How many reticulocytes should there be in the blood?
The normal number of young red blood cells depends on the age characteristics of a person.
In the blood of recently born children, at least 0.15% of reticulocytes are normally present, but their number should not exceed 1.5 percent.
Young red blood cells reach this maximum value when the baby is two weeks old. At this time, the RET is just over two percent.
In the blood of children who are already a month or two old, there is a lower level of young red blood cells. The RET rate at this time is 1%.
For preschool children, the RET value should be no more than 0.7 percent. From 6-7 years this figure increases and is 1.3 percent.
From the moment of puberty (at approximately 12-13 years old), RET scores begin to differ between boys and girls.
As the time of menstruation approaches and hormonal disruption occurs in the body of young girls, red blood cell precursor cells are produced by the bone marrow in significant quantities.
In the male half of humanity, the quantitative value of reticulocytes is slightly lower - a maximum of 1.7%.
The percentage of young red blood cells is calculated using several methods. Their quantity can be determined using a hematology analyzer or microscope.
If the norm of their content in the blood is violated, then they talk about pathologies of the bone marrow, liver, as well as anemia.
Diagnosis of reticulocytosis
There are certain indications for performing a reticulocyte test:
- The need to evaluate erythropoiesis in the presence of hemolysis or bleeding.
- Assessment of the bone marrow's ability to recover after the patient has undergone treatment with cytostatics or after transplantation of this organ.
- Assessing the potential for erythropoietin production in patients undergoing kidney transplantation.
- Passing doping control for people professionally involved in sports.
- Diagnosis of anemia, regardless of its cause.
- Search for the reasons leading to a decrease in the level of red blood cells.
- Search for the causes that lead to insufficiency of bone marrow hematopoietic function.
- Search for the causes that lead to disruption of the regenerative ability of the hematopoietic organs during treatment for anemia. Evaluation of the effectiveness of anemia treatment.
- Assessing the effectiveness of therapy using erythropoietin or erythrosuppressors.
Reticulocyte counting can be carried out in several ways: using the luminescent microscopy method, counting the number of reticulocytes in a blood smear with the addition of special dyes, counting the number of reticulocytes using a hemolytic analyzer.
Reticulocytes are elevated
A condition in which the level of these cells in the blood increases is called reticulocytosis. This is usually associated with a sharp unnatural decrease in the number of red blood cells, as a result of which the bone marrow begins to hastily replenish their reserves.
- Destruction of red blood cells (hemolysis)
RET in this case can exceed the norm by three times! Hemolysis is caused by intoxication of the body (viper venom), malaria, taking medications for ertremia, as well as the occurrence of autoimmune reactions - processes that are aimed at destroying red blood cells by one’s own immune cells due to a malfunction.
- Blood loss
Heavy bleeding causes a response in the body in the form of accelerated production of reticulocytes. This can be called a positive option if the bleeding is eliminated. Soon the blood will be replenished to normal. In the normal value for women, reticulocytes, which change during menstruation, are also taken into account.
- Oncological diseases
Penetration of metastases into the bone marrow, tumors and inflammatory processes can cause a sharp increase in reticulocytes. This also includes chemotherapy and the recovery period after it.
- Positive prognosis for anemia treatment
With a deficiency of iron and folic acid, anemia develops, which is manifested by a decrease in red blood cells in the blood. If treatment is prescribed correctly, after about a week a sharp increase in reticulocytes occurs in the body. This should be noted by the attending physician as a positive, but controllable fact.
- Taking certain medications
Even antipyretic medications can affect the fact that reticulocytes in the blood are elevated in an adult.
- Smoking
- Mountain climbing or other elevation gain.
- Pregnancy.
Information about RET alone is not enough to determine the exact reason why your reticulocyte count has risen. It is necessary to undergo related examinations.
Reticulocytes are elevated - what does this mean?
Increased values of the content of young forms in the population of erythrocyte cells may indicate the presence of various pathological processes and the reaction of the bone marrow to their presence:
- It is unlikely that blood loss, especially massive, will not force a healthy brain to work intensively - after all, losses need to be replenished as soon as possible, so the number of reticulocytes can be increased to 10 - 12% (100 - 120‰ or 100 - 120 reticulocytes per 1000 red blood cells - 1/10 Part).
