Cardiac arrest is the equivalent of clinical death. As soon as the heart stops performing its pumping functions and pumping blood, changes in the body begin, called thanatogenesis or the onset of death. Fortunately, clinical death is reversible, and in a number of situations of sudden respiratory and cardiac arrest they can be restarted.
Actually, sudden cardiac arrest is precisely the cessation of its effective work. Since the myocardium is a community of many muscle fibers that must contract rhythmically and synchronously, their chaotic contraction, which will even be recorded on a cardiogram, can also refer to cardiac arrest.
For what reason can cardiac arrest occur?
Many different conditions can cause cardiac arrest.
These include both organic pathology of the circulatory system and the impact of external factors on the body. The main reasons are:
- Ventricular fibrillation is a sudden disturbance of the heart rhythm that never stops on its own and leads to sudden death of a person.
- Asystole is the absence of any cardiac activity.
- Massive pulmonary embolism occurs when a large part of the vessel is blocked. The person instantly suffocates, turns blue, and blood flow to the heart is disrupted.
- Cardiac tamponade occurs after operations, injuries, and pericarditis. Fluid accumulates between the leaves of the heart sac and compresses the organ, preventing it from functioning fully.
- Myocardial infarction can lead to a number of serious complications due to the death of a section of the heart muscle. The organ loses its contractility, which threatens to stop the heartbeat.
- Arrhythmias, such as ventricular tachycardia (VT), atrial fibrillation or flutter - all these disorders are based on the chaotic contraction of individual areas, as a result of which the ventricles inadequately eject blood into the bloodstream, causing an acute lack of oxygen.
- Brugada syndrome is a hereditary disease that is characterized by frequent fainting and a high risk of developing recurrent ventricular arrhythmias.
- Overdose of alcohol, opiates.
- Acute respiratory failure.
- Electrical injury.
- Thermal shock, hypovolemic as a result of burns over a large area of the body and blood loss.
- Chronic kidney diseases lead to endogenous intoxication with nitrogenous substances.
- Heart failure.
- Poisoning with muscarine, poison ricin and puffer fish, mercury vapor and sarin gas, potassium cyanide, arsenic. The action of all these substances has similar characteristics. Clinical manifestations have stages, starting with headache, weakness and ending with respiratory and cardiac paralysis.
Sometimes it is difficult to name the exact causes of cardiac arrest. Physical or emotional stress, heredity, chronic diseases and a combination of these factors can contribute. A sudden acute condition may occur if certain medications are taken incorrectly.
It is worth noting that the drug causes cardiac arrest only in case of careless use, non-compliance with the dosage and frequency of administration, severe somatic pathology, disturbances in the content of electrolytes in the blood, and cross-reactions. Individual drug intolerance deserves special attention, as it can lead to anaphylactic shock.
Heart attack concept
This is an acute serious condition, which is provoked by a sudden development of heart failure . When the coronary vessels are spasmed or blocked by a thrombus, a section of the myocardium dies. No one is immune from a heart attack - both people with cardiovascular diseases and any healthy person. Often emotional women with vegetative-vascular dystonia are susceptible to this condition. Heart attacks most often occur in the spring, under the influence of magnetic storms and in the heat. Women in their childbearing years are least likely to have a heart attack. After menopause, the risk increases. And the survival rate of older women is lower than that of men.
What should you do if the patient has no heartbeat?
Cardiac arrest can be suspected if a person suddenly loses consciousness and does not respond to external stimuli (beat him on the cheeks, clap his hands loudly, sprinkle water on his face). So, if someone has lost consciousness in front of you, you need to immediately check the pulse in the main vessels. To do this, use your fingertips to feel the middle of the neck (Adam's apple in men) and move it to the side until it touches the sternocleidomastoid muscle. It is along its course that the carotid arteries are located (photo 1).
It is also necessary to check whether the person is breathing or not. How to do this is shown in photo 2.
By placing your ear to the victim's nose and looking at his chest, you can hear breathing and notice the rise and fall of the chest.
