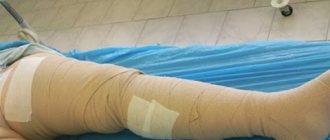
A trophic ulcer on the lower extremity is a defect in the skin and underlying tissues that does not heal for more than one month.
The cause of the development of a trophic ulcer on the leg is a violation of tissue nutrition due to pathological changes in the vessels of the lower extremities with varicose veins.
The favorite localization of ulcerative defects is the lower extremities. This is due to the fact that the vascular system of the legs experiences increased exposure to gravitational forces, which complicate blood circulation.
Causes
The development of a trophic ulcer with varicose veins is caused by a violation of the integrity of the skin. With the normal functioning of all human organs and systems, defense mechanisms come to the rescue, and the process of reparation (restoration) of the skin begins; with impaired trophism, any trauma to the skin leads to the development of a trophic ulcer.
Injuries lead to damage to the skin:
- Cuts.
- Diaper rash.
- Scratches.
- Insect bites.
- Bruises.
- Burns.
For patients suffering from varicose veins, it is especially important to protect the skin from traumatic effects.
There are several factors contributing to the occurrence of trophic ulcers:
- Disturbance of metabolic processes in the body.
- Pathology in the functioning of the immune system.
- Increased blood pressure.
- Intoxication.
- Various types of dermatitis (allergic, contact).
- Long-term compression caused by wearing uncomfortable, tight shoes.
What treatment methods should I use?
Treatment of varicose ulcers is a long and very complex process. The very appearance of such ulcers practically confines the patient to bed. But bed rest in such patients will only worsen the condition. Therefore, treatment is usually carried out on an outpatient basis and only in complex advanced cases - in a hospital setting.
Until the ulcer epithelializes, patients are recommended to stay indoors to avoid injury from clothing and infection of the wound.
Pathogenetic therapy
Varicose ulcers appear in the later stages of the disease, when severe venous insufficiency of the lower extremities develops. The primary goal of treating varicose ulcers is pathogenetic therapy, which provides for the maximum possible restoration of blood circulation in the legs. To reduce the manifestations of blood stagnation and venous insufficiency in the legs, patients are shown:
sleeping at night on a bed with the foot end raised;
- in the case of single shallow defects - bandaging the legs with soft bandages in the direction from the toes to the groin in order to minimize the swelling of the leg tissues and reduce the amount of stagnant blood in the limb;
- independent movement around the house;
- applying compresses soaked in decoctions or infusions of phyto-raw materials (horse chestnut, white willow, walnut) to the skin of the leg;
- taking medications:
- diuretics (Furosemide, Veroshpiron, Diacarb);
- systemic enzymes (Wobenzyma, Phlogenzyme);
- multivitamin complexes (Supradina, Alphabeta, Undevita).
venotonics (Aescusan, Actovegin, Venoruton);
This therapy, along with the anti-edematous effect, is aimed at increasing the patient’s immunity. Considering the fact that most patients with varicose ulcers have a tendency to sensitize the body, it is advisable to supplement the complex therapy of varicose ulcers with antihistamines:
- Suprastin;
- Tavegil;
- Pipolfen.
Treatment of trophic ulcers
The appearance of varicose ulcers is a sign of severe damage to the limbs and decompensation of blood circulation in the legs. It is difficult to treat such defects. Long-term complex treatment is required, which requires a lot of patience from both the doctor and the patient.
The resulting wounds are an open gate for infection to enter the body. Against the background of reduced immunity, such an infection is capable of spreading rapidly. To avoid generalization of infection, it is necessary to treat varicose ulcers by strictly adhering to antiseptic rules:
Treat the surface of the wound daily with an antiseptic.
Antiseptics prevent wound suppuration by having a bacteriostatic (inhibiting the growth and reproduction of bacteria) or bactericidal (killing bacteria) effect. To treat wounds, you can use a solution of Furacilin, Chlorhexidine or Miramistin. These products must be changed from time to time to avoid the development of bacterial resistance to them.- Treat the wound with ointments containing bacteriostatic antibiotics (Tetracycline ointment, Levomekol) or other antimicrobial substances (Argosulfan).
