- Google+
To begin with, it should be noted that bigeminy and trigeminy are variants of ventricular extrasystole . Extrasystole is one of the types of heart rhythm disturbances, which is characterized by the occurrence of ectopic heart rhythms. This concept reflects a condition in which contractions of the atria or ventricles do not occur in those pathways of the conduction system along which the normal conduction of impulses occurs. Extrasystole can be atrial or ventricular.
In cases where extrasystoles alternate with normal contractions of the heart through one contraction, they speak of cardiac bigeminy (1:1), and when after two normal contractions, they speak of ventricular trigeminy (1:2). Accordingly, one extraordinary contraction after three normal ones is called quadrigeminy (1:3), and after four - pentageminy. These types of extrasystole are united by the concept of allorhythmia.
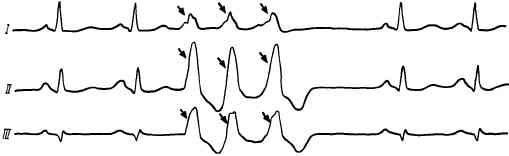
bigeminy on the ECG: every second complex is an extrasystole
In addition, paired extrasystoles (two in a row) and frequent group extrasystoles are distinguished if they follow three or more in a row. In the latter case, the extrasystole can be regarded as a short jog of ventricular tachycardia.
According to statistics, extrasystole occurs in more than 68% of people. In this case, the majority (63%) are ventricular extrasystoles, about 25% are atrial, and the remaining cases are supraventricular bigeminy and trigeminy, as well as their combinations. The occurrence of ventricular bigeminy is also noted in more than 60% of patients with myocardial ischemia and more than 80% of patients with acute myocardial infarction.
Causes of bigeminy and trigeminy
Ordinary single atrial and ventricular extrasystoles are normally found in a healthy person. They are practically not felt and do not cause discomfort. More frequent extrasystoles, such as allorhythmia, as well as frequent paired extrasystoles and runs of ventricular tachycardia, cannot be considered a variant of the norm and are a reason for a detailed examination of the cardiovascular system.
So, the main reasons for the occurrence of episodes of bigeminy and trigeminy are:
Acute myocardial infarction, Overdose of cardiac gligosides, or so-called glycoside intoxication with digitalis and digitalis preparations - strophanthin, digoxin, corglikon, etc., Acquired defects of the mitral and aortic valves, history of rheumatic fever (rheumatism) with damage to the inner lining of the heart - endocarditis, Consequences of myocarditis - an inflammatory process in the thickness of the heart muscle, and even minor cicatricial changes are the basis for pathological impulse circulation along the myocardial fibers. Post-infarction cardiosclerosis (PICS) is cicatricial changes in the normal structure of the myocardium.
If the patient, after a complete examination, does not find organic damage to the myocardium, it is most likely that the cause of bigeminy and trigeminy is a violation of the autonomic influences on the heart due to vegetative-vascular dystonia. This pathology requires consultation with a neurologist.
Causes, symptoms and treatment of bigeminy
To begin with, it should be noted that bigeminy and trigeminy are variants of ventricular extrasystole .
Extrasystole is one of the types of heart rhythm disturbances, which is characterized by the occurrence of ectopic heart rhythms.
This concept reflects a condition in which contractions of the atria or ventricles do not occur in those pathways of the conduction system along which the normal conduction of impulses occurs. Extrasystole can be atrial or ventricular.
In cases where extrasystoles alternate with normal contractions of the heart through one contraction, they speak of cardiac bigeminy (1:1), and when after two normal contractions, they speak of ventricular trigeminy (1:2). Accordingly, one extraordinary contraction after three normal ones is called quadrigeminy (1:3), and after four - pentageminy. These types of extrasystole are united by the concept of allorhythmia.
In addition, paired extrasystoles (two in a row) and frequent group extrasystoles are distinguished if they follow three or more in a row. In the latter case, the extrasystole can be regarded as a short jog of ventricular tachycardia.
According to statistics, extrasystole occurs in more than 68% of people.
At the same time, the majority (63%) are ventricular extrasystoles, about 25% are atrial, and the remaining cases are supraventricular bigeminy and trigeminy, as well as their combinations.
The occurrence of ventricular bigeminy is also noted in more than 60% of patients with myocardial ischemia and more than 80% of patients with acute myocardial infarction.
bigeminy on the ECG: every second complex is an extrasystole
Symptoms of bigeminy and trigeminy
Symptoms of extrasystole of the bi- or trigeminy type consist of cardiac and neurological symptoms.

Cardiological manifestations consist in the patient feeling rhythmic shocks in the heart area, alternating with a feeling of stopping, freezing of the heart. This period corresponds to a compensatory pause on the ECG. There is also internal trembling, a feeling of lack of air and discomfort behind the sternum or in the left half of the chest of a pressing or burning nature.
Neurological symptoms arise due to disruption of the full cycle of heartbeat, resulting in insufficient blood flowing to the brain. The patient may experience lethargy, drowsiness, spots flashing before the eyes, and a faint state. In rare cases, short-term fainting may develop, especially if allorhythmia is combined with other heart rhythm disorders.
If such symptoms occur, especially when combined with high or low blood pressure, the patient should immediately consult a doctor (at a clinic or emergency room).
How do episodes of trigemy manifest?
In most cases, patients suffering from one of the varieties of trigeminy do not notice signs of freezing, cardiac arrest followed by a powerful beat. Meanwhile, it is the appearance of a clear disruption in the rhythm of heartbeats that is considered the main symptom of arrhythmia. The intensity and criteria of symptomatic sensations depend on the type of pathology that has started.

The supraventricular (supraventricular) type of heart disease can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- interruptions in cyclicity in the functioning of the cardiac system;
- feeling as if the heart is turning over behind the sternum;
- deterioration of general condition against the background of panic anxiety.
Ventricular trigeminy (ventricular) is signaled by similar clinical manifestations of disturbed rhythm:
- an uneven type of heart pulsation, which can be detected by palpation of the sternum in the area where the upper part of the organ is located;
- premature contraction of the heart muscle, accompanied by a tone of increased volume, while listening to the heart rhythm;
- irregular pulse beat.
Among the symptoms common to the two types of pathology, mention should be made of the appearance of shortness of breath, occasional dizziness, weakness, and pain behind the sternum in the area where the heart is located. However, these are not signs of a disturbed rhythm, but a reaction of the patient’s autonomic system.
Important: If the symptoms of the idiopathic type of trigeminy in a healthy person go away on their own after eliminating the provoking agent, then a persistent disturbance in the rhythm of the vital muscle must be treated.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of bigeminy and trigeminy becomes obvious after an ECG.
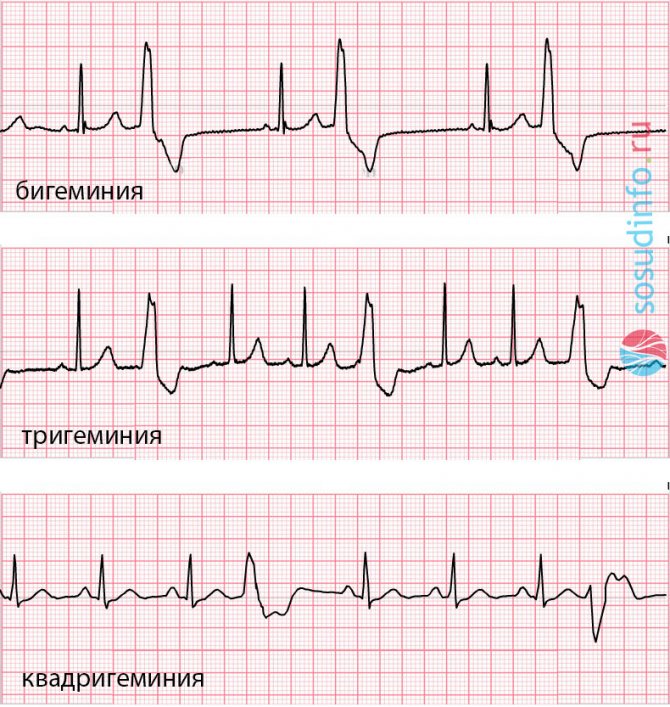
extrasystoles according to the type of bigeminy, trigeminy and quadrigeminy on the ECG
In the case where the patient notes periodic similar complaints, but only single extrasystoles are recorded on the ECG, the patient requires 24-hour blood pressure and ECG monitoring (Holter). This is necessary in order to “catch” the extrasystoles, evaluate the gradation of extrasystoles according to Rayn or Low and obtain a prognostic classification of extrasystoles (see below).
Further, in the case when the patient actually has bigeminy or trigeminy, it is necessary to conduct a full examination to determine the cause of the arrhythmia. Additional examination methods are prescribed:
General and biochemical blood tests to exclude an inflammatory process, as well as to assess the lipid spectrum of the blood (for atherosclerosis and coronary disease), ultrasound of the heart, or Echo-X (echocardioscopy), which allows you to identify structural or morphological changes in the heart, Physical tests load (treadmill test, 6-minute walking test, bicycle ergometry) to assess the significance of physical activity in the occurrence of bigeminy and trigeminy, as well as to assess exercise tolerance in ischemia or chronic heart failure.
Video: bigeminy on ECG
Methods for diagnosing extrasystole
Heart pathology is discovered accidentally in most cases. If a patient comes to the doctor with specific complaints about a failure in the cyclicity of heartbeats and noticeable discomfort, even short-term fainting, the initial stage of diagnosis will be the appointment of an electrocardiogram.
If rare extrasystoles are detected on the ECG and the non-systemic nature of the symptoms that the patient complains about, he will have to go through the stages of additional examination.
- Monitoring the functioning of the organ according to Holter. Thanks to the Holter monitoring technique, it is possible to detect isolated disruptions in the rhythm of beats throughout the day.
- Ultrasound diagnostic method. Ultrasound allows you to assess the condition of the heart muscle by identifying hidden pathologies that can lead to the development of trigeminy.
- Samples. Testing the rhythm of heart contractions under the influence of physical activity (walking, bicycle ergometry) and without it is necessary to assess the influence of the load factor on arrhythmia.
