Smoking affects human blood vessels every day and exposes all systems to unreasonable risk. Smoking causes negative changes at every level of the cardiovascular system: small and large vessels, heart muscle, and blood suffer from tobacco. A third of deaths from coronary heart disease are caused by cigarette use.
Death from smoking
Smoking and type 2 diabetes
Is it possible to smoke tea?
Myths about smoking
Use search
Are you having any problem? Need more information? Type in the form and press Enter!
Mechanism of action
The effect of smoking on the cardiovascular system is due to the presence of nicotine and carbon monoxide in tobacco smoke. Nicotine has a stimulating effect on the sympathetic nervous system, which leads to an increase in heart rate and blood pressure.
The lumen of the smoker’s blood vessels narrows, vascular spasm occurs, forcing the heart to work under additional stress. Carbon monoxide, which enters the body along with smoke, combines with hemoglobin, reducing the respiratory function of the blood.
Under the influence of nicotine, the coagulating properties of blood change: viscosity increases, the amount of fibrinogen - a specific protein found in the blood plasma and is responsible for its coagulation. A smoker is at increased risk of thrombosis.
Smoking leads to dysfunction of the endothelium - the layer of flat cells that cover the inner surface of blood vessels - due to which the synthesis of prostacyclin is reduced, which helps damage the cardiovascular system.
The listed factors provoke the development of a number of diseases:
- Atherosclerosis;
- IHD;
- Endarteritis of the lower extremities;
- Aortic aneurysms;
- Myocardial infarction;
- Angina pectoris;
- Ischemic cerebral stroke;
- Hypertension.
Completely quitting the habit reduces the risk of developing – sometimes to the level of non-smokers – the listed diseases. And in case of existing pathology, abstinence from cigarettes improves the prognosis and effectiveness of treatment, and reduces the likelihood of relapse.
Take the Attention Test! Find 10 differences! (click right here!)
Test for smokers
Smoking and brain disorders
Smoking and brain disorders
The wide prevalence and accessibility of tobacco smoking remains one of the important causes of morbidity and premature mortality from heart disease, cerebral stroke and malignant tumors. At a 1997 World Health Organization conference in Beijing, it was noted that quitting smoking could save over 100 million lives over the next 20 years. Data were cited according to which in developed countries, for example, in the USA and Great Britain, half of smokers die from diseases associated with this addiction, with 25% aged 35-69 years.
Let us consider the results of studies related to cerebral vascular lesions. The pathogenic effect on brain cells is based on rapidly occurring changes in the composition of the blood or the so-called systemic effects of smoking. Within seven seconds after inhaling tobacco smoke, nicotine reaches the brain cells, exerting a specific effect on them. Under its influence, as well as under the influence of carbon monoxide and other substances (in total, smoke contains about 3,400 compounds), blood pressure rises and the heart rate increases. Smoking can increase blood clotting, viscosity, and hemoglobin content. The function and activity of blood platelets are impaired. These changes in hemorheological parameters indicate an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases in smokers, deterioration of blood flow and microcirculation. Nicotine affects different levels of the central nervous system, its autonomic formations, and therefore vascular tone and the ability of blood vessels to adapt to other factors are disrupted.
Inhaling tobacco smoke increases blood pressure and causes emphysema. This effect increases the risk of hemorrhagic stroke in smokers by 2.5 times. Mortality from subarachnoid hemorrhage is especially high among those who smoke a pack or more of cigarettes daily and drink alcohol every day.
It has been experimentally proven that large doses of nicotine can cause degenerative changes of the anoxic type in the walls of arteries and arterioles. Smoking significantly reduces local cerebral blood flow. The risk of blockage of the great vessels of the head increases. Atherosclerotic plaques can form in them, narrowing the lumen of blood vessels, worsening the conditions of blood supply to the brain. The activity of the heart is impaired. These changes in the cardiovascular system contribute to the development of both chronic (initial manifestations of insufficient blood supply to the brain, dyscirculatory encephalopathy, vascular dementia) and acute (transient cerebrovascular accidents, minor stroke, ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes) cerebrovascular lesions.