- Such wounds should be treated by administering antibacterial drugs parenterally (intravenously, intramuscularly) or orally. This will ensure that the required concentration of the antibiotic is maintained in the patient’s blood and will prevent the spread of the infectious process from the wound throughout the body. Preference should be given to broad-spectrum antibiotics: penicillins: Augmentin, Ampiox, Clonacoma-X;
- tetracyclines: Doxycycline, Tetracycline;
- cephalosporins: Cefaclor, Ceftriaxone, Cefpirome.
Use drugs that stimulate regeneration (Solcoseryl, Methyluracil). The active ingredients of the reparatives stimulate metabolism in cells, thus improving their regenerative function.
Treatment begins with parenteral (intramuscular or intravenous) administration, and after signs of epithelization of the ulcer appear, they switch to local therapy. These drugs in the form of ointments are applied to the wound surface previously treated with an antiseptic. In this case, the skin around the wound should be covered with zinc paste to avoid irritation.
Folk remedies for varicose ulcers
Traditional medicine has many recipes, the use of which promotes the healing of varicose ulcers. Healing agents for healing ulcers are prepared from:
bee products (honey, propolis, bee bread);
- vegetable oils;
- vegetables (onions, carrots, cabbage);
- meat, lard;
- medicinal plants (oak bark, bergenia root, mistletoe, horsetail).
Indoor medicinal plants – aloe and Kalanchoe – have good reparative and antibacterial properties. Tinctures are prepared from them, which are used for rubbing and compresses. To prepare the tincture, the crushed leaves of these plants are placed halfway in a container, then filled with vodka to the top. This tincture must be shaken for 7 days. Store in a dark place. Before going to bed, lubricate the skin around the wound and over varicose veins with a tampon soaked in the tincture.
The substances contained in flax seeds have a good wound-healing effect. For external use, use an infusion of flax seeds. To prepare it, one tablespoon of seeds is ground in a coffee grinder or mortar. Pour in two tablespoons of water, add a tablespoon of linseed oil, and mix. Apply to soft tissue and apply to the wound. In this case, it is necessary to strictly monitor so as not to introduce an infection into the wound: the fabric must be clean, the prepared gruel must be used immediately after preparation.
Trophic ulcers with varicose veins can be treated with yolk ointment. An ointment is prepared by mixing equal parts of chicken egg yolks and a 5% iodine solution.
The resulting ointment is applied directly to the wound and bandaged. Dressings are done twice a day. After hardening, the ointment can be easily removed, after which the wound can be treated with an antiseptic.
When using traditional medicine, you must be very careful, since some herbal remedies can provoke allergies. In addition, non-sterile preparations applied to the surface of the wound can cause infection.
Therefore, you should strictly monitor the cleanliness of the instruments used to apply the prepared products, the sterility of the dressings and the condition of the wound itself.
When the first signs of infection appear (redness, swelling of the tissues, the appearance of a whitish or yellowish coating or discharge, an increase in the local temperature of the tissues), you must immediately consult a doctor for immediate treatment of the wound and prescription of antibiotics.
Trophic venous ulcer
A trophic ulcer on the lower limb with varicose veins does not occur “suddenly”; it is preceded by years of illness with varicose veins. In the absence of proper therapy, bad habits, especially alcohol and nicotine abuse, rejection of preventive measures and lack of desire to take care of oneself, the stage of circulatory decompensation begins.
Irreversible disorders occur in the venous system, which lead to congestion in the legs and swelling. The pathological process is aggravated by the addition of lymphostasis (stagnation of lymph), the mass of the limb increases, and local skin immunity suffers. When bacteria attach, secondary infection develops, which is a factor that aggravates the prognosis.
Lymphostasis is swelling and swelling of the limbs.
With complications of varicose veins, progressive venous insufficiency, thrombophlebitis and post-thrombotic pathology, venous trophic ulcers develop.
