A high pulse during pregnancy may indicate disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular and hormonal systems. The danger of this condition exists for both the mother and the fetus - oxygen starvation occurs, which provokes a disruption in the development of the unborn child, increasing the risk of premature birth and miscarriage.
In the 1st trimester, the limit is 100 beats per minute, in the 2nd trimester - 120 beats. Figures of 140 beats or higher in a state of relative rest make it necessary to provide immediate medical attention.
At home and with the permission of a doctor, a pregnant woman herself can lower her heart rate by walking, doing yoga, and normalizing her daily routine. You can also take gentle sedatives, but strictly after a specialist’s prescription.
What can be dangerous about a high heart rate during pregnancy?
A high pulse during pregnancy is an abnormal condition that may indicate the development of various pathological conditions:
- infectious processes;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels in the mother and fetus;
- anemia;
- kidney and liver diseases.
Often it is a rapid pulse that becomes the only symptom of the above diseases, although they can also occur secretly. The danger is that an increased pulse provokes malfunctions of the mother’s heart. This entails chronic oxygen starvation of the fetus, and the result can be disturbances in the development and formation of its organs and systems.
Diagnosis of the pathological condition
In a normal emotional state, the heart rate is 60–80 beats per minute. This heart rate regime provides the body with the necessary amount of vitamins and microelements. Carrying a child is accompanied by an increase in the volume of circulating blood. This is necessary to serve the fetus, the expectant mother. Sometimes doctors record an increase in heart rate up to 100 – 150 beats/min. This condition is called physiological tachycardia.
To diagnose increased heart rate in pregnant women, doctors do not need additional equipment. At every routine examination of the expectant mother, the woman must have her pulse and blood pressure measured. You can control your heart contractions at home; it’s not difficult if you know where to feel the pulsation.
How to determine heart rate? To do this, you need to find the pulsating artery located in the front of the neck, on the wrist. Then we apply the phalanges of our fingers to the pulsation area, concentrate, and count the number of rhythmic beats in one minute. The described procedure must be carried out at rest. It is important that the pregnant woman calms down and rests (for example, after climbing stairs or walking for a long time). You should not measure your pulse after eating a large, fat-rich meal.
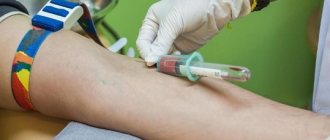
You can also determine the number of heart beats per minute using an electrocardiogram. If the doctor suspects the presence of any heart disease, he can refer the pregnant woman for additional diagnostics (ultrasound of the heart, recording heart rate throughout the day using a special Holter device).
To measure your pulse at home, you can use an electronic tonometer. This device is easy to use and can be purchased at any pharmacy. If the pregnant woman has no significant deviations from the norm, childbirth occurs naturally. If any pathological changes in the functioning of the heart are detected that accelerate the frequency of contractions of this muscle, doctors prescribe a cesarean section.
High pulse during pregnancy in the third trimester: causes of occurrence
A high pulse during pregnancy in the third trimester may be due to physical reasons - the woman’s body is forced to pump a large amount of blood through the pulmonary and systemic circulation and do this at high speed. This is the only way to provide oxygen and nutrients to the organs and systems of not only the pregnant woman, but also the unborn child.
But an excessive increase in indicators may indicate the development of serious conditions:
- nephropathy – problems with kidney function;
- gestational diabetes;
- liver dysfunction;
- disturbances in the production of thyroid hormones.
The listed conditions can provoke premature birth, eclampsia, intrauterine fetal death and death of the woman.
What should a normal heart rate be?
For a healthy adult, the normal heart rate is between 60 and 80 beats per minute. During periods of physical activity, this value can increase to 120 beats - this is a completely natural phenomenon, since working muscles need additional oxygen supplied with accelerating blood flow.
During pregnancy, the pulse may also increase by an average of 10-15 units (but in some cases up to 40); as a rule, this phenomenon is purely physiological in nature and is not a cause for concern.
Factors affecting heart rate during pregnancy
There are several reasons why a pregnant woman’s pulse may change, and most of them do not indicate the presence of any pathology. These reasons include:
- changes in hormonal levels (increased levels of sex hormones);
- an increase in blood volume in the body by an average of 1.5 liters;
- displacement of internal organs (including the heart) due to the growing uterus;
- rapid weight gain;
- stress and unstable emotional state;
- severe toxicosis, causing a disturbance in the water-salt balance in the body.
As a rule, several reasons in combination affect an increase or decrease in heart rate, and before taking any measures, you must always consult a doctor, because self-medication during pregnancy can cause irreparable harm to the baby’s body.
Slow heart rate
Doctors call a decrease in heart rate bradycardia; it is not a separate disease, but only a symptom. During pregnancy, we can talk about bradycardia if the pulse drops below 60 beats per minute. This condition is quite rare and may be accompanied by dizziness, weakness, nausea and fainting. If such symptoms occur, you should immediately report them to the doctor managing your pregnancy, as they may be evidence of an exacerbation of a chronic disease or the emergence of a new one.
