17.03.2016
Some people sometimes experience stabbing pain in the area of the heart against the background of the normal state of the cardiovascular system. In such conditions, one should suspect the presence of intercostal neuralgia of the intercostal spaces. But how to distinguish one from the other? Often, a person experiencing pain does not fully correctly assess his subjective sensations. To understand and avoid confusion, the main differences are detailed below.
Symptoms of neuralgia on the left side of the heart
Intercostal neuralgia is closely associated with the manifestation of pain in the chest. This can happen due to a deterioration in the full functioning of the intercostal nerve fibers against the background of pinching, infections, or hypothermia. This problem can arise at any age, but still the largest percentage of patients is recorded among older people.

Intercostal neuralgia
Such a pathology can also occur due to the presence of pathologies in the patient such as osteochondrosis, hernia of the thoracic ridge or herpes zoster. Often neuralgia is a symptom of more serious diseases - for example, pleurisy or various types of oncology. In addition, neuralgia on the left side of the chest can cause symptoms associated with heart disease.
Neuralgia in the heart area develops as a result of pinching or irritation of the fibers of the intercostal nerves.
Helpful information
The main sign of pathology is pain. It can have a sharp, dull, aching and burning character.
The pain is paroxysmal and localized to the left of the sternum, as a result of which most people think that it is associated with cardiac activity.
Discomfort in the cardiac zone increases with physical activity, breathing, coughing, which is accompanied by a feeling of squeezing of the ribs. The patient may also experience local hyperemia or blanching of the skin, as well as involuntary muscle twitching. Often there may be tingling in the chest and numbness of the skin between the ribs.
Diagnosis of the disease
Neuralgia in the heart area is diagnosed both by physical examination and by the results of the following studies:
- electrocardiograms;
- X-rays of the chest area, or the same study using a contrast agent (to assess the condition of the nerve endings in the affected area);
- general analysis of urine and blood.
The diagnosis of neuralgia occurs if the results of radiography and laboratory tests are normal, and myelography (x-ray with a contrast agent) shows a deviation from normal values.
Sources
- https://hondrozz.ru/oslozhneniya/nevralgiya/v-oblasti-serdca.html
- https://NashiNervy.ru/perifericheskaya-nervnaya-sistema/lechenie-mezhrebernoj-nevralgii-v-oblasti-serdtsa.html
- https://fb.ru/article/163921/nevralgiya-v-oblasti-serdtsa-simptomyi-i-lechenie
- https://nevrology.net/sindromy-i-zabolevaniya/perifericheskoj-nervnoj-sistemy/nevralgiya/mezhrebernaya-simptomy-sleva-v-oblasti-serdtsa.html
- https://insultinform.ru/bolezni/mezhryobernaya-nevralgiya/v-oblasti-serdtsa
[collapse]
Treatment of intercostal neuralgia on the left with folk remedies
In most cases, the patient undergoes therapy at home. Moreover, depending on the severity of the disease, the patient is placed on bed rest from three days to a week. The bed must have a flat and hard surface. It is better if the bed is equipped with an orthopedic mattress, but if this is not possible, then you need to put something flat and hard under a regular mattress that can be adjusted at home. If the patient uses a bed during treatment, for example, with a sagging mesh, then his condition will only worsen.
For therapy prescribed:
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, for example, Diclofenac or Meloxicam. These drugs have an analgesic effect coupled with an anti-inflammatory effect. In addition, their zone of action affects the problematic nerve and can relieve syndromes of associated ailments. This type of medication is available in tablets, injections or suppositories;
- muscle relaxants - "Mydocalm" or "Sirdalud" - relieve discomfort in the form of spasms of skeletal muscle tissue;
- sedatives based on natural ingredients. These may be medications such as Sedosen, Persen, Novopassit and many others;
- vitamin B complexes, for example, Neurorubin. Their main effect is to restore damaged nerve roots and increase the interconnection between them.

To get rid of the symptoms of thoracic neuralgia, doctors prescribe medications
The main method of local therapy is the application of dry heat to the affected area of the body. It should be noted that this method involves the use of an indirect source. Woolen items or down scarves are perfect for dry warmth. It is strictly forbidden to apply hot objects to the area affected by neuralgia - this can only cause harm to the patient.
Pharmacy medications in the form of ointments and gels without NSAIDs include anesthetics. Such drugs include Capsicam or Finalgon.
For targeted treatment, ointments and gels are used, as well as special patches.
Along with other treatments, special patches impregnated with anti-inflammatory and analgesic medicinal components are also used in treatment. Using this product involves sticking it to the affected area of the body. Moreover, they are designed for a long-lasting effect due to the slow release of beneficial components.
After the symptoms of the acute stage of neuralgia have been successfully eliminated, you can begin to restore the normal functioning of the areas of the body affected by neuralgia. The following methods for restoring the body are non-drug in nature.
- Massage of the paravertebral muscles is aimed at improving the metabolic processes of the patient’s body, as well as toning muscle tissue, relieving swelling and pain.
- Therapeutic exercise allows you to strengthen the muscle structure of the torso. It is prescribed individually for each patient depending on the physical fitness and condition of the patient.
- Manual therapy can relieve the patient of pinched nerves and restore normal relationships between the vertebrae.
- Acupuncture.
- Physiotherapy such as UHF, electrophoresis, magnetic or laser therapy.
- Thermopuncture, the main effect of which is aimed at “cauterizing” biologically active points of the body. It is believed that the stronger the damage to the skin on certain points of the human body, the more effective the treatment result. Impact on one point can occur up to ten times.
Thermopuncture
You can fight neuralgia with the help of traditional medicine recipes, but only in parallel with the main treatment prescribed by the doctor. Below are a number of methods to combat the disease.
- The affected area of the body must be lubricated with fresh radish or horseradish juice. This will help relieve pain.
- During severe pain, a compress of rue tincture will help.
- Wormwood lotion has an anti-pain effect. To do this, you must first steam the wormwood, then grind it to a paste, add sea buckthorn oil to the mass and apply it to the problem area.
- Geranium is also rubbed on the sore spot, and then wrapped in dry heat.
- A gauze compress soaked in flax seed tincture is also used to treat diseased nerves.
- You can rub homemade ointment based on Vaseline and aspen buds into problem areas. To do this, you need to mix the ingredients in a ratio of 1:4, where one part is Vaseline and four parts aspen.
- It is also recommended to take baths with sage and sea salt.
- Chamomile flowers, lemon balm, orange peel and honey are used in the form of a healing decoction. This remedy strengthens the entire nervous system.
Traditional medicine methods cannot completely get rid of the disease, but they can speed up the treatment process.
If it is not possible to prepare special products, you can simply buy ready-made drugs based on natural ingredients at the pharmacy. Such drugs include, for example, pepper patch. The main thing is to carefully read the instructions before use and degrease the skin at the site of future application with alcohol.
Before performing exercises for neuralgia of the thoracic spine, it is important to know how to do it correctly. Otherwise, it is easy to harm yourself and make the situation worse.

