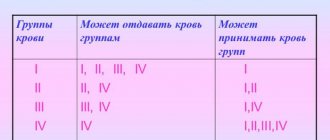
What are the health consequences of donating blood, platelets and granulocytes?
A decrease in hemoglobin levels can occur due to the temporary loss of red blood cells during blood donation. This is the most negative consequence. If you have a tendency to decrease hemoglobin, you are not recommended to donate blood. When donating blood, there are strict rules, including the hemoglobin standard, beyond which the analysis of your blood should not go beyond. That is, if the indicators are underestimated, even by one, blood will no longer be taken.
Negative consequences are also possible when donating platelets, but with constant donation. The Ministry of Health allows you to donate platelets once every two weeks. With hardware platelet phresis, it is allowed no more than once a month.
All standards are related to the speed of restoration of cells necessary for donation and the prevention of stress in the donor’s body. It turns out that during this time the body should not only recover, but also rest. The procedure for donating platelets is that the blood taken from the donor passes through a centrifuge, where platelets and plasma are separated, i.e. The platelets and some plasma are separated, and the rest of the blood is returned back to the donor. For this procedure, it is necessary to use a substance called sodium citrate. It is used in this case to preserve blood and prevent clotting. Since a person’s blood is thick, citrate, very usefully, helps to dilute it and prevent it from clotting during the platelet transfusion procedure.
Citrate is bad because its presence removes calcium from the bones. In order to restore calcium levels, calcium gluconate is injected several times during the donation of platelets to the donor. After the test, doctors will advise you to take vitamins with calcium (for example, Calcium D3 Nycomed or Calcium Vitrus).
In addition, citrate is very poorly excreted from the body, so if you constantly donate platelets, there is a high chance of developing a citrate reaction. The reaction manifests itself in the fact that the body ceases to tolerate citrate entering the blood. The citrate reaction may involve feeling unwell during and after donating platelets: nausea, weakness, dizziness, severe chills.
Don't be afraid to become a platelet donor. The citrate reaction will appear with continuous donation of platelets and after several years, and not in two donations.
Granulocytapheresis is a new procedure in transfusiology. There is almost no data on its negative effects on the body. Due to bone marrow stimulation, the donor may experience slight bone pain for a while and may also experience cold-like symptoms. For granucitapheresis, heparin is used, which is harmless.
Source: www.baby.ru
Harm
Donation itself is safe and cannot harm a healthy human body. According to studies, problems associated with blood withdrawal occurred in only 2 out of 1000 people and they were associated with a vomiting state provoked by a sharp drop in blood pressure.
However, risks of donation exist and are associated:
- With the development of iron deficiency anemia caused by a decrease in hemoglobin levels after blood sampling. Good nutrition and inclusion of iron-containing foods in the diet will help prevent this pathology.
- Deterioration of capillary permeability occurs with regular bloodletting and can worsen the blood saturation of a person’s lungs.
- Increased risk of developing neoplasms. A decrease in red blood cells causes their active division and, at the same time, can provoke the growth of atypical cells. This theory has its place, but has not been proven until now.
- Associated with a decrease in the required amount of fluid in the body, donation is accompanied by a decrease in physical blood pressure indicators, which is especially contraindicated for people suffering from hypertension.
WHAT DOCUMENTS ARE REQUIRED TO DONATE BLOOD?
In accordance with Art. 12 of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation dated July 20, 2012 No. 125 “On the donation of blood and its components”, in order to perform the donor function, the donor is obliged to: 1) present a passport (when visiting the State Budgetary Institution “PKSPK” and its separate divisions, registration must be in the city of Perm or the Perm region at least 6 months old); 2) provide information known to him about infectious diseases, being in contact with infectious patients, using narcotic drugs, psychotropic substances, working in harmful and/or dangerous working conditions, as well as vaccinations and surgical interventions performed within a year before the date donating blood; 3) undergo a medical examination at a blood transfusion station.
