0
Author of the article: Marina Dmitrievna
2017.08.02
1 202
Leukocytes
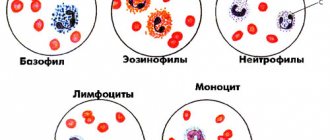
Granulocytes are white blood cells that perform the most important functions of protecting the body from various foreign substances and objects. They received this designation because of the granules contained in the cytoplasm of the cells. There are three types of granulocytes:
- neutrophils;
- eosinophils;
- basophils.
Granulocytes originate in the bone marrow. After maturation, they leave it and go on combat duty in blood and tissue. The use of military vocabulary in this case is quite acceptable, because, having discovered a pathogenic pathogen in the blood, the white cells enter into battle with it and die themselves.
Metamyelocytes in the blood
To assess the condition of the body and, in particular, the performance of the immune system, a general blood test (CBC), or, as it is also called, a clinical test, is performed.
The composition of blood is very complex and is represented by various shaped elements, and the protective function is assigned to white bodies - leukocytes. They originate and mature in the red bone marrow, gradually passing through all stages of development, and only then enter the bloodstream. However, when a certain number of pathologies occur, young, not yet fully formed cells can be released into the bloodstream, which should be the reason for ordering additional examinations to look for the disease.
If, for example, according to the results of diagnostic measures, metamyelocytes are detected in the blood, then with a high degree of probability it can be argued that the quality of functioning of the immune system has decreased.
Reasons for detecting metamyelocytes
Normal levels of a general blood test for leukocytes depend on the age of the patient. In addition, an important role is played by the psycho-emotional state at the time of blood donation and even the region of residence. During decoding of the blood test, metamyelocytes should be absent. If this condition is not met, then it is worth asserting the presence of pathology and the development of the disease. Most often, this indicator indicates the development of leukocytosis. This can be caused by a number of diseases, which include the following:
The reasons for the detection of metamyelocytes in plasma may lie not only in the disease. This process can be accompanied without any specific pathology in the human body. As numerous studies show, the presence of metamyelocytes in the plasma may indicate severe exhaustion of the body after hard work or physical activity.
In addition, the presented elements can be present in the plasma during a depressed mental state resulting from a stressful situation, insoluble problems, or psychological trauma.
The formation of metamyelocytes can be provoked by various poisonings, consumption of fatty and heavy foods in large quantities, use of medications, and an autoimmune response. The presence of such elements in the plasma can also be provoked by physiological reasons, which are called physiological leukocytosis. It bothers a person in episodes and its duration is short. You just need to re-test your blood to find out the cause. Metamyelocytes can be detected in a person who suffers from the following diseases:
You need to be very careful about your health and undergo all necessary diagnostic tests on time. This is the only way to avoid dangerous pathologies and cure the disease in time. Metamyelocytes are important elements when deciphering a general clinical blood test. Despite the fact that they are just a type of leukocyte, their presence in the plasma can also indicate the development of a certain pathological process. Therefore, be more attentive to your health and follow all recommendations before taking the test in order to obtain accurate data as a result.
How many metamyelocytes should there be normally?
In a person who does not have disorders of the immune system, metamyelocytes should not be present in the bloodstream. These are not yet mature, in other words, young bodies going through the last stage of development, that is, they are the precursors of neutrophils.
They are formed from myelocytes located in the bone marrow and are sometimes able to enter peripheral blood vessels only after they pass into the stage of band neutrophils. The latter will then form full-fledged segmented neutrophils.
The above means that the norm is when immature forms are not contained in the bloodstream. If, on the contrary, young leukocytes are detected during a blood test, then the reason for their appearance is almost always a lack of mature cells responsible for the protective function.
This state of the body is often characteristic of an infectious process, when during the destruction of the pathogen there is a massive death of leukocytes, and the bone marrow produces and releases immature formed elements into the blood.
Reference! At the same time, we should not forget about certain situations when metamyelocytes, or myelocytes in the blood, can be increased, and such changes are not pathological.
For example, a slight increase in the percentage of young white blood cells in children with weakened immune systems and in pregnant women is considered acceptable. In addition, young patients often experience an increase in the level of immature white cells in a blood test due to an infectious disease such as rubella, chickenpox, influenza, etc.
To determine the indicator of metamyelitis, more than 200 white formed elements are counted in the laboratory. Then the percentage of each type of leukocyte is calculated. The detection of young blood cells in the studied material indicates difficulties in the maturation of cellular elements of the plasma.
This disorder is often observed during severe infection and is usually accompanied by an increase in the number of neutrophils. So, the permissible level of metamyelocyte content in newborn infants should not exceed 4%.
In babies from 1 to 4 days of life - 2.5%, in infants up to 2 months - 1.5%, and in all children older than this age, as well as adults, metamyelocytes are not normally detected during analysis. The only exception is women during pregnancy; in this condition, the indicated coefficient can range from 0 to 2%.
Normal levels of immature leukocytes in the blood
Reasons for appearance
The appearance of young forms of granulocytes in the blood indicates that the body is intensively producing new cells that fight harmful agents.
The reasons for this phenomenon may be different. Among them:
- Bacterial infections, as a rule, are acute in nature, with the addition of purulent-inflammatory processes. Typically, the appearance of myelocytes in the blood is observed with tonsillitis, acute pyelonephritis, ENT infections, scarlet fever, pneumonia, tuberculosis, sepsis, cholera and others.
- Severe infections: typhoid, brucellosis, paratyphoid.
- Intoxication with toxins of pathogenic bacteria in the absence of infection by the microorganisms themselves.
- Necrosis, or cell death, associated with diseases such as extensive burns, gangrene, stroke, and heart attack.
- Disintegration of malignant tumors, metastases in the bone marrow.
- Bleeding is acute.
- Radiation and chemotherapy, radiation exposure.
- Some severe viral infections: measles, rubella, influenza.
- Taking certain types of medications (painkillers, immunosuppressants).
- Lead or alcohol poisoning has a negative effect on the bone marrow, which produces white blood cells.
- Comatose states.
- Acidosis (acid-base imbalance).
- Blood diseases: anemia, leukemia, deficiency of folic acid and vitamin B12. Particularly high levels are typical for myeloid leukemia.
- The presence of myelocytes in the blood is possible for some time after recent infections.
- State of shock.
- Physical overexertion.
