Types of violations
Extrasystolic arrhythmia, depending on the causes that caused it, can be functional, organic or toxic.
Functional occurs in healthy people under the influence of changes in the body or external factors. Organic manifests itself as a result of pathologies of the cardiovascular system. Toxic is the body’s reaction to the effects of drugs and to a malfunction of the thyroid gland. Enter your pressure
Move the sliders
- Atrial: occurs due to damage to the heart. Characterized by atrial contractions. It has a favorable course.
- Ventricular: occurs in different parts of the heart muscle. With single fluctuations, the condition does not pose a danger. As the pulsation increases, the patient’s well-being worsens and treatment is required.
- Atrioventricular: develops in the tissue between the atria and ventricles of the heart.
Based on pulsation frequency, the following types are distinguished:
- rare - less than 5 beats per minute;
- medium - from 6 to 15 blows;
- frequent - more than 15 strokes.
Types of arrhythmia
The following types of extrasystolic arrhythmia are distinguished:
- Benign. This pathology is characterized by the absence of organic lesions of the heart muscle. Sudden cardiac arrest does not threaten patients.
- Potentially malignant. This pathology is characterized by initial hemodynamic disorders. Some organic changes occur in the heart. There is a risk of cardiac arrest.
- Malignant. This pathology is characterized by serious damage to cardiac tissue and severe hemodynamic disorders. The risk of mortality is very high.
Depending on the location of the additional source of excitation, the following are distinguished:
- Ventricular extrasystoles. This pathology is the most common.
- Atrial extrasystoles. This pathology is recorded in 25% of patients.
- Atrioventricular extrasystoles. This pathology occurs in 10% of cases.
general information
One of the most common heart diseases is extrasystole. This term refers to disturbances in the rhythm of the heart muscle, in which it contracts prematurely.
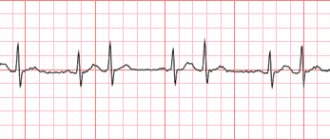
It is very easy to identify this disease using an ECG, which shows rapid or premature extrasystolic complex.
In general, a premature complex can be either extrasystolic or parasystolic. The fact is that extrasystoles and parasystoles are integral attributes of the work of the main muscle in the body, and the treatment of disturbances in their rhythm is absolutely the same.
It is worth saying that none of the researchers classifies extrasystole as a dangerous ailment of the heart muscle.
Campbell and other world-famous cardiologists view it primarily as a “cosmetic” heart failure, which does not in any way affect the quality of this work.
However, if extrasystole is frequent, and symptoms of tachycardia, “jogging” of the rhythm are also noticed, then this should definitely become a reason for examination so that doctors can clearly understand the cause of such a disorder.
After all, the symptoms of this disease may hide much more significant and dangerous ones, so an examination must be scheduled and completed without fail.
Symptoms that can lead to therapy for extrasystole are:
- Hemodynamic disorders that are caused by an uneven rhythm of the heart muscle.
- A person’s own feelings when he himself feels instability of the heart rhythm, which brings discomfort.
- Upon examination: structural changes, as well as deterioration of the myocardium, which can lead to very serious consequences without medical intervention.
What to do during an attack?
If symptoms persist for a long time, you should call an ambulance
An attack of arrhythmia cannot be tolerated. First of all, you should calm down and take a few deep breaths and exhalations. If such a simple technique does not bring your heart rate back to normal, you need to take a tablet of the drug recommended by your doctor for such cases.
If an attack of extrasystolic arrhythmia does not go away within 24 hours, you need to call an ambulance at home.
Causes and risk groups
Extrasystolic arrhythmia can manifest itself as a reaction to external influences and internal disturbances in the body. Patients with pathology of the cardiovascular system are at risk for developing pulsation failures. The main causes of heart rhythm disturbances are described in the table.
| Kinds | Causes |
| Functional |
|
| Toxic |
|
The formation of heartbeat failures is also affected by diseases of organs and systems: malignant processes, hepatitis, viral and bacterial infections, pathologies of the intestines, esophagus, gall bladder, gynecological and urological diseases. After the underlying disease is cured, the pulsation returns to normal.
Diagnosis of the disease
The main type of diagnosis is an ECG study. But it is informative only for frequently occurring extrasystolic arrhythmia. Holter study (daily ECG monitoring) allows you to obtain a much larger amount of information. Because in this case, the device records all heart rate disturbances that occur throughout the day, including at night.
An oral interview with the patient is required, including the collection of information such as:
- Do your immediate family members have cardiovascular diseases?
- usual daily routine;
- bad habits;
- general psycho-emotional state.
Listening to the heart allows the doctor to hear premature 1st and 2nd heart sounds. The first (louder tone) indicates incomplete filling of the ventricles with blood, and the second (more dull) indicates insufficient blood flow into the pulmonary artery and aorta.
Palpation of the radial artery also allows you to feel a wave, followed by a slight delay in the pulse. This is a sign that during contraction the blood did not completely fill the ventricle.