Active donors of both sexes who have 3 or more blood (plasma, cyto) donations per year submit, in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated September 14, 2001 No. 364 “On approval of the procedure for medical examination of a blood donor and its components”: - every six months a medical certificate on an outpatient basis - a polyclinic institution at the place of residence or place of attachment, indicating the diseases suffered over the past six months; - once a year, data from a laboratory clinical analysis of urine, fluoroscopic (or fluorographic) examination of the chest organs, electrocardiography; — every three months a certificate of no contact with hepatitis A; — every six months a certificate of no contact with hepatitis B and C; - for each application for blood donation - a certificate of no contact with other infectious diseases.
Advantages
Blood donation (the pros and cons of the procedure make many people afraid of a completely painless procedure due to false fears) is the only way to help people in need of transfusion of blood or its components, and also allows the donor to:
- stimulate natural blood circulation in the body;
- update the composition of accumulated blood;
- prevent the development of liver cancer pathologies;
- increase your own life expectancy;
- maintain optimal iron levels in the blood;
- alleviate the course of hemochromatosis;
- accelerates wound healing;
- maintain youthful skin, improve mood and burn extra calories
You can donate blood free of charge, for a monetary reward, or in order to receive social support measures in the form of monetary compensation immediately after donation or when making a certain number of donations per year.
Donating blood free of charge is considered the basis for receiving a reward for food in the amount of 1,130 rubles, and also allows you to be nominated for an award as an “Honorary Donor of a city or country.”
The financial reward for donating blood is:
| Donation of whole blood with a rare red blood cell phenotype | 1800 rub. |
| Plasma collection | 3375 rub. |
| Platelet donation | 7900 rub. |
| Red blood cell donation | 5616 rub. |
Payments for donating blood in order to receive social benefits:
| Whole blood donation | 5208 (4080+1128) rub. | 24,000 for 4 annual fences |
| Plasma donation | 4728 (3600+1128) rub. | 72,000 rub. per year for 20 donations |
| Donation of red blood cells | 7128 (6000+1128) rub. | 19200 rub. for 2 donations during the year |
| Platelet donation | 6888 (5760+1128) rub. | 62400 rub. for 10 donations |
Additionally, donors are also given 2 additional days off at the place of their main activity with continued pay.
In addition to monetary rewards, the state provides donors with priority rights to receive vouchers to sanatorium-resort institutions, various benefits and discounts.
Personnel donors
Special privileges are enjoyed by regular donors, which include persons who have practiced 3-day blood donation for one year and have given consent to the collection of biomaterial at any necessary time. Such donors can donate blood a large number of times, and also undergo a medical examination once every six months, the data of which is sent to institutions reporting to the Blood Service.
Personnel donors donate blood both free of charge and for a fee.
When becoming a career donor, a person signs a consent to make a donation at any necessary time and undertakes at least:
- 1 time per year, provide information about the general physical fitness, ECG and chest fluorography;
- every 6 months, provide data on diseases suffered during the specified period, signed by the district police officer;
- Once every six months, provide a certificate of absence of contact with people infected with hepatitis A.
Before each blood donation, regular donors are required to provide documents confirming their absence of viral infectious pathologies.
Women who are considered human donors are additionally required to visit a gynecologist at least once every six months, providing a certificate of their gynecological health to the Blood Service.
Honorary Donors
Honorary donors of Russia who have received awards, subsidies and benefits receive special credit.
The title of “Honorary Donor of Russia” is awarded to persons who donate without financial compensation:
- about 40 times whole blood;
- about 40 times plasma and about 25 times various blood components;
- about 60 times plasma.
In addition to conferring the title, persons recognized as honorary donors:
- once a year they receive financial compensation in the amount of 12,400 rubles;
- have the first priority right to receive free medical care;
- can apply for annual paid leave at the required time;
- undergo treatment in sanatorium-resort institutions at reduced prices.
WHAT MEDICAL EXAMINATION SHOULD BE PASSED TO BECOME A DONOR?
