone on the left means that a girl will be born, and on the right - a boy.
The third folk method says that the number of heartbeats can indicate the gender of the baby, but there are so many versions of this method that they have become very confusing. Some argue that in girls the number of heartbeats should be either more than 150 or less than 140 beats per minute, and that in boys the heart beats either more than 160 beats per minute or about 120.
The exact timing of such testing also varies.
As entertaining as these methods are, they are nothing more than a guessing game. All these methods are completely refuted by scientifically proven facts showing that the number of heartbeats is affected by:
- gestational age;
- the position of the mother's body while listening to the heartbeat;
- motor and emotional activity of the mother;
- health status of the unborn baby and mother.
Medical research confirms that finding out the sex of an unborn child with 100% accuracy is only possible through a special method, during which amniotic fluid or a piece of placental tissue is taken for examination.
When studying the norms of heart rate first in the embryo and then in the fetus, note that reservations about gender or the dependence of heart rate on gender are not found anywhere.
There are boundaries of the maximum permissible lower and upper pulse values for determining pathologies of perinatal development:
- intrauterine bradycardia - heart rate less than 110 beats/minute;
- tachycardia - heart rate of 180 beats per minute or more.
There are also data such as fetal heart rate by week in the table. The gender of the child is also not considered in these data. The explanation for this is very simple.
Heart rate is an individual and variable indicator, depending on many reasons, including the health of the mother and congenital pathologies of the fetus.
Therefore, some future babies may have a heart rate of 80-85 beats per minute, while others may have 150-170.
By changing the parameters of the heart rate, the doctor is able to predict the presence of intrauterine diseases of the fetus, but it is impossible to determine the sex of the child by the heartbeat.
The health of the unborn child is in the hands of the mother.
At different stages, the heartbeat of the embryo can be determined using the following methods:
- Ultrasound – from 4 to 20 weeks;
- listening through a phonendoscope - from 20 weeks. before giving birth;
- listening through a tube – from 20 weeks. before giving birth;
- echocardiograph - in the last stages of pregnancy;
- cardiotocograph – used during childbirth.
In the early stages of pregnancy, the heartbeat of the embryo is shown by an ultrasound machine. The study is safe for the fetus and allows you to identify possible deviations from the norm. Ultrasound is performed as planned:
- 10-13 weeks – first (transvaginal ultrasound);
- 20-22 weeks – second (transabdominal);
- 32-34 (7-8 months) - third.
To do this, the doctor determines the position of the baby, places a tube on the pregnant woman's stomach and listens to the baby's heartbeat. For experienced gynecologists, such a study provides a complete picture of fetal development by month.
During childbirth or in cases where abnormalities are diagnosed in the future toddler, a carditocograph or echocardograph is used. A special belt with sensors is attached to the belly of a pregnant woman during contractions. The obstetrician listens to the knocking and determines how the uterus contracts, how the baby tolerates childbirth, and whether he is experiencing oxygen starvation.
Heartbeat disturbance
The number of contractile movements in an unborn baby can be measured in several ways.
| Name and appearance of the method | Its features |
| The most common way to monitor a baby’s cardiac activity. During the procedure, not only the work of the heart is assessed, but also other parameters of the development of a small organism. The study is carried out according to the plan of screening studies or unscheduled if indicated |
| The simplest and does not require the use of any equipment. Listening to the heart is performed using a special stethoscope by an obstetrician-gynecologist. In this method, the specialist focuses exclusively on his own hearing, which means he requires experience and knowledge of listening areas. The opportunity to listen to the baby's heartbeat appears around the 20th week. Despite this, the method makes it possible to determine the position of the baby in the womb, that is, presentation |
| This method is one of the ultrasound methods. Provides information about heart rate in the form of a graphic image. Often used during contractions and allows you to monitor the condition of the baby as it moves through the birth canal |
These methods allow you to listen to the baby’s heart function one time. However, there are situations when the work of a small heart needs to be monitored for a long time, continuously.