Rules for performing exercises
As a preventive measure for immediate treatment, the following exercises are allowed:
- turning the arms from a supine position. The legs are extended and the arms are bent at the elbows. It is necessary to turn your arms in a horizontal position so that they end up along the body. Repeat 7-9 times;
- body rolls. Performed lying on your back with bent legs, raised gluteal muscles and raised arms up. It is necessary to make smooth rolls. Repeat 10-12 times;
- turns are made from a standing position, with the arms raised at the shoulders parallel to the floor. Turn your torso in different directions, while straining the muscles of your sternum and abdomen. Repeat 20-25 times.

A set of exercises to get rid of thoracic neuralgia
Distinctive signs of heart pain and intercostal neuralgia
Under certain circumstances, diagnosing diseases is difficult even for specialists - it may be impossible to figure out why a particular symptom occurred without testing. For example, it is difficult to understand whether heart pain or neuralgia is bothering the patient.
The symptoms of heart pain and neuralgia are very similar
What's the difficulty?
It is impossible for a person to distinguish pain in the heart from neuralgia on the left - both are characterized by pain in the chest. Most often, a pinched nerve is mistaken for a cardiac pathology.
However, these pains may have other explanations:
- Intercostal neuralgia – pinching of the intercostal nerve;
- Psychovegetative syndrome;
- Pathological processes of other organs of the chest and mediastinum.

Despite the fact that the symptoms of neuralgia and cardiac pathology are similar, there are also differences. You need to know: your heart hurts or neuralgia is manifesting itself, so that, if necessary, you can provide adequate first aid.
Various disorders in the cardiovascular system have their own characteristics.
- Angina pectoris. Spasms occur clearly in the heart area, but the sensations are characterized by blurriness and patients report pain throughout the sternum. The pain can be described in different ways: as cutting or pressing. They can radiate to the left arm, neck, under the shoulder blade. The pain does not go away when changing body position, attacks can be repeated many times in a short period of time. Their duration ranges from a couple of seconds to 20 minutes. In addition, there is a feeling of suffocation and lack of air. The fear of death appears.
- Heart attack. It is accompanied by sharp pain of high intensity; it can hurt in the left half of the sternum and the spinal column. Always accompanied by pale skin and increased sweating. The pain is so severe that it can lead to loss of consciousness. Pressure is felt in the area of the heart. Any movement leads to an increase in pain and increased breathing. The fear of death appears.
- Myocarditis and pericarditis. Inflammatory processes in the myocardium and pericardium are manifested by moderate intensity nagging pain. When the myocardium becomes inflamed, sharp stabbing sensations appear. With myocarditis, pain is localized in the left half of the body - under the shoulder blade, just above the heart or in the upper abdomen. An attack of pericaditis is accompanied by pain in the upper part of the heart, radiating to the right arm. The pain increases when trying to lie down, coughing, or taking a deep breath. Shortness of breath occurs. With both pericarditis and myocarditis, an increase in temperature and a change in heart rate may be observed.
- Aortic aneurysm. Accompanied by pain in the upper chest. In this case, the pain can be prolonged - if no measures are taken, it can last for several days. When trying to move, their intensity increases.
- Pulmonary embolism. The nature of the pain is similar to that of angina pectoris, but does not radiate to other organs and parts. Accompanied by increased heart rate and shortness of breath. Blueness of the skin and lips is observed, and a sharp drop in blood pressure is noted.
- Hypertension. A sharp jump in blood pressure leads to the stabbing, pressing sensations in the heart being duplicated in the head. At the time of the attack, pronounced facial hyperemia is observed. “Goosebumps” and spots appear before the eyes, and confidence is lost when walking.
Hypertension is one of the causes of heart pain
Initial symptoms of cardiac pathology will include:
- Burning;
- Tingling;
- Pressure in the region of the heart.
These symptoms are characteristic of a heart attack and angina. During a heart attack, the arteries are blocked, so blood does not flow to the myocardium. The result is a sharp pressing pain that goes away fairly quickly.
With angina pectoris, the vessels are blocked by fatty plaques, and blood does not flow in the required quantity to the heart. It is necessary to pay attention to the presence of provoking factors. For example, an attack of angina may develop after high physical exertion or as a result of psychological trauma or severe stress. Nitroglycerin will help to quickly relieve these sensations, but you should definitely consult a doctor.
Neuralgia can occur anywhere where nerves pass, i.e. almost everywhere. Pain in the heart area occurs when the intercostal nerves are pinched.
It is necessary to know the distinctive features of pain due to neuralgia:
- Neuralgia is always accompanied by pain of high intensity, which increases with movement, inhalation, exhalation, and can also intensify without additional provoking factors.
- Spasms can vary in description: from stabbing to burning.
- Neuralgia can manifest itself in frequent attacks or continuously. The duration of pain can reach several days.
- Pain can be traced along the course of the nerve. If you touch the intercostal area, the pain becomes unbearable along the entire length of the nerve. It can radiate to the arm, lower back, neck, chest.
- Loss of sensation in the area of the pinched nerve.
- Pale skin and increased sweating, muscle cramps. The cause is insufficient blood supply to the area.
- Local decrease in temperature (only in the area where the nerve is pinched).
- In some cases, nausea and vomiting occur.
To summarize, we can say how to distinguish neuralgia from heart disease:
- The duration of pain in cardiac pathologies is shorter. Its intensity does not increase with palpation of its localization zone.
- Cardiac medications do not help with neuralgia, but the pain may decrease slightly after taking a sedative.
- Heart diseases are accompanied by arrhythmias, difficulty breathing, and pressure surges. Neuralgia is not accompanied by shortness of breath, and the change in heart rate is of a psychological nature, so it goes away quickly.
- Physical activity does not have a significant effect on pain intensity. With neuralgia, movements increase pain, and the patient cannot always move.
- You can recognize the cause by which drug will help eliminate the pain. Pain in coronary pathology is relieved by glycerin; non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs help with intercostal neuralgia. This could be Diclofenac, Nurofen.
- A provoking factor for an attack associated with the work of the heart can be physical activity or stress. With neuralgia, sudden movement and uncomfortable posture act as a trigger.
- Neuralgia is more common in older people. Heart pathologies can develop regardless of age.
Heart diseases are always accompanied by high blood pressure and arrhythmias
Additional research will tell you how to distinguish neuralgia from heart pain. First, the doctor focuses on the patient’s medical history and complaints. Then the following may be assigned:
- ECG. Electrocardiography is performed in cases where there is a suspicion of coronary pathology. Thanks to this study, it is possible to determine heart rhythm disturbances and dysfunction of the conduction system. This clinic is typical for heart attack and ischemia. In case of ischemia, a study at rest may not reveal abnormalities; an ECG with stress is necessary.
- Coronary angiography. Coronary angiography involves the use of a contrast agent to determine the patency of blood vessels. By studying how the contrast agent is distributed, you can see the location and degree of stenosis of the main artery of the heart.
- Echocardiography. This ultrasound examination is performed if there is a suspicion of heart pathologies not related to the condition of the coronary artery. Thanks to ultrasound, you can find out the thickness of the walls and volume of the heart chamber, as well as see how the valves work. This method allows you to identify various heart defects and inflammatory processes.
- Tomography of the spine. It is carried out if heart pathologies are not confirmed.
If there are fields in the heart area, you must consult a specialist and undergo an examination
If intercostal neuralgia is severe and does not go away within a few days, you should consult a doctor. Full treatment is possible only after identifying the cause that caused the neuralgia, i.e. after diagnostics. In any case, treatment will be comprehensive and should include pain relief and treatment of the disease that is the root cause.