All necessary tests are usually done directly at blood transfusion stations. A certain amount of blood donated by a donor is taken for testing. Determined: blood type and Rh factor; general blood test data (hemoglobin, leukocytes, erythrocytes, ESR, etc.); as well as markers of pathogens of blood-borne (blood-borne) infections: human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B and C viruses; the causative agent of syphilis.
If desired, in 1-2 days the donor can come with a passport to the Station and receive the results of his tests. Results are reported only in person and confidentially. If signs of infection are found in the blood, only the person who donated the blood and the doctor will know about it. And the doctor will advise where you can go to find out your health situation.
In addition to a blood test, a potential donor undergoes a medical examination, during which the doctor measures blood pressure, temperature, pulse, and asks about his health. Before the blood donation procedure, each potential donor fills out a special “donor questionnaire” in which he answers questions about his state of health and previous diseases.
The final decision on admission to blood donation is made by a transfusiologist, who also evaluates the psychoneurological status of the donor and can reject him if he is suspected of using drugs, alcohol, or leading an antisocial lifestyle.
Contraindications
Before donating blood, the donor undergoes a free medical examination, which includes an examination by a therapist and preliminary laboratory testing.
At the same time, there are a number of contraindications to donation: absolute, that is, independent of the duration of the disease and the results of treatment, and temporary - valid only for a certain period.
Absolute contraindications are the presence of such serious diseases as HIV infection, syphilis, viral hepatitis, tuberculosis, blood diseases, cancer and others.
Temporary contraindications have different durations depending on the cause. The most common prohibitions are: tooth extraction (10 days), tattooing, piercing or acupuncture treatment (1 year), sore throat, flu, ARVI (1 month from the moment of recovery), menstruation (5 days), abortion (6 months), period pregnancy and lactation (1 year after birth, 3 months after the end of lactation), vaccinations.
HOW IS BLOOD DONATION DIFFERENT FROM PLASMA DONATION?
When donating plasma, blood, after part of the plasma is separated from it, is immediately poured back into the donor’s body. Plasma can be donated up to 6-12 times a year at intervals of at least 2 weeks, and whole blood - no more than 3-5 times a year at intervals of 3 months.
After five regular blood donations, it is better to take a break for 3-4 months. Plasma is restored within a few days, blood within a month.
The process of removing plasma takes about 40 minutes, taking blood - about 10-15 minutes. However, the total time that the donor will need to spend in a medical facility in the first case will be about two hours, in the second case - about one and a half hours.
"DONARE" - from the Latin "to give". Donation is a selfless gift of one’s own blood in order to help loved ones or complete strangers. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) resolution, the collection of blood only on a voluntary and free basis from donors from low-risk populations is the main guarantee of the safety, quality, availability and affordability of blood for transfusion.
In accordance with the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated September 14, 2001 No. 364 “On approval of the procedure for medical examination of a blood donor and its components,” admission to donation, determination of its type, as well as the volume of blood or its components taken is carried out by a transfusiologist at a blood transfusion station. Thus, cases in which it is possible to donate blood and (or) its components for a fee are confirmed by medical indications established on the basis of a medical examination of the donor of blood and (or) its components and recorded in the medical documentation of the donor of blood and (or) its components. If the donor cannot be allowed to donate blood and (or) its components for a fee, then the donation is carried out free of charge, and in this case the donor is given monetary compensation for food (5% of the subsistence level of the working-age population established in the constituent entity of the Russian Federation, on territory of which blood and (or) its components were donated). In the Perm region this amount is 620 rubles.
Cases in which it is possible to donate blood and its components for a fee are regulated by Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated December 17, 2012 No. 1069n “On approval of cases in which it is possible to donate blood and (or) its components for a fee, as well as the amount of such payment.”