- The destruction of red blood cells due to the ingress of hemolytic poisons or due to other circumstances will also not leave the bone marrow “indifferent” - the increased breakdown of mature red blood cells will certainly increase the proportion of young forms (sometimes this proportion can reach 50%).
- Such a serious disease as hemolytic anemia, which leads to an increase in RET by as much as 300%, does not go unnoticed, that is, it is no longer necessary to look for reticulocytes in erythrocytes, but vice versa, since all forms will be young, and adults will have time to break down.
- Reticulocytosis is also accompanied by other hematological pathologies (polycythemia, thalassemia), as well as metastases to the bone marrow of neoplasia of various locations.
- Reticulocyte values will be increased in the case of acute hypoxia (oxygen starvation) due to various circumstances that can haunt a person from birth to old age.
- Infections such as malaria can cause increased numbers of young cells.
- Reticulocytosis is observed with effective treatment with iron supplements for IDA (after 1-2 weeks); a jump to 200% is possible (reticulocytic crisis) approximately a week from the start of therapeutic measures in the case of B12-folate deficiency anemia.
Blood sampling mechanism
A blood sample is taken to determine this indicator as part of a general analysis. If there is a need to determine the level of reticulocytes, then the doctor who ordered the test indicates the need for additional counting.
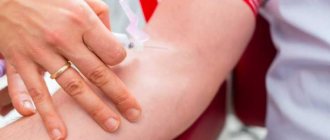
This test does not require special preparation, but traditionally it is taken on an empty stomach in the morning. At the same time, if there is a need, it can be taken at any time of the day. Blood for analysis should be taken from a finger prick; its examination is carried out in the laboratory, in the hematology department.
The number of reticulocytes is counted in a supravital stained smear. The microscopic method is used, that is, their number is simply counted by placing a blood sample under a microscope. Today there is a hardware method of counting. It is used in modern laboratories.
The designation for reticulocytes in a blood test is RET.
How is blood taken for reticulocytes?
Let's say you take a blood test. Reticulocytes - what are they? Are they detected in any analysis? Blood is taken for this indicator during a general analysis. If this is necessary, the doctor who ordered the test will indicate in the direction that an additional reticulocyte count needs to be done.
This test does not require special preparation, but it is still customary to take it in the morning on an empty stomach. This analysis can be done at any time of the day if necessary. Blood is taken from a finger and is examined in the hematology department of the laboratory.
Reticulocytes are counted in a supravital stained smear using a microscopic method, i.e. by counting their number under a microscope. In modern laboratories today there are hardware methods for counting reticulocytes.
How to donate blood for reticulocytes? What is it and where can such an analysis be performed? These questions have been answered. Now let's talk about the normal values of this indicator.
Symptoms of reticulocytosis
Reticulocytosis in itself is not a pathology. Moreover, in some cases, this laboratory indicator is considered by specialists as a sign of good bone tissue regeneration (true reticulocytosis). However, the number of reticulocytes should increase not only in the peripheral blood, but also in the bone marrow itself.
If reticulocytosis develops against the background of aplastic anemia, the patient will complain of the following symptoms:
- Increased fatigue and tiredness.
- Pale skin.
- Frequent nose and gum bleeding.
- Diseases such as stomatitis, pneumonia, skin and urinary tract infections.
Hemolytic crisis is a syndrome that is accompanied by intravascular or intraorgan destruction of red blood cells.
The following signs indicate a hemolytic crisis:
- Tachycardia, shortness of breath, dizziness, pale skin, or its icteric color.
- Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, increased body temperature.
- Impaired consciousness and convulsions.
- Enlargement of the spleen.
- Darkening of urine.
Symptoms of hidden bleeding depend on its intensity. Common signs include dizziness, shortness of breath, thirst, pale skin, fainting or lightheadedness. The rate at which these symptoms increase will depend on the intensity of the bleeding.
Malaria, which is accompanied by reticulocytosis, can begin acutely, or manifest itself as a slight increase in body temperature, headaches, and malaise. On the 3-5th day of illness, the patient begins to experience attacks, which are alternately replaced by chills, fever and sweating. These paroxysms are repeated up to 10-14 times, after which improvement occurs. However, the disease tends to recur.
