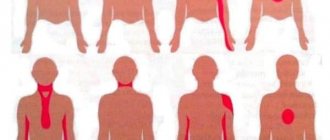
Anatomical features
First, it’s worth explaining what is on the right side of the chest. In fact, the answer is not entirely clear-cut. After all, the sternum is a long bone to which the spine and ribs are attached. They form the chest. And it, in turn, protects the organs that are located underneath it. The list is as follows:
- Thymus.
- Heart.
- Esophagus.
- Liver.
- Lungs.
- Pancreas.
- Nerves and blood vessels.
- Gallbladder.
Therefore, if a person feels tingling in the designated area, the problem could be related to anything.
Tingling in the chest: causes, diagnosis and treatment
Tingling in the chest is not a diagnosis, but a serious pathological syndrome. It is very blurry, as it appears in many ailments. Having noticed its systematic presence, it is necessary not to self-medicate, but to consult a doctor. After making a diagnosis, he will determine the exact cause of the disease, and then the treatment.
Now we will talk about the most likely prerequisites for the appearance of the syndrome, the principles of examination and further therapy.
Discomfort on the right
Often a person is able to listen to his feelings and determine where exactly the pain is localized. Often the discomfort is widespread, and this is difficult to do. But if a person clearly feels a tingling sensation in the chest on the right, then there is a high probability that the cause lies in one of the following conditions:
- Injury resulting from vigorous physical activity. If, for example, a person’s body is not prepared for high loads, then he can simply stretch his chest muscles.
- Fractured ribs. This is usually indicated by sharp tingling sensations. If a person coughs or squeezes that area, the pain will become much stronger.
- Injury. If this is indeed the reason, then a bruise will be visible at the place where the discomfort is localized.
- Pathologies of the respiratory or gastrointestinal tract.
If in the first three cases everything is more or less obvious (it is difficult not to notice the fracture), then in the case of diseases it is a little more complicated. Therefore we should dwell on them.
Pneumonia
With this acute lung injury, tingling in the chest often occurs. Pneumonia is caused by a bacterial infection. The disease can also develop due to chest trauma, exposure to allergens or toxic substances. At risk are people who smoke, as well as anyone who abuses alcohol.
In addition to tingling in the chest on the right side, the following symptoms are observed:
- High temperature (more than 39 °C).
- Chills.
- Weakness.
- Dyspnea.
- Dry and unproductive cough, which is replaced by “rusty” sputum on days 3-4.
- Cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle.
- Hyperemia of the skin.
- Rapid shallow breathing.
- Frequent, arrhythmic pulse, low blood pressure, muffled heart sounds.
For diagnosis, ultrasound of the pleural cavity, echocardiography, X-ray of the lungs, blood and urine tests, and sputum analysis are performed.
Treatment is carried out in a hospital, in the pulmonology department; bed rest, a high-calorie diet, and plenty of fluids are required. In serious cases, oxygen inhalations are prescribed.
But the main principle of treatment is antibacterial therapy. Doctors also often prescribe antihistamines, expectorants, mucolytics, antipyretics and immunostimulants.
Pleurisy
Under this name, inflammation of the parietal and visceral layers of the pleura is known. The cause is not always an infection. It can be trauma, a malignant tumor, diffuse lesions, pulmonary or myocardial infarction, etc.
Pleurisy can be dry and exudative. Typically the symptoms are:
- Tingling in the chest, aggravated by movement, breathing and coughing.
- Gentle, shallow breathing.
- Slightly elevated body temperature.
- Chills, night sweats, weakness.
- Dull pain in the side.
- Painful dry cough.
- Hoarseness of voice.
- Swelling of the neck and face.
- Hemoptysis (if serous pleurisy).
As part of the diagnosis, an ultrasound, x-ray, pleural puncture, and blood test are performed. Thoracoscopy with pleural biopsy may be necessary.
The goal of treatment is to eliminate the etiological factor and alleviate symptoms. If pleurisy is caused by pneumonia, the patient is prescribed antibiotic therapy.
A rheumatic disease is treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as glucocorticosteroids. For tuberculous pleurisy, streptomycin, isoniazid, and rifampicin are prescribed.
To eliminate symptoms, diuretics, analgesics and cardiovascular drugs are prescribed.
Cholecystitis
Inflammation of the gallbladder is also accompanied by tingling in the chest. Cholecystitis occurs due to stagnation of bile and infection.
It does not appear on its own; it is preceded by some illness. This could be cholelithiasis, dyskinesia, congenital anomaly, tumor, cyst, etc. In addition to tingling, the following symptoms are observed:
- Paroxysmal pain in the right side of the abdomen, which radiates to the shoulder, collarbone and scapula.
- Neurosis-like conditions.
- Weakness.
- Insomnia.
- Sweating.
- Dyspnea.
- Nausea and vomiting with bile.
- Bloating and bowel irregularities.
- Belching with an unpleasant aftertaste.
- Feeling of bitterness in the mouth.
- Chills.
- Tachycardia.
- Hypotension.
After a general examination, ultrasound of the gallbladder, fractional duodenal intubation, cholecystocholangiography, and laboratory blood tests are prescribed.
Usually these measures are enough, but they can additionally perform MSCT, FGDS, hepatobiliscintigraphy, and laparoscopy.
The patient is prescribed a strict diet No. 5, physiotherapy, as well as taking antispasmodics, painkillers, and antibacterial agents. When remission occurs, the patient is prescribed choleretic, choleretics and cholekinetics.
