ROE in the blood: what is this indicator
Currently, the abbreviation ESR is used. The first letter “S” stands for speed. The reaction or speed shows the ratio of blood parts according to established standards. It does not define or even indicate a specific diagnosis. Any violation is a cause for concern, as it is associated with an inflammatory process. Doctors focus on the boundaries of the norm, which are influenced by gender and age characteristics.
Laboratory tests reflect disturbances in the body that occur due to encounters with infections. These can be both viruses and bacteria, as well as diseases of the systemic/autoimmune type.
Attention! Despite the fact that in recent years information has appeared about the lack of information value of this analysis, the indicators are especially important for women. Thanks to this study, doctors determine the presence of cancer.
Table of ESR norms in men by age
For healthy representatives of the stronger sex, the following indicators are accepted, measured in millimeters per hour:
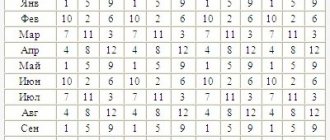
| Age, years | ESR value, mm/hour |
| 15-20 | From 1 to 10 |
| 20-50 | From 2 to 15 |
| 50- | From 2 to 35 |
Why is the ESR rate in the blood of men after 50 years higher than at a young age?
This is explained by the natural processes of aging: organ cells renew themselves more slowly, and destroyed ones that have outlived their usefulness remain in the body longer. This is also facilitated by various chronic diseases that occur in most patients by these years.
Decoding ESR in men
Decoding includes several degrees of deviation:
- I degree – deviations are no more than 1 mmh, and other clinical indicators correspond to healthy norms;
- II degree – the increase reaches 15-30 mm/h, indicating a minor inflammatory process;
- III degree - an increase in the ESR rate exceeds 30 mm/h, which is a sign of a pronounced inflammatory process;
- IV degree – deviation of ESR in men reaches 50 mm/h, which means that the patient is suffering from an acute form of severe infection. It is also possible to have a malignant neoplasm or an autoimmune lesion of the connective tissue.
All standards are relative, and in each laboratory they may differ slightly. Therefore, when decoding, you should always focus on the data specified in the research form, i.e. accepted in a specific clinic.
Normal for women
There are certain standards for healthy people and those whose bodies have encountered infections. Establishing the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is considered the easiest step in a complete blood count. The blood is stratified into dark and light, and laboratory technicians determine the presence of a problem based on the level of the light fraction.
ROE norm table
| Age | mm/h |
| Newborns | 0 – 2 |
| 0 – 6 months | 12 – 17 |
| 6 – 15 years | 4 – 12 |
| 15 – 25 years | 2 – 15 |
| 25 – 60 years | 4 – 12 |
| After 60 years | 10-20 |
Deviations that are noticed during the study of fractions can be either increased or, conversely, decreased. But laboratory technicians study precisely the sedimentation rate.
Decrease in ROE
But often when conducting tests, on the contrary, a decrease in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is detected. There are several reasons for this phenomenon. The first is hyperproteinemia, that is, an increase in total protein in the bloodstream. Also affected are changes in the shape of red blood cells, the presence of erythrocytosis, hepatitis, and intravascular disseminated coagulation syndrome. The rate of sedimentation can slow down if a man often goes hungry, does not eat meat in his daily diet, his muscle mass decreases, dystrophy of the heart muscle occurs, and overhydration occurs.
Sedimentation often depends on some external factors. During the daytime, the ROE indicator is maximum. But closer to evening, he hesitates. A decrease in ROE may be due to a pathology such as damage to the pituitary gland.
The presence of asthenia and neurotic syndrome also has a certain effect. Some factors can give false positive test results. That is, the man will have no diseases, but the ROE indicator will be unstable. The result of any examination depends on how correctly it is carried out. And the definition of ROE is no exception. A decrease in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is a consequence of technical errors or the use of Cortisone or Corticotropin during the examination period.
ROE can be determined only with strict adherence to all existing rules. The air temperature should be optimal - 18-25 degrees. The material from which the test tubes are made also plays an important role.
