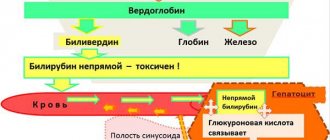
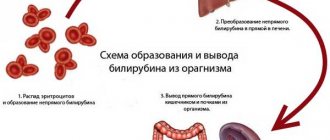
Bilirubin is one of the most important components of bile, formed as a result of the breakdown of heme-containing proteins (hemoglobin, cytochrome and myoglobin). There are two types of this pigment - indirect and direct (conjugated). The first is formed after the destruction of non-viable red blood cells. Then, with the blood flow, it enters the liver, where, due to the action of enzymes, it is converted into a direct one.
An increase in the level of bilirubin indicates a violation of its excretion from the body or excessive destruction of red blood cells, which can lead to serious malfunctions in the functioning of organs and systems.
Normal pigment content in blood
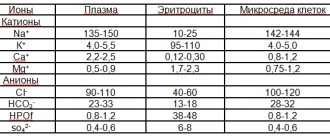
In the body of an adult, the content of total bilirubin should not exceed 20.5 µmol/l: up to 5.1 - indirect and up to 16.5 µmol/l - direct. In children older than one month, this indicator is no more than 19.5 µmol/l: 4.5 - indirect and 15.0 - indirect. If the values deviate from the norm, serious diseases can occur - hepatitis, hemolytic anemia, vasculitis, coronary heart disease.
Norm of bilirubin in blood by age:
| Age | Total bilirubin , µmol/l | Indirect bilirubin, µmol/l | Direct bilirubin, µmol/l |
| Newborns, 1st day of life | 24,1 | 9,6 | 14,5 |
| 2-5th day of life | 54,4-89,5 | 7,0-8,9 | 45,5-82,3 |
| 6-14th day of life | 52,5-70,4 | 7,1-8,2 | 44,3-63,3 |
| 1 month | 9,3-19,5 | 2,6-9,1 | 6,7-10,4 |
| Over 1 month and adults | 3,3-20,5 | 1,4-5,1 | 1,9-16,5 |
Can bilirubin be too low?
Usually no, except in exceptional cases. For example, the cause of low bilirubin may be taking certain groups of medications that affect the state of the blood, as well as pregnancy. Low bilirubin is normal in the first or second trimester of pregnancy. It should be noted that such values in this case do not pose a health hazard.
Reasons for increasing the amount of pigment
The most common causes of a sharp increase in the level of total bilirubin in the blood are pathologies of the circulatory system, accelerated destruction or excess content of red blood cells, impaired outflow of bile, blockage of the bile ducts or liver diseases, and diabetes.
The amount of pigment may increase with congenital or acquired anemia, the presence of helminths in the body, poisoning by fungi and toxins, and a lack of cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12).
In addition, long-term use of broad-spectrum antibiotics has a negative effect on the breakdown of heme-containing proteins.
Hyperbilirubinemia is the main manifestation of Gilbert's syndrome. This is a congenital disease characterized by the accumulation of lipofuscin pigment in hepatocytes, resulting in an increase in the level of unconjugated bilirubin fraction.
It is normal for women to increase bilirubin levels during ovulation or during sudden climate change. This usually manifests itself in the fact that a woman wants sweets.
If bilirubin is elevated
Problems with the liver or gall bladder can be seen visually if you feel your body well. Problems that should be addressed may include:
- sudden vertical wrinkles between the eyebrows,
- spots (in most cases brown or green) especially on the right side of the face or in the temporal part,
- a feeling of oily skin on the forehead,
- the appearance of baldness (especially the central part of the head in both men and women) or gray hair,
- occurrence of vision problems,
- causeless inflammation of the gums and throat,
- problems with stool.
All these manifestations may indicate problems with the removal of bilirubin and literally call for a visit to the doctor and a general blood test.
So, you saw in the test results that bilirubin is indeed elevated. It should be understood that the fraction of unconjugated bilirubin may indicate liver failure or may be associated with Gilbert's syndrome.
