Pregnancy0
- 1 Leukocytes - what are they?
- 2 Norm of leukocytes during pregnancy
- 3 Why do leukocytes appear?
- 4 Prevention
- 5 Treatment
Hello, dear expectant mothers!
Every woman expecting a child often worries, especially if she has elevated white blood cells. But we know that stress can negatively affect the condition of the pregnant woman and the fetus. Therefore, in the article we will discuss whether you should worry if you have leukocytes in your blood and what the norm is for the trimesters of pregnancy.
White blood cell count during pregnancy
In an adult, the number of leukocytes in the blood is 5 x 109/l.
In pregnant women, the level of leukocytes can reach 15.0 x 109/l, since many leukocytes accumulate in the submucosa of the uterus. A large accumulation of white blood cells is called leukocytosis during pregnancy. It is not considered a disease. In addition, leukocytosis prevents the penetration of an infectious disease to the fetus and stimulates the contractile functions of the uterus.
The number of white blood cells in the blood may change throughout the day, but there is no need to worry about this fluctuation. The causes of leukocytosis may be:
- eating;
- emotional overload;
- taking a cold or hot bath;
- faulty nutrition;
- the course of pregnancy itself;
- engaging in difficult physical work, etc.
This type of leukocytosis is called physiological. To ensure that the blood test result is as close as possible to the actual one, blood is donated in the morning, in a calm state and on an empty stomach.
Leukopenia in children: causes, symptoms, treatment, drugs, diet, folk remedies, photos, videos
Leukopenia is a decrease in the content of leukocytes in the peripheral blood of children below 4500 per 1 μl, or 2000 less than the age norm. This phenomenon is observed with a decrease in the formation or rapid destruction of leukocytes. Basically, leukopenia in children is a symptom of pathological processes. It is one of a number of unstudied hematological diseases.
Drugs
Restoring the normal ratio of leukocytes is carried out using medications:
- Leukocyte mass (intravenous drip method);
- Glucocorticoids (only for immune leukopenia);
- Medicines that improve metabolism in the body (Leukogana, Pentoxyl, Methyluracil);
- Drugs for detoxification;
- Medicinal substances that enhance bone marrow functions (Lenograstin, Filgrastin).
The lack of positive dynamics in the treatment of autoimmune leukocytopenia suggests removal of the spleen (splenectomy).
Diet
A balanced and rational diet plays an important role in the formation of blood cells. The treatment menu offers substances necessary for the construction of hemoglobin, the maturation of blood cells, and the stroma of formed elements.
Children suffering from leukopenia need easily digestible proteins, polyunsaturated fatty acids, vitamins, and dietary fiber.
The following products must be included in the diet of a small patient:
- Turkey meat, poultry;
- Sea fish;
- Assorted cereal products;
- Canned cod liver;
- Legumes;
- Nuts (walnuts, hazelnuts);
- Fresh fruits, vegetables, herbs, berries;
- Dairy products.
You should not use:
- Beef;
- Pork;
- Liver;
- Kidneys.
In case of disturbances in the digestive tract, intravenous nutrition is provided.
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine can be used as an addition to complex treatment. The following folk recipes increase immunity:
- Rose hip decoction. Raw materials in the amount of 50 g, pour boiling water and infuse. It's better to cook in a thermos. Used as a tea drink.
- Aloe. The mixture of honey and crushed leaves is kept for some time. Add 200 g of water to the composition. Directions for use: 1 teaspoon every day.
- Mumiyo is used in accordance with the attached instructions.
- Wormwood decoction. A tablespoon of the plant is poured with 50 g of boiling water and left to stand. Take a teaspoon in the morning and evening before bedtime.
Before using the products, you should consult your pediatrician.
Prevention
Preventive measures are aimed at eliminating those factors that provoke leukopenia.
- To avoid drug-induced neutropenia, doses of medications taken should be reduced to avoid severe forms of the disease.
- To improve the immune status, introduce more proteins, fresh vegetables, fruits, and herbs into the children's menu. At the same time, limit carbohydrates.
- To form the rules of a healthy lifestyle in children. Accustom to compliance with hygiene rules and feasible physical activity.
