Primary acrocyanosis
Essential (or primary) acrocyanosis is a benign condition sometimes associated with a neurohormonal disorder. In general, it tends to regress spontaneously and does not require special treatment. On the other hand, emergency medical intervention may be required if the extremities are exposed to extreme cold for a long time.
However, acrocyanosis is different from hypothermia: the latter condition is often associated with pain (the reflex pathway of thermal nociceptors warns of danger).
A number of other conditions affecting the arms, legs and parts of the face, with associated changes in skin color, should be distinguished from acrocyanosis:
- : reversible episodes of skin pallor of the fingers or toes due to narrowing of small blood vessels exposed to cold or severe emotional stress;
- Geloni (erythema pernio): skin irritation caused by prolonged exposure to extreme and damp cold (see photo above);
- Acorygosis: a constant and symmetrical sensation of coldness in the extremities associated with pale skin;
- Erythromelalgia: vasodilation caused by an increase in skin temperature, which occurs with local heating, severe redness and very severe pain.
In some cases, diagnosis can be difficult, especially if these syndromes coexist.
Additional symptoms of acrocyanosis
Depending on the cause of acrocyanosis, the patient may have the following symptoms:
- soreness in places where the skin turns blue;
- mild swelling of the feet, hands and fingers;
- increased sweating, “cold” sweat;
- dyspnea;
- tachycardia, bradycardia;
- weakness;
- chest pain;
- wheezing in the lungs and wet cough;
- impaired skin sensitivity in the form of tingling, numbness, goosebumps;
- sleep and appetite disorders.
Information about additional symptoms helps doctors determine the cause of skin discoloration and make the correct diagnosis. For example, with severe dehydration, the patient may have tachycardia, dry mucous membranes, decreased elasticity of the skin, pulse lability, decreased blood pressure, pallor and cyanosis of the skin. And heart disease is often accompanied by a wet cough, pain and shortness of breath.
Varieties and reasons
The most common phenomenon is acrocyanosis, characterized by a change in the color of the skin on the distal parts of the body, that is, the limbs and face. Acrocyanosis predominantly develops in patients with cardiac pathology and may be evidence of the development of heart failure in a child or adult. In adults, acrocyanosis is also a sign of the development of atherosclerosis, vegetative-vascular dystonia, varicose veins and some other pathologies. But the pathology also occurs in infants who do not have anomalies in the development of the cardiovascular system.
With this type of pathology, cyanosis is localized on the hands and feet, ears, tip of the nose and lips. For a baby in the first days of life, acrocyanosis is a normal phenomenon, since his lungs have not yet begun to function fully, which is manifested by an insufficient supply of oxygen to the blood. Acrocyanosis is more pronounced when the baby cries, makes excessive efforts during feeding, or is restless.
It is important to understand that there are different varieties of this pathological condition. So, in medical practice they talk about central and local cyanosis
Central cyanosis develops in cases where arterial blood is not sufficiently saturated with oxygen, which happens in severe diseases such as respiratory failure, erythrocytosis, heart defects and others. This condition may indicate the need for urgent medical care for a person. This type is also called diffuse cyanosis, and it has the maximum severity.
Acrocyanosis
With local cyanosis, impaired blood circulation is observed in a localized area due to local disruption of blood circulation. This form of pathology is observed in places of increased accumulation of blood vessels - around the mouth, around the eyes.
The local form is also called peripheral cyanosis. The causes of this form of the disease can be the following pathological conditions:
- slowing of blood flow in the capillaries due to thrombophlebitis or compression by a tumor;
- poisoning and intoxication of the body;
- heart and vascular diseases;
- tuberculosis and pneumonia, which prevent sufficient oxygen from entering the blood;
- chest deformation as a result of traumatic injury with impaired respiratory function.
Cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle is often diagnosed in infants, which indicates malformations of the lungs, heart and neuralgia.
In general, peripheral cyanosis occurs in medical practice more often than central cyanosis, since there are many more reasons that cause it.
Acrocyanosis of the hands
Graphic registration of changes in the volume of organs and the study of blood capillaries with acrocyanosis of the hands often reveals an increase in the tone of small blood vessels that end the branching of the arteries with a narrowing of the tone and an increase in the lumen of the venous region of the blood vessels included in the vascular network from which the veins and subcutaneous capillaries originate. It is the different level of reaction of the blood vessels that are part of the vascular network that can explain why acrocyanosis does not begin to develop in all cases with obstruction of arteries distant from the center (atherosclerosis, thromboangiitis obliterans) and conditions of reduced cardiac output (aortic defects).
Stridor in newborns - what is it?
Experts believe that stridor is not a disease, but only symptoms. Sometimes they can indicate that the baby has a serious illness, but in most cases, stridor disappears without a trace even without taking medications. Noises are heard when inhaling and exhaling, they are especially pronounced when the child is excited. The volume and timbre of such sighs can vary significantly among different children.
For some babies, breathing noise appears only when crying or screaming. But most babies suffer from wheezing around the clock, and their symptoms worsen during sleep. This disease occurs in infants because their laryngeal cartilages are still very soft. And for kids with established disabilities, they are like plasticine. When inhaling, the cartilages close and, under the influence of negative pressure arising in the bronchi, the air in the child’s upper respiratory tract vibrates.
The identified violation will not affect the children’s voice in the future. Don't worry about it getting rough or hoarse. The type of stridor is determined by the nature of the sound the baby makes. The breathing phase and voice pitch are taken into account. A loud noise indicates that the baby's airway is narrowed. Weakening of stridor after its loud manifestation indicates increasing obstruction. Breathing with a low noise level is a sign that the cause of the disease is located below the vocal cords.
What is acrocyanosis
This term refers to a condition in which there is a blue discoloration of the skin. Pathology develops when the blood supply to small vessels is disrupted. Acrocyanosis in children and adults is most pronounced in areas remote from the heart muscle.
The degree of change in skin color varies, from bluish to dark blue. This depends on the severity of the vascular damage. Accordingly, mild, moderate and pronounced acrocyanosis are distinguished.
Forms of the disease
Various reasons can provoke the development of acrocyanosis. Taking this fact into account, several types of pathology are distinguished:
- Anesthetic. This form develops due to the effect of negative temperatures on the skin. Moderate anesthetic acrocyanosis is not considered dangerous, since it is a physiological reaction of the body to low temperature.
- Idiopathic or essential. It is provoked by a spasm of small arteries and is manifested by cyanosis of the lips, hands, ears, tip of the nose, etc. This form is typical for teenage girls during puberty. Can be observed even in a warm room at rest.
- Central acrocyanosis manifests itself as a result of a decrease in oxygen concentration in the pulmonary circulation. This can happen if the amount of reduced hemoglobin increases.
- Diffuse acrocyanosis occurs when hemodynamics are impaired in the right side of the heart.
- Spasmodic cyanosis occurs when small blood vessels spasm in response to various stimuli. For example, mild acrocyanosis is often observed in adolescents with neurotic problems.
Causes of acrocyanosis
Many factors can provoke the development of such a pathology, but the main reasons are:
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system. If the heart does not work at full strength, then it cannot provide satisfactory blood supply to small capillaries.
