Extrasystoles represent additional contractions of the myocardium, “interfering” with its work rate. This process increases the load on the heart and can ultimately lead to the development of a number of cardiac diseases. The mechanism for the occurrence of extrasystoles is quite simple. They appear when, in addition to the sinoarterial node, electrical impulses are supplied to the myocardium from the outside (due to neurological disorders). As a result, disruptions occur in the system for regulating the heart rate, which the patient feels, as a rule, only during physical exertion and in stressful situations. At rest, the disease does not make itself felt in any way.
Main symptoms
According to statistics, an adult experiences about 30-40 “extra” heartbeats per hour. Below is the daily value for people with certain heart rhythm problems:
- from 720 to 960 additional impulses is the norm for people who do not have any problems with the cardiovascular system;
- from 960 to 1200 - the norm for those who have been diagnosed with “polymorphic extrasystoles” does not pose a threat to health;
- 1200 and above is no longer the norm and indicates the presence of problems with the heart rate, up to tachycardia.
Today, according to the results of the survey, 75% of people on the planet fall into the first two groups, and this does not at all indicate that this is fraught with any serious consequences for them. However, if extrasystoles are accompanied by severe clinical symptoms, it is not recommended to postpone going to the doctor. Among these symptoms, first of all, it is necessary to note:
- sensation of tremors in the chest in the region of the heart (occurs with vigorous contraction of the ventricles after a compensatory pause);
- interruptions and “fading” in the work of the heart, which are accompanied by lack of air, sweating, fever and weakness;
- in advanced cases: dizziness and faintness, which occurs due to a decrease in blood flow to the brain during moments of “shocks” and “fading” of the heart.
Norm of extrasystoles per day: what to do in case of rhythm disturbances
Additional education:
"Cardiology"
State educational institution "Institute for Advanced Medical Studies" of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Chuvashia
Contacts
Such a phenomenon as extrasystoles significantly complicates the work of the heart muscle, causing its additional “unscheduled” contraction and stimulating more active wear and tear of the myocardium. Manifesting externally in an uneven rhythm of heart contractions, extrasystoles cause a feeling of lack of oxygen and interfere with the patient’s breathing.
The greatest manifestations of an increase in the number of extrasystoles are observed when receiving a load - physical and psychological; At rest, this phenomenon is usually not felt by the patient.
The average rate of exvarasystole per day may vary somewhat in different patients; much of this indicator depends on the state of health in general and the cardiac system in particular, the degree of load during the day and the person’s lifestyle.
Modern medicine provides data on the number of contractions of the heart muscle, which can be called the average statistical norm for a healthy person. Each case is individual, therefore there may be various deviations from the average figure.
To identify a condition such as extrasystole, you should pay attention to your own sensations, and if you suspect disruptions in the heart rhythm, contact a cardiologist for a full examination.
After all, extrasystoles, which often occur throughout the day, not only worsen the general well-being of the patient, but can also cause serious cardiac changes.
Possible consequences of frequent cardiac extrasystoles
With the frequent appearance of human-perceptible extrasystoles in the heart, the total volume of load placed on the heart muscle increases significantly.
This leads to an increase in the rate of wear of the myocardium, increasing the likelihood of developing serious consequences for overall health.
Cardiac diseases caused by frequent extrasystoles in the heart are accompanied by damage to the tissue of the heart muscle, deterioration of the myocardial process and the likelihood of having a negative impact on human health.
Extrasystoles occur when there is an increase in the rate of occurrence of electrical impulses that arise from the outside (usually due to psychological experiences and emotional overload) and affect the myocardium. The impact of such unscheduled extrasystoles on the sinoarterial node, which is less susceptible to such influences, is considered normal.
An extrasystole is essentially an empty, idle contraction of the heart muscle, which does not lead to the release of blood into the vessels of the heart. This is explained by insufficient filling of the heart with blood, when receiving an electrical impulse it contracts without pumping blood in the right direction.
In this case, muscle contraction is observed without the desired result.
One-time extrasystoles do not entail serious damage to the heart, however, if such a manifestation is repeated frequently, there is a high probability of pain in the heart, thinning of its tissues and a decrease in the conductivity of the electrical impulse.
Difference between types of extrasystoles
Depending on what type of this pathology has arisen in the body, its main symptoms may vary. The number of contractions of the heart muscle during the day is also in accordance with both the general state of human health and the type of cardiac lesion.