An increased level of direct (bound) bilirubin is most often associated with disease of the biliary tract, which indicates a violation of the outflow of bile.
But in the primary results we are given a total value, based on which it is impossible to make an assumption. It is important here whether you know your disease, in which bilirubin may increase, or whether this is news to you.
If this is the first time, then you should not wait or try to reduce bilirubin at home - this can lead to irreparable consequences. Visit your doctor and have him prescribe an in-depth examination. Be guided by the fact that this is necessary first of all for you, and not for the doctor.
If you know of a disease that can increase bilirubin, you should:
- start taking medications for a disease you know (this means an exacerbation has occurred). Most often, such diseases include hepatitis or hemolytic anemia.
- start taking medications or dietary supplements that will help normalize liver function: hepatrin,
- phenobarbital (0.05 - 0.2 g per day for 2 - 4 weeks),
- zixorine (0.05 - 0.2 g per day for 2 - 4 weeks),
- essentiale,
- you can even try Detralex (read about clinical trials of Detralex in the Pyatigorsk branch of Volga State Medical University in comparison with Karsil),
- hepatoprotectors.
How to quickly lower bilirubin levels at home?
Before reducing the amount of pigment and taking medications to normalize its level, you need to find out the etiology of its increase. To do this, it is necessary to conduct additional examination.
Based on the results obtained and the reason why the pigment increases, different treatment regimens are prescribed. These may include taking medications that support the liver, folk remedies and diet.
If excess bilirubin levels are detected, you should contact a specialist to develop a treatment regimen. Only a thorough medical diagnosis and compliance with the doctor’s recommendations will help normalize pigment levels and stabilize the body’s functioning. If left untreated, the condition may worsen, leading to serious consequences.
Treatment with medications
One of the main links in the treatment of hyperbilirubinemia is the use of medications.
Synthetic drugs
The most commonly prescribed treatment is infusion therapy. It involves intravenous injection of medical solutions into the bloodstream. Once in the blood, they are able to flush out excess bilirubin, reducing intoxication.
For this purpose, use:
- saline solution (NaCl 0.9%);
- glucose solution 5%;
- rheosorbilact.
Effective is the use of activated carbon, sorbents and gels that remove toxins and cleanse the body. These include:
- Absorbent;
- Enterosgel.
Semi-synthetic drugs
The main components of these drugs are turmeric and field artichoke. The most important properties of these medications include the ability to improve liver function, stimulate the production and normal flow of bile, cleanse the body of toxins and remove them.
The following drugs are prescribed:
| Name | Effect |
| Hofitol | With its help, the outflow of bile increases, microcirculation improves, and redox reactions in the liver are accelerated. |
| Artichoke extract | The product contains phenolic compounds of cynarin, which normalize the metabolic processes of the gallbladder. The body gets rid of toxic compounds, and bilirubin levels normalize |
| Holyver | The drug is able to have a choleretic effect due to the presence of medical bile, normalizes the formation of direct bilirubin |
Preparations based on herbal ingredients
To maintain the functioning of the liver during the treatment period, products made from natural ingredients are used: milk thistle extract, Karsil.
The following drugs are used:
| Name | Indications and effect |
| Silibinin | When using the drug, the production of bile is normalized, and heavy metals and harmful compounds are removed from the body along with it. This helps detoxify the body and reduce bilirubin levels |
| Silibor | The drug is used in the treatment of hepatitis and its complications. Helps normalize the functioning of the liver and biliary tract, has an antioxidant effect, stimulates cellular protein synthesis, normalizes the metabolism of hepatic phospholipids |
| Silymarin-Hexal | The product accelerates recovery processes in the liver and improves microcirculation processes. The flavone molecules included in the drug act as antagonists of hepatotoxic substances and stimulate the neutralization of indirect bilirubin in the liver |
A complex of drugs for various liver diseases
If the disease is inflammatory in nature, it is advisable to take the following medications:
- antiviral;
- enzymatic (pancreatin, Mezim, Festal);
- immunomodulatory (interferon preparations);
- antibacterial (cephalosporins, aminoglycosides, fluoroquinolones);
- hepatoprotectors (Bicyclol, Darsil).