If there is no heartbeat or spontaneous breathing, you should immediately call an ambulance and immediately begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation. The actions consist of indirect cardiac massage, which is performed by chest compressions, and artificial ventilation of the lungs using mouth-to-mouth or mouth-to-nose breathing. If there is only one resuscitator, compressions are preferred. It is important not to stop providing assistance until the team arrives or cardiac activity is restored, because within 6-10 minutes irreversible hypoxic changes occur in the brain, which leads to the death of its cells and severe neurological disorders in the future (if the measures are successful).
In many countries, defibrillators are installed in public places so that immediate assistance can be provided to a dying person. This significantly increases the chances of resuscitating a person effectively and in a timely manner.
First aid for a heart attack
If a person experiences chest discomfort or other symptoms of a heart attack in a loved one, they should immediately call emergency medical services. While the first instinct may be to rush the heart attack victim to the hospital, it is better to receive or provide emergency medical treatment at the scene. At the same time, emergency medical personnel can begin treatment while en route to a medical facility. They are trained to provide resuscitation if a person's cardiac activity stops (heart stops).
If you cannot contact an ambulance, you need to take the victim to the hospital. If the victim is yourself, you need to go to the hospital if there is no other way out.
In many cases, treatment is delayed because doubts arise as to whether a heart attack has actually occurred? Often, victims in such cases do not want to worry or worry about their friends and relatives.
It is important to remember that a heart attack is a critical condition, so it is always better to worry and be safe than to be sorry later.
Acting quickly can save lives. If the necessary medications are used as quickly as possible after the first symptoms develop, the risk of death and various complications can be significantly reduced. In particular, drugs are used to thicken the blood and widen the arteries, which can stop the progression of a heart attack, and even a closed blood vessel can open when catheterized with a stent inserted.
The longer the time passes from the onset of the attack to treatment, the lower the chances of survival, since the degree of damage to the heart becomes more severe.
About half of those who die from heart attacks seek help an hour or more after the onset of the clinical picture.
First aid provided in case of a heart attack before the arrival of doctors:
- You need to try to make the injured person calm down.
- The patient needs to be laid down or seated.
- If a person is not allergic to aspirin, chew or swallow the appropriate dose, usually 0.3 g. (Aspirin works faster if you chew it rather than swallow it whole).
- Nitroglycerin, which should be taken in a dose of 0.5 g, can improve blood circulation.
- If the patient stops breathing, a person nearby who is appropriately qualified or skilled should immediately perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). If you don't know how to perform CPR, an ambulance operator can help with it before the medical team arrives.
First aid to yourself when there is no one around
During a heart attack, people are often left alone with themselves and at such moments it is extremely difficult to reach anyone. A person can be at home, in the evening on a deserted street, or somewhere on the road in a car. In this case, it may happen that the phone is discharged, and there is no one nearby at all.
How to prevent asystole in a patient?
Since the main causes of cardiac arrest are cardiovascular diseases, it is necessary to try to prevent their development. The main preventive measure is a healthy lifestyle, that is:
- sufficient physical activity (at least 30 minutes a day);
- balanced diet excluding fatty meats, canned food, soda, fast food, large amounts of flour, etc.;
- maintaining normal body weight;
- quitting smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
If you have chronic diseases, you must regularly visit the doctor (at least once a year) for examination and examination, and correction of the prescribed therapy. Be sure to consult with a specialist and not self-medicate, even with cough syrup. It must be remembered that uncontrolled use of medications can cause sudden cardiac arrest at home!
An important aspect of the prevention of cardiovascular accidents is long-term drug support. For coronary heart disease, the following are indicated:
- Antiplatelet drugs prevent the formation of blood clots by thinning the blood.
- Anticoagulants also reduce the risk of stroke in atrial fibrillation/flutter after heart surgery.
- Statins lower cholesterol levels and reduce atherosclerotic plaques that are deposited on the walls of blood vessels.
- Beta blockers have cardioprotective properties, reduce myocardial hypertrophy and the ischemic zone against the background of a heart attack, and improve blood flow to the left ventricle.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and some sartans have proven effective in preventing sudden cardiac death, cardiac and nephroprotection.
Popular drug causes sudden cardiac arrest
Sudden cardiac arrest accounts for about half of cardiac deaths and one in five natural deaths. In this case, the heart stops working as a result of cardiac arrhythmia (ventricular fibrillation/tachycardia) and death occurs within 10 minutes.