Today in medical practice there are two main types of extraordinary extrasystoles:
- Supraventricular extrasystoles are extrasystoles that occur when an electrical impulse is transmitted from any part or area of the atria of the heart muscle, but not from the sinus node.
- The ventricular variety of extrasystoles is characterized by their occurrence in any part of the ventricles of the heart.
There is also a special classification of such a phenomenon in the work of the heart muscle as extrasystoles, according to the number of consecutive ineffective contractions of the heart, during which the heart does not pump blood. This classification looks like this:
- single extrasystoles;
- paired, or couplets;
- group ones, which are felt to the greatest extent. Usually there are three (triplets) or four cardiac extrasystoles in a row.
The listed methods for classifying extrasystoles help make a preliminary diagnosis based on the examinations performed.
The most characteristic manifestations
Depending on the specific case, the indicator of extrasystoles may vary. Normally, a person who does not have significant problems with the cardiovascular system can experience about 30-40 “unscheduled” contractions of the heart muscle per day, which does not have pronounced negative consequences for the myocardium.
According to numerous studies, extrasystoles in the heart do not always lead to serious cardiac pathologies. There is a certain system of norms for this manifestation, which is recognized as the norm and does not pose a real danger to human health.
Norm and excess of norm in the manifestation of extrasystoles
Depending on the number of registered extrasystoles, a cardiologist can make a diagnosis of the presence or absence of cardiac pathology.
The number of daily contractions of the heart without pumping blood, which are essentially extrasystoles, for a completely healthy person is about 100 times.
An increase in this figure may already indicate the presence of cardiac pathology, which requires prompt therapeutic intervention to prevent harm to the body and the heart in particular.
To identify the presence of pathology, the doctor calculates the number of contractions per day. It is this figure that determines the presence or absence of cardiac pathology. Extrasystoles in the heart are formed due to the appearance of electrical impulses that are transmitted to the myocardial tissue and provoke ineffective contractions.
The number of extrasystoles may vary depending on whether a person has certain deviations from the norm in the state of the cardiovascular system as follows:
- additional electrical impulses in the amount of 650 to 960 can be called the average norm for a person who does not have serious health problems;
- impulses in the amount of 960-1150 are not a significant danger to health and are classified as “polymorphic extrasystoles”;
- with an increase in the number of electrical impulses affecting the myocardium, more than 1200, there is already a basis for concern and a danger to health arises. The most common consequence of this phenomenon is tachycardia, as well as disturbances in the frequency and rhythm of heart contractions.
Normally, it is considered to be about 580-850 impulses entering the cardiac muscle tissue: in this situation, there are no pronounced changes in the condition of the heart, the frequency of its contractions and the general well-being of the person. The first two groups of manifestations of electrical impulses listed above do not pose a health hazard, do not worsen a person’s general well-being, and therefore may not be considered hazardous to health.
However, if unpleasant subjective manifestations or increased heart rate occur, you need to consult a cardiologist who will check other health indicators and make a preliminary diagnosis.
The number of heartbeats per minute depends on the individual; According to medical statistics, almost 75-80% of the entire population of the Earth has a small number of “unscheduled” extrasystoles throughout the day, which does not have a pronounced negative impact on health.
Even in the initial stages of the onset of this pathology, preventive action should be started, which will prevent the main symptoms from passing into an advanced state.
It is the initial stages that are most amenable to complete cure.
Therefore, even minor manifestations of health problems and the appearance of the first symptoms should be a good reason to consult a doctor.
The most characteristic symptoms of extrasystoles
Using the characteristic manifestations of a condition such as extraordinary extrasystoles listed below, it is possible to promptly identify the initial stage of this cardiac lesion. The main symptoms of extrasystoles include:
- subjective sensations characterized by disturbances in the rhythm of heart contractions, a decrease in the amount of blood transported by the heart, which leads to insufficiency of air and inferior breathing;
- “fading” and disruptions in heart rhythm, in which many patients experience fever and sweating, as well as severe weakness;
- at later stages of the disease, many patients complain of dizziness and instability of self-awareness. These sensations arise due to insufficient blood flow to the tissues of the body due to interruptions in its contractile activity.
In a normal heart rate, the above manifestations are not felt. The occurrence of excessively frequent electrical impulses leads to a lack of oxygen in the consumed air, an increased level of fatigue and dizziness.
