17.02.2019
A diagnosis such as “Impaired uteroplacental blood flow” is given to pregnant women quite often, but not every gynecologist finds the time to explain to the expectant mother what it is. Let's figure out in this article why this conclusion is dangerous and why disturbances in the uteroplacental blood flow occur.
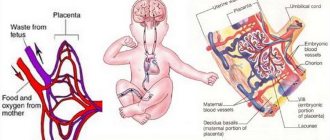
A pregnant woman’s body has an established system that allows the baby in the womb to receive all the necessary nutrients. An approximate diagram of this system consists of three components: “mother’s body - placenta - fetal body.” If any part of this relationship is disrupted, this leads to complications in the condition and development of the baby with simultaneous complications during pregnancy.
There are three levels of impairment:
- The first degree, when the development of the fetus is satisfactory, and the disorders are not dangerous and relate exclusively to the uteroplacental blood flow. In the absence of a response from specialists and proper treatment, this stage can last 3-4 weeks on average and moves to the next 2nd level. Divided into 2 types:
- The second degree is characterized by disturbances in the movement of blood through the vessels both in the fetus and in the uterine blood flow. This grade can very quickly (sometimes within 1 week) progress to grade 3.
- The third degree means that the blood supply to the fetus is at a critical level.
1A) When the fetal-placental circulation is normal, and disturbances are noticed in the uteroplacental blood flow. Fetal growth restriction syndrome develops in approximately 90% of cases.
1B) Characterized by normal uteroplacental circulation, but complications in the fetal-placental circulation. Fetal growth restriction syndrome develops in approximately 80% of cases.
What complications and diseases lead to the risk of placental insufficiency?
- hypertension of varying severity;
- threat of interruption;
- pyelonephritis;
- previous birth of children with fetal growth retardation syndrome;
- previously suffered a severe form of gestosis.
Table. Course of pregnancy depending on the degree of disturbances of uteroplacental blood flow
| Degrees of impairment | Doppler ratio control | Direction of treatment | Method of delivery |
| 1 | Up to 30 weeks - once every three weeks; 30-34 weeks - once every two weeks; 35-40 weeks - 1 time per week. If the obstetrician-gynecologist suspects that the fetus’s condition has worsened, then Doplerometry is performed unscheduled | Elimination of complications from the pregnant woman that are associated with diabetes, gestosis and other pathologies. Mandatory treatment of placental insufficiency. | There will be an antenatal hospitalization at 37 weeks. Childbirth takes place naturally with early artificial puncture of the membranes. |
| 2 | Every 3-4 days | The pregnant woman is immediately sent to the hospital. Treatment is aimed at maturing the child’s lungs, eliminating complications on the part of the woman, and intensively restoring placental insufficiency. | Caesarean section using epidural anesthesia. |
| 3 | In dynamics | Determining the cause and carrying out treatment | A caesarean section is performed immediately. If the pregnancy is premature, then the decision is made based on the wishes of the pregnant woman |
Treatment of grade 1A uteroplacental blood flow disorders is carried out comprehensively, based on the reasons that caused it. Drugs: Actovegin, Ginipral, Curantil, Pentoxifylline and others.
Attention! This article contains general information only and is not intended to substitute for advice from a qualified professional.
A clearly functioning “mother-placenta-baby” system is the key to the health of a woman expecting a new addition to the family and her baby. A failure in this system, resulting in impaired blood flow, can lead to negative consequences for the child, the reversibility of which is often simply impossible. Violation is fraught with delayed development of the fetus in the womb. The consequences of impaired blood flow during pregnancy also include hypoxia, malformations and even embryonic death.
An additional circle of blood circulation in a pregnant woman requires additional examination by a specialist. This examination is called Doppler ultrasound. Doppler is an ultrasound diagnosis of the intensity of blood flow in different vessels. Diagnosis is carried out in the third trimester of pregnancy. It is at this time that Doppler shows almost 100% reliable results. In some cases, Doppler measurements are performed at twenty weeks.
By comparing the information received on the device and guided by blood flow standards, the diagnostician determines whether the child is experiencing oxygen starvation or not.
Doppler testing has its own approved standards, which include: index of vascular resistance of the uterus, umbilical cord, aorta and fetal cerebral artery. Independently deciphering and comparing the data obtained after diagnosis and Doppler measurements is a thankless task. Only a doctor can calculate the vascular resistance index using the appropriate formula.
What should you do if the doctor, having deciphered the Doppler data and compared it with the norms, notes a violation of the blood flow of the pregnant woman? Well, definitely don’t panic and don’t get nervous. It won't be good for the child either. Timely treatment is quite effective in combating blood flow diseases.
Disturbances in the circulation of blood through the blood vessels during pregnancy vary in severity.
In the first degree, blood flow disturbance does not reach critical values. The fetal hemodynamics are positive.
The hemodynamics of the fetus in the second degree of the disease is impaired. In half of the cases, the maximum speed of blood movement through all heart valves is reduced. In this case, blood flow is disrupted both in the child and in the arteries of the uterus of the expectant mother. In a very short period, the second degree can develop into the third.
The third degree is destructive for the child. Its diagnosis states the critical state of the blood supply to the fetus. Intracardiac hemodynamics at this stage have profound changes. Fetal hypoxia is most likely in this case.
Can a pregnant woman experience blood flow problems? There are certain symptoms. But, for example, in the first stage, placental insufficiency does not manifest itself in any way. It can only be diagnosed by ultrasound. A second degree symptom is a change in the baby’s behavior. He is either too active or, conversely, inactive. Secondary signs of blood flow disease may be the release of protein in the urine, insufficient or excessive amounts of amniotic fluid, edema, gestosis (late toxicosis), pressure surges, and sudden weight gain.