In addition to instrumental diagnostics, the patient needs to obtain the results of a comprehensive blood test (general plus biochemistry) in order to exclude hidden inflammatory processes occurring in the body. An assessment of the lipid component in the blood will reveal the presence of atherosclerosis and the presence of coronary heart disease. Analysis of magnetic resonance imaging images will help obtain more informative information about the structure of the heart muscle.
MRI examination
Treatment
If the patient has excluded organic heart disease as the cause of bigeminy and trigeminy, then he requires examination by a neurologist with treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
First of all, it is necessary to correct the lifestyle with adequate nutrition and a regime of work and rest. It is also necessary to normalize the patient’s psychological state and provide psycho-emotional comfort. Contrast showers, dousing and rubbing with a damp cloth are very good for training the cardiovascular system.
In the case when a patient is diagnosed with one or another heart disease as the cause, it requires mandatory treatment. In some cases, surgical correction of heart disease may even be indicated.
In addition to the main treatment, the patient is prescribed beta-blockers for constant use, for example, sotalol, nebilet, coronal, concor, etc., as well as calcium channel blockers - diltiazem, verapamil, etc. These drugs can reduce the heart rate and reduce the conduction of pathological impulses along the ventricular myocardium.

Cordarone, lidocaine and intravenous quinidine are used as emergency treatments for sudden frequent bigeminy or trigeminy.
In cases where antiarrhythmic therapy is contraindicated for a patient, or its poor tolerability and/or ineffectiveness is noted, the issue of the need for RFA (radiofrequency ablation) must be resolved - that is, cauterization of the tissue of the atrium or ventricle through which pathological impulses pass.
Features of the treatment process
Treatment of a pathological condition of the cardiac system begins after analyzing the results of a diagnostic examination and making an accurate diagnosis. Most often, treatment of trigeminy is carried out using a complex technique that combines therapeutic and medicinal assistance. The general direction of the treatment process is as follows:
- eliminate the cause of heart failure;
- select an individual set of antiarrhythmic drugs;
- review your diet in favor of a healthy diet;
- do not neglect the motor regimen in the light of the doctor’s instructions.
Please note: If the symptoms of arrhythmia are severe, the patient should receive emergency care. During an attack, you need to administer a drug prescribed by a doctor to urgently normalize the heart rhythm - intravenous infusion of Cordarone, Quinidine, Lidocaine, Blocalcin.
Justification for therapeutic treatment
The technique does not involve treating the patient with medications in the absence of heart disease and endocrine disorders. To get rid of extrasystole, it is enough to balance your diet, follow a good rest regime without exposure to stress and excessive physical overload. We should not forget about walks in the fresh air and regular medical monitoring of the functioning of the cardiac system.

Principles of drug therapy
The need to take medications is relevant when more than 200 extrasystolic bursts are recorded during the day. What groups of drugs are used to treat trigemynia:
- Antiarrhythmic medications normalize heart rhythm, monitoring therapy based on cardiogram results;
- the connection of a group of cardiac glycosides helps to slow down the contractile function of the organ to restore rhythm;
- Antihypertensive drugs reduce blood pressure.
Along with the main treatment regimen, the patient will have to constantly take medications from the group of beta blockers, as well as calcium channel blockers. The drugs help reduce the heart rate and reduce the conduction of pathological impulses.
Need for surgery
The lack of effectiveness of drug treatment, and also if the organ is extensively affected, urgent measures are required to save the patient - surgical treatment of trigeminy. What surgical techniques are used:
- open heart surgery is performed to remove ectopic areas surgically;
- during radiofrequency ablation under X-ray control, destruction of the ari focus is performed. "395"[/img]
The operation using the radio wave method is performed under combined anesthesia. Electrodes for cauterizing pathologically affected tissues of the atrium or ventricle are inserted through a vein in a location chosen by the surgeon. Having reached the arrhythmogenic zone with the help of a probe, it is subjected to high-frequency exposure.
Helping the heart of folk recipes
Bigeminia and trigeminia of non-severe forms can be successfully treated using alternative medicine methods, but in combination with therapy prescribed by a doctor. Valerian is recognized as the most effective remedy - in tablets or in the form of an infusion prepared from natural raw materials.
To obtain a decoction, dry valerian root is crushed, a teaspoon of herb is poured into 1/4 cup of hot water and brought to a boil in a water bath. After infusion, the healing solution darkens, it is filtered and boiled water is added to the volume of half a glass. A folk medicine to support the heart is taken daily 3-4 times a day for 10 days. After a week's break, taking the drink is resumed.
Recipes for folk remedies that are relevant for episodes of trigeminy:
- An infusion is prepared from the lemon balm herb - one teaspoon is steamed with a glass of boiling water. The infused and strained decoction is taken for no more than 3 months.

- A medicinal mixture is obtained from black radish juice and honey, taking the recipe components in equal proportions. The drug is taken in half a teaspoon.
- An alcohol tincture is prepared from hawthorn fruits - dry berries (10 g) are poured with vodka (100 ml). After 10 days of infusion, take 10 drops three times a day.
Please note: Herbal decoctions according to the regimen chosen for treatment are taken 20-30 minutes before meals, slightly warming the drug. Alcohol tinctures, which dilate blood vessels and reduce blood pressure, are best consumed a few minutes after eating, diluting the solution with a tablespoon of boiled water.
Are there possible complications of bigeminy and trigeminy?
Complications can develop in patients with any extrasystole - ventricular and atrial.
Thus, atrial extrasystole can turn into atrial fibrillation and flutter, and ventricular bigeminy or trigeminy can turn into ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation and lead to asystole (cardiac arrest). Prevention of complications is the timely initiation of treatment for diseases that led to bigeminy and trigeminy.
Forecast
Single extrasystoles are, in principle, not dangerous without organic heart pathology, in contrast to group and paired ones, which can lead to paroxysm of ventricular tachycardia.
table of classification of ventricular extrasystoles according to Lown
The prognosis for bigeminy and trigeminy is determined by the prognostic classification of extrasystole according to Lown:
Class 1 - less than 30 single extrasystoles per hour, Class 2 - more than 30 single extrasystoles per hour, Class 3 - polymorphic (different shapes) and polytopic (from different parts of the ventricular myocardium) extrasystoles, class 4A - paired extrasystoles, class 4B - group extrasystoles, class 5 - “early” extrasystoles, when an extrasystole pops up against the background of a still ongoing normal contraction of the heart.
Thus, the prognosis for the first two classes is favorable, for example, if the patient has several extrasystoles within an hour, regularly alternating with normal heart contractions every other one or two. The third to fifth grades are prognostically unfavorable, since there is a high risk of developing fatal rhythm disturbances. That is, if bigeminy and trigeminy alternate with paired, group or early extrasystoles, they can be dangerous in terms of the development of complications.
In conclusion, it should be noted that extrasystole of the bigeminy and trigeminy type is dangerous only if it is caused by serious myocardial pathology. Otherwise, for example, with vegetative-vascular dystonia, this type of extrasystoles disappears when the influence of the autonomic nerves on the heart is normalized.
Step 1: pay for the consultation using the form → Step 2: after payment, ask your question in the form below ↓ Step 3: You can additionally thank the specialist with another payment for an arbitrary amount ↑
Evaluation and characteristics of extrasystoles. Allorhythmia, bigeminy, trigeminy
On ECG
most extrasystoles differ from OP cycles in a different shape or direction (relative to the isoline), or the location of the P wave (supraventricular extrasystoles) or the width, shape and direction of individual teeth of the QRST complex (ventricular extrasystoles), some other features, as well as the presence of the following extrasystole increased pause. This pause is called compensatory, because it is longer than the inter-cycle intervals of the OR, as if compensating completely or incompletely (full or incomplete compensatory pause) for the shortened pre-ectopic interval. A complete compensatory pause (CP) is called if it, together with the pre-ectopic interval, is equal in duration to the sum of 2 inter-cycle intervals OP. An incomplete CP is shorter than a full one. There is no compensatory pause after intercalary extrasystoles if the extrasystole is registered against the background of atrial fibrillation and if the localization of the extrasystoles and the main pacemakers coincide.
Determining the localization of monofocal extrasystoles, the P wave
or QRS complex often have the same shape, but may differ due to conduction disturbances.
Extrasystoles are assessed using various parameters.
Single (single) extrasystoles
are represented by individual premature cycles in a total amount of no more than 5 per minute. Moderately frequent single ES are represented by individual premature contractions in the amount of 6 to 10 per minute. If the number of single ES in 1 min. more than 10, they are designated as frequent single extrasystoles.
Extrasystole
is called early if its first wave (P or QRS) overlaps the T wave of the OP cycle preceding the extrasystole.
Paired extrasystoles (paired extrasystoles)
. these are two ES in a row with a short interval (less than 0.6 seconds). The first of them is preceded by an adhesion interval, after the second a compensatory pause is determined. Such extrasystoles are unfavorable prognostically, since they often precede the onset of paroxysmal tachycardia.
Interpolated extrasystole
(VES) is an extrasystole located between two adjacent cycles of the main rhythm. Most often, VES is early or occurs against the background of bradycardia. Usually this is a ventricular or AV extrasystole, but in rare cases, VES can also be atrial. WES does not have a compensatory pause. The OR interval into which it is wedged (P - P) is not changed, but there is often a slight increase in the R - R interval of this cycle due to an increase in the P - Q interval of the post-extrasystolic cycle. Aberrance of the post-extrasystolic QRS complex is often noted due to functional intraventricular block.
Allorhythmia (allorhythmic extrasystole)
- extrasystole, in which ES occur regularly after the same number of OR cycles: bigeminy, trigeminy, etc.
Bigeminy (extrasystolic bigeminy)
. Extrasystoles are recorded regularly after each OP cycle, i.e., there is an alternation, for example, of sinus and extrasystolic cycles in a 1:1 ratio. The coupling intervals of all extrasystoles are equal.