In some cases, a person does not have any complaints, while myelocytes are present in his blood. This may indicate that hidden infections or inflammatory processes are occurring in the body.
Myelocytes are usually detected in tests during pregnancy. This is due to the increased formation of granulocytes and the release of immature forms into the bloodstream. In peripheral blood during pregnancy they can contain up to 3%.
Myelocytes during pregnancy are considered normal, but at the same time they can also indicate pathological processes. This may be a reaction to inflammation, for example, of the throat. In this case, you need to consult a doctor and monitor changes in your blood test. As a rule, the presence of immature forms of granulocytes during pregnancy does not adversely affect the placenta and the health of the fetus.
The appearance of myelocytes in the blood of a child most often indicates an infectious disease. Just like in adults, a healthy child should not have them.
Causes of early release of metamyelocytes
Mainly immature forms of neutrophils and band cells indicate increased regenerative activity of the bone marrow. To assess its status, it is necessary to study peripheral biomaterial for the presence of young white cells, which are not observed in healthy people.
Metamyelocytes, as well as myelocytes, differ from full-fledged cells by an unsegmented nucleus, which has a round or bean-like shape. They stand out for their large size and coarse-grained structure. The precursors of these elements are myeloblasts and promyelocytes.
Therefore, if immature granulocytes with a characteristic non-segmented nucleus are determined in the diagnosed biomaterial, then this is a clear sign of an altered white germ of hematopoiesis. The entry of metamyelocytes into the bloodstream prematurely may be due to factors such as:
- infectious process (viral or bacterial infection in severe form);
- carrying out chemotherapy, radiation exposure during the treatment of cancer pathologies;
- severe intoxication with various substances, waste products of harmful microorganisms or parasites;
- necrotic tissue damage (due to heart attack, burns, etc.);
- autoimmune diseases;
- oncological diseases of the hematopoietic system.
As numerous studies show, young white cells can be found in the blood during less significant inflammatory processes, as well as during various physiological activities. For example, in the diagnosed biomaterial they often appear during physical or psycho-emotional stress or exhaustion of the body.
Sometimes even consuming excessive amounts of fatty foods or food poisoning can provoke an increase in the coefficient of this type of cell. In addition, in some cases, the concentration of immature leukocytes may increase due to the use of medications that have a depressing effect on the human immune system.
And if the subject has temporary leukocytosis - an increase in the number of leukocytes, which is not accompanied by pathology, then the periodic appearance of immature forms in the peripheral blood is considered acceptable if the coefficient is low. In other situations, such deviations in the composition of the blood indicate the presence of serious disturbances in the functioning of the hematopoietic system.
There is a type of leukemia called myelosis, that is, a pronounced increase in myelocytes and metamyelocytes in the bloodstream. With this pathology, an excessive amount of myeloid tissue is formed in the bone marrow, and the level of immature formed elements can reach 20–40%.
In myelosis, the function of hematopoiesis is taken over by the spleen, lymph nodes and liver, which is why they significantly increase in size. It should be noted that the acute form of this type of leukemia is much more severe than the chronic form.
Treatment
Since myelocythemia is caused by the development of a disease, it is the root cause that requires treatment.
Only after the cause of the pathological change in blood composition has been clarified, treatment is prescribed.
There are many reasons for the penetration of immature blood cells, in particular myelocytes. The vast majority of such triggers, unfortunately, are dangerous diseases that can quickly claim a human life. At the slightest transformation in the composition of the blood, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor, diagnose and prescribe the necessary treatment methods.
source
Reasons for the increase in children
As mentioned above, young forms of white cells in newborn babies can reach 4%, and this figure will be regarded as normal. But at the same time, by the end of the second month of a baby’s life, the coefficient should drop to 0% and remain unchanged throughout a person’s existence.
Main laboratory signs of chronic myeloid leukemia
In any case, if elevated myelocytes were detected in the test results, you should definitely undergo a full examination. This will help to exclude or identify the presence of pathological abnormalities in the functioning of the hematopoietic system in the child. It is very important not to miss the development of serious diseases in your baby.
Most often, a shift in the leukocyte formula in childhood is caused by the following disorders:
- burn lesions of large areas of the body;
- allergic reactions, autoimmune diseases;
- side effects from taking medications;
- severe psychological experiences, stress;
- food or heavy metal poisoning;
- intoxication due to a severe infectious disease.
With a leukemoid reaction, that is, a reversible change in the state of white blood, the child’s immune system is not able to fully cope with the responsibilities assigned to it, since a child at this age does not yet have enough mature leukocytes.
But sometimes the presence of up to 1% metamyelocytes in the studied biomaterial without changing the number of other formed elements is regarded as a physiological increase. To solve the problem of an increase in the described cells, experts first set the task of finding out the causes of abnormalities in tests in children, after which they develop appropriate therapeutic tactics.
For mild infectious diseases, vitamin complexes are prescribed, the diet and diet are adjusted, and, if necessary, medications are prescribed to destroy the pathogen. After a two-week course of therapy, re-diagnosis is performed.
If the leukocyte count is restored to normal, this means that the treatment has been chosen correctly. In the case when the values of metamyelocytes remain unchanged, that is, overestimated, doctors review the prescriptions and choose alternative medications.
Features of children's blood tests
It is also important that complex preparation for the procedure is not required: a general blood test is prescribed even in case of emergency admission to the hospital. However, if there is no rush, then to obtain objective results it is better to follow some rules. The main thing is not to feed or water children before visiting the laboratory, this will distort some indicators. It is optimal to donate blood early in the morning so that the baby does not have time to get hungry. It is also important to prepare the child for the procedure so that he is not nervous before the injection, since severe stress affects the properties of the blood. Blood for general analysis in children is taken from a finger.
Indicators of a child’s general blood test
Blood is a complex fluid, which consists of a liquid part and formed elements - cells responsible for oxygen transport and performing protective functions. It is these cells - red blood cells, platelets and leukocytes - that are the main subject of study when performing a general blood test, because their number and appearance can tell a lot about the probable causes of a small patient’s illness.
The design and contents of the form with the results of the UAC, which you receive from the laboratory, have their own characteristics. This is determined primarily by whether a short or extended version of such a study was conducted. The doctor makes the decision about this.
For preventive purposes, when there is no cause for concern, children are prescribed a “triple test” - an analysis that includes determining only the level of hemoglobin, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and the number of leukocytes. This procedure allows you to get a general idea of the child’s health.