Increased heart rate
As mentioned earlier, palpitations or tachycardia in one form or another is observed in the vast majority of pregnant women. The accelerated work of the heart is explained by the fact that the growing body requires an increasing amount of oxygen and nutrients, which it receives from the mother’s blood. Therefore, the peak of physiological (natural) tachycardia during pregnancy usually occurs at the end of the second or beginning of the third trimester, when the baby is growing most actively. In the last few weeks, the heart rate, on the contrary, returns to normal, as the body of both mother and child prepares for the upcoming birth.
The main reasons leading to an increase in heart rate during pregnancy are:
- high blood pressure;
- overweight;
- stress and emotional stress;
- sleeping in the wrong position (on the back), which causes compression of the abdominal aorta;
- active physical activity, sports;
- drinking coffee, strong tea and other products containing caffeine;
- medications that contribute to the occurrence of tachycardia.
Is it normal for a pregnant woman to have an elevated heart rate in the 1st-2nd trimester?
In the 1st-2nd trimester, pregnant women may have an increased pulse for physiological reasons: if it does not exceed normal values by more than 20 units, then there is nothing to worry about. This “behavior” of the cardiovascular system is explained simply:
- the fetus is actively growing;
- the woman’s body adapts to new operating conditions;
- blood flow speed increases;
- The kidneys are forced to work hard.
But too high values are dangerous, because it can cause miscarriage or premature birth.
For the first trimester, the maximum heart rate is 100 beats per minute, for the second - 120 beats.
Reasons for the increase
During pregnancy, the female body begins to work differently. This is largely due to the abundance of various hormones that are released during the period of gestation.
All these hormonal substances have a strong effect on cardiac activity. Ultimately, this condition contributes to the appearance of a high pulse in the expectant mother.
Pregnancy is a physiological period when the functioning of the cardiovascular system changes. In the early stages of pregnancy, the heart rate, as a rule, does not change. A change in this indicator indicates trouble in the female body. In this case, additional diagnostic methods are required, aimed at identifying the cause that led to the development of this condition.
The number of heartbeats per minute in pregnant women begins to increase by the second trimester. Usually it increases by 10-20 beats per minute relative to the average norm and is 85-90. This reaction is completely physiological. By the third trimester of pregnancy, most women's heart rate can increase to 120 beats per minute.
A rapid pulse in the first weeks of fetal development is an extremely unfavorable indicator. Usually it indicates the presence of some pathology in the female body.
Anemia, accompanied by a decrease in hemoglobin and red blood cells in the blood, often leads to the development of this condition. To compensate for these violations, the prescription of special compensating drugs is required.
A rapid heart rate may also occur if the expectant mother is carrying twins or triplets . Reviews from mothers who had multiple pregnancies indicate that by the end of 35-38 weeks of pregnancy they were seriously worried about tachycardia. To correct these disorders in this case, the prescription of medications is required.
An increased heart rate also occurs with any pathology of the kidneys, liver and other organs. If the expectant mother falls ill with some kind of infectious pathology, then one of the symptoms of intoxication is a rapid heartbeat. At the same time, the pulse increases due to various viral and bacterial toxins that are formed during any infection.
Quite often, an increase in heart rate occurs in expectant mothers after physical exertion. Lifting weights can also provoke tachycardia. Excessively fast walking also leads to the development of adverse symptoms.
How to measure your heartbeat correctly if you feel a rapid pulse
A rapid pulse is easily determined by a woman without a doctor, because it is characterized by:
- dyspnea;
- flushed face;
- mild tremor of the upper extremities;
- headache;
- feeling of heart fluttering.
To understand how dangerous this condition is, a pregnant woman should measure her pulse and do it easily as follows:
- place the fingers of one hand on the inside of the wrist of the other;
- lightly press them and feel for the place where the most clearly audible strokes of blood movement through the vein can be heard;
- Press your fingers harder and count the number of beats for 60 seconds.
You need to measure your pulse at rest, for which the woman should sit on a chair or armchair, relax, and try to restore her breathing. The manipulation cannot be carried out after minor or excessive physical exertion, eating, walking, or doing household chores, as the results will be uninformative and false.
When does your heart rate increase during pregnancy?
If a pregnant woman has an increased pulse and feels discomfort (shortness of breath, feeling tired, headaches, dizziness, and sometimes fainting), you should notify your doctor as soon as possible.
An increased heart rate is observed in the expectant mother already in the third trimester. Tachycardia during this period becomes quite common. Doctors themselves say that this is usually considered the norm, since the woman’s body does double work, provides the baby with oxygen, so the heart also works doubly. But if a pregnant woman has nausea and vomiting, then this should be alarming. These symptoms may indicate the possibility of some kind of heart disease in a woman. In addition, attacks of tachycardia for a long time are considered a deviation from the norm.
It is worth considering several reasons for the appearance of tachycardia in pregnant women. It should be noted that during pregnancy a woman gains significant weight. This puts additional stress on the heart. Even when lying on your back, the weight of your abdomen can put pressure on your heart muscle, naturally increasing your heart rate. Physical activity can also cause a rapid heart rate.
Anemia of the pregnant woman can serve as a provocateur; along with tachycardia, hypotension can be observed.