Trigeminy
. It is observed in two variants: 1) extrasystole follows regularly after two OP cycles, repeating many times, i.e. alternating sinus and extrasystolic cycles in a ratio of 2:1; 2) two extrasystoles in a row (paired extrasystoles), regularly following one OP cycle, i.e., the ratio of sinus and extrasystolic cycles is 1:2. The second option is more correctly designated as a paired extrasystole of the trigeminy type and is assessed as a more severe pathology of rhythm disturbance.
Quadrigeminy
- extrasystole, in which the extrasystole follows regularly after three OP cycles, i.e. the ratio of OP and extrasystolic cycles is 3:1. A second option, similar to the second option of trigemy, but with a ratio of 1:3 or 2:2, is rarely possible.
Hidden extrasystole (allorhythmic)
. Against the background of registered allorhythmia (of any form), ECG sections without extrasystoles and with an odd number of OR cycles are observed between the last ES in the allorhythmia recording and the first ES of the next allorhythmia period.
Table of contents of the topic “ECG with extrasystoles”:
Bigemeny and trigemeny (ventricular allorhythmias): what is it, signs on the ECG, treatment
Bigeminy and trigeminy are the most common types of allorhythmia.
Allorhythmia is a form of arrhythmia of the heart muscle. When the heart is working properly, myocardial contractions are stable (normal heart rhythm). In this case, impulses arise in the sinus node, which transmits them to the muscles at regular intervals.
What are their differences?
The normal heart rate is 60-90 beats per minute. When it is violated, extrasystoles (extrasystoles) occur at different intervals.
When they originate from the sinus node, it is called sinus arrhythmia. In other cases, they are formed not in the sinus node, but in other parts of the myocardium.
An extraordinary contraction that occurs after each normal impulse is called bigeminy. In other words, the ratio of correct and premature impulses is 1:1. This is the most common heart rhythm pathology. It is registered in 60% of cases.
When for two regular contractions there is one extraordinary contraction, this is trigemy (2:1).
With a ratio of 3:1, after three normal beats one abnormal beat occurs, this is quadrigeminy.
There is also pentageminy (4:1) and paired extrasystoles - double atypical contractions.
How dangerous is this?
Heart rhythm disturbances are always dangerous. When allorhythmic impulses occur, the correct movement of blood through the heart stops, and areas with stagnation and turbulence appear.
Because of this, blood clots form in areas with “improper” blood flow, which break off and cause deadly complications.
Extrasystole of the bigeminy type can cause the following complications:
- Atrial fibrillation (a pathological condition caused by random contraction of fibers in the myocardium).
- Atrial flutter (atrial fibrillation, in which an increased rhythm of contractions predominates - the pulse reaches 200-400 beats per minute).
- Rapid heartbeat caused by rapid contraction of the ventricles.
- Ventricular fibrillation (chaotic, uncoordinated contractions).
- Asystole - cessation of bioelectrical activity of the myocardium. This is very dangerous for the patient, as it leads to cardiac arrest, followed by clinical death.
When predicting the consequences of bigeminy, it is necessary to take into account the patient’s age, his physical condition, and the presence of concomitant diseases. If a person does not have serious pathologies of blood vessels and heart tissue, then there will be no serious complications.
When rhythm disturbance occurs due to myocardial damage, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease. Ignoring it can be fatal.
Bigeminia itself is not a disease. The occurrence of extrasystoles also occurs in healthy people. Extraordinary impulses sometimes appear and then disappear within 24 hours, which is recognized as the norm.
If a heart rhythm disturbance lasts 5-15 minutes a day, this is not considered a pathology. But when episodes of chaotic contractions become very prolonged, you should pay attention to this and undergo an examination.
Transient rhythm disturbances are common in pregnant women. Rare extrasystole does not pose a threat to the fetus. After birth, the mother's condition usually stabilizes.
Acquired bigeminy in children is associated with previous infections and heart complications after complex diseases. In older children, it occurs due to drug intoxication and food poisoning.
Classification
With allorhythmia, extraordinary impulses appear not in the sinus node, like normal contractions, but in other parts of the myocardium.
In bigeminy and trigeminy, the focus of the ectopic signal is located in the atrium or ventricles.
Depending on this, arrhythmias are of two types:
- Ventricular (ventricular). Excitatory impulses come from a source located in the ventricles. This is the most common type of pathology - it occurs in 60% of people with bigeminy.
- Supraventricular (atrioventricular). Ectopic impulses are formed in the atrium or atrioventricular node located in the interatrial septum.
Ventricular type pathology is common in older people. Often it indicates existing myocardial diseases.
Supraventricular is more typical for young patients. Their heart rhythm disturbances occur due to stress and increased physical activity.
If one of the types of allorhythmia is detected, it is necessary to conduct an in-depth examination to exclude serious heart pathology and prevent complications.
Provoking factors
The reasons why allorhythmia occurs are divided into external and internal.
External causes include functional reasons (the functions of an organ fail without destroying its structure). Internal - organic disorders.
Idiopathic development of the pathology is also possible when the cause could not be identified.
Functional causes of rhythm disturbances can be caused by mental disorders (stress, neuroses) or intoxication of the body.
Extrasystoles provoked by intoxication occur due to:
- chemical poisoning of the body;
- frequent smoking or alcoholism;
- abuse of coffee, strong tea, energy drinks;
- antibiotic treatment for severe infections;
- long-term use of steroids;
- overdose of cardiac glycosides;
- thyroid dysfunction.
Poisoning of the body provokes ventricular-type bigeminy.
Organic factors include the following diseases:
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Inflammation of the heart muscle tissue.
- Atherosclerosis is the appearance of plaques on the walls of the coronary arteries that impede blood circulation.
- High blood pressure.
- Cardiosclerosis.
- Defects of the mitral and aortic valves.
- Cardiomyopathy is a chronic neuromuscular pathology of the heart.
- Cor pulmonale is an enlargement of the right side of the heart due to lung disease.
- Damage to the serous membrane of the heart.
- Impaired heart function due to intense physical exertion.
- Heart defects.
Sometimes an abnormal heart rhythm causes surgery. Extrasystoles can also appear due to coronary angiography and probing of the heart muscle.
Symptoms
Bigeminy and trigeminy do not have specific symptoms. This means that there are no pronounced signs by which pathology can be determined.
Manifestations of heart rhythm disturbances are similar to other cardiac pathologies: discomfort behind the sternum, a feeling of interruptions in the functioning of the heart, a general deterioration in well-being.
Symptoms are divided into cardiac and somatic. Patients experience attacks differently. Their well-being depends on their physical condition, individual characteristics, and age.
Characteristic features:
| Cardiac | Somatic |
| Strong heartbeats alternating with freezing | Lethargy, weakness |
| Nausea | Dizziness |
| Feeling short of air | Visual impairment |
| Heaviness, pressure in the chest | Appearance of anxiety |
| Shiver | Fainting conditions |
| Pale skin | Decreased sensitivity in hands and feet |
| Increased sweating | Rarely – speech disorders |
Signs on ECG
Electrocardiography is a reliable way to detect bigeminy and other types of allorhythmia.
Heart rhythm disturbances are easily recognized on cardiogram graphs. Upon examination, the doctor sees that every normal contraction of the heart is followed by an extraordinary impulse. This looks like two QRS waves next to each other. They are separated by a horizontal line showing relaxation of the heart muscles.
The shape of the pulse is determined by the change in electrical forces when overcoming the excitation wave in the myocardium. The extrasystole has a long, narrow wave preceding the normal QRS complex. Its frequency is less than that of the impulse coming from the sinus node.
When interpreting the ECG, the cardiologist should pay attention to the site of the premature impulse. Early ventricular impulses (when the previous wave is superimposed on the next one) are of great concern.
In the case when rare extrasystoles are recorded on the ECG and bigeminy is not systemic in nature, but the patient complains about the heart, he is sent for additional examination.
Other diagnostic methods
In case of allorhythmia, in addition to conventional electrocardiography, comprehensive studies are carried out to identify its causes.
To clarify the degree of rhythm disturbance, a Holter ECG is performed. This is a diagnostic method that involves long-term recording of the electrical activity of the heart.
24-hour Holter monitoring is an informative examination that allows you to effectively identify cardiovascular pathologies.
Additionally, the patient is prescribed:
- Clinical and biochemical blood tests. These studies make it possible to establish the presence of an inflammatory process in the body and the state of metabolism.
- Ultrasound examination of the heart muscle. It allows you to detect changes in the structure of the myocardium.
- ECG with stress tests. Prescribed to compare cardiac arrhythmias with physical activity.
Urgent Care
If severe symptoms occur, when a person does not tolerate arrhythmia attacks, he is provided with emergency care.
It consists of taking medications that normalize heart rhythm (Quinidine, Cordarone, Blockalcin, Lidocaine).
Drug therapy
If the patient is not indicated for surgery, he is treated with medications.
The choice of medications is made by the attending physician depending on the existing disease.
The following drugs are prescribed as auxiliary therapy:
- Coronal.
- Concor.
- Sotalol.
- Verapamil.
Radiofrequency ablation
If the patient has poor tolerance to antiarrhythmic drugs or therapy has shown ineffectiveness, he is prescribed radiofrequency ablation. This is a minimally invasive surgical procedure performed under the control of X-ray equipment.
The source of arrhythmia is destroyed under the influence of radio waves.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia. The patient has a vein pierced in a certain place. Then catheters are installed and, using X-ray observation, electrodes are inserted into the heart cavity through the puncture site.
After reaching the arrhythmogenic zone, it is exposed to radiofrequency energy. After this, the electrodes are removed. The patient is allowed to get up after 12 hours.
Preventive measures
Prevention of allorhythmia consists of procedures for the general improvement of the body:
- Quitting bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol).
- Perform moderate physical activity with the exception of heavy lifting.
- Normalization of nutrition. You need to give up unhealthy foods - fatty, fried, spicy, in favor of natural foods - vegetables, fruits, herbs, dietary meat, fish.
- Stabilization of mental state. Therapeutic baths and walks in the fresh air help well.
- Therapeutic exercise, sanatorium-resort treatment
To prevent heart disease, prevention is important.
A correct lifestyle and a comfortable mental state of a person are the key to good health.
