The chest is shaped like a cone, there are ribs, a spinal column and a sternum. There are many organs in the cell space. The respiratory rate of the lungs is 14 movements per minute. But why do we feel pain and other unpleasant sensations when we inhale?
Chest pain when inhaling, or otherwise thoracalgia, is the most common complaint; many people experience it to one degree or another. To avoid complications, it is recommended to go to the hospital and undergo a preventive examination.
An example of where pain is located during a heart attack
Classification of pain
Chest pain during inspiration can be divided according to several factors: location, severity of occurrence, duration, intensity, etc.
But it is most convenient to consider pain by location:
- in the middle - in this case we can assume that the diaphragm, heart, lungs or esophagus are affected;
- on the right – the cause may be injury to the ribs, infection or oncology;
- on the left - injuries, renal colic, inflamed pleura.
But these are not all the reasons that can lead to pain during inhalation.
Etiology of appearance
Why might pain occur?
If we talk about general reasons, we can highlight the following:
- subcutaneous fat or skin is affected;
- muscles, ligaments, bone frame are affected;
- diseases of the peripheral nervous system of the spine.
The clinical picture and nature of the pain largely depend on what kind of disease develops in a person, as well as what caused it.
Pain can take a person by surprise
Causes
Doctors divide all the reasons that cause breathing problems in a person into 3 large groups. However, each of them can be closely intertwined with the other, since all processes occurring in the body are interconnected.
Physiological
This type of cause of deterioration in breathing is considered the most harmless. They can cause deterioration in breathing due to the following factors:
- Insufficient oxygen. If a person is in a place where there is little air, for example, in the mountains, this can cause breathing difficulties due to the fact that the person will not have enough oxygen. Therefore, if you are in an area that is much higher than sea level, this phenomenon will most likely overtake you.
- Stuffiness in the room. Due to this reason, there may be either a lack of fresh air due to crowds or excess levels of carbon dioxide. Therefore, a small room needs to be ventilated frequently.
- Tight or uncomfortable clothing. Many people don’t even think about the fact that tight clothes can harm their health, so they sacrifice it for the sake of fashion and beauty. As a result, a woman or man experiences a significant lack of oxygen, which disrupts the normal functioning of the body. There is no need to see a doctor, since after changing clothes, the patient will again feel a normal flow of oxygen and will be able to breathe enough.
- The person is in poor physical shape. If people are sedentary and like to drink alcohol, this negatively affects respiratory function. Any tension in the body causes serious breathing difficulties, as a result of which the patient is often tormented by yawning. Often this cause of insufficient air is observed in people who have lain in bed for a long time while undergoing treatment.
- Excess body weight. If a child or adult is overweight, they often experience yawning and difficulty breathing. However, this is not the worst thing - with excess weight, heart disease and stroke often develop, the severity of which depends on the number of extra pounds compared to normal weight.
Sometimes people find it difficult to breathe in the heat, especially if the body is severely dehydrated. In this case, the blood becomes thicker, making it more difficult for the heart to push it through the vessels. This causes serious deterioration in breathing, which can be cured on your own.
Medical
Yawning, shortness of breath and lack of air appear due to the course of serious illnesses. Moreover, these symptoms allow a person to identify the disease at the initial stage of development.
Often, symptoms of lack of air attack a person during the development of the following diseases:
- VSD. This disease develops as a result of severe nervous exhaustion. A person often feels fear, panic attack and other unpleasant symptoms. In order to notice the development of a dangerous disease in time, you need to pay attention to its first signs, including constant yawning and heaviness when inhaling.
- Anemia. This disease is characterized by a lack of iron in the body, with the help of which oxygen is transported through organs and systems. The disease can be detected by deteriorating breathing quality.
- Diseases of the lungs or bronchi. Pneumonia, bronchitis, cystic fibrosis, pleurisy, asthma, and so on can cause a feeling of lack of air. In some cases, the patient may also be bothered by belching, for example, during sputum separation.