Coronary heart disease (CHD)
This ailment is often indicated by tingling in the left side of the chest. IHD is a functional and organic damage to the myocardium, caused by cessation or lack of blood supply to the heart muscle. About 97-98% of cases are caused by atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries.
The disease is usually asymptomatic and can last for decades. But the manifestations are still present. Most often the symptoms are as follows:
- Pain in the lower jaw, arm and back.
- Increased heart rate.
- Dyspnea.
- Nausea.
- Dizziness and weakness.
- Blurred consciousness.
- Excessive sweating.
- Fainting.
IHD often leads to heart failure. Therefore, if a person feels a suspicious tingling sensation in the left side of the chest, he should go to a cardiologist.
Diagnosis is carried out in a dispensary or hospital. They prescribe the study of specific enzymes, ECG, echocardiography, stress echocardiography, functional exercise tests, 24-hour monitoring, transesophageal electrocardiography, coronography.
The treatment is specific. It can be non-drug, drug, surgical or endovascular. It all depends on the specific case.
Angina pectoris
This is one of the forms of ischemic heart disease, and therefore it also causes tingling in the chest on the left side. Predisposing factors for its development include physical inactivity, smoking, hyperlipidemia, arterial hypertension, obesity, diabetes mellitus, severe stress, increased blood viscosity, intoxication and anemia.
The main symptom is pain. The discomfort first manifests itself as a tingling sensation on the left side of the chest. As the disease progresses, the sensations become squeezing, burning, pressing, drilling, pulling, cutting. At first, the pain is simply unpleasant, but then it becomes so severe that patients have no strength left to restrain their screams.
In addition to the examination methods already listed, a blood test is required for cholesterol, ALT and AST, lipoproteins, electrolytes, creatine kinase and other substances. Velgoergometry is also required.
If we talk about treatment, it is aimed at stopping and further preventing attacks of angina pectoris. Patients are prescribed nitroglycerin, which must be taken when they approach. Planned therapy involves taking antianginal drugs, molsidomine, b-blockers, as well as calcium channel blockers, antioxidants, antiplatelet agents and anti-sclerotic medications.
Pericarditis
Do you feel a tingling sensation on the left side of your chest? Perhaps the reason lies in inflammation of the pericardial sac. It may be post-infarction, rheumatic or infectious in nature. Prerequisites include viral and bacterial infections, heart damage, allergic and systemic connective tissue diseases, metabolic disorders, defects, etc.
In addition to tingling, the following symptoms are observed:
- Conditions resembling an angina attack.
- Dyspnea.
- Dry cough.
- Chills.
- Increased heart rate.
- Feeling of tightness in the chest.
- Hiccups.
- Dysphagia.
- Fever.
- Swelling of the neck and face.
- Skin cyanosis.
- Swelling of neck veins.
Diagnostic measures are similar to those listed above. Treatment is determined taking into account the clinical and morphological form of the disease. In any case, until the activity of the process subsides, the person must remain in bed.
Myocarditis
Another common reason why tingling sensations are felt in the chest area. Myocarditis is an inflammation of the muscular lining of the heart. It is usually caused by viral, bacterial, parasitic and fungal diseases.
Clinical symptoms depend on how severely the myocardium is damaged, where the damage is localized, how quickly the inflammation progresses, etc. In any case, there is a disturbance in the heart rhythm and insufficiency of contractile function.
Mostly, patients who are subsequently diagnosed with myocarditis complain of increased fatigue and weakness, increased sweating and joint pain. Attacks of atrial fibrillation occur less frequently.
In addition to the diagnostic methods listed above, bacteriological blood culture is also required to identify the pathogen. They may prescribe PCR diagnostics, endomyocardial biopsy, scintigraphy, MRI and radioisotope studies.
The acute stage is an indication for hospitalization. The patient is prescribed bed rest for 4-8 weeks, a diet enriched with proteins and vitamins, as well as therapy in 4 areas - metabolic, etiological, symptomatic and pathogenetic.
Aortic aneurysm
This illness is possible if a person feels a tingling sensation in the middle of the chest. An aneurysm is a condition in which a section of the main artery is pathologically dilated. The reason is the weakness of its walls.
Clinical manifestations are variable. Often there are no symptoms at all. But specific manifestations include increased pulsation in the abdomen, tachycardia, headaches, swelling of the upper half of the body and face, as well as shortness of breath.
Increased salivation, bradycardia, hoarseness, dry cough, pain in the left shoulder blade and arm are rare.
As part of the diagnosis, ultrasound, tomography and x-ray examinations are performed. And not only the heart, but also the abdominal cavity and esophagus.
If the disease does not progress, the patient is simply observed by a surgeon and undergoes regular X-ray monitoring. If the diameter of the thoracic aneurysm exceeds 5-6 cm, surgery is indicated.
Myocardial infarction
A sharp, dagger-like pain in the middle of the chest, radiating to the lower jaw, collarbone, ear, teeth, neck and shoulder, indicates an acute violation of coronary circulation.
An attack can last from 30 minutes to several hours, or even days, and cannot be stopped by taking nitroglycerin. The patient feels severe weakness, but at the same time excitement. There is pallor of the skin, shortness of breath, anxiety, and high blood pressure.
There is only one indication here - emergency hospitalization in the cardiology department. After emergency assistance is provided, treatment will continue there. And in the first 24 hours, perfusion is restored through emergency balloon coronary angioplasty or thrombolysis.
Hepatic colic
This phenomenon often occurs in the presence of chronic diseases of this organ. In 75% of cases, hepatic colic indicates cholelithiasis. The cause of this disease is usually poor nutrition.
