Systemic pathology atherosclerosis has several types, which depend on the location of atherosclerotic plaques, and also differ in their form of plaque development.
Atherosclerosis can be either stenotic or non-stenotic. Also, sclerosis of the BCA can be with or without stenosis.
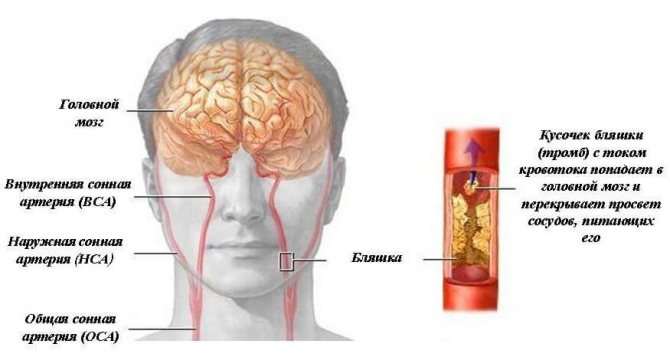
This pathology affects the brachiocephalic arteries, hardening them and blocking the normal flow of blood to brain cells. Narrowing of the lumen threatens to clog the arteries and stop the flow of blood into the cerebral intracranial vessels.
Quite often, stenosing atherosclerosis of the BCA, or carotid arteries, appears in elderly patients, when changes occur in the blood flow system and in the structure of the arterial membranes.
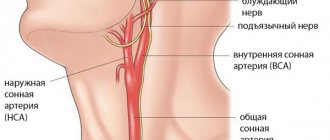
Brachiocephalic arteries and their function
The brachiocephalic arteries (BCA) are a system of arteries covering the brain and the entire right half of the shoulder girdle with several branches.
The origin of the artery is taken from the largest main vessel - the brachiocephalic trunk, which, in turn, connects the aorta and three leading arteries:
- subclavian;
- sleepy;
- vertebral
The subclavian and carotid arteries create a closed system at the base of the brain called the Circle of Willis.
Due to the fact that the blood supply to the brain is completely provided by this system of arteries, any disruption in their activity is fraught with serious complications, for example, acute cerebral hypoxia, hemorrhagic stroke.
Types and signs: how to recognize the disease?
When the vessels leading to the brain are damaged, symptoms such as ringing and noise in the head or ears appear.
There are:
- Atherosclerosis of extracranial sections, that is, vessels going to the brain. Signs of non-stenotic atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries: frequent dizziness and headache;
- noise and ringing in the head or ears;
- decreased performance and concentration;
- memory impairment for current events, absent-mindedness;
- persistent increase in blood pressure;
- “floaters” or whitish fog before the eyes;
- fatigue;
- fainting.
- Cheyne-Stokes breathing;
The disease is also divided into stenotic and non-stenotic types. Stenotic atherosclerosis of the BCA is characterized by complete narrowing of the vessel cavity by cholesterol plaque. In case of non-stenotic, the vascular lumen is partially blocked by the formation. Since the arteries supply the brain with oxygen, if the blood supply is disrupted, the organ tissues experience hypoxia.
If atherosclerosis of the BCA occurs with stenosis, signs of the disease may not appear immediately. In approximately half of the cases, the pathology does not bother the person until the irreparable happens - a cerebral hemorrhage. Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to symptoms, which, it would seem, do not indicate serious problems with blood vessels, but should alert you:
- dizziness for no reason and frequent headaches - they appear unexpectedly, but more often after trying to get up abruptly or a decrease in blood pressure;
- frequent mood swings - a cheerful, excited mood is replaced by depression and apathy, irritability;
- failures in the intellectual sphere - decreased performance, concentration and attention, forgetfulness, absent-mindedness;
- sudden loss of consciousness;
- ringing in the ears that occurs regularly and without reason;
- deterioration of visual function - “spots” flash before the eyes or colored (sometimes dark) spots appear;
- increased fatigue, a person cannot perform the same amount of work due to a constant feeling of fatigue;
- tingling and numbness in the limbs, cold hands and feet even in hot summer weather.
If such symptoms are not caused by any concomitant disease, then the patient should immediately think about the cause of the pathological condition and consult a doctor. The fact is that the signs of atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries remain hidden for a long time, manifesting themselves in the form of dizziness and fatigue.
A person may attribute deterioration in health to high physical activity, stress and fatigue and not realize that the disease is developing.
Atherosclerosis of the BCA
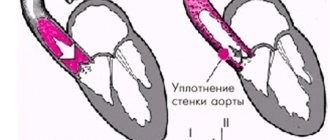
In a normal state, vessels of the elastic and muscular-elastic type, having a lumen in cross-section, ensure the flow of blood to the organs in a volume corresponding to the needs of a particular organ.
As a result of cholesterol deposits on the inner walls of blood vessels, atheromatous plaques form. In the future, the plaques do not continue to remain on the vessel wall, but they also begin to grow.
Connective tissue, enveloping deposits, grows into the walls of the vessel, creating destruction in the vascular tissues, and blocks the lumen until the vessel is completely blocked.
What does traditional medicine advise?
It cannot be said that traditional treatment is a panacea for BCA atherosclerosis. Although experts have proven that some means of such medicine are still capable of reducing the number and size of atherosclerotic plaques . Treatment with folk remedies should be carried out under the strict supervision of the attending physician, since independently made decisions regarding such therapy can have very unpleasant consequences.