Additionally, the following may be prescribed:
- MRI;
- EchoCG;
- Ultrasound examination of the chest.
Prevalence and features
Extrasystole can be recorded in absolutely anyone, even a healthy one, so such a disruption does not necessarily require medical intervention.
Most people encounter this heart rhythm disorder, but do not even realize it, because no significant symptoms other than minor disturbances appear during a cardiogram.
There is a certain norm at which the number of extrasystoles per day is not considered dangerous: up to 200.
If fewer of them are registered, then the person is most likely absolutely healthy. After all, the human heart, like any other organ, cannot work with standard stability.
If less than 300 extrasystoles are recorded per hour, then according to the classification of medical researchers Wolf and Lown, extrasystoles are considered rare, but if more, then frequent.
At the same time, in no case should it be confused with tachycardia. It is possible to distinguish these diseases without any problems if you have an ECG device.
As a rule, extrasystoles are either single or double (paired). If there are 3 or more extrasystoles in a row, then this disease is already called tachycardia and requires more decisive therapy. With tachycardia, a significant malfunction of the heart muscle is noticed, in which it works unevenly and unstable.
Previously, doctors believed that children mainly experienced ventricular arrhythmia. But the results of modern research prove that all types of extrasystoles occur with almost identical frequency. The reason for this phenomenon is quite simple: the child’s body is rapidly growing and developing, the heart cannot cope with the additional functional load, so it begins to compensate for the “lag” with extrasystoles.
As a rule, as soon as the period of active growth ends, the arrhythmia disappears without drug intervention.
Why is extrasystole dangerous in children: this pathological phenomenon can be a consequence of various pathologies of the thyroid gland, lungs, and myocardium. At the same time, small patients complain of the same symptoms as adults - frequent dizziness, weakness, cardiac “shocks” in the chest. Important: drug treatment of ventricular arrhythmia is indicated only when the daily number of extrasystoles reaches 15,000 (children are prescribed metabolic, antiarrhythmic therapy). Such patients must be registered at the dispensary and comprehensively examined at least once a year.
Classification of ZhES
Systolic arrhythmia, depending on the number of sources of impulses and heart rate, is divided into:
- polytopic (several ectopic sources);
- monotopic (one source of cardiac impulses).
According to the daily results of ECG monitoring, 6 types of PVCs are distinguished:
- 0 class. VES is not observed.
- 1 class. About 30 single heart impulses are recorded in one hour.
- 2nd grade. More than 30 frequent single heart impulses are recorded in one hour.
- 3rd grade. Several ectopic sources are recorded.
- 4th grade. Paired polytopic or monotopic sources of cardiac impulses are recorded.
- 5th grade. Group ectopic impulses are recorded.
Ventricular arrhythmia is classified by frequency of occurrence:
- frequent – more than 15 pulses per minute;
- average – 5–10 pulses per minute;
- rare - less than 5 pulses per minute.
The frequency of extrasystoles is of great importance
Symptoms of pathology
In some cases, extrasystolic arrhythmia is characterized by an asymptomatic course.
The main symptoms of the pathology include:
- Interruptions in the functioning of the heart. Patients complain of sharp and strong tremors behind the sternum. Such a symptom can cause severe fear, which will lead to tachycardia and increased blood pressure, which will aggravate the patient’s condition.
- Pulse disturbances. It cannot be felt on the radial artery.
- Chest pain.
- Shortness of breath.
- Sweating.
- Anxiety.
- Pale skin.
Clinical manifestations of the pathology may worsen after:
- eating;
- emotional outburst;
- sexual intercourse;
Quite rarely, the disease manifests itself at rest.
In the presence of atherosclerotic changes in the vessels of the brain, patients additionally complain of tinnitus, loss of speech and severe dizziness. In some cases, patients even lose consciousness.
In the absence of adequate therapy, the pathology can cause dangerous complications.
These include:
- ventricular fibrillation;
- complete blockade of the heart muscle;
- heart failure, etc.
All these conditions require urgent treatment. Some require hospitalization and long-term treatment.
Almost 50% of all pregnant women have extrasystole in one form or another. The main reason for this is and will be hormonal changes in a woman’s body. Expectant mothers are very concerned that this problem may cause a contraindication to pregnancy. In fact, there is nothing to be afraid of. Extrasystoles in the heart are normal. It is important that the pregnant woman does not have heart disease.
And to prevent extrasystoles of the heart, it will be enough to ensure a calm environment during pregnancy, not to overwork (physically and emotionally), and to spend more time in the fresh air. Today, medicine has stepped forward and doctors have the opportunity to measure the heart rate of the developing fetus.
If a woman has “simple” extrasystoles, then natural childbirth is not contraindicated for her. But if a woman in labor is diagnosed with an organic heart pathology, then she should be observed by a cardiologist throughout pregnancy, and it is advisable to give birth by cesarean section.
The heart begins to pump less blood. This causes blood flow to slow down.