These are the cases:
- the presence of a chronic lack of oxygen (hypoxia) and delayed physical development of the baby;
- if the child was born premature or the gestational age has been exceeded;
- if the birth process is stimulated;
- when performing epidural anesthesia;
- if there is a diagnosis of gestosis;
- carrying more than one fetus;
- chronic diseases of a pregnant woman that can harm the health of the child.
When assessing heart rate, the diagnostic specialist always relies on indicators that differ depending on the stage of pregnancy.
| Gestational age in weeks | Normal physiological values, beats per minute | |
| Minimum indicators | Maximum performance | |
| From 6 weeks | 90 | 110 |
| From 6 to 7 | 100 | 130 |
| 8 to 9 | 130 | 150 |
| From 10 to 11 | 130 | 160 |
| From 12 to 13 | 140 | 170 |
| From 14 to 15 | 140 | 180 |
| From 16 to 17 | 140 | 170 |
| From 18 to 19 | 140 | 180 |
| From 20 to 21 | 140 | 170 |
| From 22 to 23 | 130 | 160 |
| From 24 weeks until the baby is born | 120 | 160 |
Throughout the entire period of a baby’s intrauterine life, there are several turning points when the contractility of the heart changes significantly:
- The first month is different in that the heartbeat changes every day. Heart rate increases by 3 beats per minute. Taking this fact into account, it is possible to calculate the age of the embryo with maximum accuracy.
- From 6 to 8 weeks, the heart takes on the appearance of a four-chambered organ. Now the heart rate increases to 120-130 beats.
- Between 8 and 10 weeks, the heart can reach a contraction speed of 170-180. Such indicators indicate the immaturity of regulation of the cardiovascular system by the autonomic system.
- Throughout the entire period of development, the baby’s heart rate is influenced not only by the state of his own body, but also by the health state of the expectant mother - chronic and acute conditions. Not only the mother’s physical well-being is affected, but also her psycho-emotional state and stress level.
- Throughout the second semester, the maximum figure is 200 beats per minute. The minimum indicator is 85 strokes. If these boundaries are not respected, then the baby may be diagnosed with tachycardia or bradycardia, respectively.

Untreated heart problems can lead to various complications.
A fast heartbeat, a slow heartbeat, or other problems with the functioning of this important organ may occur for the following reasons:
- excessive physical activity of a pregnant woman;
- emotional and psychological stress, stress;
- dysfunction of the placenta;
- problems with the condition of the umbilical cord;
- late toxicosis;
- other pregnancy disorders.
Monitoring the baby’s heartbeat is carried out for every pregnant woman, because it allows:
- First of all, confirm or deny the very fact of pregnancy. Using ultrasound research methods, a heartbeat can be detected literally from the first weeks of pregnancy, and its absence often indicates a frozen pregnancy.
- Monitor the condition of the fetus. Deviations in the rhythm and heart rate (HR) may indicate circulatory disorders, deteriorating health, insufficient oxygen, some kind of illness in the mother, or a woman experiencing a stressful situation.
- Monitor how the baby feels during labor. This is a huge burden for the baby, he feels a lack of oxygen, so the heart rate is constantly monitored. It is this indicator that helps to find out if umbilical cord entanglement or placental abruption has occurred.
Why should you be wary of hypoxia?
Almost all studies conducted during pregnancy are aimed at promptly identifying possible oxygen deficiency (hypoxia), which can cause a whole range of negative changes in the body of an unborn baby.
Typically, the cause of a lack of oxygen in the fetus is various pathologies in the body of the pregnant woman, in the placenta and in the body of the fetus itself.
- hypoxia disrupts the functioning of the entire body;
- hypoxia changes the course of metabolic processes in the body;
- hypoxia at the beginning of pregnancy leads to abnormal development of the embryo;
- at the end of pregnancy, lack of oxygen leads to growth retardation, damage to the central nervous system, and disruption of the fetal adaptive capabilities.