Polycythemia with reticulocytosis develops over a long period of time and gradually. Most often it is diagnosed accidentally during a blood test. The patient is periodically bothered by heaviness in the head, dizziness, his vision may deteriorate, and sleep disturbances appear. The most pathognomic sign of polycythemia is vascular congestion, when the skin acquires a cherry-red color, especially noticeable on the face, neck, hands and mucous membranes. In this case, the patient's hard palate has a normal color, and the soft palate acquires a cyanotic tint.
Acute hypoxia with reticulocytosis develops quickly, within a few minutes. If oxygen starvation is not stopped, then irreversible consequences occur in organs and tissues and the person may die. This condition is manifested by insufficiency of all organ systems. First of all, the central nervous system suffers, breathing and heartbeat slow down, and blood pressure decreases. Organ failure progresses to coma and agony, after which the person dies.
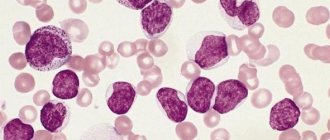
Counting reticulocytes in a blood smear (quantities)
What are reticulocytes?
Reticulocytes are young forms of erythrocytes (precursors of mature erythrocytes), containing a granular-filamentous substance, revealed by special (supravital) staining. Reticulocytes are detected both in the bone marrow and in the peripheral blood. The maturation time of reticulocytes is 4-5 days, of which within 3 days they mature in the peripheral blood, after which they become mature erythrocytes. In newborns, reticulocytes are found in greater numbers than in adults.
The number of reticulocytes in the blood reflects the regenerative properties of the bone marrow. Their counting is important for assessing the degree of activity of erythropoiesis (production of red blood cells): when erythropoiesis accelerates, the proportion of reticulocytes increases, and when it slows down, it decreases. In the case of increased destruction of red blood cells, the proportion of reticulocytes may exceed 50%. A sharp decrease in the number of red blood cells in the peripheral blood can lead to an artificial increase in the number of reticulocytes, since the latter is calculated as a percentage of all red blood cells. Therefore, to assess the severity of anemia, the “reticular index” is used: % reticulocytes x hematocrit / 45 x 1.85, where 45 is a normal hematocrit, 1.85 is the number of days required for new reticulocytes to enter the blood. If the index is < 2, it indicates a hypoproliferative component of anemia; if > 2-3, then there is an increase in the formation of red blood cells.
Indications for the purpose of analysis:
- diagnosis of ineffective hematopoiesis or decreased production of red blood cells;
- differential diagnosis of anemia;
- assessment of response to therapy with iron, folic acid, vitamin B12, erythropoietin;
- monitoring the effect of bone marrow transplantation;
- monitoring of erythrosuppressor therapy.
- Preparation for the study: the study is carried out on an empty stomach or at least 2 hours after
- the last meal, when taking blood, it is necessary to avoid prolonged compression of the vein with a tourniquet.
When does the number of reticulocytes increase (reticulocytosis)?
- Posthemorrhagic anemia (reticulocyte crisis, increase 3-6 times).
- Hemolytic anemia (up to 300%).
- Acute lack of oxygen.
- Treatment of B12-deficiency anemia (reticulocyte crisis on days 5 - 9 of vitamin B12 therapy).
- Therapy of iron deficiency anemia with iron preparations (8 - 12 days of treatment).
- Thalassemia.
- Malaria.
- Polycythemia.
- Tumor metastases to the bone marrow.
When does the reticulocyte count decrease?
- Aplastic anemia.
- Hypoplastic anemia.
- Untreated B12 deficiency anemia.
- Metastases of neoplasms to bone.
- Autoimmune diseases of the hematopoietic system.
- Myxedema.
- Kidney diseases.
- Alcoholism.
Norms
Doctors usually designate these cells with the abbreviations RET or RTC. They are usually measured as a percentage of the total number of red blood cells, but often their absolute volume is also measured (the unit of measurement is 1 * 109 units per liter of blood).
The level of these cells is not constant, and largely depends on the age of the person: for example, in infants there are much more of them than in adults and elderly people. There is a certain dependence on the gender of the subject: in adolescent girls from 12 years of age and women, the reticulocyte rate is higher than in men. The reason for this is the menstrual cycles and the associated blood losses, which trigger the processes of hematopoiesis.