Forecasts for detected extrasystoles in the heart
According to the majority of modern cardiologists, both types of extrasystoles, when their frequency of manifestations is within the established norm, do not cause significant inconvenience to the patient and do not harm his health.
The therapeutic methods in this case do not bring significant positive changes, therefore, for stable and uninterrupted functioning of the heart muscle, it is enough to regularly conduct a complete examination of the entire cardiovascular system.
According to research, supraventricular extrasystole is the least likely to pose any health hazard. Its manifestations are less noticeable in everyday life and do not affect either the rhythm of heart contractions or the quality of blood pumping by the heart muscle.
Ventricular extrasystole also does not pose a significant danger to human health. However, if the indicators of extrasystoles per day exceed more than 3,000, a full examination of the cardiac system should be carried out: there is a possibility of heart failure and tachycardia, which already pose a danger to health, and in an advanced state - a danger to the patient’s life.
Source: https://CardioPlanet.ru/zabolevaniya/aritmiya/norma-ekstrasistol-v-sutki
Ventricular extrasystole
The most common heart rhythm disorder, characterized by interruptions in ventricular contractions. Research shows that it affects 50% of young people worldwide, and the chances of being at risk increase with age. Ventricular extrasystole is caused by the premature supply of electrical impulses from the His bundle and Purkinje fibers, which leads to “extra” contractions of the ventricles. It most often affects people who abuse alcohol and smoking. Another reason for the development of pathology can be stress. However, in medical practice there are also cases when the disease affects people leading a healthy lifestyle.
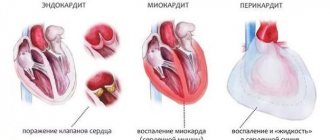
In 90% of cases, ventricular extrasystole is observed in patients who have suffered a myocardial infarction and suffer from coronary heart disease. Pericarditis, myocarditis and various forms of cardiomyopathies can also cause the development of the disease. In addition, the possibility of developing pathology due to long-term use of beta-agonists, antidepressants, antiarrhythmic drugs and diuretics cannot be excluded.
Treatment of ventricular extrasystole is applicable only to those individuals who have severe symptoms of the disease described above. Patients are usually prescribed sedatives (including tranquilizers) - Obzidan and Anaprilin. If treatment does not produce results, anticholinergic drugs are used: Belloid, Bellataminal, etc. Self-medication in this case is contraindicated: a course of therapy can only be prescribed by a cardiologist.
Extrasystoles normal per day - General Doctor
Supraventricular (supraventricular) extrasystole is considered one of the most common arrhythmias.
It is characterized by the sudden occurrence of an extraordinary cardiac contraction, followed by a short pause.
The source of the impulse in this case is located above the ventricles - in the atria, atrioventricular junction. In ICD-10 it is encrypted with code I49.2 and is less common than the ventricular form.
Causes
NVEs develop due to many reasons. Even a simple sneeze or fear can cause extraordinary contraction of the myocardium. The most common culprits of extrasystoles are various heart diseases: coronary disease, cardiomyopathies, congenital and acquired defects, myocarditis, pericarditis, chronic heart failure, etc.
Also, supraventricular extrasystole develops under the following factors, conditions and diseases:
- violation of autonomic regulation (autonomous dysfunction syndrome);
- physical and emotional stress;
- neurotic disorders;
- reflex irritation of the cardiac nerves in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract: duodenal ulcer, cholelithiasis;
- presence of bad habits;
- coffee addiction;
- taking pills: antidepressants, psychostimulants to reduce appetite, vasoconstrictor nasal drops, medications for high blood pressure. Even some antiarrhythmic drugs in some cases cause EVE;
- infectious diseases;
- severe diseases of the respiratory system: bronchial asthma, chronic broncho-obstructive pulmonary disease;
- pathology of endocrine organs: Graves' disease, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, diabetes mellitus;
- excess or deficiency of minerals in the body (calcium, magnesium, sodium);
- chest injuries.
In some cases, the cause of the rhythm disturbance cannot be identified. Then a diagnosis of “NVE of unknown etiology” is made.
Daily norm of supraventricular extrasystoles
Large-scale clinical studies were conducted, during which it was possible to establish the norm of LVE. In a healthy person without cardiac pathology, the norm of supraventricular extrasystoles per day is about 200-300. This amount of NLE does not pose a health hazard.
Classification and types
There are many types of NLEs, divided according to different characteristics.