If the pain is very severe, bed rest is required. In this case, the surface must be hard. As for treatment, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs are used, as well as blockades with novocaine.
Physiotherapeutic procedures have proven their effectiveness in treatment. Ultraviolet heating, UHF, electrophoresis, and acupuncture may be prescribed. Ointments and gels with anti-inflammatory, warming, and analgesic effects are suitable for external use. They are necessary to relieve muscle spasms, normalize metabolic processes, and improve blood supply.
To prevent a neuralgic attack from leading to the development of a chronic disease, precautions must be taken. Prevention includes:
- Avoid high physical activity;
- Avoid being in drafts;
- Keep your back straight and watch your posture, especially for those who spend a lot of time at the computer;
- Provide additional intake of vitamins and microelements.
Greetings, my dears, and I want to ask you right away. Do you know how to correctly determine whether your heart hurts or whether thoracic osteochondrosis has worsened? If so, well done, take it off the shelf
1. A sure way to diagnose a heart attack and exacerbation of thoracic osteochondrosis;2. The difference between the mechanisms of the first and second pain; 3. At least one time-tested and life-tested method of getting rid of each of these problems.
So, let's start in order.
This method was taught to me by an elderly therapist who taught at our medical college. I thank him so much for this, with the help of this simple technique I was able to help so many people in a timely manner, and I also earned respect from my patients. After all, the device is outrageously simple, but only doctors know about it, and only a few use it.
To carry out this diagnosis, you only need the hand of your “patient” if you are checking someone close to you, or your own hand if you are diagnosing yourself. Well, and the presence of pain in the chest area, especially if it is mostly localized on the left. When someone tells you that their heart seems to hurt, or you feel something similar yourself, ask yourself the following question.
Is it possible to point with your finger at one single point where it hurts the most, or maybe it is precisely at this point that the pain is located? If you manage to indicate the point, you are guilty of osteochondrosis and intercostal neuralgia, but if in response to the question asked you want to cover your chest with your entire palm, but no clear pain point is detected, sound the alarm on your heart. Now let's figure out what causes such a pain difference.
Neuralgia - specialists in Moscow
Choose among the best specialists based on reviews and the best price and make an appointment.
Chest pain on the left, which is caused by neurological pathologies, develops due to pinching or irritation of the intercostal nerve fibers. This can be due to a number of factors, the most common of which are:
- chest injuries;
- Bekhterev's disease;
- herniated intervertebral discs;
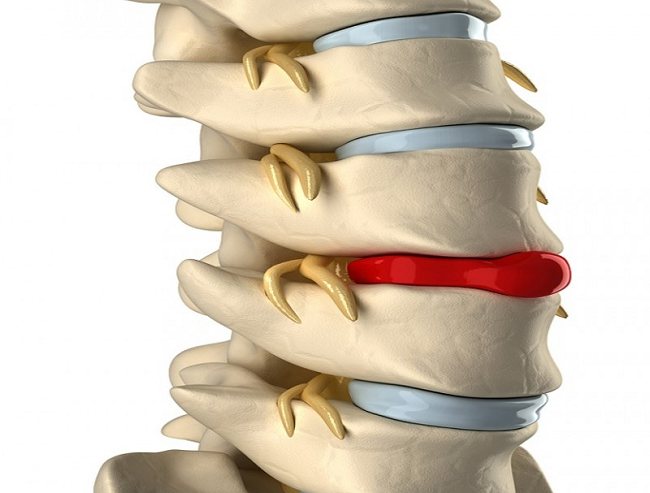
- prolonged tension of the intercostal muscles;
- curvature of the spinal column.
The development of neuralgia in the heart area is often associated with psycho-emotional stress, hypothermia, the action of infectious agents or intoxication of the body. Rarely, pain syndrome to the left of the chest is observed with herpetic lesions, pleurisy, or taking certain medications.
The tactics of treating neuralgia on the left side in the heart area consists of the integrated use of various techniques, among which the most effective are:
- drug treatment;
- physiotherapy;
- therapeutic massage and exercise therapy;
- alternative medicine.
The main method of eliminating discomfort to the left of the sternum is taking medications. The most effective groups of drugs for neuralgia in the heart area are:
- Painkillers. Acute stabbing pain can be effectively relieved with Analgin, Paracetamol, Tramadol, Baralgin, Piralgin, Pentalgin, Sedalgin.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. To eliminate foci of inflammation, Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Nimesulide, Celecoxib, Diclofenac are used.

- Selective and non-selective muscle relaxants. Most often, doctors prescribe Baclofen, Mydocalm, Sirdalud.
- Cardiac glycosides. Neuralgia of the heart is eliminated by Digoxin, Strofactin, Korglykon.
- Chondroprotectors. For the regeneration of cartilage tissue, the drugs Artra, Alflutop, Rumalon, Structum, Teraflex, and Chondroitin are used.
In case of acute heart pain, as first aid it is worth taking a supine position and placing your legs below body level. After this, it is recommended to remove thick clothing and provide the patient with fresh air. This is done so that a person can breathe normally and receive the necessary amount of oxygen for the functioning of organs.
Next, you need to take a Nitroglycerin tablet under the tongue. If there is no effect, you need to take another one. It is not recommended to take more than two tablets of the drug, as this can lead to a sharp decrease in blood pressure, which will aggravate the situation.
Physiotherapy
Along with drug therapy, the doctor may prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures. For cardiac neuralgia the following are used:
- electrophoresis;
- water and mud procedures;
- laser treatment;
- magnetic therapy;
- acupuncture.
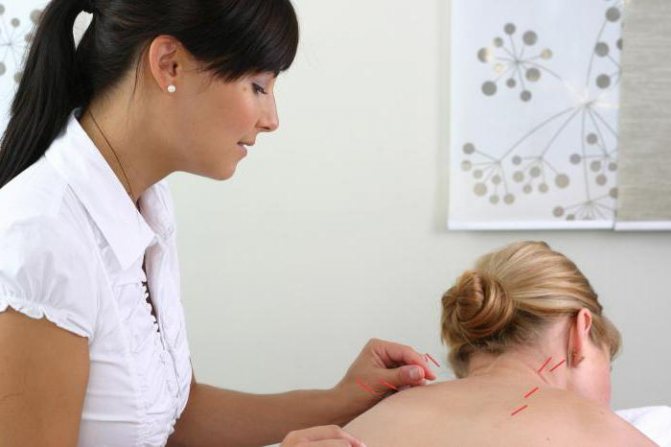
In the conservative treatment of some diseases, therapeutic exercises and massage are prescribed. With their help, they improve blood circulation in the affected area and relieve spasms of muscle fibers. An experienced massage therapist should select a set of exercise therapy exercises. This will avoid the development of complications and make the treatment safe for the patient’s health.
Treatment of neuralgia of the heart
If there are no heart problems, then you need to begin the long process of getting rid of neuralgia. First you need to relieve the pain and give the person a rest.
The pain from intercostal neuralgia can be so annoying and severe that a person is unable to move or even sleep. Therefore, treatment should be divided into:
anesthesia; finding out the cause; getting rid of the cause of the disease.