If a person eats too fatty, spicy and salty foods, then his gallbladder begins to contract less actively. And the stones are sent to the ductal system. Because of this, the outflow of bile is disrupted, and intravesical pressure increases. As a result, a person not only has a stabbing sensation under his right breast, he also develops other symptoms:
- Night attacks: a person tosses around in bed, trying to find a position that will relieve the pain.
- Discomfort in the area of the right shoulder blade, shoulder, neck and supraclavicular area.
- Irradiation of pain in the heart.
- Nausea.
- Vomiting bile.
- Bloating.
- In especially severe cases – high temperature.
Diagnosis of colic involves conducting a physical examination and studying medical history. The doctor examines the skin, palpates the abdomen, sends the patient for an ultrasound, radiography and tests. Sometimes you can’t do without MRI and CT.
And if a person has a tingling sensation under his right breast due to hepatic colic, he is hospitalized in the gastroenterology department. In the first days hunger is shown, then table No. 5. They also prescribe “Atropine sulfate”, “Mebeverine”, “Platifillin”, “Papaverine” or another effective remedy. Pain syndrome is relieved with Ketorolac, Ketoprofen or Metamizole sodium.
Stitches in the chest: right, left, middle, when inhaling, what is it? – Pulmonologist
07.11.2019
The chest contains several vital organs. A malfunction of one of them leads to the appearance of sharp pain, forcing a person to dramatically change their lifestyle and seek medical help.
It is very important not to ignore pain or try to self-medicate, especially if the exact cause of the discomfort is unknown.
Uncontrolled use of medications can aggravate the situation and accelerate the development of a dangerous disease, reducing the chances of its successful cure.
Why does it sting in the right side of the chest at the level of the heart?
With rib fractures, there is sharp pain in the chest, intensifying with inhalation and pressing on the chest
Chest pain on the right can accompany various diseases - from neurology to pathology of the gastrointestinal tract or respiratory organs. Therefore, for patients who have a stabbing sensation in the sternum on the right, it is important to describe their sensations as accurately as possible so that the doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis and prescribe studies to confirm or refute it.
Traumatic consequences
In patients who are actively involved in sports or have recently suffered a serious injury, tingling in the right side of the chest may be due to:
- Muscle strains due to physical activity. Increasing the load can lead to overstrain of muscle tissue, to which it will respond with sharp pain when moving.
- Fractured ribs. The nature of the pain in this case is acute, increasing with inhalation and when pressing on the sternum area. At the same time, an inflammatory process is observed in the tissues in the area of the fracture.
- Chest tissue bruise. The pain symptom in this case is accompanied by blue discoloration of the skin.
Treatment of traumatic lesions of the chest is aimed at eliminating the main causes of pain. As soon as the bone or muscle tissue is restored, the discomfort will disappear or be less frequent.
Respiratory system diseases
Pneumonia symptoms and risk factors
A significant proportion of the total causes of pain in the chest are diseases of the respiratory tract.
Pneumonia is a bacterial infection that has entered the respiratory tract. It can cause a noticeable tingling sensation in the chest on the right or left when inhaling.
Allergens, other concomitant diseases, as well as bad habits: smoking and alcohol abuse can aggravate the pain symptom. In addition to tingling, patients with pneumonia experience a sharp increase in body temperature, chills, shortness of breath and weakness.
The skin tone becomes painful, the nasolabial triangle turns blue, the pulse becomes arrhythmic, breathing becomes frequent and shallow.
An accurate diagnosis can be made based on the results of ultrasound, echocardiography and x-rays. In addition, pneumonia can be confirmed based on clinical tests of blood, urine and sputum.
Treatment is carried out in a hospital setting under the constant supervision of doctors. Oxygen treatments, drinking plenty of fluids and nutritious nutrition can speed up the healing process and completely defeat the causative agent of the disease.
Drug treatment involves taking antipyretic, antibacterial and immunostimulating drugs.
Pleurisy - the diagnosis is made when the layers of the pleura become inflamed, which makes itself felt by pain in the chest and side of the affected lung.
Causes include bacterial infection, heart disease, traumatic injury or the development of cancer.
Added to the discomfort are symptoms such as shallow breathing, a slight increase in body temperature, weakness and sweating, dry cough and noticeable hoarseness in the voice. If the patient is diagnosed with serous pleurisy, sputum with blood is released when coughing.
To confirm or refute the diagnosis, the patient is referred for a pleural puncture, blood test, ultrasound and x-ray. A biopsy of a sample of pleural tissue can exclude the development of a malignant tumor.
Treatment is aimed at eliminating the underlying causes and making breathing easier. The patient is prescribed a course of antibiotic and anti-inflammatory drugs, specialized medications are prescribed depending on the nature of the underlying disease.
Cholecystitis
Inflammation of the gallbladder, which occurs as a result of stagnation of bile and the development of infection, makes itself felt by tingling pain in the chest. As a rule, the pathological process is caused by cholelithiasis, the development of neoplasms, congenital anomalies of the gallbladder, cysts, etc.
In addition to discomfort in the chest area, the disease is accompanied by symptoms such as pain in the right side of the abdomen, neuroses, weakness and shortness of breath, and insomnia. The patient has a visually noticeable bloating of the abdomen, which causes nausea, belching, and stool disturbances.
The inflammatory process causes chills and tachycardia.
An accurate diagnosis can be made based on the results of an ultrasound examination, laboratory blood test, duodenal intubation or cholecystocholangiography.
Less commonly, to clarify individual specific symptoms, the patient may be referred for laparoscopy or an MSCT procedure.
