Bilirubin is a red-brown compound formed during the breakdown of hemoglobin. In both adults and children, it is present in the blood and bile. The liver is responsible for the production of this organic substance.
Serum bilirubin concentration is the most important diagnostic marker with which doctors can identify the presence of various pathologies. According to statistics, increased bilirubin in the blood is almost always detected in cases of jaundice, liver pathologies, and bone marrow dysfunction.
Bilirubinuria is often diagnosed not only in adult patients, but also in newborns. Since this condition indicates the presence of pathogenic processes, it is necessary to immediately find out what was the root cause of the increase in the amount of the compound.
What does bilirubinuria mean?
Bilirubin - what is this substance? This is one of the most important products of the breakdown of red blood cells, which is produced continuously. The importance of bilirubin cannot be overestimated, since it is responsible for many metabolic processes.
Initially, only indirect bilirubin is formed in the blood and tissues, which in itself is a toxic compound. Since this type of substance does not change structure when in contact with water, it is quite difficult to remove from the body.
If a person is healthy, indirect bilirubin will be delivered to the liver, then processed and transformed into direct bilirubin. Excretion from the body occurs during defecation and along with urine.
Doctors assure that this product of the breakdown of red blood cells is not initially dangerous to health; only its increased content can cause harm.
If an adult has an increased concentration of this substance in the body, this condition will be accompanied by certain external manifestations. Sure signs of deviation are yellowing of the skin, eye whites and mucous tissues. If these symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a doctor.
An increased pigment content is diagnosed if its value per liter of blood exceeds 30 µmol.
Symptoms of bilirubinuria
If the metabolism of bilirubin is impaired, its serum level begins to increase. The following symptoms occur:
- change in the shade of the epidermis and mucous membranes (tissues become yellow-gray);
- darkening of urine to a dark brown hue;
- change in color of stool to a lighter color;
- the appearance of bitterness in the mouth, which will not go away even after eating;
- general weakness of the body and decreased muscle tone;
- impaired attention and memory impairment;
- increased liver volume and discomfort in the hypochondrium on the right side.
The diagnosis depends on how much the indicator exceeds the permissible value. If the pigment concentration is no more than 85 µmol/l, the patient is diagnosed with a mild form of bilirubinuria.
Moderate jaundice is confirmed at levels of 85-170 µmol/l, severe form is diagnosed when the value exceeds 170 µmol/l.
It is important to remember that the severity of symptoms largely depends on what type of jaundice the patient is experiencing.
Infectious liver inflammation
Mainly hepatitis. In the vast majority of cases, there is a viral form caused by one of the known strains.
At the same time, there are other types of pathological process. Toxic, drug-induced or alcohol-induced. No comments here.
Sooner or later, the disorder progresses to the death of liver cells, the so-called cirrhosis. Indirect bilirubin is increased, since the organ is not able to inactivate toxic substances; they remain in the form in which they were originally formed, which is very dangerous.
Hepatitis, regardless of type, is accompanied by a characteristic clinical picture.
Among the manifestations:
- Sharp pain in the right side. Pulling or pressing. Shooting.
- Burning and stinging are not typical.
- Discomfort in the same area.
- Unpleasant feelings after eating.
- Increased production of intestinal gas.
- Nausea.
- Vomit.
- Jaundice. Changes in the color of the dermis and sclera of the eyes.
- Impaired consciousness.
- Increased body temperature.
- Decreased blood flow. Insufficient coagulation as a result of poor production of special substances-factors.
Treatment takes place under the close supervision of a hepatologist. Sometimes a gastroenterologist is brought in instead; the required specialist is not always on staff.
Therapy consists of the use of hepatoprotectors and special antivirals. Sometimes such treatment is carried out for many years to maintain the organ in normal condition. Or in courses, systematically.
Increased bilirubin in the blood is the result of liver damage, for the most part, since this is where the indirect form of the substance is inactivated.
Causes of elevated total bilirubin levels
The amount of total bilirubin in the blood may increase due to a variety of factors, but in most cases this disorder is provoked by the following reasons:
- Too rapid breakdown of red blood cells (an individual feature of the body’s functioning).
- The presence of stones in the kidneys and other organs of the genitourinary system.