The fact that the stop is sudden does not mean, however, that a healthy heart stops for no reason at all. In fact, diagnostics could identify problems in advance, but not everyone is in a hurry to carry it out.
Apart from congenital heart damage, the risk factors for sudden cardiac death are about the same as for a heart attack: smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol and blood sugar, excess weight, sedentary lifestyle, male gender; as well as strokes, heart attacks and sudden cardiac death in close relatives under 60 years of age.
However, doctors modestly keep silent about the fact that even medications can provoke cardiac arrest. And the sad thing is that some of these drugs are supposed to improve heart health. This is exactly what happened to a drug called nifedipine , widely used to treat high blood pressure and angina.
Cardiologists often prescribe dihydropyridines - nifedipine and amlodipine . The choice usually depends only on the personal preferences of the doctor. Both drugs are considered equally effective and safe. More precisely, they were considered - until recently.
Researchers from the European Network for the Prevention, Education and Effective Treatment of Sudden Death (ESCAPE-NET) analyzed data from 2,503 patients from the Dutch Resuscitation Research Registry and 10,543 age- and sex-matched controls. Data from 8,101 patients from the Danish Cardiac Arrest Registry (matched by 40,505 controls) were also analyzed.
The doses of nifedipine studied in this study were 30 mg and 60 mg (these are the most commonly prescribed), and the doses of amlodipine, respectively, were 5 mg and 10 mg (these are also the most commonly prescribed). The standard practice for doctors is to start with a lower dose and then give a higher dose if blood pressure or chest pain is not reduced enough.
conclusions
Sudden cardiac arrest is the cause of death for the majority of the population, due to many factors. One of them is the side effect of medications, which can cause severe arrhythmias, bradycardia, anaphylaxis and asystole, so the most dangerous drugs are available only by prescription.
The following sources of information were used to prepare the material.
Every person should know that there are drugs that cause cardiac arrest. In this regard, experts do not advise self-medication. It is necessary to take medications only after the approval of the attending physician. After all, even a simple analgesic taken to eliminate a headache can cause coma with subsequent cessation of cardiac activity if there was alcohol in the person’s blood.
Options for medications that negatively affect the heart
All drugs that cause cardiac arrest are well known. Doctors who often use these medications (cardiologists, general practitioners, surgeons, psychotherapists) are well aware of the possibility of negative effects on the functioning of the heart. It is important to know which medications require careful attention to dose selection and mandatory medical supervision during treatment. The following groups of drugs can cause cardiac arrest:
- cardiac glycosides;
- potassium-containing drugs;
- medicines used in surgery and anesthesiology;
- antibiotics;
- means for psychotherapy.
Cardiac glycosides and drugs containing potassium are widely used in cardiology and have a direct effect on the functioning of the heart muscle, so it is extremely important to strictly adhere to the dosage of medications.
Medicines that can cause cardiac arrest
Many patients do not even have an idea which drug causes cardiac arrest, neglect the doctor’s recommendations, do not visit a medical facility and ignore prescriptions. They purchase a popular product with a well-advertised name at a pharmacy kiosk and hope to get a positive result. At the same time, they completely do not take into account that taking the medication incorrectly can provoke fatal consequences. Here is a list of which pills cause cardiac arrest:
- Muscle relaxants - reduce the tone of skeletal muscles, thereby reducing motor activity.
- Cardiac glycosides have cardiotonic and antiarrhythmic effects.
- Medicines containing potassium.
- Antibacterial drugs have a suppressive effect on bacteria, affecting their vital processes.
- Heartburn pills.
- Vitamin complexes.
- Psychotropic drugs - affect the central nervous system and change the mental state.
Using drugs that are incompatible with each other or taking them while there is alcohol in the body can trigger irreversible processes. Overdose, abuse and individual intolerance to one of the components of the drug also lead to dangerous complications.
How to quickly and effectively lower your heart rate at home
If you need to quickly lower your heart rate at home, you can use one of the following methods:
- take a deep breath and, holding your nose and mouth, try to exhale - this will stimulate the vagus nerve and, as a result, reduce the heart rate;
- close your eyes and press your fingers on the eyeballs - light pressure on the eyelids for 20-30 seconds is enough to normalize the heartbeat;
- lie down on a flat surface, face down and lie there for 30-40 minutes;
- provoke a gag reflex - just like the methods described above, this leads to activation of the parasympathetic nervous system and causes bradycardia;
- A tablet of validol, valocordin or valoserdin, which is placed under the tongue or 20-30 drops of Corvalol with cold water, helps to reduce the pulse and heart rate.