The main symptoms of heart rhythm disturbances:
- pain, throbbing, tremors in the chest area;
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- increased sweating, hot flashes;
- fluctuations in blood pressure, pulse;
- temperature increase;
- nausea;
- feeling of lack of air;
- anxiety, fear;
- presyncope, fainting.
| Group | Properties and action |
| Beta blockers | Lower blood pressure, block excitation, reduce the force of heart contractions |
| Glycosides | Regulate pulsation, improve conductivity, nutrition |
| Antiarrhythmic | Reduce excitability, normalize pulsation |
| Potassium, magnesium, B vitamins | Improve metabolism |
| Sedatives, anti-anxiety, neuroleptics, tranquilizers | Calm the nervous system, relieve physical and psycho-emotional stress, improve mental activity |
| Ganglioblockers | Reduces the frequency of nerve impulses |
| Diuretics | Helps remove excess fluid, reduce blood pressure, improve blood circulation |
As such, the subjective sensations accompanying extrasystole are not always present. This abnormal phenomenon is tolerated worse by patients with vegetative-vascular dystonia, but patients with organic myocardial lesions experience virtually no changes in their own body.
People who have experienced what extrasystoles are like complain of tremors or beats of the heart muscle (these symptoms are a consequence of increased contraction of the ventricles after a compensatory pause).
Other signs of extraordinary myocardial impulses:
- the so-called turning over or tumbling muscle;
- malfunctions, heart palpitations;
- functional extrasystoles (symptoms: weakness, lethargy, frequent hot flashes, unreasonable anxiety, hyperhidrosis, shortness of breath, a person may not have enough air, deterioration in general well-being).
Treatment of extrasystole
Treatment of extrasystolic disorders depends on the form of the disease. In some cases, extrasystole poses a serious danger to the patient's health. Especially if it occurs after a severe heart attack or is provoked by coronary artery disease.
To treat a patient in a similar condition, the following medications can be used:
- quinidine sulfate;
- procainamide (procainamide);
- alprenolol;
- diuretics;
- propranolol;
- ganglion blockers;
- potassium and magnesium preparations;
- B vitamins
- cardiac glycosides;
- cocarboxylase;
- sedatives.
The choice of a specific drug, the required dose and regimen of its use is determined only by the attending physician.
Surgical intervention.
Complex forms of extrasystole require surgical treatment. The main methods in this case:
- ablation;
- defibrillation.
When performing ablation, the ectopic focus is cauterized using special methods. Defibrillation is necessary to apply an electrical shock to the heart. This helps restore normal cardiac electrical activity.
Mode correction.
With frequent attacks of extrasystole, correction of the regimen is important for the patient. Therefore, the patient is prescribed:
- quiet lifestyle;
- reduction of physical activity and nervous experiences;
- increase in positive emotions;
- gymnastic exercises;
- rejection of bad habits;
- limiting the consumption of salt and foods containing sodium.
After a medicinal course of treatment, patients with a tendency to rapid extrasystole are recommended to undergo a course of maintenance treatment in boarding houses or sanatoriums.
Localization of the disease
Extrasystole as a disease is divided into several types of localization, which have already been listed earlier.
- Ventricular extrasystole occurs due to the appearance in the cardiac ventricles of an independent focus of contraction impulses, which interferes with the normal functioning of the heart muscle.
This disorder is most often observed in men, especially in old age. This disorder of the heart muscle has virtually no symptoms. As with other arrhythmic disorders, patients experience increased heart rate.It is not a threat to the patient’s life, however, with high rates of rhythm disturbance, it requires in-depth examination and subsequent therapy. It should be said that the symptoms and medical indications are the same for any location.
- Supraventricular appears due to arrhythmia caused by independent foci of impulses of the heart muscle, which occurs in the supraventricular region, the atrioventricular septum.
- Atrial is caused by the appearance of foci of electrical impulses of the heart in the atria.
- Atrioventricular occurs due to the occurrence of a lesion in the area of the ventricular-atrial septum.
Irregular heart rhythm causes a slowdown and decrease in blood flow throughout the body, and a lack of oxygen supply to the brain. Subsequently, angina pectoris, fainting, loss of sensation in the limbs, atrial fibrillation, and sudden cardiac arrest develop. Severe complications of cardiac arrhythmias without timely medical care can result in death.
Forecast
Despite possible complications, the prognosis is generally favorable. Drug therapy allows the heart rate to normalize within a month in approximately 90% of cases. However, even after the symptoms have stopped, the patient cannot consider himself completely healthy, so an ECG is mandatory at least twice a year.
Normally, the cardiac cycle consists of alternating periods: systole (contraction) and diastole (relaxation). During diastole of the atria, blood enters them from the vessels, then they contract (systole) and expel the blood into the ventricles. The latter are also filled with blood in diastole from the atria and then expelled during systole into the general circulation.