The greatest therapeutic effect is provided by an alcohol preparation prepared on the basis of dry clover, which must be drunk for two weeks. Good results can be achieved if you apply compresses with nettle decoction to the BCA projection area every day for a month and consume a tablespoon of natural bee honey on an empty stomach.
Today, atherosclerosis of the extracranial sections of the brachiocephalic arteries is a very common phenomenon, which is diagnosed in every tenth patient over the age of 35 years. The older a person is, the more likely he is to get this disease. It is important to remember that the disease does not appear suddenly, but develops over several years. That is why everyone should be more attentive to their health, eat high-quality food and avoid bad habits, which will prevent the deposition of harmful cholesterol on the walls of blood vessels and help maintain their normal functioning for many years.
Types of atherosclerosis BCA
The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries has two development options:
- Non-stenotic atherosclerosis.
- Stenosing atherosclerosis.
- Diffuse atherosclerosis
In the first case, atherogenic damage grows along the vessel wall, causing its destructive changes (thickening, calcification), but does not block the lumen for blood flow.
In the second case, the proliferation occurs with closure of the lumen and leads to a complete stop of blood flow. Diffuse atherosclerosis is a manifestation of not the most severe form of the disease, as a rule, it has multiple lesions.
Diagnosis of atherosclerosis
If there are signs of atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries, a person is usually prescribed a number of different diagnostic procedures, through which doctors can assess the stage, and, in addition, the severity of the existing pathology. First of all, for these purposes, ultrasound examination of the relevant arteries is performed. In addition, patients are prescribed Doppler examination of blood vessels.
Such methods make it possible to assess the degree of narrowing of the lumen, the size of plaques, and the speed of blood flow. Establishing an assessment of these indicators allows specialists to select the optimal treatment for each patient individually.
Causes of vascular damage by atherosclerosis
The most common opinion about the causes of atherosclerosis is the consumption of fatty foods. This statement is partly true, since cholesterol contained in fatty foods can be one of the reasons for the development of atherosclerosis.
The main reason is dysfunction of the inner surface of the vascular wall (endothelium).
Endothelial dysfunction can have different origins:
- excessive accumulation of lipoproteins (LDL) in blood vessels;
- dysfunction of the protective mechanism of the inner surface of the vascular wall;
- damage to the vascular wall by leukocytes (inflammatory diseases of the vascular system);
- congenital defect of the vascular wall;
- viral damage to the vascular wall;
- damage to the vascular wall of a parasitic nature (chlamydia);
- hormonal disorders.
How it manifests itself
Signs of non-stenotic atherosclerosis include:
- headache, nausea, dizziness with normal blood pressure;
- general weakness;
- tinnitus that gets worse when you turn your head;
- decreased vision, spots before the eyes;
- numbness of the legs.
The most common symptom of BCA atherosclerosis is dizziness. A sharp turn of the head provokes its intensification, because arteries do not have time to redirect blood bypassing the affected area. Coordination of movements is often impaired, and a person may fall and be injured.
As cholesterol clots accumulate and the arteries narrow, symptoms increase. The patient develops headaches that are associated with increasing cerebral ischemia.
Atherosclerosis often spreads to the entire aorta or to individual sections of it. The following symptoms occur:
- aortic murmurs;
- migraine;
- blood pressure surges;
- abdominal pain that is not associated with eating;
- cough and hoarseness.
With the development of non-stenotic atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities, the following symptoms are observed:
- limping when walking, because pain appears in the calf muscles;
- leg cramps at night;
- spontaneous disappearance of pain after rest;
- cold feet, even if they are warm;
- weakening of the pulse upon palpation below the blockage.
The development of non-stenotic atherosclerosis of extracranial and brachiocephalic arteries is possible, which has an unfavorable prognosis.
Diagnostics
To accurately diagnose non-stenotic atherosclerosis of the arteries of the lower extremities, aorta and extracranial arteries, Doppler ultrasound is used. Such a study helps to identify damage to the walls of blood vessels, determine the speed of blood flow and the degree of development of stenosis.
In addition, the following methods are used to make a diagnosis:
- General blood analysis. Reveals an inflammatory process in the body.
- Blood chemistry. Helps determine the ratio of the amount of good and bad cholesterol and the value of other indicators that affect the appearance of atherosclerotic plaques.
- Vascular ultrasound. With the help of such a study, the location of plaques and their size, the degree of disruption of blood flow and narrowing of the artery, and the condition of the inner surface layer of the walls of blood vessels are determined.
- X-ray with contrast. A contrast agent is injected into the affected artery, thereby determining the condition of the vascular walls and the degree of narrowing of the blood vessels.
- Auscultatory and palpation techniques. Allows you to identify pulsation disorders in the legs.
The mechanism of formation of atherosclerotic plaques
The development of atherosclerosis is a complex process of interaction between lipoproteins and leukocytes.
Cholesterol consists of:
- low density lipoproteins (LDL);
- very low density lipoproteins (VLDL);
- high density lipoproteins (HDL).
Normally, the inner surface of the arteries (endothelium) is smooth, and minor damage leads to the formation of a lipid stain on the surface. Only LDL and VLDL have atherogenic properties, that is, the ability to close damage on the surface of the endothelium.