- Respiratory diseases occurring in acute or chronic form. As a result of the drying out of the mucous membrane of the nose and larynx, many people are unable to breathe normally. In addition, some people notice increased breathing, which allows a small amount of oxygen to enter the lungs.
- Heart diseases. These include ischemia, cardiac asthma, heart failure, and so on. Improper functioning of the heart causes breathing difficulties. If this is accompanied by discomfort and chest pain, you should definitely consult a doctor.
These diseases pose a significant threat to the patient’s health, so they should not be neglected.
Psychogenic
We should not forget about stress, which often causes the development of health-threatening diseases.
Yawning during stress (for example, neuralgia) in a patient is considered an unconditioned reflex, which is inherent in a person by nature. Therefore, if people are often nervous, this will cause yawning, and, as a rule, a lack of oxygen.
During stress, capillaries spasm, which causes the heart to work excessively. This causes an increase in pressure. In order not to harm the brain, a person begins to yawn frequently, while inhaling air deeply.
Also, lack of air occurs with muscle spasms, which makes it difficult for the patient to make a deep entrance.
Lung diseases
Chest pain during inspiration may be associated with diseases in the lungs.
Most often these are the following pathologies:
- Tuberculosis. During inhalation, the pain becomes severe, the skin turns pale, the person loses weight, and appetite disappears. Body temperature may rise, cough and hemoptysis may bother you.
- Pleurisy – many factors can cause its development. The cough with this disease is dry, when inhaling there is a burning pain, the face turns blue.
- Tumor formations in the lungs - pain in the cell when inhaling is constant, when coughing, blood is released, the heartbeat quickens. In most cases the temperature rises.
- Pneumonia - in the evening the temperature rises sharply, sweating increases at night, breathing is hoarse, wet or dry wheezing in the lungs. There is severe pain when breathing, and when coughing, sputum with pus is released.
- Pneumothorax. There should be a small amount of fluid in the pleural cavity so that the leaves of the pleura are lubricated. If air gets in there, expansion of the lungs becomes impossible, collapse develops, and pain appears during inhalation.
- Pulmonary embolism – the pulmonary artery is blocked by a blood clot. This is most often caused by varicose veins. Despite the fact that a person feels completely healthy, he suddenly experiences pain when inhaling. Shortness of breath, coughing up blood. This condition is considered extremely dangerous; in the absence of medical attention, a person can die in just a few minutes.
One of the possible causes of discomfort
You may experience a dull pain in the chest when coughing; this is the main symptom that ARVI is developing.
Pulmonary embolism
When it hurts to breathe deeply, this illness is often the cause. This is one of the pathologies when emergency medical care is needed. With it, a reflex stop of the heart occurs.
Pain is typical for emobs of small branches, causing recurrent infarction-pneumonia. It causes widespread pain in the chest, which intensifies when you inhale. A cough and fever may also occur. Symptoms of respiratory failure are likely.
Pulmonary embolism usually appears against the background of good health. This develops from:
- deep vein thrombosis;
- heart pathologies;
- atrial fibrillation, cardiomyopathy, cardiomyopathy;
- oncology;
- antiphospholipid syndrome;
- various thrombophilias.
If it hurts to inhale deeply in the chest, then the reasons may be pulmonary ailments. There are no pain receptors in the lung tissue; its pathologies cannot manifest themselves in the form of pain if the pleura is not affected.
The cardiovascular system
Diseases of the cardiovascular system can also lead to chest pain during inhalation.
The most common of them are the following:
- Angina pectoris. The pain appears suddenly, its character is strong, it often appears during physical activity or during an emotional failure. The face becomes pale, the chest feels full and compressed. This spasm can last up to 15 minutes.
- Pericarditis is an inflammatory process in the heart sac. When breathing, chest pain is localized on the left and also in the middle. The nature of the sensations is not very sharp. However, stress can make them worse. The patient must be hospitalized as soon as possible.
- Aortic aneurysm – very severe pain appears, radiating to the back, abdomen, neck, abdomen. The duration of the attack persists for several days.
- Myocardial infarction. It feels like angina pectoris, however, the attack is more severe. Pain in the chest area on the left.