It is possible to cope with the disease thanks to a medication course based on antibacterial drugs and antispasmodics, as well as through physical therapy and a strict diet.
Cardiac ischemia
Pain in this disease is most often localized in the left side of the chest. But sometimes patients talk about the vague nature of the pain, which allows the doctor to assume a problem with the heart.
Coronary artery disease is associated with damage to the heart muscle, which lacks nutrition and oxygen due to a sharp deterioration or cessation of blood supply.
The overwhelming majority of cases of the disease are a consequence of atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries.
The problem with coronary heart disease is its asymptomatic course. Signs are subtle and can be easily ignored, especially if the patient leads an active lifestyle and often experiences physical fatigue.
Suspicion of IHD may be caused by complaints of pain in the back and arm, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, weakness and dizziness. The patient also notes clouding of consciousness, nausea, fainting and increased sweating for no apparent reason.
Ignoring these symptoms can lead to heart failure, the treatment of which is more difficult and longer. Therefore, at the first signs of heart problems, it is important to visit a cardiologist as soon as possible.
The main methods for diagnosing coronary heart disease are daily monitoring, ECG, echocardiography, coronography, electrocardiography and other additional studies that allow you to obtain a complete clinical picture. Depending on the results, the patient is prescribed medicinal, surgical or endovascular treatment, taking into account the general condition of the body and the degree of development of the pathology.
Angina pectoris
One of the common forms of coronary heart disease, the development of which is provoked by bad habits, hypertension, diabetes, stress or obesity. Painful sensations increase as the disease develops, gradually acquiring a cutting and burning character.
The diagnosis is made based on the patient’s complaints and is confirmed by the results of a chemical blood test and bicycle ergometry.
Treatment is aimed at reducing the frequency and severity of angina attacks, which can be controlled by taking nitroglycerin, antioxidants and antianginal drugs.
Aortic aneurysm
If the pain is not precisely localized to the right side of the chest and is vague, the patient may have an aortic aneurysm. This is the name for the condition of pathological expansion of the artery due to weak, too elastic walls.
Symptoms of the disease may be completely absent, but more often there is pain, which is accompanied by a rapid pulse, shortness of breath, and severe swelling of the upper body.
Some patients also complain of intense salivation, dry cough and hoarse voice.
In order to clarify the diagnosis, an ultrasound examination, tomography and x-ray are performed, including the entire chest, esophagus and abdominal cavity in the area of study.
If the aorta is slightly enlarged, no treatment is prescribed; the patient is prescribed periodic monitoring with X-ray examination. If the aortic fragment increases to 5-6 cm in diameter, surgical intervention is indicated.
If the disease is detected in the early stages of development, its symptoms can be completely managed with minimal risk of their recurrence.
When Chest Pain Cannot Be Ignored
If you experience dizziness with chest pain, you should consult a doctor.
You should not tolerate tingling on the right side of the chest because this symptom may hide a serious illness. But there are situations when you should see a doctor immediately.
- sharp throbbing pain on the right;
- labored breathing.;
- nausea;
- sudden pallor of the skin;
- dizziness;
- increased heart rate;
- sweating;
- a sharp drop in blood pressure.
The results of ultrasound, radiography, computed tomography, and blood tests allow us to establish the exact cause of pain and prescribe effective treatment. Treatment is prescribed depending on the refined diagnosis and the clinical picture of the development of the underlying disease.
Source:
Tingling in the chest: causes, diagnosis and treatment
Tingling in the chest is not a diagnosis, but a serious pathological syndrome. It is very blurry, as it appears in many ailments. Having noticed its systematic presence, it is necessary not to self-medicate, but to consult a doctor. After making a diagnosis, he will determine the exact cause of the disease, and then the treatment.
Now we will talk about the most likely prerequisites for the appearance of the syndrome, the principles of examination and further therapy.
Discomfort on the right
Often a person is able to listen to his feelings and determine where exactly the pain is localized. Often the discomfort is widespread, and this is difficult to do. But if a person clearly feels a tingling sensation in the chest on the right, then there is a high probability that the cause lies in one of the following conditions:
- Injury resulting from vigorous physical activity. If, for example, a person’s body is not prepared for high loads, then he can simply stretch his chest muscles.
- Fractured ribs. This is usually indicated by sharp tingling sensations. If a person coughs or squeezes that area, the pain will become much stronger.
- Injury. If this is indeed the reason, then a bruise will be visible at the place where the discomfort is localized.
- Pathologies of the respiratory or gastrointestinal tract.
Source: https://nyaganngp1.ru/legkie/kolet-v-grudnoj-kletke-sprava-sleva-poseredine-pri-vdohe-chto-eto.html
Malignant liver diseases
Because of them, many patients also have a tingling sensation under the right breast. If a person has developed a malignant neoplasm, the discomfort also radiates to the side. Other symptoms include the following:
- Causeless weakness.
- Increased fatigue.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Tendency to diarrhea and constipation.
- Anemia.
Subsequently, nasal and gastrointestinal bleeding, ascites, telangiectasias on the skin, fever, chills, jaundice, itching appear, and urine and feces may also become colored (dark and light colors, respectively).
It is very important to do an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, percutaneous biopsy, MRI or CT, static scintigraphy, celiacography, splenoportography, laparoscopy and PET scan of the liver on time. In addition, to clarify the diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a number of other related studies.
And if a person has a stabbing sensation under the right breast due to the development of a malignant tumor, then he will be prescribed a combination treatment, which involves liver resection combined with a course of chemotherapy.
When Chest Pain Cannot Be Ignored
You should not tolerate tingling on the right side of the chest because this symptom may hide a serious illness. But there are situations when you should see a doctor immediately.