- The presence of heart disease is often manifested by acrocyanosis of the lips and nail plates.
- Poisoning with certain types of toxic substances or medications can cause cyanosis.
- Hypothermia of the body.
- Exposure to external stimuli that provoke vasospasm.
- Hormonal changes can cause peripheral circulation problems.
- Thromboembolism of the pulmonary arteries often provokes diffuse acrocyanosis. This disease, like others, requires serious therapy.
- Venous diseases.
Manifestations of acrocyanosis
Acrocyanosis can be recognized by the following characteristic manifestations:
- The skin of the feet and hands becomes bluish at low temperatures.
- Moderate acrocyanosis is a blue discoloration of the lips, ears, and tip of the nose.
- The intensity of the blue color increases in the cold; when moving to a warm room, the blue color disappears.
- There is slight swelling of the fingers and toes.
- In the presence of cardiac pathologies, cyanosis is also accompanied by increased sweating.
- The skin, even at normal temperature, is always cold.
- If the cause of the disease is lung pathology, the skin becomes ash-gray in color.
When visiting a doctor, it is imperative to inform the specialist under what conditions cyanosis appears, whether it is permanent, and what factors aggravate it. This will make it easier for the doctor to recognize the cause of the pathology and prescribe therapy.
Acrocyanosis (blueness of the skin) is a symptom, not a disease
Acrocyanosis is the name by which in medicine we mean a change in color (blue discoloration) of the skin of the hands, feet, ears, tip of the nose and lips in humans.
Often, bluish skin is not dangerous to health and is considered a normal physiological reaction of the body - for example, to cold.
But acrocyanosis can also be a symptom of serious respiratory and circulatory diseases.
Why does the skin turn blue?
Doctors distinguish several types of blue discoloration of the skin, each of which has its own causes and mechanisms of development. Acrocyanosis occurs due to impaired blood circulation in the smallest capillaries and manifests itself in areas of the body farthest from the heart. This is its main difference from “ordinary” cyanosis, in which the blueness of the skin is general.
The bluish coloration of the skin during acrocyanosis is caused by an increased content of carboxyhemoglobin in the blood, which accumulates due to a slowdown in blood flow in the peripheral vessels.
At normal blood circulation rates, hemoglobin and carbon monoxide compounds are “evacuated” from the capillaries in time, while the skin remains healthy pink.
Acrocyanosis develops when the outflow of blood is impaired for some reason, and reduced hemoglobin accumulates in the smallest vessels, causing the skin to darken and acquire a bluish tint.
Forms of acrocyanosis and their causes
Depending on the causes of occurrence, several forms of acrocyanosis are distinguished.
Doctors consider its simplest and most natural type to be anesthetic, in which the skin turns blue due to the effect of cold on the body.
The essential (idiopathic) form often occurs in healthy female adolescents and young women. The cause of circulatory disorders in peripheral vessels are hormonal changes in the body, accompanied by temporary disruptions in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system. In this case, the bluishness of the skin increases not only from cold, but also from physical activity or excitement.
The central (diffuse) type occurs when there is insufficient oxygen saturation of the blood, which often accompanies serious diseases of the cardiovascular system and respiratory system.
The spasmodic form is typical for adolescents and people with mental disorders; it can be a symptom of astheno-neurotic syndrome and some neuroses that affect the functioning of the autonomic nervous system.
Acrocyanosis in newborns is observed in the first days or even months of life. This is due to a change in the intrauterine type of blood circulation to “adult”, which does not imply the supply of blood to the body through the umbilical cord.
The cyanosis of the extremities is especially pronounced in children born prematurely or physiologically immature, with low weight. As a rule, cyanosis in newborns goes away on its own and does not require any treatment, but the child should be shown to a doctor, since cyanosis of the skin is also characteristic of serious heart problems, including congenital malformations.
Diseases that cause acrocyanosis
Permanent or temporary blue discoloration of the skin can be caused by a number of diseases.
And even in the absence of chronic diseases, a person sometimes develops an acute form of cyanosis, which occurs suddenly, with rapidly increasing bluishness of the skin. This condition requires emergency care and hospitalization to find out the causes of poor health.
Chronic acrocyanosis and cyanosis can continue for a long time, while the bluish color of the skin changes from faint to clearly noticeable.
List of diseases in which this condition may develop:
- bronchial asthma;
- acute bronchitis or pneumonia;
- pulmonary embolism (PE);
- pulmonary tuberculosis;
- lung cancer;
- pulmonary infarction;
- Congenital heart defect;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- anxiety and depressive disorders;
- inflammatory diseases of arteries and veins;
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease;
- scleroderma;
- chronic cardiac or respiratory failure.
Also, cyanosis of the hands and face occurs when poisoned by poisons and certain medications , under the influence of which hemoglobin derivatives accumulate in the blood and are unable to transport oxygen to the body’s tissues.
The blood becomes thicker and darker, peripheral circulation is disrupted, causing the fingers and nasolabial triangle to turn blue.
Additional symptoms of acrocyanosis
Depending on the cause of acrocyanosis, the patient may have the following symptoms:
- soreness in places where the skin turns blue;
- mild swelling of the feet, hands and fingers;
- increased sweating, “cold” sweat;
- dyspnea;
- tachycardia, bradycardia;
- weakness;
- chest pain;
- wheezing in the lungs and wet cough;
- impaired skin sensitivity in the form of tingling, numbness, goosebumps;
- sleep and appetite disorders.
Information about additional symptoms helps doctors determine the cause of skin discoloration and make the correct diagnosis.
For example, with severe dehydration, the patient may have tachycardia, dry mucous membranes, decreased elasticity of the skin, pulse lability, decreased blood pressure, pallor and cyanosis of the skin. And heart disease is often accompanied by a wet cough, pain and shortness of breath.
Diagnosis of acrocyanosis
To determine the cause of acrocyanosis, the patient is prescribed a number of examinations, including:
- general and biochemical blood tests
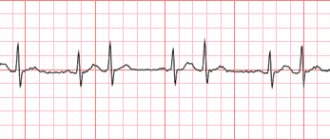
- ECG
- pulse oximetry (determining blood oxygen saturation using a sensor that is worn on the finger)
- chest x-ray
The doctor will definitely find out from the patient when the blueness of the skin appeared, how its shade changes during the day, whether physical activity and other irritants provoke increased cyanosis, whether the limbs turn blue at rest and during sleep.
To differentiate acrocyanosis from angioneurosis, a test with raising an arm is used - the patient is asked to raise one arm up and hold it in this position for about 30 seconds. In this case, the bluishness of the skin caused by acrocyanosis (especially in adolescence) immediately disappears.
If necessary, the patient is prescribed specific tests:
- determination of blood gas composition;
- measurement of blood flow speed;
- CT or MRI of the chest;
- ultrasound and Doppler, Holter monitoring.
How is acrocyanosis treated?
Therapy directly depends on the reasons why the patient’s skin color has changed. If during the examination a disease was discovered that causes blue skin, then first of all it is necessary to treat it.
If the cause is a heart defect, the patient is sent for surgery, after which the cyanosis often goes away without specific therapy.