Bloody discharge from the birth canal is the most dangerous sign of a disorder associated with placental abruption. In this condition, only emergency medical help will help.
The consequences of impaired blood flow are very sad if treatment is not prescribed in time. This is, at a minimum, acute or chronic hypoxia, as well as intrauterine growth retardation. More severe complications: premature birth; pregnancy fading; miscarriage; development of congenital pathologies, including those incompatible with life; intrauterine fetal death.
To prevent the disastrous consequences of impaired blood flow, we need, first of all, thorough prevention.
In order for the baby to be fully nourished, a woman must consume a balanced diet during pregnancy. These are products with the maximum possible amount of vitamins and microelements. High-quality proteins, carbohydrates and fats. Frequent consumption of water (more than one liter) is also required. Except in cases where the expectant mother is prone to swelling.
Prevention of blood flow disorders involves monitoring weight changes during pregnancy. An increase of more than 10 kg by the end of pregnancy is considered excessive.
If a pregnant woman is at risk (under 17 years of age or over 36 years of age; with bad habits; with chronic diseases, etc.), then prevention should include taking medications that prevent blood flow diseases.
A woman who dreams of becoming the mother of a healthy baby in the future should, already during pregnancy planning, analyze her lifestyle and, if possible, eliminate potential risks.
How it works?
The movement of blood through the blood vessels is carried out in two circles of blood circulation - large and small. A pregnant woman has 3 circles of blood circulation: an additional blood circulation system appears between the woman and the placenta. The child, in turn, also has its own, separate circulatory system, which is connected to the placenta. The blood of mother and child never mixes, and the entire exchange of nutrients and oxygen occurs in the placenta.
Editor's choice: At what week of pregnancy does the baby begin to move - how to tell?
Causes
Hemodynamic disturbances between the fetus and the woman’s body are provoked by many factors. They affect the placenta both during its formation and in later stages of pregnancy. Accordingly, primary and secondary circulatory failure are distinguished. As a result, all functions of the placenta as a separate organ are disrupted: transport, metabolic, protective, immune and endocrine. This is caused by the following conditions:
- Tumors of the uterus.
- Structural anomalies.
- Genetic defects.
- Hormonal dysfunctions.
- Consequences of abortion.
- Late toxicosis.
- Infectious diseases.
- Atherosclerosis, thrombosis.
- Hypertonic disease.
- Diabetes.
- Diseases of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands.
Most often, a woman has an underlying risk factor that can cause placental insufficiency. A combination of several similar conditions is often observed when carrying a child.
To identify the causes of placental blood flow disturbances, it is necessary to conduct periodic screenings at various stages of pregnancy.
Symptoms
Each pathology has its own clinical picture, which allows us to make a preliminary conclusion. Hemodynamic insufficiency is manifested by changes in all functions of the placenta, and as a result, mainly the fetus suffers. It receives all nutrients and oxygen in insufficient quantities, and the excretion of metabolic products may slow down. Signs of fetal hypoxia appear, which subsequently leads to intrauterine growth retardation. As a result, the following symptoms are noted:
- Increased heart rate.
- Increase in physical activity, and then its decrease.
- Abdominal volume does not correspond to the duration of pregnancy.
As a rule, such signs appear in the decompensated form of placental insufficiency. If the blood flow disorder has a 1a or 1b degree, identified during a timely examination, then these symptoms do not yet exist, since the hemodynamics are compensated.
Classification
Symptoms depend on the severity of changes in BMD, which are recorded during additional examination. Based on a clinical and gynecological examination, it is impossible to say for sure about this, but one can first judge hemodynamics based on indirect data. Thus, blood flow disorders during pregnancy are classified according to degree:
- 1a degree - changes affect only the uteroplacental part of the blood flow.
- 1b degree - only fetal-placental blood flow is weakened.
- 2nd degree - disturbances affect all hemodynamic processes, but diastolic blood flow is still preserved.
- Grade 3 – a situation where the fetal-placental blood flow has critical disturbances while maintaining or changing the uteroplacental hemodynamics.
This classification is based on the relationship between the speed of uterine and umbilical blood flow. In addition, disorders are identified in individual branches of the afferent artery.
Signs of impaired blood flow from the fetus may not be noticeable to the woman, but the doctor is obliged to pay attention to them.
Consequences
Placental insufficiency poses a risk to fetal development. Therefore, the main obstetric complications concern the condition of the unborn child. The greatest danger comes from severe blood flow disorders, which can have both a chronic and acute course. In this context, degrees 1a and 1b of hemodynamic disorders are not mentioned, as they are the mildest.
Placental abruption
Sudden disturbances in blood flow can be provoked by injuries, thrombosis or embolism of the uterine artery. Then a situation arises when the placenta exfoliates in one of the areas. Depending on its location, the pathology occurs as a central or peripheral type. The following symptoms appear:
- Pain in the area of detachment.
- Local protrusion of the uterine wall.
- Bloody issues.
- Worsening of the fetal condition.
If the detachment is of the central type, then there may be no external discharge at all, but blood seeps into the wall of the uterus, which is why it loses its contractility. This is fraught with atonic bleeding and disseminated blood coagulation (DIC syndrome).
When placental complications are mild, they can be eliminated with adequate therapy.