Provided that metabolic processes are normal and the blood flow rate in the body is satisfactory, endothelial tissue is restored and the lipid stain is subsequently rejected.
HDL is directly involved in the rejection process, the high content of which significantly reduces the risk of developing atherosclerosis.
The impact of negative factors that violate the integrity of the endothelium (smoking, alcohol) introduces an imbalance in the interaction of HDL and LDL, the latter begin the process of plaque formation. Blood flow speed plays a major role in the development of atherosclerosis. It has been proven that the higher the speed, the lower the likelihood of the formation of atherosclerotic plaques.
You should know: Regular aerobic exercise significantly reduces the risk of developing atherosclerosis, as it increases the speed of blood flow
Drug treatment
To undergo therapy, the patient is registered with a neurologist. The course of treatment is determined by a specialized specialist, individually for each patient. The only general requirement is the need for lifelong use of antiplatelet agents. This is aspirin and other blood thinning medications. The second mandatory element of drug therapy is control of blood cholesterol levels. Even when limiting the consumption of cholesterol-containing foods, you must not forget about monitoring. There are two reasons for this:
- Less than 20% of cholesterol enters the body with food, the rest of the substance is biosynthesized in the liver.
- The main contribution to the growth of atherosclerotic plaques is made by “internal” cholesterol.
You can begin to follow these simple rules without identifying the disease. They turn out to be an effective prophylaxis to prevent atherosclerosis of the BCA.
Signs of development of atherosclerosis of the BCA
The first manifestations of BCA atherosclerosis, as a rule, are dizziness, which manifests itself with sudden movements of the head. This phenomenon indicates a decrease in oxygen supply to the brain.
The main signs of the development of atherosclerosis of the BCA are:
- dizziness;
- noise in ears;
- lack of coordination;
- visual impairment;
- numbness of the limbs;
- angina pectoris;
- loss of consciousness;
- headache;
- sleep disorders;
- memory loss
Symptoms
The symptoms of systemic atherosclerosis depend on the location of atherosclerotic changes in the vessels. When the aorta is damaged in the abdominal cavity, symptoms appear in the digestive tract; with atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries, the heart organ suffers.
If atherosclerosis develops in the arteries of the lower extremities, then the legs suffer.
Atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries is the most dangerous type of pathology, because the BCAs are located quite close to the brain, and they supply the brain vessels and cells with blood.
Symptoms and signs of atherosclerotic changes in the BCA:
- Sleep apnea;
- Circling in the head of varying intensity;
- Head pain;
- Fog in the visual organ;
- Decreased vision;
- Flashing of flies before the eyes;
- Constant fatigue of the body and very rapid fatigue;
- Weakness in the body;
- Insomnia at night, and severe drowsiness during the day;
- Darkening in the eyes;
- Fainting;
- Temporary loss of consciousness;
- Disorientation in space;
- Decreased memory;
- Decreased intellectual abilities;
- Problem with concentration;
- Psychical deviations;
- Overexcitement;
- Behavioral change and aggression;
- Constantly cold feet and hands;
- State of depression.

Behavioral change and aggression
Symptoms of the development of atherosclerosis begin with dizziness and pain in the head.
As the disease progresses, painkillers no longer help the patient.
With the development of sclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries with stenosis, dementia begins to progress in a person and the patient begins to have poor control of his emotions and his behavior.
In addition to the general symptoms of atherosclerosis of the BCA, there are pronounced signs of stenotic atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries and the development of cerebral stroke in the severe process of stenosis of the main vessels in the brain.
The first symptoms of a cerebral stroke:
- Paresis appears;
- Paralysis of body parts;
- Asymmetry in the face;
- Photosensitivity and sensitivity of organs disappear;
- The functioning of the speech apparatus is disrupted - the patient cannot pronounce words;
- Loss of hearing, possible complete deafness;
- Vision is greatly reduced to the point of complete blindness;
- The functionality of the pelvic organs is impaired - the patient cannot control the process of urination;
- Coma state.
Quite often, the development of a cerebral stroke leads to death.
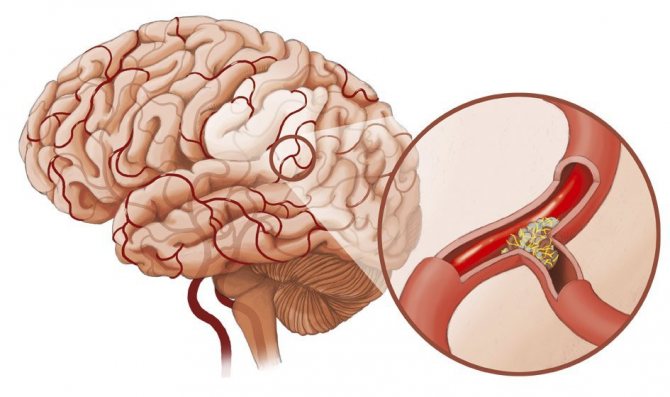
Brain stroke
Diagnosis of atherosclerosis
Diagnosis of atherosclerosis is carried out based on the manifestations of signs of its development. Very often, the development of the disease is asymptomatic and pronounced symptoms occur when the blockage of the vessel is more than 75%.