The contractility of the heart is assessed precisely by its performance during systole, that is, by the ejection fraction. Normally it is 55-70%
Systolic function is the capacity of the heart, assessed by measuring ejection fraction. This indicator is determined using ultrasound diagnostics of the heart. If less than 40% is determined, then they speak of systolic insufficiency
functions, since less than 40% of the blood volume enters the general blood supply. This pathology is also known as heart failure with left ventricular systolic dysfunction. Systolic arrhythmia may also develop; whether this condition is dangerous can only be understood by considering the presented topic in detail.
Video: Cardiac cycle
Treatment methods
To establish a diagnosis, a consultation with a cardiologist is necessary. Based on the examination and collection of complaints, diagnostic measures are prescribed. The following studies are being carried out:
- electrocardiogram: shows the rhythm of pulsation and the work of the heart muscle;
- echocardiogram: evaluates blood circulation, pressure in the pulmonary artery;
- electrocardiography using the Holter method: round-the-clock monitoring of heart function;
- magnetic resonance imaging: condition of the heart, blood vessels;
- coronary angiography: shows blood flow in the arteries of the heart;
- ventriculography: x-ray examination of the heart;
- echocardioscopy: ultrasound examination;
- bicycle ergometry: study of pulsation frequency during physical activity.
The main diagnostic test is an ECG.
To identify common diseases that provoke pulsation failures, the body is diagnosed. Based on the results, the need to consult specialized doctors is determined. Basic diagnostic measures:
- general tests (blood, urine);
- blood chemistry;
- blood test for the presence of infectious diseases (HIV, hepatitis, syphilis);
- chest x-ray;
- ultrasonography.
Sometimes such an illness requires only psychological treatment. It happens that you just need to get a person out of an anxious or depressive state for this illness to go away. To do this, you can contact psychiatrists and psychologists.
You can also be treated with medication. What kind of medicine should I take for extrasystole of the heart for unpleasant symptoms? In this case, the following drugs are used:
- Allapinin, etacizin, which are used for arrhythmia
- Metoprolol, Sotalol, which are adrenaline blockers
- Verapamil is a calcium antagonist drug.
Some do not want to turn to drug treatment methods, preferring folk remedies for cardiac arrhythmia in the form of extrasystole. Here are some recipes for treating cardiac extrasystole:
- Hawthorn tincture 10 drops 3 times a day. To prepare it, pour vodka over the hawthorn and leave for 10 days.
- A mixture of valerian in the same mode. To make it, pour a few teaspoons of this plant into 100 ml of boiling water and cook for 15 minutes. Next, the mixture must be filtered.
When the above remedies are ineffective, you should turn to surgery.
Most often, a special catheter is used for treatment, which is “delivered” through the arteries to the desired part of the heart and from it, using radio frequencies, the impulses necessary for the correct heart rhythm are sent.
Treatment
If you have pathological symptoms, it is recommended to seek medical help, since in the vast majority of cases drug therapy . Self-medication in this case is strictly contraindicated: all medications and dosage are prescribed by a doctor.
If there is no effect from drug treatment, the drug is replaced with an analogue, the doctor selects a treatment regimen until the desired effect is obtained. The use of herbal preparations and plants with calming properties (valerian, lemon balm, peony) also shows high effectiveness. Physiotherapy is used as an additional method of therapy.
The following drugs are used in treatment:
- beta blockers (help with ischemia) - their action is aimed at reducing contractions of the heart muscle, resulting in a decrease in the number of contractions;
- magnesium and potassium preparations are prescribed in cases where the pathology develops against the background of a deficiency of these substances.
If there is no effect from conservative therapy, surgical intervention . The procedure is indicated if there is a serious risk to the health and life of the patient. Most often, traditional surgery is replaced by minimally invasive ablation; as part of the procedure, the damaged area of the myocardium is cauterized. After such an operation, the heart begins to beat at a normal rhythm.
Causes
Extrasystole occurs for various reasons and therefore has various consequences. There are several groups of factors that increase the risk of arrhythmias.
Factors provoking extrasystole:
- Structural heart diseases: coronary heart disease, cardiomyopathy, pericarditis, heart failure, heart defects, heart attack, acute coronary syndromes, ventricular myocardial hypertrophy.
- Extracardiac diseases: defects of the respiratory system, digestive organs, thyroid gland, spine, systemic allergic reactions, neoplastic processes, electrolyte metabolism disorders, arterial hypertension.
- Toxic effects of certain groups of drugs, such as cardiac glycosides, tricyclic antidepressants, glucocorticosteroids, sypatolytics, diuretics. As well as the effect of thyrotoxicosis on the body, intoxication in infectious diseases.
- Reasons of a functional nature are daily stress, psycho-emotional and autonomic disorders, increased physical activity, abuse of alcohol, strong tea, coffee, smoking.
- Idiopathic causes are the spontaneous occurrence of disruptions in the normal heart rhythm of unexplained etiology for no apparent reason.
In addition, it is known that extrasystole progresses with age. It has also been noted that extrasystole occurs more often in the morning and almost never happens at night.
The causes of extrasystole are similar to the causes of many other heart diseases:
- Smoking cigarettes
- Ischemic heart problems
- Abuse of caffeine-containing drinks: coffee, energy drinks, etc.