- Impaired flow of bile.
- Jaundice.
- Formation of benign or malignant neoplasms on the walls of the liver.
- Biliary cirrhosis.
- The presence of parasites in the body.
- Problems with the production of enzymes on which the production of bilirubin depends.
- Hepatitis of various forms provokes changes in the structure of the liver, which leads to partial dysfunction of the organ.
Depending on what exactly is the primary source of the pathology, the concentration of not only total bilirubin, but also its fraction may increase in the serum. If, according to tests, an increase in the general indicator is diagnosed, then the reason for this is problems with the liver .
Factors influencing the increase in direct bilirubin
An increase in value is always a consequence of dysfunction of the bile outflow. Such a violation leads to the fact that bile is sent not into the blood, but directly into the stomach.
Doctors say that pathology often appears due to the following factors:
- Hepatitis A, B or bacterial in nature.
- Chronic or autoimmune form of hepatitis.
- Poisoning with toxic substances (chemical compounds, gases, mushrooms).
- Liver diseases caused by long-term use of certain medications.
- Cholelithiasis.
- Cancer of the liver, pancreas and gall bladder.
Reasons for increased indirect bilirubin
Indirect bilirubin is usually produced in excess when:
- The presence of infectious diseases.
- Congenital anemia of various forms.
- Gilbert's syndrome (this is the initial inability of the liver to process toxic substances and remove them from the body).
- Poisoning with poisons and chemicals, insect bites.
- Acquired forms of anemia.
With this diagnosis, the primary source of pathology is always excessive destruction of red blood cells.
Blood test for bilirubin
The outcome of treatment for any disease largely depends on the accuracy of the diagnosis. Quite often, the doctor has to carry out differentiated diagnostics, analyzing the indicators of laboratory, instrumental and instrumental studies, since different diseases may have similar symptoms.
First of all, the doctor focuses on a biochemical blood test due to the universality of the characteristics of this complex test. Among the basic indicators, one of the most important is the content of bilirubin in the blood, which assesses the functioning of the liver, pancreas and gall bladder. The special significance of the “bilirubin” indicator and its relationship with other blood characteristics will be confirmed by any medical forum with numerous questions on this topic.
If the test results indicate an increase in bilirubin in the blood, this may indicate the presence of serious diseases and pathological conditions:
- hereditary or caused by other diseases liver enzyme deficiency;
- liver cirrhosis and hepatitis;
- diseases of the biliary tract and gallbladder;
- hemolytic anemia;
- cancer or metastases to the liver from other organs;
- vitamin deficiency B12;
- injuries with multiple hematomas.
An exception is infant physiological jaundice, which occurs due to the restructuring of the newborn’s body after intrauterine development. In all other cases, it is necessary to determine the exact cause of high bilirubin levels.
Bilirubin and hemoglobin. Hemoglobin and bilirubin are substances connected by a single chain of chemical reactions, which increases interest in comparing their values in blood tests and serves as additional information in diagnosing diseases. Hemoglobin breaks down during the process of red blood cell renewal into globin chains and heme, which is converted by enzymes into toxic indirect bilirubin.
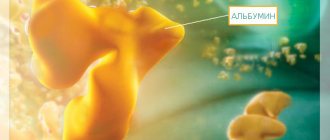
Therefore, high levels of hemoglobin and bilirubin indicate hemolytic anemia or injuries with contusions and bruises with a large number of destroyed red blood cells. If low hemoglobin and high unconjugated bilirubin are observed, then the pathology may be associated with a lack of albumin, which is responsible for moving the yellow pigment to the liver.
Bilirubin and cholesterol. Increased cholesterol and bilirubin may indicate an incorrect dietary pattern, as a result of which the biliary system suffers, and fatty liver hepatosis is possible. As a rule, such a diagnosis is clarified after considering bile pigment fractions, other indicators from a detailed biochemical blood test, and ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
Bilirubin appears in the body when hemoglobin (a complex iron-containing protein) in old red blood cells breaks down.
The breakdown of old cells is a normal, healthy process. After circulating in the blood, bilirubin is sent to the liver.
In the liver, bilirubin is conjugated, mixed with bile and released into the bile ducts and remains for some time in your gallbladder. Eventually, the bile is released into the small intestine to help digest fats, and then passes out of the body in your stool.