Miscarriage
In turn, placental abruption causes spontaneous abortion or premature birth, which is included in the concept of miscarriage. This is a situation that obviously all women are afraid of, because losing a child is the worst thing that can happen during this period. Then the following signs appear:
- Pain in the lower abdomen, in the sacrum, rectum.
- Bloody discharge of varying intensity.
- Increased urination.
- Hypertonicity of the uterus.
- Gradual dilatation of the cervix.
If the process is stopped at the threat stage, the child will be saved. But when the placenta has completely detached and an abortion is diagnosed, unfortunately, it is no longer possible to correct anything. In the future, the pathology may be complete or incomplete. When parts of the fetus or membranes are retained in the uterine cavity, there is a risk of infection and severe bleeding, which often ends in hemorrhagic shock or disseminated intravascular coagulation.
Frozen pregnancy
In addition, the fetus may die if left in the uterine cavity. Then a so-called frozen pregnancy is formed. The woman herself can note some symptoms that indicate what happened:
- Fetal movements stop.
- You can't feel his heartbeat.
- The abdomen does not increase in volume.
- Bloody discharge occurs periodically.
- I am worried about abdominal pain.
- Body temperature rises.
- An infection sets in.
A frozen pregnancy must be removed. If this is not done on time, then there is a danger to the life of the woman herself.
Diagnostics
To determine placental blood flow disorders during pregnancy, it is necessary to use additional diagnostic methods. They allow you to determine the type and degree of changes, as well as determine the condition of the fetus. To do this, use the following procedures:
- Blood test for hormones (estrogens, progesterone, human chorionic gonadotropin).
- Ultrasonography.
- Cardiotocogram.
- Doppler.
Some data can also be obtained after a doctor’s examination - the child’s condition can be judged by the heart rate calculated during auscultation. But the most reliable results are obtained after instrumental and laboratory research.
Diagnosis of pathology
If the disease is mild (first degree), the doctor may prescribe medications that improve blood circulation.
The dynamics of the fetal condition are carried out; weekly, until the indicators normalize, the pregnant woman undergoes Doppler measurements and checks the fetal heartbeat. If the indicators stabilize, the woman will continue to bear the child. In case of deterioration, it is recommended to have a cesarean section (if the pregnancy is more than 25–28 weeks).
In the second degree, the pregnant woman is hospitalized and treated under the strict supervision of medical staff. If the condition worsens, an unscheduled operation is performed.
As for the third degree, it cannot be treated, since irreversible changes begin in the development of the fetus. Therefore, in order not to risk the child’s life, doctors insist on an immediate cesarean section.
Treatment
In case of disturbance of uteroplacental blood flow of any severity, therapeutic measures are indicated. This is mainly aimed at preventing the progression of the pathology, while normalization of hemodynamics, according to observations, is possible only at stage 1b. At the same time, they try to use all possible means to improve the condition of the fetus. Of course, conservative measures come first. Surgical intervention is used only for complications and for health reasons. In addition, great importance is given to the prevention of placental insufficiency.
Treatment of blood flow disorders during pregnancy is complex - etiotropic, pathogenetic and symptomatic.
Drug therapy
The main means of correcting placental blood flow is the use of medications. When only initial signs of disorders are identified, you can undergo treatment on an outpatient basis. If the deficiency is more pronounced, then hospitalization in a hospital is necessary. This need also exists for extragenital pathology in women. The following drugs are mainly used:
- Antispasmodics (No-shpa, Eufillin).
- Tocolytics (Ginipral, Partusisten).
- Vascular (Actovegin).
- Improving microcirculation (Trental).
- Antiplatelet agents (Curantil).
- Antihypoxants (Instenon).
- Vitamins and microelements (Magne B6, ascorbic acid).
- Metabolic (ATP).
- Hepatoprotectors (Essentiale, Hofitol).
As a rule, it is recommended to undergo two courses of therapy - immediately after diagnosis and at 32-34 weeks. After this, the issue of delivery is decided. This is especially important in severe circulatory disorders. If violations are recorded at stage 1a or 1b, then childbirth occurs naturally.
During pregnancy, only proven medications that have proven their safety and effectiveness are used.
Operation
When placental insufficiency is severe, emergency delivery is necessary. If conservative measures are ineffective, even with mild violations, a decision should be made within 2 days. The most commonly used procedure is a caesarean section. If it is planned before 32 weeks of pregnancy, then it is necessary to proceed from the condition of the fetus and its viability.
When it is necessary to ascertain that a spontaneous abortion has occurred, it is necessary to carry out curettage of the uterine cavity or vacuum extraction of the fetus. In case of a frozen pregnancy, surgical intervention depends on the gestational age and the condition of the woman.
Prevention
To avoid many unpleasant situations during pregnancy, including placental insufficiency, it is necessary to follow preventive recommendations. They mainly relate to lifestyle and include the following principles:
- Healthy eating.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Walking outdoors.
- Elimination of stress factors.
- Follow all doctor's recommendations.
- Timely treatment of concomitant diseases.
If you take care of your own health during pregnancy, you can prevent disruption of blood flow in the mother-placenta-fetus system. And if this pathology is detected, it is necessary to carry out timely treatment, which will allow saving the child.
The body of a woman and a child during pregnancy is connected by the placenta; it is the placenta that performs all vital functions during this time. The normal growth and development of the fetus depends on the placenta. It provides it with oxygen, nutrients, removes metabolic products and synthesizes hormones necessary for the normal course of pregnancy.
In the communication system between mother and fetus (fetoplacental system), there are two types of blood circulation - placental and fetal. If the uteroplacental blood supply is disrupted, placental insufficiency develops and the fragile relationship fails. This can manifest itself in the form of pathological conditions and severe complications of pregnancy.