Dmitrieva Yulia (Sych) – In 2014, she graduated with honors from Saratov State Medical University named after V. I. Razumovsky. Currently working as a cardiologist at the 8th City Clinical Hospital in the 1st clinic.
Source: https://infoserdce.com/serdce/bigeminiya/
Internet Ambulance Medical portal
Write about any bugs you find
Trigeminy
Trigeminy is a cardiac arrhythmia in which the heartbeats are combined into groups of three. The first contraction is usually normal, and the second and third are early extrasystoles (see Ectopic systole).;
Found in 15 questions:
cardiologist March 12, 2020 / @anonymous / Nazarovo
. from 18:00 to 19:00. Of these: • Singles 422 (188 at night), max. number per hour - 62 from 18:00 to 19:00. Trigeminy type
3 (at night) in 1 episode. Episode duration 00:00:00. Total day night 13:22- -14:00 14:00- -15:00 15:00- -16:00 16:00- -17. open
cardiologist June 3, 2014 / Alena / Tver
. or sinus arrhythmia. Table of general statistics of heart rhythm disturbances: ventricular total 116 pieces single 116 pieces bigeminy 5/25(ep/pieces), supraventricular 535 pieces single 388 pieces paired 71 pieces group 1/5(ep/pieces) trigeminy
1/4(ep/pieces) open
cardiologist February 6, 2014 / @anonymous / Moscow
. sinus rhythm. Min. heart rate 69, max. 173, average 98. Circadian index 1.19, Ventricular e/s 2. Supraventricular e/s 5180, single and group, trigeminy
. No significant fluctuations in the ST segment were detected. Thanks in advance for your answer. Best regards, Irina open
cardiologist April 21, 2013 / Alexandra…
. during the day, 106 at night), single 7603 (4862 during the day, 2741 at night), by bigemia type 1081 (410 during the day, 671 at night), by trigeminy
2173 (1227 during the day, 946 at night). Dynamics st-t. deviations of the st segment were not recorded. Dynamics of the qt interval. Long qt syndrome: qt. open
pediatric cardiologist September 13, 2012 / Elena / Komsomolsk-on-Amur
. ECG for a 6 year old child. The conclusion says: Sinus bradyarrhythmia (Severe). Single supraventricular extrasystoles. Trigeminy
. Semi-vertical electrical position of the heart. Deviation of the electrical axis to the right. Shortened PQ interval (syndromic open
cardiologist August 22, 2012 / Marina
Dear doctor! I am 54 years old, I suffer from cardiac extrasystole, sometimes trigenemia and paroxysms of cardiac tachycardia. Ultrasound - within the age range. No antirhythmics help, I tried... open (1 more message)
Last 5:
August 22, 2012 / Marina
unstable ventricular tachycardia, extrasystolic ventricular arrhythmia, including allorhythmic (bi, trigeminy
) look
pediatric cardiologist May 24, 2012 / Elena / Vladimir
. AQRS, deg. 71 HR, 152 Conclusion: migration of the pacemaker with HR=152 beats/min Single and group ventricular extrasystoles. Trigeminy
. Complete block of the right bundle branch. How serious is this and are the ECG results correct if the child is in. open
cardiologist May 23, 2012 / Natalya / 0
. and a steam room. Temporary allorhythmic bi-, trigeminic ventricular extrasystole. (VES total 8667, bigeminy total 551, trigeminy
38) After the recommendation is issued. concor 5 mg once a day. following a diet and limiting physical activity. open
cardiologist September 7, 2010 / Alexey / Surgut
. per minute during active time, Frequent ventricular ectopic activity - 3291 ventricular extrasystoles, Ventricular bitrigeminy
- 15, Paired - 1, Single ventricular extrasystoles - 3236, No transient changes in the ST segment were registered; EchoCG. open
cardiologist March 4, 2010 / Valentina... / Saki
. Normal heart rate. Heart rate=66 beats/min. Frequent (57 per record) ventricular extrasystoles. Bigeminy. Trigeminy
Powerful slow waves of a short period (from 10 to 30 s), possibly of central origin, against an inadequate background. open
cardiologist December 18, 2009 / Ekaterina... / 0
. -Betalok ZOK 2p/d + Allapinin 3t/d for a month 4. After a month I put Holter again - Gastric extrasystoles 22052, bigeminy 551, trigeminy
- 448, min heart rate - 52, max heart rate - 164, sinus pauses up to 1.5 seconds were detected. episodes of 1st degree AV block. open
. Heart rate 83/min, max. 148/min, min. 58/ min. 28872 ventricular extrasystoles were recorded, including 588 couplets, trigeminy
a total of 1465 and 6 - bigeminy, 20 atrial extrasystoles. I have been taking amiodorone for a month, 2 tablets a day. The pain has become a little less, but. open
. ectopic activity with max. amount 854e/s per hour, doubles. Polymophoric ventricular extrasystoles, bigeminy, trigeminy
. rhythm variability is normal. The cardiologist prescribed Concor Cor, Magne B6, but there were no changes, the interruptions continued. open
Types of bigeminy
In order for a specific area of the heart to contract, it must be affected by an electrical impulse, the formation of which occurs in the sinus node.
In order for systole or contraction of the ventricle to occur, the heart must receive an electrical impulse, which in a healthy person is formed in the sinus node. Bigeminy is characterized by the fact that after each systole an additional (extraordinary) contraction or extrasystole occurs, but, most importantly, they are not caused by the sinus node.
| Ventricular form |
|
| Supraventricular form |
|
Arrhythmia is divided into types depending on the location of the focus in which the impulse is born.
Bigeminy differs in what type of extrasystoles manifests itself in the work of the heart.
Ventricular extrasystole
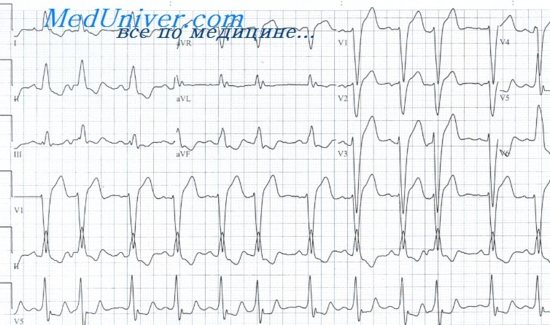
Ventricular extrasystoles (like atrial extrasystoles) can occur even in healthy individuals, without clinical symptoms and without significant consequences (Fig. 12.19). The source of ventricular extrasystoles is usually the ectopic center in the ventricles. Wide QRS complexes are recorded on the ECG, since the impulse slowly spreads through the ventricular myocardium, mainly due to intercellular contacts, and not through the conduction system of the heart. There is no P wave before the QRS complex of the extrasystole.
Ventricular extrasystoles in patients with damage to the heart structure require special attention. For example, ventricular extrasystoles are often observed in patients with myocardial infarction. Frequent ventricular extrasystoles (more than 10/hour), as well as paired or triple ones, are an unfavorable prognostic sign, indicating a high risk of death in patients in this category.
Extrasystoles can regularly follow a certain number of normal heart contractions. So, bigeminy is the following of an extrasystole after every normal ventricular complex, trigeminy - after every second, quadrigeminy - after every third, etc.
Asymptomatic ventricular extrasystoles in healthy individuals do not require treatment. Beta-blockers (class II antiarrhythmic drugs) are indicated for persons in whom ventricular extrasystoles are accompanied by clinical manifestations.
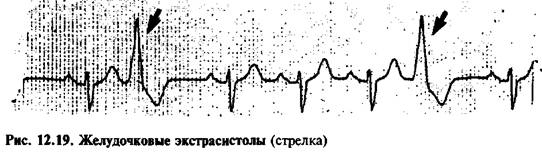
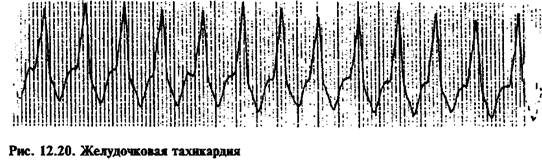
Ventricular tachycardia
Three ventricular extrasystoles in a row should be considered as a paroxysm of ventricular tachycardia (Fig. 12.20). There are 2 forms of ventricular tachycardia (VT): sustained, which lasts more than 30 s or requires interruption due to severe symptoms, and unstable. Both forms of VT are usually observed in patients with structural changes in the myocardium, but sometimes they can also occur in healthy individuals.
Clinical signs of VT vary depending on the duration of the tachycardia paroxysm and the presence of underlying heart disease. Typical symptoms of low cardiac output are arterial hypotension and loss of consciousness.
With VT, wide QRS complexes with a frequency of 100-200 min-1 are recorded on the ECG. In monomorphic VT, the QRS complexes have the same shape; with polymorphic VT, their shape changes all the time, indicating that depolarization occurs under the influence of impulses arriving from different foci of automaticity in the ventricles. Some arrhythmias, such as atrial tachycardia with bundle branch block, may resemble VT. Differential diagnosis in these cases is carried out on the basis of an analysis of the relative position of the P waves and QRS complexes (in VT there is no connection between them). The electrophysiological mechanisms of VT vary between patients. Although the cause of VT may be an increase in the automaticity of ectopic foci, it is now generally accepted that this rhythm disturbance is most often caused by re-entry of the excitation wave.
Accompanied by clinical manifestations or sustained paroxysms of VT require special attention, as they can transform into ventricular fibrillation, a condition that threatens the patient’s life in the absence of emergency assistance. Treatment of patients with VT usually begins with electrical cardioversion followed by antiarrhythmic drugs to suppress the ventricular rate. In some cases, implantation of a permanent defibrillator is indicated. Treatment methods for asymptomatic or non-sustained VT remain the subject of debate, since the use of antiarrhythmic drugs does not seem to improve the long-term prognosis, but may worsen it due to the side (arrhythmogenic) effects of antiarrhythmics.