Unconjugated bilirubin can harm the developing central nervous system of the newborn (up to 2-4 weeks), it does not pose a threat to adolescence and adults.
In adolescents and adults, the “blood-brain barrier” is more developed and prevents bilirubin from reaching brain cells. However, high bilirubin levels indicate the presence of some process or disease in the body that needs to be diagnosed and treated.
Bilirubin is not usually present in urine. However, the conjugated (direct form) is water soluble and can be excreted through urine if it cannot pass into bile.
Found bile pigment in the urine usually indicates poor functioning of the liver or bile ducts, hepatitis or some other pathological process associated with this organ and can be detected in the early stages of the disease.
Possible diseases
Doctors say that a variety of ailments can provoke an increase in bilirubin levels. To make a correct diagnosis and choose the optimal treatment method, you need to visit a specialist and do certain tests.
Liver diseases
Statistics show that in 80% of cases it is liver dysfunction that leads to increased production of total pigment. If the liver cannot function properly, the process of transforming indirect bilirubin into direct bilirubin becomes almost impossible.
Similar pathologies usually occur with various forms of hepatitis and liver cancer.
Diseases can be suspected based on the following signs:
- discomfort and pain in the right hypochondrium;
- lightening of stool and changing the shade of urine to a darker one;
- the appearance of bitter belching;
- general weakness, frequent dizziness,
Diagnosis of bilirubin levels
To determine the level of pigment in urine, the Harrison test is most often used. This diagnostic method consists of deciphering a reaction based on the oxidation of a compound upon interaction with Fouche’s reagent to biliverdin.
To carry out diagnostics, a laboratory technician mixes trichloroacetic acid with ferric chloride (observing certain proportions). You can get a reliable result using Harrison's test.
Also today, many clinics use a biochemical blood test to determine the concentration of bilirubin..
This method is universal because it gives doctors the opportunity to determine the content of major formed compounds and hemoglobin.
In addition, biochemical analysis is very effective if there is a suspicion of liver disease or dysfunction of the circulatory system.
Diagnostics
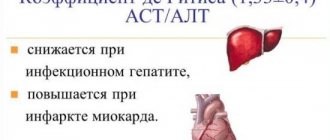
Doctors diagnose elevated bilirubin in combination with other laboratory tests (alkaline phosphatase, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT)) associated with liver problems.
Laboratory diagnosis of bilirubin is carried out when:
- Jaundice (Gospel's disease);
- When the patient suffers from alcoholism or often abuses alcohol;
- If you suspect that you are taking narcotic or toxic drugs;
- When a person has been exposed to viruses that cause hepatitis.
A blood chemistry test may also be done if hemolytic anemia is suspected as the cause of anemia (a condition characterized by low levels of hemoglobin or red blood cells in the blood).
In this case, additional tests are often prescribed to evaluate hemolysis (complete blood count, reticulocyte test, haptoglobin and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)).
Reasons why you may not be able to take the test or why the results may be incorrect include:
- Drinking coffee or caffeine-containing products, which can reduce bile pigment levels.
- Avoiding food for an extended period (fasting), which usually increases indirect bilirubin levels.
A comprehensive bilirubin blood test will show the exact amount of all three levels of bilirubin in your blood: direct, indirect and total. Below are the norms for all three values in an adult:
- Normal values for direct bilirubin range from 1.8-5.2 mmol/L.
- Normal values of indirect bilirubin vary between 3.5-12 mmol/l.
- Total bilirubin (direct and indirect) varies in the range of 5.2-17 mmol/l.
Basic treatment methods
Experts warn that treatment can be carried out only after it is possible to find out what was the primary source of the pathology. To do this, you need to take tests for liver tests, hepatitis, undergo an ultrasound and other specific examinations.
Therapy is always aimed at combating the pathology that provokes increased production of the compound. If the primary source of the disease is formed stones or neoplasms, first of all it is necessary to try to get rid of them.
Very often, patients are also prescribed infusion therapy (if the increase in the concentration of the substance is a consequence of severe hemolysis). In any case, it is impossible to say in advance which treatment method will be prescribed, since everything depends on the specific situation.