If a woman does not give up bad habits during pregnancy, in particular alcohol and smoking, this can have a detrimental effect not only on the well-being and health of the mother, but also on the future health of the baby.
The expectant mother may also change taste preferences, and her body may become intolerant to some foods that she previously consumed. And one of the body’s reactions to some product or medicine may be tachycardia.
During pregnancy, you should be wary of various medications: if previously they seemed quite harmless, then during pregnancy they can cause significant harm to the body and the baby, in particular. One of the body's reactions may be an increased heart rate.
Return to contents
How to lower your heart rate during pregnancy at home
If a rapid pulse after examination by doctors is not a consequence of pathological conditions, then during pregnancy it can be reduced at home:
- Do breathing exercises at least 3 times a week. This method has many contraindications, so a preliminary consultation with a gynecologist is necessary.
- Walk in the fresh air every day, you can do yoga. This increases vascular tone and strengthens the heart muscle.
- Normalize the daily routine - periods of rest and wakefulness should clearly alternate. Night sleep is at least 8 hours.
- Avoid drinking coffee and tea. These drinks can be replaced with compotes, jelly, and fruit drinks.
- Take vitamin complexes, especially those containing potassium and magnesium. But such prescriptions must be made by a doctor.
If the pulse increases sharply and reaches critical levels (above 140 beats per minute), then it is better to call an ambulance. Before her arrival, you can use a quick way to stabilize your condition:
- feel the carotid artery in the neck;
- Rub the area lightly with your fingertips for 15 minutes.
As soon as a high pulse is diagnosed, the woman should sit down, close her eyes, and drink a glass of clean water at room temperature in small sips. After this, she needs to lie down and take several deep breaths.
When to call an ambulance
An ambulance must be called if:
- pulse rate exceeds 140 beats per minute;
- the woman is in a semi-fainting state;
- there are complaints of nausea, the pregnant woman begins to vomit;
- bothered by convulsive twitching of the lower extremities;
- a woman complains of dizziness;
- the patient is cold or, conversely, too hot, regardless of the ambient temperature.
The reasons for receiving urgent medical care are pain and a burning sensation in the area of the anatomical location of the heart, acute urinary retention, severe yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes, pain in the lumbar region and lower abdomen.
Tip 1: What to do if a pregnant woman’s pulse is more than 100
- What to do if a pregnant woman's pulse is more than 100
- What should be the normal heart rate and blood pressure?
- How to listen to the fetal heartbeat
The heart pumps blood into the veins and arteries, delivering oxygen to the body's organs. It is at the moment of such a push that the walls of the blood vessels expand and fluctuate - that’s what 1 beat of the pulse is. In healthy adults, the heartbeat reaches approximately 60-80 beats in one minute.
For a pregnant woman, things may be different. And all only because another person is growing inside her, who has the same heart, which also pushes blood and delivers oxygen. And while the child is in the mother’s tummy, the mother “works for two” and the mother’s heart must also pump blood, and through it oxygen and all the necessary nutrients for the fetus.
In the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, the pulse rate can increase first to 100 beats per minute, and then to 110 and even 115. The thing is that during the period when a new life is born inside a woman, the body changes in accordance with what kind of needs are necessary for the child. The body must provide the fetus with everything necessary for normal development and growth.
By the second trimester, all organs of the fetus have already formed and each of them naturally needs oxygen. As mentioned above, all the necessary nutrients and oxygen come to the child from the mother, which is the reason for the woman’s rapid heartbeat.
A large number of pregnant women, noticing an increase in their pulse and heart rate, consult a doctor with complaints. Of course, it should be noted that such a step is 100% correct, since nothing should threaten the health of the mother and child.
Doctors call a rapid heart rate during pregnancy “physiological tachycardia,” which in most cases goes away on its own after childbirth. The symptoms in question will not harm the woman, although we must not forget that there are always exceptions. If nausea and vomiting are also added to your rapid pulse and heartbeat, the first step, of course, is to visit your doctor, because these symptoms may be evidence of heart disease.
Dear women, don’t worry – it’s harmful. Remember that an increase in heart rate is quite possible during pregnancy and, most often, there can be no threat to health. Consult your doctor and follow the recommendations. Walk more and worry less, and everything will be fine!
Source: www.kakprosto.ru
What is rapid heart rate? This is the increased speed at which the human heart begins to contract. In medicine, this phenomenon is called tachycardia. Such symptoms do not threaten a person’s life, but can cause him a lot of unpleasant moments. You shouldn't ignore it either. In this article we will try to figure out how the high heart rate that occurs during pregnancy affects the development of the fetus and the health of the woman herself?
From the moment when the future human being begins to develop in the mother’s womb, colossal transformations occur in a woman’s body. Its biological systems begin to rebuild, changing their rhythm in order to provide the embryo with ideal conditions for full growth and development. Therefore, when the expectant mother begins to feel an increased heartbeat, it scares her and she begins to worry about her baby. Her anxiety can only aggravate the condition, although in most cases the causes of high heart rate during pregnancy are the most trivial and do not require any medical intervention. Doctors even have a kind of norm for the level of increase in a pregnant woman’s pulse. If the heart rate does not reach the permissible limit, then the health and life of the fetus and the woman are not in danger.
