Ocular pressure, or increased ophthalmotonus, is a process of heaviness, “expansion”, under the influence of which the eye shell appears. The internal contents of the eye - the vitreous body and fluid - affect the sclera and cornea. As a result of this influence, compression of blood vessels and optic nerve fibers occurs. Failure to see a doctor in a timely manner often leads to their atrophic state and the subsequent formation of glaucoma or cataracts. The process of vision loss as a consequence of constantly high eye pressure inevitably leads to complete blindness. Only treatment in the initial stages can eliminate the progressive atrophic process affecting the optic nerves.
Elderly people are more likely to experience eye pressure; the number of people suffering from increased ophthalmotonus is almost a quarter of the world's population.
Eye pressure may also be low, which is also considered a pathology. In this case, painful and itchy sensations occur, constantly irritated mucous membranes and signs of deteriorating vision are observed.
Causes of eye pressure
The duration of disorders occurring inside the eye is characterized by three types of high blood pressure:
- Transient (one-time increase for a short period with subsequent normalization of the condition).
- Labile (temporary increase with a return to normal).
- Stable (always high eye pressure, at which various complications develop).
In the first case, the causes of transient pressure are eye fatigue and hypertensive crisis. Long-term work at a computer forces the arterial, capillary and venous systems of the eyeball to be under constant “pressure” of tension and work in an enhanced mode with additional accompaniment of intracranial pressure.
The causes of pathological conditions during “bloating” can be provoked by certain diseases:
- hypertension;
- hypotension;
- diabetes mellitus;
- colds;
- respiratory viral;
- migraine;
- glaucoma;
- cataracts;
- inflammation of the eyes of various origins, including “dry eyes” from prolonged and regular work at the computer.
Another cause of one-time manifestations of intraocular pressure can be nervous disorders and stress. This happens because eye pressure is controlled by the nervous system and a number of hormones. Functional failures lead to increased intraocular pressure.
Pathologies of the kidneys and vascular system, which can provoke fluid retention in the body, also lead to eye diseases.
Patients with Graves' disease (another name for "diffuse toxic goiter") have all the risks of "getting" increased ophthalmotonus. The same problem can be caused by other endocrine diseases: Itsenko-Cushing syndrome (as a result of a significant content of adrenal hormones in the bloodstream) and hypothyroidism (for example, in women with an unusual menopause).
It is important to know! The chemicals used and some medications, as a result of their overdose, can cause increased intraocular pressure.
The manifestation of secondary increased ophthalmotonus is caused by various pathological processes in the eyes that occur as an occurrence:
- neoplasms that compress the structural components of the eye and prevent the outflow of fluid from it;
- iritis, iridocyclitis, uveitis - inflammatory diseases that can both reduce eye pressure and increase it;
- inflammatory processes after eye injury, which are characterized by swelling, congestion of blood vessels, stagnation of blood and fluid.
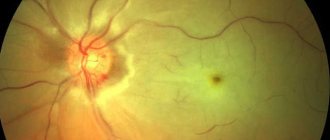
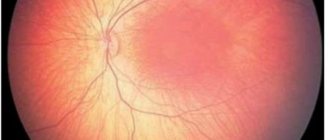
The above pathologies cause an increase in pressure inside the eyes periodically: for that time period while any pathological process is occurring. The big risk is that if pathological processes are allowed to continue uncontrolled for many years, transformation into glaucoma occurs. It is this that causes a persistent increase in pressure in the eyes.
In medical practice, there are cases where glaucoma appeared not only in older and older people, but also in newborns, called “hydrophthalmos” or “buphthalmos” (“dropsy of the eye”).
It is important to know! This disease is characterized by a crisis – a sudden deterioration in the patient’s condition. During this period, intraocular pressure increases significantly on any one side.
Prevention
The main recommendation regarding the prevention of the disease will be systematic clinical observation. In addition, everyone should ensure that they do not experience increased eye fatigue. First of all, this is relevant for those who work a lot at the computer. In order to maintain normal visual acuity and IOP level, do eye exercises for at least one hour a day. Mirzakarim Norbekov’s technique has proven itself very well, which is aimed not only at developing a visual analyzer, but also allows you to use VNI.
You definitely need to reconsider your diet. Add to your food as many plant-based foods as possible, enriched with vitamins and minerals, and exclude foods with high cholesterol. Carrots, blueberries, sea fish, and watermelon should dominate in the diet of a patient with increased IOP.
Physical therapy and massage are important elements in the prevention of glaucoma, but they should only be performed under the supervision of a physician.