- Myocarditis is an inflammatory process in the myocardium. Pain of a pulsating nature, weakness throughout the body, body temperature rises, pain when breathing.
Another common cause of discomfort is ischemic rupture of the heart arteries. This does not happen often, but if it happens, the person will most likely die.
What is it like when there is a stabbing sensation in the chest?
When there is a stabbing sensation in the chest, this is a signal indicating the presence of health problems. Both a pinched nerve and a myocardial infarction can cause tingling. When this kind of discomfort occurs in the chest area, it is worth assessing how serious it is.
On right
When it stings on the right side of the chest, it may not be so easy to immediately make a diagnosis. Additional symptoms often appear, such as increased blood pressure, and attacks of suffocation occur. Sometimes there is numbness.
One of the most common causes of tingling on the right side is diseases of the spine. Stitching in the right side of the chest when intercostal neuralgia, osteochondrosis or costovertebral osteophyte is observed.
Many people wonder when there is a stabbing sensation on the right side of the chest, what is it? This area of the body contains some important organs. Therefore, it is important to recognize the disease in time. Common reasons for stabbing on the right side of the chest include:
- Injury due to vigorous physical activity. If the body is not prepared for heavy loads, a significant increase in their volume will lead to stretching of the chest muscles. As a result, discomfort and pain are felt in this area.
- Pain in the chest on the right, stabbing, occurs due to fractured ribs. The nature of the tingling is sharp. If you start to cough or put pressure on the area, the pain gets worse.
- Bruises often cause stabbing pain on the right side. The presence of a bruise helps to recognize this cause.
- Pathologies of the respiratory system. Pneumonia can cause similar discomfort, adding to the general condition with fever and cough. Pleurisy can cause tingling on the right side.
- Constantly or periodically stabbing on the right side of the chest due to diseases of the digestive tract. Heartburn, food stagnation, chronic cholecystitis cause tingling on the right side.
Some of the listed reasons can be eliminated independently, for example, by changing the training program, normalizing the amount of physical activity.
On the left side
If there is a stabbing sensation on the left side of the chest, it is recommended to visit a therapist. Ischemic disease can provoke such ailment in the form of stabbing pain. The heart muscle needs oxygen, and with a lack of it, pain receptors begin to be irritated.
Sometimes the pain radiates to the left shoulder blade. It is a symptom indicating that cardiac pathology has begun to develop.
Many people, when a tingling sensation occurs in the left side of the chest, begin to worry more than with similar sensations on the right. All because of the cardiac projection located in this area. Left-sided tingling is often radiating heart pain.
Among the reasons why there is a stabbing sensation in the left chest, it is worth noting:
- attacks of angina pectoris, manifested precisely by left-sided pain;
- pericarditis;
- myocarditis;
- rheumatic carditis;
- tumor or tuberculous lesion of the left bronchus.
An accurate diagnosis can be found by undergoing an examination.
In the middle
Stitching between the chest in the middle is often due to pathologies associated with the heart. The most common diseases causing this symptom are:
- angina pectoris;
- myocardial infarction;
- aortic aneurysm.
Angina pectoris is one of the first signals indicating problems with coronary circulation. The pain manifests itself not only in the middle, but can radiate to the shoulder, left arm, and under the shoulder blade. The attack appears suddenly, causing the patient to literally freeze in place. The pain varies in intensity, from severe to barely noticeable, more like discomfort. In addition to tingling, a burning sensation and a feeling as if there is pressure on the chest may occur.
Stitching in the middle of the chest is often due to myocardial infarction. An attack of pain can be single and prolonged or occur several times, each time increasing in intensity. One of the differences between myocardial infarction and angina is the nature of pain. They last longer and are more intense. Among the accompanying symptoms it is worth noting:
- the appearance of shortness of breath or an attack of suffocation;
- nausea and vomiting;
- increased sweating;
- headache;
- increased heart rate.
Weakness, fever and dizziness appear much less frequently. Pain during myocardial infarction is characterized by a constant increase. It is difficult for the patient to tolerate it. If there is a slow-flowing myocardial rupture, “dagger pain” may occur.