Depending on the source of the impulse, atrial extrasystoles and extrasystoles (ES) from the atrioventricular (AV) connection are distinguished. Based on the number, they distinguish between single and double. Three or more ES in a row is already considered an episode of tachycardia (also called a “jog”).
In my patients, I often observe such an ECG phenomenon as allorhythmia - the regular occurrence of extrasystoles. There are the following types:
- bigeminy - the appearance of ES on the cardiogram after each normal contraction of the heart (read more about this phenomenon here)
- trigeminy - after every second complex;
- quadrigeminy - after every third complex.
Depending on the cause, the following types of NVEs are distinguished:
- functional - during physical activity, reflex effects;
- organic - for heart diseases;
- toxic - in case of drug overdose;
- mechanical - for injuries.
Single extrasystoles
The most benign variant of NVE, mainly found in healthy individuals, are single supraventricular extrasystoles. They almost always go unnoticed by humans and do not pose a threat to health.
Frequent symptoms
In most of my patients, supraventricular extrasystole occurs latently, without symptoms.
And yet, with a prolonged course of the disease, some people may experience a feeling of fear, an unpleasant sensation of freezing, interruptions in the functioning of the heart, and “rolling” in the chest.
Some patients suffering from heart disease complain of short-term difficulty breathing, dizziness and weakness. Sweating and fever are also sometimes observed.
Signs on ECG
Supraventricular extrasystole is very easy to recognize on a cardiogram. Main features:
- extraordinary (extrasystolic) appearance of a pathological deformed P wave and the following unchanged QRST complex;
- the presence of a compensatory pause, i.e. a straight line on the film.
If the P wave has a different shape in different leads, this phenomenon is called polytopic atrial extrasystole. Its detection is highly likely to indicate a heart or lung disease and requires a more thorough diagnosis.
It happens that after an extraordinary P wave there is no QRST complex. This happens when atrial extrasystole is blocked. ES from the atrioventricular junction differs in that the P wave is negative or not recorded at all due to overlap with the T wave.
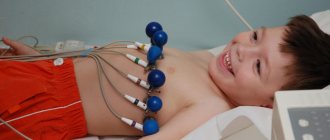
When taking an ECG at rest, extrasystoles may not be detected. Therefore, in order to “catch” them and find out how often they occur, I prescribe Holter monitoring to my patients. In case of concomitant diseases, a person undergoes a cardiac ultrasound (EchoCG).
After supraventricular ES, the pause lasts less than with ventricular ES.
Treatment: when, how and with what
Supraventricular extrasystoles are almost always benign. If extraordinary contractions of the heart are single, are not accompanied by any symptoms and do not provoke the occurrence of severe rhythm disturbances, treatment of supraventricular extrasystole is not required. The main thing is to fight its cause.
When EVE worsens the patient's condition, I prescribe drug therapy. The most effective drugs for stopping SE are beta-blockers - Bisoprolol, Metoprolol.
If there are contraindications to their use (for example, severe bronchial asthma), I transfer the patient to slow calcium channel blockers - Verapamil, Diltiazem.
Read about how extrasystole is treated with medications here.
As for traditional methods, to date there is no convincing evidence of their effectiveness. In my practice, I recommend that patients under no circumstances replace traditional treatment with traditional medicine. But if you have a different opinion, we invite you to read the material here.
If the development of NVE is associated with emotional stress or a neurotic disorder, you can take sedatives and make an appointment with a psychotherapist.
The main criteria for the success of therapy are the cessation of symptoms and normalization of the patient’s condition.
In rare cases, when drug treatment does not have the expected positive effect, surgical intervention is used, in particular, a technique such as radiofrequency catheter ablation. I usually prescribe this operation to young patients, since with age the risk of developing severe complications, including death, increases.
It is extremely rare, for health reasons, that an open access operation is performed, with dissection of the chest and removal of the portion of the myocardium where extraordinary impulses are formed.
Why are supraventricular extrasystoles dangerous and what are their consequences?
Extraordinary supraventricular extrasystoles themselves do not pose a threat to human life and often go unnoticed.
However, they can provoke the appearance of more severe rhythm disturbances: supraventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation and flutter, which lead to a sharp decrease in blood pressure, deterioration of blood supply to the myocardium and an increased risk of blood clots in the heart. A combination is often observed .