[adsp-pro-1] [adsp-pro-2]
Hypertension
Symptoms of increased intraocular pressure
Increased or decreased pressure inside the eyes can be determined outside of a hospital setting by lightly pressing the eyeball through the eyelid with a fingertip (palpation-indicative method). A feeling of hardness indicates increased ophthalmotonus, softness indicates decreased ophthalmotonus.
Let's look at the main symptoms of intraocular pressure:
- In general, the most important sign of concern should be recurring or constant pain present in both eyes or temples. The pain may be one-sided.
- Eye pressure that differs from normal results in constant eye fatigue (even in the morning after waking up). This especially affects people who work daily and overtime in offices at computers. They develop “computer vision syndrome,” which is associated with both eye fatigue and intraocular pressure.
- “Red” eyes, noticeably deteriorated visual function, cloudiness and discomfort when performing any visual activity - all these are also the “first bells” signaling an unfavorable eye condition.
- In practice, cases have been recorded when the symptoms of the disease do not manifest themselves in an acute course, but together with other pathologies. For example, endocrine diseases or hypertension provoke destruction of the vascular system of the retina and cornea. The patient feels a “bloating” or heaviness inside the eyeballs. Vision problems are often observed.
- The course of diabetes mellitus can disrupt the integrity of small capillaries. Their fragility leads to rapid destruction even with the slightest external influence. 90% of diabetics have intraocular pressure and are at risk of going completely blind any day.
- Arterial hypertension , which predisposes to the manifestation of symptoms of increased ophthalmotonus, should be carefully treated, since it is the “provocateur” of eye pathology. When the crisis ends, the symptoms are either not determined or partially observed. Ophthalmologists call this disease “ophthalmic hypertension” and monitor their patients.
- Glaucoma and cataracts are of particular attention and concern to medical professionals . Patients rapidly lose their vision until their ability to see is completely limited. The symptoms of these diseases often “let us down” in the sense that the patient cannot feel the signs of slight “bloating” and therefore is in no hurry to visit the doctor. This only happens when the patient begins to observe signs of double images of objects or the appearance of “blind spots”.
Comment from a doctor. According to ophthalmologist Elena Moikina, there are 1,250 thousand patients with glaucoma in Russia. Only timely detection of pathology and treatment can stop optic nerve atrophy. Therefore, it is important to undergo regular medical examinations, especially for those who suffer from diabetes and hypertension.
| Risk of nerve damage from eye pressure |
Measuring intraocular pressure in adults
In medical institutions, doctors use proven techniques with which they get the right results. These include tonometry according to Maklakov and Goldman. These are effective methods that have been used for many years.
| Measuring intraocular pressure: | Description of the procedure |
| according to Maklakov | The essence of the procedure is that a weight moistened with paint is placed on the eye. After this, an imprint is made on the paper and special measurements are taken. The higher the IOP, the less paint is washed off from the plates. This is explained by the fact that the cornea is flattened quite a bit under the weight of the weights. Therefore, contact with the surface of the convex part of the eye is minimal. |
| according to Goldman | In modern ophthalmology, a non-contact Goldmann tonometer is more often used to measure indicators. With this type of pressure level determination, the norm is approximately 11-13 mm Hg. The Goldmann tonometer releases a certain volume of air at a given pressure. Using a special sensor, the device reads the tension of the cornea, which changes shape under the influence of air flow. After this, the level of intraocular pressure is calculated. The design of the Goldmann tonometer is complex, so you cannot use this device yourself. |
How is intraocular pressure measured without the help of instruments?
Of course, this technique allows you to assess the condition of the eye very roughly, but still doctors advise every person to master it. The eyeball is felt through closed eyelids with one finger. In order to evaluate the result, you need to apply slight pressure. Normally, your finger should feel an elastic ball that is slightly pressed.
IOP measurement result:
- If the eye is hard as a stone and does not deform at all when pressed, then there is a high probability that intraocular pressure is increased.
- If it is completely impossible to feel the spherical shape, and the finger easily “falls” inside the eye, then this indicates a strong decrease in intraocular pressure.
According to medical recommendations, every person should visit an ophthalmologist at least once a year. If discomfort occurs in the eyes or the quality of vision deteriorates, it is necessary to make an unscheduled visit to the ophthalmologist's office. Many serious illnesses can be prevented if the cause of changes in blood pressure is diagnosed in a timely manner and appropriate treatment is started.