Timely diagnosis makes it possible to identify foci of atherosclerosis generation in order to determine further treatment strategies.
Diagnostic methods used to detect atherosclerosis:
- blood cholesterol test (LDL, HDL);
- Dopplerography;
- duplex scanning of the vessels of the lower extremities;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Carrying out an examination using Doppler ultrasound allows you to visualize the volume of blood flow and, by volume and speed, identify areas with disturbances.
The duplex (triplex) scanning method allows you to obtain more detailed information about the state of the vascular system:
- vessel wall thickness;
- the size of atherosclerotic lesions;
- the presence of congenital and acquired deformities;
- the size of the vessel lumen;
- degree of elasticity of the vascular wall;
- blood flow speed;
- presence of an aneurysm
Duplex scanning is the most used method, as it combines accessibility, security and information content.
An MRI examination makes it possible to obtain a three-dimensional image of the affected area and identify any pathologies at the earliest stages.
You should know: MRI is contraindicated for people with a pacemaker or implanted metal objects (Elizarov apparatus)
Causes and risk factors
The disease is mainly diagnosed in people over 40 years of age. The exact cause of the formation of the pathology is currently unknown. Risk factors contributing to the development of the disease:

The man smokes. A bad habit is harmful to the whole body, but it has a particularly negative effect on blood vessels. Vascular walls become brittle, hypertensive attacks and vasoconstriction occur. This leads to atherosclerosis.- High cholesterol levels. It is this that forms the basis of atherosclerotic plaques. Fat covers the vascular and arterial walls, as a result the lumen gradually narrows. Blood circulation is impaired, which leads to the formation of the disease.
- Hypertension. At first, atherosclerosis forms without stenosis, but then the disease progresses, the vessels are damaged, become fragile and lose elasticity. Stenotic atherosclerosis of the BCA is formed.
- Hormonal balance is disrupted (often due to the use of contraceptives).
- A person leads a sedentary lifestyle.
- Predisposition at the genetic level.
Treatment of atherosclerosis BCA
Drug treatment
Drug treatment for atherosclerosis is designed to maintain the patient’s current condition and prevent further progression of the disease. Drug therapy is carried out in the following areas:
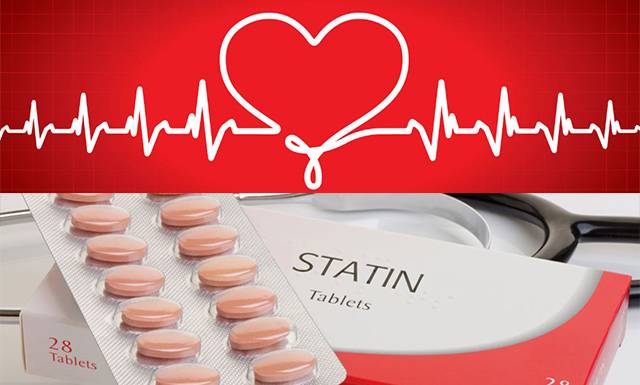
- Reducing blood cholesterol, in order to reduce the risk of further development of atherosclerosis. For this purpose, the following drugs are used:
- statins;
- vitamin PP (nicotinic acid);
- substances containing high density lipoproteins (HDL);
- vitamins A, E
- The use of vasodilators for relieve symptoms of hypertension and reduce the risk of stroke:
- antihypertensive drugs;
beta blockers;
- calcium channel blockers;
- angioprotectors. We tell you what angioprotectors are here.
- Prevention maintaining the tone of the vascular wall:
- hypoglycemic drugs;
ATP drugs;
- thiamine (vitamin B1)
- Decreased blood clotting rate:
- antiplatelet agents;
anticoagulants
The drugs have a vasodilating effect, relieve vasospasm, allowing you to partially restore the required volume of blood flow.
Hypoglycemic drugs, maintaining normal glucose levels, slow down the process of destruction in damaged vessels.
ATP and thiamine preparations promote restoration and metabolic processes in tissues, maintain the tone and elasticity of the vascular wall.
Antiplatelet agents have the ability to block the ability of platelets to “stick together,” which helps reduce the risk of stroke when a blood clot breaks off or when a plaque ruptures.
Anticoagulants help normalize blood flow through problem areas by reducing its viscosity. Read more about what anticoagulants are here.
Surgical intervention
- Carrying out an operation to replace (prosthetics) the site of vessel destruction.
- Carrying out endovascular surgery (stenting).
- Carrying out balloon angioplasty;
- Carrying out open surgery to remove the plaque with subsequent restoration of the vessel.
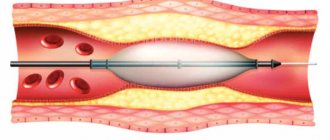
Stenting is the least traumatic of all the above invasive surgical methods. The method does not require the use of anesthesia; the patient remains conscious throughout the operation.
At the site of blockage of the vessel, a stent is installed, which expands, supports the walls of the vessel and opens up the possibility of normal blood flow. Stents with medication are used (such stents do not allow plaque to form again) and without medication.
Angioplasty is also performed endoscopically, but unlike stenting surgery, the vessel is stretched using a balloon inserted into the vessel, and a stent is not installed.
