Thrombocytopenia
This is a condition caused by a decrease in the number of platelets in the blood.
It is caused by autoimmune pathologies (thrombocytopenic purpura, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus). This pathology can be a complication of viral infections, alcohol abuse, chemotherapy or radiation. Thrombocytopenia is manifested by frequent bleeding from the nose and gums, an increased tendency to bruise, and the presence of blood in the feces and urine. Patients often develop a small rash all over their body. Women experience prolonged menstruation. Treatment of the problem depends on its severity.
Symptoms in men
With age, the disease in men becomes progressive. Symptoms become pronounced and can cause serious harm to the body:
- Bleeding in the retroperitoneal region. Over time, they lead to acute diseases of the internal organs, which can be cured exclusively by surgery.
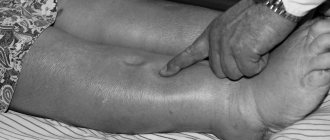
- Subcutaneous and intramuscular bruises. Their danger lies in the high probability of tissue necrosis and infection in the blood.
- Anemia of posthemorrhagic type.
- Bleeding into bone tissue. Without proper treatment, this will soon lead to its death.
- Large area hematomas causing paralysis and gangrene.
- Hemorrhages in the joint area, osteoarthritis. Limitation of their mobility and partial atrophy of the muscle fibers of the limbs will subsequently lead the patient to disability.
How to diagnose the disease?
To identify the causes of pathology and select highly effective treatment, the patient must undergo an examination, which includes:
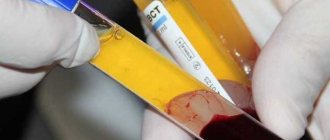
- Comprehensive blood test. This test determines how many white and red blood cells are in the blood;
- Platelet aggregation assay. This study will make it possible to understand whether platelets can attach to each other;
- Determination of bleeding duration. This study shows how long it takes for the blood vessels to become blocked after puncture of the skin surface.
Possible complications
If the causes of low blood clotting are discovered, it is necessary to begin treatment as quickly as possible , since this is the only way to get good results. If this is not done in time, the following complications may occur:
- Bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract;
- Bleeding in the brain;
- Severe pain and bleeding in the joints.
Video about bleeding disorders
In this video, Dr. Komarovsky will perform a clinical blood test:
Hemophilia
This is a hereditary pathology associated with a violation of blood clotting processes. It is inherited through the female line, and men are affected.
Its main symptoms are hemorrhages in the joints, severe bleeding that occurs after even the smallest injuries. Recurrent hemarthrosis leads to damage and immobilization of the joints, which is why disability develops by the age of 20. Large retroperitoneal or muscle hematomas may appear. Due to their compression of the nerves, severe pain, paresis and paralysis occur.
Read also Why the bleeding does not stop after tooth extraction
Severe forms of hemophilia lead to severe abdominal bleeding. These conditions are life threatening.
Patients should always strictly follow all doctor's recommendations. When contacting specialists, you need to inform about hemophilia. Treatment of the disease is carried out by introducing clotting factors into the body.
Symptoms in children
The disease is characterized by severe severity if it develops during the first 6-12 months of a child’s life. Its main symptoms:
- Bloody discharge occurs from the child’s umbilical wound for a long time.
- small hematomas that are localized in different parts of the body or on mucous membranes.
- bleeding at puncture sites for vaccines and other necessary injections.
As soon as the child reaches two years of age, capillary (petechiae) and joint hemorrhages are added to the above symptoms. They can form for no apparent reason or as a result of minor physical activity.
Genetic hemophilia in preschool children is characterized by symptoms:
- heavy bleeding from the nose;
- bleeding from the gums, especially during daily dental hygiene;
- periodic appearance of blood in the urine, the level of which is outside the normal range;
- hemarthrosis, the prolonged presence of which leads to chronic contractures and synovitis;
- detection of blood elements in the child’s stool, which indicates an early stage of progressive anemia;
- hemorrhages in some internal organs;
- a tendency to cerebral hemorrhages, which pose a real threat of damage to the central nervous system.