Supraventricular extrasystole
This disease is a fairly common type of arrhythmia, which is characterized by premature delivery of electrical impulses to the upper parts of the heart. Supraventricular extrasystole can begin to develop in a patient in adolescence for no apparent reason and, as a rule, affects people who are tall and thin. The causes of the development of pathology can be neurogenic, toxic and medicinal factors. Recent studies show that extrasystoles of this type make themselves felt at the first prerequisites for tachycardia.
As with ventricular extrasystoles, supraventricular extrasystoles can be caused by alcohol consumption, smoking and stress. Taking heart medications without consulting a doctor can also trigger the development of the disease. In some cases, the disease develops against the background of disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas.
You can get rid of supraventricular extrasystoles at the initial stage of the disease with the help of drug treatment. As a rule, drugs of the antiarrhythmic group, glycosides and drugs that normalize blood pressure are used. Almost all of them have side effects and therefore should be used only after examination under the supervision of a physician. In advanced cases, the possibility of surgical intervention cannot be ruled out, so you should contact a specialist immediately after the first symptoms appear.
Extrasystole. Information for patients.
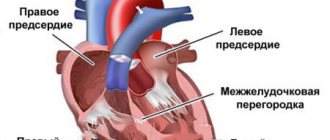
One of the most important functions of the heart is pumping - that is, supplying organs and systems with blood. For a full pumping function, it must constantly contract, dispersing blood through the vessels. Constant contraction is ensured by the equally constant generation of electrical impulses in the heart itself.
One of the unique features is that each cell of the heart organ is capable of producing and conducting electrical current. There are several areas in which a cluster of cells constantly generate impulses at a certain frequency. The main generator is the so-called sinus node, which ensures normal heart contraction.
Atrial fibrillation. Symptoms Treatment. Prevention.
Atrial fibrillation. Clinic, diagnosis, treatment, class.
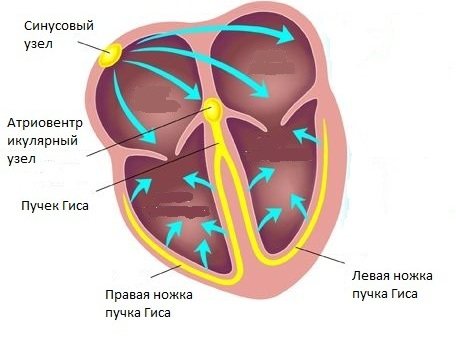
Considering the importance of this organ for ensuring the vital functions of the body, nature provides backup sources that begin to generate impulses if for any reason the main generator (sinus node) fails. The sinus node is capable of generating impulses at a frequency of 40-180 beats per minute, and while it is working normally, impulses generated by other areas are suppressed.
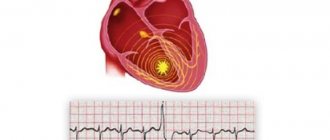
An extrasystole is an extraordinary contraction of the heart due to the fact that another (non-sinus) impulse generator is active. This is what it looks like on an electrocardiogram:
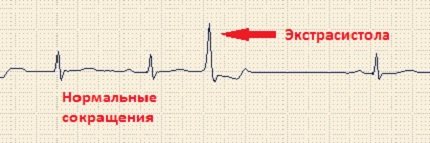
In fact, an extrasystole is an early contraction of the heart, when there is not yet enough blood in it to release it into the vessels of the heart, i.e. it may be an empty and ineffective shortcut.
Extrasystoles are divided according to the location of the pulse generator, the activity of which causes the appearance of:
- Supraventricular extrasystoles - if an extraordinary impulse is generated in any part of the atria, but not in the sinus node
- Ventricular extrasystoles - if an extraordinary impulse is generated in any part of the ventricles of the heart.
Example of ventricular extrasystole on an ECG
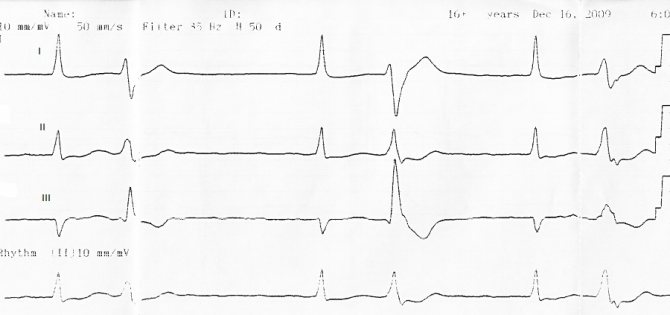
Another classification indicates extrasystolic heart rhythm:
- A single extrasystole is one extrasystole that occurs haphazardly relative to the normal rhythm.
