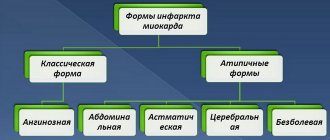
What is the prognosis of a patient with a heart attack and how to influence it
The general prognosis in the post-infarction period is calculated separately for each patient, since additional data from the comorbid background and individual characteristics are taken into account.
Modern methods of diagnosis and emergency care increase survival after a heart attack to 90% during the first year.
To improve the prognosis on their own, patients are recommended to:
- monitoring the course of the disease with regular examinations and additional studies;
- Seeing a doctor if new symptoms appear;
- lifestyle changes;
- systemic medication (for the treatment of hypertension, arrhythmia, prevention of lipid disorders and thrombus formation).
After an MI, lifelong treatment and rehabilitation are required to prevent complications and the development of pathologies in other organs and systems.
Correction of risk factors
The death of a patient in the early or late post-infarction period is largely determined by risk factors for the development of complications or recurrent MI.
In order to prevent and increase life expectancy, it is recommended:
- lifestyle modification: adequate physical activity, giving up bad habits and balanced nutrition;
- weight normalization using non-drug methods. If ineffective, pharmacological agents are prescribed;
- control of blood pressure indicators;
- avoidance of stressful situations;
- systemic intake of prescribed drugs.
Treatment of concomitant pathologies
Injuries, infectious and endocrine diseases aggravate the course of coronary heart disease, so control and adequate treatment of concomitant pathologies affects the prognosis for the patient. Mandatory correction is required:
- diabetes mellitus - glucose level monitoring is carried out in a cardiology hospital to take into account the risk of complications and prescribe treatment;
- myocarditis – inflammation of the muscle mass of the heart worsens the course of the post-infarction period with the development of rhythm disturbances and decreased contractile function;
- kidney disease - impaired excretion of fluid from the body, disorders of hormone synthesis lead to damage to the vascular wall, increased blood pressure;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland (Hashimoto's goiter, diffuse toxic goiter and others).
Traumatic brain injuries with damage to the medulla oblongata (this is where the center for regulating vascular tone and cardiac activity is located) worsens the prognosis for rehabilitation after a heart attack.
Treatment tactics
Treatment of a heart attack takes place only in the cardiology department of a hospital. Indications for hospitalization are ECG results indicating a pathological process, symptoms of heart failure. The main tasks of this period:
- Eliminate pain
- Reducing the area of cardiac necrosis,
- Restoration of blood flow in the coronary arteries,
- Reducing the risk of blood clots,
- Unloading the heart, fighting arrhythmia,
- Maintaining optimal blood pressure levels.
To eliminate pain in the most acute and acute periods, narcotic analgesics (Morphine, Promedol, Fentanyl, Omnopon) are used.
They are administered intravenously in the first minutes of medical care and effectively relieve pain. If it is necessary to relieve fear or excessive excitement, then tranquilizers (Relanium, Diazepam) are used.
Dissolution of blood clots and restoration of blood flow in the coronary and small arteries of the myocardium is the goal of thrombolytic therapy. Timely administration of thrombolytics reduces the size of the focus of myocardial necrosis, which significantly improves the prognosis of the disease.
Streptokinase, Fiboinolysin, Alteplase have thrombolytic activity. Prevents thrombus formation Heparin prevents thromboembolism.
Such therapy should be carried out in the first 6 hours after a heart attack to quickly restore blood flow.
Contraindications for it are sudden bleeding. It is necessary to exclude a history of stroke, gastrointestinal diseases with damage to the mucous membrane, and recent surgical interventions.
Therapy for the treatment of myocardial infarction includes the use of anticoagulants, the main drug from this group is Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid). Its use prevents platelets from sticking together and attaching to the walls of blood vessels, and red blood cells are able to be easily transported through the bloodstream.