However, a much more complete picture can be seen with a detailed blood test, which includes counting the number of all types of formed elements, as well as some additional indicators.
- Hemoglobin (Hb) . This substance is found in red blood cells and is responsible for gas exchange in the body.
- Red blood cells (RBC) . The most numerous blood cells, thanks to which it acquires its red color. In addition to carrying oxygen and carbon dioxide, the functions of red blood cells include transporting nutrients, drugs and toxins.
- Color index (MCSI) . How do you know if there is enough hemoglobin in each red blood cell? Measure the color index or, in simple terms, understand how “colored” the red blood cells are (after all, their color is determined precisely by hemoglobin). If the red blood cells are too pale or too bright, you should think about possible health problems in the child.
- Reticulocytes (RTC) . This is an important indicator in a general blood test in children. Reticulocytes are young immature red blood cells, the number of which determines the speed at which the composition of the blood in the child’s body is renewed.
- Platelets (PLT) . Blood platelets responsible for the ability of blood to clot and form blood clots.
- Thrombocrit (PST) . This indicator determines the proportion occupied by platelets in the entire volume of circulating blood. Thrombocrit allows us to draw conclusions about the functioning of the blood coagulation system. Problems in the functioning of platelets are in most cases of hereditary origin, so it is important to make sure that there are no such disorders from the very first months of the baby’s life.
- ESR (ESR) . If an inflammatory process is observed in the body, red blood cells change their properties - they stick together and become “heavy”, which is why the rate of their sedimentation in the test tube increases. Therefore, ESR is one of the most important indicators of a general blood test, which makes it possible to quickly confirm or exclude the presence of infection in a child.
- White blood cells (WBC) . White blood cells are the main “weapon” of the immune system. These cells come in many varieties, each with its own special function. But even an assessment of the total number of leukocytes can indirectly tell the doctor whether inflammation is present in the child’s body or not. The leukocyte formula indicates the relative percentage of different types of leukocytes in a blood test.
- Neutrophils are the most numerous group of white blood cells. Their main task is to surround bacteria at the source of infection and destroy the latter. These cells are divided into several groups depending on the degree of cell maturity - band cells, segmented cells, myelocytes, metamyelocytes. Doctors often use such concepts as a shift in the leukocyte formula: we are talking about the predominance of young (shift to the left) or mature (shift to the right) neutrophils among leukocytes. Such situations indirectly indicate how many immune system cells the body has produced in recent days.
- Eosinophils (EOS). These cells are responsible for allergic reactions in the body and for the production of immunoglobulins of group E. The number of such leukocytes is important if parasitic diseases are suspected, which often affects children.
- Basophils (BAS). A group of cells with functions similar to eosinophils. Their level allows us to draw conclusions about the presence of inflammation or manifestations of allergies in the body.
- Lymphocytes (LYM). These cells destroy viruses and also fight chronic infections. There are several types - T cells, B cells and natural killer cells (NK cells).
- Plasma cells. This is the name given to mature B lymphocytes that produce antibodies to fight infections. An increase in the number of plasma cells in a child’s blood indicates active immune resistance to viral infection.
- Monocytes (MON). A few monocytes in the process of circulation through the vessels specialize in the fight against foreign agents, and also, like scavengers, remove traces of the fight from the “battlefield” - unnecessary proteins and fragments of destroyed cells.
Results of a general blood test in children: norm and deviations
Following the needs of the growing body, the composition of the child’s blood undergoes changes. Based on this fact, to evaluate the results of a blood test, 7 age groups are distinguished, which need to be guided by when interpreting the obtained indicators. Typically, standards are given for the following children's ages: 1 day, 1 month, 6 months, 1 year, 1–6 years, 7–12 years, 13–15 years. The corresponding blood test standards are presented in the table:
A decrease in hemoglobin in a general blood test in a child makes one suspect anemia, internal bleeding, or the presence of a malignant tumor. A marked increase in this indicator is also a sign of illness, dehydration or intense physical activity.
A decrease in red blood cells (erythropenia) is a sign of anemia, blood loss and chronic inflammation. An increase in the number of red blood cells (erythrocytosis) occurs with dehydration, congenital problems with hematopoiesis, and some tumors.
Following the needs of the growing body, the composition of the child’s blood undergoes changes. Based on this fact, to evaluate the results of a blood test, 7 age groups are distinguished, which need to be guided by when interpreting the obtained indicators. Typically, standards are given for the following children's ages: 1 day, 1 month, 6 months, 1 year, 1–6 years, 7–12 years, 13–15 years. The corresponding blood test standards are presented in the table (see table below).
It is important to pay attention to the ESR values: in children, an unreasonable increase in this indicator is always a reason for repeated analysis. In a situation where an increase in ESR is associated with infection, a change in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate usually occurs the next day after the temperature rises. But a decrease in ESR in newborns is almost always a physiological phenomenon.
A lack of platelets (thrombocytopenia) indicates disorders in the blood coagulation system in hemophilia and other hereditary diseases or recent bleeding. Sometimes a deficiency of blood platelets occurs due to infections, certain types of anemia and malignant diseases, as well as when taking certain medications. If there are more platelets than normal (thrombocytosis), then the pediatrician will suspect a chronic inflammatory disease (for example, tuberculosis) in the child.
A change in the content of leukocytes in a general blood test in children (leukocytosis or leukopenia) almost always indicates an infection in the body or a disorder of hematopoietic function. The doctor will make a more accurate conclusion based on an analysis of the leukocyte formula indicators - the predominance of certain types of cells and a shift in the formula to the left or right are an important diagnostic sign of viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases.