- Monitor blood counts regularly. Treat diseases in a timely manner.
Patients who have undergone treatment are monitored at the dispensary, with periodic blood leukogram monitoring.
Source: https://LechenieDetej.ru/onkologiya/lejkopeniya.html
Causes of increased leukocytes during pregnancy
The main causes of increased leukocytes in the blood include infectious diseases of the respiratory tract: bronchitis , pneumonia . These diseases are accompanied by fever and cough. It can also be a serious disease, which is characterized by inflammation of the membranes of the brain or spinal cord - meningitis. Otitis media will not pass by either. It is characterized not only by an increase in white blood cells, but also by ear pain and hearing loss. In this case, pus is released from the ear.
Acute bacterial infections include: cholecystitis, appendicitis, pyelonephritis . In this case, as a rule, the temperature rises due to an increase in neutrophils. The cause of a very high level of leukocytes in the blood (up to 50x109/l) can be purulent infections such as:
- peritonitis;
- abscesses;
- sepsis.
In addition, severe inflammatory bowel disease, hepatitis, arthritis and rubella can also cause elevated white blood cell levels. Also, the number of leukocytes increases if there was any damage received during injuries and after the surgical period. Poisoning, allergies, and even long-term use of medications can lead to deviations from the normal level of leukocytes in the blood.
If an increased level of leukocytes in the blood of a pregnant woman is detected, it is necessary to immediately consult your doctor. Immediate contact with a doctor will help to make a timely diagnosis and begin treatment of the disease. This will allow mother and baby to avoid the threat and risk that occurs due to an increase in the level of leukocytes in the blood during pregnancy. Self-medication is strictly not recommended. This can lead to irreparable consequences.
Leukopenia in children: causes, symptoms and treatment of agranulocytosis at different ages
Leukopenia (neutropenia) in children is a decrease in circulating leukocytes in the blood below 4500 per 1 μl, or 2000 less than the age norm. Leukocytes are reduced due to inhibition of their formation or rapid destruction. A decrease in the number of leukocytes below 1500 per μl is called agranulocytosis - this is an extreme manifestation of leukopenia.
Classification of leukopenias
By origin, leukopenia in children is primary (congenital) and secondary (acquired).
Primary (aka hereditary):
- Kostman's hereditary neutropenia is a decrease in neutrophils below 300 in 1 μl with a compensatory increase in other cells of the leukocyte series, which provide a normal total leukocyte count.
- Gensler's syndrome - benign neutropenia with a long cyclical course, characteristic neutrophilic crises (short-term drop in leukocyte levels);
- Chediak-Higashi syndrome - neutropenia develops due to a decrease in the lifespan of neutrophils. Children with this syndrome also have albinism (lack of corneal pigmentation).
Secondary – provoked by the influence of various factors:
- physical (ionizing radiation);
- chemical (medicines – barbiturates, cytostatics, immunosuppressants, sulfonamides);
- biological (exogenous and endogenous factors). Exogenous biological factors include: bacteria, viruses, parasites, protozoa. Endogenous biological factors - hormonal disorders, inflammatory processes.
Causes of leukopenia in children:
Infectious origin:
- sepsis;
- herpes virus types 6 and 7;
- typhus and paratyphoid.
Non-infectious origin:
- ionizing radiation;
- acute leukemia;
- systemic connective tissue diseases;
- anaphylactic shock;
- plasmacytoma;
- Addison-Brimer disease;
- hypersplenism (enlarged spleen);
- tumor metastases to the bone marrow;
- drug-induced leukopenia.
Pathogenetic mechanisms of leukopenia
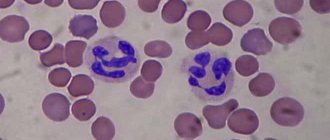
Leukocytes: classification
- Impaired formation of leukocytes. The leukocyte lineage is very sensitive to various pathological influences, therefore there are many factors that cause inhibition of the formation of leukocytes. The differentiation of leukocytes is affected by disorders of the mechanism of humoral regulation as a result of hypothyroidism (decreased levels of thyroid hormones), hypocortisolism (adrenal insufficiency), deficiency conditions (hypovitaminosis of B vitamins, folic acid, insufficiency of amino acids for the synthesis of leukocyte components). Tumor processes in the bone marrow also have a negative effect on the differentiation of leukocytes. Ionizing radiation affects all germs of hematopoiesis.