To reduce the concentration of bilirubin and minimize its toxic effects on the body, you can take drugs in the following categories:
- Plant-based products (synthetic and semi-natural) that improve protein production in affected liver tissues. The most effective drugs in this group are Silibinin, Heparsil and Silibor.
- Semi-synthetic agents that improve bile production and regulate liver function. Such medications are also indispensable because they help remove heavy metals from the body. The most popular medications are Hofitol and Holiver.
- Preparations of animal origin aimed at restoring damaged liver tissue. When taken regularly and competently, they help not only reduce bilirubin levels, but also activate many metabolic processes. Most often, doctors prescribe Sirepar and Hepatosan to their patients.
The relationship between nutrition and increased indicators
Experts warn that if the patient does not receive adequate nutrition or simply abuses harmful foods, this can lead to excessive production of bilirubin. The person will experience general weakness and decreased performance.
If the diet is not adjusted, after a while the symptoms will intensify, a constant headache, nausea will appear, and in the evening there may be an increase in body temperature.
The occurrence of such symptoms is due to the fact that bilirubin is a toxin, which, when excreted slowly, gradually begins to poison the body. To prevent the occurrence of various complications and undesirable consequences, a special diet is required.
The basis of the diet should be:
- fermented milk products with a minimum percentage of fat content;
- butter and vegetable oil;
- vegetable dishes (soups, salads, lecho) and fruits;
- various porridges (they should be consumed in their pure form, without adding jam or honey);
- boiled meat and fish.
To reduce bilirubin levels, it is necessary to completely exclude flour and sweets, seafood, hot sauces and seasonings, mushrooms, fast food, and alcoholic beverages from the diet.
Diet and medications
Nutrition for elevated bilirubin plays an important role in matters of quick and effective treatment. If you want to achieve quick results, it is worth knowing which foods you can eat and which you cannot. This must be done, since an incorrect diet with high bilirubin can aggravate the problem.
This must be done, since an incorrect diet with high bilirubin can aggravate the problem.
A diet for high bilirubin involves avoiding salt, including pickles and preservatives, and fermented foods. When choosing products such as bread, it is best to choose a salt-free option.
A diet for high bilirubin involves excluding from the diet flour products that use soda or baking powder. Products such as biscuits, cakes and pastries should be excluded.
The diet for high bilirubin is based on the principles of using only healthy foods. The diet should avoid foods such as smoked meats, very sour fruits, spicy and fatty sauces, including tomato-based ones.
You will have to avoid strong, pungent vegetables such as radishes or green onions. Mushrooms and garlic are also on the list of forbidden pleasures.
A diet for elevated bilirubin involves exclusion:
- rich broths;
- hot spices and seasonings;
- refractory fats;
- seafood such as mussels and oysters;
- canned food;
- any alcohol;
- fatty meat;
- cheeses, especially sharp ones;
- ice cream
If you want to create a diet for yourself, then you should give preference to milk, which has a low percentage of fat content, juices, compotes and jelly, and still water should be consumed. Oils you can use are vegetable and butter.
It is better to take boiled lean meat, adding it to vegetables. An option for sweets can be honey or jam. A minimum amount of salt must be added to porridge. Load up on sweet fruits and fish
In addition, it is important to maintain a plentiful drinking regime. Meals should be fractional. In particular, it is best to divide your usual diet into six meals, the breaks between which should not be more than two and a half hours
In particular, it is best to divide your usual diet into six meals, the breaks between which should not be more than two and a half hours.
Medicines are an integral element of the treatment of elevated bilirubin. We are talking about choleretic drugs. If we are talking about diseases of a hereditary nature, then symptomatic treatment is recommended. In particular, preference is given to sorbents and vitamins.
If the cause of high bilirubin is infection or inflammation of the liver, then the use of hepatoprotectors, antiviral and antibacterial drugs will be required. First of all, of course, hepatoprotectors are prescribed, which help improve the condition of the liver and normalize its function.
If increased bilirubin causes intoxication, then antioxidants and sorbents will help improve metabolism and reduce the amount of toxins. In addition, you can try infusions of special antitoxic drugs or glucose. However, such treatment is required only in severe cases.