Painkillers
Since self-treatment is extremely undesirable, only General recommendations from doctors on taking medications are presented below:
- These can be medications in the form of tablets or ointments. The latter, by the way, are able to relieve pain faster. It is better to start treatment with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
There is no need to rub yourself with pepper ointments or try to warm up, give your nerves peace.
- It would be a good idea to take sedatives, which will relax and help the nerves return to their places if they are pinched.
Possible treatments
Treatment will depend entirely on the cause of the problem. For example, if neuralgia was caused by problems with the spine, it is necessary to take a number of measures to strengthen bone and renew cartilage tissue.
It is worth noting several nuances:
Exercise therapy can be used only after pain has completely subsided as a prevention of relapse. Massage is contraindicated in the acute phase. It is better to refrain from such therapy until there is a complete absence of pain. Folk remedies include rubbing with alcohol tinctures, taking herbal mixtures and other measures that can be classified as additional treatment measures, but should not be made the main ones.
The main rule in the event of an attack is to control yourself and try to think soberly. In order to complete this, you need to remember the following warnings:
- Don't bring yourself to a nervous breakdown. There is no need to try to diagnose yourself. Nitroglycerin should not be taken without a prescription.
If you feel pain, consult a doctor. Only a qualified specialist can quickly bring you back to normal and help you get rid of pain. Feel free to ask questions to our specialists online. This will help you determine a strategy for further action.
Structure of nerves
Intercostal nerves consist of several types of fibers: motor, sympathetic and those responsible for sensitivity. Each of these nerve endings is located in the intercostal space and runs along the lower edge of each rib. The closing pair of nerve roots is called “subcostal” and is located under the 12th rib.
Each pair of nerve fibers is covered by a special pleura, starting from the spinal canal to the corners of the ribs. The intercostal nerves are responsible for the sensitivity of the muscle tissue of the chest, abdomen and mammary glands, and also innervate the skin in these areas of the body.
Causes of neuralgia on the left
There are a huge number of prerequisites for the diagnosis of “intercostal neuralgia of the thoracic region”. But all the reasons ultimately come down to two main conditions: irritation of nerve fibers in the intercostal space or pinched nerve in the thoracic region.
Pinched nerves can occur due to osteochondrosis, kyphosis, hernia
Pinched nerves in the chest often occur against the background of osteochondrosis in this area. Also, causes of discomfort can be ankylosing spondylitis, herniated intervertebral discs, spondylitis, and kyphosis.
Irritation of the nerves in the area between the ribs can occur as a result of trauma of various etiologies, overexertion during excessive physical activity, or even as a result of psychological stress.
Intercostal neuralgia in rare cases can result from the following ailments:
- acute gastroenteritis;
- spondylopathy;
- allergy;
- damage to nerve fibers due to regular alcohol intake;
- diabetes of various types;
- aortic aneurysm localized in the sternum;
- hepatitis;
- gastritis or ulcer;
- diseases of the duodenum.
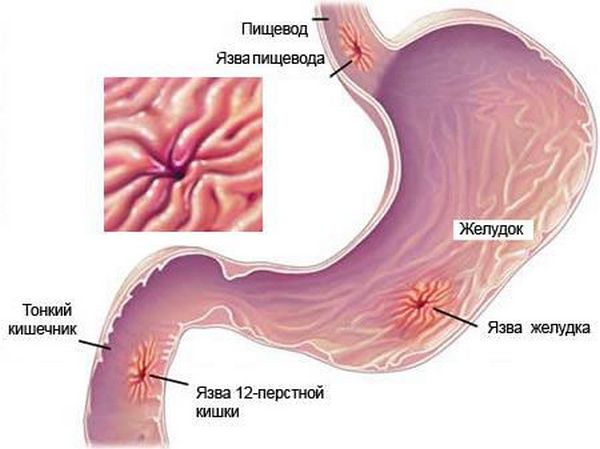
Oddly enough, gastrointestinal diseases can also cause thoracic neuralgia
The nature of pain in cardiac diseases
The pain occurs behind the sternum, it can be squeezing, squeezing, sometimes cutting, but never sharp, but always dull. It arises exactly where the heart is. The person cannot pinpoint exactly where it hurts and puts his hands all over his chest. The pain radiates to the area between the shoulder blades, to the left arm, jaw, and neck. Usually appears during emotional stress, physical exertion, when leaving a warm room in the cold, while eating, at night. When your heart hurts, the discomfort lasts from a few seconds to twenty minutes. Usually the patient freezes in place, he develops shortness of breath, a feeling of lack of air, and a feeling of fear of death. Significant relief or complete relief of the attack occurs immediately after taking nitroglycerin. Pain in the heart does not depend on the position of the body, inhalation or exhalation.
Sudden sharp pain behind the sternum of a pressing or burning nature, radiating to the left side of the chest and back. The patient feels as if there is a very heavy burden on his heart. A person experiences a feeling of fear of death. During a heart attack, breathing quickens, and the patient cannot lie down; he tries to sit up. Unlike angina, pain during a heart attack is very sharp and can be aggravated by movement. They cannot be removed with the usual medications for the core.
Inflammatory heart diseases
Heart pain occurs during inflammatory processes such as myocarditis and pericarditis.
With myocarditis, the sensations are almost the same as with angina pectoris. The main signs are aching or stabbing pain, radiating to the left shoulder and neck, a feeling of pressure behind the sternum, usually a little to the left. They are almost continuous and long-lasting, and can intensify with physical activity. After taking nitroglycerin, do not release it. Patients suffer from attacks of suffocation and shortness of breath during physical work and at night, swelling and pain in the joints are possible.
Signs of pericarditis are moderate, dull, monotonous pain and fever. Painful sensations can be localized in the left side of the chest, usually above the heart, as well as in the upper left part of the abdomen, the left shoulder blade. They get worse when coughing, when changing body position, when breathing deeply, or when lying down.
Aortic aneurysm is expressed by pain in the upper chest, which lasts several days and is associated with physical effort. It does not spread to other parts of the body and does not go away after nitroglycerin.
Dissecting aortic aneurysm is characterized by severe bursting pain behind the sternum, which may be followed by loss of consciousness. Emergency assistance required.
Pulmonary embolism
An early sign of this serious disease is severe chest pain that gets worse when you inhale. Resembles the pain of angina, but does not radiate to other parts of the body. Doesn't go away with painkillers. The patient experiences severe shortness of breath and palpitations. There is a bluish appearance of the skin and a rapid decrease in pressure. The condition requires immediate hospitalization.
Symptoms of neuralgia
The most common symptom of neuralgia is pain attacks. They can appear in the patient in conditions of complete rest and seemingly excellent health. However, the highest percentage of pain occurs after a sudden change in body position, for example, when turning or bending the body.
The duration of pain attacks varies from several minutes to a couple of days. In this case, there may be a prolonged numbness of the torso area located above the inflamed nerve roots.

An attack of pain caused by thoracic neuralgia can last from several minutes to several days.
Having felt paroxysmal pain, the patient often tries to reduce its intensity by holding his breath or changing his body position to a more relaxed one. Often the patient may think that the nature of the pain is caused by heart problems. However, this can often be misleading.