- Increased destruction of leukocytes. This variant of leukopenia in children is extremely rare. The essence of the pathological process is the body's production of anti-leukocyte antibodies, which destroy leukocytes. Large doses of radiation can also cause destruction of white blood cells.
- Redistributive leukopenia. These are leukopenias that occur as a result of shock conditions, heavy muscular work, and the phenomenon of marginal standing of leukocytes. In this case, leukocytes do not completely disappear from the bloodstream, but temporarily leave it, being in the capillaries of the muscles, kidneys, and lungs.
- Increased loss of lymphocytes. Occurs with burns of large areas of the body, purulent processes, the presence of fistulas of the lymphatic vessels, lymphorrhea (violation of the integrity of the lymphatic vessels).
- Leukopenia as a result of hemodelution (blood dilution). This type of relative leukopenia is extremely rare and is the result of excessive fluid replacement therapy.
Symptoms of leukopenia in children depend on the form of the disease and the severity of the pathological process.
The main signs of the development of leukopenia are an increasing decrease in the child’s immunity.
This condition manifests itself through frequent infectious processes, such as pneumonia, stomatitis, gingivitis, periodontitis, pharyngitis, and pustular skin diseases.
The child is significantly behind his peers in development. Infectious diseases that a child suffers are severe and often cause complications.
The extreme degree of leukopenia in children is agranulocytosis. There are two types of this pathological condition: immune and myelotoxic.
Immune agranulocytosis in children most often occurs due to the toxic effects of medications. Develops acutely, several hours after taking myelotoxic drugs.
The onset of the disease is characterized by high body temperature and the rapid onset of concomitant infections (pharyngitis, gingivitis, fungal diseases of the oral cavity and nasopharynx). A typical symptom is necrotizing tonsillitis; areas of necrosis often bleed. It is possible to develop pneumonia, which is complicated by a lung abscess.
Leukopenia and absolute agranulocytosis are observed in the blood. The remaining blood cells remain within normal limits. The main and most dangerous complication of immune agranulocytosis is sepsis.
One of the reasons to prescribe additional tests for a child is a low level of immature granulocytes in a blood test: https://krasnayakrov.ru/analizy-krovi/nezrelyie-granulotsityi-v-analize-krovi-vazhnyiy.html
Myelotoxic agranulocytosis in children develops suddenly, for no apparent reason. The number of leukocytes, reticulocytes and platelets in the blood sharply decreases. This is characterized by the absence of any clinical manifestations.
The first signs of the disease are fever, necrotizing tonsillitis, stomatitis, and hemorrhagic syndrome.
Clinical manifestations of this form of acute agranulocytosis in children indicate the development of profound changes in the cellular composition of the blood and significant damage to the bone marrow.
It is important to note another type of leukopenia, this is post-infectious leukopenia. Leukopenia is most common in children after influenza. This is a short-term process and after the body is freed from the virus against the background of adequate treatment, blood counts return to normal on their own without any special correction.
Diagnosis of leukopenia
The first diagnostic indicator for leukopenia is a general blood test with a leukocyte formula.
Important indicators in a blood test are the absolute level of neutrophils, leukocyte formula and the number of red blood cells and platelets.
In children, the main indicator in a general blood test is the leukocyte formula, since it is important to determine the ratio of all formed elements. If this method is not enough, then spinal puncture is examined.
A blood test with a leukocyte formula is the primary method for diagnosing childhood leukopenia
Additional diagnostic methods may include a biochemical blood test and markers of viral hepatitis.
Laboratory indicators indicating leukopenia are as follows:
- a decrease in the level of leukocytes to 4.5 g/l (with a normal ratio of lymphocytes to them);
- neutropenia – a decrease in the level of granulocytes less than 1.5 g/l. The severity of the pathological process directly depends on the number of granulocytes.