Early signs of cerebrovascular pathology in the presence of an underlying vascular disease (atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension) may include frequent complaints of headaches, dizziness, noise in the head, memory impairment, and decreased performance. If these complaints are noted quite regularly over a long period of time (at least once a week over the last three months), then, according to the “Classification of vascular lesions of the brain and spinal cord” developed by the Research Institute of Neurology of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, a diagnosis of “initial manifestations of blood supply insufficiency” is made brain." This is a serious risk factor for the development of cerebral stroke. Even with this early form of vascular brain damage, patients are strongly recommended to quit smoking in order to reduce the possibility of disease progression and stroke development.
The risk of hemorrhagic stroke among smokers is 2.5 times higher compared to non-smokers and 2.8 times higher after eliminating (using mathematical modeling) other associated factors: age, levels of diastolic blood pressure and cholesterol in the blood serum, alcohol consumption, hematocrit values and body weight. Long-term, long-term smoking abuse has a particularly harmful effect. Thus, American neurologists concluded that for people aged 60 years who have smoked for 40 years, the risk of having severe atherosclerosis increases by approximately 3.5 times compared to non-smokers. Evidence has been obtained that pathology of the great vessels of the head progresses more slowly in people who quit smoking compared to smokers.
Reducing the bad effects of nicotine on blood vessels
The only effective method to avoid the effects of tobacco smoke on health is to completely quit smoking.
But if a person is unable to get rid of a bad habit, then it is worth adhering to a number of measures:
- Reduce the number of cigarettes you smoke per day.
- Use products from well-known brands.
- Avoid smoking before and after exercise, stress, food and alcohol.
- Take regular walks in the fresh air.
- Switch to smoking an electronic cigarette.
By following these rules, a person suffering from nicotine addiction will be able to smooth out the negative effect of cigarettes on the cardiovascular system.
These recommendations are effective only when there are no cardiovascular diseases and the smoking history is short. The ultimate goal should be to get rid of a bad habit.
Take the smoking test
Cleansing blood vessels after quitting cigarettes
There are no methods or drugs for cleansing after quitting smoking. The body's self-regulation mechanisms will do everything. Yesterday's smoker just has to stay out of the way.
To increase the effectiveness of CVS recovery, you should:
- Stop drinking alcohol and caffeine.
- Take a course of vitamin complexes, taurine - a substance that is used as a food additive and has a positive effect on the cardiovascular system.
- Start physical therapy classes.
- Eliminate fatty and fried foods from your diet.
- Drink more water to detoxify your body.
- Treat chronic diseases.
Compliance with these points will lead to the effective use of self-regulation processes and will have a positive effect on the cardiovascular system and other body systems: nervous, digestive, endocrine.
Consequences of smoking
A bad habit affects the functioning of the entire vascular system and causes various diseases. Large vessels such as the carotid artery or small capillaries located in the skin are affected.
During the combustion of tobacco, complex chemical compounds and substances are released that directly affect the state of the vascular system. After 3-5 years of smoking experience, the most common diseases associated with the vasoconstrictor effect of nicotine may appear - intermittent claudication, thrombophlebitis, atherosclerosis. They indicate irreversible disorders in the body.
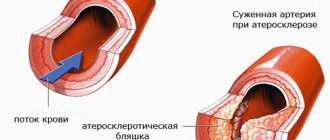
Atherosclerosis
This disease is caused by high levels of fat in the blood. The arteries and veins of the lower and upper extremities, kidneys, heart, brain and intestines are affected. Due to the release of adrenaline during smoking, the production of cholesterol is stimulated. There is a thickening of the vascular walls, accumulation of fatty plaque, and a decrease in the lumen. Blood circulation becomes difficult.
The following factors contribute to the development of atherosclerosis:
- eating unhealthy foods (fried, smoked, flour);
- alcohol consumption;
- lack of physical activity;
- overweight;
- hereditary factor;
- diabetes;
- frequent nervous tension;
- age after 45 years.
Smoking has a vasoconstrictive effect on blood vessels, which is doubly dangerous for patients with atherosclerosis. The already narrow lumen after smoking a cigarette decreases even more, so blood circulation is impaired. All organs begin to suffer from a lack of oxygen and nutrients.
How smoking affects the blood vessels of the brain
The main consequences are:
- Electrical activity of the brain decreases, intelligence decreases;
- Memory deteriorates;
- Solving even simple problems takes longer;
- A decrease in brain activity leads to behavioral disorders, irritability and unmotivated aggression appear, and there is a risk of nervous disorders.