- Bigeminy is an extrasystole following each normal contraction.
- Trigeminy is an extrasystole that occurs after two normal contractions.
- Quadrigeminy is an extrasystole that occurs after every three normal contractions.
Diagnostics
Extrasystoles of all types can be detected by a cardiologist during the process of palpating the pulse. However, to create a clear picture of the disease, a patient with suspected pathology must undergo an ECG diagnosis. The device will allow you to determine the source of extrasystoles and their type with 100% accuracy. Cardiac ultrasound and MRI can also be performed as additional diagnostic tools at the doctor’s initiative. Extrasystole appears on the electrocardiogram in the form of the following signs:
- decreasing the interval between the P wave of the main rhythm and the P wave of the additional impulse;
- decreasing the interval between the QRS complex of the main rhythm and the QRS complex of the additional impulse;
- obvious deformation and increased amplitude of the extrasystolic QRS complex;
- absence of a P wave before the ventricular extrasystole.
It is worth noting that the ECG in this case is performed using the Holter system. It follows that the patient must participate in the examination for 24 to 48 hours at a time without removing the measuring device. In addition, the patient must periodically change the level of his activity and record all his sensations and changes in well-being in a diary.
Forecasts for detecting extrasystoles
Most cardiologists agree that ventricular and supraventricular extrasystole within normal limits does not pose a threat and does not impair the quality of life. At this stage, it will not be possible to achieve a serious change in the condition, therefore, in order to maintain the heart muscle in working condition, it is necessary to regularly check the functional state of the cardiovascular system.
According to statistics, supraventricular extrasystole poses less of a health hazard compared to ventricular extrasystole. It is also less pronounced and causes less discomfort. In this case, it can be noted that there is no effect on heart rate and hemodynamics.
Although ventricular extrasystoles are not life-threatening, with more than 3000 extrasystoles during the day, the likelihood of developing heart failure or tachycardia increases, which can already pose a threat to health and life.
An experienced doctor can determine extrasystoles by feeling the pulse, but in order to fully see the picture of the patient’s condition, it is necessary to conduct an electrocardiogram.
Attention! To determine the number of extrasystoles per day, daily Holter monitoring is performed using a portable ECG.
Using an ECG, the location and type of extrasystoles are determined with high accuracy. If ECG data does not allow a complete picture of the situation, the doctor may prescribe a cardiac ultrasound or MRI.
You can judge extrasystole on an ECG by the following signs:
- There is a decrease in distance between the P waves of the main heart rhythm and the additional one.
- Also, the QRS complexes will be less spaced.
- There is a pronounced deformation and increased amplitude of the extrasystolic QRS complex.
- There is no P wave before the ventricular extrasystole.
To identify the number of extrasystoles and compare them with the daily norm, monitoring is carried out using the Holter method. In this case, continuous examination can last up to 2 days. Such an examination is necessary in order to assess the reaction of the heart muscle to rest, physical activity, sleep, wakefulness, eating and stressful situations.
It is worth noting that only severe extrasystole is treated. In this case, extrasystoles may itself be a symptom of another more serious disease, after the elimination of which the extrasystoles also disappear.
For example, if a patient has ischemic heart disease or thyrotoxicosis, then when cured of these diseases he will not experience cardiac arrhythmia. According to medical practice, drug treatment of extrasystoles begins after exceeding 700 extrasystoles per day. This is because therapy may otherwise do more harm than good.
To effectively treat extrasystoles, therapy with antiarrhythmic drugs is used. During the therapy period, the patient's heart rate normalizes, however, due to serious side effects, beta-blockers and Amiodarone are additionally prescribed to these drugs.
However, treatment can vary greatly in each individual case, so doctors can take quite a long time to select the appropriate treatment method. The first days of primary therapy, which is characterized by trial and error, will consist only of selecting the necessary drugs to correct the problems. Once the right option has been selected, the patient will experience positive dynamics.
The daily rate of extrasystoles determines the course of treatment and the need for it. If the number of extrasystoles does not exceed 700 times a day, then this can be considered normal and not interfere with the functioning of the heart, but only undergo regular examinations by a doctor.