The formation of an aortic aneurysm interferes with the normal flow of blood. With this disease, pain occurs that can radiate to the back and neck. The pain is severe and lasts from several hours to a couple of days. The following symptoms may also occur:
- The appearance of shortness of breath. May be accompanied by noisy wheezing. Inhalation is difficult.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Pressing pain in the stomach area. May be accompanied by heartburn and vomiting.
When inhaling
Stitches in the chest when inhaling, if the standard volume of physical activity is exceeded, when walking. Pain of this nature can be provoked by a variety of factors.
When taking a deep breath, tingling sensations can radiate to any area of the chest, including the right area, left and in the middle.
Such pain is usually accompanied by several other symptoms:
- difficulty breathing occurs;
- the temperature rises;
- shortness of breath and a feeling of weakness appear;
- cough.
Among the most likely reasons why the chest stings upon entry, it is worth noting:
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular system. Then it stings on the left side of the chest when inhaling. With such indicators, a common diagnosis is angina pectoris, which appears against the background of coronary artery disease. The impetus for the onset of the disease is excessive physical activity, overexertion and stress.
- Pathology associated with the respiratory system. Taking a strong breath, the patient, in addition to tingling, may feel weak, shortness of breath will appear, and severe coughing attacks will begin. There will be a feeling of lack of air. Pain of a stabbing nature with localization in the middle can indicate any bronchopulmonary problem.
Diseases of the spinal column
Among all the pathologies of the spine we can distinguish:
- Osteochondrosis. When the vertebrae are deformed or displaced, pain occurs. It can be so strong and painful that a person cannot change his position.
- Costal chondritis, also known as Tietze syndrome, is an inflammatory process in the cartilage of the ribs at the edge of the sternum. It begins to develop after injuries or blows have been received. When inhaling, the pain is dull in nature, the deeper the depth of inspiration, the stronger it is.
- Scheuermann-Mau disease. Out of a hundred people, only one is susceptible to the disease. Pathology begins to develop in adolescence, resulting in kyphosis. Unpleasant sensations between the shoulder blades.
- Ankylosing spondylitis. A large amount of calcium salts accumulate in the ligaments of the spinal column, causing nerve endings to be destroyed. Pain, unfortunately, will accompany a person for life.
Development of osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition in which there is not enough calcium in the bones. The entire spine is subject to pathological influence, it becomes crooked, posture becomes distorted, and when inhaling there is moderate pain.
Neurogenic pain
The cause of pain is irritation of the nerve roots, spinal or intercostal nerves.
The most common etiological factors include:
- inflammation of the nerves (neuritis);
- neoplasms (neuroma, schwannoma);
- inflammation of surrounding tissues (nerve compression by edema).
The pain is most often localized along the nerve trunks (in the intercostal spaces) and has a girdling character. The pain syndrome is very intense and has a cutting nature. Hyperpathy (diffused burning pain when touched) or hyperesthesia (pain when touched) may appear.
There are many reasons for the pain that appears when you inhale. For adequate treatment, it is important to correctly identify the etiological factor and eliminate it. In this case, the therapy will be successful and will help the patient improve his quality of life.
Author:
Matveeva Maria - Medical journalist. First category nurse in the department of traumatology and orthopedics
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
Chest pain when inhaling may also appear because a person develops diseases of the gastrointestinal tract:
- Narrowing of the esophagus. In this case, discomfort in the chest appears during swallowing. If after a while the symptom becomes stronger, and there is difficulty in trying to swallow, this indicates that esophageal cancer is developing.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease. After eating, the contents from the stomach are thrown into the esophagus. This especially occurs when bending or lying down. In all cases, there is heartburn; associated symptoms include chest pain and sore throat.
- Stomach ulcer. The pain that appears during breathing can radiate to the sternum or back. When eating, the discomfort subsides.
- Pancreatitis is an inflammatory process in the pancreas. The pain is very strong, chest pain appears frequently.
- Hiatal hernia. Sighing is painful, heartburn is present.