What numbers can be considered high? If there are more than a hundred contractions of the heart muscle per minute (100 BPM - beats per minute), doctors are already talking about a rapid pulse or tachycardia. This indicator means that the heart is having a hard time maintaining an effective level of pumping blood through the circulatory system.
There are two types of this pathology. If an increased rate of contraction is observed directly in the ventricles, this clinical picture is called ventricular tachycardia. If the failure occurs higher, already in the upper heart chamber, supraventricular tachycardia is obtained. It occurs more often and is most gentle on a woman’s body, without bringing any special complications, but only if its symptoms, with accompanying manifestations, do not bother the expectant mother for a long time.
What are the main reasons for high heart rate during pregnancy?
- If a woman moves a lot and her body receives increased stress.
- Excess weight and excessive growth during pregnancy.
- If the expectant mother lies on her back for a very long time.
- Vitamin deficiency and deficiency of microelements necessary for the normal functioning of a woman’s body.
- Emphysema or COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) is the gradual formation of a heart defect that develops on the basis of constantly arising obstacles to blood flow. With this pathology, a deterioration in tissue elasticity is observed, which is an obstacle to the normal rate of blood flow through the system. The main causes of the pathology are diseases of the pulmonary localization and smoking.
- The cause of a rapid heartbeat in a pregnant woman may be pathological tachycardia caused by the woman’s history of chronic diseases.
- Failure of metabolic processes. The thyroid gland is responsible for the level of metabolism in the human body. If she produces more enzyme than normal, this leads to a disruption in the woman’s natural metabolism. This moment is the starting point in increasing the heart rate. In addition to the thyroid gland, other malfunctions that affect the body’s metabolism can affect the level of heartbeat.
- Habits that do not fit into the rules of a healthy lifestyle (smoking, alcohol, etc.).
- Some medications can also cause tachycardia.
- The use of substances with a stimulating effect in the diet: coffee, strong tea, energy drinks.
- Any deviation from the norm in the structure of the upper chamber of the heart (unevenness or other defect) can cause a high pulse during pregnancy. Such defects weaken muscle tissue, while the load on the heart itself increases and it has to increase the pace of work in order to provide the body with the necessary amount of nutrients.
- Overeating, eating salty and fatty foods.
- A stressful situation leading to increased excitability of the nervous system.
- Nervousness and present state of anxiety.
- Anemia.
- Infectious or viral pathology, accompanied by high temperatures.
- Electrolytic imbalance in a woman’s body during the period of illness.
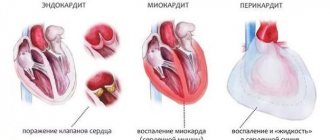
- Multiple heart diseases: Hypertension.
- Ischemia.
- Pericarditis is a pathological inflammatory process in the pericardial sac with primary damage to the visceral layer of the pericardium.
- Heart valve defect.
- Loss of artery elasticity.
- And others.
Only by eliminating the root cause can you get rid of the accompanying symptoms.
What are the symptoms of rapid heartbeat? It is not difficult to answer this question: the body begins to feel that an “anvil” is working in its chest, the heart is simply ready to “jump” out of the chest. Concomitant symptoms of high heart rate during pregnancy are also quite often observed.
- A pregnant woman may experience nausea, the intense manifestations of which can lead to gag reflexes. If a pregnant woman observes a combination of such factors, it is necessary to notify her obstetrician-gynecologist about this; the specialist’s task is to establish the source of the woman’s uncomfortable well-being. One of these reasons may be cardiac pathology, which requires accuracy in diagnosis and drug therapy.
- The expectant mother may feel a muffled or distinct pulsation in her stomach. Most often it is felt in the lower part of the tummy. One source of pulsation may be fetal hiccups, another may be plasma traffic through the aorta. Such symptoms can develop at any week of gestation. If the rhythmic movement is not accompanied by pain symptoms and other discomfort, there is no need to be especially alarmed. Such manifestations fit well into the normal course of pregnancy.
- If a pregnant woman experiences dizziness, accompanied by a decrease in the general tone of the body, low blood pressure and periodic loss of consciousness, you should not hesitate, you must urgently tell the doctor about these manifestations, who, having prescribed the necessary therapy, will normalize the condition.
- Sometimes, against the background of tachycardia, a woman begins to feel a lack of air (hypoxia develops). The pregnant woman begins to breathe intensely, as the lack of oxygen can harm the baby. In this situation, it is necessary to walk more in the fresh air and ventilate the room more often.
- A rapid heartbeat may be accompanied by a headache. These may be the first symptoms of hypotension.
A healthy heart during a period of normal emotional state works at a speed of 60 - 80 beats per minute. This reduction regime makes it possible to provide the human body with a sufficient amount of substances necessary for normal functioning: vitamins and microelements. During the period of bearing a baby, the volume of circulating blood increases, serving both the fetus and the expectant mother. Accordingly, in a pregnant woman, the number of beats may increase slightly to one hundred, and in some cases to 115. Doctors call such an increase in indicators physiological tachycardia.