The table below shows the differences between the symptoms of neuralgia and heart pain.
| Heart attack, angina, other coronary pain | Non-coronary pain | Intercostal euralgia of the thoracic region | |
| The sensations experienced, the nature of the pain | Very strong, accompanied by a feeling of squeezing | Dull, aching | Strong, with “lumbago” |
| Associated symptoms | Feeling of lack of air, pale skin, feeling cold | Sweating, sudden increase or decrease in blood pressure, redness or paleness of the skin. If a person tries to move suddenly, the pain intensifies. | |
| Place of manifestation | On the left side of the chest | On the left side of the chest | Along the intercostal nerve |
| The most common causes of manifestation | Excessive nervous and/or physical stress | Excessive nervous and/or physical stress | Sudden movements |
| What happens when you take medications? | Heart attack - no reaction; Angina pectoris - pain relieved with nitroglycerin | The pain becomes weaker if you take a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug - Nurofen, Diclofenac, etc. |

Often the symptoms of thoracic neuralgia are confused with manifestations of heart disease
Herpes zoster often “gives” symptoms of neuralgia of the region, additionally accompanied by the appearance of bubbles with fluid along the path of the nerve fiber. This disease is not contagious, but requires additional treatment.
Similar leading symptoms
Naturally, you need to start with a symptom such as pain. Strong stabbing sensations can occur with one pathology or another. But with heart disease, pain tends to radiate to the arm, back, neck, and there may be a feeling of numbness in the latter. Intercostal neuralgia worries clearly at one point. A change in body position can provoke an increase in attacks. Therefore, you need to carefully monitor whether pain occurs when turning, bending, or straightening the body.
The pain of neuralgia is explained by the fact that, due to destructive processes in the joints, their nerve endings are compressed. In addition, the origin may be neuropathic, i.e., with damage to the nervous system. Different patients report both constant pain and short-term episodic pain. In case of severe disorders in the joints and pinched nerves, coughing, sneezing, deep inhalation and exhalation, i.e., slight movement of the chest, can serve as a provoking factor.
Intercostal neuralgia is also painful when palpated (probing) near the area of pain, i.e. there is a pathological focus. The location of the pain and the area that requires treatment may differ. This is not the case with heart disease. Impaired activity is accompanied by changes in blood pressure, dizziness, nausea, loss of consciousness, etc.
The body is designed in such a way that it always tries to independently get rid of irritants, which is pain due to neuralgia. Therefore, in the absence of therapy, the nerve roots die and are no longer restored. It would seem that what's wrong with this? On the contrary, the pain goes away. But with this outcome, the tidal volume of the lungs decreases, and slight shallow breathing appears.
Features of symptoms in pregnant women
Intercostal neuralgia is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The pain is aching, dull, burning. It can radiate to the ribs, back, lumbar region, neck and shoulder blades;
- The pain may be stabbing in the sternum area;
- The pain intensifies when inhaling;
- The pain is cyclical, it decreases until it disappears completely, and then appears again;
- Certain areas of the skin may become numb;
- Sweating increases;
- Tingling of the skin;
- Possible redness of the skin;
- Increased temperature with bouts of heat or cold;
- Muscle cramps.
Since this disease can easily be confused with a heart attack, you can take drops of Corvalol or Valocordin. If the attack passes, then first of all, you need to check the heart.
Neuralgia in the heart area during pregnancy is associated with the characteristics of the woman’s body during this period. The figure is subject to significant changes, which consists of a shift in the center of gravity and an increase in body weight. In combination with hormonal imbalance, these factors can lead to chest pain on the left.
The unpleasant sensations are nagging in nature. They intensify as pregnancy progresses. If pain occurs in the intercostal spaces, you should seek help from a doctor so that the pathology does not interfere with the course of pregnancy.
Possible differences between intercostal neuralgia and cardiac
The nature of sensations
- Cardioneurosis
- Unpleasant sensations such as burning or heaviness may be detected
- Sometimes it can just feel uncomfortable, which is why the nature of heart pain in the chest can be so misleading.
- A common, but unconvincing manifestation of chest pain against the background of neuralgia of the heart is a kind of compression of the chest.
- Intercostal neuralgia
- The pain can range from a burning sensation to sharp, dull, aching and burning, stabbing and stabbing
- Chest pain due to anxiety can also lead to pain that is similar to heart pain.
- Cardioneurosis
Location
- Unpleasant sensations usually occupy a central position (closer to the center of the chest) and spread outward (diffuse).
Irradiation
- Cardioneurosis
- Pain is often transmitted to the jaw, neck, shoulder, arm (either in one place or in several at the same time), and return irradiation can also be detected.
- Sometimes pain can be transmitted to the upper abdomen.
- Intercostal neuralgia
- There may not always be any irradiation of pain or it may be transmitted to other places other than those mentioned above.
- If the patient, in addition to intercostal neuralgia, also has gastritis with concomitant GERD, then burning pain in the chest may occur, as well as pain in the upper abdomen, and this is often perceived as irradiation.
Provoking factors
- Cardioneurosis
- The condition may worsen due to stress or emotional distress.
- From time to time, excessive food intake or even extreme changes in temperature, especially cold ones, can cause or worsen pain.
Facilitating factors
- Cardioneurosis
- The pain subsides noticeably during rest and after taking nitrate medications.
It is important to know that pain caused by antacids may be associated with gastrointestinal disorders. Pain that subsides when bending forward may be due to pericarditis (inflammation of the sac around the heart).
Concomitant/associated signs and symptoms
- Cardioneurosis
- Severe shortness of breath – the patient may report suffocation.
- Dizziness
- Fainting (blackouts)
Video: How to distinguish intercostal neuralgia from heart disease. Signs, nature, localization of pain
Complications of the disease

Complications arising from neuralgia can be successfully treated in the early stages of the development of the disease. But in advanced cases, when the patient experiences pain for quite a long time, the “problem” nerve may even die. Then the excruciating pain disappears, but this is the first sign of the disease moving to a new stage, for which the characteristic symptoms are shortness of breath and the appearance of a feeling of heaviness in the chest.
Finding a person in a constant sitting position or other static position can result in dysfunction of the spinal canal and the development of osteochondrosis and other related pathologies. The occurrence of complications can only be prevented by timely treatment and prevention.
Consequences
The consequences of the disease do not pose a danger or threat to the patient’s life. The negative impact can have indirect consequences in the form of constant pain, lack of sleep against its background, and disruption of the usual rhythm of life.
Since the cause of intercostal neuralgia is usually some more serious disease of the spine, it can worsen its course. Since the pain is especially severe when inhaling, a person reduces the frequency and depth of his breaths, this can lead to oxygen starvation.
Diagnostic methods
To diagnose this disease, the following studies are required:
- Ultrasound diagnostics of the heart and kidneys, to exclude diseases with similar symptoms;
- In case of an inaccurate diagnosis, computed tomography may be used;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- Chest X-ray;
- Examination by a doctor;
- Electroneurography;
- General urine analysis;
- General blood analysis.
If after several studies the diagnosis is confirmed, then a whole range of studies is not required. This will save both time and money for the patient.
Attention! Only a specialist can establish an accurate and correct diagnosis!
If the patient has unpleasant sensations to the left of the sternum, the doctor collects complaints. During this, he determines the nature and location of pain, as well as the presence of accompanying symptoms.
After this, the doctor begins to collect an anamnesis of the disease and life. This procedure makes it possible to obtain the necessary information about the onset of pathological processes, their possible cause, as well as the characteristics of the course of clinical symptoms.