- increase in lymphocytes in the blood;
It is worth noting that diagnosis in children directly depends on their age. It is worth paying special attention to children aged 6 months and 6 years, since during this period physiological changes in the ratio of granulocytes to lymphocytes occur, which can be mistakenly taken for pathology.
Treatment of leukopenia in children
Not every decrease in white blood cells requires therapeutic intervention. Treatment of leukopenia with impaired bone marrow function is mandatory. The volumes and methods of treatment directly depend on the severity of the pathological process.
Treatment measures for leukopenia include:
- patient isolation (children are placed in isolation wards);
- exclusion of cytostatics and ionizing radiation;
- constant sanitation of the skin and mucous membranes.
Drug treatment includes:
- the use of physiological stimulators of leukocyte formation;
- antibiotic therapy for bacterial complications (use broad-spectrum antibiotics);
- in case of intestinal damage, intravenous nutrition is used for patients;
- the use of corticosteroids is indicated for immune-based leukopenia.
After suffering from leukopenia, the child needs clinical observation, during which the level of leukocytes in the blood is monitored.
It is worth noting that in infants there is a phenomenon of transient leukopenia, when a decrease in the level of leukocytes does not cause pathological conditions and does not need correction. The occurrence of such leukopenia in a child of a different, older age group is a pathology and requires therapeutic intervention.
Prevention of leukopenia is carried out only if the cause of its occurrence is known.
- Anastasia
Source: https://krasnayakrov.ru/organizm-cheloveka/rebenok/lejkopeniya-u-rebyonka-bez-paniki.html
Diagnosis of leukocytosis in pregnant women
In their first weeks of pregnancy ( 8-9 ), young expectant mothers undergo medical diagnostics at the antenatal clinic. At this point, gynecologists take a smear from the vagina, followed by a series of other tests. During diagnosis, more women are found to have white blood cells. Typically, this is normal during pregnancy. But, if the number reaches 20, then this may indicate the presence of leukocytosis during pregnancy.
The cause of leukocytosis in pregnant women can be not only banal thrush, but also cystitis, vaginitis and even colpitis. The source of the disease is often a partner, hormonal disorders in the female body, or the weakened immune system of a pregnant woman.
How to lower white blood cells: basic therapy
There is no special treatment for leukocytosis, since this pathology is always secondary and develops against the background of the underlying disease, being a symptom of inflammatory processes in the body of the mother or fetus. The basis of treatment is a comprehensive diagnosis and identification of all hidden diseases, as well as their treatment. If the cause of leukocytosis is viral infections (ARVI, mononucleosis), antiviral drugs with an immunomodulatory effect are prescribed. Rectal suppositories “Genferon” and “Viferon” are considered the most gentle. They need to be used 2 times a day (morning and evening) for 5 days. If necessary, the doctor can extend the course of treatment to 7-10 days.
If there are signs of a cold, symptomatic therapy is also prescribed, including the following drugs, which is carried out according to the standard scheme given below.
Table. Treatment of respiratory infections in pregnant women (symptomatic).
| Group of drugs | What to take? |
| Saline solutions for rinsing the nose and removing mucus and dirt from the mucous membranes | "Afrin", "Aqualor", "Aquamaris", "Dolphin" |
| Vasoconstrictor drops to restore breathing and eliminate swelling | "Vibrocil", "Naphthyzin", "Nazivin" |
| Antiviral nasal agents | "Oxolinic nasal ointment", "Grippferon" |
| Aerosols and sprays with bactericidal and disinfectant effects for sore throats | "Inhalipt", "Tantum Verde", "Gexoral" |
| Medicines for fever and pain (at temperatures above 38°C) | "Paracetamol", "Cefekon", "Ibuprofen" |
At the antenatal clinic
If an ultrasound examination reveals signs of an inflammatory process in the organs of the genitourinary system, the woman may be prescribed antibiotics for the treatment of cystitis and pyelonephritis: Furagin, Nitroxoline, Monural.
"Monural"
A fairly effective complex drug of plant origin used to treat cystitis is Canephron. It has antispasmodic, diuretic, anti-inflammatory and disinfectant effects, and also has no contraindications other than individual intolerance.