What is HDN during pregnancy: pathologies, risks
The placenta is an organ that forms from the end of the first trimester. The main purpose is to protect and ensure the safety of the child. For the normal functioning of the placenta and the development of the baby, oxygen and nutrients are needed, which are found in the mother's blood. Monitoring of MPP is carried out using Doppler ultrasound.
The vascular system of the placenta has a complex anatomical structure. The mother's blood penetrates the placenta cavity, but does not mix with the formed elements of the fetus.
Hemodynamic changes in fetoplacental blood flow are a pathological phenomenon, with the development of acute placental insufficiency.
Insufficiency of placentation leads to many negative factors, complicates the course of pregnancy, determines the outcome of childbirth and affects the health of the fetus.
With HDN, a lack of oxygen develops, the child does not receive the required level of nutrients, his development is disrupted and developmental delay syndrome occurs.
In severe cases, antenatal death or severe disability occurs because the nerve cells of the brain fade away.
Placental blood flow during pregnancy: disruption of its functioning
The symbiosis “mother and child” is connected by two arteries (left and right) and one vein of the umbilical cord.
Trace elements and oxygen penetrate the amniotic fluid to the baby through a special hole. Pathogenic viruses and bacteria penetrate the venous system and provoke phagocytosis.
Hemodynamics can be disrupted in any of the vessels.
The causes of impaired fetoplacentation are divided into exogenous (external) and endogenous (internal) factors.
Exogenous ones include:
- poor nutrition;
- Unhealthy Lifestyle;
- smoking;
- alcohol addiction;
- influence of production factor;
- patient's age;
- physical exercise.
Endogenous:
- hereditary mutation;
- chromosomal damage;
- structural anomalies of the reproductive organs;
- hereditary blood diseases;
- endocrine pathologies;
- chronic diseases of internal organs;
- unfavorable obstetric or gynecological history;
- STI;
- inflammatory and infectious processes in early gestation.
Conditions such as hypertension and a tendency to form blood clots are provoking factors. The formation of HD disturbances during pregnancy is associated with changes in the morphological characteristics of the vascular system.
There are no external clinical signs of HDN; sometimes late gestosis may develop due to impaired blood flow.
There are no specific signs of pathology; the diagnosis is made by an obstetrician-gynecologist based on a series of diagnostic tests.
Diagnosis
Despite the absence of symptoms, it is not difficult to diagnose placental insufficiency. At each visit to the doctor, the gynecologist measures the volume and girth of the abdomen and listens to the heartbeat.
If external data does not change, and the fetal heart rate changes up or down, the child may not have enough strength for full growth and development. He experiences hypoxia.
It is possible to confirm or refute the diagnosis using ultrasound and Dopplerography.
Diagnostic measures of the HDN include:
- examination by a gynecologist;
- Dopplerography (allows you to evaluate the speed of blood flow and identify areas with possible disturbances);
- Ultrasound of the fetus and child's place to detect changes (delayed development, premature aging, membrane width, presence of infection or genetic abnormalities);
- laboratory testing (coagulogram, hormone and D-dimer analysis);
- Fetal CTG.
Ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound are performed three times during the gestation period (in the case of a normal pregnancy) - at the end of the first trimester, and in the middle of the II and III trimester.
Diagnosis of disturbances in the MPP of blood flow is necessary to identify the extent of the pathological process. There are the following degrees of GDN:
- Grade 1 is diagnosed with primary changes in one of the vascular systems. It can be corrected with medications and is not an indication for early delivery. It is represented by two subspecies: “a” and “b”. At grade 1a, initial disorders of hemodynamic changes develop without signs of hypoxia. 1b is characterized by a change in the symbiosis “fetus and placenta”. The phenomenon is common and is diagnosed in 80% of patients. Grade 1 can be treated and pregnancy has every chance of further prolongation;
- Grade 2 is accompanied by impaired blood flow in the fetal aorta, uterine and umbilical arteries. The level of essential substances is significantly reduced. The fetus experiences acute hypoxia. The degree of the pathological process is unstable, because it can quickly move to the extreme - third stage. If there is no therapeutic effect during treatment, early delivery is indicated.
- Grade 3 is a severe and dangerous form of placental insufficiency. Treatment is not carried out, but an emergency caesarean section is performed to save the baby’s life, however, practice shows an unfavorable prognosis for childbirth. Critical changes affect the fetal brain and heart muscle.
Treatment of the pathology is carried out conservatively, using oral and parenteral methods. Preference is given to vitamin therapy and anticoagulants.
Bed rest is recommended for pregnant women. Additional therapy is procedures for oxygen saturation (oxygen cocktails, pressure chambers).
The goal when blood flow in the placenta is disrupted is to prolong pregnancy until 37 weeks. Self-medication is strictly unacceptable.
To avoid negative consequences, pregnant women should not neglect medical prescriptions and visit an ultrasound specialist on time.
In the case of primary symptoms, it is necessary to begin treatment as quickly as possible, otherwise disturbances in the uteroplacental-fetal blood flow will progress to a more severe stage.
There should also be no less effort on the part of the pregnant woman. You should review your diet, monitor your weight gain, and stop drinking alcohol and nicotine.
Eat more vegetables and fruits, walk in the fresh air.
Classification of blood flow disorders in the placenta
Placental insufficiency negatively affects the functioning of the placenta. It can be acute or chronic.