- sharp throbbing pain on the right;
- labored breathing.;
- nausea;
- sudden pallor of the skin;
- dizziness;
- increased heart rate;
- sweating;
- a sharp drop in blood pressure.
The results of ultrasound, radiography, computed tomography, and blood tests allow us to establish the exact cause of pain and prescribe effective treatment. Treatment is prescribed depending on the refined diagnosis and the clinical picture of the development of the underlying disease.
Breast diseases
This is a problem that women under 50 years of age often face. And it often causes pain in the sternum. The most common disease is fibrocystic mastopathy. It is characterized by an excess of hormones, which leads to the tissue growing and growths forming.
There can be many reasons - lack of sexual intercourse due to psychological disorders, pathologies of metabolic processes, heredity, chronic fatigue syndrome, lack of fiber and others.

After the doctor has performed palpation, biocontrast mammography, ultrasound, MRI, diaphanoscopy and ductography, other diagnostic measures may be prescribed. This is a breast biopsy, ultrasound of the thyroid gland, liver and adrenal glands, CT scan of the pituitary gland, etc. Then treatment is prescribed aimed at correcting the hormonal balance of the body.
How to recognize kidney pain
However, other diseases can have almost the same symptoms, so recognizing what exactly hurts can be very difficult. According to statistics, 90% of such pain is associated with diseases of the spine, 6% with the kidneys, and 4% are due to other ailments.
However, by some signs it is possible to determine what exactly caused the painful syndrome or what form indicates other diseases:
- So, if pain coincides with limited mobility or subsides with the use of warming and anti-inflammatory connections, and if only the right or left kidney hurts, we can say with confidence that the kidneys have nothing to do with it.
- The organs are located on both sides of the spine and slightly above the lower back. Therefore, if the pain syndrome is localized in the center or below the lower back, then its cause is some other injury.
- Kidney problems are often accompanied by characteristic swelling in the morning: first there is swelling under the eyes, a little later the face swells, and then the limbs.
- More severe stages of kidney damage are accompanied by cloudy urine, the appearance of a drop of blood in it, unusual distribution of urine - for example, more urine is released at night than during the day, and so on.
- Pain when urinating, increased blood pressure is a fairly characteristic symptom in combination with pain in the kidney area when inhaling.
- Kidney diseases can be accompanied by visual impairment, the appearance of skin rashes, as a result of intoxication of the body. But, as a rule, at this stage the pain is localized very clearly and accompanies not only inhalation, but is constant.
- It is important to pay attention to previous circumstances. If before the onset of the symptom the patient performed heavy and unusual physical work, then the problem is most likely in the muscles. And if before this there was hypothermia or wet feet, then inflammation of the kidney is a more likely cause.
- The Pasternatsky test is quite effective - up to 70%. When tapping in the area where the kidneys are located, painful sensations occur.
Of course, the final diagnosis of why the kidneys hurt when you inhale is made by a doctor, and, as a rule, more than one. However, a preliminary conclusion, albeit an independent one, is also important. The fact is that the usual method of treatment for muscle strains or osteochondrosis - which is incorrect, but at least safe - is to warm up the lower back.
If the cause of the pain syndrome is inflammation of the kidneys, this should not be done under any circumstances. During inflammation, the kidney tissue swells, the kidney capsule, which is rich in nerve endings, stretches. This stretching leads to pain. When this area is heated, the swelling will increase, which, accordingly, will only worsen the patient’s condition.
Cholecystitis
It is possible that a person has a stabbing sensation on the right side of the chest due to this disease. Cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder, combined with motor-tonic dysfunction of the biliary system. The reasons for its development may be different:
- Infection in the gallbladder and congestion.
- Housing and communal services
- Dyskinesia.
- Congenital anomalies.
- Cysts, tumors, valve system dysfunction.
- Discholia.
- Poor nutrition.
- Hereditary dyslipidemia.
- Abuse of nicotine and alcohol.
- Hormonal disorders.
In addition to the fact that a person feels pain in the heart area when taking a deep breath, he also suffers from other unpleasant manifestations of the disease - weakness, insomnia, sweating, neurosis-like conditions, nausea, bloating, vomiting with bile, bowel dysfunction.
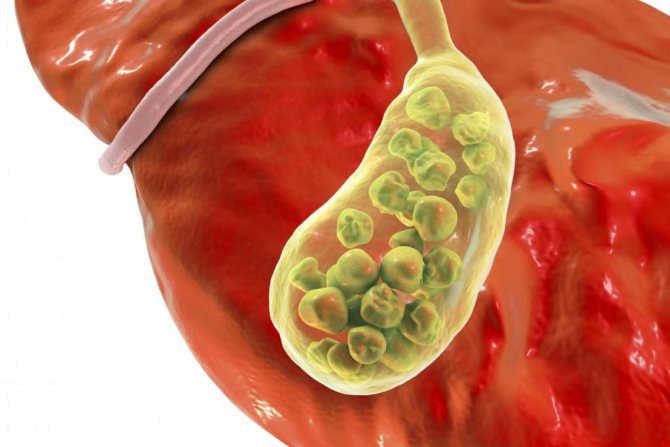
To diagnose cholecystitis, and determine its type and nature, it is necessary to perform an ultrasound of the gallbladder, duodenal fractional intubation, cholecystocholangiography and laboratory blood testing.
Then treatment is prescribed - diet, physiotherapy, as well as the use of antispasmodics, antibiotics and painkillers. In moments of remission, choleretic agents, choleretics and cholekinetics are prescribed.