| Indicators | Age | ||||||
| 1 day | 1 month | 6 months | 1 year | 1–6 years | 7–12 years | 13–15 years old | |
| Hemoglobin (Hb), g/l | 180–240 | 115–175 | 110–140 | 110–135 | 110–140 | 110–145 | 115–150 |
| Red blood cells (RBC), ×10 12 cells/l | 4,3–7,6 | 3,8–5,6 | 3,5–4,8 | 3,6–4,9 | 3,5–4,5 | 3,5–4,7 | 3,6–5,1 |
| Color index (MCHC), % | 0,85–1,15 | 0,85–1,15 | 0,85–1,15 | 0,85–1,15 | 0,8–1,1 | 0,8–1,1 | 0,8–1,1 |
| Reticulocytes (RTC), ppm | 30–51 | 3–15 | 3–15 | 3–15 | 3–12 | 3–12 | 3–12 |
| Platelets (PLT), 109 cells/l | 180–490 | 180–400 | 180–400 | 180–400 | 160–390 | 160–380 | 160–360 |
| Thrombocrit (PST), % | 0,15–0,35 | 0,15–0,35 | 0,15–0,35 | 0,15–0,35 | 0,15–0,35 | 0,15–0,35 | 0,15–0,35 |
| ESR (ESR), mm/hour | 2–4 | 4–8 | 4–10 | 4–12 | 4–12 | 4–12 | 4–15 |
| White blood cells (WBC), 109 cells/l | 8,5–24,5 | 6,5–13,5 | 5,5–12,5 | 6,0–12,0 | 5–12 | 4,5–10 | 4,3–9,5 |
| Band neutrophils, % | 1–17 | 0,5–4 | 0,5–4 | 0,5–4 | 0,5–5 | 0,5–5 | 0,5–6 |
| Segmented neutrophils, % | 45–80 | 15–45 | 15–45 | 15–45 | 25–60 | 35–65 | 40–65 |
| Eosinophils (EOS), % | 0,5–6 | 0,5–7 | 0,5–7 | 0,5–7 | 0,5–7 | 0,5–7 | 0,5–6 |
| Basophils (BAS), % | 0–1 | 0–1 | 0–1 | 0–1 | 0–1 | 0–1 | 0–1 |
| Lymphocytes (LYM),% | 12–36 | 40–76 | 42–74 | 38–72 | 26–60 | 24–54 | 22–50 |
| Monocytes (MON),% | 2–12 | 2–12 | 2–12 | 2–12 | 2–10 | 2–10 | 2–10 |
Today, when a general blood test in most cases is performed using automated laboratory systems, and not through the painstaking work of laboratory assistants at a microscope, doctors without hesitation prescribe it in any situation if there is a suspicion of a childhood infection or other health problems in the child. And this is correct - provided that the procedure is performed efficiently, its results will help both the doctor and worried parents quickly navigate the current situation. And a preventive blood test, which is recommended for both children and adults at least once a year, allows you to avoid unnecessary worries about minor ailments and other minor changes in well-being.
Source: www.kp.ru
What can affect the result of the analysis?
An increase in the coefficients determined during a general blood test is not always associated with the occurrence of any pathological process. Sometimes the result obtained can be influenced by physiological temporary changes, external factors and neglect of the rules for collecting or donating biomaterial.
That is why people preparing to undergo this analysis should be sure to familiarize themselves with the list of recommendations with which they can significantly reduce the likelihood of error or error. So, before donating blood, you need to consider the following:
- Analysis indicators may be overestimated if the subject consumed a large amount of fatty foods the day before.
- It is necessary to submit biomaterial for laboratory study in the morning, and at least 8 hours must pass after the last meal (dinner).
- Two days before the procedure, you should stop drinking alcohol, as alcohol-containing drinks often lead to distorted results.
- 2–3 days before blood sampling, you cannot undergo physical procedures and x-ray examinations.
- Half an hour before the actual test, smoking is prohibited, as this can also affect your blood counts.
Attention! In addition, we should not forget that any physical activity several hours before diagnosis can provoke a temporary change in blood characteristics and the study data will lose reliability.
Therefore, even after climbing the stairs, it is recommended to rest in order to bring your body into a calm state. All of the above rules will help to avoid inaccuracies and save the patient from going through the procedure again.
Following all recommendations regarding taking a blood test will help avoid inaccuracies in the results
Correction methods
Even minor changes in the indicator should in no case be ignored, but diagnosis and, if necessary, treatment should be carried out exclusively by a specialist. Self-medication or unconventional methods are not suitable if a person has abnormalities in the functioning of the immune or hematopoietic system.
An unskilled approach to therapy can miss the occurrence of a dangerous disease at an early stage or oncopathology, which without proper treatment will lead to the death of the patient. Any therapeutic measures must be carried out exclusively under the strict supervision of the attending physician or specialized specialist.
This will allow you to adjust the dosage of medications taken or the duration of treatment at any time. Considering that in most cases of increased metamyelocytes there are pathological processes that are quite easily treatable, the prognosis for the course of the disease is most often favorable.
If deviations in the coefficient are associated with the entry of infectious agents into the body, then anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs will necessarily appear on the prescription sheet. During the recovery period, the doctor will recommend taking dietary supplements and vitamins that will improve the quality of metabolic processes and help remove toxins from the body.
In situations where the increase in metamyelocytes is due to malfunctions of the hematopoietic system, therapy will be required under the coordination of a hematologist, based on the causes of the identified abnormalities. Accordingly, when identifying dysfunction of the immune system, treatment will be prescribed under the clear guidance of an immunologist.
Prevention and prognosis
Given that such cells appear in the blood only during the occurrence of any pathology, first of all, it is worth preventing its occurrence. To do this, it is necessary to undergo a full laboratory and instrumental examination several times a year at a medical institution with mandatory visits to all clinicians.
Additional preventive measures include:
- complete cessation of bad habits;
- maintaining an active lifestyle;
- healthy and balanced diet;
- avoiding prolonged exposure to radiation and physical exhaustion of the body;
- taking medications strictly as prescribed by the attending physician and with mandatory compliance with all recommendations;
- avoiding the entry of chemicals and toxic substances into the body.
In itself, the presence of myelocytes in the blood is not at all dangerous, however, it is necessary to take into account the factors that led to such a disorder, since each underlying disease has many of its own complications and consequences.
source
What are myelocytes and their types
The predecessor of absolutely any blood cell is a special stem cell. It has two important features:
- Capable of transforming into any other cytological structure. That is, to differentiate.
- Does not die after a certain number of divisions. As it happens with an ordinary, functionally defined cell.
In special structures known as bone marrow processes, differentiation of cytological units occurs. Myelocytes in the blood are special intermediate cells, no longer stem cells, but not yet functionally active. Normally, they should not be present in the analysis.
Some exceptions are permitted. For example, when taking drugs that inhibit hematopoiesis. But these are rather rare possible cases, rather than natural changes and processes.
At the first stage, stem cells differentiate into two types:
- Maternal myelopoietic. The granulocytes themselves are formed from them, but not immediately. That is, the cells that are mainly responsible for the immune response. Erythro- and platelets also appear from these structures.