To confirm the diagnosis, instrumental and laboratory research methods are used. For the differential diagnosis of neuralgia of the heart with intercostal attacks, the following is used:
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- X-ray diagnostics;
- ultrasonography;
- ECG;
- EchoCG;
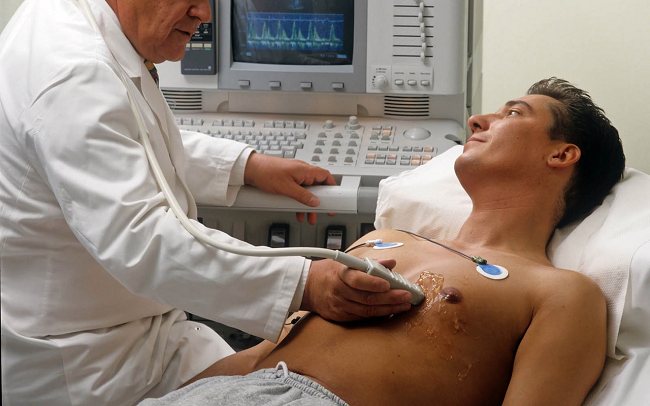
- computer and magnetic resonance imaging.
Using an electrocardiogram, the doctor evaluates the functioning of the heart. This method, in combination with x-ray diagnostics, makes it possible to identify pathological foci that can cause acute, severe pain to the left of the sternum.
A timely and adequate examination eliminates the possibility of establishing an incorrect result. It also significantly reduces the likelihood of disease progression and the development of severe complications.
A neurologist will help the patient identify the presence of thoracic neuralgia. A specialist can make a diagnosis based on examination data and a survey for complaints. During the examination, special attention is paid to the patient's posture. Indeed, with neuralgia, a person, trying to reduce discomfort, involuntarily tries to change the posture of the body in a “painless” direction.
An important task in diagnosing neuralgia is to determine the nature of pain, which is specific to thoracic neuralgia. In this case, the goal of a neurologist is to exclude heart diseases - for this, an electrocardiogram is prescribed and, if necessary, a consultation with a cardiologist is held.
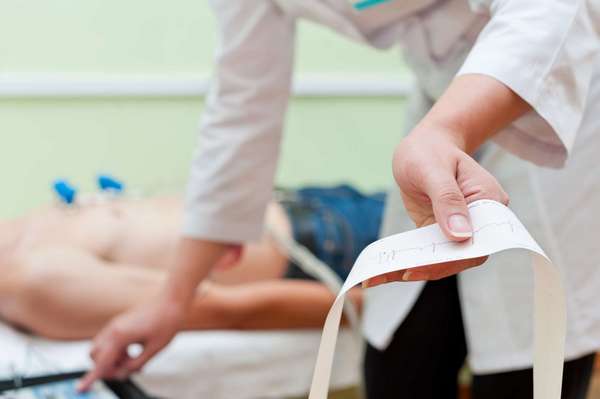
To rule out heart disease in a patient, doctors perform an electrocardiogram.
In addition to the fact that the symptoms of neuralgia are similar to the manifestations of heart disease, they can often be put on a par with the manifestations of stomach diseases. For example, the symptoms of gastritis or stomach ulcers, as well as manifestations of acute pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) are very similar to the symptoms of thoracic neuralgia.
However, there are some nuances in the nature of the pain. In gastrointestinal diseases, the painful condition is more prolonged and less severe. It is also often associated with food intake. With pancreatitis, pain has a pronounced bilateral manifestation and also mainly appears after eating.
To exclude radiculitis from the possible causes of neuralgia, an x-ray is prescribed, and if a spinal hernia is suspected, an MRI is prescribed.
MRI and thoracic x-ray results can help determine the diagnosis.

Intercostal neuralgia of the thoracic region may be similar in its manifestations to pathologies of the respiratory system, such as pneumonia, pleurisy or lung cancer. To detect these diseases, radiography or computed tomography is used.
Learning to distinguish heart pain from neuralgia
Is it possible to understand what is bothering you about pain in the heart or neuralgia, how to distinguish the symptoms of the pathology yourself? After all, this plays an important role in providing first aid. Timely treatment allows you to avoid the development of serious complications, irreversible disorders, and irreparable consequences. Problems in the cardiovascular system and neuralgia can cause general symptoms, including pain of varying intensity. An unknown diagnosis causes panic, confusion, and fear in patients for their lives.
To determine the cause of pain in the chest area, it is recommended to take into account their characteristics, the presence of additional signs of a pathological condition and the living conditions of patients, as well as the results of diagnostic measures.
In the case of the development of pathologies of the cardiovascular system, painful sensations are accompanied by burning, tingling, and strong pressure in the chest area. Such symptoms appear as a result of the development of angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, pericarditis or inflammation of the heart sac, accompanied by shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling, coughing attacks, changes in blood pressure and pulse.
Myocardial infarction occurs as a result of blocked arteries and problems with blood transportation through the vascular system. Such pathological phenomena cause short-term, sharp, pressing pain in the chest. Determining the exact location of their localization is difficult. Painful sensations affect not only the chest, but also the esophagus, cervical and lumbar spine. The development of myocardial infarction is accompanied by the appearance of cold sweat, nausea, and vomiting.
When the walls of blood vessels are blocked by atherosclerotic plaques, cardiologists diagnose angina pectoris. This type of pathology causes limited access of blood to the heart muscle in full. Angina appears during increased physical activity, which causes overstrain of the human body, as well as after stressful situations that cause strong negative emotions.
The desire to independently relieve the symptoms of the disease will not be successful and will lead to the loss of precious time. The appearance of pain is a signal to urgently call a doctor and ambulance. Before their arrival, the sick person is recommended to take a horizontal position and measure blood pressure and pulse. If they deviate from the norm, it is recommended to take a Nitroglycerin tablet and then wait for the arrival of medical workers.
Timely treatment of pathologies of the cardiovascular system eliminates the risk of developing irreversible processes in the human body and the death of the patient. Knowing how to distinguish heart pain from neuralgia, you can save the life of a loved one by providing him with effective first aid.
Cardiologists are involved in identifying heart pain. Treatment of diseases involves drug therapy after receiving the results of diagnostic measures. The nature of pain in the chest area makes it possible to assume the presence of heart disease and the vascular system. To clarify the diagnosis, the following tests are prescribed:
- electrocardiography, which refers to a diagnostic study designed to identify disturbances in the rhythm of the heart and the function of its conduction system;
- coronary angiography, which makes it possible to identify the location and degree of narrowing of the arteries;
- echocardiography, which involves ultrasound examination of the heart, identifying its congenital or acquired defects, determining the thickness of the vascular walls, and assessing the functioning of the valve system.
If heart pathologies are excluded, a computer or magnetic resonance imaging scan of the thoracic spine is prescribed. The results obtained form the basis for identifying the causes of heart pain or neuralgia. Treatment prescribed by a cardiologist is supplemented by strict adherence to a nutritious diet and reduced physical activity.
Smoking tobacco products and drinking alcoholic beverages are also strictly prohibited, regardless of the concentration of ethanol contained in them. Only doctors have the right to diagnose neuralgia or heart pain. Self-treatment of an unpleasant syndrome in the chest area can cause serious complications and death of the patient.