Diagnosis of high heart rate during pregnancy does not require any additional equipment. A woman undergoes this procedure at every doctor’s appointment (be it a therapist, cardiologist or obstetrician-gynecologist). But a pregnant woman can easily cope with such measurements on her own. It would be a good idea to monitor your heart rate at home. It’s not difficult to make such a measurement; you just need to know where and how to count.
Whether it is a therapist, a cardiologist, an obstetrician-gynecologist or a doctor of any other specialization, at his appointment he must check the pulse rate of a pregnant woman. But a pregnant woman must monitor this indicator on a daily basis. It's easy to determine:
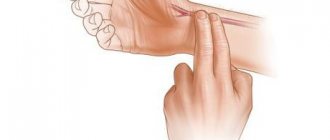
- The best place to get a numerical reading of your heart rate (HR) is the pulsating artery on the front of your neck or on the wrist of one of your hands.
- The phalanges of the fingers must be applied to the place of pulsation, concentrate and count the number of rhythmic manifestations determined over the course of one minute.
- The procedure should be carried out only at rest, when the pregnant woman has rested and calmed down. You should not do the calculations after a large, fat-rich meal.
In addition, it is also possible to diagnose the number of beats per minute using an electrocardiogram (ECG). If the doctor has suspicions about the patient’s history of any heart disease, he will refer the pregnant woman for additional diagnostics. Such techniques can be ultrasound (ultrasound examination) of the heart or innovative technology for recording heart rate - the procedure lasts a day. In this case, a special Holter device constantly records the heart rhythm without causing any inconvenience to the patient.
You can also measure your heart rate using a modern electronic tonometer, which can be purchased today at any pharmacy.
If significant deviations from the norm and anomalies are not observed, the woman gives birth quite successfully naturally. Certain pathological changes in the heart that lead to an increase in heart rate can also become an indication for a cesarean section. In this case, the obstetrician-gynecologist together with the cardiologist makes their verdict.
Source: m.ilive.com.ua
During the period of bearing a child, fundamental changes in all processes and the functioning of organs occur in a woman’s body. This is necessary to ensure that the fetus receives the necessary substances.
Often expectant mothers experience palpitations and shortness of breath. The heart rate may also increase slightly during pregnancy, usually by no more than 10-15 units per minute.
From a physiological point of view, this is a normal phenomenon, but if the numbers significantly exceed the norm or do not reach the borderline values and at the same time the woman feels dizziness, nausea, and vomiting, then this may indicate the development of serious diseases.
In this case, you need to consult a doctor and undergo the necessary examinations to prevent negative consequences for yourself and the child.
Normally, an adult's heart rate should be between 80 and 90 beats per minute. This value is so unstable that it can fluctuate under conditions of changes in humidity and air temperature, when taking medications or during psychological and physical stress.
At the same time, the number of reductions varies slightly.
For expectant mothers, due to the correction of hormonal levels, uterine growth and other features of pregnancy, an increase in contractions by 10-20 units is considered normal and does not cause any particular concern.
When the heart pushes blood into the vessels, they expand and oscillate. This phenomenon is called heartbeat.
If the number of beats increases, the heart begins to contract intensively to ensure the supply of oxygen, activating metabolic processes.
This is often observed during pregnancy, when the heart needs to pump a large volume of blood due to physiological characteristics. At the same time, the load increases along with the weight, which forces the organ to accelerate movement.
When there is a stable upward increase in the rate, tachycardia develops. If there is a prolonged slowdown of the pulse below 60 beats, then bradycardia appears. The irregular rhythm is called arrhythmia.
This can be dangerous for both mother and child, since the failure is often caused by diseases of the heart or other organs. Therefore, if this indicator changes and symptoms of pathology appear, you should consult a doctor to eliminate discomfort.
How to reduce heart rate during pregnancy using drugs
You can reduce your heart rate during pregnancy with “mild” sedatives, but they should be prescribed by a doctor and only in the absence of positive dynamics while following other recommendations:
- Persen - has a positive effect on the cardiovascular and central nervous system;
- Valerian tincture – gives a cumulative effect, it is important to take the medicine regularly and for several weeks;
- motherwort herb is a herbal tea that can be used instead of regular drinks, but in strictly dosed doses.
Any pills with a pronounced sedative effect are strictly contraindicated during pregnancy. They inhibit the functioning of the central nervous system of the expectant mother, penetrate into the fetus’s body and lead to problems in the development of the baby after birth.
What diagnostics are needed during pregnancy?
A woman carries a baby under her heart for nine months.
At this time, colossal changes occur in the body, it works under intense pressure, so now it takes two to provide everything necessary. The load on the vascular-cardiac system increases.
One of the important indicators during the period of bearing a child is the pulse rate.
It is necessary to measure constantly; changes in one direction or another can indicate possible problems. What is the norm? How to measure your heartbeat correctly?
The embryo develops in the uterine cavity, and at the same time its own blood circulation is formed. During a normal and healthy pregnancy, a woman’s hormonal background changes and regulates the functioning of the heart, metabolism, etc. As the fetus grows, its needs increase, requiring significantly more nutrients and oxygen.