Cardiac glycosides and drugs containing potassium
It is worth noting that cardiac glycosides force the muscle tissue of the heart to contract much more strongly. This effect is similar to the release of adrenaline, taking caffeine-containing drinks or camphor. Such drugs are prescribed to patients who suffer from heart failure. Due to the presence of adenosine triphosphatase in their composition, the process of saturating the body with calcium, sodium, and potassium significantly improves. Thanks to this, high-quality absorption of creatine phosphate occurs and water-salt metabolism is restored.
Instant death when taking these drugs occurs due to an overdose. But they can be dangerous even at normal concentrations in the blood. They should be taken with extreme caution in patients diagnosed with renal failure, hypokalemia, hypercalcemia and hypomagnesemia.
Potassium is important in the mechanism of heart contractions. This microelement takes part in cellular metabolic processes and ensures water-salt balance. The heart can temporarily or completely stop either due to an excess of calcium or due to its deficiency.
Muscle relaxants and gastroenterological drugs
Major operations cannot be performed without general anesthesia. For this purpose, muscle relaxants can be used to reduce muscle tone. If a patient has an individual intolerance to one of the substances of the drug, he must provide this information to the anesthesiologist. Even a small dose of an administered muscle relaxant can cause anaphylaxis and instant cardiac arrest (ventricular asystole). According to statistics, about 12% of patients survive.
This type of medication cannot be used if you have the following health problems:
- diseases of the respiratory system;
- heart pathologies;
- vascular defects.
Against the background of these problems and taking muscle relaxants, a person suddenly feels worse and has an increased heart rate. This may ultimately result in cardiac arrest.
Antibiotics and vitamins
Drugs of this type cause immediate cardiac arrest in those who suffer from allergies.
The risk group is represented by people who have diabetes, heart failure or angina pectoris.
Antibacterial drugs are used to treat infectious diseases. They are prescribed for pneumonia and bacterial bronchitis. But along with the therapeutic effect, they can cause serious harm to the body. Their powerful action primarily affects the heart muscle. This increases the risk of heart failure and heart rhythm disorders. Stopping the work of the main organ of the circulatory system is also possible. As a rule, such consequences are inherent in drugs from the macrolide group.
As for vitamins, their intake also requires supervision by a doctor. Otherwise, health problems cannot be avoided. For example, uncontrolled use of the vitamin complex “Vikasol” (vitamin K, which prevents internal bleeding) can provoke vascular thrombosis. But an excess amount of calcium in the body negatively affects the conduction system of the heart, which loses the ability to fully perform its basic functions. You should not get carried away with vitamins if you have mitral valve prolapse, because this can also cause cardiac arrest.
Psychotropic drugs
This drug group includes tranquilizers, antidepressants and sedatives. They are used to treat nervous system disorders. They are indicated for use by epileptics and patients with schizophrenia.
Tranquilizers suppress emotions and reduce thinking abilities. At the same time, they cause contraction of the muscles of the face and heart. Tablets prescribed for the treatment of schizophrenia initiate psychosis, which may be accompanied by an increase in blood pressure and the appearance of arrhythmia. In the presence of cardiac pathologies, this can cause cardiac arrest.
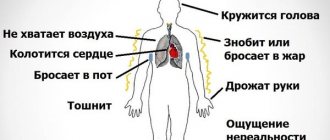
Heart Attack Symptoms
This condition occurs more often in the morning. When a person, without listening to his own well-being, begins to carry out his usual routine. Here are the symptoms of a sudden heart attack:
- Severe pain in the chest, accompanied by palpitations. The pain can radiate to the neck, lower jaw, left shoulder blade or arm, and sometimes to the stomach.
- Nausea, heartburn, vomiting.
- Shortness of breath.
- Pale skin with cold sweat.
- Dizziness.
- Possibly increased blood pressure.
Causes of death from medications
Death occurs in 2% of cases due to medication use. To prevent such an outcome, you must adhere to the instructions and prescriptions of a specialist. It is worth understanding that an overdose or a combination of different drugs can lead to dangerous consequences.