An important part of drug therapy is the use of ACE inhibitors to slow down cardiac activity, reduce blood pressure, and dilate blood vessels. Indications for their use are acute heart failure. These are Captopril, Ranipril, Enalapril.
Additionally, cardioprotectors are prescribed to treat arrhythmia and limit the area of myocardial damage. These can be beta-blockers (Atenolol, Propranolol), nitrates in the form of intravenous infusion of Nitroglycerin, vitamins.
If drug treatment does not alleviate the patient’s condition, he is prepared for surgical treatment for aortic bypass surgery, angioplasty, or installation of a stent in the coronary artery.
The rehabilitation period requires constant use of medications to prevent thrombosis and arrhythmia, and maintain optimal blood pressure levels. In addition to them, you can use traditional medicine recipes in the form of tinctures and decoctions of aloe, hawthorn, calendula, and motherwort.
A significant part of maintenance therapy for those who have suffered a myocardial infarction is diet and optimal and dosed physical activity.
You need low-fat, easily digestible food that is beneficial for blood vessels and the heart muscle. These can be cereals, dairy products, dried fruits, juices, light vegetable and fruit salads.
To prevent congestion, it is recommended to engage in physical therapy, measured walking under the guidance of a specialist; these activities should be started as early as possible.
Rehabilitation after a heart attack can take place in cardiac sanatoriums if there are no contraindications for this. A special commission decides whether or not to grant disability after a myocardial infarction, and whether it is possible to return to work after rehabilitation.
Why do people often die from heart attacks?
Our heart is at the same time the most reliable and unreliable organ. Heart muscle cells work as long as a person lives. However, the circulatory system of the heart is designed in such a way that if the lumen of the vessel is blocked completely or partially, some of the cells die.
Cardiomyocytes do not know how to multiply, so neighboring ones have to take on an increased load. Therefore, after a heart attack, any overload can lead to serious problems.
In the initial post-infarction period, death most often occurs due to the following reasons:
- Ventricular arrhythmia is a severe type of heart rhythm disturbance, manifested by an isolated increase in heart rate or asynchronous work of the ventricles. The most common cause of death in the initial period of the disease.
- Acute heart failure is a common complication of a major heart attack. Accompanied by symptoms of pulmonary edema. May lead to cardiogenic shock.
- Cardiogenic shock - develops with severe insufficiency of the left ventricle. Accompanied by high mortality (up to 80%).
- rupture of the interventricular septum;
- rupture of the wall of the left ventricle;
- atrial fibrillation;
- left ventricular dysfunction;
- heart failure.
conclusions
The death of part of the heart muscle is always accompanied by generalized disorders throughout the body. The quality of medical care significantly influences the prognosis of post-infarction patients. If you follow the recommendations and pay attention to your health, the patient can live a long, fulfilling life after a heart attack.
The following sources of information were used to prepare the material.
Life after myocardial infarction is often shortened, which is due to the development of irreversible changes in tissues (necrosis), a decrease in the contractile function of the heart, the development of heart failure and other consequences. Such people need proper care from relatives and constant monitoring. Failure to comply with medical recommendations can cause repeated heart attacks and death.
Heart attack and risk of death
The life expectancy of an individual person is very difficult to estimate. Some can live for a month, others for many years. After all, at the time of the development of a heart attack, the age and health status of people are very different. Therefore, doctors do not estimate life expectancy, but the probability of death. The higher it is, the greater the risk of death.
During a heart attack, there are 2 dangerous periods: before the ambulance arrives (the highest number of deaths), the first 3 days after hospitalization (the second highest number of deaths). If the patient survives both periods, he recovers. Hospital mortality is about 3.8-5.3%.
How long do they live after a major myocardial infarction? About the same as after a microinfarction. According to statistics, hospital mortality rates for both forms are almost the same. People with a large heart attack die less often in the first year after the attack (9.0%), with a small-focal heart attack more often (11.6%) (1). Most deaths from microinfarction occur due to noncardiac problems.