At the same time, the volume of blood and the speed of flow through the vessels increases. Extra pounds have a negative impact. The heart experiences a double load even during a stable pregnancy. Therefore, the pulse rate and blood pressure are generally elevated. In the absence of other problems or pathologies, this is considered normal.
You can measure your heart rate at home, on your own:
- In a calm state, you need to sit down or lie down.
- Place your middle or index finger on your wrist near the protruding vein.
- When you feel the pulsation, turn on the stopwatch for one minute and start counting.
In addition to this method, you can measure the pulse in the cervical artery using the same method. Some modern tonometers simultaneously calculate the heartbeat along with the pressure level.
In the hospital, it is sometimes measured using an ultrasound or ECG of the heart.
The pulse is the dilation of blood vessels that occurs when the left ventricle contracts. The organ pushes blood into the vessels and they expand, causing vibrations, which are perceived as the heart rate.
While carrying a child, a woman’s heart is subjected to double load; the volume of blood pumping can be one and a half, two liters more than usual. This is an emergency value of 10-15 units.
It is not difficult to calculate the normal state of the heartbeat: add 10-20 units to the normal heart rate before pregnancy.
1st trimester
At the beginning of pregnancy, in the first weeks, the formation of fetal organs occurs; the body actively nourishes and saturates the embryo with oxygen through the mother’s blood. Because of this, the heart muscle is forced to work with double force, which increases the heart rate. Early toxicosis also contributes to this.
The rate of heart rate can reach 110 beats per minute in a calm state. The highest value is allowed during physical exertion, fatigue or severe anxiety.
2nd trimester
In the middle of the period, the organs of the embryo are formed and the heartbeat decreases to 80-95 beats per minute. Often by the twenty-fifth week of pregnancy it increases again and can reach 120 beats. This is due to the fact that the child’s cardiovascular system has developed and more circulating blood is needed to deliver nutrients and oxygen.
3rd trimester
The last period of pregnancy is accompanied by active growth of the fetus and a high load on the entire body. The volume of circulating blood increases by one and a half liters.
This is necessary for normal blood supply to the baby and additional reserve in case of bleeding after delivery. All processes affect the rhythm of the heart, the pulse quickens.
Shortness of breath and swelling often occur.
The average heart rate in the third trimester is 120 beats per minute. The norm is considered to be values ranging from 110 to 150 beats, depending on the individual characteristics of the woman. Often, high readings are a sign of gestosis, so it is important to be constantly monitored by a doctor.
Immediately after birth
In the postpartum period, a rapid heartbeat is often observed, but rhythmic. The body returns to normal after the process. In some women, the heart rate sometimes slows down to 60-50 beats per minute. This is called bradycardia.
The phenomenon often accompanies women in labor in the first hours after the birth of the child. There is no exact explanation for bradycardia; doctors have differing opinions.
Also, blood pressure may decrease immediately after childbirth, but just as quickly returns to normal.
High during pregnancy occurs due to many factors:
- The first trimester, the laying of organs and the formation of the fetus force the body to work doubly, which contributes to an increased heart rate.
- On average, a pregnant woman has a heart rate of 110-120 beats per minute. This is due to the increased work of the heart muscles and other organs.
- Hormones of the expectant mother and increased emotionality affect the heartbeat, contributing to an increase.
- In the first and last weeks of emergency, students suffer from toxicosis.
- Overwork, stress, anxiety - all this provokes an increase in heart rate.
- Sharp jumps appear during periods of active fetal growth.
- When lying on your back for a long time, the heart rate becomes more frequent, because the uterus puts strong pressure on the abdominal aorta, squeezing it, so this position is not recommended, especially in the last stages.
- With respiratory and infectious diseases, the heart rate increases.
- Some medications increase heart rate.
- If a woman has bad habits: drinks alcohol and smokes cigarettes.
- Women in labor who have heart problems before pregnancy often suffer from a rapid heart rate.
- Exercise stress.
- Overweight.
- Poor nutrition and absence or lack of vitamins.
- Foods high in caffeine increase your heart rate.
This type of heart activity causes dizziness, nausea, shortness of breath in the expectant mother, makes it difficult to breathe, and may cause pain in the chest area. You should tell your doctor about all changes in your health and well-being.
Slow heartbeat is rare among pregnant women. Most often this happens in athletes who have been actively involved in strength training and have a trained heart.
Bradycardia occurs against the background of some chronic diseases:
- thyroid diseases;
- kidney pathologies;
- disruption of the circulatory system;
- problems with the nervous system.
If you experience any symptoms of abnormal heartbeat, you should immediately inform your doctor and seek help. An increased pulse - tachycardia - can cause gestosis, which is dangerous to the health of the woman and child.
Reduced heart rate - bradycardia, can cause complete cardiac arrest, this occurs when the pulse drops to 40 beats per minute. At the same time, the pressure decreases greatly.
Another pathology of heart rate is arrhythmia - frequent pulse surges. It also poses a high risk to the woman and baby. Possible cardiac arrest and death for both.
For any problems with the pulse, a specialist must find out the cause; the health of the woman in labor and the child, as well as the type of delivery, depends on this.