Symptoms of eye pressure in children
Children, just like adults, experience increased or decreased pressure in the eyeball. They become sluggish and tired in the evening, complain of headaches, feel uncomfortable, experience symptoms of heaviness in the eyes and anxiety.
At the first complaints, the child should be shown to a doctor to measure intraocular pressure, which most often foretells not an eye disease, but thyroid dysfunction. Young patients need timely treatment, although eye pressure itself in this case does not pose a danger.
Betaxolol
Russian drops that have a very affordable price - a 5 ml bottle can be bought for about 140 rubles. The composition is based on the substance of the same name, betaxolol. Instill one drop twice a day.
Contraindications to the use of Betaxolol:
- bradycardia,
- diabetes,
- thyroid diseases,
- Raynaud's syndrome.
Drops can cause an allergic reaction, eye discomfort, conjunctivitis, irritation, redness of the eyes, photophobia, insomnia and even depression!
It is important to remember that this article is for informational purposes only! The presented drugs can be used in medical therapy only as prescribed by a doctor!
Ocular pressure measurement
Increased ophthalmotonus is determined in two ways:
- Pneumotonometry (exposure to an air jet of a certain power from a special apparatus on the eyeball) is the most common method in modern medicine. Normal pressure is considered to be in the range of 10-21 millimeters of mercury. The allowed limit is 23-26 mmHg.
- Tonometry (by introducing anesthetic substances, after which objects of a given load are placed on the surface of the eyes). The so-called Maklakov method shows more accurate results, but due to the need to use anesthetics and the likelihood of eye infection through the use of weights, this method is currently practically not used. This method determines the norm of eye pressure within the range of 15-26 mmHg.
- Electrotonography (taking into account the increased production of fluid inside the eye and the accelerated outflow of this fluid).
Expert advice
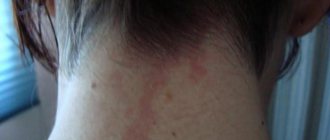
It's no secret that the best treatment is prevention. But what conditions must be observed in order to quickly relieve pressure inside the eyes and continue to maintain it at normal levels? • Use high pillows when sleeping. • Do not skimp on lighting in the evening. • Avoid outfits with tight collars (ties). Clothes that are too tight around the neck block the flow of blood from the head veins. • Avoid sudden downward bends when performing household work. • Perform massage in the collar area, as well as perform eye exercises. • Refuse to watch films in the cinema. • Protect yourself from stress.
Follow these rules regularly, do not forget to carry out vision diagnostics, and you will forget about what eye pressure is, symptoms and treatment at home. Health to you!
Treatment of intraocular pressure
Therapeutic measures depend on the diagnosis and are aimed at eliminating the causes of the patient’s complaints. An ophthalmologist most often prescribes eye drops designed to reduce intraocular pressure for glaucoma, antibacterial for inflammation, and vitamin-moisturizing drops for dry eyes in combination with eye exercises.
Drug treatment involves therapy of intraocular pressure using the following solutions:
- Prostaglandins (“Tafluprosta”, “Xalatana”, “Travatana”, etc.) increase the outflow of fluid inside the eyeballs. The effective effect is noticeable 1-2 hours after instillation.
- Cholinomimetics (“Carbocholine”, “Pilokartina”, etc.), contract the eye muscles and constrict the pupils, which helps increase the amount of fluid outflow.
- Beta blockers (Betoptika-s, Okumeda, Okumola, Timolol, etc.), designed to reduce the fluid produced inside the eyeballs. Effectiveness appears within 30 minutes after instillation.
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (Trusopta, Azopta, etc.), designed to reduce the amount of intraocular fluid.
As systemic therapy for acute glaucoma attacks, when intraocular pressure rises to 70 mm Hg, acetazolamide and glycerol are prescribed orally (by swallowing drugs). Injection treatment is also provided by intramuscular or intravenous methods for the administration of mannitol, urea, furosemide, and a lytic mixture.
To stop the attack and prevent a recurrence, laser iridectomy is performed on both eyes. If it is impossible to stop the attack within 12-24 hours, surgical intervention is necessary.
Drops to reduce eye pressure in all their variety are available in pharmacy chains. Their action is based on the possibility of increasing the outflow of excess fluid from the eyeballs and effectively nourishing the tissues of the entire visual apparatus.
It is clear that for each individual patient an individual approach is used, taking into account the side effects of drugs, the complexity and course of the disease, age and resistance to allergens. Treatment with medications can only be prescribed by a doctor.