Pancreatitis is a possible cause of pain
It is impossible not to note problems in the gallbladder. Pain may appear on the right hypochondrium, as well as in the lower chest. Discomfort appears immediately after a person has eaten.
What can sting on the right side of the chest?
Have you been trying to heal your JOINTS for many years?
Head of the Institute for the Treatment of Joints: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure your joints by taking the product every day for 147 rubles ...
Read more "
Most often, unpleasant sensations in the thoracic region of the human body appear as a result of injury during excessively intense physical exercise. If the load increases and the body is not prepared, the muscles located in the sternum begin to stretch.
OUR READERS RECOMMEND!
Our readers successfully use Sustalaif to treat joints. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
This leads to painful sensations that begin to increase with deep breaths. Do not worry, since this situation is the body’s standard reaction to a large volume of lactic acid secreted. This can develop into microtrauma of the part of the muscles that strained the most.
The occurrence of such signs indicates that the study schedule is incorrect. This phenomenon can be eliminated by temporarily refusing to play sports. Moreover, you should start practicing again gradually.
Pain in the chest on the right side may also indicate a rib fracture. In such a situation, a sharp stabbing pain appears in the injured area, which intensifies during compression of the sternum or when the victim begins to cough. The discomfort will go away if the patient takes the most comfortable position in which his body completely relaxes.
The cause of severe pain on the right side of the chest can be bruises, which can be recognized by bruises that appear in this area.
You should know that severe bruises pose a danger to humans, as they can lead to lung rupture, which can be fatal. In this case, you need to consult a doctor.
Also, often pain in the chest indicates the development of an acute respiratory viral infection. In this case, discomfort appears in the place where the lesion is located.
Pain in this area may occur if the patient has recently been treated with medications.
The pain is aggravated if he lies in one position for a long time, observing bed rest. In such a situation, the muscles located between the ribs, weakened after illness, hurt.
Stitching pain on the left
The left side of the chest is a cardiac projection, so if there is pain there, then you need to seek help from a cardiologist. What can provoke this ailment? Development of ischemic disease. The heart muscle begins to lack oxygen, it stretches, and this leads to irritation of pain receptors.
When stabbing caused by heart disease, the pain goes away very quickly, it is relieved with validol.
If it stings constantly when performing any physical activity, this is anginal pain. It radiates under the left shoulder blade and indicates the development of a dangerous cardiac pathology.
If it stings and hurts in the chest in the form of lumbago, this may be due to disorders of the coronary vessels. In any case, those who experience such severe symptoms should immediately consult a cardiologist.
If this diagnosis is not confirmed, doctors go further and study the condition of the pleura, lungs, and look at how the intercostal nerves react to mechanical influence from the outside.
If these organs function in their normal mode, then doctors go lower. Sometimes stabbing pains appear in the chest due to spasm of the esophagus, due to the presence of a peptic ulcer.
The described pain syndrome can be provoked by biliary colic and inflammation of the walls of the rib cage.
Causes
There are several most common reasons that can lead to the indicated problem. Each has its own characteristic symptoms, so it is useful to learn more about them.
Other causes of pain
In addition to the reasons listed above, pain can also occur due to other conditions, among which are:
- Neoplasms. Lung cancer is a constant pain when breathing, its nature is burning.
- Shingles. The disease is of infectious origin. A few days before the rash appears on the body, discomfort appears when inhaling
- Klepatura. After physical activity, painful sensations appear in the muscle area. This cannot be classified as a disease, even though there is pain when inhaling.
- Chest injury - appears after a fall or bruise. Soft tissues swell and there is pain when inhaling. In order to exclude a fracture, it is necessary to take an x-ray.
- Rib fractures. The pain that makes itself felt most strongly is not during inhalation, but when coughing. Pain is also present during palpation.
- Intercostal neuralgia. Symptoms of this disease can cause the patient's mobility to be limited.
There are a lot of reasons that can cause chest pain during inhalation, and as you can see, many of them are not as harmless as they may seem at first glance.