About the occurrence of a heart attack
In order to understand the question of what are the consequences of myocardial infarction, let’s find out what kind of disease it is and why a heart attack is dangerous.
A heart attack is characterized by the formation of a place in the heart muscle where oxygen does not flow. It can be of different sizes. As a result of this, the cells begin to die and a scar appears in their place. The consequences of a microinfarction are the formation of scars that a person learns about only during hospitalization after the next attack.
In the area of the heart where the scar has formed, the heart muscle begins to contract not at full strength, therefore, this leads to an inadequate supply of blood to the human body, which in turn affects the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the body’s cells. The scar prevents the penetration of electrical impulses from the cells of the heart tissue to ensure its synchronous contractions.
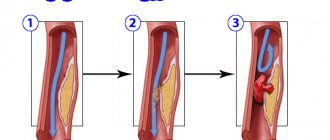
A place where oxygen does not flow is formed due to atherosclerotic damage that occurs due to the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque on a vessel. A blood clot forms from the escaping blood. The flow of blood into the vessel is blocked. This vessel in the heart is called the myocardium. The consequences of this process are irreversible.
What determines life expectancy?
Life expectancy after a heart attack varies widely. Scientists analyzed cases of death and compiled a list of factors that increase the risk of death.
There are several approaches to determine the prognosis. The TIMI system, which determines the risk of death in the next 2 weeks, has gained the most popularity. It is very easy to use and quite accurate. Each risk factor is assigned a certain score. Based on the sum of points, you can determine the probability of death.
- diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, angina attacks – 1 point;
- systolic pressure Probability of relapse
Until humanity has discovered effective treatments for coronary heart disease, people who have had a heart attack will be more likely to develop a new one.
Recurrent myocardial infarction occurs, according to various sources, in 4-31% of people (2). Although there is less optimistic data, according to which a recurrence of a heart attack develops in 40% of patients. A new heart attack significantly increases the likelihood of death (35% of hospital mortality cases).
Often, a recurrent attack develops in people with (risk factors):
- arterial hypertension;
- early post-infarction angina;
- smoking;
- high cholesterol levels in the blood;
- poor tolerance to physical activity (positive stress tests).
Diagnostics
For primary diagnosis, the doctor collects anamnesis, analyzes the nature of the pain, assesses the external condition, palpates and listens to the heart. These methods can reveal:
- Increased heart rate;
- Systolic murmurs;
- Violations of heart sounds of various origins.
Characteristic symptoms may be a decrease in blood pressure and an increase in body temperature to 38⁰C for a week.
To clarify the diagnosis, laboratory blood tests are used, which can determine the following changes:
- Increased level of white blood cells;
- Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate;
- Biochemical symptoms of the inflammatory process;
- The emergence of biochemical markers of myocardial cell necrosis.
The most important diagnostic method is the electrocardiogram (ECG). By analyzing its results, the following characteristics of a heart attack can be determined:
- Localization
- Prevalence
- Depth
- Complications
In a separate article you will find ECG signs of myocardial infarction with photos and interpretation.
Additionally, the doctor may prescribe radioisotope scintography, echocardiography to determine myocardial contractility, MRI and CT to detect blood clots, determine the size of the heart and its cavities.
How to influence the forecast?
How many years a person lives after a heart attack largely depends on the person himself. Disciplined adherence to doctor's recommendations significantly increases life expectancy. To live longer, you need to undergo a rehabilitation course and make its principles the basis of your life (3):
- Give up cigarettes. Smoking increases the likelihood of death by 35-43%. since tobacco smoke promotes thrombus formation due to spasm of the vascular wall;
- Physical exercise. Daily physical activity reduces heart attack mortality by 26%. It is useful to alternate different types of exercise: walking, performing physical therapy exercises, working in the garden, around the house;
- Normalize weight. People with a BMI of more than 30 kg/m2 and/or a waist circumference of 88 cm (women), 102 cm (men) are at risk of developing fatal complications.