Other methods involve open intervention followed by removal of either an atherosclerotic plaque or a fragment of a vessel
Physiotherapeutic procedures aimed at improving blood oxygen supply showed good results. For example, oxygen or radon baths.
Features of treatment
Atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries cannot be completely cured. The goal of therapy is to slow down the development of the disease and prevent the development of complications. At the initial stage, you can try to get by with diet and lifestyle changes. More serious forms of BCA atherosclerosis require medications and surgical intervention. When choosing a treatment method, the doctor takes into account the degree of narrowing, the general condition of the patient, and the presence of signs of previous micro-strokes.
Lifestyle, diet
Non-stenotic atherosclerosis of BCA can be tried to be stopped without resorting to drugs or surgery. To do this, you need to move more, quit smoking, do not abuse alcohol, and try to avoid stress.
Proper nutrition plays an important role. The goal of the diet is to limit the consumption of saturated, trans fats, which are responsible for high cholesterol, sugar, which can cause diabetes.

They contain a lot of saturated and trans fats:
- fast food, unhealthy snacks;
- butter;
- salo;
- red meat;
- sausages, sausage products;
- whole milk, cream, fatty cheeses, cottage cheese;
- coconut, palm oil;
- coconut cream;
- cakes, pastries with butter cream.
Moderate consumption of liver, shrimp, and eggs is allowed. Although these foods contain a lot of natural cholesterol, they do not affect blood sterol levels.
Plant foods do not contain cholesterol. Therefore, whole grain cereals, vegetables, fruits, herbs, and legumes should become the main components of the diet.
It is especially worth paying attention to:
- barley;
- oatmeal;
- oat bran;
- baked beans;
- beans;
- lentils;
- vegetables rich in soluble nutritional fiber: eggplant, sweet potato, zucchini;
- tofu;
- unsalted walnuts, cashews, pecans, peanuts.
Include turmeric and garlic in your diet. These products have a hypolipid effect, which helps control atherosclerosis.
A healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition can significantly increase the effectiveness of other methods of treating atherosclerosis. In some cases, diet is a prerequisite for successful therapy.
Conservative therapy
Treatment of BCA atherosclerosis without surgery is indicated for asymptomatic forms or for minor vasoconstriction. Drug therapy is prescribed to patients who have contraindications to surgery.
The standard treatment regimen includes drugs from the following groups:
- anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents (aspirin, warfarin). When an artery narrows, the likelihood of blood clots increases. Firstly, at the site of narrowing, blood flow slows down, which creates favorable conditions for cell adhesion. Secondly, atherosclerotic plaques can damage the vessel wall, which provokes the formation of blood clots. The use of anticoagulants helps prevent these processes;
- medications that lower cholesterol levels. Statins, cholesterol absorption inhibitors, fibrates, bile acid sequestrants, omega-3 fatty acids are all drugs of choice for normalizing sterol levels. The most effective of them are statins. Reducing cholesterol and individual lipid fractions stops the growth of atherosclerotic plaques;
- antihypertensive drugs. Drugs in this group reduce blood pressure. With abnormal pressure levels, the walls of blood vessels experience increased stress. After some time, they become inelastic and are easily damaged. All these are prerequisites for the development of atherosclerosis.
Surgery
Treatment of stenotic atherosclerosis of advanced forms of brachiocephalic arteries requires surgery. Other indications for surgical intervention are having suffered one or more micro-strokes. The purpose of the procedure is to restore normal blood flow by increasing the lumen of the vessel.
There are several methods of surgical treatment:
- Angioplasty (stenting) is the most non-traumatic operation. A catheter with a deflated balloon at the end is inserted into the vessel through a tiny incision. Using a special monitor, the doctor controls the location of the catheter and gradually moves it to the site of narrowing. Having reached the atherosclerotic plaque, the balloon is inflated. The deposit takes on a flat shape, and the lumen of the vessel expands. To consolidate the result, a miniature spring - a stent - is delivered there using a catheter in a folded state. When it is opened, a metal frame is formed that keeps the lumen of the artery widened.
- Shunting. An operation involving minimal intervention. To provide the brain with an adequate amount of blood, an artificial or natural vessel is sewn above and below the site of narrowing. Thanks to this, instead of trying to “break through” the narrow gap between the artery wall and the cholesterol plaque, the blood begins to flow along a spacious bypass path.
- Endarterectomy. Atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries sometimes requires complete removal of the deposit. This surgical method is the most traumatic. Through the incision, the doctor provides access to the diseased artery. Clamps are applied above and below the narrowed area, and the atherosclerotic plaque is excised. The operated artery and the wound are sutured. During surgery, the brain is supplied by other brachiocephalic arteries.
ethnoscience
Before the first symptoms appear, you can try to get rid of atherosclerosis using traditional methods. We have collected the most effective recipes for you:
- Buckwheat jelly. Add 3 tbsp to a glass of cold water. l. buckwheat flour, mix well. Boil 1 liter of water, add the preparation to it. Cook over low heat for 5-7 minutes. To improve the taste, add 1 tbsp. l. honey Drink 100 ml in the morning and evening for a month.
- Salad that lowers cholesterol. Peel the raw carrots and grate them. Add finely chopped grapefruit to it. There is no need to remove white veins. Season with 2 tsp. honey mixed with low-fat kefir, sprinkle with nuts.