Source: lechiserdce.ru
Treatment methods
Before you begin treatment of the disease, you need to make sure that it is severe. Extrasystoles are often secondary to a more serious disease and can be eliminated in the process of eliminating it. For example, having cured thyrotoxicosis or coronary heart disease, the patient in most cases gets rid of arrhythmia. Practice shows that it is worth starting treatment for extrasystoles only if their number exceeds 700 per day. Otherwise, therapy can do much more harm to the patient than good.
The greatest effect in the treatment of extrasystoles is achieved when taking antiarrhythmic drugs (AAP). During the period when the patient undergoes a course of therapy using them, the number of heartbeats returns to normal. However, the presence of side effects with these drugs is extremely high and therefore their use is accompanied by the prescription of beta-blockers and Amiodarone. The patient must be prepared for the fact that specialists will not immediately be able to choose the right treatment method for him. Primary therapy is almost always carried out by trial and error, and in the first 3-4 days, doctors will only be busy looking for the best options for solving the problem. After determining the treatment method, the patient shows positive dynamics.
Forecasts for detecting extrasystoles
Most cardiologists agree that ventricular and supraventricular extrasystole within normal limits does not pose a threat and does not impair the quality of life. At this stage, it will not be possible to achieve a serious change in the condition, therefore, in order to maintain the heart muscle in working condition, it is necessary to regularly check the functional state of the cardiovascular system.
According to statistics, supraventricular extrasystole poses less of a health hazard compared to ventricular extrasystole. It is also less pronounced and causes less discomfort. In this case, it can be noted that there is no effect on heart rate and hemodynamics.
Although ventricular extrasystoles are not life-threatening, with more than 3000 extrasystoles during the day, the likelihood of developing heart failure or tachycardia increases, which can already pose a threat to health and life.
An experienced doctor can determine extrasystoles by feeling the pulse, but in order to fully see the picture of the patient’s condition, it is necessary to conduct an electrocardiogram.
Attention! To determine the number of extrasystoles per day, daily Holter monitoring is performed using a portable ECG.
Using an ECG, the location and type of extrasystoles are determined with high accuracy. If ECG data does not allow a complete picture of the situation, the doctor may prescribe a cardiac ultrasound or MRI.
You can judge extrasystole on an ECG by the following signs:
- There is a decrease in distance between the P waves of the main heart rhythm and the additional one.
- Also, the QRS complexes will be less spaced.
- There is a pronounced deformation and increased amplitude of the extrasystolic QRS complex.
- There is no P wave before the ventricular extrasystole.
To identify the number of extrasystoles and compare them with the daily norm, monitoring is carried out using the Holter method. In this case, continuous examination can last up to 2 days. Such an examination is necessary in order to assess the reaction of the heart muscle to rest, physical activity, sleep, wakefulness, eating and stressful situations.
It is worth noting that only severe extrasystole is treated. In this case, extrasystoles may itself be a symptom of another more serious disease, after the elimination of which the extrasystoles also disappear.
For example, if a patient has ischemic heart disease or thyrotoxicosis, then when cured of these diseases he will not experience cardiac arrhythmia. According to medical practice, drug treatment of extrasystoles begins after exceeding 700 extrasystoles per day. This is because therapy may otherwise do more harm than good.
To effectively treat extrasystoles, therapy with antiarrhythmic drugs is used. During the therapy period, the patient's heart rate normalizes, however, due to serious side effects, beta-blockers and Amiodarone are additionally prescribed to these drugs.
However, treatment can vary greatly in each individual case, so doctors can take quite a long time to select the appropriate treatment method. The first days of primary therapy, which is characterized by trial and error, will consist only of selecting the necessary drugs to correct the problems. Once the right option has been selected, the patient will experience positive dynamics.
The daily rate of extrasystoles determines the course of treatment and the need for it. If the number of extrasystoles does not exceed 700 times a day, then this can be considered normal and not interfere with the functioning of the heart, but only undergo regular examinations by a doctor.
Source: lechiserdce.ru
Classification of ventricular (ventricular) extrasystole
Extrasystole according to the ventricular type is divided into the following classes:
- monomorphic single extrasystoles are recorded (up to 30 within an hour);
- the appearance of more than 30 single supraventricular extrasystoles of a monomorphic type per hour;
- when polymorphic ventricular extrasystoles are recorded on the electrocardiogram;
- divided depending on the presence of extraordinary paired contractions: monomorphic and polymorphic type;
- registration of group premature contractions (3 or more within 30 seconds) so-called early extrasystoles.