Red blood cells and proteins
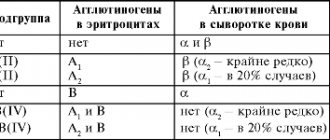
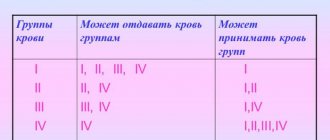
Erythrocytes are red blood cells that transport oxygen and carbon dioxide through the bloodstream. On their surface there are proteins in complex with carbohydrates (glycoproteins) - agglutinogens. The presence or absence of various agglutinogens determines what type of blood system a person has. We, of course, remember about the AB0 system, according to which there are four blood groups: I (0), II (A), III (B) and IV (AB). This system is based on the presence or absence of only two agglutinogen proteins.
In fact, over the last hundred years, scientists have discovered about 30 different systems. In some areas (transplantology, donation), doctors take them into account for various pathologies and conditions.
The most famous and most often used of the blood systems remains AB0. And in second place is the Rh system, or Rhesus system.
How is Rh conflict diagnosed?
At the planning stage or at the earliest stages, the individual blood parameters of the mother and father of the child are determined. Detailed information is collected from the woman about the course of previous pregnancies, if any, and about previous blood transfusions. An antibody test is performed every two months until week 35. After 35 weeks, analysis is done every 7 days.
To assess the impact of the conflict on the child’s condition, an ultrasound scan is performed. From 2 to 35 weeks, four ultrasounds are performed. To assess the risk of hypoxia in the child, an electrocardiogram is performed. Timely diagnosis of the likelihood of a negative impact on a child is already a way to protect the baby. Timely implementation of all diagnostic procedures reduces possible risks.
What is the Rh factor?
We will again talk about the agglutinogen protein on the surface of the red blood cell. But even here, not everything is as simple as we thought at school. In fact, the Rh system consists of 50 proteins. The most significant of them are five agglutinogens: C, D, E, c, e. For a general understanding of the complexity of the situation, it should be added that these proteins are encoded by linked genes, and there are two systems of their classification (nomenclature).
We are most interested in agglutinogen D (RhD). It is this protein that determines whether a person has a Rh factor: positive or negative. If this protein is not on the surface of red blood cells, we are talking about a negative Rh factor, and vice versa.
There are many more people with Rh(+) on the planet than people with Rh(-). Moreover, the frequency of occurrence of people without agglutinogen D depends on race. The ratio of 85% Rh (+) and 15% Rh (-) is typical for Europeans, among Africans there are people with a negative Rh factor - 7%, and among Asians and Indians - less than 1%.
First and subsequent pregnancies with negative Rh blood
Scientists have found that Rh conflict during pregnancy and birth of the first child occurs much less frequently. The reason for this is that during the first pregnancy, large antibodies are produced, which cannot always enter the bloodstream and attack the fetus.
But still, any relationship with inappropriate blood, be it premature birth, abortion, blood transfusion, etc., forces the woman’s body to develop immunity to the Rh factor. Thus, during the second pregnancy, more antibodies will be produced in the woman’s body. It is because of this that the second pregnancy with negative Rh and subsequent ones much more often entail alarming consequences. To combat such protection of the body and avoid serious consequences, the mother is given a special drug - immunoglobulin; such a vaccine suppresses the production of antibodies, for example, during the second pregnancy, which helps reduce the occurrence of Rh conflict to a minimum.
Rh factor and human health
Long-term observations show that the presence of the RhD protein affects the body, giving it some additional properties and affecting health. That is, physiologically, people with a negative Rh factor will be slightly different from people with a positive Rh factor. Question: which way?
Hemolytic disease
Not so long ago, when medicine did not know all the above nuances, Rh(-) women during pregnancy from an Rh(+) man could encounter hemolytic disease of the fetus. What does it mean? Each agglutinogen protein has its own agglutinin antibody.
An agglutinogen and an agglutinin of the same type cannot be present in the blood of one person, because when they meet, they immediately agglutinate, that is, stick together. Such clumped red blood cells are destroyed (hemolysis occurs), which is the basis of hemolytic disease.
So, if the mother has Rh(-), and the child from the father has Rh(+), then there is a risk that maternal antibodies to the RhD protein (which she does not have) will reach the fetal red blood cells through the placenta, which just have the RhD protein . A Rh conflict occurs and, as a consequence, hemolytic disease of the fetus and, accordingly, in the newborn.
Toxoplasmosis and road accidents
In 2008, a study was published showing that people with Rh(-) are more vulnerable to exposure to Toxoplasma gondii, an intracellular parasite that has been linked to cats. Why did scientists become interested in Toxoplasma? But because it has a similar distribution of occurrence: in developed European countries, 20-70% of residents are carriers of toxoplasma, and in developing countries - 90% or more. It was noted that people with latent toxoplasmosis and a negative Rh factor have a reduced reaction rate, as a result of which they are 6 times more likely to get into an accident than Rh(+) carriers of toxoplasma. Scientists suggest that the RhD protein plays a protective role, although it is not yet clear what exactly it is.