- Malfunctions of the myocardium
- Heart defect (congenital or acquired)
- Potassium deficiency
- Various disruptions in the activity of the arterial system
Reasons for development
Bad habits and excess weight can cause the development of pathology
The causes of extrasystolic arrhythmia can be divided into organic and functional. Organic causes are any pathologies of the cardiovascular and nervous system. Among them:
- cardiac ischemia;
- myocarditis;
- heart failure;
- mitral valve prolapse;
- arterial hypertension.
There is such a thing as malignant arterial hypertension. This pathology is characterized by a persistent increase in blood pressure and the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment. The danger of this disorder lies in the high risk of developing secondary complications. First of all, hemodynamic parameters are affected. Severe hypertension can provoke the development of extrasystolic arrhythmia.
A pathological process in the ventricles and atria can occur against the background of diabetes mellitus and disturbances in the production of thyroid hormones.
Functional reasons for the development of the disease include:
- excess weight;
- smoking;
- alcoholism;
- stress;
- neurosis;
- VSD;
- long-term medication use.
Arrhythmia caused by functional, rather than organic, pathologies of the heart is called idiopathic extrasystolic arrhythmia, since all of the listed conditions are not the exact causes, but only predispose to the development of cardiac arrhythmias.
Symptoms and first signs
Common symptoms of extrasystole are the following:
- Sense of anxiety
- Insomnia
- Dizziness and weakness
- Palpable arrhythmia that the patient himself feels: “fading”, acceleration
- Increased sweat production
It should be said that these symptoms are common to many heart diseases, so the easiest way to identify them is with an ECG.
Extrasystolic arrhythmia develops for a number of reasons.
Among them:
- heart failure;
- acquired or congenital heart defects;
- myocarditis;
- cardiomyopathy.
The following factors can provoke the development of pathology:
- Taking certain medications (glycosides, diuretics and sympathomimetics). Thus, diuretics help remove potassium from the body, which is necessary for the proper functioning of the heart muscle. Glycosides can provoke tachycardia and atrial fibrillation. Sympathomimetics not only increase blood pressure, but also lead to stimulation of the central nervous system.
- Diabetes.
- Abuse of nicotine and alcohol.
- Pathologies of the adrenal glands.
- Hyperfunction of the thyroid gland.
- Overvoltage and stress.
Often the disease actively manifests itself in pregnant women. This is due to the fact that there is a double load on the heart and circulatory system. At the same time, hormonal changes occur. Arrhythmia does not pose a danger to mother and child. After childbirth it is easily eliminated.
Treatment of extrasystolic arrhythmia of a functional and toxic nature consists of eliminating provoking factors and changing lifestyle. Key recommendations include:
- normalization of the daily routine;
- nutrition correction, dieting;
- connection of feasible physical activity;
- eliminating bad habits;
- replacing medications that cause side effects;
- stabilization of the psycho-emotional state.
Treatment of pathology with medication is necessary for the following conditions:
- coronary disease, atrial fibrillation;
- persistent pain, constant poor health of the patient;
- ventricular extrasystole, sinus arrhythmia;
- after myocardial infarction;
- with severe circulatory failure.
In most cases, symptoms of extrasystole are absent, especially if additional myocardial contractions are isolated and do not occur often.
Clinically significant manifestations of the disease include:
- feeling that the heart muscle is working intermittently;
- pronounced or increased heartbeats;
- feeling of cardiac arrest;
- heart sinking;
- a feeling that something has turned over in the chest;
- anxiety;
- inability to take a breath;
- fear.
These complaints are not always associated with impaired blood flow in the heart and large arteries; often symptoms of additional contraction of the myocardium appear against the background of a decrease in the threshold of human sensations.
Also, the severity of the patient’s complaints does not always correspond to the severity of the extrasystole detected on the electrocardiogram, which is associated with different perception thresholds in different patients.
If extrasystoles are associated with organic damage to the heart muscle, then the clinical manifestations of the underlying cardiac pathology come to the fore, and extraordinary myocardial contractions are a finding during a diagnostic search.
Any forms and types of extrasystole are well tolerated by patients, without affecting their ability to perform any type of activity. Poor general health, decreased resistance to stress are signs of impaired heart function against the background of a disease that has caused extraordinary contractions of the myocardium.
Systolic arrhythmia
Among the various types of heart rhythm disturbances, it stands out in a special way. systolic arrhythmia. What is this known to experienced cardiologists, who, along with ventricular dysfunction, often encounter the presented pathology.
Normally, the cardiac cycle consists of alternating periods: systole (contraction) and diastole (relaxation). During diastole of the atria, blood enters them from the vessels, then they contract (systole) and expel the blood into the ventricles. The latter are also filled with blood in diastole from the atria and then expelled during systole into the general circulation.