When to call an ambulance
Depending on the progression of the disease, the condition can get very worse
If the symptoms listed below appear, you should call an ambulance as soon as possible:
- along with the pain there is a feeling of squeezing, shortness of breath, the pain spreads to neighboring parts of the body;
- the heartbeat quickens, the head becomes dizzy, nausea occurs, the skin turns gray, cold sweat runs through the body, and the person loses consciousness.
If the condition does not improve after taking medications, and the pain lasts more than twenty minutes, it is also recommended to call an ambulance.
Why does it hurt when you inhale?
Pain with inspiration , coughing, or other respiratory movements usually points to the pleura and pericardium or mediastinum as a possible source of pain, although pain in the chest wall is also likely to be influenced by respiratory movements. Most often, the pain is localized in the left or right side and can be either dull or sharp.
The pain that occurs when inhaling, especially deeply, never appears “just like that.” It is always a symptom of some disease. If such unpleasant sensations occur, you must consult a doctor to establish an accurate diagnosis and undergo a course of treatment appropriate to the identified disease.
Pain when inhaling and breathing can occur due to inflammation of the pleura (the connective tissue membrane that covers the lungs and the inner surface of the chest).
Pain when breathing will occur only if inflammation of the pleura is not accompanied by the accumulation of fluid between the layers of the pleura, that is, with dry pleurisy . A characteristic sign of pain caused by damage to the pleura is a sharp increase in pain at the height of inspiration. Along with increased pain, a dry cough usually appears.
Pain when taking a deep breath can occur many years after suffering from pleurisy. The reason for this condition is irritation of the nerve fibers in the adhesions between the layers of the pleura.
Pain when breathing can occur with pleural tumors.
Another cause of pain when breathing is inflammation of the pericardial sac (pericarditis). With dry pericarditis, the pain intensifies when inhaling, so patients try to breathe shallowly.
Inflammation of the intercostal nerves (intercostal neuralgia) can also be attributed to the causes of pain in the chest area, which intensifies with deep inspiration. With this pathology, the location of the pain corresponds to the affected intercostal space. The pain intensifies not only with a deep breath, but also with tilting the body to the painful side.
Inflammatory processes in the muscles of the chest (they are called myositis) can cause pain in the chest, which intensifies slightly when inhaling. Pain with myositis also increases when the body is tilted to the healthy side and when the affected muscle is palpated.
Severe pain in the chest area, sharply increasing with breathing and chest movements, is a characteristic sign of rib fracture . In addition to this symptom, it is sometimes possible to listen to the crunching of the rubbing edges of fragments or to palpate the fracture site.
Pain in the right hypochondrium can occur with renal colic , if the stone is located in the area of the right kidney or ureter. This pain intensifies when inhaling and can radiate to the right shoulder, under the right shoulder blade.
Chest pain, worsening with deep inspiration, can occur with thromboembolism of a large branch of the pulmonary artery . The location of such pain is behind the sternum or in the left half of the chest; in its clinical picture, this condition resembles a myocardial infarction.
The main diseases accompanied by pain when inhaling:
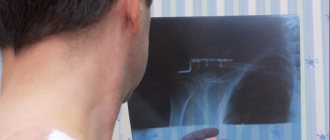
1. Pain when inhaling occurs due to inflammation of the membrane lining the inside of the chest cavity and covering the lungs, called the pleura. Dry pleurisy can occur with various diseases, but most often with pneumonia. Pain during dry pleurisy decreases when lying on the affected side. There is a noticeable limitation in the respiratory mobility of the corresponding half of the chest; with unchanged percussion sound, weakened breathing may be heard due to the patient sparing the affected side, and pleural friction noise. Body temperature is often subfebrile, there may be chills, night sweats, and weakness.
X-ray of exudative pleurisy
2. Restriction of chest movement or pain when inhaling and exhaling with shallow breathing is observed with functional disorders of the costal frame (rib fractures) or the thoracic spine (limited mobility), pleural tumors, pericarditis.
3. With dry pericarditis, the pain increases with inhalation and movement, so the depth of breathing decreases, which aggravates shortness of breath. The intensity of pain when inhaling varies from slight to severe.