Thus, the norm of erythrocyte sedimentation rate in representatives of the stronger sex should be no more than 10, but not less than 1 mm/h. This indicator largely depends on age, the presence of pathologies, and the characteristics of external conditions. Of course, over the years this rate increases. In medical practice, an increase in this indicator is observed quite often. This becomes a signal about the presence of inflammatory processes in the body. To identify the underlying disease, the doctor must conduct a specific examination that will provide more information about changes in the man’s health. ROE is a most valuable diagnostic indicator that is always included in a general blood test. Therefore, if there are deviations from the norm, you cannot remain idle. It is important to promptly identify the causes of changes and select the optimal therapeutic approach to solve the problem.
Research methods
Blood is divided into a liquid part (plasma) and blood cells (erythrocytes). The essence of the study is that the laboratory assistant observes how red blood cells settle to the bottom of the test tube. There are two accessible and not very expensive research methods.
Panchenkov method
The biomaterial is taken from the finger and placed in a special Panchenkov capillary with an anticoagulant (5% sodium citrate solution). Mixing occurs at the rate of 4/1. The device remains at rest for an hour, after which the study takes place using a scale of one hundred millimeters. This option is considered somewhat rough, but more common.
Westergren method
This method is used in Russia and abroad. The material is taken from a vein, placed in a test tube, diluted with the same anticoagulant, but with a 3.8% solution. The laboratory assistant observes the sedimentation of the bodies and records the data according to a two-hundred millimeter scale. This option is considered more accurate, but is recommended less often, since not all laboratories have capillaries for testing.
The differences between the two methods are in the percentage of sodium citrate, as well as in the scale of measurement. If there are two hundred divisions, the sensitivity is considered higher.
What does increased ESR in the blood mean in men?
It is impossible to establish the exact pathology only based on ESR data in men, but its importance increases in diseases:
- musculoskeletal system (arthritis, rheumatism);
- endocrine system (hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus);
- respiratory organs (tuberculosis);
- myocardial infarction;
- paraproteinemias;
- hyperfibrinogenemia;
- injuries and fractures;
- burn injuries;
- infectious, viral (rare) and bacterial etiology;
- autoimmune nature;
- injuries (burns, fractures);
- oncological processes.
Taking tests
Depending on the choice of method, the clinic recommends preparation options. It is important to follow all the advice of your doctor. Dietary and bad habits can give not entirely correct results. Also, the subsidence reaction will be influenced by sports and active physical activity at home. It is advisable to stop them the day before the examination.
According to Panchenkov, the procedure is considered easier. When collecting capillary blood, no special preparation is required. The last dinner should be taken no later than 21 pm, without spicy or highly salty foods on the table. It is not recommended to even drink tea in the morning; blood must be donated on an empty stomach.
The second method is more complex and informative, so preparation for it will be different. Dinner must take place before 19:00. Eliminate from the diet 24 hours before:
- roast;
- fat;
- salty;
- spicy.
In the morning, it is forbidden not only to drink tea, but also to brush your teeth. Smokers and people who drink alcohol will have to abstain from it too. The more thorough the preparation, the more accurate the results.
Laboratory tests are usually carried out in the morning. When examining capillary biomaterial, the ring finger is treated, then a small puncture is made. Using a bulb and a glass rod, blood is drawn into a test tube whose walls are lubricated with a coagulant. It is required to prevent blood from clotting in conditions alien to it. When working with venous biomaterial, prepare the inner bend of the elbow joint by first applying a tourniquet to the shoulder. The test tube is connected to the needle, and after collection, it is automatically closed with a lid.
What happens in the laboratory?
The walls of the tube into which blood is collected must be coated with an anticoagulant. This is a substance that prevents blood from clotting. The test tube must be placed on a special stand in a vertical position so that the blood can independently separate into fractions. The lowest layer is formed by red blood cells.
On a note! For the first time, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate was determined by Fakhraeus, who studied the composition of the blood of pregnant women. Later, this method became routine (i.e., used constantly, in everyday practice).
Test tube with blood
Today there are two ways to determine the erythrocyte sedimentation reaction.
- According to Panchenkov - the blood is sent first into a glass tube, then onto the glass to mix with an anticoagulant, and then again into the tube and into a special installation - a tripod. After an hour, the size of the plasma segment is determined, which is located a layer higher than the red blood cells.