A hemophiliac child usually stands out from other children because of his thin build and poor appetite. The disease is dangerous because it can cause severe complications: thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, renal failure, leading to disability at an early age.
Danger during pregnancy
During pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes enormous changes. Because of them, hemostasis primarily suffers. Poor coagulation is caused by amniotic fluid embolism and premature placental abruption.
Impaired blood clotting during pregnancy has a negative impact on a woman's health. There is a high risk of postpartum hemorrhages, which are particularly resistant to treatment. Therefore, gynecologists prescribe a series of examinations necessary to determine the causes of impaired coagulation and prescribe effective therapy.
A pregnant woman should completely stop smoking and drinking even the slightest amount of alcoholic beverages. The menu should contain a sufficient amount of vitamin B12. If you are prone to poor clotting, you should limit your fluid intake.
Symptoms in women
Hemophilia, or bleeding disorder, in women is an exception to the rule. In the entire history of mankind, only sixty cases of this disease have been recorded in females. In most situations, the transfer of a gene from a father or mother that has succumbed to mutation leads to the death of a female fetus.
True, in rare cases survival occurs. It is possible that a genetic change may occur during life. As a rule, in women this pathology occurs in a milder stage than in men, and is characterized by the following symptoms: The presence of heavy menstruation. Prolonged bleeding immediately after the removal of tonsils or teeth.
The happiness of motherhood is in question
Poor blood clotting in all cases threatens with bleeding, which at any moment can get out of control, but this pathology is especially dangerous during pregnancy, when the body, in preparation for childbirth, tries to “foresee” everything and put all hemostasis in ideal order (to avoid and bleeding, and thrombosis). The likelihood of avoiding complications of this kind is high in women who do not have hereditary pathologies of hemostasis and acquired diseases listed above, in which decreased blood clotting is noted. Unfortunately, desires do not always coincide with reality.
This is interesting: Atherosclerosis of the vessels of the head: its causes, symptoms and treatment
Having discovered problems with the hemocoagulation system in the expectant mother during registration, the obstetrician-gynecologist classifies her as a high-risk group and subsequently resolves the issues together with other specialists (hematologist, therapist, rheumatologist, allergist). In particularly serious cases (acute leukemia, hemolytic anemia), the doctor warns the woman about impending complications and offers to terminate the pregnancy for medical reasons.
Meanwhile, married couples who want to have a healthy child do not need to wait for an unplanned pregnancy; they should try to prepare for such an event in advance and with all seriousness. For example, a woman should get her liver in order as much as possible, if the organ is not completely healthy, treat other chronic diseases, and, if possible, deal with the allergic status.
A family history of hemophilia is very important - the presence of a similar disease in the family of the mother or father requires mandatory consultation and a conclusion from a geneticist.
Of course, each specific variant of pathology requires separate consideration and a special approach, so it is hardly possible to give recommendations for all cases. However, women with a burdened heredity and medical history, in the hope of safely giving birth to a healthy child, should remember that during pregnancy, many hidden, asymptomatic diseases can suddenly manifest themselves in the worst possible way, therefore, they will have to listen to the advice of a doctor and constantly monitor their health.
To conclude this section, I would like to provide a table of normal values of individual (most significant) indicators during pregnancy:
| Laboratory indicator of blood clotting | Normal during pregnancy |
| APTT (activated partial thromboplastin time) | 17 – 20 seconds |
| Platelets | 150 – 380 x 109/l |
| TV (thrombin time) | 18 – 25 seconds |
| Prothrombin (Quick test) | 78 – 148% |
| Fibrinogen | Up to 6.0 g/l |
| AT III (antithrombin III) – a coagulation inhibitor, tends to decrease during pregnancy | 115 – 70% |
| Lupus anticoagulant | — (negative) |
| D-dimer | 33 – 726 ng/ml |
Treatment
Therapy for impaired blood clotting requires patience, as it can be quite lengthy. Medicines are prescribed only on the recommendation of a doctor. Their independent use can cause serious complications. Proper nutrition and the use of some effective folk remedies are of great importance.