Overdose
Overdose symptoms vary. As a rule, they manifest themselves in the form of attacks of nausea, dizziness, and convulsions. More serious conditions are accompanied by depression and cessation of respiratory function, hallucinations, visual disturbances, and cessation of heart function.
To neutralize the effect of a drug that causes cardiac arrest, you should try to induce vomiting, but only if the drug was taken in tablet form. After this, you need to call an ambulance or take the patient to the toxicology department yourself. It is advisable to have the packaging of the medication you took with you.
Use by children
A particularly dangerous situation in terms of overdose in children. The following symptoms will help you suspect that cardiac arrest is approaching and promptly respond to it:
- loss of consciousness;
- bluish or pale skin;
- rare breathing;
- lack of pulse;
- dilated pupils that do not respond to light.
The lack of resuscitation measures leads to hypoxic changes in tissues and organs, followed by the so-called biological death.
To help your child at home, you need to act quickly (about 5 minutes to spare). First of all, he needs to be laid on the table, undressed, and foreign objects removed from his mouth.
After this, the pads of the fingers apply pressure to the lower part of the sternum with a frequency of 120 shocks per minute. These manipulations are recommended to be carried out carefully, but intensively. After 15 compressions have been done, artificial respiration begins, 2 breaths into the mouth, and then into the nose. In parallel with resuscitation, an ambulance team is called.
Worsening of existing pathologies
It is highly undesirable to take any medications without your doctor's approval, especially if you have serious health problems. Pills that cause cardiac arrest act very quickly. It is easiest to harm yourself, but not everyone succeeds in restoring the functioning of the body. Therefore, you need to take your health as responsibly as possible. Optimal drug therapy should be selected only after a series of studies.
Competent first aid in case of cardiac arrest
The algorithm of actions at home in case of respiratory and cardiac arrest is as follows:
- reaction check;
- heart massage;
- clearing the airways;
- performing artificial respiration.
After calling an ambulance, specialists will carry out fibrillation and other necessary actions.
Any drug has a number of side effects, but the greatest caution should be taken with those drugs that can cause cardiac arrest.
For this reason, it is not recommended to take medications before examination and consultation with a doctor. Self-medication can be very dangerous and lead to so-called clinical death (cardiac arrest within 4-5 minutes), after which irreversible changes occur in the body, leading to biological death.
It is important to prepare in advance for a heart attack
No one can plan for a heart attack or know where or how it will happen, so it's best to be prepared in advance. This is especially true for those people who have an increased risk of developing myocardial infarction. Steps you can take before symptoms begin include:
- Memorize a list of heart attack symptoms and warning signs.
- Remember that you need to call an ambulance within 5 minutes after the attack begins.
- Talk to family and friends about the warning signs and the importance of calling emergency services immediately.
- Know your risk factors and do everything you can to reduce them.
- Create an immediate response plan for a heart attack that includes information:
- about the medications you need to take;
- about possible allergic reactions;
- about the telephone number of the attending physician;
- about all relatives who need to be contacted if you have to go to the hospital.
You need to store this information in your wallet or other quickly accessible place.
Additionally, you need to think about your wards in advance and talk with those who can take care of them if an emergency arises.
Video: HOW TO RECOGNIZE AND PREVENT A HEART ATTACK IN A MONTH
Cardiac glycosides
Cardiac glycosides are herbal preparations that normalize heart rhythm
Drugs in this group are used to improve heart function. They enhance the contraction of the heart muscle (myocardium), improve blood supply to organs and tissues, and thereby relieve swelling.
Many plants are natural glycosides, for example, lily of the valley, adonis. Medicines that cause cardiac arrest include glycosides, as they directly affect the heart, increasing its activity.
Glycosides enhance metabolism. These are usually herbal preparations, but this does not make them safe. An overdose and the wrong combination of drugs can lead to cardiac arrest. However, overdose is not the only danger. These drugs should only be taken after evaluation, as even small doses can be fatal for some people.
The risk group includes people with a large amount of calcium in the blood, a lack of potassium and magnesium, renal failure, thyroid dysfunction, and hypoxia.