Panchenkov capillary
- According to Westergren , blood is mixed with an anticoagulant substance in a test tube, and the size of the plasma column is measured in it.
Conducting analysis. Blood
Reasons for increasing ROE
The reasons affecting subsidence may lie not only in cases of damage by viruses and bacteria. The more acute the disease, the higher the rate at which the cells fall. It is impossible to determine an accurate diagnosis only by the state of the red blood cells; this will require additional examination or decoding of the remaining components of the biomaterial. A slight increase in response will most likely not indicate pathology.
Factors causing deviations from the norm:
- heart failure;
- genetic inheritance concerning the deformation of red blood cells;
- childhood and retirement age;
- taking medications (antibiotics or NSAIDs);
- a laboratory technician’s mistake or problems with the temperature regime of the laboratory (the temperature should not be lower than 23 and higher than 28 degrees Celsius).
Clearly expressed deviations indicate an inflammatory process. The sooner treatment is prescribed, the greater the chance of bypassing the acute period and a sharp jump in red blood cell speed.
Diseases with accelerated sedimentation:
- ARVI, acute respiratory infections;
- infections of viral etiology (influenza, mononucleosis, chicken pox, herpes, cytomegalovirus, measles, mumps, rubella, viral hepatitis);
- ENT diseases (otitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis);
- respiratory tract diseases (pneumonia, tracheitis, bronchitis);
- inflammatory processes of the gastrointestinal tract (pancreatitis, appendicitis);
- disorders of the liver (hepatitis);
- inflammation of the gallbladder;
- helminthic infestations;
- sexually transmitted diseases;
- diseases of the skeletal system (arthritis, osteomyelitis);
- pathologies of the genitourinary system (cystitis, pyelonephritis, prostatitis);
- systemic diseases (lupus, vasculitis).
Reasons caused by slowing down sedimentation reactivity:
- intoxication;
- dehydration;
- swelling;
- increased bilirubin;
- avitaminosis;
- anemia.
The reaction or erythrocyte sedimentation rate allows the doctor to draw conclusions about the patient’s condition and prescribe further examination of the body.
There are many circumstances affecting women's health: poor environment, poor nutrition, genetic inheritance, weakened nervous system, promiscuity. All this weakens the immune system, the body becomes open to viral and bacterial attacks.
ROE during pregnancy
The results of studying ROE directly depend not only on age-related characteristics, but also on physiological changes. One of these is pregnancy. Hormonal changes cause deviations from the norm. This is due to the condition of the blood. It becomes viscous so that the baby can eat. This process occurs through the umbilical cord, which communicates between the hematopoietic system and the fetus. Therefore, the results are different from the results of any other girl of the same age.
Gestational age table
| Trimesters | mm/h |
| I | 45-55 |
| II | 50-60 |
| III | 60-70 |
The tables contain numbers provided that everything is in order with the pregnant woman and her child. Any disturbances in the process of gestation will have higher rates.
Expectant mothers should definitely pay attention to the following problems:
- prolonged toxicosis, weight loss;
- high or low-grade fever;
- headache, fainting;
- yellowness of the skin;
- increased swelling;
- painful sensations in bones and joints.
If you have at least one point, you don’t have to wait until the next test is due. You should contact a doctor immediately. Pregnancy is a complex process; events directly related to health can occur every day.
For oncology
One of the most dangerous conclusions that a doctor can make when studying a general blood test is the suspicion of oncological processes occurring in the body. An elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate may indicate a number of diseases of this type. The most dangerous are:
- malignant neoplasms and their metastasis.
- myeloproliferative diseases of the blood system (leukopenia, lymphoma, leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis, lymphocytic leukemia).
ROE will not give a reliable answer about the body’s collision with oncology. If the numbers are inflated, these laboratory tests are not enough; you need to use tests for tumor markers, do a biochemical blood test, as well as an MRI of the organs.
Indicators for oncological processes:
- results will exceed 70 mm/h;
- there is a drop in hemoglobin below 85 g/l;
- the body does not accept either anti-inflammatory or antibacterial therapy;
- sudden weight loss;
- general malaise, weakness.
Oncological diseases are not detected immediately. Very often, after reading the tests, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory or antiviral therapy, which has no effect on the body. If the indicators are high, the patient himself must insist on a more in-depth examination.