Questions of etiology
Pain can be of different types:
- 1. People have pain under the chest, cutting, aching, burning or piercing on the left side.
- 2. The intensity of symptoms in men and women can vary from mild to severe pain, periodic and constant.
- 3. Gives off to different parts of the body. Usually it stabs under the shoulder blade, in the heart area, abdominal cavity, jaw, neck, upper limb or shoulder.
- 4. Soreness can change location when inhaling, changing posture, or performing hand movements.
The causes of such symptoms may be diseases:
- 1. Digestive tract.
- 2. Thoracic spinal column.
- 3. Heart, especially angina and heart attack, damage to the membranes and cardiac tissue.
- 4. Lesions of a rheumatic nature.
- 5. Neurological diseases.
- 6. Damage to the ribs.
Why does it hurt in the heart area? Pain in the area of the left sternum is associated with the heart, and this is precisely the reason for contacting cardiologists so that they can explain what this or that symptom means.
Doctors divide heart pain into 2 large groups:
- 1. Anginal, which are associated with coronary disease.
- 2. Cardialgia caused by inflammatory heart diseases, congenital pathologies, vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Ischemic and angina pectoris, severe or mild pain in the chest appears when a person experiences emotional tension, stress, or increased blood pressure or blood flow. They manifest themselves during movement, emotional disorders, leaving a state of rest, and occur in the form of attacks.
The pain differs in nature:
Localized in the left shoulder, arm, behind the sternum, lower jaw, accompanied by shortness of breath. If the pain is strong and pressing, radiating to the sternum, then this is a sign of a heart attack. It is urgent to call an ambulance or take the patient to the hospital, since pain cannot be relieved with nitroglycerin drugs.
The cardiological group of heart pain manifests itself in diseases such as:
They have an aching, stabbing character that lasts for a long time. The pain is localized to the left of the sternum, becoming stronger when coughing or sighing. It can be eliminated for a short time with painkillers, but not with Nitroglycerin.
For what reasons can chest pain occur when inhaling?
Other reasons. Factors that provoke pain in the heart area are also caused by other diseases, not just heart ones. It can be classified according to the manifestations and intensity of pain:
- 1. When turning the body or bending, moving the arms, breathing, it is very painful - this is a symptom of the development of thoracic radiculitis, costal cartilage.
- 2. During movement, severe pain appears that affects the intercostal space, which indicates the activation of the shingles virus in the human body. If mild or intermittent pain is observed when walking, then this is evidence of the onset of neurosis.
- 3. Depression or stress provokes pain that radiates to the neck and shoulder.
- 4. Shortness of breath occurs due to problems with the gastrointestinal tract, when there is pressure on the heart, especially after eating. Particularly noteworthy are pathologies of the small intestine, stomach ulcers, gastritis, dyspepsia, accompanied by nausea and pain, the development of a hiatal hernia, and the formation of cancerous growths that arise in the gastrointestinal tract.
- 5. Shortness of breath and pain can be caused by a pinched cardiac nerve, curvature of the spine, or the development of osteochondrosis.
- 6. Problems with the spleen, its inflammation or pathologies provoke a heart attack. This includes an abscess, a splenic cyst, its injuries, rupture, twisting of the pedicle, and the development of infectious mononucleosis. The consequence of such processes can be a heart attack or coronary heart disease.
- 7. Problems with the bronchi and lungs, among which pneumonia and pleurisy of a left-sided nature stand out. Their signs include dull, weak pain in the side, back, and chest.
- 8. Oncological diseases of the mammary glands, or the occurrence of a cyst, abscess, fibroadenoma there.
A simple but effective way to get rid of occipital or cervical headaches! The result will not be long in coming! Our readers have confirmed that they successfully use the method of treating cervical osteochondrosis, which is the cause of such pain. After carefully studying it, we decided to share it with you.
Pyelonephritis
This is the name of an infectious kidney disease caused by exposure to various bacteria. Pronounced symptoms include pain in the lumbar region, signs of intoxication and high fever. The person also develops a stabbing pain in the right side of the chest, appetite disappears, and severe weakness appears.
It will not be difficult for a nephrologist to make a diagnosis. Hyperthermia, combined with characteristic pain and changes in urine, is a clear sign of pyelonephritis. For laboratory confirmation, urine and blood analysis is prescribed, as well as identification of the microflora that caused the inflammation. Then an ultrasound of the kidneys and excretory urography are prescribed.
Pyelonephritis is treated in an inpatient setting. Be sure to prescribe antibacterial therapy, correction of immunity, and also a diet with a reduced protein content. If the disease has become chronic, the patient is prescribed long-term symptomatic treatment, lasting at least a year.
Pain in the sternum on the right: causes. Why does it hurt on the right side of the chest?
- Causes of chest pain on the right
- Diagnosis of pain in the right side of the chest
Patients often go to medical institutions with complaints of pain in the chest.
Moreover, pain and discomfort on the left side often cause concern. This happens because people associate such pain with heart problems and, accordingly, with a direct threat to their life.
And although pain in the right side of the chest does not always have a direct connection with cardiac problems, such a symptom can be caused by no less dangerous reasons.
Therefore, you should not ignore the sign that appears and let the situation take its course. Self-medication can be not only ineffective, but also dangerous! Timely medical care will not allow diseases to worsen and cause serious harm to the body.
Pleurisy
This is a complication of pneumonia or a concomitant symptom of tuberculosis. The disease manifests itself in inflammation of the outer membrane of the lungs - the pleura. There are two types of pleurisy: dry and exudative. In the first type of disease, pain occurs when the diaphragm is tensed, sneezing, coughing and is stabbing in nature.