- Maternal lymphopoietic. As the name suggests, further maturation results in the formation of lymphocytes, agranulocytic types of immune cells.
At the second stage, three new types of more mature variants appear from the myelopoietic cell:
- Erythroblast. Red blood cells are formed from it.
- Megakaryoblast. Platelet precursor.
- Myeloblast. All granulocytes are formed from it.
At the third stage, promyelocytes appear from the myeloblast and then the myelocytes in question. If we look at the diagram in more detail, there are three types of myelocytes: neutrophilic, basophilic and eosinophilic.
At the next stage, myelocytes are divided into metamyelocytes; these are the precursors of granulocytes, special cells of the human immune system that participate in the work of the body’s defenses.
As soon as this stage ends, the final stage begins. From the precursors of cytological structures, 3 types of leukocytes are formed - cells of the myeloid series.
Basophils
The largest white blood cells. Much more than others from the named group. Has the ability to inactivate bacteria and viruses. This occurs due to the special structure of the cell.
- On the one hand, it is capable of phagocytosis. That is, the absorption of a foreign object.
- On the other hand, it releases histamine and other toxic substances into the environment to destroy foreign agents.
- Thirdly, it carries special immunoglobulins that suppress the development of bacteria and viruses.
Basophils play a major role in allergic reactions. There are only about 1% of the total mass of granulocytes in the blood.
Eosinophils
They have a rounded shape and a double core in the form of a jumper. Like the cells mentioned above, it has the ability to phagocytose. However, the main function of the eosinophil is antiparasitic.
Due to the special structure of the outer membrane, the cytological structure adheres to the helminth larvae and dissolves them. This is the main task, but not the only one.
Like basophils, cells are capable of fighting viruses and bacteria. They ripen for about 12 hours, after which they enter the bloodstream. This distinguishes them from previous structures, which require almost two days to “prepare.”
Eosinophilia also often indicates an allergy. The number of cytological structures of this type is almost 5%.
Neutrophils
The most numerous. According to various estimates, they constitute up to 80% of the total mass of granulocytes. There are other calculations as well. Apparently, the discrepancies are associated with the dynamics of the process of hematopoiesis and cell maturation. There are several options.
Neutrophils themselves are heterogeneous. Their modifications are found in the bloodstream. Including immature ones. Or segmented, rod-nuclear.
They perform different functions, but both absorb and digest foreign structures. This is the so-called microphagocytosis.
The approximate lifespan of neutrophils is 12 days. Plus or minus.
Read more about the norms and causes of deviations in the concentration of neutrophils in the blood.
Reasons for the increase
There can be quite a few factors for the growth of indicators. Here are just a few of the possible culprits.
Acute infectious processes
It doesn’t matter what type, bacterial, viral or fungal. Accompanied by corresponding symptoms. Sometimes they occur without manifestations. Why does the concentration of precursors, immature cells, increase in this case?
The reason is simple - the body strives to cope with the disorder as quickly as possible. Localize the area, separate it from others and fight the infection.
For these purposes, many neutrophils and other structures are synthesized. But with such active work, the tissues malfunction; some of the immature cytological units enter the bloodstream.
Treatment. Is therapy for this particular process necessary? No, as you recover, hematopoiesis will return to normal. Everything will return to normal.
It is important to correct the underlying pathological process—the infectious disease itself. Antibiotics and antivirals are used for this purpose.
If fungal agents are to blame, then fungicides. Also non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (glucocorticoids suppress the immune system), antipyretics to reduce fever. For example, Nurofen, Ibuprofen. It is important to consult a doctor to prescribe a course of therapy.
The duration of correction is about 2 weeks on average. Plus or minus. Gradually everything will return to normal on its own. No special treatment is required for excessive production of precursors.
Tumors
Mostly malignant, with the breakdown of tissue with an abnormal structure. As a rule, we are talking about advanced stages of the pathological process.
Cancer cells are extremely voracious. There is no longer enough food for everyone. At a certain point, the death of cytological structures from malnutrition begins. All toxins enter the bloodstream.
The immune system sends “cleaners” to the site of the lesion, which absorb abnormal dead cells. However, as the disease progresses, the number of cytological structures increases.
Hence the need to direct additional forces to combat this “garbage”.
The appearance of promyelocytes and myelocytes in the blood is the result of bone marrow hyperfunction; at a certain point, it simply stops coping and releases immature cells into the bloodstream.
Treatment. As in the previous case, it is necessary to correct the main pathological process - a cancerous tumor. There are several options here.
The gold standard is surgery. Doctors remove the neoplasia. Then, as needed, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are prescribed. They are not always effective, so the oncologist decides the issue. On the spot.
Tissue necrosis
In other words, cell death. Approximately the same process occurs as with cancer. Only this time it is not abnormal malignant cells that die, but completely normal cells, for example, in case of massive burns or gangrene.
The body immediately encounters the need to remove “garbage” from the bloodstream as quickly as possible. This is the task of neutrophils, basophils - granulocytes. However, there are not enough of them, so we have to urgently develop new ones. A general breakdown ensues.
Treatment. It is necessary to remove dead cells as quickly as possible.
- In the case of gangrene - surgically.
- For burns, special solutions and ointments are used to quickly cope with the disorder.
After this, for several days the concentration of myelocytes in the blood should be around zero or slightly higher. Minor errors are also acceptable.
Anemia
Develops with insufficient intake of iron, vitamins B9, B12. The last two forms are called megaloblastic. The reason is quite simple. In order for blood cells to mature normally, they need these substances.
If the concentration and intake are insufficient, hematopoiesis first slows down and then goes into an abnormal format. This is exactly what we are talking about.
Megaloblasts or myelocytes make up a significant portion of the total cell mass. This, of course, should not be the case. The more advanced the process, the more serious the pathology is.
Treatment. Loading doses of B vitamins are indicated, at least for several weeks. The question is complex.
Sometimes the disorder accompanies diseases of the digestive tract. In this case, treatment of the underlying disease is necessary. Otherwise, as soon as the concentration of vitamins decreases or they are no longer administered, the disease will return to normal. Half measures are not enough.
Poisoning
As a rule, we are talking about domestic disorders. For example, ethanol intoxication. Less commonly, the same effect occurs after taking a dose of opioid and cannabinoid drugs.
Synthetic, homemade psychoactive substances are dangerous. Serious changes in the blood picture are observed in patients with a decent history of taking any kind of chemical obscenity. But not only.