When pathology occurs due to hepatitis, the main treatment is aimed at combating the virus itself and the complications of the disease. At the same time, the patient is prescribed drugs that protect the liver. If treatment of the hepatitis itself is successful, after stabilization of liver function, bilirubin levels gradually return to normal.
If the cause is a hereditary predisposition, then treatment should include vitamins and medications that lower the level of bilirubin in the blood. For Gilbert's syndrome, phenobarbital and Zixorin are used. Course duration is from 15 to 31 days. Patients are also prescribed Ursosan in short courses of 7-10 days 3 times a year. The drug has the ability to change the composition of bile, eliminating the risk of stone formation, which is important when bilirubin levels regularly increase.
To prescribe therapy, you should consult a specialist, since self-treatment with medications can cause a number of side effects.
Folk remedies
To normalize bilirubin levels at home, with a slight increase, decoctions of medicinal herbs can be used. Folk remedies should be used only after consultation with your doctor and in addition to drug treatment.
The most common recipes are the following:
- Infusion of motherwort herb . Take 20 grams of dried leaves and pour 250 milliliters of boiling water. Leave to infuse for a day. Take 3 tablespoons on an empty stomach half an hour before meals.
- Herbal collection . Mix motherwort herb, chamomile, corn silk, and birch leaves in equal parts in a large container. Brew 2 tablespoons of the resulting mixture in 200 milliliters of boiling water. Leave for 40-60 minutes. Drink 20 minutes before meals 2 times a day.
- Beetroot juice . Wash and peel one medium-sized root vegetable. Squeeze out the juice using a juicer. Take in the morning before breakfast.
- St. John's wort decoction . Brew 2 heaping tablespoons of dry herb with 250 milliliters of boiling water. Drink one half in the morning 15 minutes before meals, the second in the evening an hour before bed.
You can add mint, rose hips, ginseng tincture, aralia leaves, and lemongrass to these recipes.
How can you reduce it?
Before using methods to lower bilirubin in the blood, it is necessary to find out the reason for its increase. Some diseases accompanied by a similar symptom require complex treatment. If you lower bilirubin and do not take measures to treat existing diseases, the concentration of the substance will increase again after a short period of time, and the pathologies will progress.
Medicines
Drugs to reduce the level of bilirubin in the blood should be selected by a specialist depending on the clinical picture of the patient’s health condition. Medicines are necessary to treat diseases that provoke an increase in the substance. Taking any medication must be combined with a special diet and supplemented with traditional medicine or herbal medicine recipes.
Examples of drugs to reduce bilirubin levels in the blood:
- adsorbents (activated carbon, Enterosgel);
- choleretic drugs (Allohol, Chofitol);
- antibiotics (Diazepam, Furazepam);
- hepatoprotectors (Pancreatin);
- drugs to protect the liver (Karsil);
- drugs for digestion (Festal, Mezim).
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine recipes can be used as a complement to the main treatment of diseases that cause increased bilirubin in the blood.
Natural components have a beneficial effect on blood vessels and the circulatory system as a whole. You can use folk remedies not only if there are abnormalities in tests, but also to prevent violations of bilirubin concentration.
The following recipes will help reduce bilirubin in the blood in adults and children:
- corn silk (pour one teaspoon of the ingredient into a glass of boiling water, leave for half an hour, it is recommended to take the product on an empty stomach, 50 ml);
- beetroot juice (you should take one third of a glass twice a day before meals, the product has a diuretic effect and reduces bilirubin well);
- motherwort (pour one teaspoon of the dry ingredient into a glass of boiling water and leave for twenty minutes, take the product on an empty stomach every day for two weeks);
- herbal mixture of chamomile, motherwort and St. John's wort (mix the ingredients in equal quantities, pour a tablespoon of the mixture with a glass of boiling water, leave the broth for half an hour, take half a glass twice a day twenty minutes before eating);
- birch leaves (pour one tablespoon of the ingredient into a glass of boiling water, leave for half an hour, strain the infusion before use, take it before bed for a week).