The following drugs are classified as cardiac glycosides:
- Digitoxin. This drug significantly increases the force of heart contractions. It is prescribed for heart failure, chronic or acute. The drug tends to accumulate in the body, so the dosage must be strictly observed. The drug is taken orally. For indigestion, it can be used in the form of suppositories.
- Gomphotin. A cardiac glycoside of plant origin obtained from harga leaves. It increases the strength of heart contractions but decreases heart rate. It is prescribed, as a rule, for chronic heart failure, but is contraindicated in severe forms of cardiosclerosis.
- Strophanthin. A fairly strong glycoside, which is prescribed for various forms of heart failure, circulatory disorders, and supraventricular tachycardia. Not prescribed for acute myocardial infarction, thyrotoxicosis.
An overdose of glycosides causes tachycardia, dizziness, possible delirium and hallucinations. If these signs appear, you must immediately call an ambulance.
Muscle relaxants
The main purpose of using drugs to relax the muscles of the human body is anesthesia during surgery. The complete muscle relaxation caused by the injection of the drug into a vein helps the anesthesiologist to provide adequate pain relief during any surgical procedure. When the correct dose is used, only skeletal muscles are relaxed without a negative effect on the heart muscle. Natural muscle relaxants include the snake venom curare.
Drugs from this group are used only under the constant supervision of a doctor, so it is extremely difficult to provoke accidental cardiac arrest caused by muscle relaxants.
An overdose of the drug leads to relaxation of all types of muscles with a high risk of death in the absence of resuscitation care.
Preparations with potassium
Potassium is an essential trace element for the heart!
Potassium itself is an important trace element necessary for the normal functioning of the body. Potassium affects heart contractions and normal heart function. Cardiac arrest can be caused by both a deficiency and an excess of this microelement. Therefore, its level in the body must be carefully monitored.
Potassium supplements must be taken with caution. When administered intravenously, this substance is especially dangerous. The heart stops quickly even at the slightest overdose. In some countries, injections of pure potassium are used as a death penalty for especially dangerous criminals.
Causes of a heart attack
A month before the onset of a heart attack, a person may discover some of its precursors. Pay attention to them and at the slightest suspicion, consult a doctor:
- Extreme fatigue. When you don’t have the strength to even do simple actions at the beginning of the day.
- Mild migrating chest pain.
- Shortness of breath even at rest.
- Dizziness in the morning, cold sweat, pale skin.
- The appearance of edema that does not disappear for a long time.
- A condition similar to that of influenza.
If you do not consult a doctor promptly with these conditions, a heart attack may occur. Such symptoms accompany a microinfarction, which in the future may develop into a large one.
Antibacterial drugs and vitamin complexes
Self-medication is a threat to the heart
Many people consider antibiotics unsafe for various reasons, but people take vitamins without fear. However, vitamins can be dangerous not only if you take 50 tablets at once. Systematic intake of vitamin complexes increases the level of calcium in the blood. If a person already had heart problems, then excess calcium can lead to cardiac arrest.
To prevent bleeding, Vikasol is also often used, which is classified as a vitamin. But it can provoke the formation of blood clots. Antibiotics can cause cardiac arrest in the elderly, allergy sufferers, people with diabetes, severe heart failure, and angina.
Useful video - The most unusual causes of cardiac arrest:
Antibiotics from the macrolide group are considered the most dangerous drugs for the heart. They have a minimum of side effects for the intestines, but have a negative impact on the cardiovascular system:
- Azithromycin. A semisynthetic antibiotic that is often prescribed for the treatment of bacterial infections of the upper respiratory tract. Side effects from the cardiovascular system are considered rare (less than 1%), but if the patient is at risk, the effect on the heart will be greater.
- Clarithromycin. The most popular antibiotic prescribed for various infections. It quickly copes with bacteria and respiratory diseases, but at the same time has a negative effect on the heart and blood vessels.
- Vilprafen. Antibiotic based on josamycin. A fairly strong macrolide that is used to treat ENT organs and various bacterial infections. There are no contraindications for heart disease, but it is not recommended for people with heart failure.
- Clubax. A drug based on clarithromycin. Prescribed for otitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis, pneumonia, eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Not recommended for people with kidney and liver failure.