Possible complications
The danger of excessive concentration of this substance in the blood is that in the absence of timely treatment, the patient will begin to develop various pathologies associated with the liver and central nervous system. Most often, bilirubinuria causes the following complications:
- Hypovitaminosis. Leads to digestive problems and liver dysfunction. The likelihood of stone formation in the genitourinary system also increases.
- Brain pathologies. When there is an excessive concentration of toxins in the blood, the development of neurons slows down, which negatively affects the functioning of the entire body.
- Kidney problems.
High levels of the compound are especially dangerous for newborns. This condition can provoke a loss of the sucking reflex; the baby’s blood pressure may also drop and convulsions will appear. In 90% of cases, an increase in the volume of the liver and spleen is diagnosed.
Increased bilirubin in the blood is a very dangerous disease that requires immediate treatment. It is necessary to understand that the pathology will not go away on its own or after using folk remedies .
The only way to stay healthy is to go to the clinic in a timely manner and do the necessary tests, after which a specialist will prescribe the optimal treatment regimen.
The complex of biochemical blood analysis includes the determination of pigment metabolism in the human body. It is assessed by bilirubin, but most people do not know what this substance is, what it is responsible for and why its increased concentration is dangerous. When its amount becomes very high, this indicates certain diseases and disorders in the body.
What is bilirubin?
Every person has bilirubin in their blood. This pigment substance, colored yellow-green, arises as a result of the destruction of hemoglobin. The liver monitors the proper metabolism of bilirubin and also controls its values.
The pigment substance is produced in two environments of the human body:
- blood
; - bile
.
High bilirubin in the blood in adults usually indicates jaundice, which signals serious pathological changes in the liver or bloodstream. There are two types of bilirubin: direct (leaves the body along with bile) and indirect (very toxic to humans, neutralized by the liver). The level and type of substance helps determine the biochemical composition of the blood.
Types of bilirubin
Bilirubin is called a product of material metabolism. The substance is formed from hemoglobin, which is broken down inside the liver and excreted in urine, feces and bile. There are three types of bilirubin:
- direct - it is water soluble and is also called conjugated. Formed in the liver as a result of connection with glucuronic acid;
- indirect does not dissolve in water. It is toxic and is a breakdown product of heme substances;
- total is the total amount of both forms of the substance in human blood plasma.
What level means that bilirubin is not elevated?
We figured out what the different types of bilirubin are, but what indicators are considered normal? When its concentration is elevated, this may indicate various diseases. So, the norms according to modern medical tables are as follows:
- in indirect form – no more than 16.2 µmol/l;
- in the straight line – not higher than 5.1 µmol/l;
- the amount of total bilirubin varies from 0.5 to 20.5 µmol/l.
Even figures of 21-21.7 units are considered overestimated, but this is not a reason for concern. The predominance of a certain form of a substance may be due to various reasons. When the concentration of the substance reaches 35-36 units, the patient may experience the first symptoms of jaundice, and read more about them below.
Symptoms of elevated bilirubin
When the analysis reveals high levels of bilirubin, a person’s skin may turn slightly yellow, and the urine will take on a dark tint (on average, with a reading of more than 34 units).
As a result of increased concentration, a person may experience a number of symptoms after physical activity:
- temperature increase;
- discomfort in the left hypochondrium;
- lethargy;
- general weakness.
The doctor determines what is causing the disorder and prescribes appropriate treatment. When the bilirubin level is increased significantly (60, 71.3, 96, 120 units), some disease is definitely developing in the body, requiring qualified treatment.
In rare cases, the concentration of the substance reaches critical levels of 220-300 µmol/l, and this is very dangerous. This is rare in adults, but occurs in children and adolescents under 15 years of age.
Why does the amount of bilirubin increase and what are the consequences of such a violation we will now understand.
What are the dangers of increasing indicators?
As mentioned, bilirubin is toxic, therefore it contributes to intoxication of the body and disruption of organ function. The brain tissue is the most sensitive, while the liver, kidneys and heart have higher resistance. In any case, everything depends on the exact concentration determined from the test results.
If the norm is slightly exceeded, when the concentration of the substance reaches 29-30 or higher values of 46-80 units, this is not dangerous to the patient’s health. This is not yet severe intoxication and the organs do not suffer toxic damage, and some people live with such indicators, although this is not normal.