In the second case, there is a dull aching pain, shortness of breath, and a dry cough. The patient is unable to breathe deeply and feels painful spasms in the chest area. In severe cases, suffocation may occur.
Upper respiratory tract infections
Flu, ARVI, bronchitis and tonsillitis are often the cause of chest pain. It manifests itself especially clearly when a person coughs or inhales sharply, irritating the inflamed bronchi.
The patient’s body temperature can vary, from low-grade to very high (for example, with the flu) and depends on the type of infectious disease and the severity of its course and neglect. The pain is localized on the right or left in the upper chest.
If bronchitis is not treated, the inflammation goes down and affects the lungs, causing such a serious complication as pneumonia.
Pneumonia or otherwise pneumonia
Pain may be one-sided or spread throughout the area behind the chest.
A strong breath or coughing increases pressure on the lungs, thereby exacerbating the severity of the pain syndrome.
It is very important that doctors correctly diagnose inflammation and select an appropriate treatment regimen, otherwise the disease may worsen and ultimately lead to death.
The later stages of pneumonia are characterized by a significant increase in temperature and fever, but it begins with a slight increase in low-grade fever. Doctors begin to suspect such a disease when a patient’s body temperature does not normalize for a long time. Often at the initial stage, pneumonia is mistaken for a common cold.
Pneumonia is detected by X-ray examination or fluorography. Characteristic wheezing that appears in the lungs may alert the doctor. The cough with worsening inflammation is more severe and deep. Patients are also characterized by weakness and lethargy.
Oncology
If you complain of severe pain in the chest on the right, the doctor may make a diagnosis such as a tumor of the lungs or bronchi. The pathology is characterized by a dry, suffocating cough, during which the patient coughs up blood. Bleeding occurs in the affected lungs in response to the pressure received when the diaphragm is tense.
In the early stages, the tumor does not manifest itself with any special symptoms, especially with peripheral lesions. Later, lung cancer can provoke such symptoms as weight loss, loss of vital functions, increased pain due to the appearance of metastases and their deepening into organ tissue.
If lung cancer is suspected, a biopsy is performed followed by histological examination of the material.
Chest pain on the right may appear due to problems with the spine.
Intercostal neuralgia
This is damage to the intercostal nerves, which occurs as a result of hypothermia, infectious diseases, pinching, irritation and intoxication. It is accompanied by pain, which is localized behind the chest, closer to the back. The nerves, according to the name of the pathology, are located between the ribs. But the pain is widespread and often spreads radially around.
The pain is paroxysmal. It can be shooting or burning. Many different factors can precede the appearance of such a pathological process.
For example, herpetic infection (herpes zoster), scoliosis, osteochondrosis, spinal hernia, reflex impulses during pleurisy, and so on.
If the patient has a history of such diseases, the doctor may assume that the pain is intercostal neuralgia.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
The pathological process manifests itself in inflammation of the paravertebral tissues. It occurs as a result of pinched nerve roots due to dissection of the intervertebral discs. This cause of chest pain on the right is more typical for the elderly and people who are significantly overweight. In the first case, the discs are worn out due to age, and in the second, due to constant excessive load on them.
Now the problem of osteochondrosis is becoming a scourge even for young people and children due to the spread of a sedentary lifestyle.
This diagnosis, in addition to chest pain (during physical activity, lifting heavy objects, deep breathing), is characterized by numbness of the extremities, a local decrease in their temperature, and a sensation of “pins and needles.”
Scoliosis
Curvature of the spinal column leads to deformation of the chest, as it is connected to the spine by the ribs. This can also cause pain. If there is a right-sided curvature, then the pain will be localized on the right.
The patient may also experience right-sided pain due to heart problems. It is commonly believed that the heart is on the left. But actually it is not. The heart is located at the top between the lungs, almost in the center, and only part of one of the ventricles extends to the left. Heart pain is short-lived, appears quickly, but does not last longer than an hour.
Pericarditis
The pericardium is the pericardial sac that performs a protective function for the heart. Most often, its inflammation is a symptom of autoimmune, infectious or oncological processes in the patient’s body. When diagnosed, such a pathology can easily be confused with dry pleurisy or angina pectoris.
One of the special characteristic features of pain with pericarditis is its sharp increase with a deep breath, coughing, and also when the patient is in a horizontal position.
With pericardial effusion, fluid is released, which leads to increased pressure in the heart area and characteristic chest pain. This makes breathing difficult and causes shortness of breath. In this case, the patient's condition is aggravated by fever, swelling of the face and neck.
Angina pectoris
When the myocardium is poorly supplied with blood, it experiences a lack of oxygen. This causes pressing pain in the chest. They can appear on both the right and left. The patient experiences sudden short-term attacks of pain. A visit to the hospital is required, as the patient needs continuous observation and control.
Several other factors can also cause chest pain.
Bruises, injuries
This is fraught with hematomas, ruptures and sprains. The positive side is that this reason is initially clear and no time is wasted figuring it out.
However, many patients neglect their injuries and go to medical institutions only after some time, when they have been bothered by chest pain for a long time.
In these cases, most often the consequences of bruises and fractures are already aggravated and are more difficult to treat.
Spasm of the pectoralis major muscle
The diagnosis is made very simply by palpation. In this case, muscle tightness will be noticeable.
Stagnation of food in the esophagus
This phenomenon occurs when overeating or obstruction. In this case, the pain is explained by the increased pressure of food on the walls of the esophagus. This is characterized by increased pain during swallowing or tension of the diaphragm.