The amount of payment for donating blood and (or) its components: a) in cases where the donor of blood and (or) its components has a rare blood phenotype or does not have one of the erythrocyte antigens, for one blood donation in the amount of 450 (+/-10 %) ml - 8% of the subsistence minimum for the working-age population in effect on the date of donation of blood and (or) its components, established in the constituent entity of the Russian Federation in whose territory the blood and (or) its components were donated - in the Perm Territory 1,420 rubles;
b) in the case when a donor of blood and (or) its components can be allowed to donate plasma, platelets, erythrocytes or leukocytes by apheresis:
1) for one donation of plasma in a volume of 600 (+/- 10%) ml - 15% of the subsistence level of the working-age population in effect on the date of donation of blood and (or) its components, established in the subject of the Russian Federation in the territory of which the blood was donated and (or) its components (in the Perm region 1,788 rubles);
2) for one donation of platelets in a volume containing at least 200 X 109 platelet cells - 35% of the subsistence level of the working population in force on the date of donation of blood and (or) its components, established in the subject of the Russian Federation in whose territory the blood was donated and (or) its components (in the Perm region - 3588 rubles)
3) for one donation of erythrocytes in a volume of 400 ml (10%) - 25% of the living wage in effect on the date of donation of blood and (or) its components established in the constituent entity of the Russian Federation;
4) for one donation of leukocytes in a volume containing at least 10 x 109 leukocyte cells, using the apheresis method - 45% of the living wage in effect on the date of donation of blood and (or) its components, established in the constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
Benefits for donors
In order to understand how much a donor’s blood costs, it is necessary to take into account not only the monetary payment, but also the benefits that are entitled to people who donate their bio-material at transfusion points.
In addition to direct financial compensation, people who donate blood are entitled to benefits from the state. For donors who do not have the title of Honorary, the following types of benefits apply:
- Lunch after the blood donation procedure to restore the citizen’s strength. In a number of regions, it is possible to replace a meal with compensation for its cost in the amount of up to 500 rubles. This depends on the established cost of living in the region. The amount of compensation is calculated as 5% of it. But this opportunity is not available in all regions of the country;
- The blood donor has the right to use 2 additional paid days off. The donor receives one day off on the day the material is submitted and he can choose the second at his discretion. If the day of blood donation falls on a weekend or holiday, then the donor has the right to take this day off on another day;
- If a donor has donated blood of the maximum volume at least 2 times per year, then he has the right to receive a ticket to the sanatorium out of turn.
Blood center where you can donate plasma for money
Regions have the opportunity to assign their own types of benefits for donors. For example, this could be free travel on the day of blood sampling or other services that can be provided to a citizen. As part of the program to support the donor movement, local measures have been taken in the capital region to stimulate the interest of blood donors - for a blood draw in the amount of 450 milliliters, compensation of 3,400 rubles is paid. The region has also established the amount of money paid for voluntary plasma donation - the amount of cash payment is 3,000 rubles, and blood components reach 5,000 rubles.
One of the most popular questions at blood transfusion centers is how much it costs to donate plasma. Most often, this is what is donated, since the price for collecting the material is higher than for blood and plasma can be donated more often, once a month, while blood is donated no more than once every 2 months. And people who go to blood points for financial support choose this particular type of collection of bio-material.
Donating blood for platelets. Thrombocytopheresis
The procedure for a donor to donate platelets for medical purposes is called thrombocytopheresis. You can donate them voluntarily by visiting a blood donation station or making an appointment by phone. The components obtained as a result of donation by a donor can help save a human life. They go to help people suffering from cancer or hematological diseases.
The components that protect the human body from possible injuries and bleeding are called platelets. When a vessel is damaged, a protective biological component is formed - a blood clot. It is necessary to create an obstacle to blood loss for victims. Plateletpheresis may be prescribed to reduce high levels of platelets in the blood. This procedure is prescribed to reduce the likelihood of blood clots. If necessary, the doctor prescribes a blood test for the patient. Medicines and blood substitutes are made from the platelet mass obtained as a result of donation by a donor.
At the registration desk, the donor is offered a questionnaire to fill out. In it you need to indicate your passport details, address of actual residence, telephone number, past illnesses. A donor card is created for the newly arrived person. After this, the future donor will be given his card for donating blood from a finger. Based on the results of a blood test, hemoglobin levels, group, and platelet counts are determined. Next, with the results obtained, the donor undergoes examinations by a transfusiologist. They measure his weight, height, blood pressure, pulse, and inquire about the general well-being of the donor.