It is necessary to observe the contractions in order to:
- Confirm that conception has occurred and the embryo is developing. If the first signs of pregnancy appear, the woman is recommended to have an ultrasound examination to rule out an ectopic pregnancy. With the help of modern technologies, fetal heart contractions can be recorded three weeks after conception. If the examination was able to confirm pregnancy, but the pulse is not detected, there is no need to be nervous. Repeated examination after a week helps to hear the heartbeat. But, if in the future nothing can be heard, fading of pregnancy is detected. It is impossible to help in this situation, so the uterine cavity is cleaned.
- Assess the condition of the fetus. Stressful situations, maternal illness, physical activity, oxygen levels, periods of sleep and wakefulness affect the fetal heart rate. But these are temporary changes. If the pulse is too fast for a long time, fetoplacental insufficiency is diagnosed, when the embryo does not have enough oxygen. This problem is often chronic. If the heartbeat slows down, this indicates depletion of compensatory mechanisms and a deterioration in the condition of the fetus. Therefore, you will have to resort to emergency delivery.
- Monitor the condition of the fetus during labor. This period is characterized by a significant increase in the load on the baby’s body. It is compressed by the birth canal and suffers from a lack of oxygen. In most cases, the body tolerates stress well, but with placental abruption, clamping of the umbilical cord, and in other cases, urgent help is needed.
Echocardiography is a more in-depth diagnostic method that allows you to see the structure and functions of the heart and the functioning of blood vessels. This method is prescribed to pregnant women from 18 to 28 weeks.
In the early stages, echocardiography is ineffective, since the organ is still very small, and in the later stages, the amount of amniotic fluid is small, which makes examination difficult. With echocardiography, in addition to conventional ultrasound diagnostics, 2 more examination methods are used: M-mode and Doppler, which show a complete picture of the heart’s functioning and the likelihood of blood flow disturbances.
Echocardiography is prescribed for pregnant women at risk: maternal age over 38 years, infectious diseases during pregnancy, diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular diseases in the mother, disorders of the fetal heart.
Fetal tachycardia
Fetal tachycardia is not common - it occurs no more than 0.5-1% of all pregnancies that have been diagnosed.
Gestational age, duration of tachycardia, and the presence of cardiac dysfunction can help the doctor determine the nature of tachycardia.
Tachycardia can range from simple sinus to various “tachyarrhythmias.”
Causes:
- on the maternal side: hyperthyroidism or medications taken;
- from the fetus: intrauterine infection, hypoxia, fetal anemia, chromosomal abnormalities: trisomy 13 or Turner syndrome.
Treatment: the long-term prognosis with timely treatment is usually favorable, tachycardia disappears during the first year of the child’s life.
Oh yes, we almost forgot. It is impossible to determine the sex of a baby by its heartbeat, so don’t believe in old wives’ tales.
Fetal tachycardia is an increase in fetal heart rate above normal values.
Heart rate and gender of the child
No matter how much you would like it, it is impossible to find out the baby’s gender by heart rate
The gender of the baby is perhaps the first thing that interests future parents and close relatives when pregnancy is confirmed. There are a lot of signs and prejudices that seem to hint at the gender of the baby. Among other things, there is a misconception that you can determine who will be born by the heart rate of the baby in the womb. Like all signs, this one is also a misconception.
The sex of the baby can only be determined using an ultrasound, and even in this case there is an error and the result may be a mistake.
There are two types of Doppler measurements:
- The Duplex
Wave is not sent continuously, but in cycles. As a result, the sensor catches the reflected ultrasound, sends it for processing, and at the same time “produces” a new “portion” of signals. The results are displayed in black and white. - Triplex
Based on the same method, only the speed of blood flow in different parts of the vessels is coded in different colors. These shades are superimposed on a two-dimensional image. The blood flow will be colored red and blue. The color does not depend on the type of vessel (vein or artery), but on the direction of blood flow - from the ultrasound sensor or towards it. A color picture gives a clearer image and allows you to notice what is impossible to see in a two-color image.