- Pumpkin juice. Prepare 150 ml of freshly squeezed pumpkin juice. Drink the indicated amount 1-2 times/day 10-15 minutes before meals. Gradually increase your daily juice intake to 2-3 glasses/day. It is allowed to dilute the drink with cold water (ratio 1:1). Pumpkin juice is contraindicated for high acidity, stomach ulcers, and diabetes.
- Decoction of rosehip, hawthorn. Pour 25 g of the fruit mixture into 200 ml of boiling water, let it brew for 5 minutes. The infusion is drunk before meals, as well as a glass of drink at night.
- Pollen. Three times a day, 30 minutes before meals, eat 1 tsp. flower pollen. Duration of therapy is a month. Repeat after 2 months. You can take four such courses in a year.
- Herbal decoction. Mix 10 g of valerian root, 15 g of rue herb, 25 g of flowers, hawthorn fruits. Pour a tablespoon of the mixture into a glass of cold water and let it brew for 4 hours. Put on fire, bring to a boil, cook for 4 minutes, let stand for 15 minutes. Drink 1 glass in the morning and 1 glass in the evening.
BCA atherosclerosis is not recommended to be treated with “grandmother’s recipes”, only after consultation with a doctor. Herbal medicines, like synthetic ones, have a number of contraindications, side effects, and can interact with medications that a person takes.
Prevention of atherosclerosis BCA
You should think about preventing the development of atherosclerosis even before symptoms appear. But even in the presence of a diagnosed disease, adherence to certain rules will contribute to positive dynamics in treatment.
For the purpose of prevention, it is necessary to adhere to certain rules:
- maintain a sleep schedule;
- perform feasible aerobic exercise (walking, swimming) every day;
- eliminate smoking;
- stop drinking alcohol;
- limit the consumption of animal fats;
- monitor blood sugar levels (especially for people with diabetes);
- During the postmenopausal period, women should use hormone replacement therapy to prevent a decrease in estrogen levels, which prevents the development of atherosclerosis.
The application of all these measures should not be temporary, but should become a way of life.
The main causes of atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries
Atherosclerosis does not occur overnight; it develops over many years, causing gradual vascular damage and circulatory dysfunction. There is no single cause of the disease.
But there are several factors that provoke and accelerate its development:
- improper and unbalanced diet with excess fat, which increases cholesterol levels;
- a sedentary lifestyle, which provokes congestion in the circulatory system and metabolic disorders;
- bad habits, especially smoking, which reduce the elasticity of blood vessels and increase blood pressure;
- excess body weight, which puts a strong burden on the entire body;
- arterial hypertension with constant surges in blood pressure;
- immune and endocrine diseases, including diabetes;
- persistent hormonal disorders and concomitant hormonal therapy that thickens the blood;
- congenital predisposition to atherosclerotic changes.
All these unfavorable factors can cause atherosclerosis of the BCA, which after 40–50 years manifests itself with unpleasant symptoms and deterioration in well-being.
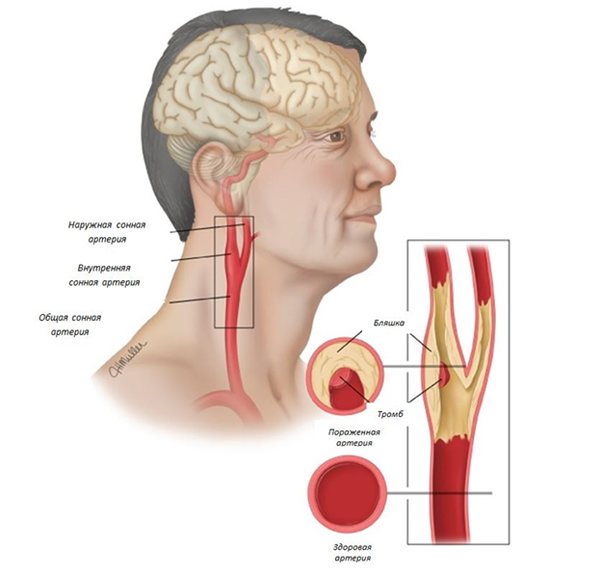
The brachiocephalic arteries are a set of vessels that supply the brain
How to cure
Treatment of non-stenotic atherosclerosis of the BCA, aorta and leg arteries should be aimed at preventing its transition to stenotic atherosclerosis, which has a more severe course. To do this, the doctor recommends leading a healthy lifestyle, prescribing medications that thin the blood and prevent the formation of blood clots, medications that normalize the lipid composition of the blood, medications that dilate blood vessels, and vitamin complexes necessary to maintain the vascular system. In severe cases, a stent is placed on the affected area of the artery.
Medicines
Non-stenotic atherosclerosis of the extracranial parts of the BCA, aorta and arteries of the lower extremities responds well to conservative therapy without surgical intervention.
The doctor prescribes the following medications to patients:
- Statins are medications that inhibit enzymes that promote the production of cholesterol, prevent the formation of blood clots and the development of inflammation, and reduce the amount of bad cholesterol. These include Simvastatin, Simvacard, Vasilip.
- Fibrates - under their action, harmful fats break down, blood flow is restored, glucose levels are normalized, and atherosclerotic plaques are resolved. But such drugs are contraindicated for cholecystitis, diseases of the pancreas, liver and kidneys. These include drugs such as Clofibrate, Fenofibrate, Bezafibrate.