"Canephron"
For bacterial infections of the respiratory system, systemic macrolide antibiotics or penicillin drugs (Augmentin, Zinnat, Amoxicillin, Hemomycin) can be used. Cephalosporins are usually not prescribed to pregnant women, as they have many contraindications and can cause severe side effects.
"Hemomycin"
If inflammation is caused by an intestinal infection, the treatment regimen includes:
- drugs with antibacterial action based on nifuroxazide (“Enterofuril”, “Stopdiar”);
- sorbents (“Neosmectin”, “Polysorb”);
- saline solutions for rehydration (“Regidron”);
- anti-vomiting drugs (Motilium, Cerucal injections).
Important! Under no circumstances should you self-prescribe treatment during pregnancy. Many medications are not suitable for use during pregnancy and can harm the development of the fetus, so any medications, as well as their dosage and duration of use, must be prescribed by your doctor.
Treatment of leukocytosis during pregnancy
How to treat a disease during pregnancy
When health workers detect a disease, they first of all try to get rid of the source itself, which is the instigator of letcocytosis. Gynecologists try to prescribe a gentler treatment so as not to harm the unborn baby and mother. In turn, a pregnant woman will have to fully comply with all medical recommendations, because as soon as this will give her the opportunity to completely get rid of the disease. There is no need to get carried away with self-medication, because this is exactly what can lead to the most unexpected consequences.
- There is bleeding from the ear: causes and first aid
- DISCUSSION OF RESULTS AND CONCLUSION
- Leukocytes in the blood are increased
- Blood test during pregnancy: normal
Leukocytes and blood cell levels
Leukocytes are white blood cells that play the role of monitor of the human immune system. How many white blood cells are contained in biological fluid primarily depends on numerous factors:
- stressful situations;
- improper diet;
- various diseases;
- constant physical activity.
If the test is performed during pregnancy, the test results may show a high white blood cell count. For reference, leukocytes in the blood during pregnancy must correspond to a certain norm, namely from 4 to 9 units before the 12th week, 10-12 units in the second and third trimesters . If the analysis showed an elevated leukocyte count, for example, 14-16-17, then the doctor must determine the reason for this indicator.
Pregnant women take the first test before 12 weeks. It should be noted that when taking an analysis for the level of leukocytes during the second trimester of pregnancy, at 16-17 weeks, an overestimated level can be considered the norm. Therefore, there is no need to lower this indicator, because it does not harm either the expectant mother or the child. Thus, by the end of pregnancy, the number of leukocytes increases to 12 x / l, and this is considered normal, but 14 units requires intervention, and the indicator needs to be lowered. To lower the level of white cells, the doctor prescribes medications. Folk remedies are also used to lower the level of leukocytes.
Prevention
If a person’s leukopenia is caused by genetic disorders or congenital (hereditary), then he should carefully follow the rules of prevention in order to prevent infectious complications:
- take medications that stimulate the synthesis of leukocytes in accordance with all instructions of the attending physician;
- in the presence of inflammatory, infectious (viral, bacterial, fungal) diseases, immediately consult a doctor and begin immediate treatment;
- observe sanitary and hygienic standards, use antiseptics and sanitizers to prevent infection of the body;
- eat well, eat foods rich in vitamins and minerals, and avoid nutrient deficiencies;
- use soft toothbrushes (to prevent damage to the gums), electric razors (to avoid cutting the skin);
- do not squeeze pimples or comb the skin;
- wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly with soap and scald with boiling water, meat and offal are subjected to full heat treatment;
- wear medical masks in public places.
The right regime is the basis of health
A properly designed regimen for pregnant women is not only a necessity for the treatment of leukocytosis, but also an excellent prevention of many diseases of the nervous, digestive, and vascular systems. High-quality sleep is of great importance: it should last at least 8 hours, and, if necessary, supplemented by daytime rest lasting 1-2 hours . Sleepwear should be as comfortable as possible (it is better to choose seamless ones from natural fabrics), like other bedding.