Initially, high rates are observed in children and adolescents prone to drug addiction and alcoholism.
The treatment is simple. It is enough to give up the psychoactive substance. Carry out special detoxification measures with infusion solutions and drugs of a special group (Disol, Trisol, specific antidote Naloxone). The issue is resolved by addiction specialists.
Effects of radiation on the body
Ionizing radiation has an extremely negative effect on the bone marrow. In this case, even a small dose is enough. In everyday life, people encounter such a dangerous factor, for example, when performing frequent x-rays or treating cancer.
Other possible options are work at uranium mines or a nuclear power plant, especially if safety regulations are violated. Identical problems are possible for submariners.
Treatment is to quickly eliminate the effects of radiation. For this purpose, iodine preparations are used.
A special diet high in protein and fat is also prescribed. For example, fermented milk products. It is necessary to eliminate the damage factor itself.
Rare, severe infectious processes
They stand apart from others. We can name such pathologies as typhus, advanced forms of syphilis, genital lesions, herpetic and other plans. This also includes disorders such as tuberculosis, HIV, and AIDS.
They cause long-term, if not permanent (constant) changes in the blood picture. Since these pathologies themselves are difficult with high myelocyte counts.
The more advanced the deviation, the worse the situation with the concentration of immature cytological structures in the body. Therefore, you need to start treatment as early as possible.
Incomplete forms are not able to perform the functions of granulocytes. That is, fight the infection. This means that immunity is seriously reduced. Against the backdrop of AIDS, this is a de facto death sentence.
Therapy depends on the disease itself. Immunomodulators and broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed. In the case of tuberculosis, we are talking about fluoroquinolones.
Taking certain medications
There are quite a lot of them. For example, anti-inflammatory drugs of non-steroidal origin. Also hormonal medications such as Prednisolone and its more powerful “brothers” in the group.
Immunosuppressants have a negative effect on the blood: detection of myelocytes in tests is possible after chemotherapy with Methotrexate and other drugs.
Is special treatment needed in this case? No, therapy as such is not required. It is enough to abandon a specific pharmaceutical product and/or replace it with another. Not so dangerous for the immune system.
But this issue should be decided by a doctor, since without a qualified assessment it is easy to harm yourself. When purchasing medications, it is strongly recommended to check the label to see how the medication affects the hematopoietic system.
Pregnancy
Not a pathological process, but a completely natural phenomenon. However, this doesn't make it any easier. The problem is that closer to the third trimester of pregnancy, when the fetus is gaining strength, disruptions in the functioning of the mother’s hematopoietic system and the appearance of myelocytes and metamyelocytes in tests are possible.
This is the result of hidden pathological processes and health problems. For example, insufficient nutrition often affects the body; an incorrect diet does not provide the body with vitamins B9 and B12. Megaloblastic anemia begins.
The issue of treatment should be discussed with the gynecologist who is caring for the patient. In relatively mild cases, nothing needs to be done.
In more dangerous cases, when life is at stake, it is necessary to use drugs to stimulate hematopoiesis. It is possible to prescribe a course of vitamins to support the body.
The question is complex, it all depends on the situation. The golden rule is that the expected benefit outweighs the possible harm.
Increased physical activity
There is an increase in myeloblasts in the blood in patients who engage in intense physical activity. The reason in this case is the active formation of metabolic products of vital activity.
In such a situation, concentrations increase insignificantly. The norm is restored on its own within a few hours after physical activity. Therefore, no special treatment is required.
This is not a complete list of reasons. Only the most common options. The appearance of metamyelocytes in the blood means that a pathological process is occurring on the part of the digestive tract, hematopoietic system, and oncological plan.
There can be many options. The issue is resolved through diagnostics.
Myelocytes: norms in blood tests, causes of increase, treatment – Vascular health
- Metamyelocytes or myelocytes are immature granulocytes that are normally localized in the bone marrow.
- Myelocytes should not be present in blood tests of healthy people.
- What does it mean if myelocytes are found in the blood?
The appearance of these cells indicates serious pathologies in the body.
Myelocytes: structural features and types
A myelocyte is an immature representative of leukocytes. It consists of a large round kernel. Its cytoplasm is saturated with granular inclusions or granules.
- Under natural conditions, myelocytes having reached maturity should degenerate into segmented granulocytes.
- Leukocytes
Cytological analysis shows that during the period of maturation, myelocytes are painted in a rich red-violet color. Protoplasm acquires a blue tint, and during ripening it has a pink color.
Varieties
Experts distinguish the following types of myelocytes:
- Neutrophilic. Mature representatives have pink protoplasm, younger ones have pink-violet protoplasm. It contains both fine grain and larger granules.
- Eosinophilic. They have weakly basophilic protoplasm. It contains a large number of large grains. The color of eosinophilic cells is pinkish-red.
- Basophilic. The protoplasm of these cells is oxyphilic, and the grain is violet.
Stages of maturation
To become full-fledged granulocytes, myelocytes undergo the following stages of maturation:
- myeloblast,
- Promyelocyte,
- Metamyelocyte.
Reference! Promyelocytes are larger than myeloblasts. They have “primary granules” in the cytoplasm and condensed chromatin.
Myelocytes and the pathological process
When pathogenic flora invades the body, mature segmented granulocytes are the first to come to defense.
If there are not enough of them or they cannot cope with the harmful agent, band granulocytes are sent to their aid. Normally, their quantity in the blood is limited.
The stronger the disease, the more young immature cells are neocytized (accumulated). First, the level of band myelokaryocytes increases; as the condition worsens, metamyelocytes appear in the blood (one of the stages of myelocyte development).
If things are really bad, very young cells – myelocytes – join the fight. This means that the body has no strength left to protect itself.
Why do myelocytes appear in the blood?
The reasons for the appearance of myelocytes in the blood are different.
The most common of them:
- Infectious diseases of an acute nature, which occur with the presence of inflammatory and purulent foci. This is observed with pneumonia, sore throat, tuberculosis, and sepsis.
- Poisoning with heavy metal salts (lead) or alcoholic beverages.
- Cell death during a pathological process. It occurs in patients with stroke, gangrene, and extensive burns.
- Benign or malignant tumors.
- Pathological changes in the blood system. Example: leukemia.