In percentage terms, the normal numbers are:
- for newborn babies – ranging from 0.15 to 1.5;
- at the age of up to 2 weeks – from 0.45 to 2.1;
- in six-month-old babies – at a level from 0.2 to 1;
- from six months to 6 years – from 0.2 to 0.7;
- from 6 to 12 – from 0.2 to 1.3;
- in adolescence, over 12 years of age and beyond, the typical norm for girls is from 0.12 to 2.05, for boys and men – from 0.24 to 1.7.
In absolute terms, the norms of the reticulocyte number are as follows (109 units per liter):
- In adult men - ranging from 23 to 70.
- For women - from 17 to 64.
Who are they and how many are there?
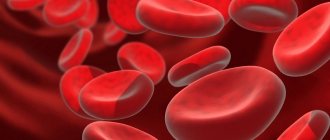
Reticulocytes are “newly made” red blood cells that have just left the bone marrow.
The norm of reticulocytes in the peripheral blood of an adult barely exceeds 1% (according to various authors from 0.8 - 1.3 to 0.2 - 2% ). In children just born, the norm may be 10%, but as the baby grows and develops, the indicators begin to decrease and by two weeks of life they are as close as possible to the normal values of adults.
In general, erythropoiesis of newborns is a separate topic: a test taken 12 hours after birth shows a noticeable increase in the level of hemoglobin (up to 200 g/l), red blood cells (up to 6.0 x 1012/l and higher) and reticulocytes. This blood picture is observed for several days, then these indicators begin to fall, which is associated with a decrease in the production of erythropoietin. After two weeks to a month, the production of erythropoietin increases again, which leads to an increase in the level of reticulocytes and erythropoiesis is normalized (in a six-month-old child, the norms are no longer much different from adults). In this regard, I would like to draw the reader’s attention to the designation of units for measuring the number of reticulocytes; their content can be expressed in ppm, then the numbers will increase 10 times.
Table: reticulocyte norms by age
| Unit measurements | Up to a year | 16 years | 6 – 12 years | 12 – 16 years old | Adult men | Adult women |
| Percent (%) | 0,3 – 1,5 | 0,3 – 1,2 | 0,2 – 1,2 | 0,2 – 1,1 | 0,8 – 1,2 | 0,2 — 2 |
| Permille (‰) | 3 — 15 | 3 — 12 | 2 — 12 | 2 — 11 | 8 — 12 | 2 — 20 |
However, the age “up to one year” includes different periods that are very important for the child’s body. In addition, it would be useful to take into account the opinion of various authors who are considering other options, where the norms for children are written literally by day and month and, therefore, are somewhat different from the previous values. There is a noticeable difference in the norms of adults.
| Age by days, months, years | Number of reticulocytes in ppm |
| Up to 14 days | 1,5 — 15 |
| From two weeks to 1 month | 4,5 — 14 |
| 1 to 2 months | 4,5 — 21 |
| From two months to six months | 2,5 — 9 |
| From 6 months to 2 years | 2 — 10 |
| From 2 to 6 years | 2 — 7 |
| From 6 to 12 years | 2 — 13 |
| People over 12 years old female | 1,2 – 20,5 |
| People over 12 years old male | 2,4 — 17 |
It is up to the patient to choose which table to believe, although several more can be found in different sources; however, in doubtful cases, it would not hurt to ask the laboratory by what method the calculation was made (microscopy or automatic analyzer) and what reference values the laboratory uses.
Treatment
IMPORTANT! Only a doctor can prescribe the correct medications after a detailed study of the tests and a personal examination of the patient. The main thing is not to neglect going to the hospital, since deviations from the norm may indicate very serious diseases, for example, oncology (if the indicator is higher than normal)
In case of serious blood loss, a transfusion of blood or its components is prescribed, which restores the level of reticulocytes in the body; If the bleeding is chronic, then you need to treat the disease that is the root cause of blood loss; For cancer of the bone marrow, chemotherapy and surgical removal of the affected areas are used. In severe cases, a donor bone marrow transplant is required; If toxic poisoning is obtained, operations are performed to cleanse the body and administer antidotes; If a person is diagnosed with anemia, it can be well treated with diet and taking vitamins and iron. Only after visiting a doctor. The diet consists of eating foods rich in folic acid and iron: greens, seaweed, salad, cereals
It is important to remove coffee drinks from your diet, as caffeine interferes with the normal absorption of iron in the body.
Treatment for low reticulocyte levels is prescribed after diagnosis.