Once examined by a transfusiologist, the donor is allowed to donate platelets.
The procedure has two ways:
How donors donate platelets: instructions
In the intermittent method, blood is taken from the donor and platelets are separated from it. This procedure uses a centrifuge. After the platelet collection procedure is completed, the donor’s blood is returned. The time it takes for the procedure depends on how quickly the required number of blood platelets is collected. This indicator is influenced by the total weight of the donor. This method is not widely used due to its complexity and duration.
In the second, special devices are used. They create a continuous flow of blood. This leads to the fact that a nurse or doctor can monitor the speed of donation and the well-being of the donor. Sterility is ensured due to the lack of contact during operation of the mechanism.
Having passed the necessary tests and received the doctor’s permission, the donor:
- Drinks hot, sweet tea with cookies, sometimes chocolate is available;
- On call, occupies an empty chair for donation;
- A completely sterile needle is inserted into the donor's vein by a nurse;
- The nurse enters the necessary parameters into the sampling machine. The device starts working in automatic mode;
- The donor clenches and unclenches his fist to create pressure and improve platelet collection;
Modern devices operate automatically. When donating, they use a sound signal to tell the donor when to release his fist and not work with it, and when to start squeezing and unclenching it. The procedure itself takes from forty-five minutes to an hour. After donating platelets, the donor is given a form to receive free social assistance.
Platelet donation procedure
Persons who are citizens of the Russian Federation and other states with a residence permit and temporary registration are allowed to donate platelets. They must be registered on the territory of the Russian Federation for at least one year. Donors who regularly donate platelets or newcomers may be allowed to donate platelet mass. The latter, as a rule, will be thoroughly checked using tests (taking blood from a finger, providing a medical certificate from a therapist, infectious disease specialist, dermatologist, sometimes a heart cardiogram is required).
After the donor has donated platelets, he can be re-assigned for the next donation in two weeks or a month. The period after which he can come again is approved by the doctor. The doctor assesses the donor’s condition and his medical indicators.
Transfusion of one dose of platelets taken from a person in one procedure can help patients with leukemia, aplastic anemia, and during complex operations.
The platelet donor must voluntarily agree to the procedure. Two days before donation, it is prohibited to take medications that thin the blood (aspirin, Trental, chimes). They can cause bleeding and hematoma during donation. It is also prohibited to use any types of drugs, alcohol, or nicotine before donation.
Contraindications for donation are:
- people with hepatitis of all categories;
- patients with tuberculosis;
- HIV infected, AIDS carriers;
- oncological diseases;
- addicted to drugs and tobacco;
- mental disorder;
- disorders of the cardiovascular system, heart;
- persons suffering from asthma;
- people with kidney disease, vision problems, hearing and speech impairments;
- persons who have undergone organ transplantation or organ removal;
- persons suffering from ulcers, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
It is temporarily prohibited to donate blood if:
- viral diseases;
- during the vaccination period;
- after tattooing, permanent makeup, body piercing;
- abortion, pregnancy, breastfeeding;
- after operation;
After the platelet donation procedure is completed, it is recommended not to give your body physical activity on this day, observe the intervals between donations, and adhere to a special diet to restore platelet levels or raise (if there is a low level) hemoglobin level.
Preparation
Before undergoing thrombopheresis, the donor must prepare thoroughly. At the initial stage, he undergoes a complete diagnosis of the body for the presence or absence of contraindications. To do this, he needs to donate blood for analysis. Upon completion of the examination, the therapist writes a conclusion.
If there are no contraindications to donating platelets, the donor proceeds to the second stage - direct preparation for the procedure. Basic rules to follow:
- Two weeks before thrombopheresis, you should stop taking medications.
- 5-7 days before the test, you should not drink alcohol or nicotine.
- Avoid excessive physical and mental stress for 3-4 days. At the time of the procedure, the body must be rested.