Acute placental insufficiency can occur throughout pregnancy or during labor. Impaired gas exchange in the placenta, and as a result, acute fetal hypoxia, can cause the death of the child. Often this occurs after premature destruction of the uterine walls, the formation of blood clots in its vessels, placental infarction and hemorrhage.
Chronic fetoplacental insufficiency (FPI) is much more common than acute. As a rule, it develops in the second trimester, but is detected only at the beginning of the third. Premature aging of the placenta is caused by the deposition of fibrin on the surface of the villi. This substance interferes with normal metabolic processes.
Chronic FPN is divided into types:
- Compensated is the most favorable form of placental insufficiency; the fetus does not suffer and continues normal development. The protective and adaptive mechanisms of the female body are able to compensate for these changes. With adequate therapy, the child will be born healthy and on time.
- Decompensated - compensatory mechanisms are no longer able to effectively resist pathological changes in the placenta, which interferes with the normal development of pregnancy. The fetus experiences oxygen deficiency, developmental delay and cardiac dysfunction. In the decompensated form of FPN, intrauterine death of the child is likely.
- Subcompensated - the woman’s body cannot cope with placental insufficiency, and the fetus lags behind in development. The risk of serious complications is significant.
- Critical - serious morphological and functional changes occur in the placenta, which cannot be influenced, and the death of the unborn child is inevitable.
There are 3 degrees of blood flow disorders:
- The fetal condition is normal
. The disorders are not dangerous and develop at the level of the uteroplacental blood flow. If such changes were not detected or the woman did not receive proper treatment, then the pathological changes within 3-4 weeks become more complicated and move to the second level.The first degree of blood flow disturbance has two types: 1A. The uteroplacental blood flow is impaired, but the fetal-placental circulation is normal. In 90% of cases, the fetus experiences developmental delays. 1B. Uteroplacental blood flow is normal. Changes in fetal-placental blood flow are noted. Delayed fetal development is observed in 80% of women with this pathology.
- Disruption of blood movement in the uterine bloodstream and in the vessels of the fetus
. This condition tends to rapidly progress to the third stage, which can occur within one week. - Critical level of blood supply to the fetus, its complete absence or reverse (reverse) blood flow
.
Only stage 1B can be treated; more severe blood flow disorders are irreversible. This leads to impaired development of the fetus or even its death in the case of reverse blood flow, which continues for more than 72 hours. Such severe conditions are indications for premature delivery.
What blood flow problems occur during pregnancy?
Mother and child are connected not only by the placenta, but also by a complex system of blood vessels. Therefore, all joint blood circulation is usually divided into levels that cannot exist in isolation, but work only in combination.
- The central part of the system is the placenta. It ensures the “absorption” of products from the maternal blood through the villi that have grown deep into the wall of the uterus. At the same time, the blood of mother and child does not mix. Several rows of special cells form a hematoplacental barrier, which is a serious obstacle to substances unnecessary for the fetus. Through it, the waste blood returns to the mother's venous system.
- The second part of the blood flow consists of the branches of the uterine arteries. If before pregnancy in the female body they are in a collapsed state and are called spiral, then from the period of 1 month they lose the muscle layer that can cause spasm. And by four months, the arteries transform into full-fledged trunks, filled with blood and heading to the placenta area. It is this mechanism, useful for feeding the fetus, that can turn out to be fatal during uterine bleeding: the walls of the vessels can no longer contract.
- The vessels in the umbilical cord form the third pathway of blood flow. There are 2 arteries and a vein here. They connect the baby with the placenta and form the fetal-placental circle. Reduced blood flow at this level causes the most severe damage to the fetus.
Poor blood flow associated with the placenta is called placental insufficiency. It can occur at any stage of pregnancy in two forms.
Acute appears suddenly, even during childbirth, and does not depend on the duration of pregnancy. The fetus falls into a state of hypoxia (oxygen deficiency), which threatens its death.
The main pathological mechanisms of this condition:
- premature placental abruption;
- heart attack due to thrombosis.
Chronic often complicates the course of pregnancy after 13 weeks. Symptoms appear in the third trimester. The mechanism of formation is early aging of the placenta due to the deposition of fibrin on the villi.
As a result of changes in the structure of chorionic villi (placental tissue), the functioning of the hematoplacental barrier ceases, metabolic processes between the maternal body and the fetus are disrupted
Negative consequences in such conditions, depending on the degree of violation, can lead to inevitable death of the fetus.
Various reasons can cause disruption of uteroplacental blood flow. These include common maternal diseases:
- pathology of the neuroendocrine system (diabetes mellitus, diseases of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands, changes in the hypothalamus region of the brain stem);
- lung diseases (emphysema, bronchial asthma);
- disorders in the cardiovascular system caused by developmental defects, the consequences of hypertension, a tendency to hypotension;
- renal pathology (chronic nephritis, pyelonephritis, especially in the stage of renal failure;
- anemia (anemia) associated with deficiency of iron and vitamins;
- conditions accompanied by increased blood clotting contribute to increased thrombus formation in the vessels of the placenta;
- acute and exacerbation of chronic infectious processes cause corresponding inflammation in the placenta, vascular edema and reduction in blood flow; in the first trimester this can result in miscarriage.
Pathology of the uterus creates local conditions for inadequate blood flow:
- any changes in the layers of the uterus (myometrium, endometrium);
- malformations (for example, “bicornuate”, “saddle-shaped” uterus);
- underdevelopment (hypoplasia);
- tumor formations from muscle tissue (fibroids), especially in a primiparous woman over the age of 35; at a younger age, small fibroids help compensate for blood flow.