- Nicotinates are medications based on nicotinic acid. With their help, the level of triglycerides and bad cholesterol is reduced, the body's lipid balance is restored, and the amount of good cholesterol in the blood increases. These include nicotinic acid, Niacin.
- Omega-3 triglycerides. They help normalize metabolic processes, reduce the amount of bad cholesterol, and prevent the formation of blood clots. This is fish oil, Omacor.
- Natural herbal dietary supplements that normalize lipid levels. These include Ravisol.
- Antiplatelet agents, anticoagulants are drugs that slow down the rapid clotting of blood, prevent the formation of blood clots, and have an anti-inflammatory effect. These are the following medications: Aspirin, Sinkumar, Warfarin.
- ACE - used for high blood pressure. The most commonly prescribed drug is Captopril.
- Venotonics for external use - restore the patency of blood vessels, strengthen their walls, and normalize the tone of the veins in the legs. These are drugs such as Lyoton, Troxerutin.

By surgical methods
Surgical treatment methods are used when dangerous lesions of blood vessels are detected. The following surgical methods exist for the treatment of non-stenotic atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries, vessels of the lower extremities and the aorta:
- An open operation that is performed when the artery is severely blocked. Part of it is removed, and an artificial prosthesis is installed in this place. In some cases, the vessel is sutured.
- Endovascular surgery. In the place where the plaques are found, a stent is installed, which widens the vessel. This method is the most gentle, and the patient returns to a normal lifestyle after a few days.
Prevention
In order to prevent the development of atherosclerosis of the extracranial parts of the brachiocephalic arteries, aorta or vessels of the lower extremities, or to improve the condition of such a disease, you need to adhere to the following preventive measures:
- do not overeat;
- engage in physical therapy, swimming, dancing, yoga;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- limit salt intake;
- get enough sleep;
- avoid stressful situations;
- exclude from your diet fried foods and foods containing large quantities of animal fats (lamb, liver, lard, butter);
- limit the consumption of sweets (cakes, sweets, cakes, etc.);
- The diet must include cereals, fruits, vegetables, cottage cheese, kefir, and low-fat yogurt.
The patient should eat boiled poultry, boiled or steamed fish, egg whites and seaweed 3 times a week. When the first signs of the disease appear, you should visit a doctor who will prescribe the correct treatment.
Characteristics of the pathology
Gradual overgrowth of the vessel with cholesterol plaques is observed to one degree or another in every person. But the problem is especially acute for those who have crossed the 40-year-old threshold. The main causes of the pathology are an unbalanced diet, a sedentary lifestyle, as well as addiction to bad habits and exposure to frequent stress.
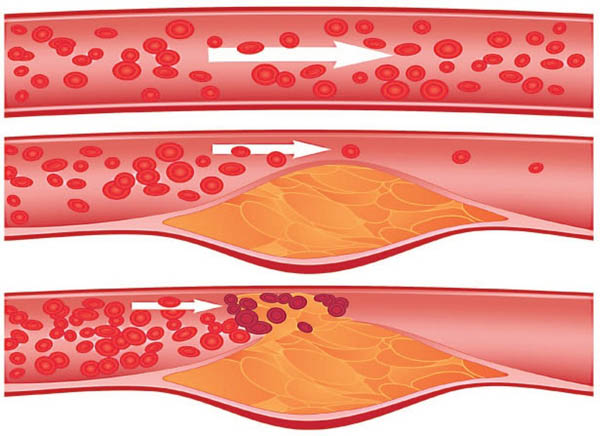
The process of the appearance of atherosclerotic blood clots occurs in several stages:
- As a result of frequent surges in blood pressure, inflammatory processes, or toxic-chemical damage, the inner surface of the lining of the arteries receives injuries of varying severity.
- Special macrophage cells, which are activated in response to tissue irritation, use lipid cells to treat damaged blood vessels.
- At the site of the wound, a microscopic plaque of blood cells and fats appears, which, when growing, interferes with the normal transport of nutrients and oxygen along with the blood flow.
Important! As the size of the lipid thrombus increases, atherosclerotic stenotic vascular lesions develop, which is dangerous due to complications, including death.
When the affected areas grow, diffuse atherosclerosis is diagnosed. It simultaneously affects the walls of various large vessels.
Depending on the type of arteries affected by the disease, various types of non-stenotic atherosclerosis are distinguished. The largest vessels of the general circulation, through which organs and systems are supplied with oxygen and nutrients, are the subclavian, pulmonary, brachycephalic, carotid, carotid arteries, as well as the main arteries of the head and the aorta. The location of lipid plaques affects both the manifestation of the clinical picture and treatment methods.