The contractility of the heart is assessed precisely by its performance during systole, that is, by the ejection fraction. Normally it is 55-70%
Systolic function is the capacity of the heart, assessed by measuring ejection fraction. This indicator is determined using ultrasound diagnostics of the heart. If less than 40% is determined, then they speak of systolic insufficiency
functions, since less than 40% of the blood volume enters the general blood supply. This pathology is also known as heart failure with left ventricular systolic dysfunction. Systolic arrhythmia may also develop; whether this condition is dangerous can only be understood by considering the presented topic in detail.
: Cardiac cycle
Description of systolic arrhythmia
Systolic arrhythmia is a change in normal cardiac activity that is associated with the phase of systole, most often the ventricles. With this disorder, an increase or decrease in heart rate is observed with the appearance of clinical signs characteristic of arrhythmia.
People over 60 years of age who have been diagnosed with coronary heart disease or have other cardiac pathologies are more susceptible to attacks of systolic arrhythmia.
The development of the disease is based on mechanisms characteristic of arrhythmia. The first is a violation of conduction function.
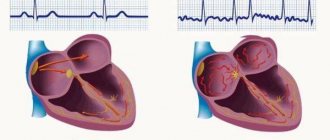
With organic lesions of the heart, the path of impulse conduction may change, as a result of which during systole the ECG shows a change in the form of an extraordinary contraction (extrasystole).
Also, similar reasons contribute to an increase in the automaticity of heterotopic foci and the amplitude of trace potentials. In addition, uneven repolarization of the myocardium may be observed, which is quite typical for the affected heart muscle in coronary artery disease.
Symptoms of systolic arrhythmia
The pathology is characterized by almost all signs of cardiac arrhythmia. Mainly complaints are made about:
- sensation of jerky beats in the heart area;
- increase or decrease in heart rate;
- autonomic disorders in the form of dizziness, feelings of weakness, increased sweating, and feelings of anxiety.
If other diseases are associated with systolic arrhythmia, then their characteristic signs are added to the above symptoms. First of all, rhythm disturbances often develop against the background of other cardiac pathologies. Therefore, the patient may have shortness of breath, heart pain, and swelling. This clinical picture is more pronounced in heart failure with left ventricular dysfunction.
Autonomic disorders can enhance the clinical picture with a pronounced feeling of anxiety, reaching in some cases a panic attack. Patients may complain of clammy sweat, weakness throughout the body, or a feeling of hot flashes or heat. Externally, such manifestations can be expressed in excessive paleness or redness of the face.
This type of arrhythmia is more typical for older people, so among children it occurs only in combination with congenital defects or acquired severe cardiac pathology. It is difficult for children to explain what is wrong with them, so they may complain in the form of frequent heartbeats, “the heart beats poorly,” etc.
: Systolic anterior valve movement
Causes of systolic arrhythmia
The disease is most often associated with other cardiac pathologies. The highest percentage of occurrence is with coronary heart disease . With this disorder, organic damage to the myocardium is observed due to insufficient coronary circulation, which affects the functioning of individual parts or the heart as a whole.
Other cardiac causes include:
- heart failure;
- acquired and congenital heart defects;
- cardiomyopathy;
- infectious lesions of the myocardium.
External influences on the heart also play an important role in the development of arrhythmias. This may be incorrectly selected dosages of medications that increase the ejection fraction - adrenergic agonists, or, on the contrary, weaken it - cardiac glycosides, antiarrhythmic drugs, diuretics.
Electrolyte imbalance often causes arrhythmia, since the activity of the heart depends a lot on the concentration of microelements such as magnesium and potassium in the blood. Both a lack of potassium and magnesium, as well as an excess of the former and an excess of calcium in the blood, negatively affect the functioning of the heart.
In some diseases, the heart rate increases with the possible development of systolic arrhythmias.
This primarily concerns thyrotoxicosis, when the thyroid gland begins to intensively produce thyroxine and triiodothyronine.
Diabetes mellitus can also cause systolic arrhythmia, since impaired carbohydrate metabolism affects the functioning of many systems and organs, including the heart.
Types of systolic arrhythmia
The presented type of arrhythmia is not classified separately, but in clinical practice it is customary to conventionally distinguish different types of changes in heart rate. These can be tachycardia, bradycardia and extrasystoles.
Tachycardia
Characterized by an increase in heart rate more than 90 times per minute.
Some patients do not feel a change in heart rate, but as a rule, older people are very sensitive, so for them every rhythm disorder is a whole unpleasant event.
Therefore, tachycardia is often experienced in combination with headaches and heart pain, increased fatigue and weakness.
Tachycardia in itself is not dangerous, but in combination with other disorders of cardiac origin it can lead to a number of serious complications - myocardial infarction, stroke, cardiac arrest.
Tachycardia often develops after overeating. This is due to increased digestion, which contributes to an increase in heart rate. Also, physical activity can increase the number of heart contractions, but unlike the pathological condition, physiological tachycardia normalizes over time. Therefore, the presence of palpitations at rest is an ominous sign of severe organic heart damage.
Bradycardia
It is a sign of slow heart function and is determined by measuring heart rate, which in case of bradycardia is less than 60 times per minute. In some people, most often athletes, physiological bradycardia is determined. This option is considered normal because it does not cause health problems for humans.