- Particular attention must be paid to nutrition. The donor must refuse fast food and other junk food. You need to eat healthy food containing sufficient amounts of useful minerals and vitamins. Consumption of spicy and fried foods should be kept to a minimum, because... they negatively affect the functioning of the liver.
- The consumption of citrus fruits and dairy products is also prohibited. On the day of donating blood platelets, the donor should have a hearty breakfast. Porridges, breads and buns containing complex carbohydrates, which will provide the body with energy for a long time, are perfect.
- Try to minimize the risk of injury, because in the near future the body will be weakened and less capable of regeneration.
- Immediately before thrombopheresis, the donor should get a good night's sleep.
All necessary information regarding the procedure is provided by a medical professional. Failure to follow the recommendations can lead to health problems, so you should approach this issue responsibly.
Platelet donation: benefits and harms
One of the factors in the development of cardiovascular diseases is that the blood is viscous. In this case, strong friction occurs against the blood vessels, blood circulation and hemodynamics become worse. All this increases the occurrence of blood clots in the vessels. Blood clots that block blood vessels can lead to cardiac arrest. To avoid these consequences, it is recommended to donate blood at least once every six months.
The platelet donation procedure is absolutely safe. Restoration of the cellular composition of human blood occurs in fourteen days, all consumables are completely disposable. There are many more positive properties from renting.
These include:
- Moral satisfaction, improved mood;
- Activation of the functioning of all internal organs;
- Improving the immune system;
- Reducing the risk of oncology, the risk of cardiovascular diseases;
- The realization that by donating platelets, you are saving someone’s life, you are helping people;
- Receiving social support measures (compensation for food in cash equivalent);
- The opportunity, when donating 40 times (or more) blood and its components free of charge (except for donating blood plasma), or 25 times (or more) blood and its components + 40 times blood plasma or 60 times or more blood plasma, to receive the title of honorary donor of Russia. This title provides social benefits in public transport, when visiting the dentist, and when paying for utilities;
Negative consequences appear to a lesser extent when donating platelets than when donating blood. In some cases, the donor may feel weak, drowsy, and tired in his body. This condition is caused by the fact that the composition of his blood changes. This feeling goes away after a few days. After the procedure, possible damage to the body should be avoided, because the ability of blood to clot is reduced. It is almost impossible to become infected during the donation procedure, provided, however, that it is carried out only in a special medical institution.
If platelet donations are too frequent, the condition of the blood and bone marrow may worsen. Sodium citrate is used to improve donation. It slows down blood clotting. Over time, the body may become less able to tolerate citrate entering the bloodstream. This substance removes calcium from the body and can provoke pain during donation, as well as after it (weakness throughout the body, a state of nausea, dizziness, chills). When accumulated in large quantities of this substance, individual intolerance may occur.
However, it's not all bad. Such a reaction can occur only after several years, and not after two donation procedures. To restore the donor's calcium level, calcium gluconate is infused several times during donation. After completion of the procedure, the doctor may advise the donor to take vitamins with calcium (Calcium D3 Nycomed, Calcium Vitrus).
Nutrition of the donor in the period between blood donations
To completely protect your health, you must follow the rules established by doctors. Men can donate blood a maximum of 5 times a year, and women - 4 times. At the same time, nutrition plays a huge role in the recovery process.
In the intermediate periods, you should enrich your diet with protein foods:
- dairy and fermented milk (milk, kefir, cottage cheese, cheeses);
- meat;
- good to include poultry, eggs, fish and seafood;
- vegetable (buckwheat, lentils, pomegranate, soybeans, beans, chickpeas).
But in everything you need to know when to stop. The diet should not only be high in calories, but also balanced, and do not forget to drink plenty of water. By following these simple rules, you will help your body achieve recovery in just 2 weeks.
Take this important and noble cause very seriously. Remember that patients, and this could include anyone, need high-quality blood from a healthy person
By becoming a donor, you help other people. This should not be your goal to receive free food or cash benefits. Please take all these recommendations seriously!