The use of physiotherapeutic procedures is also indicated as prescribed by a specialist. Their use helps preserve visual functions in cases of glaucoma; they are influenced by color pulse therapy, phonophoresis, vacuum massage and infrasound. The portable eye device “Sidorenko Glasses” is widely used, which can be successfully used at home, including for children from the age of three.
Treatment options
The problem can be solved by taking a number of medications.
Elevated levels of eye pressure quite often have a secondary basis. Their occurrence is caused by other diseases: injuries, tumors. Methods for stabilizing intraocular pressure are as follows:
- drug treatment;
- ethnoscience;
- physiotherapy.
Drugs
All medications for the treatment of glaucoma must be prescribed by a doctor, as they can cause side effects and develop unwanted symptoms. He also selects individual treatment for eye pressure and monitors its progress. List of prescribed medications that can help with glaucoma:
- Beta blockers. They help reduce the synthesis of fluids inside the eye. They are often prescribed with another medicine - prostaglandin. Available in the form of drops. If you have diabetes or lung diseases, they can cause unpleasant consequences. Prominent representatives are “Timolol” and “Cumol”.
- Cholinomimetics. Medicines that constrict the pupil and thereby promote the outflow of excess fluid from the fundus of the eye. Pilocarpine drops are popular.
- Prostaglandins. Promote the outflow of intraocular fluid. Drugs that cause a rapid decrease: Travatan, Xalatan, Taflotan.
- Inhibitors. Serve as an obstacle to the production of eye fluid. Side effects include redness and burning in the eyes, a bitter taste in the mouth. Representatives: Azopt, Trusopt.
- Combined means. They help reduce production levels and increase fluid outflow. An example is “Proxofelin”.
- Diuretic tablets to stabilize high blood pressure are used only as part of complex therapy.
Folk remedies
Honey with water can be used for local procedures.
To cure and completely get rid of the problem, only alternative medicine is not enough. Treatment with folk remedies is suitable only for prevention or part of complex therapy. Bee products and medicinal herbs are considered more effective. Recipe examples:
- For a compress, you need to dissolve a spoonful of honey in boiled water, moisten a bandage or cotton wool and apply it to your eyes.
- First aid to relieve blood pressure is dill tincture. Dry the plant seeds and grind them. Add 1 tablespoon of dill to 500 ml of boiling water and leave until cool. Drink 10 minutes before meals.
- A compress before going to bed based on seeds placed in boiling water and left to cool completely.
- Eyebright grass. Make a decoction based on this plant, soak bandages or cotton pads in it. Apply throughout the day.
- Grind 2 potato tubers to a puree, add 1 teaspoon of vinegar and leave for half an hour. Place this mixture on a bandage and apply to your eyes.
- Eating fresh blueberries, compotes, and tinctures from them will help.
- Carrots help a lot. Grated fresh with a little addition of apples or sugar. Drink concentrated fresh juice from it.
Exercises
To prevent the disease, you need to regularly do simple exercises to relax the eyes, which can be combined with any type of treatment to remove high blood pressure. To do this you need:
It is useful to draw different geometric shapes with the eyeballs, with the eyelids lowered.
- Close your eyes and in this state draw circles, rectangles, squares, diagonals for about a minute, and then open them, take a break for up to 2 minutes and repeat the exercises 3 times.
- Look out the window at an object that is closer, then into the distance. Repeat 5 times.
- Stretch your arms in front of you and begin to move your fingers, slowly moving them towards you, monitoring the process all the time. Repeat 2-3 times.
After any exercise, you need to blink quickly to normalize your blood pressure. You can do this with both eyes at the same time or alternately, first close your left eye with your palm and blink your right eye, and then vice versa. And also perform another simple procedure to relax the eye muscles, lower pressure and improve blood flow. To do this, you need to rub your palms until they are completely warm, and then close your eyes with your hands and, relaxing, spend up to 3 minutes in this position. Then, after a short break, it is recommended to repeat the gymnastics.
Treatment with traditional medicine
Traditional medicine takes its rightful place in the treatment of intraocular pressure. Herbal decoctions, lotions, compresses and infusions have a positive effect on the eyes.
For example, a decoction that uses nettle, knotweed, birch leaves, St. John's wort and lingonberry, horsetail, string, plantain, rose hips. Equal parts of the ingredients are mixed with the addition of a small handful of rose hips and two teaspoons of St. John's wort. 2 tbsp. spoons of the mixture are placed in a thermos, 700 g of boiling water is poured in and infused for 10 hours. Cool, strain and drink throughout the day in small doses.