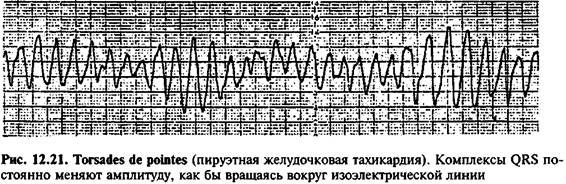
Torsades de pointes
Torsades de pointes or torsade de pointes ventricular tachycardia is characterized by the fact that on the ECG the QRS complexes constantly change amplitude, as if rotating around the isoelectric line (Fig. 12.21). The cause of torsades de pointe may be post-depolarization in the altered myocardium (trigger activity), especially in patients with prolongation of the QT interval, for example, while taking certain antiarrhythmic drugs, including in 2% of patients taking quinine, with electrolyte disturbances (hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia ) or congenital prolongation of the QT interval.
Torsades de pointes is almost always accompanied by hemodynamic disturbances, but often goes away on its own. Paroxysm of torsades de pointe is associated with the risk of sudden loss of consciousness and the development of ventricular fibrillation. If torsades de pointe occurs while taking medications or electrolyte disturbances, then discontinuation of drugs or restoration of input-electrolyte balance helps eliminate the arrhythmia. Intravenous administration of magnesium also helps restore normal rhythm. In addition, treatment of patients in this category should be aimed at shortening the QT interval and preventing repeated paroxysms (including intravenous injections of isoproterenol and installation of an artificial pacemaker).
On the contrary, in patients with congenital prolongation of the QT interval, beta-blockers are the first-line drugs, because in these cases, stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system can lead to an increase in arrhythmia.
Read more: Ventricular fibrillation
Trigeminy of the heart is a type of extrasystole, in which every third excitation and contraction of the myocardium is premature. Episodes of bigeminy and trigeminy can also occur in practically healthy individuals, but in many cases they indicate the presence of structural and functional disorders of the cardiovascular system.
Bigeminy: what is it, causes, symptoms, treatment
Bigeminy and trigeminy are medical terms that reflect disturbances in normal heart rhythm. This is not heart block or bradycardia .
This is a situation where an additional contraction is inserted into the normal rhythm. Or maybe more than one. In fact, there is a failure in the system of conducting heartbeat control impulses. Such failures are highly undesirable, since the consequences can be bad. Especially in the case of an existing disorder in the heart muscle. And the sensations of heart fluttering carry great anxiety.
In addition, abnormal heart rhythms create the risk of blood clots forming inside the heart. Once formed, clots can travel throughout the cardiovascular system, causing serious problems.
It's better to see a doctor.
What is heart rate
Heart rhythm is a progressive combination of processes that manifest themselves in one cardiac cycle, which includes:
- Atrial systole is a contraction.
- Ventricular systole.
- Diastole – relaxation.
The rhythmic, repeated beating of the heart is called the heart rhythm, or heart rate.
What causes a normal heart rhythm to form is called impulses, which originate in the sinus node - the pacemaker.
The sinus node is part of the conduction system of the heart, the cells of which are localized at the junction of the superior vena cava and the right atrium. It is the sinus node that sets the normal rhythm of the heart and transmits impulses after the same amount of time to other cellular elements.
For reference. Typically, the sinus node produces impulses whose frequency ranges from 60 to 100/min. It is important that at the same time other pacemakers are in a state of suppression, which is the norm.
If there is a failure at any level of the conduction system of the heart, heart rhythm disturbances occur.
What is arrhythmia and its types
Any abnormal heart rate is called arrhythmia. All possible arrhythmias are divided into:
- Automatic disorder.
- Violation of excitability.
- Conduction disturbance.
- Mixed.
Those forms of arrhythmia that are accompanied by impaired automatism are:
- Nomotopic - in such cases the pacemaker is located in the sinus node:
- Sinus tachycardia.
- Sinus bradycardia.
- Sinus arrhythmia.
- Sick sinus syndrome.
- Sinus arrhythmia of non-respiratory origin.
- Heterotropic - in these cases the pacemaker is located outside the sinus node:
- Inferior atrial rhythm.
- Idioventricular rhythm.
- Atrioventricular rhythm.
Heart rhythm disturbances that occur as a result of pathological excitability (often due to premature excitation) are divided into:
- Extrasystoles:
- Quantitative – monotopic, polytopic.
- Temporary – early, late, intermediate (interpolated).
- Based on the source - atrial, ventricular, atrioventricular.
- By frequency – single (up to 5/min), multiple (more than 5/min), group, pair.
- By ordering - allorhythms (bigeminy, trigeminy, quadrigymeny), disordered.
- Paroxysmal tachycardia:
- Atrial.
- Atrioventricular.
- Ventricular.
Arrhythmias in which conduction disturbances are observed:
- Conduction extension.
- Decreased conduction (heart block).
Rhythm disturbances that combine several manifestations:
- Atrial flutter.
- Atrial fibrillation.
- Ventricular flutter.
- Ventricular fibrillation.
One of the most common types of arrhythmias is extrasystoles.
What is extrasystole
The form of arrhythmia, which on the ECG is characterized by extraordinary contractions (premature contractions) of the heart as a whole or its parts, is called extrasystole.
Changing the main rhythm and extrasystoles in a strictly defined sequence is called allorhythmia.
What are bigeminy and trigeminy
The most common types of allorhythms are:
- Bigeminy is the occurrence of extrasystole after each normal contraction.
- Trigeminy - the appearance of extrasystoles after two contractions or two extrasystoles after one contraction.
In order for the heart to contract and relax, an electrical impulse is required, which is normally generated in the sinus node.
Attention. When there is bigeminy/trigeminy, this does not happen, since the impulse does not come from the sinus node .
For these pathological conditions, the pacemaker is other foci. According to this principle, all bigeminia are divided into two types:
- Ventricular bigeminy - impulses are produced by the ventricle. Most common among older people. In most cases it is accompanied by organic lesions of the heart.
- Supraventricular (supraventricular) - impulses come from the atrioventricular node or atrium. This type is often characteristic of young people, the causes of which can be severe physical activity and stressful situations.
The formation of extrasystoles in a healthy person is allowed, the number of which per hour can be from 30 to 60 (from 700 to 1400 per day).
For reference. There are quite a lot of factors that influence heart rhythm and premature excitation, and correctly identifying the cause will help in the future to choose the right tactics for treating and monitoring patients.
As already mentioned, single extrasystoles of the type of bigeminy or trigeminy can be physiological - a variant of the norm.
With the development of any unhealthy condition, such arrhythmias become pathological. It is important to determine the reasons that lead to disruption of the rhythm:
- Acute myocardial infarction.
- Intoxication due to the intake of cardiac glycosides.
- Congenital and acquired heart valve defects.
- Rheumatism accompanied by endocarditis.
- Myocarditis.
- Cardiosclerosis as a result of a heart attack.
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Smoking.
- Alcoholism.
- Addiction.
- Periodic changes in hormonal levels in women.
- Stressful situations.
- Imbalance of microelements - electrolyte dissociation.
- Vegetovascular dystonia.
- Neurasthenic conditions.
- Osteochondrosis, especially of the cervical region.
- Hyperfunction of the thyroid gland.
- Hyperthermic syndrome.
- Excessive consumption of coffee, tea.
- Fatigue, severe overwork.
- Electrostimulation of the heart.
- Some diagnostic procedures.
As you can see, there are quite a lot of reasons for the occurrence of extrasystoles. Some of these factors, such as smoking, cause functional conduction disorders, which can be successfully corrected after eliminating the provoking factor and properly selected treatment.
And causes such as, for example, myocardial infarction are classified as organic causes, when there is not only a malfunction in the conduction system of the heart, but also a violation of the structure of the heart muscle and valves.
Important! Separately, it is necessary to point out that bigeminy or trigeminy is most dangerous in children. As a result of this pathological condition, loss of control of the sinus node over rhythm control can occur, which can lead to death.
It is important to promptly pay attention to signs in your condition that may indicate the appearance of an arrhythmia such as bigeminy/trigeminy.
Symptoms
All symptoms that arise during such arrhythmias in patients are of two types:
- Cardiological.
- Neurological.
Cardiac symptoms:
- Feeling of heart contractions, accompanied by a feeling of freezing, stopping.
- Pale skin.
- Fear of death.
- Interruptions.
- Internal restlessness, trembling.
- Nausea, sometimes with vomiting.
- Cold sweat.
- Lack of air.
- Unpleasant sensations behind the sternum and/or in the left half of the chest of a burning, pressing nature.
Neurological symptoms:
- Lethargy, fatigue.
- Drowsiness.
- Dizziness.
- Anxiety, restlessness.
- Flashing "flies" before the eyes.
- Blurred vision.
- Speech impairment.
- In some cases, pre-fainting.
- Disorders of sensory and motor activity in the upper and lower extremities.
It should be borne in mind that in some cases, rhythm disturbances are not accompanied by any subjective sensations at all.
In each case, careful diagnosis is necessary for an accurate diagnosis and correct treatment.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, the patient must undergo the following diagnostic procedures:
- Anamnesis collection.
- An ECG is the very first study that needs to be performed. Depending on what type of bigeminy the patient has, certain signs on the ECG are characteristic.
- Supraventricular bigeminy/trigeminy shows: A premature QRS complex preceded by a P wave.
- Narrow, less than 0.12 seconds, QRS complex (sometimes it may widen).
- Incomplete compensatory pause.
- Ventricular bigeminy demonstrates:
- Premature QRS complex without preceding P wave.
- The duration of the QRS complex is more than 0.12 seconds.
- In its shape, the QRS complex resembles a bundle branch block.
- The presence of a complete compensatory pause.
- 24-hour Holter monitoring – the purpose of the procedure is to monitor blood pressure and heart contractions over a 24-hour period. Only with the help of a Holter study can arrhythmias be assessed.
- Echo-CG – the activity of the myocardium and conduction system of the patient’s heart is assessed.
- Ultrasound of the heart - is prescribed to assess the state of the structure and morphology of the entire heart.
- Exercise testing – assesses the ability to withstand physical activity.
- General and biochemical blood test.
- General urine analysis.
Only after a thorough diagnosis and determination of the causes of extrasystoles should treatment begin.
Treatment
In cases where physiological bigemy is observed, patients are advised to avoid exposure to provoking factors. In some cases, medication correction is prescribed for a short time.
In the case where organic bigeminy occurs, the following measures are used:
- Treatment of the underlying disease that led to the development of arrhythmia.