Medicinal herbs
A good way to reduce bilirubin are decoctions of medicinal herbs. They are prepared according to the traditional method. One or two teaspoons of the dry mixture should be poured with a glass of boiling water. The product must be infused for at least twenty minutes, after which it can be used once or several times a day. The components can be combined with each other. If you take a decoction of several medicinal herbs, its effectiveness will increase.
The following types of herbs are used to reduce bilirubin:
- chamomile;
- peppermint;
- St. John's wort;
- calendula;
- rose hip;
- chicory;
- oregano;
- tansy;
- milk thistle;
- motherwort.
Therapeutic diet
A special diet is a mandatory addition to any method of reducing bilirubin in the blood. Junk food must be excluded from the diet. During therapy, you should not eat sweets, flour products, carbonated and alcoholic drinks. Alcohol, coffee, smoked foods, citrus fruits, mushrooms, radishes and spicy seasonings are forbidden foods. Food dyes should be completely eliminated from the diet.
What can you eat if you have high bilirubin:
- fruits (especially sweet varieties);
- vegetable soups;
- buckwheat, rolled oats and rice porridge;
- milk products;
- herbal decoctions;
- compotes, jelly and juices;
- lean meat and fish.
It is recommended to eat food in small portions, but up to six times a day. It is better to prepare dishes by boiling, baking or steaming. Hot spices and seasonings should not be used. Fried and fatty foods are excluded from the diet. The daily menu should contain a sufficient amount of vegetables and fruits. Products containing food additives or colorings are prohibited.
Sample menu for the day:
- breakfast - boiled rice, banana;
- second breakfast - apple, glass of freshly squeezed juice;
- lunch - buckwheat soup, carrot pancakes, boiled chicken;
- afternoon snack - cottage cheese casserole;
- dinner - homemade noodles, baked fish;
- before bed - persimmon, a glass of kefir.
To prevent an increase in bilirubin in the blood, it is recommended to take preventive measures. If the concentration of a substance has increased, then the cause of this condition must be clarified. Under no circumstances should symptoms that appear be ignored. Therapy should be comprehensive and include not only traditional methods of treatment, but also additional ones. These include proper nutrition, a healthy lifestyle and regular exercise.
Diet to lower the level of bilirubin in the blood
In addition to medications and alternative medicine, you can quickly lower the level of bilirubin in the blood with the help of proper nutrition. Healthy food can have a positive effect on the functioning of the liver, removing excess load from it and normalizing metabolic processes. During treatment, it is necessary to limit or eliminate foods that may cause disruption of its functioning. To do this, you need to follow a specially designed diet.
Prohibited Products
You should stop eating the following foods:
- salt - you can use a moderate amount of spices when preparing dishes, but salting food is strictly prohibited;
- citrus fruits and berries - fruits with a high acid content should not be consumed;
- mushrooms;
- fatty foods - you should limit the consumption of fried and smoked foods, as they are difficult to digest and lead to overload of the liver;
- alcohol;
- radish, hot pepper, mustard;
- canned food and salted caviar;
- high fat dairy products: cream;
- chocolate.
It is necessary to avoid products containing preservatives, food additives, dyes and leavening agents.
Healthy foods
Patients with hyperbilirubinemia are recommended to consume foods high in fiber, protein and vitamins. These include:
- low-fat dairy products;
- grains and cereals;
- dietary meat (chicken, turkey, veal);
- vegetables and non-acidic fruits;
- olive and linseed oil;
- seafood;
- green tea, mineral waters.