For chronic problems with pulse rate, the doctor selects treatment based on the characteristics of the mother’s body and the course of pregnancy. There are general recommendations that help stabilize the heartbeat:
- healthy lifestyle;
- being in the fresh air;
- moderate physical activity;
- it is advisable not to be nervous, not to worry, to avoid stress;
- rest and get enough sleep.
For bradycardia, pregnant women are more often prescribed drugs:
- "Eufillin."
- "Atropine".
- "Izadrin."
In case of tachycardia, sedatives Novo-Passit, Concor, Persen and others are allowed. They are mainly used in conjunction with medications that improve heart function: rose hips, hawthorn.
For arrhythmia, a pregnant woman will be prescribed treatment depending on the causes of the disease.
Problems with the heartbeat of a pregnant woman can provoke various pathologies in the child, mainly:
- Anemia.
- Hypoxia.
- Intrauterine infections.
- The development and growth of the fetus slows down.
- The child's brain suffers the most.
Pregnancy is, at the same time, the best and difficult period. A woman should be extremely careful about her health and well-being. You need to visit your doctor regularly and follow the recommendations. Any changes in heart rate can negatively affect pregnancy and the general condition of the expectant mother and child.
Red blood cells: normal during pregnancy, causes of deviations. When a pregnant woman with signs of anemia undergoes tests, the doctor’s main focus is on the number of red blood cells.
It is their quantity that shows the level of oxygen saturation of the body. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, which affects the growth of the fetus and the general physical condition of the pregnant woman.
If they leave the blood and are then redirected into the urine, this proves that there is a serious pathology.
The state of the body changes greatly when carrying a child, the same applies to the number of red blood cells, which increase by 25%.
The normal course of pregnancy involves an increase in blood plasma by half, and red blood cells by only a quarter, but at the same time, the hematocrit and hemoglobin concentration, on the contrary, decrease.
As a result, hemodilution anemia is often detected, which differs from iron deficiency anemia.
Red blood cells in the blood during pregnancy are normally considered to be above 3.5*1012/l.
They are formed in the bone marrow, and from there they are sent into the bloodstream and circulate freely throughout the body. Due to the fact that this substance is constantly produced, its amount on average does not change.
Red blood cells, the norm for which during pregnancy may differ slightly in different laboratories, are detected quite simply - using a regular CBC. It shows the percentage of the volume of blood plasma and all its components; in addition, this value can be measured in other units.
Due to the fact that the total blood volume increases significantly, a woman’s red blood cells vary at different times, for example:
- In the first trimester from 4.2 to 5.4 million.
- On the second, the normal level is from 3.5 to 4.8 million.
- In the third trimester from 3.7 to 5.0 million per 1 µl.
An interesting fact is that severe toxicosis at any period provokes excess of the norm due to the resulting dehydration. They increase not only in the blood, but also in the urine, which indicates more complex diseases in the expectant mother and baby.
Deviation
Why does high heart rate occur after childbirth?
After childbirth, the pulse may also be high, the reasons for this are:
- another restructuring of the hormonal system;
- active lactation;
- a consequence of complications during childbirth - for example, there was bleeding;
- recovery after incisions/ruptures of the perineum.
But an increase in indicators may also be associated with the development of pathological conditions: an inflammatory process in the uterus, suppuration of external or internal sutures, the development of acute mastitis due to improper breastfeeding, chronic constipation, intestinal dysbiosis while taking antibacterial drugs, increased blood pressure. These conditions must be diagnosed by doctors, and the woman is monitored until full recovery.
At home, a postpartum increase in heart rate is associated with disruption of the daily routine, sleepless nights, and emotional distress.
A high pulse during pregnancy can be a physiological phenomenon, but it is often a symptom of complex pathologies that occur secretly. A woman should be able to independently take readings, know the symptoms of deterioration of the condition and follow the recommendations and prescriptions of specialists.
Why follow changes?
Basically, when they talk about the pulse during pregnancy, they mean the heart rate of the expectant mother. This is a variable value that depends on a variety of factors.
Each scheduled appointment with a doctor begins with the pregnant woman having her blood pressure and pulse measured. An increased heart rate during pregnancy or too low will never go unnoticed by a doctor. You will definitely be asked leading questions or ordered an additional examination to find out the reason. This is important, because the well-being of the fetus directly depends on the well-being of the mother.
You can find out whether your heart rate is high during pregnancy or not from the table below.
| Gestational age | Normal indicators |
| 1st trimester | Up to 110 beats/min. at rest, during physical activity 120-140 beats/min. Average value 70-95 beats/min. |
| 2nd trimester | Up to 120 beats/min. Average value 100 beats/min. |
| 3rd trimester | Up to 120 beats/min. The average value is 110-115 beats/min. |
Heart rate monitoring
Reasons for high values
The interpretation of a normal indicator during pregnancy, as can be seen from the table, implies its slight fluctuations down or up. The only condition is that the woman does not feel bad. In general, a slightly elevated heart rate while feeling normal is normal during pregnancy. Already from the first trimester, it is higher than it was before conception by about 10-15 beats/minute. The above data will help you determine pregnancy by pulse.