Oxygen therapy, which is also used in the treatment of respiratory and heart failure, helps reduce the manifestations of cyanosis. For newborns, gas therapy in an oxygen tent is best; for adults, it is advisable to use an oxygen cylinder, pillow or mask.
A good adjuvant treatment method is oxygen-enriched cocktails. They are sold in pharmacies, available to adults and children, and are often prescribed by doctors to prevent oxygen starvation of the body.
Acrocyanosis in adolescents can be cured with physical therapy and a balanced diet. Especially often, a bluish tint to the skin is observed in boys and girls with reduced body weight, and in this case, a nutritionist prescribes a course of maintenance vitamin therapy and creates an individual diet so that the growing body receives the right amount of proteins, fats, carbohydrates and minerals.
Therapeutic massage and physiotherapy help restore impaired peripheral circulation. Sometimes a contrast shower can be useful, as it “trains” the blood vessels and prevents their spasms.
All of these methods are suitable for the treatment of cyanosis in cases where it is not a sign of serious pathologies. But when the skin turns blue not for physiological, but for medical reasons, it is advisable to prescribe medications:
- bronchodilators (“Berodual”, “Salbutamol”) - to dilate the bronchi and relieve spasm
- antihypoxants (“Actovegin”) - to activate metabolism in tissues and prevent oxygen starvation
- respiratory analeptics (“Cititon”), stimulating the respiratory and vasomotor centers of the brain
- anticoagulants (“Warfarin”), which prevent blood clotting and the formation of blood clots
Important! Even if the patient is firmly convinced that it is acrocyanosis, and its cause does not relate to severe pathologies, self-prescription of drugs is unacceptable! Only a doctor can select drug therapy after a comprehensive examination of the patient.
Acrocyanosis is not dangerous to health, but bluish skin should not be ignored so as not to miss the development of serious diseases.
See also other skin diseases here.
Source: https://boleznikozha.ru/bolezn-akrotsianoz/akrotsianoz
Treatment of sepsis in newborns
The patient is hospitalized in a separate room in a specialized department of a children's hospital. Breastfeed the baby or use freshly expressed breast milk. The number of feedings is increased by 1-2. In severe cases, feed through a tube (in the absence of a sucking reflex) or from a bottle. You can feed your baby pasteurized human milk. In the absence of donor milk, it is advisable to feed with sour formulas with the addition of 10 mg of lysozyme to each portion of the mixture, which reduces the manifestations of dysbacteriosis.
Organization of optimal care: the participation of the mother in nursing the patient is mandatory, maintaining a positive emotional state, prevention of cross-infection, prevention of cooling - use of an incubator, systematic thorough toileting of the newborn, regular ventilation and quartzing of wards and boxes.
Drug treatment: antibiotics, detoxification therapy, infusion of solutions, plasmapheresis, hemosorption, xenoperfusion of blood through the pig’s spleen, replacement blood transfusion, for staphylococcal sepsis - antistaphylococcal plasma, antistaphylococcal immunoglobulin.
For sepsis caused by gram-negative flora, gamma-M concentrate is injected intramuscularly, and antipseudomonal or antiprotean, anti-clebsiella plasma is transfused. In case of sepsis occurring against the background of a viral infection, the administration of specific immunoglobulins (anti-influenza, anti-herpetic, anti-cytomegalic, etc.) has a positive effect, fresh frozen plasma is transfused, plasmapheresis, and hemosorption are performed.
New methods in the treatment of sepsis: transfusion of granulocyte mass (no later than 6 hours after preparation), fibronectin.
Local treatment of purulent foci of infection is carried out jointly by a pediatrician and a pediatric surgeon - opening abscesses, pseudofuruncles, osteomyelitis. For lung pathologies, aerosols with antibiotics are used, for endobronchitis - washing with antiseptic solutions, etc. Physiotherapy is carried out: first, microwave or UHF on the purulent focus, and then electrophoresis of antibiotics is carried out. Symptomatic therapy: intravenous administration of contrical or trasylol, vitamins C, Be, E, KKB, B2 according to other indications - B12, PP, treatment of DIC syndrome.
Prescribe drugs necessary to maintain a normal microbial biocenosis - internally lactobacterin, bacteriophages - Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Coliproteus, staphylococcal, pyophage. An antistaphylococcal bacteriophage for intravenous administration has been developed.
During the recovery and convalescence period, nonspecific immune stimulants are prescribed: sodium nucleinate, pentrxyl, dibazol, metacil, apilac, iron supplements. Massage, gymnastics, physiotherapy, and walks are especially important.
After being discharged from the hospital, the child is monitored at the clinic for 3 years. Observed by a pediatrician, neurologist, immunologist and other specialists according to indications. Professional vaccinations are carried out no earlier than six months after recovery. For six months, the child is prescribed nootropic drugs (Phenibut, Pantogam, Aminalon, Encephabol, Nootropil - in courses of 1-1.5 months. Preventive treatment of anemia, rickets, hardening, massage, gymnastics is carried out.
Mortality in sepsis, depending on the etiology, ranges from 20% to 80%; mortality is especially high in cases of fulminant sepsis, as well as in sepsis caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and anaerobic bacteria.
Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia is a blood disease in which there is a significant decrease in the level of platelets in the plasma, which leads to insufficient clotting. This disease is not only dangerous to health, but can also be fatal if extensive bleeding occurs as a result of injuries.
The main manifestations of thrombocytopenia are:
- the occurrence of bruises and bruises under the skin;
- regular nosebleeds;
- the appearance of a rash on various areas of the skin;
- Duration of the coagulation process even with small cuts.
Other signs of blood disease are expressed by the appearance of blood impurities in urine, feces, bleeding gums, and esophagus. Women suffering from thrombocytopenia experience greater blood loss during menstruation, which can eventually develop into anemia.
Symptoms
The main signs of asphyxia in newborns are breathing disorders, which subsequently lead to disruption of the functions of the cardiovascular system, reflexes and muscle tone.
To assess the severity of asphyxia in newborns, the Apgar method (scale) is used. It is based on a score of the following criteria:
- heel reflex (reflex excitability);
- breath;
- heartbeat;
- muscle tone;
- skin coloring.
Assessment of the newborn's condition using the Apgar scale:
| Parameter | Score in points | ||
| 1 | 2 | ||
| Heart rate, beats/min | Absent | Less than 100 | More than 100 |
| Breath | Absent | Bradypnea, irregular | Normal, loud scream |
| Skin coloring | Generalized pallor or generalized cyanosis | Pink coloration of the body and bluish coloration of the limbs (acrocyanosis) | Pink coloring of the whole body and limbs |
| Muscle tone | Absent | Slight degree of limb flexion | Active movements |
| Reflex excitability (reaction to suction of mucus from the upper respiratory tract, irritation of the soles) | Absent | Grimace | Cough |
With a mild degree of asphyxia, the condition of newborns on the Apgar scale is assessed at 6–7 points, moderate severity – 4–5 points, severe – 1–3 points. In case of clinical death of a newborn, the Apgar score is 0 points.
Mild asphyxia of a newborn is characterized by:
- first breath in the first minute of life;
- decreased muscle tone;
- cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle;
- weakened breathing.