Many patients experiencing discomfort in the chest area want to know what is causing them: pain in the heart or neuralgia. An unambiguous answer can be obtained after consulting a specialized specialist, who, based on the results of diagnostic measures, will clarify the diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment. Its main goal is to relieve pain and prevent relapse.
Neurological pain in the chest area appears as a result of the development of a number of diseases. These include:
- osteochondrosis of the thoracic vertebrae;
- state of protrusion or the appearance of herniated intervertebral discs;
- injury to the upper part of the spinal column;
- diagnosis of neoplasms;
- damage to the thoracic spine due to the development of tuberculosis or syphilis;
- spondylosis due to growing osteophytes;
- untimely treatment of colds and infectious diseases;
- high frequency of hypothermia, nervous shock, stressful situations.
Intercostal neuralgia can be distinguished by the nature of the unpleasant sensations, which differ from pain in the heart. The pathology is characterized by the presence of severe discomfort, the elimination of which is possible after taking non-steroidal painkillers. Compression of the intercostal nerve processes provokes intense pain. It can manifest itself in a variety of forms. There will be constant or occasional pain in the chest, stabbing, burning, aching.
The acute form of intercostal neuralgia, which is associated with a knife blow, subsides over time and passes into the stage of aching pain syndrome only after taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory dosage forms in the form of tablets, gels, ointments, injections. The use of nitroglycerin or heart medications will not help eliminate the symptoms of the pathology.
Unpleasant sensations caused by pathology of the nervous system in the chest area can bother the patient for several days, in contrast to heart pain that fades over time. The slightest manifestation of activity, including moments of sneezing, coughing, careless deep breaths or exhalations, leads to a deterioration in the patient's condition.
The pain syndrome, which increases several times, makes you want to exclude any movement and ensure shallow breathing. Neurologists and vertebrologists know how to distinguish neuralgia from heart pain. To clarify the reasons for the development of pathology, a history is taken, palpation of the chest area, and an MRI or CT scan is prescribed. The diagnostic results form the basis for the choice of drug therapy and methods of physiotherapeutic procedures.
Intercostal neuralgia, having similar manifestations to pain in the heart, significantly reduces the quality of life and requires prompt treatment.
And the ability to distinguish heart pain from the symptoms of intercostal neuralgia will help for preliminary diagnosis and exclude the possibility of a serious illness.
After all, the pain that is characteristic of intercostal neuralgia is almost identical to the pain that a patient feels during a heart attack, and this condition can have the most serious consequences for both a person’s health and his life. How to understand what hurts: your heart or neuralgia? Read below.
The reasons that cause the occurrence of this pathological condition are currently not fully understood. Therefore, it is possible to study the factors that can cause manifestations of intercostal neuralgia.
Damage to the nerve fiber - and this is the root cause of the development of intercostal neuralgia - can occur due to the manifestation of certain factors that cause pinching of the nerves in the intercostal space or in the chest area. These risk factors can be considered precipitating factors that can lead to damage to the intercostal nerves.
Risk factors include the following:
- Genetic predisposition.
- Disorders in the articular and skeletal systems - arthrosis of the joints and pathological conditions in the spine become the most common provoking factors in the occurrence of intercostal neuralgia (kyphosis and scoliosis of various natures).
- Hypothermia.
- Displacement of the vertebrae in the spinal trunk often causes the onset of pathological processes in adjacent tissues and subsequently inflammatory processes occur in the nerve fiber tissue.
- Prolonged stress or depression.
- Wearing tight underwear - this causes constant compression of the nerves that are located in the sternum area and leads to their damage.
The listed factors can provoke damage to the nerve fibers in the chest area and the further development of neuralgia will significantly reduce the quality of life, causing pain even with the most seemingly insignificant actions.
Intercostal neuralgia is quite difficult to diagnose because it does not have clear manifestations and characteristic conditions. The pain is periodic; the location of the pain can also shift significantly even in one patient.
Therefore, a timely visit to the doctor will help to accurately establish the diagnosis, prescribing treatment that eliminates the unpleasant symptoms of this pathological condition.
For this condition, the most typical manifestations are pain in the area of the ribs of a girdling nature. This is the first and main sign of the disease.
Difference in reasons
During pregnancy
Intercostal neuralgia is a common occurrence among pregnant women. During this wonderful period, the load on the spinal column increases, and the growing uterus increases pressure on the internal organs, which leads to pinching of the intercostal nerve.
In this case, the pain is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- The pain radiates to the heart area, stomach and shoulder blades;
- Painful, localized in the intercostal space on the left;
- As pregnancy progresses, the course of the disease worsens.
Treatment in this case is symptomatic and only after consultation with a doctor. Often, the disease goes away on its own after childbirth.
What is the difference between neuralgia and heart pain?
Pathology affecting the heart and blood vessels often leads to deterioration in the nutrition of myocardial cells. This is accompanied by the development of pain in the chest area on the left side. The diseases include several common processes:
- Stable angina pectoris - a violation of tissue nutrition is caused by a narrowing of the coronary artery, which exceeds 50% of its diameter. A decrease in diameter is usually a consequence of the formation of an atherosclerotic plaque (localized deposition of cholesterol in the wall of an arterial vessel, which narrows its lumen). The pain has the character of compression and intensifies after physical or emotional stress.
- Unstable angina is a pathological process characterized by a sharp and sudden deterioration in myocardial nutrition. Its development is accompanied by severe pain, and a person cannot determine the provoking factors. Unstable angina refers to pre-infarction conditions.
- Myocardial infarction is a serious disease accompanied by the death of a section of the heart muscle. Myocardiocytes are very sensitive to insufficient supply of oxygen and nutrients, so a sudden cessation of blood circulation is accompanied by their death and very severe acute pain.
A complex of pathological processes that are united by a violation of the supply of oxygen and nutritional compounds to the cells of the heart muscle is called coronary heart disease. Less commonly, pain in the heart area can be associated with inflammation of the endocardium (the inner lining of the heart wall) or the pericardium (the outer lining).
The possible development of heart pathology with the appearance of corresponding clinical subjective symptoms is indicated by several specific features of pain:
- Unpleasant sensations are predominantly localized on the left side of the sternum (the area of the projection of the heart), they often radiate to the left shoulder girdle and shoulder.
- Mostly, there is a clear connection between physical or functional stress and the occurrence of pain (with the exception of cases of unstable angina, as well as myocardial infarction).
- Painful sensations usually have a pressing, squeezing nature, they are accompanied by shortness of breath. In the event of myocardial infarction, as well as unstable angina, the pain becomes acute.
- Heart pain predominantly develops in older people with cardiovascular pathology.
Many diseases can be recognized at their very beginning by paying attention to the body's signals for help. Signs of the development of heart disease are common to several other pathologies. The first thing you need to pay attention to is whether the person is at risk. For example, people with elevated cholesterol levels, blood pressure, excess body weight and diabetes should not ignore the following symptoms:
- Discomfort in the chest, which manifests itself in different ways (pressure or feeling of fullness, burning, pinching). The sensations occur both during physical activity and at rest. The discomfort usually goes away after a few minutes.
- Stomach pain, heartburn, nausea, upset. Such symptoms in themselves indicate pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, but sometimes they signal heart disease in women if there are risk factors.
- Referring pain to the arm. It is felt that the onset of discomfort is localized in the chest area. But sometimes my hand hurts more.