- Normalization of nutrition.
- Compliance with the regime.
- Taking antiarrhythmic groups of drugs of various classes, depending on the form of arrhythmia, type, severity.
- If the patient exceeds 20,000 extrasystoles per day, radiofrequency ablation is used.
- Dynamic ECG monitoring.
Attention. Since bigeminy/trigeminy are not an independent nosological entity, but appear as a consequence of any disease, it is necessary to take the most responsible approach to the treatment of the underlying disease.
Like any pathological process in the human body, both bigeminy and trigeminy can be dangerous for humans.
Are complications possible?
In the case of extrasystoles of functional impairment, the prognosis is usually favorable if all necessary measures are taken.
With regard to organic disorders, it is much more difficult to predict the course. In such cases, many factors are taken into account:
- Age.
- Main disease.
- Condition of the myocardium and blood vessels.
Atrial bigeminy can cause complications such as:
- Atrial fibrillation.
- Atrial flutter.
Ventricular bigeminy/trigeminy can lead to:
- Ventricular tachycardia.
- Ventricular fibrillation.
- Asystole.
Careful diagnosis, treatment of the underlying disease and compliance with all doctor’s prescriptions will help improve the prognosis for patients.
Forecast
If the patient does not have serious heart lesions that have led to an abnormal heart rhythm, the prognosis is usually favorable.
Important! If bigeminy/trigeminy occurs against the background of severe damage to the heart muscle, the prognosis for the patient can be extremely unfavorable.
In any case, when the first signs of arrhythmia appear, you should consult a doctor to rule out dangerous diseases.
Source: https://serdcet.ru/bigeminiya.html
Causes of trigeminy
An episode of trigeminy can also occur in a healthy person. According to various data, the frequency of detection of this type of arrhythmia during the day against the background of complete health is 50-90% with a tendency to increase with age.
However, often the occurrence of trigeminy is caused by certain pathological processes in the body, such as:
Bad habits: smoking, alcohol abuse, taking narcotic and other psychoactive substances. Excessive consumption of tea and coffee. Structural damage to the myocardium. Endocrine diseases. Electrolyte imbalance, and others.
It is not always possible to identify the cause of its development after trigeminy is identified. Further therapeutic tactics depend more on the specific type of arrhythmia than on the cause of its development.
Trigeminy: causes, types, treatment
- 1 Trigeminy: causes, types, treatment 1.1 Trigeminy
- 1.2 Causes of trigeminy
- 1.3 Types of trigeminy
- 1.4 What are bigeminy, trigeminy and quadrigeminy?
- 1.5 What are their differences?
- 1.6 How dangerous is it?
- 1.7 Classification
- 1.8 Provoking factors
- 1.9 Symptoms
- 1.10 Persistent, ventricular, asymptomatic trigeminy of the heart: treatment, episodes, causes
- 1.11 Features
- 1.12 Forms and types
- 1.13 Causes of trigeminy
- 1.14 Diagnostics 1.14.1 Therapeutic
- 1.14.2 Medication
- 1.14.3 Folk remedies
17 How allorhythmia differs by type, its manifestation and treatment
- 1.19.1 Trigeminies
- 1.22.1 Medication
31 Supraventricular trigeminy: features
37 Symptoms of bigeminy and trigeminy
- 1.38.1: bigeminy on ECG
Trigeminy of the heart is a type of extrasystole, in which every third excitation and contraction of the myocardium is premature. Episodes of bigeminy and trigeminy can also occur in practically healthy individuals, but in many cases they indicate the presence of structural and functional disorders of the cardiovascular system.
What are bigeminy, trigemy and quadrigemy?
Source: https://cardiomanual.ru/trigeminiya-serdca-chto-eto-takoe.html
Types of trigeminy
Trigeminies vary depending on the location of the focus of premature excitation. In accordance with this, supraventricular and ventricular trigeminies are distinguished.
The source of supraventricular trigeminy is a focus of premature excitation located in the conduction system of the heart above the branching point of the His bundle. This area includes the structures of the conduction system passing through the thickness of the atrial myocardium.
Ventricular trigeminy develops due to the occurrence of a premature impulse below the branching point of the His bundle. Typically, the sources of extrasystole are Purkinje fibers penetrating the ventricular myocardium.
Supraventricular trigeminy: what is it?
The cause of the development of supraventricular trigeminy is a pathological impulse that occurs in the structures of the conduction system of the heart located in the region of the atrial myocardium. From a clinical point of view, this type of arrhythmia may not manifest itself in any way, however, most patients present complaints such as:
“Interruptions” in the work of the heart. Feeling of “turning over” in the chest. General discomfort, anxiety.
Some patients also describe shortness of breath, dizziness, and chest pain that occurs during an episode of extrasystole. These symptoms, however, are due to an autonomic reaction rather than significant circulatory disorders.
On the ECG, supraventricular trigeminy is characterized by premature QRS complexes with preceding P waves, as well as an incomplete compensatory pause. An extrasystole occurs every two normal heartbeats. To clarify the diagnosis, Holter monitoring is required.
Supraventricular trigeminy usually does not require special treatment. In some cases, the patient is indicated for antiarrhythmic therapy with beta blockers or calcium antagonists, as well as sedatives, since this type of arrhythmia very often accompanies mental and psychosomatic disorders of a neurotic level.
Ventricular trigeminy
Ventricular extrasystole of the trigeminy type develops as a result of premature excitation, the source of which is the myocardium of the ventricles of the heart. This type of arrhythmia, much more often than supraventricular extrasystole, occurs against the background of structural changes in the cardiovascular system, which leads to other therapeutic approaches.
The clinical picture of ventricular trigeminy is similar to that of supraventricular trigeminy, however, objective symptoms of arrhythmia are often identified:
Irregular pulse. Uneven pulsation, determined by palpation of the apex of the heart. On auscultation, a premature heartbeat with a characteristic loud first sound is heard.
Ventricular trigeminy is much more often accompanied by shortness of breath, weakness, dizziness and chest pain.
Ventricular trigeminy on ECG
In typical cases, the electrocardiographic characteristics of ventricular trigeminy include:
Presence of premature QRS complexes without preceding P waves. QRS complexes are widened (more than 0.12 sec), deformed, and may resemble a bundle branch block. The presence of a complete compensatory pause.
Extrasystole occurs every two normal contractions (allorhythmia type trigeminy). To clarify the diagnosis, Holter monitoring is required, which can detect a combination of bigeminy and trigeminy, as well as other disturbances of cardiac rhythm and conduction.
Trigeminy of the heart: what is it and how to treat it?
Patients are often diagnosed with a condition such as extrasystole. This is the name for a type of heart rhythm disorder in which ectopic rhythm of the organ occurs. The forms of extrasystole are bigeminy, quadrigeminy and trigeminy. What is the cause of the last type of pathology?
What is trigemy?
Trigeminy is a heart rhythm disorder characterized by extraordinary contraction of muscles or their individual parts. The pathology is benign and therefore does not threaten the patient’s life. But if there is no treatment or the wrong treatment tactics are prescribed, adverse complications may occur.
Doctors distinguish several types of trigemynia depending on its location:
- Ventricular. On the ECG, this type is manifested by the presence of premature QRS complexes without preceding P waves. They are wider and deformed. There is also a complete compensatory pause. Ventricular extrasystole of the heart of the trigeminy type appears every 2 full contractions.
- Supraventricular. The cardiogram reveals the presence of premature QRS complexes, and there are P waves preceding them. With this type of trigeminy, an incomplete compensatory pause is observed on the ECG. Extrasystole occurs in the same way as in the first case - after 2 contractions.
- Mixed, affecting several areas of the heart at once.
There are also types of the disease depending on the frequency of occurrence:
- Frequent: appears more than 30 times per hour.
- Average: no more than 15 times per hour.
- Rare: less than 5 times per hour.
Trigemy is divided into varieties and according to the number of pathological foci. If there is one, then there is a monotopic form, and if there are two or more, it means a polytopic form.
Causes
Trigemynia can appear in a completely healthy person. With age, the likelihood of heart rhythm disturbances increases. But most often the following factors provoke pathology:
- unhealthy lifestyle: smoking, alcohol abuse and taking drugs and psychotropic substances;
- frequent consumption of coffee and strong tea;
- damage to the structure of the muscle tissue of the heart;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- imbalance of electrolytes in the body;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- heart disease;
- overdose of cardiac glycosides.
Doctors are not always able to identify the culprit in the development of trigeminy. Therefore, therapy depends more on the type of disease.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of heart disease may vary depending on what type of pathology develops in the patient. If supraventricular (supraventricular) trigeminy occurs, the patient may not feel any symptoms. But still, many people complain of the following symptoms:
- “interruptions” in the activity of the heart;
- sensation as if this organ were turning over in the chest;
- general deterioration of condition, panic anxiety.
Some patients experience shortness of breath, attacks of dizziness, and pain in the sternum. But such signs appear not due to rhythm disturbances, but as a result of the reaction of the body’s autonomic system.
The clinical manifestations of ventricular (ventricular) trigeminy are similar to the symptoms of the supraventricular form. But often patients experience specific symptoms. These include:
- Uneven pulsation, which is determined by palpating the chest in the area of the upper part of the heart.
- Premature contraction of an organ, characterized by a loud first tone, which is detected during listening.
NOTE !!! With the ventricular type of disease, shortness of breath, general weakness, dizziness, and chest pain most often appear.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of a patient begins with studying his complaints, medical history, visual examination and listening to the heart. After this, the doctor prescribes an examination. It may consist of the following procedures:
- Laboratory research. Patients undergo general and biochemical blood and urine tests, as well as a blood test for hormones. This diagnosis allows us to detect possible causes of heart disease.
- Cardiogram. A mandatory examination method for heart diseases, which helps evaluate the functioning of the organ and identify disturbances in its rhythm.
- Holter monitoring ECG. Using this study, it is possible to detect temporary irregularities in heart rhythm, for example, during physical activity.
- Ultrasound diagnostics. It is prescribed to assess the condition of the heart and identify pathologies that can cause the development of trigeminy.