Concept and functions of reticulocytes
Physically, these blood cells appear as pinkish formations with a slight bluish tint.
If you examine the bodies through a microscope, you can see in them internal structures in the form of threads and granules characteristic of tissue cells:
- mitochondria;
- cellular organelles;
- residual amounts of RNA.
Reticulocytes, like red blood cells, have the ability to transport oxygen in tissues, but do so with less efficiency compared to red cells.
Red bone marrow is responsible for the synthesis of the cells in question; this mainly occurs in tubular and flat bones. As already mentioned, they represent the initial stage of development of red blood cells: after production and release into the bloodstream, reticulocytes circulate in it for about 48 hours, concentrating hemoglobin. At the end of this process, they mature into fully functional bodies.
Typically, the number of these cells outside the bone marrow is minimal; it produces already mature cells, not allowing their young prototypes to enter the bloodstream prematurely. But a slight increase, even if it was detected, does not yet indicate a pathological process, more often signaling an increase in erythropoiesis - the process of generating new red blood cells. But pathological reasons are also possible, which will be discussed further.
The reticulocyte test is not included in the general blood test; the doctor prescribes an additional test in some cases.
Interpretation of results
Reticulocytes in the blood
Reticulocytes in children from the moment of birth can range from 5 to 10%. Gradually this figure returns to normal. However, it makes no sense to differentiate the measurement results depending on gender in children under 12 years of age, since their reticulocytes will be approximately the same. During this period, girls usually begin to menstruate, and the loss of blood causes the erythroid cells to increase their fluctuation ranges. Reticulocytes, the norm of which for adults varies within certain limits, have different numerical ranges depending on gender.
However, there are cases when studies show increased or decreased reticulocytes in the blood. The reasons for elevated RTCs are:
- reticulocytosis occurs when red blood cells are destroyed under the influence of poisons of both animal (toxins released during malaria, viper bite) and medicinal (medicines for the treatment of erythremia) nature. Subsequently, an autoimmune response to the death of red blood cells occurs. The norm of reticulocytes can be exceeded by 300%;
- destructive processes occurring in the bone marrow (inflammation, metastases and tumors) cause an increase in RTC;
- smoking provokes an increase in RTC levels;
- both temporary and long-term reticulocytosis provoke blood loss;
- hormonal therapy with erythropoietin to stimulate bone marrow function;
- reticulocytosis occurs in the treatment of anemia in children: iron supplements. Reticulocytes increase on days 8–12;
- medications containing vitamin B12. The increase in RTC occurs on days 5–8;
Reticulocytosis can be true or false. True is a positive indicator of blood recovery. It represents an increase in RTC levels in both the bone marrow and peripheral blood. False, on the contrary, characterizes the presence of cancerous tumors, as well as bone marrow metastases. It is determined by an increase in RTC only in the general blood flow.
A reduction in RTC indicates destruction of bone marrow function. Causes of decreased reticulocytes:
- iron and folate deficiency anemia, which occurs due to a lack of vitamin B12;
- aplastic anemia with long-term decreased RTC levels;
- chronic course of infectious diseases;
- destruction of thyroid function;
- alcoholism;
- decreased production of erythropoietin due to kidney disease;
- the presence of bone marrow tumors, as well as its metastases;
- uremia;
- bone marrow suppressant, radiation or chemotherapy;
- medications taken (“Sulfanilamide”, “Carbamazepine”, “Chloramphenicol”).
A hematologist, therapist or urologist can adequately assess RTC values and identify the reasons for its deviations from the norm.
Reticulocytes. Designation in analyzes
What is the norm of red blood cells in peripheral blood? Gender differences in the norm are significant only after 11-12 years when calculating such an indicator as reticulocytes in the blood. The norm for children up to this age is the same. Once girls begin regular menstruation, monthly blood loss causes the erythroid cell range to widen.
You can get acquainted with the norm of reticulocytes in peripheral blood in the table below.
| Age | Reticulocyte rate in % |
| Newborns | 0,15-1,5 |
| 2 weeks | 0,45-2,0 |
| 1-2 months | 0,25-0,95 |
| 6 months | 0,2-1,0 |
| 2-6 years | 0,25-0,75 |
| 6-12 years | 0,25-1,3 |
| Men after 12 years | 0,25-1,7 |
| Women after 12 years | 0,12-2,1 |
Reticulocytes are low
A decrease in the number of reticulocytes indicates that the bone marrow has begun to produce less of them, which means there will be fewer red blood cells, which can lead to tissue depletion of oxygen. This happens under the following conditions:
- Anemia
Due to a lack of iron, vitamin B12 and folic acid, hemoglobin synthesis is disrupted, which entails a decrease in the number of red blood cells and reticulocytes.