- Dizziness in combination with other signs that indicate malfunction of the heart muscle.
- Sore throat if it spreads to the maxillofacial area from the sternum.
- A sharp feeling of fatigue or shortness of breath with the slightest exertion.
- Heavy snoring indicates breathing problems that affect the heart.
- Cold sweat combined with other symptoms.
- Constant cough.
- Swelling of the lower extremities, which often indicates insufficient heart function.
- Arrhythmia at rest.
Symptoms depend on the location and extent of nerve damage. Most often the pain occurs on one side, but sometimes it is symmetrical. Discomfort radiating to the sternum area gives the feeling that the heart hurts.
Symptoms of intercostal neuralgia:
- The temperature at the site of the lesion rises (hyperemia of the skin).
- The skin in the area of inflammation changes color (slightly reddens or turns pale) and looks drier.
- Muscle tone limits mobility (a common symptom of neuralgia).
- The inflamed nerve loses sensitivity.
- It's hard to take a deep breath.
- The pain radiates to the heart when the left side is affected.
- Increased sweating.
- Attacks of discomfort, which are periodically repeated, intensify at night.
- Pain radiating along the intercostal arch.
- G.A. Akimov, M.M. Same Differential diagnosis of nervous diseases. 2001.
- Practical neurology: a guide for doctors [Electronic resource] / Ed. A.S. Kadykova, L.S. Manvelova, V.V. Shvedkova - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2011.
It is quite difficult to distinguish whether the heart is bothering you or neuralgia by external signs, since both conditions are characterized by discomfort in the chest area. Manifestations of pain syndrome are different. If men more often experience discomfort in the lower part of the chest, then women - in the upper.
A preliminary diagnosis can be made if you pay attention to the features of the symptom:
- Firstly, neuralgia occurs due to compression of nerve endings, so the pain syndrome spreads along their entire length; the patient experiences discomfort not only in the chest, but also in the area of the shoulder blade or back.
- The second diagnostic criterion is the duration of the pain syndrome. In case of cardiac pathologies, discomfort lasts for several minutes. Neuralgia provokes aching or stabbing pain that does not go away for more than 20 minutes.
- The third feature is the influence of the provoking factor. Based on this feature, it is easier to distinguish intercostal neuralgia and osteochondrosis from heart pain. The latter occurs against the background of severe stress, after physical exertion, and emotional experiences. But you need to understand that neuralgia often develops as a result of cardiovascular pathologies. With osteochondrosis, the intensity of pain increases with movement, while with cardiac pathologies such changes are not observed.
- The last diagnostic criterion is the effect of drugs on the patient’s condition. For pain in the heart, the patient feels relief after taking Nitroglycerin; for pinched nerve fibers, the drug does not help. With heart pathology, a decrease in physical activity also helps, which does not give results with neuralgia.
To distinguish heart disease from neuralgia, it is necessary to pay attention to the nature of the accompanying phenomena. When signs of heart disease occur, blood pressure often rises. Organ dysfunction leads to heart rhythm disturbances. Appropriate medications help relieve such symptoms. After taking Valocordin, blood pressure is normalized, and Nitroglycerin eliminates arrhythmia.
If we look at the causes of these disorders, we can understand the differences in heart muscle pain and neuralgia in adults. Pain in the heart develops due to myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism, myocarditis, pericarditis, aortic aneurysm, hypertension, angina pectoris. Each of these factors leads to different symptoms.
With angina, pain radiates to the left arm, neck or under the shoulder blade.
The intensity of the syndrome varies. The pain lasts for several seconds or minutes (sometimes up to 20). At the end of an angina attack, the patient feels short of breath. There may be a fear of death.
During a heart attack the following are observed:
- paleness of the skin;
- profuse sweating;
- increased breathing and increased intensity of pain when moving;
- fear of death.
In inflammatory heart diseases (pericarditis, myocarditis), the pain syndrome usually becomes nagging in nature, and its intensity is increased by physical strain. At the same time, shortness of breath, arrhythmia and an increase in body temperature are noted.
arrhythmia shortness of breath
An aortic aneurysm is indicated by prolonged painful sensations that bother you for several days. Thromboembolism is indicated by signs characteristic of the first disease. But unlike angina, the pain does not spread to other parts and is localized in the chest. The following symptoms are also possible:
- blue lips and skin;
- a sharp drop in blood pressure;
- rapid heartbeat;
- dyspnea.
With hypertension, pain occurs sharply, which is caused by an increase in blood pressure. This heart disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- headache;
- blind spots before the eyes;
- "goosebumps";
- gait disturbance.
In addition to these reasons, the heart often hurts from nerves. In this case, the symptom ceases to bother you as soon as the patient’s mental state is restored.
Neuralgia, like heart disease, occurs against a background of muscular and emotional stress. Provoking factors that cause compression of nerve fibers include:
- injuries or other damage to the chest;
- hernias and other pathologies affecting the musculoskeletal system;
- infectious and viral diseases;
- frequent hypothermia;
- pregnancy;
- salt deposits in the spine;
- deficiency of B vitamins.
Usually, when the chest is affected, the pain spreads along the rib (usually the lower one). This manifestation is not typical for a diseased heart.
Since it is not always possible to determine the type of pain - a problem in the heart or neuralgia, it is necessary to pay attention to the nature of the symptom and the accompanying signs that help determine the type of disorder. Neuralgia is caused by compression of nerve fibers, and pain is characterized by the following features:
- piercing, cutting, wavy;
- the intensity of the syndrome increases with inhalation and movement;
- pain may persist for several days;
- the intensity of the symptom increases with palpation;
- the appearance of distant pain in the area of the scapula, neck, chest and along the entire length of the nerve;
- decreased sensitivity in the problem area, which is not typical for heart disease;
- muscle cramps;
- pale skin;
- local decrease in temperature.
Let's sum it up
With proper and timely treatment, thoracic intercostal neuralgia is completely curable. Prevention of this disease is to prevent the development of “root cause” diseases, as a result of which neuralgia subsequently occurs. It is also necessary to constantly lead a healthy lifestyle in order to strengthen the immune system and maintain a healthy state of the body.
It is possible to get rid of such a disease, but it is worth starting treatment on time - this will help you forget about the discomfort as early as possible. You should not prescribe treatment methods on your own, so as not to worsen your health condition even more.
Prevention measures
To prevent the development of neuralgia in the heart area, you need to give up bad habits, lead an active lifestyle, eat a balanced diet and exercise. Compliance with these rules will significantly reduce the likelihood of developing pathological changes in the human body.
Neuralgia in the heart area manifests itself as a result of damage to many organs and systems. If they are present, it is recommended to go to a clinic or hospital for consultation with a specialized doctor. He will help diagnose the underlying disease and also prescribe effective treatment tactics, which will preserve the patient’s health.
There are a number of preventive actions that reduce the manifestations of the disease to a minimum.
In this case:
- It is necessary to avoid hypothermia, drafts, heavy lifting, and alcohol consumption.
- Regular examinations by a doctor are required.
- Hardening the body and strengthening the immune system will also be a good help in the prevention of intercostal neuralgia.
Despite the fact that the disease is not dangerous, quality treatment is required when the first symptoms appear. Thanks to this, it is possible to avoid many unpleasant consequences.
18.01.2020