Sleep patterns during pregnancy
Pregnant women need to walk from 2 to 4 hours a day. It is better not to sit in one place, but to walk at a slow pace. This will keep the musculoskeletal system in good shape, reduce lower back pain and improve overall well-being. In addition, walking at any stage of pregnancy is an excellent workout for the heart and a way to get rid of emotional stress.
If your physical condition allows, you can go swimming, water aerobics or yoga for pregnant women. There are special groups for pregnant women in almost every sports center, so if there are no contraindications, you should not refuse adequate physical activity.
Yoga for pregnant women
Leukocytosis during pregnancy is not an independent disease, but a secondary pathology that develops mainly against the background of latent inflammatory processes in the body of the expectant mother. If the underlying disease is treated in time, leukocytosis does not pose a danger to the woman or fetus, but if the course is prolonged, the pathology can lead to disturbances during labor, as well as complications in the postpartum period.
Video - Leukocytosis during pregnancy
How does diet affect white blood cell levels?
There are certain food groups that can cause an increase in white cells in the blood. This usually occurs 3-4 hours after eating, and a gradual decrease begins on days 2-3. Most often, this picture is observed with abundant consumption of fermented milk products. Many women try to include a lot of milk-based products in their diet, as they contain essential minerals (phosphorus, calcium) and a lot of protein necessary for the growth and development of the child’s musculoskeletal system.
Dairy products may affect white blood cell levels
Fermented milk products, of course, are healthy, but they should be consumed in strict accordance with the recommended standards, which are (the amount of product indicated per day):
- milk – 2 glasses;
- kefir – 1 glass;
- cottage cheese – 100 g;
- raw material – a small piece (no more than 10 g);
- natural yogurt without additives – 200 g.
A temporary increase in white blood cells can also be caused by buckwheat, oat and barley cereals, raw carrots, grapes and some types of seafood. It is absolutely impossible to refuse these products, since their vitamin/mineral composition allows them to meet all the needs of the mother and child, but if leukocytosis is diagnosed, their consumption should be minimized.
Carrot
Causes of leukopenia
Infections
One of the most common causes of leukopenia is viral and generalized bacterial infections. The pathogenesis of a decrease in the level of leukocytes can be different - direct damage to cells by lymphotropic viruses (HIV, Varicella-Zoster, measles), suppression of formation in the bone marrow, increased loss with exudation.
- Viral infections.
Leukopenia develops mainly due to a decrease in the content of lymphocytes (lymphopenia). With infectious mononucleosis, influenza, and viral hepatitis, leukocytes decrease slightly and quickly return to normal after recovery. With HIV infection, the level of lymphocytes often reaches zero during the AIDS stage. Even after treatment, white blood cell counts may remain low, as HIV drugs themselves can cause leukopenia. - Bacterial infections.
Leukopenia occurs only in severe generalized infections (meningococcemia, rickettsial infections, peritonitis). A drop in the number of leukocytes is one of the criteria for diagnosing a septic condition and systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Neutropenia is mainly observed, its degree correlates with the severity of the disease. Regression occurs almost immediately after antibiotic therapy.
Taking medications
A wide range of drugs can lead to the development of leukopenia. There are two main mechanisms of drug-induced leukopenia: toxic damage to the bone marrow, leading to impaired hematopoiesis, and the formation of immune complexes, which results in the production of antibodies that attack the body’s own leukocytes.
Leukopenia occurs on average 15 days from the start of taking the medicine. The severity can vary from a slight decrease in the number of white blood cells to agranulocytosis. Due to the defeat of all 3 germs of hematopoiesis, a combination with anemia and thrombocytopenia (pancytopenia) is often found. In most cases, discontinuation of the drug is sufficient. If agranulocytosis develops, the use of colony-stimulating factors may be required. Medicines that most often cause leukopenia:
- Cytostatics
: cyclophosphamide, clopambucil, methotrexate. - Thyreostatics
: propylthiouracil, mercazolil. - Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
: analgin, amidopyrine. - Antibacterial agents
: chloramphenicol, sulfonamides. - Anti-inflammatory drugs
: D-Penicillamine, sulfasalazine. - Antipsychotic drugs (neuroleptics)
: chlorpromazine, chlorpromazine. - Anticonvulsants
: carbamazepine, diazepam.