Attention! Hemoglobin, which can also be seen in laboratory tests, plays a large role in determining cancer. The lower it is, the fewer red blood cells there are in the blood.
Increased ROE after 30 years
If a woman feels well, and the laboratory values of ROE are high, then, first of all, pregnancy must be ruled out. Inflammatory processes give special symptoms that are difficult to confuse with something else:
- fever, chills;
- runny nose, cough;
- weakness.
Often, indolent bacterial diseases are observed. They can be determined by deciphering other components of the laboratory statement. This age is not safe for cancer. If the results are poor, you should visit the oncology center.
Increased ROE after 50 years
When studying blood test results in women at this age, first of all, all inflammatory processes are excluded. Infections can be either obvious or hidden. Weakened immunity is more susceptible to various viral attacks. Prolonged colds suffered “on your feet” can also produce inflated test results. But the most dangerous thing for women who have crossed the threshold of fifty is oncology. During this period, hormonal imbalances occur, which lead to disruptions. But you need to know that they can exceed the norm only by 5-7 mm/h. Higher rates should be studied in an oncology clinic. It is at this age that the body is most often susceptible to the growth of tumors.
In order not to miss serious viral or bacterial diseases, you should visit your doctor as often as possible. It is recommended to take a blood test at least once a year. If all obvious causes of inflammation have been excluded, you should contact the oncology center. Often, an increase in the rate of red blood cells hides more serious diagnoses than ARVI. The more careful a person is with his health, the stronger it will be.
How to reduce?
Let us immediately note that in order to normalize ROE, the doctor identifies the cause of the deviation and then prescribes appropriate treatment. At the same time, the decrease in ROE occurs at a slow pace, so the patient must first exclude possible physiological factors and analysis errors, and then conduct a full examination of the body.
Thus, treatment may include one or more of the following:
- Prevention - if there is a slight deviation in ROE, the patient should: be in the fresh air more often; to refuse from bad habits; do the exercises.
- Folk remedies, namely:
- Beets – to prepare the recipe, you need to boil 3 washed medium-sized beets for 2-3 hours. Then the patient drinks 50 grams of beetroot broth every morning on an empty stomach (for 14 days).
- Honey – It is important to consume 1 spoon of honey every morning or dilute the sweet treat in a glass of warm water.
- Herbs - it is best to use sea buckthorn, calendula, chamomile. But first you need to brew herbal tea in the amount of 2 tablespoons per glass of water. So, the patient sets the resulting solution on low heat and brings to a boil. Then the broth should be covered with a lid and cooled. Take – 100 ml 30 minutes before meals 2 times a day. The course is 1 month.
- Garlic (100 gr.) + lemon (5 pcs.) – garlic needs to be chopped and mixed with lemon juice. The resulting pulp should be stored in the refrigerator. Take – 1 time a day before bed (1 teaspoon), pre-diluted in boiled water.
- Diet – you should add to the diet: beef; liver; legumes; nuts; beet; dried fruits; veal; green vegetables; lettuce leaves.
- Medicines, including antihistamines, antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Surgery - in difficult situations, for example, with oncology.
For more information about ROE, watch the following video:
In conclusion, we note that ROE is one of the main elements of a standard blood test. If ROE is abnormal, you should not self-medicate, because in this way you can worsen the patient’s condition. Therefore, our material will help you understand the features of the abbreviation ROE, but only a therapist can prescribe the correct treatment.
How to donate blood correctly
To obtain a reliable test result, blood for ROE must be donated in the morning, on an empty stomach. A couple of days before the test, you need to limit your consumption of fatty, spicy, salty and fried foods. During the day before taking a blood test, you should not exercise, take sedatives or sleeping pills, and you should also refrain from undergoing physiotherapeutic procedures and x-rays.
In medicine, there is the concept of “false increase in ROE”. The most common reason for receiving false results is technical error. That is why it is recommended to take a blood test in one laboratory, and at regular intervals - comparing the results obtained will help to avoid possible errors.
It is also worth finding out about the normal number of leukocytes in the blood.
Importance during pregnancy
The ESR norm changes in women throughout pregnancy, as biochemical changes occur in her body aimed at the safe bearing of the fetus. Changes in ROE in this case are normal and do not require any medical measures.