A houseplant, aloe vera (agagave), will help normalize eye pressure. To prepare the solution, take not very large leaves of the flower (two), crush them, put them in a glass container and pour boiling water over them. Next, the mixture is simmered over low heat for seven minutes. The broth is cooled, filtered and used to wash the eyes (3-4 times a day) for 10-12 days with a two-week break and the resumption of further courses in two approaches.
An equally valuable medicinal plant found at home is the golden mustache. You will need one teaspoon each of mustache leaves and lily of the valley petals, 100 g of dry nettle leaves to prepare a healing collection. Add three tablespoons of hot water to the mixture, stir, close the lid and place in a place protected from light for 8 hours. Next, the mixture is used as a lotion on the eyes, applying them for 10 minutes once every 24 hours. Repeat the procedure until the increased ophthalmotonus decreases.
There are a great variety of traditional medicines for treating eyes. A specialist herbalist or ophthalmologist will help you understand them and apply them correctly. Numerous information resources will also be of great help. When using herbal medicine, you only need to take into account your own tendency to allergies.
Prevention of intraocular pressure
To prevent the disease, you should follow simple rules:
- stop excessive smoking and drinking alcohol, as well as salt;
- Use a balanced diet, avoid cholesterol-containing foods;
- do physical education;
- provide yourself with adequate rest;
- walk in the fresh air more often;
- avoid stressful situations;
- replace tea and coffee with fruit drinks, juices and herbal drinks;
- perform a light massage near the eyeballs and special gymnastics for the eyes;
- control the time spent at the computer or near the TV, in the process of reading, knitting, beading, embroidery and other activities that require eye strain.
Eye pressure is a very important indicator, indicating the absence or presence of diseases or vision dysfunction. Therefore, it is important to undergo regular medical examination (1-2 times a year), medical examination according to age categories and follow the above preventive rules. Only careful attitude towards your own health will prevent the occurrence of various pathologies associated with the eyes.
Eye pressure and its norms
The mechanism for the formation of intraocular pressure is ensured by the difference in the rate of increase and decrease of moisture in the chambers of the eye. If the first is ensured by the produced secretion of moisture by numerous processes of the ciliary body, then the second is regulated by resistance in the outflow system - this means the trabecular meshwork in the corner of the anterior chamber.
Today, the only absolutely accurate and correct method for determining intraocular pressure (the so-called true) is manometric.
To measure, a pressure gauge needle is inserted into the anterior chamber through the cornea, making direct measurements. It is clear that due to its technical complexity, this method is not applicable in clinical practice.
Chronic glaucoma patients, as well as all those who suffer from cataracts, should always monitor the IOP level at home, and thanks to transparberal measurement, which is carried out using a safe, non-contact tonometer.
A sure way to temporarily get rid of elevated IOP and reduce it in the shortest possible time is to instill pilocarpine - 2-3 drops (no more is needed - this will lead to an excessive decrease, you should not allow this indicator to fluctuate sharply). Only if you remove the increase in this indicator can you relieve an attack of intraocular hypertension.
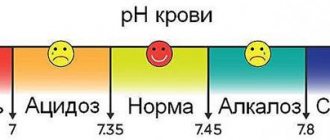
A wide variety of devices and instruments come to the rescue, through which it is possible to implement an indirect method for determining IOP. In this case, the desired pressure value will be shown by the method of measuring the eye's response to the force applied to it. Thus, an experienced doctor can give a rough estimate of the level of intraocular pressure without instruments - it is best to use the old and proven technique of palpation examination, which involves determining IOP by the resistance of the eyeball when pressing on it with fingers. The normal range for this value varies from 12-22 mmHg. Intraocular pressure exceeding 22 mm Hg. considered above normal.
It is imperative to examine the fundus of the eye using an ophthalmoscope - this will allow timely identification of developing degenerative disorders that will look like pigment spots. In healthy people, this examination should be carried out at least 1 time a year, and in elderly people - at least 2 times.
In situations where the IOP is higher than normal, but the person has no other clinically significant symptoms of glaucoma, the condition is simply called ocular hypertension. If the intraocular pressure is less than 8 mmHg, then this condition is usually called ocular hypotension.
The amount of eye pressure may vary slightly depending on the age and certain physical characteristics of the patient. But in most cases, the norm for an adult is considered to be an indicator that varies in the range from 22 to 23 mm Hg. Art.
Important!
An increase in intraocular pressure in young people, especially in adolescence, is a reason to urgently send them for a comprehensive examination, since this kind of disorder is not age-related.