The causes of insufficient blood flow include unfavorable conditions during pregnancy in the following cases:
- multiple births;
- Rhesus conflict;
- preeclampsia;
- breech presentation of the fetus;
- pathological placenta previa.
The risk of impaired blood flow occurs when:
- previous abortions;
- maternal smoking, alcoholism and drug addiction;
- constant nervous environment associated with social or everyday unsettlement;
- violation of proper nutrition of a woman.
Pregnant women and their families usually expect one answer from an ultrasound examination - what is the sex of the child. For an obstetrician-gynecologist, a research method is necessary to promptly identify impaired blood flow during pregnancy and abnormal fetal development.
The management plan and delivery tactics depend on this. To understand the mechanisms of the disorder, it is necessary to consider the capabilities of the circulatory system between mother and child.
Chronic often complicates the course of pregnancy after 13 weeks. Symptoms appear in the third trimester. The mechanism of formation is early aging of the placenta due to the deposition of fibrin on the villi.
As a result of changes in the structure of chorionic villi (placental tissue), the functioning of the hematoplacental barrier ceases, metabolic processes between the maternal body and the fetus are disrupted
- pathology of the neuroendocrine system (diabetes mellitus, diseases of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands, changes in the hypothalamus region of the brain stem);
- lung diseases (emphysema, bronchial asthma);
- disorders in the cardiovascular system caused by developmental defects, the consequences of hypertension, a tendency to hypotension;
- renal pathology (chronic nephritis, pyelonephritis, especially in the stage of renal failure;
- anemia (anemia) associated with deficiency of iron and vitamins;
- conditions accompanied by increased blood clotting contribute to increased thrombus formation in the vessels of the placenta;
- acute and exacerbation of chronic infectious processes cause corresponding inflammation in the placenta, vascular edema and reduction in blood flow; in the first trimester this can result in miscarriage.
- any changes in the layers of the uterus (myometrium, endometrium);
- malformations (for example, “bicornuate”, “saddle-shaped” uterus);
- underdevelopment (hypoplasia);
- tumor formations from muscle tissue (fibroids), especially in a primiparous woman over the age of 35; at a younger age, small fibroids help compensate for blood flow.
- multiple births;
- Rhesus conflict;
- preeclampsia;
- breech presentation of the fetus;
- pathological placenta previa.
After a woman finds out about her pregnancy, she must realize that now the body belongs not only to her, but also to her unborn child. Hormonal surges and complete restructuring of the pelvic organs quite often result in a disruption in the blood supply to the fetus. In this article we will talk about impaired blood flow during pregnancy, what it entails, what symptoms are inherent, what therapy can be used and how to bear a healthy child.
First, let's figure out how everything works in mothers' tummies. During pregnancy, the placenta is responsible for transferring beneficial microelements and oxygen to the baby. It is the same unifier through which the vascular system of the pregnant woman connects with the vascular system of the fetus, becoming common. Any disturbances in the functioning of the placenta affect the condition of the baby, so it is necessary to monitor blood flow during pregnancy. Diagnosis is made through research - Doppler. Let's talk about it in more detail below.
Impaired blood flow can appear at any stage of pregnancy. A pregnant woman is diagnosed with placental insufficiency. This is one of the most common complications during pregnancy associated with dysfunction of the placenta. This pathology occurs in two forms:
- The acute form appears suddenly and is most often a consequence of placental abruption. It can provoke a violation of gas exchange in this organ and, as a result, oxygen starvation in the fetus.
- Chronic, it is also called premature aging of the placenta. Most often detected in the third trimester of pregnancy. Divided into the following types:
- compensated - is considered minimally dangerous, since with this form the child continues normal physiological development. In the mother’s body, protective mechanisms are “turned on” to compensate for the disruption of blood flow;
- decompensated - the mother’s body cannot cope with the problem, pathological changes occur in the placenta. The first oxygen starvation of the fetus appears, leading to delays in development, and intrauterine death of the baby is possible;
- subcompensated - with this form, the condition of the fetus worsens, it lags significantly behind in development;
- critical - with this form of deficiency, the death of the child is inevitable.
We suggest you read: Can blood pressure increase during pregnancy?
Complications and dangers that can develop due to impaired blood flow include:
- placental abruption;
- hypoxia;
- fetal hypotrophy;
- developmental pathologies;
- intrauterine death.
There are many reasons that contribute to impaired blood flow during pregnancy. Let's consider the most common factors that provoke blood flow disorders.
- Diseases of the uterus: bicornuate uterus, endometriosis, uterine hypoplasia, presence of fibroids, etc.
- Maternal health problems: renal failure, diabetes mellitus, hypotension, pyelonephritis, endocrine system diseases, bronchial asthma, etc.
- Unfavorable gestation conditions: Rh-conflict, multiple births, gestosis, malpresentation of the fetus, etc.
- External factors: drinking alcohol during pregnancy, smoking, constantly being in a nervous environment, first birth (and the woman is over 35), poor (limited) maternal nutrition.
During pregnancy, it is very important to constantly monitor the condition of the mother and fetus and their performance of vital functions. One of the most significant studies is the analysis of blood flow in the arteries of the uterus, the woman’s umbilical cord, as well as in the aorta and cerebral vessels of the child.
Among the main causes of perinatal mortality and morbidity, disruption of uterine blood flow (uteroplacental and fetal placental) is not the least important.
Blood flow in the placenta
The placenta, in which the fetus is located, supplies it with nutrition and oxygen from the mother’s blood and removes metabolic products from the child’s body. It is this organ that unites two complex vascular systems - the maternal one, which connects the vessels of the uterus and the placenta, and the fetal one, which passes into the umbilical arteries and leads to the fetus.