With a pronounced increase in bilirubin, when it reaches 150-180 units, everything is quite dangerous, but still not critical. Long-term preservation of this state is accompanied by intoxication, which must be dealt with as quickly as possible.
In severe forms, when the substance content reaches 300 µmol/l, doctors talk about a threat to the patient’s life. In this situation, severe intoxication and dysfunction of many organs occur. For adolescents, this concentration of bilirubin is more dangerous than for adults.
There is also an extremely severe form, when bilirubin exceeds 300 units. Such indicators in the case of adult patients are incompatible with life. If treatment is not started within a few days and the concentration in the blood is not reduced, the consequences will be the most dire - death is possible.
Sometimes women are interested in whether it is possible to do IVF with elevated bilirubin, since this occurs quite often. Also on forums there are often questions related to the concentration of this substance and infertility. In fact, experienced doctors refute the connection between bilirubin levels and infertility, but whether to refer for IVF if its numbers are inflated or not depends on the indicators and other individual factors.
Why does bilirubin rise?
Doctors know various causes of increased bilirubin, including:
- high-intensity hemolysis of erythrocytes;
- liver damage;
- problems with the outflow of bile;
- disturbances in the production of enzymes.
In liver diseases, the secretion of direct bilirubin into bile may be impaired and the intensity of hemolysis may increase. When the content of the substance in the blood reaches high levels, and the skin acquires a yellow tint, and the urine darkens, and weakness and fatigue occur, the cause may be anemia, gallbladder pathologies, helminthic infestation or acute deficiency of vitamin B12.
Congenital or acquired anemia can contribute to a noticeable acceleration of the destruction of red blood cells in human blood, and this will lead to a slight or noticeable increase in bilirubin. Other body functions may be working normally, but the test will show only high indirect bilirubin.
Various types of cancer, cirrhosis and hepatitis can lead to high concentrations of the substance and unpleasant consequences. All of them interfere with the formation of direct bilirubin. Among the provoking factors are hereditary diseases and Gilbert's syndrome (deviations in the secretion of enzymes). In some situations, even taking medications can cause an increase in the content of the substance by approximately twofold - it’s all about side effects that affect the functioning of the gallbladder. In this case, only bilirubin can be increased, and other indicators will remain normal.
Cholelithiasis
Occurs relatively often. Direct bilirubin is elevated due to insufficient liver activity, and this condition is “complete” with damage to the gallbladder.
The disorder is accompanied by several pronounced clinical signs.
Symptoms present:
- Pain. Unlike previous situations, they will be cutting, dagger-like. Because the gallbladder is involved.
- Increased body temperature.
- Impaired sense of taste. Bitterness in the mouth.
- Strange odors that the patient perceives.
- Nausea.
- Vomit.
- Change in color of stool.
- Weakness.
- Drowsiness.
- Digestive disorders.
The list goes on and on. Gallstones are accompanied by inflammation - cholecystitis.
Recovery is carried out under the supervision of gastroenterology specialists. Anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
Surgery to remove stones is also indicated. Then, after a course of recovery, the concentration of bilirubin will drop.
How to lower high bilirubin?
We found out what kind of disease can be caused by increased bilirubin in the blood, and now we just need to figure out how to reduce it. First, any attending physician makes a diagnosis and determines what is causing the increase in the concentration of the substance. After this, the optimal therapy complex is selected.
Often, the basis of treatment for adolescents and adults over 30 years of age with high bilirubin is infusion therapy. The patient is given intravenous injections of special drugs and glucose, due to which the substance and its breakdown products are more intensively removed from the body. Typically, doctors use this technique in critical situations, and when bilirubin is 39-46 units or so, other methods are used. Also, infusion therapy may be resorted to when a slight excess of the norm does not decrease for a long time.
How to lower the level of bilirubin in the blood
This can only be done by treating the cause of its increase. Each method has its own indications, so only a specialist should determine the optimal one. Here are the main methods for reducing bilirubin levels:
- Infusion therapy - intravenous infusion of glucose and detoxification medications cleanses the body of bilirubin and other breakdown products. This is an effective measure that is used in severe conditions.