- Tests to determine the presence of arrhythmia during physical activity.
Doctors consider magnetic resonance imaging to be the most informative diagnostic method. It clearly shows the heart muscle, which helps to more accurately study its condition. But such an examination is expensive, and not every hospital has the equipment to conduct it.
Treatment
Treatment tactics are determined based on the patient’s diagnostic results. Trigeminy is usually treated with therapy and medications. Surgical treatment is rarely performed. Surgery is prescribed when extensive damage to the heart muscle is observed.
Therapeutic
The therapeutic method of treatment is sometimes not complemented by any other methods, as it helps to completely restore the functioning of the heart. This is possible if the patient no longer has any pathologies of the heart muscle or endocrine organs.
Therapeutic treatment implies that the patient must follow a work-rest schedule, monitor his diet, avoid stressful situations and excessive physical activity, spend more time in the fresh air and undergo periodic examinations.
Medication
Taking medications is necessary if the number of extrasystoles per day exceeds 200. The following drugs are used for therapy:
- Antiarrhythmic medications. Used to normalize heart rhythm. They are taken for a long time under periodic monitoring of electrocardiography.
- Cardiac glycosides. Prescribed to slow down organ contractions and restore proper rhythm.
- Antihypertensive drugs. Designed to lower blood pressure.
Medicines are prescribed individually for each patient, depending on the condition of the heart, concomitant diseases, and the type of trigeminy.
Operation
Emergency surgery is used if extensive damage to the heart is observed or therapeutic and drug treatment has not yielded positive results.
There are the following methods for eliminating trigemy:
- An open operation during which ectopic foci are eliminated.
- Radiofrequency ablation, in which electrodes are used to cauterize the affected areas of muscle tissue that cause rhythm disturbances.
If there are concomitant heart pathologies, other surgical methods may be prescribed.
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine can not cope with all heart diseases, so they are usually used as an auxiliary treatment. But traditional medicine is quite capable of helping to get rid of trigeminy.
The most popular medicine with a sedative effect is valerian. It is available in almost every home medicine cabinet. But you don't have to buy it at the pharmacy. You can prepare an alcohol tincture at home.
To do this, add a teaspoon of crushed valerian root to a quarter glass of water, boil and leave to steep until the liquid turns dark. After this, add water to make half a glass of the drink, and take it every day before meals. The course of therapy is 10 days. Take a break for seven days and repeat the course of treatment.
Melissa tincture helps very well. Infuse a teaspoon of the herb in a glass of boiling water for 15 minutes and take it before meals. The course of treatment is about 3 months.
You can also use alcohol tincture of hawthorn. It is sold in finished form at the pharmacy. Take 10 drops 3 times a day. You can prepare this folk remedy yourself. To do this, pour 10 g of fruit into 100 ml of vodka, leave to infuse for 10 days and take according to the same scheme. Even more recipes with hawthorn are collected here.
IMPORTANT !!! Before using traditional recipes, you should consult your doctor. There is no need to try to cure the pathology yourself using home remedies if the most radical treatment methods are required. Otherwise, adverse consequences may develop.
Complications
Complications with trigeminy do not occur often. This is usually due to lack of treatment or the presence of concomitant heart disease. Possible complications are the following disorders:
- Atrial flutter is a pathological condition in which the atria contract at a high speed - over 200 times per minute. At the same time, the contractility of the heart itself remains normal.
- Paroxysmal tachycardia - rapid heartbeat.
- Atrial fibrillation is an uncoordinated contraction of the muscle tissue of the atria.
Ventricular trigeminy can cause ventricular fibrillation and unexpected death.
Forecast
The prognosis is favorable in most cases. The disease can be easily eliminated if it develops independently. In the presence of concomitant diseases or complications, the outcome for the patient is not so positive.
Having considered what cardiac trigeminy is, we can conclude that in itself it does not pose a danger to human life, but its untimely treatment can lead to negative consequences. To prevent heart problems, you should undergo a preventive examination every year.
It is also important to be more attentive to your health, lead an active lifestyle, eat right, stop smoking and drinking alcohol, do not subject your body to excessive physical activity, monitor your blood pressure and promptly treat any heart disease.
Source: https://ritmserdca.ru/aritmiya/trigeminiya.html
Treatment of pathology
In some cases, bigeminy can be completely eliminated. This happens in situations where it is possible to eliminate the cause that led to allorhythmia, for example, thyrotoxicosis, myocarditis, an infectious disease, or electrolyte imbalance. In severe cases, getting rid of bigeminy is possible through surgical intervention - destruction (ablation) of the focus of pathological impulses using high-frequency current.
- For any form of bigeminy, treatment of the pathology that caused the rhythm disturbance and elimination of the causative factors of arrhythmia are indicated.
- It is useful to give up alcohol, smoking, strong tea, and coffee.
- It is recommended to maintain a healthy lifestyle and eliminate psycho-emotional stress.
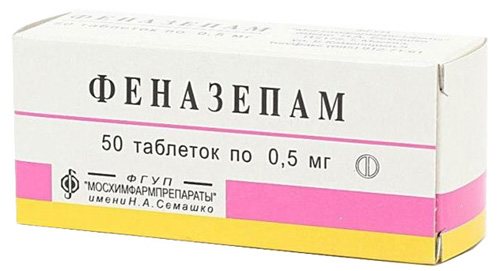
- In case of severe subjective tolerance to attacks of bigeminia, drugs with a sedative effect are recommended: tinctures of hawthorn, motherwort, tranquilizers (phenazepam, clonazepam).
Antiarrhythmic therapy
Antiarrhythmic drugs for any type of extrasystole, including bigeminy, are used according to strict indications. According to research, periodic episodes of bigeminy do not in themselves cause harm to the body and rarely lead to circulatory problems.
But taking antiarrhythmic drugs can lead to side effects. The most dangerous of them:
- increased risk of sudden cardiac death;
- arrhythmogenic effect - intensification of an existing arrhythmia or the occurrence of another rhythm disorder;
- dizziness, fainting, increase in heart failure, decrease in the number of blood leukocytes and other negative reactions.
The decision about the need for antiarrhythmic therapy depends on risk assessment. Firstly, with supraventricular bigeminy, there is a risk of developing supraventricular tachycardia - a rhythm disturbance in which the contraction frequency reaches 140-180 per minute. The condition is dangerous due to the possibility of developing heart failure and requires urgent measures to normalize the rhythm. Secondly, a consequence of supraventricular bigeminy can be atrial fibrillation, in which the atria contract at a frequency above 300 beats per minute. Ventricular bigeminy is dangerous due to the threat of sudden cardiac death.
Indications for the use of antiarrhythmic drugs for extrasystole:
- frequent attacks of bigeminy, leading to disturbances in the movement of blood in the body;
- severe patient tolerance of extrasystole;
- deterioration in the functional capacity of the heart muscle during ultrasound examination of the heart, monitored over time.
For supraventricular bigeminia, the drugs of choice are drugs from the groups of beta-blockers (anaprilin, atenolol, metoprolol) or calcium antagonists (verapamil, diltiazem). If they are insufficiently effective, effective drugs from other groups or a combination of two drugs are selected.

For ventricular extrasystole, regarded as potentially dangerous or malignant, amiodarone and beta-blockers are prescribed. These drugs can improve the prognosis for heart disease and reduce the risk of death.
Class 1 antiarrhythmics (propafenone, etacizin, ethmozin) are prescribed only for arrhythmias not associated with coronary artery disease.
Radiofrequency ablation
Radiofrequency ablation is indicated for bigeminia, which leads to disruption of blood flow in the body and an increased risk of sudden death, if antiarrhythmic therapy is ineffective. This surgical procedure is possible only if the focus of extrasystole is identified. The electrodes are inserted through a venous access and, after an electrophysiological study, exert a radiofrequency effect on the source of the arrhythmia, destroying it.
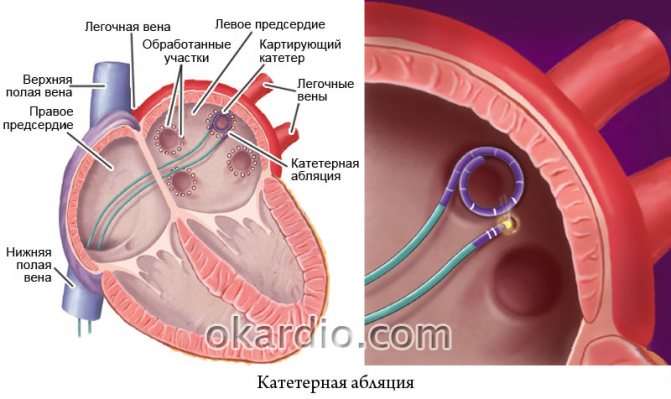
Click on photo to enlarge
Features of the pathology
Extrasystole is the main cause of bigeminy. There are several common causes of heart rhythm disturbances, namely:
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. This disease causes disruption of blood circulation directly to the brain. The vertebrae of the cervical spine are quite mobile, but, nevertheless, they are surrounded by a weak muscle corset. This leads to their mixing and pinching of the artery, which ensures normal blood circulation.
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia. The disease manifests itself as dysfunction of various organs and is diagnosed mainly through a complete examination of the body. Autonomic disorders of the cardiovascular system manifest themselves in the form of pain symptoms in the heart area, changes in blood pressure levels and the presence of a heart murmur.
- Neuroses and psychogenic disorders. Often psychological disorders, chronic depression and nervous exhaustion become the causes of extrasystole. Various diseases of the nervous system, manifested in chronic or acute forms, are psychogenic in nature.
In addition to the above factors, the causes of extrasystole can be:
- excessive drinking;
- smoking;
- addiction.
Periodic heartbeat disorders can occur in women during menstruation or with the onset of menopause.
- Cardiosclerosis. This disease occurs due to the formation of scars and growths on the tissues of the heart. Scars appear on the myocardium, provoke disturbances in the functioning of the heart, which leads to heart failure.
- Cardiac ischemia. With this disease, blood circulation to the myocardium is disrupted. The circulatory system does not transport normal amounts of oxygen to the coronary artery, which leads to angina attacks.