Aplastic anemia and chronically low reticulocyte counts can be life-threatening.
- Myxedema
Thyroid gland dysfunction.
- Tumors, chemotherapy
Oncological diseases, radiation sickness, and the effects of chemotherapy can depress the bone marrow, causing both a decreased and an increased number of reticulocytes.
- Kidney and bone marrow diseases
Sometimes, even without the presence of any disease, after prolonged erythropoiesis, these organs become depleted, which disrupts the normal number of red blood cells. Sometimes the reticulocyte level can even drop to zero.
- Alcohol abuse
Alcohol in excessive quantities acts in several ways at once:
- Negatively affects the kidneys;
- Its toxicity provokes the destruction of the cells themselves;
- Inhibits bone marrow activity.
- Use of medications
The group of drugs that can cause a decrease in reticulocytes include chloramphenicol, sulfonamides, and carbamazepine.
What can affect the RET analysis?
Incorrect blood donation
Blood must be donated on an empty stomach. At least 8 hours must have passed since your last meal. During this time you are allowed to drink only water. You must inform your doctor about the medications you are taking and, if possible, donate blood 3 weeks after discontinuation. The day before donating blood, refrain from fatty and fried foods, alcohol and physical activity.
Shortcomings in the laboratory
Incorrect selection of the anticoagulant or insufficient mixing can distort the results.
Manual analysis using a microscope
This is an outdated method, which, although it has its place, is still less accurate compared to automatic calculation.
Any deviation from the norm should lead the doctor and the patient to further examination, which will allow us to find out the causes and eliminate the possible disease in a timely manner. Don't forget to regularly take a complete blood test, as early detection of the problem can one day save you time, money and health.
Be healthy!
Causes of increased reticulocytes
Reticulocytosis is an increase in the level of reticulocytes, which can be triggered by hemolytic anemia.
This condition can occur due to blood loss, usually manifests itself after 4-5 days, polycythemia, malaria, treatment with iron supplements.
If reticulocytes are elevated, then there is reason to suspect internal bleeding, for example, in patients with stomach or duodenal ulcers.
Video:
Reticulocytosis can be true or false. The first is characterized by an increase in the concentration of reticulocytes simultaneously in the bone marrow tissue and peripheral blood - this reflects good regenerative function.
False reticulocytosis is characterized by the absence of an increased number of immature red blood cells in the spinal cord with a simultaneous increase in those in the peripheral blood.
Reticulocytosis, in the absence of an erythronormoblastic reaction of the spinal cord, is released when metastases spread to the bone marrow tissue.
An increased determination of the number of young red blood cells in the cells of the erythrocyte unit can signal the development of pathological conditions:
- large blood loss stimulates intensive production of reticulocytes;
- entry into the blood of toxins and poisons that destroy mature red blood cells;
- hemolytic type of anemia, in which almost all red blood cells are destroyed;
- hematological pathologies – polycythemia and thalassemia;
- spread of cancer metastases to any part of the bone marrow;
- severe oxygen starvation;
- infectious diseases of various etiologies, for example, malaria;
- treatment with certain medications.
In newborns, reticulocytes may be elevated for a whole month.
Video:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=hOugDDzX-sg
This phenomenon is normal for a child, as his body adapts to the conditions of the surrounding world.
After a short period of time, the indicator will return to normal, which corresponds to the age category of the child.
In a healthy state, the lifespan of red blood cells is about four months, while a functioning bone marrow ensures the necessary replenishment of red blood cells.
With a sharp decrease in the concentration of mature cells, the bone marrow intensively generates reticulocytes, which also perform the function of saturating the body’s tissues with oxygen. After 1 - 2 days, reticulocytes become mature cells.
The reasons for the increase in reticulocyte levels can be both negative and positive.
If a person is not concerned about health problems, then it is not advisable to search for young forms of red blood cells.
Therefore, this mark in the general analysis is placed only if there are direct indications.