Macrolides are considered the least toxic antibiotics and are also easy to use. They need to be taken in 1 dose for 3-5 days. This is due to the fact that the drugs circulate in the blood for a long time, maintaining their effect, which also extends to side effects.
What should you keep in your first aid kit in case of a heart attack?
The heart is our friend, not our enemy, and our first aid kit must contain first aid in the event of an attack on it.
SOOTHING ROOMS. DRUGS FOR RELIEF OF ANXIETY AND PAIN SYNDROME.
The fact is that very often patients who complain of pain in the heart area do not actually have any special problems with the heart. And the cause of pain or interruptions in the functioning of the heart are such banal things as attacks of osteochondrosis, myositis or stress. At the same time, starting to get nervous due to discomfort in the heart area, patients can gradually bring themselves to a truly threatening state, including a hypertensive crisis, a severe attack of angina, asthma, etc. In medicine, “broken heart syndrome” is even described, when against the background of strong experiences (for example, after parting with a loved one), patients with absolutely healthy hearts developed heart failure. Therefore, you should definitely keep in your first aid kit:
CORVALOL (LAT. CORVALOLUM)
This is a calming, sedative drug based on menthol, ethyl ester of α-bromoisovaleric acid and phenobarbital. Available in the form of drops and tablets for oral administration, as well as sublingually (under the tongue). It is worth noting that Corvalol is practically unknown outside of Eastern Europe and the countries of the former USSR, although its German analogue (Valocordin) and the Polish analogue of Corvalol are available in EU countries. Travelers need to remember that Corvalol is prohibited for import into Lithuania, Norway, Poland and the USA as a narcotic drug, and if you have it in your first aid kit in these countries you may be prosecuted. Why is Corvalol banned in Poland and Germany, where its local analogue is produced and sold? It's more of a business issue than a drug war issue. However, you will not explain this to the customs officers. It is also necessary to remember that although Corvalol is a truly effective sedative and anti-anxiety drug, it should not be taken regularly and in large doses. If the dosage exceeds 25 ml, Corvalol causes serious neurological and cognitive disorders (short-term memory disorders, speech disorders, unsteadiness of gait - ataxia, especially in the case of brain disorders), suppresses sexual function.
VALIDOL (LAT. VALIDOLUM)
Another time-tested drug, well known to Russians since the times of the USSR. Validol is a drug with a reflex vasodilator effect, used as part of combination antianginal therapy. Available in drops, capsules and tablets. Composition: 1 tablet contains 60 mg of menthol solution in isovaleric acid menthyl ester. Available without a prescription. When administered sublingually, the effect of the drug develops after 5 minutes. The tablet should be kept under the tongue until completely dissolved. A single dose for adults is 1-2 tablets, a daily dose is 2-4 tablets. If necessary, the daily dose can be increased. Indicated for use in neuroses, hysteria, neurocirculatory dystonia of the cardiac type, angina pectoris (as part of combination therapy), seasickness and air sickness.
VALERIAN MEDICINAL, OR CAT HERB (LAT. VALERIANA OFFICINALIS)
The rhizome and roots of the plant are used for medicinal purposes. It is used as a sedative and as an antispasmodic (against the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) and urinary system). It also has a choleretic effect, increases gastrointestinal secretion, and dilates coronary vessels. Valerian can also be brewed as tea. Teas with valerian perfectly calm, normalize heart function and sleep, and improve digestion. When taking valerian root extract, the best effect is achieved with a single dose of 600 mg and a daily dose of 3 g. Valerian causes a stable sedative (calming) effect, and can also gently reduce blood pressure in arterial hypertension. However, it should be remembered that, although in principle valerian can be taken by everyone, its use is prohibited in the first trimester of pregnancy. And constant intake of valerian leads to drowsiness and decreased performance. The most useful valerian is harvested in late autumn.