The reasons for a high rate (tachycardia) during pregnancy may be:
- stress;
- physical activity, including physical education;
- unbalanced or poor nutrition;
- growth of hormones in the blood;
- passion for caffeine-containing products;
- smoking and addiction to alcoholic beverages (including before conception);
- lying on your back (for example, at night while sleeping, that is, for a long time).
Heart rate fluctuations during pregnancy are not that uncommon. But if we are talking about a high heart rate during pregnancy in the 3rd trimester, it will not be possible to avoid medical recommendations. In this case, many women are offered to lie down for preservation. The same applies to low blood pressure and at the same time high pulse, and during pregnancy at any stage.
Tachycardia requires an immediate visit to a doctor; self-medication is unacceptable and is fraught with adverse consequences for the mother and fetus. A specialist will much more quickly determine the reason why the heartbeat has increased and offer the best solution to normalize it. Not all women will need to take special medications; the following simple recommendations can help many:
- spend more time outdoors, especially in parks or outside the city;
- eat foods high in potassium and magnesium (dried fruits, nuts, champignons, cereals, many green vegetables, root vegetables);
- sleep at least 8 hours at night;
- avoid overwork;
- do not abuse sweets, do not overeat.
What can you do right at the moment when you feel unwell?
- Breathe deeply and slowly.
- Drink a glass of still drinking water in small sips.
- Take a horizontal position, try to relax.
In the second and third trimester, a heart rate of 110 beats per minute is considered normal during pregnancy.
We measure it ourselves within a minute
Why was the rate lowered?
A low heart rate is usually found in athletic mothers, as their hearts are accustomed to heavy loads. But pathologies are also quite possible. For example:
- a woman expecting a replenishment may have problems with the thyroid gland;
- her liver or kidneys are unhealthy;
- there are problems with the central nervous system (CNS);
- the heart or blood vessels are not in order.
Look for a middle ground. The smartest thing is not to overload the body, monitor nutrition, dose both physical and emotional stress, and strive for a pulse of at least 70 and no more than 100 beats per minute during pregnancy.
Low pulse (bradycardia) in expectant mothers is a rare occurrence, but it will be impossible not to pay attention to it, since frequent dizziness (even fainting), weakness and nausea will immediately cause a visit to the clinic.
Basic therapy methods
Complex cases are examined by a cardiologist, but if the symptoms of bradycardia are not very pronounced, then the doctor monitoring the course of the “interesting situation” will limit himself to general advice and recommend:
- rationally organize the work and rest schedule;
- do not skimp on a balanced diet;
- do special gymnastics for pregnant women, but do not overdo it with physical activity;
- walk in the fresh air more often (between longer and more often, give preference to the first option).
You cannot use medications that normalize a rapid pulse on your own - this can harm the fetus. If the cause of tachycardia is emotional stress, the doctor will prescribe soothing herbal teas. Among them may be valerian, mint, lemon balm, motherwort. Sedatives that are suitable for this situation are Novo-passit, Persen.
If there are contraindications to taking the above drugs, the doctor will recommend a tincture of valerian or motherwort, which should be taken 20-30 drops 3-4 times a day. The duration of therapy will be determined by your doctor depending on your condition.
Treatment of tachycardia
If a more severe pathology is observed, the decision on treatment is made by the gynecologist together with the cardiologist. They draw up a therapy protocol that should maintain the health of the expectant mother.
Negative consequences of this problem.
- For women whose pulse is not normal in the 3rd trimester, a cesarean section is contraindicated. Sometimes, for certain indications, it is necessary, then the birth process takes place under the strict supervision of a cardiologist.
- If the pulse is constantly increased during pregnancy, this may indicate the development of tachycardia. Then the expectant mother will feel dizzy, lack of oxygen, and fainting. Such violations do not have the best effect on the development of the child.
- In expectant mothers who suffer from tachycardia, the fetus experiences oxygen deficiency, which can lead to growth retardation. The child is born prematurely, with low weight, and sometimes with symptoms of hypoxia.
- A diagnosis of hypoxia threatens intrauterine growth retardation, nervous system abnormalities, and in the early stages – the development of brain disorders in the baby.
You might be interested in these articles:
Attention!
The information published on the website is for informational purposes only and is intended for informational purposes only. Site visitors should not use them as medical advice! The site editors do not recommend self-medication. Determining the diagnosis and choosing a treatment method remains the exclusive prerogative of your attending physician! Remember that only complete diagnosis and therapy under the supervision of a doctor will help you completely get rid of the disease!
In medicine, there are many types of pulse, and there are also different characteristics (rhythmic/arrhythmic, high/low amplitude, and so on). But most often, when they talk about pulse, they mean heart rate (HR). This value can change under the influence of a large variety of external and internal factors. In particular, the heart rate of children is always slightly higher than that of adults, because they still have a small heart. But for athletes it’s the other way around: a trained heart muscle is able to pump the same volume of blood while making fewer contractions.
The work of the cardiovascular system also has its own characteristics during the period of bearing a child. The normal pulse rate for pregnant women may differ from that accepted for adolescents and adults. But, firstly, not much, and secondly, the expectant mother should feel good about it. Otherwise, you will have to look for the cause of the violation.