4. When the interpleural ligament is shortened, a constant cough is observed, which intensifies when talking, taking a deep breath, physical activity, stabbing pain when inhaling, or running. The interpleural ligament is formed from the fusion of the visceral and parietal layers of the pleura of the root of the lung. Further, descending caudally along the medial edge of the lungs, this ligament branches in the tendon part of the diaphragm and its legs. The function is to provide springy resistance during caudal displacement of the diaphragm. In the presence of an inflammatory process, the ligaments shorten and limit caudal displacement
5. With intercostal neuralgia, sharp “shooting” pains occur along the intercostal spaces, sharply intensifying with inhalation.
6. With renal colic, the pain is localized in the right hypochondrium and in the epigastric region and then spreads throughout the abdomen. The pain radiates under the right shoulder blade, to the right shoulder, intensifies with inspiration, as well as with palpation of the gallbladder area. Local pain is observed when pressing in the area of the X-XII thoracic vertebrae 2-3 transverse fingers to the right of the spinous islands.
7. A blow or compression of the chest can cause rib fractures. With such damage, a person feels sharp pain when inhaling and coughing.
If there is pain when breathing, or the pain intensifies while inhaling, you should consult a doctor.
The conditions that lead to pain when breathing are so diverse that without establishing a diagnosis, it is impossible to give any specific recommendations regarding the treatment of these pathologies. After all, treatment tactics for different diseases differ significantly.
For pleurisy caused by pneumonia, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory treatment is necessary. If pleurisy is caused by a tumor in the pleura, you will need treatment from an oncologist. For myositis, anti-inflammatory therapy is necessary. Intercostal neuralgia requires complex treatment; you will need anti-inflammatory, painkillers, and drugs that improve metabolic processes in the affected segment. For rib fractures, a special pressure bandage is applied to the chest area.
The only condition accompanied by increased pain with deep inspiration that requires immediate medical attention is pulmonary embolism. Therefore, if a severe pain attack occurs in the chest area, reminiscent of an angina attack, worsening with a deep breath, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance team.
It is worth saying right away that you should definitely consult a doctor if you have pain when breathing, but before going to the doctor, to relieve pain when inhaling, you can use time-tested non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (all of these drugs are presented in tablets and / or capsules, which should be taken 1 at a time). 2-4 times a day, preferably after meals). The most famous representatives are
- Ibuprofen (MIG)
- Naproxen (Nalgesin)
- Dexketoprofen (Dexalgin)
- indomethacin
- diclofenac
- nimesulide
- etoricoxib
- diflunisal
- aceclofenac
- etodolac
- lornoxicam
- ketoprofen
- flurbiprofen
- nabumethon
Pain in
shoulder
can be expressed in different ways and arise due to pathological processes occurring not only in the joint, but also in the body as a whole. A distinctive feature of most pain and tingling sensations in the shoulder is their wave-like nature - the pain can worsen, subside after a while, and then reappear with even greater force.
Diagnostics
In order to understand what caused such unpleasant sensations, you need to go to the hospital.
A diagnosis can only be made after a thorough examination:
- X-ray of the spine or lungs;
- biochemical and general blood test;
- sputum examination;
- in case of suspected development of oncology, MRI, ECG or CT is performed;
- performing Dopplerography of blood vessels.
Gastroscopy may be performed. Based on the test results obtained, a final diagnosis is made. If the condition is critical, the patient will need to be hospitalized.
Treatment
Treatment methods will depend on what pathology is developing.
The following methods are considered the most effective:
- for the treatment of tracheitis, pleurisy and pneumonia, antibiotics, analgesics and immunostimulants are prescribed;
- to treat PE, the thrombus is surgically removed and anticoagulants are prescribed;
- Costochondritis can be cured with the help of physical therapy and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Chest pain that appears during breathing may indicate the development of serious illnesses. If the discomfort lasts for a very long time and does not go away even after taking medications, you should go to the hospital.
As for prevention, a person should monitor his diet and engage in moderate physical activity. You should refrain from bad habits.