Symptoms of impaired blood flow
Manifestations of FPN depend on their type. With compensated chronic fetoplacental insufficiency, there are no symptoms. A woman learns about abnormalities during an ultrasound examination.
Acute and chronic decompensated forms of pathology are characterized by severe symptoms. A woman may notice periods of vigorous motor activity of the unborn child, which are followed by periods of complete rest. There are certain standards, according to which a pregnant woman over 28 weeks should feel at least 10 fetal movements per day. If the readings are lower, the woman should seek advice from a gynecologist.
Additional signs of impaired blood flow may be a slowdown in the increase in abdominal circumference. It is difficult to identify this on your own, so it is necessary to regularly visit an antenatal clinic, where such measurements are regularly carried out.
The most dangerous symptom of FPN is bloody vaginal discharge. This may be a sign of placental abruption. This condition requires urgent medical attention.
Causes of impaired blood flow during pregnancy
The occurrence of fetoplacental insufficiency can occur for various reasons. Impaired blood flow occurs as a result of the following pathologies:
- neuroendocrine diseases (hyperthyroidism, diseases of the adrenal glands and hypothalamus);
- lung diseases ();
- cardiovascular diseases (heart defects, hypotension and others);
- kidney disease (and kidney failure).
Maternal iron deficiency, or anemia, can cause placental insufficiency. Problems with blood clotting lead to the formation of microthrombi in the blood vessels of the placenta, which interfere with normal blood flow.
Exacerbation of various infectious diseases or their acute course during pregnancy often causes changes in the placenta. Pathogens provoke an inflammatory process, which in the first trimester often ends in miscarriage. The consequences of infection in the later stages depend on the severity of the placental lesions and the disease.
A significant risk factor for the development of FPN are uterine pathologies:
- pathological changes in the myometrium;
- malformations of the uterus (bicornuate and saddle uterus);
- hypoplasia;
- uterine fibroids.
The high-risk group includes women over 35 years of age with large myomatous nodes who will be mothers for the first time. Women under 30 years of age with small nodes are much less likely to develop blood flow problems in the placenta.
In addition, the causes of placental insufficiency may be the following:
- gestosis;
- Rh conflict between mother and child;
- breech presentation of the fetus;
Bad habits, a medical history aggravated by abortions, and a woman’s social and everyday problems significantly increase the risk of changes in the placenta at different stages of pregnancy.
Prevention
Every woman who wants to give birth to a child must remember that the mother’s condition is completely transmitted to the unborn baby. Therefore, in order for the fetus to develop without complications, she needs to make up her diet from food containing a maximum of vitamins, micro- and macroelements, as well as rich in the required amount of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. If a pregnant woman is not bothered by swelling, then fluid intake should be at least 1-1.5 liters.
DETAILS: Why do you feel dizzy in the evenings?
It is important to monitor changes in body weight, since by the end of pregnancy the weight gain should not exceed 10 kg.
There are risk groups that require the use of drug prophylaxis, which promotes the interaction of the body systems of the fetus and mother and prevents dysfunction of the uteroplacental circulation.
Timely adjusted methods of labor management and drug therapy will help to significantly reduce perinatal morbidity and mortality. But a high risk of severe neurological complications cannot be ruled out.
Preventive measures to avoid disturbances of the placental-uterine circulation are primarily aimed at:
- elimination of extragenital pathologies;
- following a healthy lifestyle - you need to monitor your diet, which should include all the necessary nutrients, get rid of bad habits and avoid stressful situations;
- refusal of excessive physical activity;
- reducing the risk of infectious diseases - this requires avoiding sources of potential infection.
To prevent disturbances in uterine blood flow, compliance with the norm for weeks must be monitored at the first symptoms of such a pathology. If there are prerequisites for the development of disturbances in the uteroplacental circulation, it is immediately recommended to conduct Doppler measurements to determine the extent of such changes and prescribe effective treatment.
Diagnosis of blood flow disorders
Identification of pathological disorders of placental blood flow is carried out through a comprehensive examination, but ultrasound, which is combined with Doppler measurements, plays a huge role in diagnosis. This method allows us to identify not only blood flow disorders, but also complications caused by them.
Doppler measurements are prescribed in the following cases:
- diseases of the mother that can provoke disturbances in blood flow in the placenta;
- premature aging of the placenta;
- intrauterine growth retardation syndrome;
- or ;
- signs ;
- congenital defects and genetic diseases in the fetus.
Depending on the complexity of the pathological process, disorders can be observed in the umbilical, uterine or fetal vessels. Based on the results of the examination, a diagnosis of uteroplacental, placental or fetoplacental form of blood flow disturbance is made.
Atypical blood circulation in the placenta may be indicated by such indirect signs as thinning or increasing area, symptoms of intrauterine infection and changes in amniotic fluid.
Diagnosis of pathology
The most complete picture of blood circulation between the uterus and the fetus is obtained through Doppler ultrasound, which is performed on all women three times during pregnancy.
- measure blood flow by the speed of movement of the formed elements;
- determine its direction in arteries and veins;
- record changes before clinical manifestations.
The effect is based on the properties of ultrasonic wave reflection and is completely safe for the child and mother.
All changes are recorded on the monitor, measured with special sensors, and can be photographed in the required format.
The doctor has time to prescribe treatment and check it at the next examination.