With moderate asphyxia of newborns, the following are observed:
- weakened breathing;
- bradycardia;
- faint cry;
- acrocyanosis;
- decreased muscle tone;
- pulsation of the umbilical cord vessels.
Severe asphyxia of newborns is manifested by the following symptoms:
- lack of screaming;
- apnea or irregular breathing;
- severe bradycardia;
- muscle atony;
- pale skin;
- areflexia;
- development of adrenal insufficiency;
- absence of pulsation of the umbilical cord vessels.
Against the background of asphyxia, posthypoxic syndrome may develop in newborns in the first day of life, which is characterized by signs of damage to the central nervous system (disorders of liquorodynamics, cerebrovascular accidents).
Causes of acrocyanosis
The main reasons for the development of acrocyanosis:
- The most common cause is chronic heart failure. Due to the incomplete functioning of the heart, small-caliber vessels are not properly filled with blood.
- Acrocyanosis manifests itself most clearly in patients with heart valve defects. Since these defects prevent proper cardiac functioning, as in the previous case, the tissues are not adequately supplied with blood.
- Pathology can develop due to intoxication with toxic substances or medications. In this situation, the bluishness of the skin is caused by the synthesis of methemoglobin, a pathological compound, in the tissues.
- Prolonged cold exposure to the skin can also cause blueness due to the development of spasms of small blood vessels. In addition, frequent exposure to negative temperatures often leads to the development of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- In adult patients, acrocyanosis may be caused by the influence of any irritants, leading to vascular spasms.
- Restructuring of the endocrine system in adolescence often causes blood flow disturbances, which is manifested in children of the transitional age period by the appearance of idiopathic acrocyanosis.
- Malfunctions in the functioning of the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the innervation of blood vessels.
Types of cyanosis
Based on the characteristic signs of manifestation and localization, cyanosis is divided into several types.
| Type of cyanosis | Reasons, how it manifests itself |
| Diffuse | In case of impaired blood circulation and pathological processes in the respiratory system, it is localized throughout the body |
| Peripheral | Poor functioning of the heart muscle causes ischemic manifestations of the limbs and convex parts of the face |
| Local | Appears in certain organs with poor blood circulation |
| Acrocyanosis | When venous circulation stagnates, blue discoloration of the ears, lips, and fingers is observed. Thrombophlebitis - a type of acrocyanosis |
Cordial
May be triggered by prolonged exposure to a stuffy room.
Heart failure causes an increased level of reduced hemoglobin in the blood and gives it a dark color with a hint of blue. The blood passing through the lungs does not receive enough oxygen and thickens and darkens. The contractile function of the myocardium deteriorates, which causes a slowdown in blood flow with a simultaneous increase in the amount of blood.
Capillaries, with the slow flow of the bloodstream, absorb more and more oxygen, which leads to oxygen starvation of other tissues. Hypoxia disrupts the acid balance of the blood and causes acidosis.
Respiratory
If the functioning of the bronchopulmonary system is disrupted, oxygen does not enter the lungs in the required volume, its movement along the respiratory channel is slow, this causes hypoxia.
In asthma, a local type of cyanosis appears, lips, cheeks, and ears turn blue.
In the initial stage it is easy to eliminate - it is unstable, increases with nervous excitement, and decreases in a calm state.
Respiratory is the only type of cyanosis that disappears within a few minutes after oxygen therapy.
Cerebral
It occurs when the blood is unable to combine hemoglobin with oxygen. In this case, brain cells receive blood with a small amount of oxygen, which leads to the development of ischemia of the cellular structure of the brain. Against this background, dementia, epilepsy, cerebral hemorrhages, eye diseases, and even loss of vision develop.
Hematological
Occurs with pathological blood diseases. The pathology can be congenital and transmitted at the genetic level or develops against the background of:
- anemia:
- carbon monoxide poisoning, carbon monoxide poisoning and other sources of fumes;
- water balance disturbances.
Metabolic
Occurs with a lack of calcium salts in the plasma and with hyperphosphatemia.
With tissue hypoxia, metabolic cyanosis develops, in which body tissues are not capable of absorbing oxygen. It appears in a combination of peripheral and cardiac cyanosis.
This is a mixed form of the disease and, when prescribing treatment, both types are taken into account.
Diseases that cause acrocyanosis
Permanent or temporary blue discoloration of the skin can be caused by a number of diseases.
And even in the absence of chronic diseases, a person sometimes develops an acute form of cyanosis, which occurs suddenly, with rapidly increasing bluishness of the skin. This condition requires emergency care and hospitalization to find out the causes of poor health.
Chronic acrocyanosis and cyanosis can continue for a long time, while the bluish color of the skin changes from faint to clearly noticeable.
List of diseases in which this condition may develop:
- bronchial asthma;
- acute bronchitis or pneumonia;
- pulmonary embolism (PE);
- pulmonary tuberculosis;
- lung cancer;
- pulmonary infarction;
- Congenital heart defect;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- anxiety and depressive disorders;
- inflammatory diseases of arteries and veins;
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease;
- scleroderma;
- chronic cardiac or respiratory failure.
Also, cyanosis of the hands and face occurs when poisoned by poisons and certain medications , under the influence of which hemoglobin derivatives accumulate in the blood and are unable to transport oxygen to the body’s tissues.
The blood becomes thicker and darker, peripheral circulation is disrupted, causing the fingers and nasolabial triangle to turn blue.
Manifestations in children and adults
Acrocyanosis occurs quite often in newborns. But there is no need to panic. This phenomenon cannot leave parents indifferent. Illness does not always mean an unfavorable state of health. The problem often occurs in premature babies.
Reasons for the problem.
- Heart failure.
- Hypothermia.
- Severe restlessness, expressed by screaming and crying.
- In adolescents it occurs at puberty.
Modern diagnostic methods make it possible to identify the problem in a timely manner. Therefore, if a child’s arms, legs, nose, ears or lips turn blue, you must first make sure that the baby is warm.
If there is strong crying, this phenomenon is considered normal and there is no need to be alarmed. Acrocyanosis of the lips appears in infants most often due to chills. If you turn blue for no apparent reason, you should immediately contact a pediatrician or neonatologist.
Acrocyanosis is a symptom of serious heart or artery problems in adults. The ethology is as follows.
- Chronic heart failure.
- Poisoning with drugs or poisons.
- Arteriovenous shunt.
- Cold allergy.
Cardihemodynamics of the right side of the heart is disrupted, which is why the skin turns blue. People with heart defects often face similar problems.
Arterial-venous shunt is a congenital defect between the left and right ventricles of the heart. The causes of acrocyanosis most often lie in cardiac dysfunction.
In heart failure, blood supply and circulation are impaired. That is why acrocyanosis of the hands appears first of all.
Main symptoms of the disease
The disease is expressed in blue skin. But it all depends on the general condition of the skin. Most often the disease manifests itself on:
- lips;
- nasolabial triangle;
- limbs.
At the same time, patients note strong changes in their condition. If blueness is accompanied by one of the following symptoms, then you should immediately contact a cardiologist and therapist.
Specialists will prescribe an examination, based on the results of which they will select the appropriate treatment. Additional symptoms indicating serious health problems:
- nail color changes;
- heavy sweating;
- vascular spasms.