The norm of reticulocytes in the blood of children, men and women differs, and the causes of deviations must be discovered to determine the advisability of treatment.
True and false reticulocytosis
With true reticulocytosis, an increase in young red blood cells in the blood is accompanied by an increased number in the bone marrow. This indicates the process of erythropoiesis, i.e. about the true formation of red blood cells.
With false reticulocytosis, reticulocytes increase only in the peripheral blood, and in the bone marrow their number is reduced or remains normal. This may indicate that they are being washed out into the bloodstream from the bone marrow. A similar process is observed during inflammatory or tumor processes in the bone marrow, for example, with metastases.
Indications for the study
Reticulocytes in a blood test are counted when:
- diagnosis of hematopoiesis disorders;
- suspected hemolysis;
- malaria;
- bites of poisonous spiders and snakes;
- suspected hidden (internal) bleeding;
- oncological neoplasms;
- monitoring erythropoietin production in patients after kidney transplantation;
- identifying a decreased or increased number of red blood cells;
- monitoring the regenerative capacity of bone marrow after transplantation;
- assessing the patient’s response to the therapy (treatment with ferum, erythropoietin, folic acid, vitamin B12);
- diagnostics of the quality of treatment with erythrosuppressor drugs.
Attention. Reticulocytes are also counted in pregnant women
Normally, a moderate increase in these cells indicates good adaptation of the woman’s body. This is due to the fact that pregnant women are characterized by a rapid “increase” in the total volume of circulating blood, but this occurs due to an increase in plasma elements.
The blood becomes more liquid due to a decrease in the number of cellular elements in relation to the increased plasma volume. A moderate increase in the number of reticulocytes is the woman’s body’s response to developed anemia.
Conducting and deciphering the analysis
It is important to remember that the first count of the number of reticulocytes should be carried out before taking drugs that stimulate their formation. Blood sampling to count the number of reticulocytes must be carried out in the morning, on an empty stomach.
Drinking water is allowed
Blood sampling to count the number of reticulocytes must be carried out in the morning, on an empty stomach. Drinking water is allowed.
The day before the study, it is recommended to limit physical activity and eliminate emotional stress. It is advisable to eliminate alcohol intake for a week (if the analysis is carried out as planned).
When interpreting the results, it is necessary to remember that some medications can change the reticulocyte count.
Reticulocytes will be decreased in patients taking:
- cytostatics;
- some antibiotics (sulfonamides, chloramphenicol);
- antiepileptic drugs (carbamazepine);
- antiparkinsonian drugs;
- immunosuppressants.
For reference. An increase in the level of reticulocytes is diagnosed with the use of erythropoietin, B12 and folic acid, ferrum, as well as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
In what cases is a reticulocyte level test prescribed?
A study of reticulocyte content is necessary for:
- diagnosis of anemia and its severity;
- assessing the regenerative capacity of bone marrow;
- assessing the effectiveness of therapy for patients with iron deficiency, folate and B12 deficiency anemia, tumor diseases.
If there are signs of anemia of various etiologies (pallor of the skin, flashing “spots” before the eyes, dizziness, weakness), it is necessary to check the level of hemoglobin, red blood cells and reticulocytes.
Norm of reticulocytes for men, women, children
The reference values (that is, the norm) for the content of reticulocytes are 0.2–1% of all red blood cells circulating in the blood.
The norm depends on gender only after 12 years, when menstruation begins in girls, and due to the regular loss of menstrual blood (and with it red blood cells), an expanded range of fluctuations in erythroid cells occurs.
The reticulocyte rate is specified in modern test forms, where there is a separate field for this. You should focus on these indicators. Reticulocytes are measured in ppm (indicated by the symbol ‰). If we talk about each age group specifically, then the indicators of normal values are as follows (in ‰):
| Person's age | Normal value |
| Children under 2 weeks | 1,5–15 |
| from 2 weeks to 1 month | 4,5–14 |
| 1–2 months | 4,5–21 |
| 2–6 months | 2,9–9 |
| from 6 months to 2 years | 2–10 |
| 2–6 years | 2–7 |
| 6–12 years | 2–13 |
| Women 12+ Men 12+ | 1,2–20,5 2,4-17 |
Reticulocytosis
An increase in reticulocytes (reticulocytosis) occurs in hemolytic anemia. Then their number can reach 60‰ or more (the figure increases especially strongly during hemolytic crises). This also occurs in acute blood loss (reticulocyte crisis after blood loss manifests itself somewhere on days 3–5), polycythemia, malaria, treatment of iron deficiency anemia with iron, 3–10 days after antianemic treatment of pernicious anemia has begun, when there is acute lack of oxygen. When the levels are elevated, it is possible to suspect hidden bleeding (for example, in patients with typhoid fever or peptic ulcer).