- Phototherapy is the irradiation of the patient with special lamps, under the influence of which toxic indirect bilirubin is converted into its direct form and is easily removed from the body. Phototherapy is often used to reduce bilirubin levels in newborns, and most often this measure is effective.
- If the reason for the increase in bilirubin levels is a violation of bile excretion, drugs that normalize these processes are prescribed.
- Normalizing your diet is another way to lower bilirubin in the blood. Along with this, cleansing preparations, activated carbon and detoxifying gels are prescribed. You should definitely reduce the load on the liver by eliminating all fried, peppered, and carbonated sweet drinks from your diet.
- When there is an increased level of bilirubin caused by hepatitis, the main measures are aimed at combating the virus, while at the same time the patient is prescribed drugs that protect the liver. If treatment of the hepatitis itself is successful, bilirubin levels quickly return to normal.
- Gilbert's syndrome and some liver diseases are treated with Phenobarbital. It should be noted that only a competent specialist should prescribe this or any other drug, otherwise there is a high risk of complications after improper treatment.
The level of bilirubin depends on how normally all links in the chain of binding and removing bilirubin from the body work. This is a normal process of cleansing and getting rid of decay products, one of the elements of the process of tissue renewal that constantly occurs in our body. If a failure occurs at any stage, a timely analysis and detected increase in bilirubin levels can help make a timely diagnosis and begin treatment. Therefore, you should not ignore the symptoms of excessive bilirubin concentration and immediately consult a doctor.
Symptoms of elevated bilirubin
The cells of the body are constantly renewed. Hemoglobin is synthesized in the spleen, then passes to the liver, dissolves in water and is excreted as bile.
At the slightest violation of internal processes, the body gives an alarm signal. In its direct state, bile pigment is harmless, but indirect (free) it poses a serious danger. If there are problems with the liver, the substance cannot go into direct form, and complications develop as a result.
Elevated bilirubin is a common occurrence in pregnant women.
The normal level of bilirubin in the blood is: total - 8.5-20.5 µmol/l, direct - 0.9-4.3 and free (indirect) - 17.1 µmol/l. In men, the indicators are slightly higher. A level reaching 170 µmol/l indicates a severe form of jaundice. Exceeding up to 60-70 will not cause harm to health, but it is necessary to find out why the changes occurred. The results are based on the total number.
Hereditary pathology (Gilbert's syndrome) occurs ten times more often in men due to a lack of one liver enzyme.
Symptoms of elevated bilirubin
There is general weakness. Not only the skin on the face turns yellow, but also the feet, palms, whites of the eyes, and the oral mucosa. The color of the urine darkens, sometimes turning brown. When urinating, foam forms, and when defecating, stool takes on an unnatural white color.
If the cause of the disease is a dysfunction of the liver, the person feels nausea, heartburn, bitterness in the mouth, the temperature rises, belching is tormented, and the skin has a jaundiced tint. The danger is that bilirubin, which does not leave the cells naturally, turns into a toxin and has a detrimental effect on internal organs, affecting the intestines, heart, and lungs.
Increased bilirubin: reasons
The changes can be of a different nature, often the cause of the disease is the erythrocytes (blood cells) themselves:
- A high bilirubin level is possible due to hereditary or acquired hemolytic anemia. Blood cells are broken down too quickly;
- Sometimes anemia occurs due to excessive use of medications;
- The cause may be a diseased liver (cirrhosis, cancer, alcohol exposure);
- Viral, toxic, alcoholic, drug-induced, fatty hepatitis;
- Malfunctions of the gallbladder, insufficient output of bile;
- Lack of vitamin B12. General condition – lethargy, apathy, malaise, pallor;
- Cholecystitis, cystitis;
- Painful sensations in the spleen area;
- With a sharp decrease in red blood cells, a strong heartbeat and difficulty breathing (shortness of breath) are noticed;
- The presence of helminth parasites in the intestines.
Sometimes the disease is the result of severe chemical poisoning (the influence of gasoline fumes, paints and varnishes). In this case, several factors can be combined with each other.
It is important to see a doctor on time and undergo the necessary tests. The examination is mandatory after suffering from viral hepatitis. Newborn children are also subject to the procedure.