A special, important signal is that if there is increased sweating in the blue areas, then this is a sign of acute heart failure. You need to see a doctor urgently. If venous blood flow is impaired, then the limbs may also turn blue.
Vascular spasms are an extremely dangerous phenomenon, and acrocyanosis of the limbs is not uncommon. Any symptom is a sign that a person is sick and there are serious disorders in the body. Therefore, the first thing to do is visit a doctor.
Self-diagnosing and prescribing treatment for yourself is not only impossible, but also dangerous. For example, an adult’s hands turned blue. He immediately starts taking heart medications. And the reason lies not in the disease at all, but in a typical cold allergy. As a result, the person causes serious harm to himself.
Particular attention should be paid to the general condition. If pressure drops are observed when turning blue, this has an extremely negative effect on the condition of the blood vessels.
With frequent “attacks,” a stroke is possible. Facial acrocyanosis is the first sign that it is necessary to urgently check the blood vessels.
Manifestations of diseases such as cyanosis should never be ignored. When a person is susceptible to heart failure or vascular problems, he always risks not just his health, but his life.
Diagnosis and treatment methods
Acrocyanosis of the hands, feet, and face is an alarming sign. To understand why it arose, you need to undergo a comprehensive examination. Only when considering the clinical picture will the reason be clear.
To diagnose the problem:
- the person is sent for ECG and ultrasound monitoring;
- give a referral for a blood test.
Based on the examination results, doctors draw conclusions and prescribe treatment.
When the underlying disease is identified, the patient is prescribed special medications to help combat it.
The main drugs that the specialist prescribes are general strengthening and tonic. Vasodilator therapy is necessary. Sometimes antispasmodics and external treatment are prescribed. The medicines given in the table below help fight illnesses that arise from problems with blood vessels.
Treatment
Therapy for such diseases is aimed at eliminating the underlying cause:
- surgical operations are performed if congenital or acquired heart defects are detected;
- prescribe the use of medications for blood pressure;
- use drugs to maintain heart function;
- they use medications to strengthen blood vessels - they will help prevent their expansion.
You can use camphor oil to rub the affected areas. To relieve arteriole spasms, you can use decoctions of medicinal herbs, but before using home treatments, you should consult a doctor.
Diagnostics
Recognizing acrocyanosis is not difficult, since this condition is not a disease, but serves only as an external symptom of some pathological process; the presence of acrocyanosis is judged by external signs:
- cyanosis of hands and feet;
- painlessness;
- sweating
Often not only the fingers are affected, but even the wrists, forearms, shins, tip of the nose, and ears.
When the legs are raised to the same level as the thighs, the bluish coloration of the skin disappears. Also, the skin acquires a more normal color when the limb is warmed.
Differential diagnosis is carried out mainly with Raynaud's syndrome. A cold test is used for this. After cooling and then warming the limb with Raynaud's syndrome, the skin acquires its original color, and with acrocyanosis it remains slightly bluish.
Secondary acrocyanosis often affects the fingers asymmetrically and may be associated with pain and tissue loss. Scientists have not yet determined whether this condition is part of the so-called blue thumb syndrome, which develops when atheromatous occlusion of small vessels due to oral anticoagulant therapy with warfarin, as well as when atherosclerotic plaques are injured during vascular catheterization.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with diseases that cause diffuse cyanosis. These are severe respiratory and heart failure, B12 deficiency anemia or erythromelalgia. If you have heart or lung diseases, there are corresponding symptoms. B12 deficiency anemia is accompanied by itching and painful skin.
To confirm acrocyanosis, electrothermometry is used on different areas of the skin, as well as plethysmography - the study of the speed of blood flow through tissue.
To exclude diseases of peripheral arteries (for example, atherosclerosis) and veins (varicose veins), Doppler ultrasound is prescribed. Capillaroscopy is also used - studying the structure of the capillaries of the nail bed, lips, tongue, and conjunctiva.
With acrocyanosis, during capillaroscopy, a significant increase in the diameter of the vessel is determined - up to 40 µm when the norm is up to 8 µm. Additionally, the arterial and venous ends of the capillary tube expand. However, these signs are nonspecific, so acrocyanosis continues to be considered a functional disorder with morphological changes that are only similar to some specific diseases.
If secondary acrocyanosis is suspected, the doctor may prescribe a variety of tests to identify the underlying disease - blood tests, ultrasound of internal organs, ECG, EchoCG and others.
There are no standards for the treatment of acrocyanosis. This condition in itself is not harmful to health. Often, when cyanosis appears, you just need to warm your limbs. The main direction of treatment is to avoid the effects of cold on the extremities.
For acrocyanosis causing a cosmetic defect, the following can be used:
- adrenergic blockers (Vegetrox);
- electrophoresis with nicotinic acid;
- intravenous infusions of prostaglandin E1;
- UV irradiation of the skin of the extremities;
- creams with glucocorticoids and other active substances (Akriderm, Beloderm and others);
- solutions and sprays with minoxidil (Alerana, Revasil and others);
- immunosuppressive drugs for rheumatological diseases (rituximab and others)
Secondary acrocyanosis requires treatment of the underlying disease.
Regardless of the cause of acrocyanosis, if it causes skin ulcers, they should be treated and covered with a sterile dressing.
Among the surgical methods of treatment for primary and secondary acrocyanosis, sympathectomy is used - removal of the nerve nodes responsible for regulating vascular tone in a particular area. For the consequences of spinal cord injuries, the procedure of neuromuscular stimulation has a good effect.
In newborns, acrocyanosis is a normal condition and resolves spontaneously. The primary option is a rare benign condition that is not dangerous to health. The prognosis for secondary acrocyanosis can be very serious and depends on the underlying disease. Therefore, if symptoms of this condition appear, you should consult a doctor.
Acrocyanosis increases the risk of skin infection and tissue ulceration. This is due to both poor blood supply to the extremities and damage to blood vessels when they rapidly expand while warming the hands or feet. Therefore, it is necessary to improve microcirculation when cyanosis appears gradually, avoiding overheating of the skin.
Causes of acrocyanosis
The primary variant is caused by narrowing of small blood vessels, resulting in a decrease in the flow of oxygen-rich arterial blood to the tissues. Small venous vessels begin to determine the color of the skin. The blood in them is darker because it contains a combination of hemoglobin and carbon dioxide. Therefore, outwardly it looks like cyanosis and “marbling” of the skin.
The main causes of primary acrocyanosis:
- low ambient temperature;
- staying at high altitude combined with low atmospheric pressure, wind and cold air;
- genetically determined defect in the development of blood vessels;
- low weight person;
- thick clothes and shoes.
Acrocyanosis in newborns occurs because the child begins to breathe on his own. In this case, arterial blood enriched with oxygen in the lungs is first sent to vital organs - the brain, kidneys, etc., and only later - to the skin.
Secondary acrocyanosis is a symptom of some disease.
- The most common cause of acrocyanosis is Raynaud's phenomenon. With this pathology, the limbs turn pale under the influence of cold, then acquire a bluish or purple color.
- In anorexia, weight loss disrupts thermoregulation processes, which leads to vascular disorders. Acrocyanosis is observed in 20-40% of patients with anorexia.