Nutrition for decreased blood clotting
The diet should include foods that have a positive effect on blood composition and increase blood clotting. The menu should be enriched with the following dishes and products:
- greens;
- fatty fish (salmon or trout);
- cod liver;
- vegetables;
- fruits (especially bananas, apples, pomegranates);
- red berries;
- nuts;
- legumes;
- buckwheat;
- wheat bread;
- cream, natural butter;
- fatty meats.
Read also Emergency care for hemophilia
Alcohol, mayonnaise, sweets, sausage, processed foods, and coffee should be excluded from the menu.
Folk remedies
To increase coagulation, it is recommended to take folk remedies based on medicinal plants. Traditional folk remedies are based on effective and harmless recipes.
- Decoction of pine nut shells. To obtain it, you need to pour 500 ml of boiling water into a glass of raw material and cook over low heat for a quarter of an hour. You need to drink 2 tbsp of the decoction. 3 times a day for 3 weeks.
- To prepare an infusion of yarrow, you need to take about 15 g of dry and crushed raw materials, pour a glass of boiling water over it, and leave for about 15 minutes. Take a tablespoon 3 times a day before meals.
- An infusion of nettle leaves improves blood clotting properties well due to the presence of vitamins K and C in them. To prepare the medicine, you need to pour 1 tablespoon of boiling water into a glass. dry grass (or 5 young leaves). Leave for 30 minutes. It is recommended to drink ¼ cup of this infusion before eating.
These simple homemade recipes will help normalize blood clotting.
Medications
Medications that reduce blood clotting help normalize the process of blood clot formation. The following drugs are used.
- Vitamin K in the form of injections. The amount of vitamin is adjusted depending on the degree of clotting disorder.
- Aminocaproic acid, Contrical.
- Tranexamic acid.
- Oprelvekin (restores the process of platelet formation).
- Protamine sulfate is used only for impaired blood clotting that develops during prolonged use of antiplatelet agents.
- In severe cases, the introduction of donor plasma is recommended.
Insufficient blood clotting can be dangerous to health. In order to prevent complications and blood loss, treatment must be carried out. It will bring success only with an integrated approach, which includes proper nutrition, taking herbal preparations and medications.
Treatment of causes that lead to decreased blood clotting ability
- Drugs that inhibit (slow down) the process of fibrinolysis (destruction of fibrin). These include aminocaproic acid and Contrical.
- Coagulants are drugs that accelerate the process of blood clot formation. They are divided into two large groups - direct and indirect action. Direct ones include fibrinogen, thrombin and hemostatic sponge. Indirect - this is vitamin K (or Vikasol).
- Donated blood plasma is transfused into the patient as a means of containing natural blood clotting factors.
Drug treatment for low coagulation is an ambulance for the body. Depending on the cause of poor clotting, the patient may be prescribed lifelong use of certain medications (for example, for hemophilia) and a diet enriched with vitamins and calcium. In any case, the treatment of such a pathology as reduced blood clotting ability is a complex of measures.
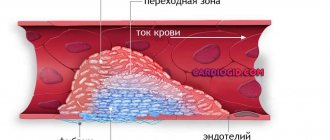
Under normal conditions, blood is constantly in a liquid state. If a vessel is damaged, tissue particles enter the bloodstream and the blood clotting process begins. In this case, a blood clot forms, which clogs the damaged area.
Poor blood clotting - causes of pathology
The pathology can be congenital or acquired. Coagulation can be impaired due to various diseases. In some cases, the causes of disorders in male and female bodies may differ. But there are a number of common factors.
- Liver failure.
- Problems with immune defense.
- Hypocalcemia is a significant calcium deficiency.
- Poor environmental conditions, hazardous production.
- A violent allergic reaction, in which the concentration of histamines in the plasma sharply increases.
- Oncological diseases.
- Lack of vitamin K.
- Long-term use of blood thinners, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Prolonged treatment with antibiotic drugs.