Other etiological factors for the occurrence of myelocytes are:
- Acute bleeding
- Poisoning with toxic substances,
- Radiation therapy and chemotherapy carried out to treat cancer,
- Radioactive radiation,
- Insufficient intake of vitamin B in the body or its absence,
- Intestinal infections
- Diseases caused by viruses (influenza, rubella)
- Increased physical activity
- Comatose and shock states,
- Using certain medications in large quantities (anti-depression pills, painkillers),
- Acid-base balance disorders.
During pregnancy
Myelocytes in the blood are normal.
Granulocytes are increased, and a large number of their immature forms are released into the bloodstream. In peripheral blood their content reaches 3%.
However, the detection of myelocytes in pregnant women may also indicate pathological processes. Their appearance is associated with the body's response, for example, to inflammation.
In general, the appearance of myelocytes in the blood of expectant mothers does not negatively affect either their health or the health of the fetus.
Rules for donating blood
To get a correct blood test and determine or refute the presence of myelocytes, patients must adhere to several rules before donating.
- You can't eat. In the evening before going to the laboratory, it is also recommended to avoid a heavy dinner. At least 8 hours must pass before donating blood and the last meal.
- For a week, you must refrain from drinking alcohol and limit your intake of salty, fried and fatty foods.
- Before collecting biological material, you should not smoke for an hour.
- It is prohibited to donate blood after intense physical activity or after undergoing an X-ray examination.
The designation of myelocytes in a blood test is Mie. They are counted using a leukogram.
If immature forms of granulocytes are present in the blood, doctors talk about the so-called “shift of the leukocyte formula to the left,” in other words, about myelocytosis.
Myelocyte normal indicators
The presence of myelocytes is normally observed only in the bone marrow.
In an adult patient and a child, the number of myeloid cells fluctuates:
| Name of myelocytes | Quantitative indicators are normal, % |
| Neutrophils | 4,8 – 9, 6 |
| Eosinophils | 0,6 — 2 |
| Basophils | 0,2 — 1 |
Myelocytes detected in the blood: what to do
When myelocytes are detected in the blood, the doctor prescribes a series of special studies to establish the cause of its occurrence, and, accordingly, the disease. No PVP required.
Only after a diagnosis has been established can treatment begin.
Doctors recommend:
- Stop taking medications that cause myelocyte synthesis. This helps bring the indicators back to normal.
- Stick to a diet for some time (in case of vitamin B deficiency).
- Use special vitamins and medications (for a direct effect on myelocytes).
Myelocytes: causes of appearance in the blood, diagnosis and treatment
The appearance of myelocytes and other maturing cells in the peripheral blood is unacceptable. Violation of hematopoietic processes indicates the development of dangerous processes in the human body of a hematological and non-hematological nature.
Types of myelocytes
Myelocyte in peripheral blood smear
- Myelocytes are the precursor cells of mature granulocytes, a type of white blood cell.
- The formation of myelocytes is an intermediate stage of granulocytopoiesis, which begins with the mitotic division of a stem cell.
- In order to fully understand what myelocytes are and what place they occupy in hematopoiesis, it is necessary to indicate all the forms of cells of the granulocytic lineage of hematopoiesis:
- Myeloblasts are cells that arise from the division of a colony-forming stem cell. Myeloblasts lose pluripotency - the ability to differentiate into any other types of cells. Their main task is to ensure normal maturation of granulocytes.
- Promyelocytes are the largest cells in all stages of granulocyte formation. Already at this stage of maturation, primary granules appear in the cells, which divide promyelocytes into eosinophilic, basophilic and neutrophilic.
- Myelocytes - are formed after the third division of promyelocytes. At this stage of maturation, the granularity of the cells (inclusions) becomes strictly specific (secondary), which makes it possible to clearly distinguish future neutrophils, basophils and eosinophils. Myelocytes are actively dividing cells. The physiological activity and functionality of granulocytes depends on the completeness of myelocyte maturation.
- Metamyelocytes (young leukocytes) - such cells have a low ability to divide. Thanks to them, the final stage of granulocyte maturation occurs. The nucleus of metamyelocytes undergoes changes, dividing the cells into two large groups - segmented and band.
- Granulocytes are the result of granulocytopoiesis. Such cells are called polymorphonuclear, since the cell type depends on their granularity.
Thus, myelocytes are the cells that determine the full growth of mature granulocytes. They belong to granular leukocytes and differentiate into three main types of white blood cells:
- neutrophils,
- eosinophils,
- basophils.
Norms of myelocytes in the bone marrow
Blood cell maturation
- Since immature forms of leukocytes must undergo all stages of maturation in the bone marrow, they should normally be present only in the bone marrow puncture.
- If a person is healthy, then there is no reason for immature forms of blood cells to enter the systemic circulation.
- To assess the consistency of granulocytopoiesis and all hematopoiesis in general, a research method such as bone marrow puncture (sternal puncture, trephine biopsy) is used.
- Normally, the granulocytic (myelocytic) lineage of hematopoiesis will give the following indicators when assessing the myelogram:
Cellular composition of the bone marrow (granulocytopoiesis) Quantity, %
| Undifferentiated blast cells | 0,1-1,1 |
| Myeloblasts | 0,2-1,7 |
| Promyelocytes | 1,0-4,1 |
| Myelocytes | 6,9-12,2 |
| Metamyelocytes | 8,0-14,9 |
| Rod | 12,8-23,7 |
| Segmented | 13,1-24,1 |
| Neutrophil Maturation Index | 0,5-0,9 |
| All eosinophils | 0,5-5,8 |
| Basophils | 0-0,5 |
Causes of appearance in the blood
Severe infection may lead to the appearance of myelocytes
In a healthy person, there should be no myelocytes or other immature cells of the myelocytic lineage of hematopoiesis in the blood test. Even minor concentrations of dividing and maturing cells are considered a variant of the pathological condition.
The detection of juvenile forms of granulocytes indicates that the body is at risk and is struggling with one of the following diseases or pathological processes:
- acute bacterial and viral infections, most often complicated by purulent inflammation. These may be purulent tonsillitis, other severe infections of the ENT organs, acute pyelonephritis, pneumonia, cholera, sepsis, scarlet fever, tuberculosis, typhoid fever, brucellosis, paratyphoid fever, measles, mumps, rubella, etc.