Pathological bradycardia is characteristic of a number of diseases, primarily heart failure. With this pathology, the left ventricle cannot release blood normally, which leads to a weakening of all vital functions of the heart. Therefore, systolic arrhythmia in the form of bradycardia can be one of the first signs of deterioration in heart function.
Diagnosis of systolic arrhythmia
The main diagnostic method for diagnosing arrhythmias is electrocardiography . With its help, both tachycardia, bradycardia and extrasystoles can be determined.
General ECG signs for sinus tachyaardia and bradycardia:
- P waves are detected before each QRS complex, indicating sinus rhythm;
- the correct rhythm is observed with tachycardia and bradycardia, as indicated by the same RR interval;
- Heart rate during tachycardia is increased, and during bradycardia it is decreased compared to the age norm.
With extrasystoles, extraordinary contractions are visible on the ECG, which are divided, depending on the location of the ectopic focus, into atrial or ventricular.
Additional information about the patient’s condition is obtained through ultrasound examination of the heart, stress tests, and daily monitoring. Laboratory tests are also done if hormonal or electrolyte disturbances are suspected.
Treatment and prognosis for systolic arrhythmia
The first attack of systolic arrhythmia should alert the patient and his relatives, since the pathology can result in a number of unfavorable complications:
- atrial fibrillation;
- ventricular fibrillation;
- aggravation of the underlying disease, in particular heart failure.
How to help a patient during an arrhythmia attack?
- calm down in possible ways, for which you should help sit down or lie down more comfortably;
- open the window and try to relax, breathing in fresh air;
- drink water at room temperature, still;
- take a sedative (a few drops of motherwort tincture, valerian);
- If the attack continues, call an ambulance.
Initially detected arrhythmia with the development of an acute clinical picture, which is not relieved using conventional methods, is treated in a hospital setting. This is necessary to prevent the above complications. Therapy is organized on the basis of antiarrhythmic drugs, general strengthening agents, and possibly the use of immunocorrectors.
: How to treat cardiac arrhythmia?
Prevention of systolic arrhythmia
Based on the use of therapy for the underlying disease. In addition, you need to follow general recommendations for the prevention of rhythm disturbances:
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, giving up bad habits and a rational, balanced diet.
- Maintain a daily routine in which time for work and rest must be properly planned.
Avoid stressful situations, and if excitement or anxiety occurs, do not wait for arrhythmia, but prudently take a sedative.
Source: https://arrhythmia.center/sistolicheskaya-aritmiya/
Distribution by age and gender
It is worth saying that this heart disease is common in men. This is due to the fact that men smoke cigarettes more often, and are also susceptible to various other negative factors. The incidence of this disease increases with age. In women, this disease is also quite common, but usually in non-critical forms.
Extrasystole is common among teenagers, as age-related changes affect the functioning of the entire body, including the heart muscle. In addition, the body in children is quite weak, so the heart does not always work correctly and extrasystole is possible.
Diagnostic measures
Before starting treatment, the doctor must determine the exact cause that is causing the heart arrhythmia. To exclude or confirm the progression of concomitant internal pathologies, it is necessary to submit blood and urine for laboratory testing. For detailed diagnosis of the condition of the heart muscle, the following methods are used:
- heart rate measurement;
- electrocardiography;
- echocardiography;
- Hotler monitoring;
- testing under calm and stress conditions;
- MRI or CT.
Traditional therapy
When the course of extrasystole is not associated with serious hemodynamic disturbances and does not pose a threat to the patient’s life, you can cope with the symptoms of arrhythmia on your own. Thus, when taking diuretics, calcium and magnesium are actively washed out of the patient’s body, so it is necessary to introduce foods containing these valuable substances (for example, chocolate or raisins) into the daily diet.
At home, you can prepare a medicinal tincture with antiarrhythmic, sedative, cardiotonic properties (take it three times a day, 1 tablespoon/time).
Medicine recipe:
- Combine 5 parts of motherwort and lemon balm herbs, add 4 parts of heather, 3 hawthorn, 2 hop cones.
- Dry crushed plant mass (2 tbsp) is poured with two glasses of boiling water, left for 1 hour, after filtering, drunk according to the scheme described above.
A person’s well-being largely depends on the health of the cardiovascular system.
Folk remedies are used as an auxiliary therapy after consultation with the attending physician. Self-medication can lead to serious complications in the body's functioning. The dosage of the drug, the duration of the course of treatment and the frequency of administration are selected by the doctor, taking into account the general health of the patient and existing contraindications, allergic reactions.
| Therapeutic effect | Components |
| Calming, relaxing | Motherwort, peppermint, thyme, lemon balm, valerian, chamomile |
| Maintaining heart rate, relieving pain | Calendula, rose hips, hawthorn, cornflower flowers, honey and radish juice, hop cones |
| Cleansing blood vessels, improving blood circulation | Lemon with garlic |
Clinical manifestations of pathology
The heart begins to pump less blood.