- Acrocyanosis can be caused by ergot-based medications used to treat migraines.
- Up to 24% of people with cancer also have this symptom.
Secondary acrocyanosis develops in the following conditions:
| Hypoxemia | |
| Stroke | |
| Myocardial infarction | |
| Buerger's disease | |
| Lung diseases | Pulmonary hypertension |
| Thromboembolism of the branches of the pulmonary artery | |
| Alveolar proteinosis | |
| Arteriovenous malformations | |
| Vascular atherosclerosis | |
| Connective tissue diseases | Wegener's granulomatosis |
| Overlap syndrome | |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | |
| lupus erythematosus | |
| Eating disorders | Anorexia nervosa |
| Constant fasting | |
| Tumors | |
| Blood diseases | Lymphoproliferative |
| Myeloproliferative | |
| Cold agglutinins | |
| Cryofibrinogenemia | |
| Antiphospholipid syndrome | |
| Side effects of medications | Tricyclic antidepressants |
| Interferons | |
| Vasopressors (dopamine) | |
| Sirolimus (after kidney transplant) | |
| Clonidine | |
| Amphotericin B | |
| Benzocaine | |
| Bleomycin | |
| Intravenous immunoglobulin | |
| Toxins | Arsenic |
| Blasticidin S | |
| Hereditary diseases | Ethylmalonic aciduria |
| Cytochrome C oxidase deficiency | |
| Mitochondrial diseases (oxidative phosphorylation disorder) | |
| Spondylochondrodysplasia | |
| Palmoplantar keratoderma | |
| Fucosidosis | |
| Down syndrome | |
| Prader-Willi syndrome | |
| Sneddon syndrome | |
| Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome | |
| Marfan disease | |
| Riley-Day syndrome | |
| Ehlers-Danlos syndrome | |
| Mental illness | Bipolar disorder |
| Asperger's syndrome | |
| Orthostatic intolerance and postural tachycardia syndrome | |
| Spinal cord injuries | |
| Ozena | |
| Chronic hypertrophic and atrophic rhinitis | |
| Atopic dermatitis | |
| Infections | HIV infection |
| Psittacosis | |
| Chikungunya infection | |
| Mononucleosis | |
| Hepatitis C |
What is retinopathy
One of the most common diseases of prematurely born children is retinopathy of prematurity, a pathology associated with impaired retinal development. The third trimester of pregnancy is extremely important for the proper formation of this organ, and it finally matures only by the fourth month of the baby’s life.
The formation of retinal blood vessels begins at 16 weeks of pregnancy and ends at 36–40 weeks.
The retina is the inner light-sensitive surface of the eye, and human vision depends on its proper formation
If a child is born prematurely, there is a high risk that the retina of his eyes will be underdeveloped, that is, it will lack the necessary vessels. However, retinopathy does not occur immediately: for about a month after birth, the body will try to recover. However, the vessels formed by it may be too fragile, and rupture of their walls leads to hemorrhages and retinal detachment.
Prevention
Simple prevention methods can protect you from this disorder. You should avoid too much hypothermia and avoid working in cold conditions. When going outside in frosty weather, it is necessary to provide adequate care for your hands, namely, warm gloves. General strengthening of the immune system is also a means of preventing acrocyanosis and includes an active lifestyle and long walks - this will help avoid frequent vasospasm.
All these methods will help if the cause of acrocyanosis is not heart pathology. In this case, only proper treatment can ensure an improvement in the patient’s condition.
Acrocyanosis is a compound name derived from the ancient Greek ακρόν, which means limb, and the ancient Greek κυανός, which means dark blue. In ordinary language, acrocyanosis refers to a change in the bluish color of areas of the body that are far from the heart.
The change in color is associated with problems with the blood supply to small capillaries that deliver blood to distant areas: fingers and toes, tip of the nose, lips, ears. The most likely cause of this disorder is heart failure in the chronic stage. Although some heart defects can also be accompanied by acrocyanosis.
It is worth noting that the color can vary from slight cyanosis to pronounced dark blue. The severity of the color is associated with the degree of disruption of the blood supply to the capillaries. Thus, based on external signs (degree of coloring), a primary assumption can be made about the degree of heart failure.
What is acrocyanosis
This term refers to a condition in which there is a blue discoloration of the skin. Pathology develops when the blood supply to small vessels is disrupted. Acrocyanosis in children and adults is most pronounced in areas remote from the heart muscle.
Fingers turning blue - this can be either a symptom of freezing or a sign of a serious pathology
The degree of change in skin color varies, from bluish to dark blue. This depends on the severity of the vascular damage. Accordingly, mild, moderate and pronounced acrocyanosis are distinguished.
Forms of the disease
Various reasons can provoke the development of acrocyanosis. Taking this fact into account, several types of pathology are distinguished:
- Anesthetic. This form develops due to the effect of negative temperatures on the skin. Moderate anesthetic acrocyanosis is not considered dangerous, since it is a physiological reaction of the body to low temperature.
When exposed to low temperatures, the body takes all measures to preserve precious heat, vasospasm occurs
- Idiopathic or essential. It is provoked by a spasm of small arteries and is manifested by cyanosis of the lips, hands, ears, tip of the nose, etc. This form is typical for teenage girls during puberty. Can be observed even in a warm room at rest.
Hormonal changes affect the entire body, and therefore can lead to impaired blood circulation in small vessels
- Central acrocyanosis manifests itself as a result of a decrease in oxygen concentration in the pulmonary circulation. This can happen if the amount of reduced hemoglobin increases.
Not only heart defects, but also serious lung pathologies can cause the development of acrocyanosis
- Diffuse acrocyanosis occurs when hemodynamics are impaired in the right side of the heart.
- Spasmodic cyanosis occurs when small blood vessels spasm in response to various stimuli. For example, mild acrocyanosis is often observed in adolescents with neurotic problems.
Causes of acrocyanosis
Many factors can provoke the development of such a pathology, but the main reasons are:
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system. If the heart does not work at full strength, then it cannot provide satisfactory blood supply to small capillaries.
- The presence of heart disease is often manifested by acrocyanosis of the lips and nail plates.
If your lips and nail plates turn blue, then first of all it is necessary to exclude cardiac pathologies
- Poisoning with certain types of toxic substances or medications can cause cyanosis.
- Hypothermia of the body.
- Exposure to external stimuli that provoke vasospasm.
- Hormonal changes can cause peripheral circulation problems.
- Thromboembolism of the pulmonary arteries often provokes diffuse acrocyanosis. This disease, like others, requires serious therapy.
- Venous diseases.
Varicose veins develop due to poor circulation in the vessels of the legs; Naturally, the color of the skin will change
Manifestations of acrocyanosis
Acrocyanosis can be recognized by the following characteristic manifestations:
- The skin of the feet and hands becomes bluish at low temperatures.
- Moderate acrocyanosis is a blue discoloration of the lips, ears, and tip of the nose.
- The intensity of the blue color increases in the cold; when moving to a warm room, the blue color disappears.
- There is slight swelling of the fingers and toes.
- In the presence of cardiac pathologies, cyanosis is also accompanied by increased sweating.
- The skin, even at normal temperature, is always cold.