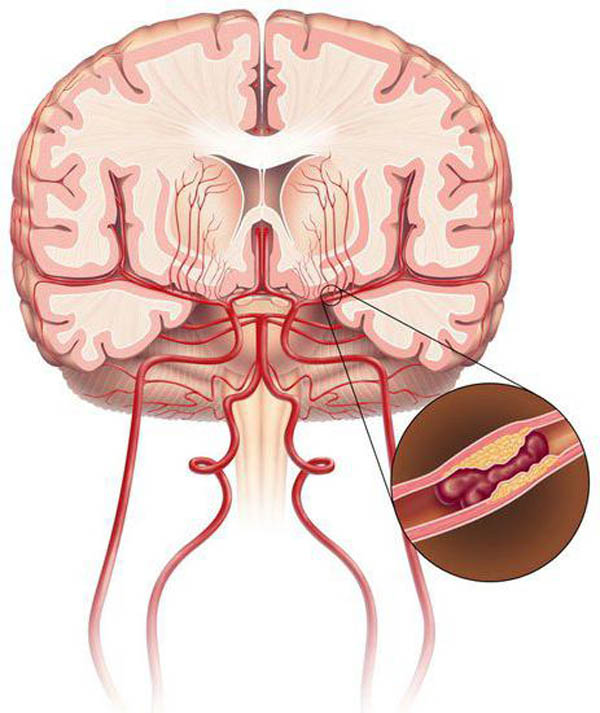
Prevention
The prognosis for the development of the disease is determined by the patient’s lifestyle. The progression of the pathology can be stopped by eliminating existing risk factors and active drug therapy.
Prevention of vascular problems should be carried out comprehensively.
If there is any risk of developing pathology, you must:
switch to proper nutrition;
stop smoking;
reduce stress factors;
devote time to physical activity.
Prevention is impossible without regular examinations and visits to the doctor. We recommend seeing a cardiologist for anyone who has a history of problems or has negative heredity.
Causes of the disease
The main cause of non-stenotic atherosclerosis of the extracranial brachiocephalic arteries is high cholesterol levels in the blood plasma.
Factors in the development of pathology include:
Patient's age. The disease usually develops after 40 years of age.
Excess weight. Obesity signals a violation of metabolic processes.
Bad habits (smoking and excessive alcohol consumption).
High blood pressure. Hypertension itself is a consequence of high cholesterol. In addition, it causes an increase in blood viscosity and slows down its circulation.
A sedentary lifestyle leads to slower blood circulation and a reduction in the nutrition of organs with valuable substances.
An unhealthy diet with a large amount of animal fats, which increases the level of low-density lipoproteins in the blood.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of pathology includes:
Inspection. At the appointment, the specialist finds out the patient’s complaints and risk factors for his disease. On a general examination, various atherosclerotic lesions are identified.
Laboratory research. Before treatment, the patient must take a blood test, which allows you to study the level of cholesterol, triglycerides and lipoproteins.
Angiography. This study evaluates blood flow disorders.
Aortography. This examination is carried out to detect elongation of the aorta and its thickening, calcification, expansion in the thoracic or abdominal regions, and aneurysms.
Coronary angiography. This examination is effective for assessing the condition of the coronary system.
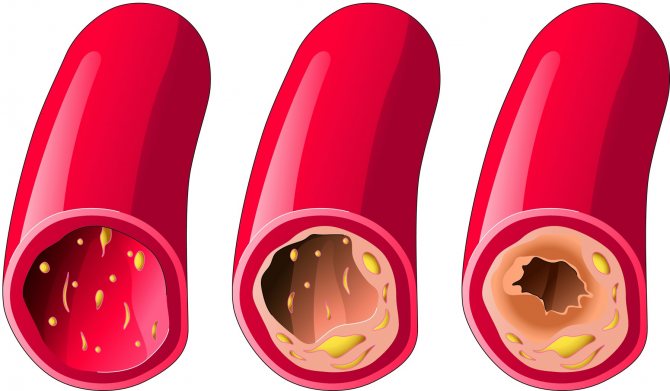
Other modern techniques are also used for diagnosis. They allow not only to make an accurate diagnosis, but also to predict the development of pathology, assess the patient’s condition, select the right medications, and adjust their dosage during therapy.
Treatment
A number of techniques are used to treat non-stenotic atherosclerosis. The patient must always adhere to all doctor's recommendations. Only in this case will he be able to prolong the period of active life and avoid negative consequences (complete blockage of blood vessels, strokes and death).
To prescribe optimal therapy for non-stenotic atherosclerosis, the doctor:
Determines the stage of the disease.
Records general symptoms.
All medications are prescribed individually and take into account the patient’s condition.
As a rule, patients take:
Anticoagulants. This reduces the risk of blood clots and strokes.
Medicines to lower blood pressure (if it increases). Such remedies can reduce the load on the arteries, dilate blood vessels, improve blood flow and relieve spasms.
Medicines to lower cholesterol levels. Typically, such drugs are taken throughout life after atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries is detected.
It is also very important to constantly monitor the patient's lipid balance. If necessary, sedatives are prescribed. They allow you to normalize the emotional background, avoid depression, improve the quality of sleep, and get rid of headaches. Patients are often prescribed physiotherapy.
The decision to undergo surgical intervention is usually made if the passages are significantly narrowed and the disease has reached a high stage of development.
The following types of operations are carried out today:
Removing part of the artery and replacing it with a prosthesis.
Stitching a vessel to reduce its size.
Endovascular operations are increasingly being performed. They are as safe as possible, and recovery from them takes a short period of time.
Are you interested in all the features of therapy? Contact our specialists. You will not have to overpay for a consultation. Prices are indicated on the website. Note! The cost is approximate. The exact price of therapy will be announced by your attending physician. In any case, you will not overpay. Our private clinic in Moscow adheres to a loyal pricing policy.