With careful attention to your health, the development of this pathology against the background of varicose veins can be prevented.
Prevention of disease development
To avoid a serious and painful complication of varicose veins - a trophic ulcer - you will have to follow preventive measures. If they are carried out properly, it will be possible to prevent the appearance of other ulcers.
It is mandatory to undergo routine examination and treatment of varicose veins several times a year; Maintain a healthy lifestyle, eat properly and nutritiously, promptly treat all diseases, the development of which can lead to ulcerative problems.
Other rules of prevention:
- Take venotonics and vitamins on a regular basis to maintain normal vascular condition.
- Wear compression underwear under your clothes, which should be selected in consultation with your doctor.
- Provide a reasonable amount of physical activity to improve the condition of your legs.
Varicose ulcers take a long time and are difficult to treat, so the disease should not be started in the initial stage. Follow all preventive measures to avoid unpleasant surprises in the future.
What should you be wary of before a peptic ulcer appears?
A trophic ulcer is a serious complication of varicose veins; its appearance is preceded by a number of signs characteristic of varicose veins:
- Feeling of heaviness and discomfort in the lower extremities, especially after physical activity.
- Skin itching.
- Pastyness of the lower extremities that does not go away after a night's rest, a mark from the sock elastic.
- Decreased sensitivity in the feet and paresthesia in the form of coldness and “pins and needles.”
- Visualization of altered veins; with varicose veins, they become veiny, tortuous, and bluish.
- The initial manifestation of varicose veins is the appearance of a vascular capillary network on the skin.
- Cramps in the calf muscles, especially at night.
- Disappearance of skin patterns, cessation of hair growth due to the death of hair follicles.
- The appearance of pigmentation on the skin.
Diagnosis of the disease
Varicose ulcers do not appear suddenly; their appearance is preceded by characteristic symptoms. Therefore, an experienced physician can determine the disease during a physical examination. Further diagnostic search is carried out to identify possible causes and determine the degree of involvement in the process of deep-lying soft tissues and bones.
Diagnostic measures include:
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- Ultrasound of the lower extremities;
- X-ray examination.
To identify possible fistulous tracts, fistulography is used - fluoroscopy using a special contrast agent.
Stages of ulcer development
Stage of initial manifestations. It begins with the appearance of a slight area of hyperemia (redness) on the skin; later, one or more tissue defects appear. Ulcerative wounds begin to merge with each other, or active progression (deepening, growth) of one defect is observed.
The cleansing stage is characterized by the acquisition of clear rounded contours by the ulcerative defect, and an increase in pain syndrome is noted. During this period, purification and growth of granulations occurs.
In the normal course of events, discharge from a varicose ulcer is transparent and odorless. A change in discharge may indicate the addition of a purulent infection.
Stage of healing (scarring). During this period, a decrease in the size of the pathological ulcerative formation is noted, the edges tighten, redness and swelling decrease. The nutrition of the affected skin area is gradually restored.
At the final stage of scarring, the skin is completely cleared.
Possible complications
The addition of complications to varicose ulcerative defects sharply worsens the prognosis and can lead to amputation of the limb.
The course of a trophic ulcer can be complicated by:
- Sepsis.
- Varicose eczema.
- Gangrene.
- Varicose dermatitis.
- Erysipelas.
- Inflammatory pathology of the lower leg joint.
To prevent the development of complications, treatment should be carried out only in accordance with the recommendations of a highly specialized specialist!
Plants for topical use
Beneficial plants with anti-inflammatory and wound-healing properties include:
- Celandine;
- Chamomile;
- Eucalyptus;
- Aloe;
- Calendula;
- A series.
I should note that as the only component of treatment, herbal lotions, decoctions, irrigations for varicose veins and for scarring ulcers of the lower extremities are ineffective, since several problems need to be solved:
- Normalize blood flow;
- Improve metabolic processes;
- Eliminate inflammation;
- Accelerate tissue regeneration.