Autoimmune inflammatory diseases
Leukopenia can be caused by autoimmune diseases. In these cases, lymphocytes and neutrophils are predominantly reduced. There are two main pathogenetic mechanisms of autoimmune leukopenia - the formation of anti-leukocyte antibodies and a decrease in the expression of special proteins on the membranes of immune cells (CD55, CD59), which protect cells from cytolysis. Leukopenia is usually moderate, regresses during remission or under the influence of pathogenetic treatment. Leukopenic syndrome is characteristic of the following pathologies:
- Joint diseases
: rheumatoid arthritis, Felty's syndrome. - Diffuse connective tissue diseases (collagenoses)
: systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren's syndrome. - Demyelinating diseases
: multiple sclerosis. - Systemic vasculitis:
granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Takayasu nonspecific aortoarteritis. - Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD)
: ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease.
Blood diseases
There are several mechanisms of leukopenia in hematological pathologies - replacement of hematopoietic tissue with malignant cells, fibrous or adipose tissue, synthesis of anti-leukocyte antibodies, deficiency of certain chemical elements for granulocytopoiesis (iron, cyanocobalamin, folic acid):
- Oncohematological diseases.
Leukopenia, up to agranulocytosis, can make the debut of acute leukemia (aleukemic form) - this onset of the disease occurs in approximately 20% of cases. Almost always, blood tests additionally reveal thrombocytopenia and anemia. Leukopenia is characteristic of lymphogranulomatosis (Hodgkin's lymphoma). White blood cell levels often remain low after treatment. - Hemolytic anemia.
With autoimmune hemolytic anemia, hemoglobinopathies, hereditary microspherocytosis, moderate neutropenia is possible. It is noteworthy that a drop in leukocyte levels occurs outside of a crisis. The period of hemolytic crisis, on the contrary, is accompanied by slight leukocytosis. - Dyserythropoietic anemia.
With aplastic anemia, as well as long-term deficiency of vitamin B12 and folic acid, pancytopenia is observed due to inhibition of the functioning of all hematopoietic germs. Leukopenia in iron deficiency anemia develops only with extreme iron deficiency and is moderate in nature.
Radiation sickness
The effect of ionizing radiation adversely affects the entire human body. First and most severely affected are organs with a high rate of cellular turnover, which include the bone marrow. Under the influence of gamma rays, which have a high penetrating ability, hematopoietic stem cells lose mitotic activity.
This inevitably leads to a drop in the level of leukocytes in the blood, as well as platelets and red blood cells. In acute radiation sickness, leukopenia occurs quickly, 48-96 days after irradiation; in chronic radiation sickness, leukopenia occurs gradually, over 1 year. The severity of leukopenia directly depends on the radiation dose received. The restoration of the number of blood cells occurs slowly or does not occur at all.
Hereditary forms of leukopenia
Primary leukopenias include genetic diseases caused by mutations in genes that regulate the maturation or differentiation of leukocytes. Some mutations lead to changes in the structure of leukocyte antigens, due to which they are subject to autoimmune destruction. In the vast majority of cases, primary neutropenia occurs.
The debut occurs from the first years of life. Some of these diseases are benign in nature (cyclic neutropenia, primary immune neutropenia, lazy leukocyte syndrome, Henslen syndrome), the decrease in the number of neutrophils is insignificant, associated infections are mild, and leukopenia regresses on its own.
Other hereditary leukopenias are often accompanied by infectious complications, which often become fatal in childhood: Kostman's disease (genetically determined agranulocytosis), primary immunodeficiencies (DiGeorge syndrome, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome), Chediak-Hegashi syndrome. In these diseases, specific treatment is required to restore normal white blood cell values.
Other reasons
- Protein fasting.
- Blood or leukocyte transfusion.
- Endocrine disorders
: hypothyroidism, acromegaly, hypercortisolism. - Diseases occurring with hypersplenism
: liver cirrhosis, malaria, visceral leishmaniasis. - Storage diseases
: Gaucher disease, Niemann-Pick disease.