There are situations when a person urgently needs blood, which can be obtained from a donor. However, whole blood donation is not the only method of blood transfusion. In some situations, the recipient does not need all the blood, but only its individual components. For this purpose, there are special methods for isolating the necessary blood microelements, which are collected from the donor. The remaining blood is returned back to the donor. One of these procedures is plateletpheresis, in which only platelets are mechanically retained from the total blood mass. The remaining mass is injected into the donor body. This procedure is quite expensive, and also has a lot of nuances, which ones we will discuss further.
How much do platelet donors get paid?
Since the adoption of the law at the federal level, which abolished paid donation, in Moscow, about forty percent of donors did not come to donate blood. To avoid this, the mayor of Moscow, Sergei Sobyanin, took a number of measures aimed at developing free donation, but with measures aimed at social support for donors who came to the blood transfusion station.
Donors who donate biological components to children do so free of charge. There is a program to develop the provision of donor services to the population free of charge. Cases in which donation is carried out on a paid basis are indicated in the documentation of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. Donors who donate must receive meals. However, as a rule, instead of food, they receive money in their hands. Compensation for food provided to a donor is not considered payment for the provision of platelets. In Moscow, for example, payment for donating platelets by a donor is approximately 7,750 rubles.
Source: transplantaciya.com
Myths
The pros and cons of blood donation have given rise to many rumors and various myths that can frighten and turn a person away from a transfusion that can save a human life.
The most popular myths:
- Donating blood is harmful to health. The human body contains equal to 4000 ml. During withdrawal, a person loses no more than 12% of this volume, which cannot negatively affect his health and the condition of the body as a whole. In addition, blood sampling has a stimulating effect on the entire circulatory system and allows you to rejuvenate the body.
- The blood donation procedure is painful and very tiring. Modern blood donation centers are equipped with modern equipment that allows people to feel as comfortable as possible, and pain during the procedure is accompanied only by a second puncture of a vein with a needle. The procedure itself takes from 15 minutes to 1.5 hours, and after it you may experience dizziness and slight fatigue, which disappear after proper rest.
- When donating blood, there is a risk of contracting infections. When collecting blood, only sterile instruments are used, which are unpacked in front of the donor and disposed of after the procedure, which prevents the possibility of any infection.
- There is no need to donate blood due to its low demand. Despite the achievements of modern medicine, experts have not yet found a single substance that can completely replace human blood or its components. Every day, from 500 to 1000 people need blood transfusions, and the need for transfusion can arise in absolutely any, even the most ordinary operation. Donor blood is needed for patients with burns, injuries and chemotherapy.
- Anyone can become a donor. Requirements for potential donors are clearly regulated in the legislation of the Russian Federation, which also stipulates mandatory conditions and contraindications that require refusal to take blood from a certain category of persons.
- Before blood collection, you should eat high-calorie foods. Such a statement is untrue and requires complete exclusion of fatty, fried, smoked foods and alcohol from the diet for up to 48 hours before taking blood.
- Donation has a bad effect on a woman’s appearance. Blood withdrawal helps to increase blood microcirculation, activating the work of the cardiovascular, digestive and nervous systems. In addition, donation promotes rejuvenation of the body.
- During a blood transfusion, recipients will share the appearance and personal qualities of the donor. This misconception dates back to the Middle Ages, who believed that blood carried a particle of a person’s soul. In subsequent millennia, medicine has repeatedly shown that blood is not capable of transmitting any personal qualities, with the exception of decay products caused by residues of nicotine, drugs and alcohol. It is this reason that requires donors to give up smoking, fatty foods and nicotine at least 48 hours before donating blood.
- The Church denies donation. The purpose of blood transfusion is to save a person’s life, and donation is perceived by the church as an act of self-sacrifice, revered by God.
With its pros and cons, blood donation is a revered, completely safe and virtually painless procedure that can save the life of another person.
The procedure, which takes from 15 to 1.5 hours, does not require special preparation and is carried out by specialized medical personnel, whose task is to carry out the procedure as quickly and painlessly as possible, as well as to preserve the health and vital functions of both donors and the recipients they save.