- conditions after severe infectious and inflammatory processes;
- appendicitis and other acute surgical pathology;
- gangrene;
- severe burn disease;
- strokes, heart attacks;
- acute blood loss of any origin;
- metastasis to the bone marrow;
- tumor collapse syndrome;
- consequences of chemotherapy, radiation treatment;
- long-term use of cytostatic, immunosuppressive medications;
- lead poisoning;
- alcoholism;
- all types of coma;
- acidosis;
- shock;
- heavy and constant physical activity;
- many types of anemia;
- leukemia;
- myeloid leukemia;
- deficiency of cyanocobalamin and/or folic acid.
Source: https://usp-crb.ru/sosudy/mielotsity-normy-v-analize-krovi-prichiny-povysheniya-lechenie.html
Additional examinations
Myeloid cells are usually absent in the blood sample; this is the clinical norm. However, if deviations are detected, special measures are needed. It's important to check what's what.
For this purpose, a blood test or a blood test alone is not enough. It is worth contacting a hematologist and undergoing a series of examinations under his supervision.
- Patient interview. The doctor clarifies the complaint, records the symptoms and then puts forward hypotheses about what it might be.
- Anamnesis collection. To study the probable origin of the pathological process.
- Advanced blood test. Necessary to identify possible inflammatory phenomena in the body. Mainly of infectious origin.
- You also cannot do without biochemistry. It is necessary to determine the concentration of elements such as iron in the blood. This is an important measure when screening for various types of anemia.
- Ultrasound of the digestive tract. In case anemia is associated with abnormalities in the functioning of the gastrointestinal structures.
- When there is a suspicion of a tumor, an MRI is indicated. True, you need to know at least the approximate localization. Otherwise, the entire body is scanned.
- CT scans are prescribed for the same purposes. In both cases, contrast-enhanced tomography is performed. Gadolinium, iodine.
- Visual assessment of fabrics. With its help, you can detect erysipelas, areas of necrosis that are located on the surface.
The list is also approximate. The last word remains with the specialist doctor - hematologist and others.
Myelocytes in a blood test are intermediate, immature precursor cells of eosinophils, neutrophils and basophils (granulocytes, in a word). Normally they should not exist at all. But there are rare exceptions to the rule.
Metamyelocytes
A general blood test is an important diagnostic method, without the results of which it is impossible to accurately establish a diagnosis. During the study, it is possible to determine the percentage of the main formed elements in the blood, namely: platelets, erythrocytes and leukocytes. One of these elements are also metamyelocytes. They belong to a number of leukocytes, and their number allows us to determine the state of human health.
- What are metamyelocytes?
- Normal indicators
- Preparing for the test
- What influences the result?
- Reasons for detection
Kinds
Myelocytes are mature cells compared to promyelocytes. They are capable of turning a bright red-violet color when ripe. Protoplasm has a blue tint, but during the ripening period it changes to pink, and abundant granularity can be found in its composition. There are the following types of myelocytes:
- neutrophilic;
- eosinophilic;
- basophilic.
Neutrophil cells of a more mature age have protoplasm of a pink hue, while less mature ones have a pinkish-violet color. In addition to abundant granularity in the protoplasm, large grains can also be found.
Eosinophilic myelocytes are characterized by weakly basophilic protoplasm, and they contain large grains in large quantities. Their color is pinkish-red.
Basophilic myelocytes have oxyphilic protoplasm, and their composition contains violet granularity.
What are metamyelocytes?
Metamyelocytes are a type of leukocytes that are concentrated in the bone marrow and for this reason their norm is not determined in a general blood test. The formation of neutrophil precursors in a general blood test is called a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left. The reasons for this may be various pathological processes, which are characterized by absolute leukocytosis (increased number of leukocytes). High levels of metamyelocytes in the blood may indicate myeloid leukemia.
Treatment
Therapy for myelocytic leukemia is carried out in oncological institutions. Cytotoxic drugs are prescribed. The basic remedy is Cytarabine, which is used in combination with other drugs of this group: Doxorubicin, Cyclophosphamide, Vepezid. Medicines have a number of side effects, so constant medical supervision is necessary. Treatment is supplemented with corticosteroids and symptomatic agents. In the terminal stages of the disease, a bone marrow transplant is necessary.
When myelocytes and metamyelocytes are detected in the blood of patients with diseases of internal organs, it is necessary to establish the cause of the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment. For purulent processes, antibiotics are prescribed. For infections, etiotropic therapy is prescribed, and corticosteroid drugs are used for inflammation. Recovery of the underlying disease will ensure normalization of blood counts.
Myelocytes and metamyelocytes in the blood are a manifestation of promyelocytic leukemia or severe pathology of internal organs. In recent years, progress has been made in the treatment of blood diseases. The use of targeted drugs and monoclonal antibodies in the treatment of myeloblastic leukemia (Ozogamycin, Decitabine) gives hope for the recovery of this severe category of patients.
source
Normal levels of metamyelocytes
During decoding, the medical professional first counts at least 200 white blood cells. He then determines the percentage of each population. When these steps are completed, you can move on to studying the structure of cells and identifying inclusions.
As mentioned above, normally the presented elements are not present. Their discovery suggests that the process of maturation of new plasma cells occurs with a certain intensity. This can occur in severe cases of an infectious disease. Typically, this disorder is caused by an increase in the total number of neutrophils. This condition is called leukemoid reaction.
Table - Reference values
The process of preparing for the analysis
If you want to be sure that this blood test will show accurate values when deciphered, then you must adhere to certain rules. These include the following:
- Carry out the diagnosis in the morning on an empty stomach. The interval between eating and taking blood should be at least 8–12 hours.
- The night before, you should have a light dinner.
- A few days before the test, stop eating fatty, fried foods and alcohol.
- If the day before it was not possible to avoid a feast or a visit to the bathhouse, the diagnostic test should be postponed for a couple of days.
- One hour before blood collection, you should not smoke.
- You cannot take the test after visiting x-rays and physiotherapeutic procedures.
What influences the result?
Running and climbing stairs are some of the factors influencing the analysis results
When going for a general blood test, every person should know the main factors that will affect the result:
- Failure to comply with the rules for preparing for the study. Blood collection occurred immediately after eating, physiotherapeutic or diagnostic procedures.
- Performing physical activities such as running, climbing stairs, emotional overstimulation. For this reason, you need to rest a little before taking the test.
- Taking certain medications. These include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, chloramphenicol, corticosteroids, heparin, levodopa, narcotic analgesics.