Experts believe that an increase in the number of reticulocytes indicates good regeneration only when there is also reticulocytosis in the bone marrow at the same time. This is true reticulocytosis. The absence of an increased number of reticulocytes in the bone marrow, when they are increased in the peripheral blood, signals an increase in their leaching. This is false reticulocytosis.
Reticulocytosis, when there is no erythronormoblastic reaction of the bone marrow, is observed when its individual areas are irritated by cancer metastases or foci of inflammation.
Reticulocytopenia
A decrease in the number or when reticulocytes are absent (that is, reticulocytopenia) occurs with regenerative aplastic, hypoplastic anemia, those caused by a deficiency of vitamin B12, iron, folic acid (microcytic-hypochromic, megaloblastic anemia), sideroblastic anemia, thalassemia, cancer metastases to the bone , radiation therapy, radiation sickness, treatment with cytostatics, autoimmune diseases of the hematopoietic system.
In kidney diseases, reticulocytes are also reduced, however, the decrease in the number of cells is often insignificant. Frequent alcohol consumption has a very large impact on the depletion of hematopoietic systems:
- alcohol inhibits kidney function;
- Once in the blood, alcohol toxins destroy cells;
- Toxins suppress bone marrow function.
In patients with cancer, the activity of the reticulocyte synthesis process may also decrease due to metastases. The reasons are different, because it is impossible to predict exactly which part of the bone marrow will be affected by metastasis, and whether metastasis will lead to an increase or decrease in reticulocytes.
Reticulocyte reference values
Normal reticulocyte values are expressed as percentage % or ppm ‰. Table 1 presents reference values of erythrocyte precursors depending on age.
Table 1. Normal values for reticulocyte levels.
| Age | Reticulocyte count in ppm (‰) |
| Up to two weeks | 1,5 — 15 |
| Up to 1 month | 4,5 — 14 |
| Up to two months | 4,5 — 21 |
| Up to six months | 2,5 — 9 |
| Up to two years | 2 — 10 |
| Up to six years | 2 — 7 |
| Up to 12 years | 2 — 13 |
| 12 years and older female | 1,2 – 20,5 |
| From 12 years and older male | 2,4 — 17 |
On average, the number of reticulocytes from 2 to 12‰ (or 0.2 - 1.2%) is considered normal for adults.
There is also a division of reticulocytes according to maturity:
- fraction with low fluorescence – LFR%. It is a population of small mature reticulocytes (87 - 99%);
- fraction with average fluorescence – MFR%. It is a population of medium reticulocytes (2 - 12%);
- fraction with high fluorescence – HFR%. This is a population of large immature reticulocytes (1 - 2%).
To more accurately assess anemia and its severity, the reticulocyte index is used. It is calculated as:
Reticulocyte index = reticulocytes in the blood (percentage) * hematocrit of the subject / 45 X 1.85
(where: 45 is a normal human hematocrit, and 1.85 is the number of days that are necessary for new reticulocytes to enter the peripheral blood)
A reticulocyte index of less than 2 indicates a low activity of red blood cell formation, and more than 3, on the contrary, indicates an increased process of red blood cell production.
Factors influencing results
Reticulocytes
When quantitatively calculating the level of RTC in the blood, erroneous results with falsely high values may appear. This picture can be observed when:
- presence of leukocytosis;
- hyperthrombocytosis;
- the presence of abnormal hemoglobin in the blood;
- the presence of gigantic platelets;
- detection of pathological inclusions inside erythrocytes, such as malaria pathogens and Jolly bodies.
In addition to the above, it is also possible to identify factors that distort the results of the analysis:
- prolonged squeezing of the hand with a tourniquet when taking a sample;
- insufficient mixing of blood and anticoagulant;
- blood transfusion performed shortly before the test;
- hemolysis of blood taken for analysis;
- incorrect choice of anticoagulant;
- taking antibacterial drugs from the sulfonamide group.