- If the cause of the disease is lung pathology, the skin becomes ash-gray in color.
When visiting a doctor, it is imperative to inform the specialist under what conditions cyanosis appears, whether it is permanent, and what factors aggravate it. This will make it easier for the doctor to recognize the cause of the pathology and prescribe therapy.
Cyanosis of the hands
Depending on what causes the blue tint to the skin, there are six forms of acrocyanosis:
- Central. Appears as a result of congenital or acquired heart defects and vascular diseases.
- Diffuse. One of the symptoms of impaired functioning of the right ventricle.
- Anesthetic. Occurs from cold. Sometimes it indicates illness, but is also typical for healthy people.
- Spasmodic. Appears due to spasm of small vessels.
- Toxic. Occurs when the body is poisoned with toxic substances.
- Idiopathic (no known cause). Does not indicate disease.
Causes of central acrocyanosis
The central form develops due to an increase in the level of reduced hemoglobin (which is not combined with oxygen) in the venous blood, as well as stagnation of venous blood and insufficient oxygen saturation of the blood in the pulmonary circle.
The reasons for this may be:
- Congenital “blue” heart defects: stenosis (narrowing) or atresia (fusion) of the tricuspid valve, tetralogy of Fallot (a combination of atrial septal defect, enlargement of the right ventricle, narrowing of the pulmonary trunk and abnormal location of the aorta), confluence of the vena cava into the left atrium, transposition of the great vessels .
- Ventricular septal defect.
- Pulmonary stenosis.
- Heart failure (it can be caused by hypertension, atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries, acquired heart defects).
- Pulmonary embolism.
- Chronic severe diseases of the bronchi and lungs, in which breathing is impaired.
Causes of central acrocyanosis
Causes of diffuse
The diffuse form appears when the functioning of the right ventricle is impaired.
Causes of anesthetic
The anesthetic variety occurs as a reaction of the body to cold (when the skin temperature drops to 15–20 degrees). This occurs in healthy people during normal heat exchange. In this case, a slight bluish discoloration of the skin appears.
A pronounced dark blue tint at the slightest frost can be observed when:
- infectious mononucleosis;
- hepatitis;
- liver cirrhosis;
- leukemia.
This is explained by the fact that in these diseases cold agglutinins are formed - substances that, when the temperature drops, “glue” red blood cells together, which impedes blood circulation.
Causes of spasmodic
The spasmodic form is a specific reaction of the body of people with astheno-neurotic syndrome. In response to any stimulus, such individuals experience a spasm of small vessels. This phenomenon is most often observed in adolescents.
Causes of toxic
The toxic type of the disease develops when poisoned by substances that lead to the formation of methemoglobin or sulfagemoglobin in the blood.
Causes of idiopathic
The causes of idiopathic acrocyanosis are not fully understood. It is known that a blue tint to the skin appears due to spasm of arterioles (small arteries) and dilation of venules (small veins). However, the person is absolutely healthy. The idiopathic form is often characteristic of teenage girls. This feature is often associated with hormonal changes or characteristics of the nervous system.
Idiopathic acrocyanosis can also occur in newborns. Premature babies are especially prone to this. This is due to the fact that the lungs and cardiovascular system have not yet adapted to life outside the mother’s body. This bluishness of the skin usually goes away within a few days or weeks.
Acrocyanosis of any type intensifies when exposed to low temperatures, as well as during physical activity.
Characteristic symptoms
The disease can manifest itself either as a slight bluish tint to the skin and mucous membranes, or as a pronounced dark color. It depends on the following factors:
- Severity of the disease - with “blue” congenital defects and severe heart failure, the symptoms are most pronounced.
- Thickness of the skin - the thicker it is, the less pronounced this symptom is.
- Skin pigmentation – in people with dark skin, bluish discoloration is more difficult to detect and may only be noticeable on the lips and nail beds.
- The number of small blood vessels in the skin. This is an individual feature. The more of them, the more pronounced acrocyanosis.
The color depends on the type of disease: with heart defects and heart failure, the skin acquires a dark blue-violet-red hue, and with lung diseases - ash-blue-gray.
Additional symptoms of acrocyanosis caused by heart disease include increased sweating of the extremities and swelling of the affected areas.
Treatment of acrocyanosis
Treatment should be aimed at eliminating the underlying disease. For acrocyanosis of cardiac origin, no specific therapy for this symptom is carried out. Eliminate the cause that caused acrocyanosis.
Congenital and acquired heart defects require surgical correction. Sometimes medicinal treatment of heart failure is carried out using drugs that lower blood pressure and improve myocardial performance.
If cyanosis is not associated with diseases, then it does not require treatment. If desired, with idiopathic acrocyanosis, you can use agents to strengthen blood vessels to avoid pathological expansion of venules. Such agents include ascorbic acid, rutin, potassium and magnesium preparations. Before taking them, consult your physician.
Also, to reduce the severity of idiopathic acrocyanosis, use contrast baths for hands and feet, contrast washing, and rubbing the affected areas with camphor oil.
To relieve arteriole spasm, you can take a course of one of these natural remedies:
- St. John's wort;
- immortelle;
- chamomile;
- Birch buds.
Herbs to relieve spasm of arterioles
Consume the plants as a decoction or tea.
Before using them, consult a therapist and carefully read the instructions if you purchase herbs at a pharmacy.
Causes of acrocyanosis
Depending on the nature of its occurrence, there are several specific types of acrocyanosis: essential (mostly observed in girls during active puberty) and anesthetic (its occurrence is facilitated by the direct influence of a cold irritant on the skin).
Source: https://yazdorov.win/potlivost/tsianoz-kistej-ruk.html
Acrocyanosis - treatment
In order to cure acrocyanosis, you should first of all know what caused its appearance. If the exact pathogenesis has not been identified, the doctor prescribes general therapy, which includes:
- Drug treatment;
- Undergoing physiotherapeutic procedures.
Drug treatment
When acrocyanosis is detected, medications that improve blood flow are first prescribed. Most often doctors prescribe
the following medicines:
- Pentoxifylline;
- Vinpocetine;
- Vazonite.
Since pathology often develops due to vascular spasms, antispasmodic drugs are also prescribed:
- Noshpa;
- Drotaverine;
- Papaverine.
In addition, the doctor must prescribe medications that strengthen the walls of blood vessels and help increase their tone:
- Vitamin B complex;
- Calcium preparations.
For reference. Acrocyanosis is also treated topically. To do this, use local warming agents - camphor oil or alcohol. These medications are used as a rub to stimulate normal blood flow in the affected areas.
Physiotherapeutic methods
The best effect from the treatment of acrocyanosis will be obtained if complex therapy is used. Physiotherapeutic procedures remarkably improve peripheral circulation.
The following procedures are usually prescribed:
- Massage;
- Ultrasonic exposure;
- Ultraviolet irradiation;
- The use of therapeutic mud;
- Applications with paraffin;
- If the arms and legs are affected, contrast baths are used.
Prevention of acrocyanosis
There are several medical recommendations to avoid the development of the disease in question:
- Avoid hypothermia;
- If acrocyanosis bothers you quite often and is associated with environmental exposure, you should think about changing your location or job;
- During winter, you need to choose your clothes wisely: wear a hat, warm gloves, and also purchase high-quality shoes that prevent hypothermia;
- Carry out general strengthening measures: take vitamin complexes, do exercises and hardening, spend more time in the fresh air, etc.;
- Getting rid of bad habits and following the rules of rational nutrition.