ROE in the blood increases in the first two trimesters of pregnancy. The maximum value of ROE is usually observed in the last stages of pregnancy, and can increase up to 45 mm/hour. This figure gradually normalizes in the postpartum period.
ESR norm in women after 60 years of age: everything you need to know about this indicator
After reading the publication, don’t forget to: – press “thumbs up”; – subscribe to the channel, because every subscriber is very important to us. - leave .
The photographic material was used from free access Yandex and is an illustration of the author’s thoughts
The older a woman gets, the greater the risks to her health. Especially after menopause. It leads to serious hormonal changes, which become very stressful for the body.
Because of this, organs begin to work more slowly, and therefore the speed of work of the entire organism as a whole decreases. As a result, immunity decreases, metabolism slows down and other disorders occur.
That is why it is necessary to always monitor your health, pay attention to nutrition and sports. And also undergo scheduled examinations on time. It is also very important to know about the basic norms. This information will help you not to worry about every little thing and get treatment on time. The ESR norm for women after 60 is one of the main indicators.
It is determined by a general blood test. It allows you to find out if there are any inflammatory processes in the body that can lead to various exacerbations and complications. Knowing what the normal ESR rate is for women over 60 years of age can help prevent the development of a number of diseases.
Therefore, the article will focus specifically on this indicator and what it depends on.
Norm of ESR in women after 60 years: features of the study
This abbreviation stands for erythrocyte sedimentation rate. To find out whether the ESR is normal in women after 60 years of age, sodium citrate is added to the test tube. This substance helps stop blood clotting so that a laboratory technician can conduct an analysis. The test tube is left for 60 minutes. During this time, red blood cells precipitate, which is examined.
ESR norm after 60 years in women: indicators
It is important to remember that norms differ between men and women. And this is normal, since the bodies of representatives of different sexes secrete different amounts of hormones and other substances that affect the organs and the blood itself.
Also, the ESR norm after 60 years in women differs from the norm of 30. It almost doubles. That is, for a thirty-year-old representative of the fair sex, the normal rate is from 8 to 25 millimeters per hour.
And the ESR norm after 60 years in women is already from 12 to 53 millimeters per hour.
How quickly red blood cells settle directly depends on their number. If there are a lot of them, then they go down quickly, but if they are sparse, they go down slowly. The latter indicates anemia.
Whether the ESR norm in women after 60 years corresponds to the test results obtained allows us to determine whether diseases are developing. But this figure does not provide a single and accurate answer. To find out what exactly is happening, you need to conduct a comprehensive study, which will help identify a possible problem.
To ensure that women have peace of mind about their health, doctors recommend that they get tested once a year. And if the ESR norm for women after 60 years of age does not correspond to the indicators, then representatives of the fair sex need to undergo repeated tests several times over the next three months after the problem is identified.
Low performance
Test results with a low ESR level indicate that the woman does not receive enough vitamins. This is caused by strict diets, fasting, and complete abstinence from food of animal origin.
Also, a decrease in the number of red blood cells is affected by a decrease in the level of bilirubin and fibrinogen. In some cases, this may also occur due to the use of certain medications.
To stabilize the condition, in most cases, it is enough to stop taking medications and change your diet.
High performance
But in this case the threat is much greater. A high ESR indicates that some inflammatory processes are occurring in the body. For example, ESR reaches 80 millimeters per hour if a woman suffers from arthritis or pneumonia.
Also, a deviation from the norm may indicate that she has:
· kidney and liver disease;
· pre-infarction and pre-stroke condition;
· anemia;
· oncology.
What do we have to do
Returning ESR to normal is quite simple. You just need to see a doctor in time. If the therapist sees this deviation, he will immediately refer you to other specialists who will help determine the exact cause and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
To solve the problem, you need to strictly follow the instructions and not panic. Also, before taking tests, do not forget to follow the simple rules that all doctors talk about: do not eat fatty, spicy and starchy foods in the evening and take the test only on an empty stomach.
There is nothing creepy or terrifying about deviating from the norm. This is just a signal that helps to identify problems in the body in time and prevent more serious consequences. This is why it is so important to always undergo routine examinations, donate blood and not self-medicate.