Diagnosis of pain in the right side of the chest
First of all, the doctor will conduct a differential diagnosis and rule out diseases with similar symptoms. Subjective complaints are then analyzed and objective obvious signs are also taken into account.
Chest pain may be:
- By intensity: dull or sharp;
- By location: in the side or front of the sternum;
- According to the nature of the manifestation: stabbing, aching, pulsating, spastic;
- Constant or periodic.
First of all, doctors provide emergency care in the presence of life-threatening symptoms. After this, studies are carried out using ultrasound, ECG, radiography, and tomography machines. The attending physician also prescribes the necessary tests, measures pulse and blood pressure.
Source: https://mag.103.ua/simptomy/19763-boly-v-grudnoj-kletke-sprava-prichiny/
Neuralgia
Another ailment that cannot be ignored. Intercostal neuralgia on the right is a common cause of sharp and severe chest pain. In addition to this symptom, muscle spasms, a burning sensation and even short-term numbness may also occur.
What are the reasons? There are many of them - injuries to the spine and ribs, diabetes, gastrointestinal diseases, deficiency of micro- and macroelements, vitamin deficiency, inflammation of the spinal muscles, the presence of tumors, as well as osteochondrosis and alcohol addiction. In women, neuralgia sometimes appears due to wearing an excessively small, constricting bra for a long time.
Diagnosis involves electroneurography, MRI and CT, as well as checking the integrity of bone tissue using X-rays. Then, based on the results obtained, the doctor prescribes the most appropriate medications that can effectively eliminate the inflammation and pain that accompany a pinched nerve.
Be that as it may, the patient will have to observe bed rest (sleep on a hard and level bed), make dry compresses, use natural sedatives and attend light warming massage sessions.
Ailments from the gastrointestinal tract
Chest pain may occur if the following gastrointestinal pathologies develop:
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). The stomach throws its contents into the esophagus after eating. This is especially evident when bending over or lying down. Heartburn is almost always present; it is accompanied by a sore throat, pain behind the sternum and in the chest.
- Narrowing of the esophagus. Chest pain may occur when swallowing. If the pain intensifies over time and no food goes away, this is a symptom of esophageal cancer.
- Stomach ulcer. Pain when breathing can radiate to the back and sternum. The pain subsides while eating or taking antacids.
- Hiatal hernia. When the ring is weak, the upper abdomen moves to the lower chest after eating. In this case, a painful sigh and heartburn occur. They always increase if the patient is lying down.
- Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. The pain is strong and sharp, pain behind the sternum is often present.
- Gallbladder problems. Pain may appear in the right hypochondrium and in the lower part of the chest on the right; most often they occur after a fatty meal.
Why is there a stabbing pain under the chest?
Pain appears in the area under the breast due to diseases of the lungs, heart, intestines, and musculoskeletal system. Therefore, it is important to find out the cause of tingling and start treatment on time.
On the right side
When it stings on the right side under the chest, various factors could provoke it. It is worth noting the most common diseases:
- diseases of the spine;
- respiratory diseases;
- diseases of the liver and biliary system;
- intercostal neuralgia;
- injury to the chest area.
The listed reasons can cause pain on the right under the breast. The final diagnosis will be made by the doctor after examination.
Left side
When it stings in the left side under the chest, you need to quickly find out the cause. The most common include diseases of the heart, spleen, stomach or lungs. Severe pain sometimes indicates cancer. Therefore, you need to quickly consult a doctor. The left side may hurt for the following reasons:
- Diseases of the respiratory tract and lungs. There may be pneumonia, as well as left-sided pleurisy.
- Diseases of the spleen or pancreas. The appearance and enlargement of a cyst, injury to the spleen, blockage of large vessels.
- In older people, it often stings under the chest on the left due to osteochondrosis, neuralgia or colitis.
Colitis may cause stabbing pain in the chest area. However, other symptoms will also be present, such as severe abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, and weakness.
Heart pain is different in that it does not decrease after taking painkillers, it occurs suddenly, and its intensity constantly increases. Also, when changing the position of the body, the strength of the pain does not change. In other cases, particularly with osteochondrosis, the pain may subside and after a while appear in another area; painkillers help improve the condition, while heart medications do not work. Often the intensity of pain changes when changing body position.
Problems of the lungs and pleura
The right lung is more prone to pulmonary pathology due to infections caused by airborne pathogens and cancers associated with smoking, environmental pollution and industrial toxins. This occurs due to anatomical differences between the right and left side of the lungs. The first one is larger, shorter, wider. Accordingly, more air passes through its bronchi of the more extensive tracheobronchial tree.
Most lung pathologies involve some degree of cough (wet or dry), phlegm, shortness of breath, and abnormal breathing sounds. Infection is indicated by an increase in body temperature, although night sweats also occur with cancer. Coughing up blood (hemoptysis) is a serious sign that you have a severe lung infection or cancer.
Infections
- bronchitis
- bronchiolitis
- pneumonia
- tuberculosis
- lung abscess
- pleurisy
Cancer
- squamous cell lung cancer, adenocarcinoma, undifferentiated
- small cell lung cancer
Non-infectious inflammatory diseases
- Congenital - pulmonary hypoplasia, lobar overinflation, bronchial anomalies, respiratory tract malformations
- atelectasis
- acute lung injury syndrome
- asthma
- bronchiectasis
- Chronical bronchitis
- chronic interstitial lung disease (interstitial pneumonia)
- diaphragmite
- pleurisy
- pulmonary embolism
- pulmonary infarction
- sarcoidosis
Other possible problems:
- Chest
- Hearts
- Gastrointestinal tract