This can only be achieved by multi-component exposure.
Treatments and activities
When treating ulcers, you should pay attention to important points.
These include:
- Proper diet.
- Proper equipment of the resting place: the foot end of the bed should be slightly raised.
- Planned daily routine.
- The need to ensure that the load on the legs is not extreme; staying in an upright position for a long time is not allowed. Strong walks in the fresh air help improve blood circulation in the affected limb.
- Wearing compression garments allows you to achieve a noticeable effect.
Bandage using Varolast zinc bandage and elastic bandage in the treatment of venous trophic ulcers.
Therapy with solutions and ointments
The affected skin is treated with various antiseptic solutions ( Dioxidine, Miramistin, Chlogexidine ).
Make sure that the opened bottle is stored properly in a cool, dark place, otherwise you will add pathogenic bacteria to the ulcerative wound yourself!
Treatment with disinfectant solutions prevents the penetration of infectious agents into the tissue and fights existing microbes.
To stimulate the processes of regeneration and reparation (restoration), ointments for varicose veins are used, which improve nutrition, moisturize, eliminate skin itching and strengthen the vascular wall. Levomekol, Panthenol ointment, Solcoseryl ointment, Baneocin are often prescribed .
Hormonal corticoid ointments are used with caution and only as prescribed by a doctor.
Tablet forms and herbal medicine
To improve microcirculation and eliminate lymphostasis, Reopoliglucin . Phlebotonics (venotonics) are taken for a long time. Detralex is the most commonly prescribed effective diosmin-based drug for varicose ulcers.
To thin the blood and prevent thrombus formation, medications such as Thrombo ACC, Acetylsalicylic acid, Cardiomagnyl . Preparations from the antihistamine group fight skin itching: Suprastin, Tavegil, Clarotadine, Claritin .
If the doctor believes that there is a high risk of secondary infection, then the treatment regimen includes antibacterial drugs: Suprax, Z-factor and others. To simulate immunity, it is recommended to take vitamin complexes with minerals, for example, Complivit .
Lasix, Furosemide combat congestion in the lower extremities with varicose ulcers , but it must be remembered that drugs from this group are taken no more than 3 times a week under the cover of potassium supplements ( Panangin ).
Physiotherapy is good for scarring a trophic ulcer; phlebologists speak especially well of laser therapy and ultraviolet irradiation as methods that promote tissue granulation.
Means for the treatment of varicose ulcers
The following drugs are widely used:
- Antibacterial drugs with a broad spectrum of action or according to the results of bacterial culture.
- Drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects: Diclofenac, Diclovit, Ortofen, Movalis, Ibuklin, etc.
- Antihistamines (allergy medicine): Clarotadine, Larotadine, Suprastin, Tavegil, etc.
- Antiplatelet agents and agents that improve blood circulation: Heparin, Pentoxifylline, Reopoliglucin.
- Venotonics: Venosmil, Detralex, Cyclo 3 Fort, Phlebodia.
Treatment at home
Before using traditional medicine recipes, be sure to consult your doctor!
Lotions with cool decoctions of herbs and natural ingredients ( horse chestnut, walnut ) at home help restore the skin and have a disinfectant and cooling effect.
Herbal medicine for varicose skin lesions is aimed at combating edema ( Fytonephrol, Brusniver, dill seeds ), strengthening the immune system ( rose hips, ginseng root ), and vitaminization.
Treatment of a trophic ulcer on the leg is a long process; it is extremely important to find and eliminate the cause that gave rise to the development of this, from all sides, difficult disease.
Curiosin gel for varicose ulcers
Additionally, Curiosin, a gel based on zinc hyaluronate, is prescribed. Curiosin gel has proven itself in the treatment of difficult-to-heal, infected wounds. The action is based on stimulation of tissue repair. The drug has bacteriostatic properties. Used as part of complex therapy.
It is recommended to apply Curizon gel once at the rate of one drop per square centimeter of skin. If maceration is significant, it can be used 2 times a day. The duration of the course is set individually.