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5cb81105374cc200b426bb50/5cc08f1098348200b0ab57a9
What is ROE and the age norm for women and men
Medical test forms contain symbols and numbers that are understandable only to specialists. One of them is ROE in the blood. Let's figure out what this diagnostic indicator means and what processes in the body it talks about. Today, the abbreviation of this study has changed somewhat and looks like ESR, but its essence remains the same.
Conducting research
First, let's figure out what ROE is. Red blood cells, as formed elements of blood, have a certain mass and settle over time, but not always with the same acceleration.
The speed depends on the red blood cells themselves and the composition of the plasma. If the immune system is active, the plasma becomes thicker due to additional protein fractions.
The latter slow down the process of sedimentation of red blood cells, which affects ROS (erythrocyte sedimentation reaction).
The study is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach. The day before it is necessary to avoid spicy, fried and fatty foods. Before the procedure, you can drink only water, do not drink alcohol, smoke, or be nervous so that the initial data does not change.
The study begins with taking blood from a finger into capillaries with an anticoagulant, which are left in a vertical position in a Panchenkov stand. Within 1 hour, the blood is divided into layers. A column of plasma appears above the layer of settled red blood cells. Its height in mm/hour represents ROE in a blood test.
There is also a more accurate modern automated modification of the Westergren test, in which results are obtained in 30 minutes, but it is rarely used.
ROE norm by age
To understand in which direction the results of the study have changed, we focus on the norms of ROE in the blood, depending on gender and age.
Table 1A. Norm ROE depending on age.
| Age | ROE (mm/hour) |
| Infants up to one month old | 0—2 |
| Children under six months | 12—17 |
| Children over 6 months of age | 2—8 |
| Men under 60 years old | 1—8 |
| Men over 60 years old | less than 15 |
| Table 1B. Norm ROE in women by age. Girls under 13 years old | 7—10 |
| Teenage girls | 15—18 |
| Women under 50 years old | 2—12 |
| Second half of pregnancy | 40—50 |
| Women over 50 years old | less than 20 |
An analysis for ROE can be prescribed if there are female complaints:
- unexplained weight loss;
- anemia;
- pain in the pelvic area;
- headache;
- poor joint mobility.
The first signs and symptoms of a stomach ulcer
Increased ROE occurs during menstruation and pregnancy. In the postpartum period, the values of the diagnostic index are normalized.
If the norm in women is increased, further examination is necessary, since the properties of the blood change due to:
- decrease in albumin-globulin ratio;
- changes in blood plasma pH;
- saturation of red blood cells with respiratory protein.
Increase in ROE
An increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation reaction is not always a sign of pathological phenomena in the body. Physiological processes can affect it:
- Intense physical activity that speeds up metabolism.
- A number of medications, in particular, contraceptives, dextrans drugs with high molecular weight.
- Diets in which the concentration of plasma proteins increases due to limited water intake. ESR also increases after a meal (up to 25 mm/hour), which is why blood is taken for analysis on an empty stomach.
An increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate also occurs in pathologies of various etiologies, among them:
- weakening of the body's defenses;
- development of the tumor process;
- formation of necrosis;
- destructive changes in connective tissue;
- foci of inflammation.
For a doctor, a prolonged increase in ROE in the blood up to 40 mm/hour in combination with other laboratory tests is of great diagnostic importance.
Reasons for increased ROE
An increase in the level of plasma proteins, cholesterol (https://proflady.ru/lechenie-i-profilaktika/kak-snizit-kholesterin.html), and the ability of blood cells to aggregate are associated with the following pathologies:
- Chronic or acute inflammation of an infectious nature. ESR allows you to find out what stage the disease is at and whether its treatment is effective. With a viral infection of the body, the index has lower parameters compared to bacterial infections.
- Impact of certain medications.
- Hypercholesterolemia.
- Severe poisoning of the body, especially with heavy metals.
- Injury to organs as a result of injury or surgery.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine glands, increased thyroxine and triiodothyronine (thyroid hormones).
- Damage to the liver, kidneys, intestines, pancreas.