- Using certain other medications or overdosing them.
- Significant blood loss.
What is the cause of the disease?
The causes of poor blood clotting can be varied. Moreover, in men and women, the disease can be caused by various factors. Nevertheless, there are a number of general prerequisites:
- Liver diseases.
- Malfunctions of the immune system.
- Long-term treatment with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Acute lack of calcium in the body.
- Allergic reactions, which are accompanied by a significant release of histamines into the blood.
- Development of cancer.
- Therapy with drugs aimed at treating cardiovascular diseases.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions, employment in hazardous industries.
- Lack of vitamin K in the body.
- Long-term treatment with potent antibacterial drugs.
- Taking medications designed to prevent the formation of new blood vessels in the body.
In women, treatment of varicose veins often causes problems. It is carried out using specialized drugs, for example, Troxevasin, Warfarin, Detralex and others. These drugs can greatly thin the blood, which leads to the formation of disorders.
In men, a common cause of the problem is a hereditary factor. A disease such as hemophilia is often passed down from generation to generation through the male line.
Causes of disease in children
Bleeding disorders can occur even at an early age. The most common causes in children are:
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Congenital hemophilia, which is inherited by the child.
- Lack of vitamin K in the body.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Performed blood transfusion.
Poor blood clotting in a child can be extremely dangerous for his health and even life. Therefore, it is necessary to diagnose it as early as possible and begin treatment.
Causes and dangers of bleeding disorders during pregnancy
While carrying a baby, a woman’s body undergoes enormous changes, so it is forced to adapt to new circumstances. Changes are happening in many systems. This often leads to disruptions, including in the circulatory system. Among the main causes of poor blood clotting during pregnancy are:
- Premature placental abruption.
- Amniotic fluid embolism.
- Restructuring of the immune system caused by pregnancy.
Blood clotting disorders in pregnant women can lead to negative consequences for health and even life . There is a high risk of postpartum hemorrhage, premature birth or miscarriage. Therefore, specialists must prescribe a number of appropriate tests to identify pathology.
A pregnant woman needs to be careful about her health. A complete cessation of smoking and drinking even small doses of alcoholic beverages is mandatory. You should properly build a drinking regime, since excess fluid in the body can cause blood thinning.
Symptoms and signs
Signs and symptoms of an increased rate will be:
- General weakness;
- Fast fatiguability;
- Feeling of a “heavy” body and “cotton” limbs;
- Headaches throbbing in the back of the skull;
- Nausea, indigestion, abdominal pain;
- Rapid occurrence of hematomas and bruises;
- Spider veins.
If you find many of them, and probably the previously listed reasons occurred , consult a doctor. He will order a study.
The right diet
An important aspect of therapy is proper nutrition. It is necessary to introduce into the diet as many foods as possible that improve blood clotting and have a beneficial effect on its composition. These include:
- Green crops. Particular attention should be paid to lettuce and spinach. They contain large amounts of vitamin K.
- Be sure to eat fatty fish, such as trout or salmon. Introduce cod liver into your diet.
- The menu should include as many vegetables as possible. Cabbage, carrots, corn, cucumbers, tomatoes and celery are considered healthy.
- There are more fruits: apples, bananas, pomegranates, pears. Drink juices.
- Red berries, such as raspberries, currants and strawberries, will also be beneficial.
- Walnuts.
- Legumes: beans, lentils, peas.
- White bread.
- Buckwheat porridge.
- Animal fats: cream, butter. When choosing meat, it is better to give preference to lamb or pork. Pork liver is also useful.
Try to completely eliminate the following foods from your diet:
- Alcoholic drinks.
- Strong black tea and coffee.
- Sausages.
- Fatty and gifted dishes.
- Mayonnaise.
- Confectionery.
- Semi-finished products.
The diet should be balanced. You need a lot of foods rich in vitamins and minerals. This is the only way to quickly restore health.
Now you know what a bleeding disorder is called, why it happens, and how to treat it. Therefore, at the first alarming symptoms, consult a doctor and undergo a medical examination.