Fetal heart rate at 4-14 weeks of pregnancy
The heart rate directly depends on the baby’s activity phase: during active movements, somersaults, and rollovers, this indicator increases. In addition, the indicator changes with increasing period. Taking into account this feature of heart development, doctors estimate the fetal heart rate by week of gestation. For each specific period there is its own norm.
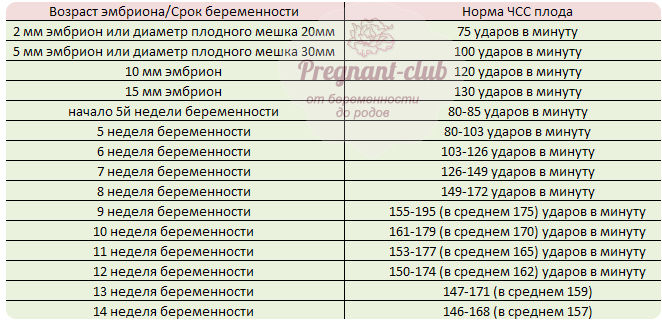
For example, at week 7, the baby’s heart should beat 115 times per minute, at week 8 this figure increases to 170. Then the heart rate gradually decreases. On average, the normal indicator throughout the entire period should be in the range of 140–160 beats per minute. How the fetal heart rate changes by week, the table of normal indicators is given below.
Although the myocardium begins to contract at 3 weeks after conception, it is not until the 6th obstetric week of pregnancy that you can hear your baby’s heart begin to beat on an ultrasound. At this moment, the normal rhythm is considered to be the number of beats equal to the mother’s pulse (about 83 beats per minute - 3). During this first month, the fetal heart rate will increase by 3 beats/min per day. During this period, the gestational age of the fetus can even be determined by heart rate.
By the beginning of the 9th week, the fetal heart rate is approximately 175 beats/min.
Such a difference in indicators indicates the development of that part of the nervous system that is responsible for the functioning of internal organs.
During these periods, the location of the heart in the fetal chest, heart rate and their character will be checked using ultrasound.
The baby's heart rate will change throughout the prenatal period. The child is not constantly at rest: he moves, sleeps, yawns, etc. All these activities will naturally affect the circulatory system and heart rate respectively.
It should be borne in mind that the audibility of the heart rate depends on the position of the fetus (pelvic, cephalic), position (how the baby is turned), the nature of the mother’s abdominal tissue, etc.
The norm in the second trimester is considered to be a heart rate of 140-160 beats per minute. A reading below 85 and above 200 is considered abnormal; a diagnosis of bradycardia or tachycardia is made according to the disorder. The initial stage of fetal hypoxia is indicated by a reading above 160 beats per minute. When a child experiences an acute lack of oxygen, the heart rate drops below 120 beats.
Development of a small heart
As the stage of pregnancy changes, the baby's heart rate also changes. Let's look at the fetal heartbeat at different stages:
- 4–6 weeks – the number of beats per minute should be 80–85;
- 6–8 weeks – 110–130 beats per minute;
- 8–11 weeks – the frequency of strokes in children increases to 190 strokes;
- From the 11th week, the heartbeat slows down, the number of beats gradually decreases to 130 beats per minute.
In the third part of pregnancy, 130–160 beats per minute is considered normal. This is much less than in the second part, but much more than the heart rate of an adult.
The baby's heart rate is very dependent on the mother's behavior. When a woman is resting, the number of strokes is one, and during physical activity it is different.
The level of audibility of the fetal heartbeat varies depending on its position (cephalic or pelvic), on which direction the baby is turned, and also on the abdominal tissue of the mother.