Attention. The listed preventive measures will allow you to avoid the development of acrocyanosis only if it is not associated with pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
Acrocyanosis - symptoms, causes, treatment
Acrocyanosis is when a person’s distal parts of the body (hands, feet, lips, tip of the nose) have a bluish coloration. The main reason for skin discoloration is a slowdown in blood flow, resulting in insufficient blood supply to small capillaries.
Acrocyanosis is often observed in girls during adolescence, in this case, the disease is most often caused by spasm of small arteries.
Reasons for the development of the disease
Acrocyanosis is caused by various reasons. Most often, this disease is associated with chronic heart failure. This disease is especially pronounced in people with heart defects.
In addition, acrocyanosis can be a consequence of poisoning with drugs or poisons.
In adolescence, acrocyanosis is often triggered by spasms of the peripheral vessels that supply blood to the distal parts of the body.
The cause of spasms or narrowing of the vascular passages is often an inadequate response of the sympathetic nerves.
If spasms of the walls of blood vessels occur on an ongoing basis, then in the long term the blood supply to the hands and feet decreases. As a rule, vessels that are located close to the surface of the skin are affected.
Symptoms of the disease
The severity of the symptoms of acrocyanosis depends on the condition of the blood vessels and the general condition of the skin. As a rule, acrocyanosis manifests itself most on the lips (the lips become bluish, but the tongue retains its natural color), on the skin of the feet and hands, and sometimes a change in the color of the nails is also observed. Sometimes acrocyanosis occurs on the skin of the ears, chin or tip of the nose.
In patients with acrocyanosis, the skin on the affected areas is always cold. Increased sweating of skin areas affected by acrocyanosis occurs if the disease is caused by heart failure.
Similar symptoms are observed with Raynaud's syndrome, with polycythemia, with cold agglutination of erythrocytes (this is a disease as a result of which red blood cells stick together in the subcutaneous vessels and capillaries under the influence of low temperatures).
Acrocyanosis can manifest itself locally, with disturbances in the outflow of venous blood. That is, this disease is one of the local symptoms indicating the presence of varicose veins.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of acrocyanosis is made based on observation of the clinical picture. The patient constantly has cyanotic and wet hands and feet and, at the same time, there is no pain syndrome at all.
To make a correct diagnosis, a simple cold test is often performed: when the hands of a patient with acrocyanosis are cooled, the skin color becomes even more bluish. When your hands are warmed, your skin takes on a more natural tone. The same test is also performed to diagnose cold urticaria and skin leiomyoma.
In addition, patients with acrocyanosis should be referred for examination to identify or exclude diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Treatment methods
If, during examination, an underlying disease was identified in a patient with acrocyanosis, which caused a slowdown in blood flow, then measures must be taken to cure it.
Acrocyanosis itself, as a rule, is not treated. The patient may be prescribed restoratives and vitamins.
As a rule, a good effect in this disease is obtained by using:
- Ascorbic acid and B vitamins;
- Calcium preparations;
- Fish oil.
Sometimes patients with acrocyanosis are prescribed vasodilators, this may be:
- Papaverine;
- A nicotinic acid;
- No-shpa, etc.
External treatment, in particular rubbing with camphor ointment, gives a good effect in the treatment of this disease. Patients with acrocyanosis benefit from contrasting (cold and hot) hand (or foot) baths.
Physiotherapeutic procedures may be beneficial for acrocyanosis. Patients may be prescribed:
- Ultrasound treatment;
- Massage;
- Diathermy,
- Ural Federal District;
- Inductotherapy;
- Paraffin, mud or ozokerite applications.
Treatment with traditional methods
Acrocyanosis can be treated using traditional medicine methods. There are many recipes that help improve the condition of a patient with acrocyanosis.
Taking honey infusion will help strengthen blood vessels and relieve spasms. To prepare this delicious medicine for acrocyanosis, you need to take two glasses of natural honey, a glass of dry dill seeds, two tablespoons of dry valerian root, ground in a coffee grinder.
All this is placed in a thermos and filled with two liters of boiling water. The product must be infused for 24 hours. After this, the infusion is filtered and, after cooling, placed in the refrigerator. For acrocyanosis, take a quarter glass before each meal.
You can prepare an infusion of herbs that relieves vasospasm, which will be useful for acrocyanosis. To do this, you need to take one hundred grams of the following medicinal plants (dry): St. John's wort, chamomile flowers, immortelle herb, birch buds. Mix the herbs and pour into an opaque container. Every day, take a full spoon of the mixture and brew with half a liter of boiling water.
After infusion for twenty minutes, strain the infusion and divide into two portions. Take the first one in the evening before bed, adding a little honey to the infusion. After taking the infusion, do not drink or eat anything else. Take the second portion in the morning, after warming it up a little and adding honey. For acrocyanosis, take the infusion until the prepared mixture of dry herbs runs out.
Pumpkin seeds for the treatment of acrocyanosis. This medicine is universal, it is suitable for both internal and external use. One hundred grams of dried pumpkin seeds need to be crushed, then pour half a liter of high-quality vodka into the raw material.
Leave in the dark, shaking regularly, for 21 days. After infusion is complete, strain the infusion. Take orally three times a day for three weeks. To make it easier to take the infusion, it can be diluted with water.
In addition, for acrocyanosis, it can be used to rub the arms or legs. For your information, pumpkin is a very healthy product and is very often used in folk medicine.
For example, pumpkin juice is used for lotions and compresses in the treatment of allergic dermatitis to shoes, Hyde nodular pruritus, oral candidiasis and other diseases.
For acrocyanosis, it is very useful to make local baths using medicinal herbs. For example, a good effect of a calendula bath. For preparation, you can use dry herbs or a ready-made pharmacy tincture. You need to prepare two bowls or basins, pour hot water into one, and cold water into the other.
Add a tincture to the water (a spoon per liter of water) or a decoction prepared from dry raw materials (a glass per liter of water). Alternately immerse your hands (or feet) in hot and cold water. Keep your hands in hot water for 2 minutes, in cold water for 30 seconds. Make 5-6 such alternations.
For acrocyanosis, such baths should be done every day until improvement.
Prevention and prognosis
Prevention of acrocyanosis consists of hardening and restorative procedures. Possible physical activity and walks in the fresh air are very useful. It is very important to protect areas of the skin susceptible to acrocyanosis from hypothermia; it is necessary to wear warm gloves, socks, and shoes according to the season.
If acrocyanosis is caused by an underlying disease, then to eliminate the symptoms it is necessary to treat this disease. Acrocyanosis can also cause other diseases, for example, vascular pathologies, so it is very important to start treatment on time.
Acrocyanosis is a persistent and difficult to treat disease. Acrocyanosis is not prone to progression, that is, even in the absence of treatment, deterioration of the condition is not observed.
Source: https://dermalatlas.ru/bolezni-soedinitelnoj-tkani/sinyushnyj-cvet-kozhi-akrocianoz/