The human body functions like a single organism. All processes occurring in it are coordinated with each other and have a direct impact on overall health.
The brain is the central control organ on which the functioning of the entire organism depends. The brain is nourished by those substances that are delivered by blood flows, so any agents that penetrate the blood also enter the brain.
During smoking, nicotine is delivered to the lungs, then enters the blood, and after about 8 seconds it reaches the brain cells through the blood vessels and affects brain function.
Under the influence of a harmful substance, the susceptibility of brain neurons decreases, and the blood vessels that deliver oxygen to brain cells are significantly reduced. A smoker experiences symptoms of hypoxia - oxygen starvation.
Due to disturbances in the functioning of blood vessels, systematic migraines, memory impairment, poor coordination of movements, and frequent yawning appear. The lack of oxygen inhibits the transmission of electromagnetic impulses, which has a bad effect on the emotional state: the smoker develops unmotivated irritability, and sometimes aggression.
Effect on the heart
The harmful effects of nicotine on blood vessels primarily affect the heart muscle. An increase in blood pressure increases the load on the heart - the smoker’s muscle constantly functions at the limit. Adapting to changes, the heart gradually enlarges due to the growth of muscle tissue - the so-called “bull heart” is formed. The disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- swelling of the legs and abdominal area
- increased heart rate
- dyspnea
- pain in the heart area
- increased sweating
Fragility of blood vessels, narrowing of the lumen, and thickening of the blood impairs the nutrition of the heart muscle, which causes oxygen starvation. Over time, complications transform into heart attack and heart failure.
How does a cigarette affect the human brain?
How does smoking affect the human brain? Harmful substances that enter the smoker's brain along with blood flow, frequent oxygen deprivation have a detrimental effect on brain cells. Studies show that the brain of a smoker is damaged over time in the frontal zones, cells die, which has a bad effect on the ability to maintain normal life activities: drive a car, maintain a conversation.
Over the years, the area of damage grows and the difficulties increase. The frontal area of the brain is responsible for mental activity, motivation of actions, motor and speech activity. Defeats in this area lead to a person losing his purpose in life.
Decreased mental activity reduces the intellectual potential of a smoker. These changes occur gradually, but after a few years of systematic smoking they will be noticeable.
Impact on legs
The negative effect of nicotine on the vessels of the lower extremities is associated with insufficient blood flow, narrowing of the lumen due to blockage by plaques and blood clots. This leads to obliterating endarteritis, which is characterized by damage to the arteries against the background of their narrowing until complete closure. The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- pain when walking
- gait disturbance
- asthenia
- decreased response to external stimuli
- paresthesia
- convulsive syndrome, worse at night
Is it possible to smoke if you have a concussion?
A concussion is characterized by painful symptoms. The victim experiences dizziness, severe headache, nausea, and sometimes vomiting. There is an increased body temperature, lack of appetite, inhibition of reactions, and short-term fainting.
Possible weakness in the legs, feeling very tired, inability to concentrate, and inability to carry on a conversation.
When smoking, nicotine enters the bloodstream and reaches the brain cells. As a result, the vessels narrow and a lack of oxygen occurs.
With a concussion, smoking increases symptoms:
- Headache;
- Nausea;
- Weakness;
- Absent-mindedness;
- Possible loss of consciousness.
Smoking harms the victim: it inhibits the recovery of brain cells after injury, the victim’s recovery slows down, and painful symptoms intensify.
A concussion subsequently leads to the appearance of epileptic seizures, chronic hypertension, and vegetative-vascular dystonia. Smoking increases the risk of these complications.
Stroke and smoking - the relationship between concepts
Smoking helps permanently change blood vessels in the brain, which leads to the development of cardiovascular diseases and stroke:
- Firstly, nicotine constricts blood vessels. With systematic smoking, this phenomenon becomes permanent and the vessels no longer return to their original state.
- Smoking increases blood pressure. As a result, the walls of the vessels will be thin, the tissues will become coarser, and elasticity and strength will be impaired. This increases the risk of blood vessel rupture and brain hemorrhage.