- Heart diseases.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
An ESR level of up to 70 mm/hour without inflammation may indicate an oncological process. This erythrocyte sedimentation reaction can be observed in various neoplasms, such as lymphosarcoma, myeloma and others.
Decrease in ESR
A drop in ROE levels may be a sign of:
The benefits and harms of succinic acid
A decrease in ESR is also observed with vomiting and diarrhea.
ROE changes differently at different stages of even one pathology:
- With tuberculosis, ROE may remain unchanged, except in advanced cases or until the disease is accompanied by a complication.
- The acute period of an infectious disease is accompanied by an increased ESR only from 2-3 days. At the same time, with a diagnosis of lobar pneumonia, the indicator remains high, even if the crisis has passed.
- At the beginning of acute appendicitis (https://proflady.ru/lechenie-i-profilaktika/simptomy-appenditsita.html), the laboratory test values remain unchanged.
- A slight increase in ROE is observed with active rheumatism, but its decrease may indicate acidosis or blood thickening.
- The subsiding infectious process is accompanied by normalization of the total number of leukocytes, ROE decreases later.
Soe in children
In children, fluctuations in ROE in one direction or another are not a sign of infection. You should be concerned at values exceeding 15 mm/hour. Values of 40 or more mm/hour accurately indicate a pathological process.
An increase in ESR in a child can be caused by: sore throat, flu, allergies, colds. Sometimes the reason may be a lack of vitamins in the baby's diet or that he is teething. But most often the ESR rate in children increases for the following physiological reasons:
- taking hormonal medications during lactation;
- anemia;
- vaccination;
- features of the diet of a nursing mother.
It is impossible to understand that the ESR is higher than normal without a special blood test. By elevated body temperature and tachycardia, one can only suspect an approaching infectious process, which is usually accompanied by altered hematological parameters.
After determining the type of pathology, appropriate treatment is prescribed, carried out under medical supervision with regular tests to determine the dynamics of the patient’s condition.
What is ROE and the age norm for women and men Link to main publication
Source: https://ProfLady.ru/lechenie-i-profilaktika/chto-takoe-roe-i-normzhenshchin-po-vozrastua-dlya.html
Different people have different erythrocyte sedimentation rates
There are indicators whose value is a constant - a value that should not go beyond specific values in any case, the same for people of both sexes and all ages. These include, for example, blood sugar levels, blood pH values, etc. But the ROE level may vary. So, in newborn babies this figure is no more than two mm/h, in children under six months old – 12-17 mm/h. In children from six months to 6-7 years, the indicator remains at the level of 1-8 mm/h. The male norm is from 1 to 10 mm in 1 hour, but for women it is slightly higher - up to 15 mm/hour.
Why can the erythrocyte sedimentation reaction be increased if there is no pathology? There may be the following reasons for this:
- taking oral contraceptives (including combined, purely progestogen and any others);
- fasting, strict diet, dehydration;
- physical activity (for example, for female athletes during active training);
- age;
- pregnancy.
Erythrocyte sedimentation reaction
Some physiological causes of changes in erythrocyte sedimentation rate are worth considering separately.
Age
It is worth noting that even among women of the same age, differences in erythrocyte sedimentation rate are quite acceptable. It depends on whether you are pregnant, age and even weight. In addition, each laboratory (not to mention different countries and their different standards) determines the boundaries of the norm in its own way. So, in the West, the upper limit of the norm for women is considered to be 20 mm/h.
Table. Normal ROE values depending on age.
| Age | Normal values |
| 0-13 years | 7-10 |
| 13-19 years old | 15-18 |
| 20-45 years | 2-15 |
| Over 45 years | 15-20 |
The value of ESR in women may depend on age
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a special condition of a woman, in which all processes in her body occur differently. Even the viscosity of her blood changes to make it “easier” for the fetus to absorb nutrients from the umbilical cord blood as part of the uteroplacental blood flow. Therefore, the value of this indicator in a pregnant woman differs from that of a non-pregnant girl.
Norms of a woman's blood parameters during pregnancy by trimester
In the first half of pregnancy, the erythrocyte sedimentation reaction normally increases to 50-60 mm/h, and in the second half – to 60-70 mm/h. This indicator also depends on the woman’s weight. The more she gained during pregnancy, the higher the indicators should be expected.