- Myocardial infarction. The disease occurs as a result of thrombosis of the coronary artery. The causes are excessive blood thickening and circulatory dysfunction.
- Cardiomyopathy is one of the myocardial diseases associated with functional or structural changes in the heart muscle. With cardiomyopathy, the functioning of the valve apparatus of the heart is disrupted.
- Heart disease. A patient with this disease experiences disturbances in the functioning of the valve apparatus and pathological changes in the walls of blood vessels. The disease leads to heart failure and is chronic.
Bigeminy is a type of extrasystole that can occur during pathological processes or without any disruptions in the body. It is considered normal if no more than 30 extraordinary contractions occur within an hour.
With frequent rhythm disturbances, after each normal contraction an extraordinary contraction occurs. Such arrhythmia can be atrial or ventricular.
Irregular bimigenia is observed throughout the day. Using an electrocardiogram in this case, it is impossible to accurately estimate the duration of attacks.
In the normal state of the body, cardiac structures contract autonomously. This gives the body some margin of safety to maintain the minimum necessary activity in emergency cases when consciousness is switched off or the brain is damaged.
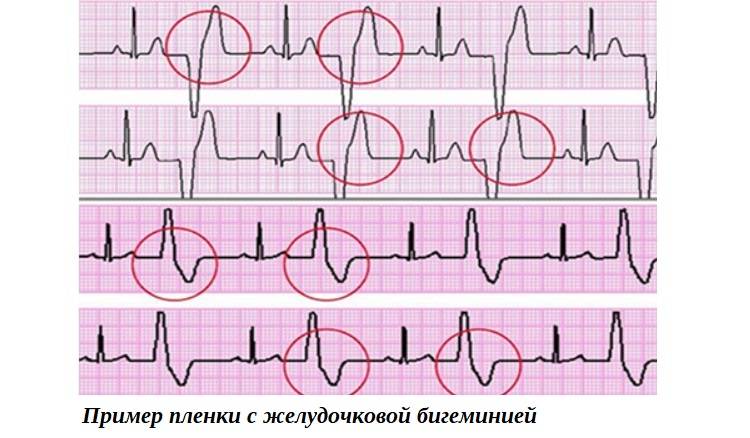
The so-called sinus node is responsible for the production of an electrical signal that excites the muscular structures of the myocardium. It is located in the upper part of the organ.
Such alternation is clearly visible on the ECG, which makes diagnosis, even in the early stages, relatively simple.
It is impossible to talk about the severity and prospects of the process based on just one factor. Much depends on the location of the anomaly (atrial forms of extrasystole almost never pose a danger, which cannot be said about ventricular ones). The underlying disease, general state of health, and the moment of contacting a doctor also play a role.
As already said, deviation is not primary. It is secondary to cardiac diseases, less often to non-cardiac pathologies.
Which one needs to be looked at during the diagnosis. Usually these are congenital and acquired defects, hormonal imbalances, bad habits that provoke temporary or permanent changes in the functioning of the whole organism, etc.
Such extrasystoles can appear even in a healthy person; there can be from 30 to 60 of them per hour, this is considered the norm. But if they occur very often, after one regular set of contractions there is an extraordinary, second one (bi is translated as two), then this is bigeminy.
Prognosis and complications
Even a leading doctor cannot give exact figures. Approximately 12% of patients with atrial bigeminy suffer from fatal or disabling complications after 10 years without treatment.
The ventricular form is even more difficult to tolerate - 30-40% have fatal consequences. With therapy, the prognosis is much more optimistic.
You can say anything specific after long-term observation of the patient, his reaction to treatment and general development paths. All questions should be asked to the doctor.
Forecasts for bigeminia

For short episodes, the patient is under medical supervision. If he changes his life in accordance with the recommendations, then the prognosis is favorable. In case of heart pathologies, it is necessary to undergo treatment and eliminate the symptoms.
The prognosis will be conditionally favorable if hemodynamics are not impaired. Frequent extrasystole leads to deterioration of blood supply in the body. To prolong the patient's life, serious efforts are required to restore rhythm and improve heart function.
Bigeminy heart
Arrhythmias are among the most common manifestations of heart disease. Extrasystoles of the bigeminic type mean a form of rhythm disturbance in which extraordinary pathological contractions from the ectopic focus appear after each normal excitation.
The causes of this disease can be functional disorders, organic changes (cardiomyopathies, carditis, ischemic heart disease), toxins, and electrolyte imbalances.
What is bigeminy
Bigeminy is a type of allorhythmia, i.e. regular repetition of extrasystoles. There are also trigeminies and quadrigemies.
Ventricular extrasystole (VC) occurs due to a pathological wave of excitation that comes from the conduction system of the ventricles.
In general, PVCs are considered a very common type of heart rhythm disorder. Probably each of us has felt it at least once in our lives. And even more PVCs occur unnoticed. During the day, the heart of even an absolutely healthy person can make up to 200 extraordinary ventricular contractions. And that's okay.
The danger of PVCs is that they can provoke severe cardiac arrhythmias, often resulting in death - ventricular tachycardia (VT), ventricular fibrillation (VF).
Another unpleasant consequence of extrasystole is the development of so-called arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy. With this pathology, the chambers of the heart expand, the ability of the myocardium to pump blood normally deteriorates, and the likelihood of blood clots increases.
There are a huge number of reasons for the occurrence of PVCs. By origin, all extrasystoles can be divided into 2 large groups: functional and organic.
Functional (non-cardiac) PVCs develop in people without heart disease for the following reasons:
- any physical activity;
- sneezing;
- sudden fear or prolonged emotional stress;
- smoking;
- use of narcotic substances – cocaine, amphetamine;
- excessive consumption of coffee and caffeine-containing drinks (Coca-Cola, energy drinks);
- infections accompanied by fever;
- pathologies of the endocrine system - for example, excess production of thyroid hormones (hyperthyroidism) or adrenal cortex (Cushing's disease, pheochromocytoma);
- the use of certain medications;
- various injuries and injuries to the chest.
Organic (cardiac) PVCs are found in people suffering from cardiac diseases (coronary artery disease, arterial hypertension, chronic myocardial failure, rheumatism, myocarditis, heart defects, etc.).
In people with heart disease, extrasystoles develop much more often, are much more severe, and are more likely to cause VT and VF.
Clinical signs of ventricular extrasystoles
Most often, ventricular bigeminy, like ordinary extrasystoles, especially short-term ones, in small quantities, are asymptomatic.
If they occur constantly, then a feeling of “freezing”, “rolling”, and interruptions in the functioning of the heart may appear. Sometimes there is slight dizziness and mild nausea.
In some of my patients, bigeminy is accompanied by a feeling of anxiety and fear.
In patients with cardiac pathologies, symptoms are more severe. Their vision becomes dark, their head feels much more dizzy, they experience a pronounced feeling of lightheadedness, vomiting, pain in the heart area, and a feeling of lack of air.
Fainting is possible. This is due to the fact that regularly repeated extraordinary contractions lead to a deterioration in blood pumping by the heart muscle.
As a result, circulatory failure occurs in the heart, brain, and other organs.
Signs of bigeminy on the ECG
Ventricular bigeminy has the following electrocardiographic signs:
- premature appearance of a wide and deformed QRS complex;
- a compensatory pause following the complex, in the form of a straight line (usually it is longer than with supraventricular extrasystoles);
- absence of P wave;
- direction of the ST segment in the direction opposite to the QRS complex.
If all QRS complexes have the same shape, this means that pathological impulses arise from the same source. Such PVCs are called monotopic and are considered the most benign.
If the QRS complexes are different, it means that the impulses originate from several foci. In this case, PVCs are called “polytopic.” They are more dangerous in terms of the likelihood of adverse consequences.
Early PVCs are also identified separately. This is when a prematurely occurring complex overlaps the T wave of the previous (normal) complex. The appearance of early extrasystoles is considered a very unfavorable sign.
It is early extrasystoles that most often cause paroxysmal VT and ventricular fibrillation.
To accurately count the number of extrasystoles that occurred per day, as well as to identify possible other arrhythmias, I prescribe Holter ECG monitoring.
Are there any peculiarities in the symptoms?
As already mentioned, ventricular extrasystoles of the bigeminy type do not have any differences in symptoms from ordinary extrasystoles. Everything is determined by the frequency of their occurrence, the number of sources of the pathological wave of excitation and the presence of cardiac diseases.
Case from practice
I would like to tell you about one clinical case. A 56-year-old man came to see me. About a month ago, he began to be bothered by sudden sensations of interruptions in his heart function, dizziness, and darkening of his eyes. Suffering from arterial hypertension.
To reduce blood pressure, she takes Lisinopril, but not constantly. When examining the patient, I discovered an irregular pulse and an increase in blood pressure to 150/90 mm Hg. I ordered Holter ECG monitoring.
Result: frequent ventricular extrasystole of the bigeminy type, episodes of paroxysmal VT.
Echocardiography (Echo-CG) revealed hypertrophy of the left heart. No expansion of the chambers, valve defects, or disturbances in myocardial contractility were noted. Drug therapy was prescribed: Lisinopril 10 mg per day, Bisoprolol 5 mg per day.
Despite drug treatment, ventricular bigeminy and the clinical picture caused by them persisted. In this regard, a decision was made to perform radiofrequency ablation. After the operation, the patient's condition improved significantly.
The symptoms bothering the patient disappeared. The cardiogram returned to normal.
Expert advice
An important role in the treatment of ventricular bigeminy is played by the elimination of causative phenomena. Therefore, I strongly recommend that my patients avoid all kinds of factors that can trigger the occurrence of extrasystoles. This means giving up bad habits (especially smoking), reducing the consumption of coffee and caffeinated drinks, and avoiding stress as much as possible.
People without cardiac pathologies, whose ECG showed frequent cardiac bigeminy, should be examined for various diseases - endocrine diseases, iron deficiency anemia, chronic infections, etc.
The following sources of information were used to prepare the material.
What are bigeminy, trigemy and quadrigemy?
Article publication date: 06/29/2018
Source: https://cardiologiya.com/bolezni/aritmiya/bigeminiya-serdcza.html