Jaundice in a baby goes away on its own, but there are cases when the blood of the mother and child does not match the Rh factor and increased bile pigment in the baby’s blood cannot be detected immediately. The consequences can be quite serious. To identify the disease in the baby, tests are taken from the heel.
Treatment of elevated bilirubin
To determine the exact amount of bilirubin, a general blood test is taken from a vein from an adult. Donate blood in the morning on an empty stomach. The day before the test, it is not advisable to eat fatty and salty foods.
Depending on the severity, medications are prescribed. To remove harmful toxins, instill a glucose solution.
If it is not possible to lower the bilirubin level, infants are prescribed Phenobarbital. The action of the drug is also aimed at treating Gilbert's syndrome. Buying medicine on your own without making a diagnosis is strictly prohibited.
Irradiation with special blue lamps (phototherapy) gives positive results: under the influence of ultraviolet rays, bile pigments are eliminated much faster.
Diet for high bilirubin
Eliminate high-calorie, fatty, smoked, peppered foods, as well as millet porridge from the menu. It is necessary to drink as much liquid as possible: fresh juices, berry compotes, teas. If the bilirubin level is not very high, you can prepare herbal decoctions of chamomile, hawthorn, and St. John's wort. For internal cleansing of the body, suspensions are prescribed: “Polysorb” or activated carbon.
The increase in bilirubin at the time of bearing a child is explained simply: the baby grows in the womb, puts pressure on the internal organs and does not allow bile to escape. For this reason, liver function may be impaired. After childbirth, bilirubin levels return to normal.
Contact specialists in a timely manner. Any changes in the blood do not allow self-medication using folk methods.
Total bilirubin 30 in an adult
Bilirubin is one of the substances found in human blood. It differs from all others in its color: this element has a yellow-green tint. Where is this substance found, and as a result of what is it produced? If the test shows “bilirubin 30” in an adult, is it worth treatment? What is the normal level of bilirubin in human blood?
Bilirubin: general characteristics
Bilirubin is a substance that is formed in the blood during the breakdown of hemoglobin. This sequence of formation of this element is very complex. Everyone knows that hemoglobin “lives” in red blood cells (or erythrocytes). They are responsible for the delivery of oxygen to all organs.
But those of them that cannot fully carry out their activities disintegrate in such bodies as:
- the main filter of the body is in the liver;
- in the spleen;
- in the bone marrow.
And the cells released in this process turn into the element “bilirubin”. It is important to understand that a newly created substance can pose a danger to the body. That is why its complete cleansing and neutralization occurs in the liver, after which bilirubin is released along with bile.
Types and forms of bilirubin
The process of formation of this element is chemically continuous. It is this property that allows us to assert that at certain stages changes in matter occur.
Yes, bilirubin has several types, as briefly mentioned above:
- Straight. This type of bilirubin is harmless to the human body. It appears in the internal environment as a result of the purification of a given element of a different type. It is the liver, being the main filter of human organs, that helps remove all unnecessary substances from this substance. It disappears from the body along with bile.
- Indirect. This type is dangerous for the internal environment, and the greatest threat it poses is to the human central nervous system. This type of bilirubin is formed as a result of the breakdown of the same hemoglobin. This element has not yet been cleansed in the liver and contains dirty and harmful bacteria.
If you combine these two types together, you can get the following name - “total bilirubin”. This is the name of the analysis, during which the amount of this element in a person’s blood is studied.
Norm of bilirubin content
Like any “blood component,” bilirubin has its own standard indicators. Below will be presented data that is common to both men and women. Their distinction is made only according to age criteria.
Normal total bilirubin for:
- newborns (up to 3 weeks) is from 0 mmol/l to 85 mmol/l;
- children from 3 weeks to 1 year is from 0 mmol/l to 29 mmol/l;
- for a person aged 1 year and older it is from 2 mmol/l to 17 mmol/l.
An increase in these values is observed in a number of diseases. For example, with hepatitis, anemia, jaundice, with disruption of the normal functioning of the liver. To identify the cause, you need to contact a competent specialist who, having prescribed all the necessary studies, will conduct a full diagnosis.
If an increased value of an element such as bilirubin is detected, you should not treat yourself. Only a doctor can create the most accurate and effective system. Therefore, you must boldly go to specialists who will tell you exactly what to do with this substance.