Cats, by the way, fit well into this scheme. In prehistoric Europe, cats (and toxoplasmosis) were much less common than in Africa, where the disease and its wild feline carriers were extremely common. So Africans who do not possess the treasured RhD protein had less chance of survival in a collision with either a car or a predator.
The evolutionary mystery of the Rh factor is that all primates except Homo sapiens have the RhD protein. There are no Rh(-) chimpanzees or other great apes. This fact gave rise to many absolutely fantastic theories about the origin of Rh(-) people, the mildest of which was the alien theory.
Prevention of Rhesus conflict
Prevention of Rh conflict before, after and during pregnancy. Postpartum prophylaxis is carried out only if a subsequent pregnancy is planned.
Prevention details:
- Preventive vaccination of women with negative antigen. Conducted during pregnancy and immediately after childbirth.
- Prenatal prevention. Planned or emergency impact on a woman by introducing immunoglobulin injections into the blood. The planned action is carried out in the period from 28 to 30 weeks. Emergency prevention is needed when exposed to external factors that cause interruption. These are the threat of miscarriage, abdominal trauma during pregnancy and exposure to medications during pregnancy. The amount and frequency of administration of drugs with immunoglobulin into the blood of the expectant mother is explained by her well-being and necessity.
- Postpartum prevention. It is more of a “prenatal prevention”, as it aims to protect a possible future birth. After the birth of a newborn, his blood is taken for analysis and if he is confirmed to have a positive antigen, the mother again receives an injection of immunoglobulin.
- Prevention during interruption. Even if a woman’s pregnancy did not end with the birth of a child for one reason or another, to prevent a possible recurrence of negative situations in the future, treatment with immunoglobulin antibodies is prescribed by the attending physician. When the next pregnancy occurs, prophylaxis is continuously repeated, since the antibodies constantly adapt to changing environmental conditions.
Gender characteristics of Rh negative people
In 2020, Czech scientists published the results of a study on Rh-negative people. They were simply interested in what and how often they got sick, compared to Rh-positive citizens. The results were not only quite entertaining, but also gender specific. Women and men who do not have the notorious D-agglutinogen on their red blood cells suffered differently from Rh(+) people.
Men Rh(-) and Rh(+)
Rh(-) men are more likely than men with Rh(+) to experience various mental disorders, including: panic attacks, problems concentrating, antisocial personality disorders, etc. Rh-negative men were also more likely to experience allergies (especially their skin manifestations), anemia, thyroiditis, liver disease, diarrhea, infectious diseases and even osteoporosis. But the stronger sex without the RhD protein was less likely to suffer from celiac disease, digestive problems, prostate adenoma, gallbladder disease, warts and some types of cancer - all these pathologies were more characteristic of Rh-positive men.
Scientists suggest that the RhD protein is involved in the removal of ammonia, a product of protein catabolism, from the cell. Thus, it is known that the concentration of ammonium in erythrocytes is 3 times higher than in blood plasma. It is possible that the RhD protein is involved in its uptake and transport to the kidneys and liver. There are other theories explaining why RhD protein is needed. But so far none of them explains where people who do not have this protein come from.
How is immunoglobulin administered?
Immunoglobulin antibodies are a special class of drugs that interfere with the woman’s body’s production of special antibodies; it collects and expels already formed antibodies from the body. Such immunization helps eliminate Rh conflict during pregnancy. An immunoglobulin injection is used to prevent the occurrence of Rh conflict during the second pregnancy and subsequent ones. Vaccination with immunoglobulin is performed after the following events:
- ectopic pregnancy;
- in the first week after the birth of the child;
- early birth;
- studies of fetal fluid;
- abortion;
- blood transfusions;
- placental abruption.
In any case, the difference in Rh in the blood of mother and child is not a disaster; modern medicine is able to use medications to prevent serious consequences, the outcome of which can be dangerous. The main thing in this is timely contact with a specialist and timely treatment.
Why does Rhesus conflict arise between mother and child?
The human body tries to fight all foreign bodies. For example, with a cold or flu, he directs all his efforts to suppress the virus. A similar effect occurs when the Rh factor of the mother and child has different values. That is, the body is constantly in a fight against antibodies, which means it threatens the life and development of the pregnant baby. In this case, the woman should be observed by doctors throughout the entire pregnancy to prevent illness and death of the baby. Modern medicine has a number of ways to solve this problem.
The state of health of an expectant mother with Rh-conflict is no different from that of other pregnant women. But such expectant mothers require regular blood donations. For the sake of the health of the unborn baby, you can endure even less. In other cases, pregnant women have to endure premature birth and blood transfusions. These procedures most often result in success and the birth of a healthy baby. That is why a negative Rh factor during pregnancy should not cause great fears in the expectant mother.