The consumption of some products is limited and depends on the method of their preparation:
| Product name | Recommended | Not recommended |
| Meat products and meat | Boiled or baked meat (veal, chicken), steamed cutlets, meatballs, diet sausages | Fatty meat (pork, lamb), smoked sausages, stewed meat |
| Fish | Baked, jellied fish | Smoked fish, canned food, cod liver |
| Eggs | Boiled eggs | Raw eggs |
| Dairy and fermented milk products | Low-fat cottage cheese, kefir and milk, hard mild cheese, sour cream | Cream, butter, sharp cheeses |
| Vegetables | Carrots, greens, zucchini, cucumbers, cabbage, potatoes, pumpkin, beets - fresh, as well as boiled or steamed | Garlic, radishes, fresh onions, sorrel, sauerkraut, pickles |
| Soups | Uncooked, with vegetable or fish broths | Rich meat broths, okroshka, solyanka |
| Fruits and berries | Apples, pears, melons, bananas, peaches, sour berries, watermelon, dried apricots, prunes, raisins | Sour and unripe fruits and berries, nuts in large quantities |
| Sweets | Honey, jam, pastille, marmalade, marshmallows | Ice cream, chocolate, confectionery |
General diet rules
To facilitate the body's work and reduce bilirubin levels in the blood, you should carefully plan your diet. To do this, you must follow some principles of a balanced diet:
- Fractional meals . It is recommended to eat 4-5 times a day, and the portion should be small. In this way, it will be possible to reduce the load on the organs during the processing of substances and their transport throughout the body.
- Diversity. The intake of a complex of nutrients into the body helps reduce bilirubin. To do this, you need to eat a variety of foods rich in microelements, proteins and vitamins.
- Choosing the right cooking method . It is recommended to steam, bake or boil food.
- Drinking fluids. You need to drink 2-2.5 liters of water per day. Plain water can be replaced with tea or compote without adding sugar.
The use of preparations will simplify the diet. You can freeze some foods or make preparations to simplify the cooking process.
Indicative menu for one day
Breakfast:
- steamed chicken cutlets;
- mashed potatoes;
- green tea.
Lunch:
- banana or low-fat cottage cheese;
- glass of water.
Dinner:
- oat bread;
- boiled egg;
- tomato and olive oil salad;
- rosehip decoction.
Afternoon snack:
- crackers without salt;
- honey;
- a glass of low-fat kefir or milk.
Dinner:
- boiled fish (hake, pollock);
- cucumber and Chinese cabbage salad;
- unsweetened dried fruit compote.
Treatment
The method of reducing high bilirubin for each individual case is different. Some patients are prescribed a light diet, while others need to take medications. Treatment methods depend on the cause of high bilirubin, which led to an elevated level of the substance.
Enzyme preparations
The reason is a violation of the processes of bile outflow. Treatment of bilirubin includes taking medications that have a choleretic effect. If a hereditary factor is present, it is necessary to carry out complex treatment, which consists of diet, vitamins and medications.
When elevated levels of bilirubin in the blood are caused by infectious liver diseases, treatment is carried out with medications that have antiviral and antibacterial effects that stimulate the immune system.
If Gilbert's syndrome develops, the patient is prescribed medications such as Zixorin and Phenobarbital. The course, depending on the complexity of the process, ranges from two weeks to one month. The patient's condition is alleviated by taking enzyme preparations - Mezim, Festal and Pancreatin.
Balancing the level of bilirubin is possible with folk remedies, for example, milk thistle decoction. In most cases, medications with natural ingredients are used - Karsil, Essentiale Forte. To speed up the process of removing substances from the body, adsorbents are used.
Features of treatment for different categories of people
Throughout life, the level of bilirubin in the blood can change slightly. Each age has its own specificity in the processes of formation and accumulation of this pigment.
Based on this, it is necessary to choose specific treatment tactics to eliminate hyperbilirubinemia.