NITROGLYCERIN (LAT. NITROGLYCERINUM, ENG. NITROGLYCERIN)
This is the common name for drugs containing glycerol trinitrate. Despite the fact that these tablets are inexpensive and far from new, they are very effective. Moreover, with all the abundance of modern drugs, there is nothing special to replace nitroglycerin in the first aid kit. Therefore, nitroglycerin still remains the drug of choice for relieving the symptoms of angina pectoris. Other organic esters and inorganic nitrates can also be used in this role, but the extremely rapid action and recognized effectiveness of nitroglycerin make it the main remedy for relieving angina attacks. Nitroglycerin relieves vasospasm, thereby improving blood circulation in the heart muscle and relieving pain. great sensations. Effective for the treatment and prevention of angina, which is characterized by attacks of chest pain. It is also successfully used in the complex treatment of the consequences of myocardial infarction. To relieve (eliminate) an attack of angina, nitroglycerin is used sublingually (the tablet or capsule is kept under the tongue until completely absorbed, without swallowing) immediately after pain occurs (0.5–1 mg per dose). If necessary, to achieve a faster effect, the capsule should be immediately crushed with teeth; the capsule can be taken again after 30–40 minutes. In many patients with stable angina, the effect occurs with a smaller dose (1/2–1/3 tablets), therefore, if the pain goes away quickly, it is recommended to spit out the remainder of the unresolved tablet. Typically, the antianginal effect appears within 1-2 minutes, 75% of patients note an improvement within the first 3 minutes, and another 15% within 4-5 minutes. If there is no antianginal effect during the first 5 minutes, you need to take another 0.5 mg of nitroglycerin. If there is no therapeutic effect after taking 2-3 tablets, you should immediately call a doctor! Duration of action after sublingual administration is about 45 minutes. For frequent attacks of angina, it is advisable to prescribe prolonged forms of nitrates. If an angina attack develops during treatment with long-acting nitrates, nitroglycerin must be taken sublingually to stop the acute attack. Tolerance to sublingual forms of nitroglycerin develops infrequently, however, if it occurs in some patients, the dose of the drug must be gradually increased, bringing it to 2-3 tablets.
OXYGEN (ADEQUATE OXYGENATION)
Oxygen therapy is a traditional method of treatment for myocardial infarction and can be used at home. Oxygen is able to very quickly eliminate hypoxia of body cells by supplying concentrated gas that can be inhaled directly through a mask. Today, oxygen cylinders are available in all sizes: from very tiny ones that can fit in a handbag, to large cylinders designed to breathe for tens of minutes. Except in emergency situations, an oxygen breathing mask can be used in conjunction with physiotherapy devices for respiratory therapy or inhalation. The mask can be used for breathing through the nose and through the mouth. This accessory is essential when carrying out oxygen therapy, providing maximum comfort. In everyday conditions, an oxygen canister with a mask is increasingly used to prepare foamy oxygen cocktails at home or at work, which can restore vigor and concentration, eliminate fatigue and lethargy, and relieve hangovers.
Other heart medications can appear in your medicine cabinet only as prescribed by your doctor! Do not be ill!
DNA HEALTH -
Psychotropic drugs
Psychotropic drugs are taken only under the supervision of a doctor!
Psychotropic drugs are typically prescribed by a doctor, sold by prescription only, and used to treat brain disorders. Psychotropic drugs inhibit mental activity, relieve anxiety and suppress emotions. They can cause cardiac arrest if overdosed or taken together with incompatible drugs or alcohol.
There are several groups of psychotropic drugs. They differ in composition and action. Some are dangerous even in small doses, others can lead to cardiac arrest only with a significant overdose (for example, sleeping pills).
- Neuroleptics. This type of medication helps eliminate hallucinations and alleviate the symptoms of schizophrenia. These drugs are never prescribed without indications. They are sold by prescription only and are intended exclusively for people with severe forms of schizophrenia.
- Antidepressants. Antidepressants fight depression, anxiety, and phobias. They are always taken in courses because they do not have an immediate effect. The maximum effect can be observed after approximately 2 weeks of use.
- Tranquilizers. These drugs eliminate more severe symptoms and can be classified as strong antidepressants. They relieve fear, panic, and anxiety.
- Psychostimulants. These drugs do not inhibit, but on the contrary, enhance mental activity, increase performance, give a feeling of vigor and reduce the need for sleep. The most accessible psychostimulant is caffeine.
- Sedatives. These are sedatives of synthetic or plant origin. In small dosages they are not dangerous. They have a general calming effect and normalize sleep.
These drugs have a number of side effects, such as causing uncontrollable and sudden muscle contractions. In case of an overdose, fever, delirium-like state, paralysis, and cardiac arrest occur.
Noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter to let us know.