This causes blood flow to slow down. The main symptoms of heart rhythm disturbances:
- pain, throbbing, tremors in the chest area;
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- increased sweating, hot flashes;
- fluctuations in blood pressure, pulse;
- temperature increase;
- nausea;
- feeling of lack of air;
- anxiety, fear;
- presyncope, fainting.
Measures to prevent and predict extrasystolic arrhythmia
Measures to prevent cardiovascular pathologies should include changes in the patient’s lifestyle:
- normalization of work and rest schedules;
- balanced diet, limiting stimulating drinks;
- eliminating bad habits;
- regular medical examination.
For chronic diseases, maintenance therapy is carried out aimed at stabilizing the condition and reducing the symptoms of the disease. It is mandatory to be monitored by your attending physician and undergo a full medical examination to monitor your health status. If you follow all medical recommendations, you can live fully with a diagnosis of systolic arrhythmia; the prognosis for the course of heart rhythm disturbances is favorable.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made based on the following examinations:
- physical examination;
- ECG;
- Holter monitoring of changes in heart rate;
- Ultrasound of the heart.
A physical examination is an initial examination performed by a physician. It includes listening to the heart, measuring pulse and blood pressure. As a rule, it is enough for an experienced doctor to listen to the patient’s heart sounds to suggest the development of an arrhythmia. However, the exact type of disorder can only be determined by an electrocardiogram. An ECG allows not only to diagnose extrasystolic arrhythmia, but also to determine its severity.
If secondary cardiac pathologies are suspected, the patient may be recommended an ultrasound or echocardiography. Daily Holter ECG monitoring is another effective diagnostic method.
Possible complications
If you do not fight the problem in any way, then this “cosmetic” disease can develop into tachycardia, which is much more serious.
In addition, the likelihood of a myocardial infarction may be increased, so it is necessary to deal with this disease if it has already occurred and the doctor talks about it. Otherwise, the consequences can be much more detrimental to the main muscle that disperses the blood. Extrasystole can be regarded as the first “bell” that can signal problems.
If you start therapy (if it is needed) promptly, then there can be no consequences or complications.
Frequent group extrasystoles entail a decrease in cardiac output, and therefore a decrease in blood circulation volume by 8–25% (both cerebral, coronary, and renal). They can also develop into more dangerous forms of arrhythmia:
- atrial leads to atrial flutter;
- ventricular ones cause ventricular paroxysmal tachycardia.
It is noteworthy that the systolic rhythm with multiple extraordinary heart impulses can not only accelerate (tachycardia), but also slow down (bradycardia). Heart rate in this situation decreases to 30 times/minute - this is a life-threatening phenomenon, since it is associated with conduction disturbances and a significant risk of myocardial blockade.
The most dangerous type of extrasystole - complicated ventricular - can cause death.
Against the background of constant extrasystole, heart and kidney failure, as well as cerebral circulatory failure, can develop. If left untreated, extrasystole can transform into more serious forms of arrhythmia (atrial flutter, paroxysmal tachycardia, atrial fibrillation), resulting in a significantly increased risk of sudden death.
Classification
Extrasystolic arrhythmia often occurs against the background of atrial fibrillation, which leads to the development of other complications.
Forms according to the etiology of occurrence:
- physiological form - develops as a result of emotional, physical stress, symptoms disappear after rest;
- pathological form - occurs against the background of pathological disorders.
Depending on the location, the following types of arrhythmia are distinguished:
- atrial - the lightest, accompanied by extraordinary contractions of the heart muscle;
- atrioventricular (nodular) - accompanied by malfunctions in two parts of the heart muscle, as well as in the area of the atrioventricular node;
- ventricular - considered safe in the presence of single impulses, with multiple impulses there is a risk of flutter.
Advantages of the clinic
When planning treatment in our clinic, be sure of:
- therapy using modern techniques;
- high-quality and complete preliminary and re-examination;
- loyal pricing policy.
We are always ready to provide comprehensive support to each client. By contacting us, you will be surrounded by attention and care. All specialists work as a single team. Therapists, surgeons, neurologists, osteopaths and other doctors may be involved in the treatment of your pathology.
Contact us! Each patient is valuable to us, first of all, as an individual, and not as a patient with an interesting medical history or a client who creates the financial well-being of a specialist. In our clinic you do not spend money on therapy, you invest it in your health.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment of extrasystolic arrhythmia of a functional and toxic nature consists of eliminating provoking factors and changing lifestyle. Key recommendations include:
- normalization of the daily routine;
- nutrition correction, dieting;
- connection of feasible physical activity;
- eliminating bad habits;
- replacing medications that cause side effects;
- stabilization of the psycho-emotional state.
Treatment of pathology with medication is necessary for the following conditions:
- coronary disease, atrial fibrillation;
- persistent pain, constant poor health of the patient;
- ventricular extrasystole, sinus arrhythmia;
- after myocardial infarction;
- with severe circulatory failure.