- Systematic smoking disrupts the ratio of lipids in the blood. This leads to the deposition of cholesterol on the walls of blood vessels, followed by hardening. The lumen narrows, blood circulation is impaired and, as a result, the risk of stroke increases. Cholesterol plaques can break off from the walls of blood vessels and travel through the bloodstream. Reaching a narrower area, they lead to blockage of blood vessels. If this happens in the vessels of the brain, an ischemic stroke occurs.
- Harmful substances contained in tobacco smoke increase blood clotting, which increases the risk of blood clots.
What vascular diseases does it provoke?
Nicotine addiction leads to the development of various diseases, but the leading positions are occupied by pathologies of the heart and blood vessels:
- arterial hypertension;
- thrombosis and thrombophlebitis;
- atherosclerosis;
- myocardial ischemia;
- stroke of the brain and kidneys.
Smoking has a particularly negative effect on the health of the fetus, since nicotine and other components penetrate the placental barrier, having a toxic effect on the developing organs and systems of the fetus.
Smoking provokes the development of diseases of the pulmonary-bronchial system, oncology, and sexual impotence. The pathologies are based on vascular insufficiency of varying degrees of intensity.
Restore the functioning of blood vessels and compensate for the damage caused
Smoking consistently kills the body, its effect on the body is so large-scale that it is impossible to make tobacco smoke less harmful: a decrease in the amount of nicotine leads to an increase in other harmful substances.
To begin restoring the blood vessels of the brain, you need to completely abandon the bad habit. Passive smoking has almost the same effect on the body as active smoking.
Now let's look at how to restore blood vessels after quitting smoking. First, consult a neurologist to undergo an examination and determine the condition of the brain vessels. The elasticity of the walls of blood vessels is restored without the use of drugs, which occurs naturally in a short period of time: on average, regeneration takes 3-4 weeks.
The vessels then dilate to normal levels to carry enough blood. The brain begins to receive enough oxygen and restores vital processes. Over time, brain cells regenerate.
Metabolic disorders associated with smoking lead to increased cholesterol levels in the blood and deposition on the walls of blood vessels. After quitting smoking, atherosclerotic lesions cannot disappear, so patients need drug therapy and a therapeutic diet.
Possible effects on the brain
Smoking causes irreversible changes in the vessels of the brain, heart or general circulatory system; there is not a single smoker who does not suffer from headaches, palpitations or shortness of breath. Of course, heart attacks and strokes develop mainly in older smokers, but hypertension, atherosclerosis and obliterating endarteritis today occur in the age group of 30 years and older.
Intermittent claudication, decreased performance, frequent headaches, thrombophlebitis and increased cholesterol levels in the blood - all these consequences of smoking begin to appear after 3-5 years of “cigarette experience”.
Every year, the number of people who die from myocardial infarction, ischemic heart disease or stroke continues to increase, and in more than 30% of cases the cause of death is smoking.
If you smoke at least 5-6 cigarettes every day and you are over 30 years old, think about it, you are at risk for several diseases at once: thrombophlebitis, arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis and obliterating endarteritis. And if you are over 40, coronary artery disease, angina pectoris and heart attack are also added to the list.
Don’t want to die, or turn into a helpless disabled person before you can retire? Then you should quit smoking and start restoring your health and strengthening your blood vessels. Unfortunately, the effect of cigarettes and nicotine on blood vessels is irreversible, but the sooner you quit smoking, the lower the risk of developing serious diseases such as stroke or heart attack.
DO YOU WANT TO QUIT SMOKING?
Then you need a strategy for quitting cigarettes. With its help it will be much easier to quit.
Almost every second person has a nicotine addiction. When inhaling cigarette smoke, a large number of toxins and poisons enter the individual’s body, which causes the blood vessels to narrow. Smoking with VSD has life-threatening consequences. A cigarette relieves pain, but instead takes away several days of life.
What happens to the brain when you quit smoking
When you quit smoking, the condition of the blood vessels returns to normal, blood circulation is restored, and the brain cells begin to receive enough oxygen. This affects the state of the nervous system: irritation and anger go away, and it becomes easier for a person to control his emotional impulses.
The unpleasant health consequences of smoking gradually disappear: memory is restored, the ability to concentrate is restored, thinking abilities are restored and the level of intellectual development returns to normal levels. Destroyed brain cells are regenerated.
Share with friends or Save for yourself!
4.4 / 5 ( 48 votes)