Children
In newborns this figure is increased several times. This occurs due to increased destruction of fetal hemoglobin in the first days after birth. However, already at the end of the first month it decreases and becomes close to the norm of an adult. That is why, at first, doctors recommend monitoring the physiological decrease in bilirubin levels in the body. If there is no normalization of pigment indicators by the end of the first month of life, treatment should be prescribed.
In the case of hyperbilirubinemia in children from one month of age, it is necessary to reduce the level of pigment by prescribing medications, eliminating antibiotics and hepatotoxic substances. To do this, it is necessary to use products containing natural ingredients, decoctions of medicinal herbs and vitamins prescribed by a doctor.
Women during pregnancy
A slight increase in this indicator may occur in women in the last trimester. However, this is not a sign of a disorder and does not affect the fetus or the mother’s body. This is due to the increased load experienced by the expectant mother’s liver.
When prescribing treatment to reduce pigment levels in pregnant women, preference should be given to herbs that do not have a negative effect on the fetus, avoiding synthetic drugs. The treatment regimen is determined by the doctor.
The second important aspect is diet.
Adults
Treatment of adult men and women suffering from disorders of bilirubin metabolism in the body should be comprehensive: etiological, pathogenetic and symptomatic.
Etiological includes identifying the causes of violations and their elimination. The goal of pathogenetic treatment is to influence pathological processes and inflammatory reactions leading to pathology. Symptomatic therapy involves eliminating individual signs of the disease. For this purpose, a complex of medications and a balanced diet is used. This will remove excess bilirubin from the body and normalize its conversion in the liver.
If the condition of hyperbilirubinemia is not critical and poses a danger to the patient, then the doctor may prescribe treatment, which consists of two phases: medication and dietary.
The pigment indicator is a reflection of the work of the whole organism. If the processes of cleansing and ridding the body of toxins cannot proceed at the proper level, this can lead to serious consequences. A timely examination and identification of abnormalities will allow timely treatment to begin. Therefore, if you have symptoms of increased bilirubin levels, it is recommended to consult a doctor immediately.
Consequences of increased bilirubin
An increased level of pigment is the initial stage of intoxication of the body. Harmful substances have a negative impact on all systems and organs. The cardiovascular system, brain, and kidneys, which have an increased burden of neutralizing toxic substances, come under attack.
As a result, liver and kidney failure are diagnosed, which leads to the development of severe diseases, including death.
The risk group includes the following categories:
- Newborn children with completely unformed internal organs that cannot cope with increased loads;
- Pregnant women;
- Patients with chronic diseases of many systems and organs who have undergone surgery or treatment with potent medications.
Patients at risk should pay attention to liver function and be able to quickly take measures to reduce the concentration of bilirubin in the blood.
Alternative medicine
Before asking yourself how to lower bilirubin in the blood using folk remedies, you should consult your doctor. Alternative medicine can only be a complement to traditional drug treatment. Among the popular grandmother's recipes are the following:
- Motherwort herb tincture reduces bilirubin. 20 grams of dry leaves are poured into 250 ml. boiling water and leave for 24 hours. Take 3 tablespoons in the morning before breakfast.
- Beetroot juice. Fresh root vegetables are washed, peeled and fresh juice is prepared using a juicer. 1/3 cup is enough, taken on an empty stomach.
- Herbal collection. Mix 1 pack of motherwort herb, corn silk, chamomile and birch leaves in a dry container. 2 tbsp. spoons of the resulting mixture are brewed with 200 ml of boiling water for at least 30 minutes. Take before meals 2 times a day. Each time you should prepare a fresh decoction.
The optimal treatment is a combination of medication and grandmother's methods proven over the years. Pharmacies offer a wide selection of herbs with detailed instructions for use. Your doctor will tell you how to lower bilirubin using folk remedies, combining them with taking medications.
Exceeding the normal bilirubin level is a serious metabolic disorder. Only a complete medical examination, blood test, correct diagnosis and compliance with the doctor’s recommendations will help maintain health. If left untreated, pigment levels will continue to increase, which can lead to serious consequences.