A type of Doppler ultrasound is Doppler ultrasound. It is prescribed for:
- maternal concomitant pathology;
- suspected premature aging and disruption of the placental barrier;
- signs of high or low water;
- preliminary data on intrauterine growth retardation, the formation of congenital malformations of the fetus;
- presence of genetic diseases in the family;
- clinical symptoms of fetal hypoxia.
The examination can reveal:
- thinning of the placenta;
- increase in growth area;
- intrauterine infection.
The method of long-term inpatient monitoring of the degree of fetal hypoxia allows you to see the results of using medications
The possibility of maintaining pregnancy with the help of conservative treatment remains with the degree of impaired blood flow Ia and b. The second degree is considered borderline, the third requires urgent surgical delivery.
Treatment takes into account the pathogenesis of disorders. To achieve results it is necessary to influence all links:
- In case of mild disturbance of microcirculation, Chofitol (with a mineral-herbal composition) is prescribed, in more severe cases - Actovegin, Petoxifilin.
- If a mother’s tendency to form blood clots and disrupt the aggregation properties of blood is detected, then drugs such as Curantil, Trental are indicated. They can improve blood flow through the vessels.
- If low blood pressure is detected, Venofundin, Stabizol, ReoHES are used.
- Vasodilators - No-spa, Eufillin in injections - eliminate spastic contraction of blood vessels.
- It is recommended to reduce the tone of the uterus with the help of Magnesia, the drug Magne B6, this acts as an antihypoxic way to improve blood flow.
- A group of vitamins with antioxidant action eliminates negative consequences (vitamin E, ascorbic acid).
- provide bed rest;
- Constantly monitor the progress of pregnancy.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with: Pulmonary hypertension during pregnancy
It has already been said that during pregnancy, blood flow disorders can be diagnosed using Doppler measurements. It is an ultrasound examination that can detect any pathological abnormalities in blood flow. When diagnosed, a pregnant woman takes a horizontal position on her back or side. The specialist conducts the examination using the transabdominal method. Usually Doppler testing is prescribed twice:
- at 20–22 weeks, to ensure that there are no abnormalities in the development of the fetus;
- at 32 weeks.
The clinical picture of blood flow disorders is determined by their severity. Compensated disorders usually occur latently and are detected only with ultrasound diagnostics. Decompensated and acute forms of fetoplacental insufficiency are usually accompanied by changes in the motor activity of the fetus, which is either minimized or becomes excessively pronounced. Normally, the fetus should move at least ten times per day.
Sometimes such deviations are accompanied by insufficient growth of the pregnant woman’s tummy, polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios, severe gestosis or hyperedema, sudden weight gain or pressure surges, and the appearance of protein compounds in urine. The most dangerous manifestation of placental circulatory insufficiency is considered to be uterine bleeding, which usually occurs against the background of placental abruption. In such a situation, a woman can only receive meaningful help from specialists, so it is necessary to call an ambulance.
If the development of placental blood flow disorders is suspected, the patient undergoes a comprehensive examination. The leading role in diagnosis is given to Doppler ultrasound in combination with ultrasound examination. Such techniques make it possible to promptly identify pathological blood flow disorders and determine the degree of complications caused by them.
The effect is based on the properties of ultrasonic wave reflection and is completely safe for the child and mother.
The method of long-term inpatient monitoring of the degree of fetal hypoxia allows you to see the results of using medications
- In case of mild disturbance of microcirculation, Chofitol (with a mineral-herbal composition) is prescribed, in more severe cases - Actovegin, Petoxifilin.
- If a mother’s tendency to form blood clots and disrupt the aggregation properties of blood is detected, then drugs such as Curantil, Trental are indicated. They can improve blood flow through the vessels.
- If low blood pressure is detected, Venofundin, Stabizol, ReoHES are used.
- Vasodilators - No-spa, Eufillin in injections - eliminate spastic contraction of blood vessels.
- It is recommended to reduce the tone of the uterus with the help of Magnesia, the drug Magne B6, this acts as an antihypoxic way to improve blood flow.
- A group of vitamins with antioxidant action eliminates negative consequences (vitamin E, ascorbic acid).
If there is an effect of conservative treatment, the woman independently carries to term and gives birth to a child. If there are no results, doctors may decide to perform an early cesarean section. In the third stage, only surgical delivery is indicated.
If a woman has increased blood viscosity or a tendency to thrombosis, most often she experiences a blood flow disorder. During pregnancy, treatment can only be prescribed by a doctor, because you will have to take serious medications. The most commonly prescribed medications are “Curantil”, “Trental” and “Hofitol”. They thin the blood and improve its movement through the arteries.
Most often, pregnant women are prescribed “Curantil”, which has been used in obstetrics for more than 15 years. The drug copes with its tasks perfectly - it normalizes blood circulation due to its dilution, prevents the formation of blood clots, helps the formation of new blood vessels, and improves immunity.
Also in demand is “Trental”, a drug that is similar in action to “Curantil”. However, it has serious advantages: the medicine does not dilate the blood vessels of the heart and continuously releases the active substance for 12 hours.
It happens that a woman experiences a slight disturbance in blood flow during pregnancy. Treatment in this case is carried out with “Hofitol” - a preparation with mineral and plant components (for example, the juice of field artichoke leaves). It has a mild diuretic effect and does not harm the liver.
Stage 2 blood flow disorders during pregnancy can also be treated. Usually the same drugs are used as in the first case, but the woman will be offered hospitalization. Doctors will monitor changes in the body and, if necessary, carry out early delivery.
The third degree cannot be treated in any way, since irreversible consequences begin to appear. In this case, specialists do not risk the child’s life and prescribe an emergency operation.