- Monitor blood pressure (BP). The presence of uncontrolled hypertension significantly increases the chances of developing a recurrent heart attack, as well as other cardiovascular pathologies.
- Prevent the development of influenza. With this viral disease, the likelihood of heart complications is high. People who have had a heart attack are recommended to be protected by vaccination.
- Follow a diet. Minimizing the amount of salt, fried, fatty foods, pickles, marinades, and alcohol increases the chances of a long life.
Psychological assistance does not affect life expectancy, but increases its quality. If socialization is difficult for you, you cannot overcome your fears, you may have developed depression - a common complication after a heart attack. Contact a cardiologist, he will write out an appointment with a psychologist.
Main goals of the recovery period
Restoring health lost as a result of a heart attack is an extremely difficult task. After all, it is not easy for any person to change their environment, but it is especially difficult to change their usual way of life for men, who are more conservative compared to women.
Many patients are under the supervision of a doctor in the first stages. Patients with a milder form of the disease and a favorable course are discharged home. But both categories of people need information on how to properly organize their daily routine, what should be abandoned, and what, on the contrary, should be made the main rule of a new life. Such knowledge is necessary for people to fully adapt after a heart attack.
If you remove minor factors, then the main points in the recovery period will be:
- A balanced diet aimed at smooth weight loss if you are overweight or obese.
- Regular monitoring of blood pressure indicators.
- Mandatory monitoring of glucose and cholesterol levels.
- The daily routine should be structured in such a way as to prevent chronic fatigue.
- Stressful situations should be avoided at all costs.
- Physical activity should be dosed.
- Therapeutic gymnastics must be included in the complex of rehabilitation measures.
- Psychological assistance will help the patient to adequately respond to changing life situations.
Important point! Physical activity for patients who have had a heart attack should be determined by a doctor based on the severity of the patient’s condition. All classes begin with minimal activity, and the load increases gradually.
Consequences of myocardial infarction and life prognosis
Sometimes complications from myocardial infarction occur that can affect the prognosis. These are cardiogenic shock, acute heart failure, severe arrhythmia. More often they develop with extensive MI 3-6.
Most of the long-term consequences of MI are associated with the formation of a connective tissue scar at the site of cardiomyocyte death. If the area of myocardial infarction (necrosis of the heart muscle) can be limited using thrombolytic therapy initiated in the first 4-6 hours or cardiac surgery (coronary artery bypass grafting, percutaneous coronary intervention), then the likelihood of adverse consequences can be reduced 3-6.
Otherwise, the connective tissue does not allow this part of the myocardium to fully contract, various conduction disorders develop, and cardiac output suffers. As a result, heart failure develops; organs suffer from a lack of oxygen, which negatively affects the functioning of the entire body.
During the rehabilitation process, the functions of the affected area will be taken over by neighboring areas. This requires a certain time, compliance with the stages of rehabilitation, continuity of the prescribed treatment and a gradual increase in physical activity under the strict supervision of a health care professional.
- A cardiac aneurysm
is a thinning and bulging of the heart wall in the form of a sac, which leads to a decrease in cardiac output and the progression of heart failure. - Thromboembolic complications
can develop due to non-compliance with physical activity or deviation from the treatment plan, which always includes drugs that affect blood clotting. - Chronic heart failure
develops due to impaired contractile function of the left ventricle. Manifested by edema of the lower extremities, shortness of breath during exercise, etc.
The risk of such complications persists throughout the first year after MI 1. After a year, the likelihood of complications is less if the patient adheres to the prescribed treatment and is regularly monitored by a cardiologist 1.
Treatment tactics
After stabilization of the condition is achieved in the hospital, and doctors are convinced that the main risks of the acute period have been left behind, the patient is prepared for discharge and further outpatient treatment. He is recommended to constantly take a certain list of medications.
These include β-adrenergic blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and antiplatelet agents. Depending on the presence of concomitant diseases, for example, arrhythmia or rheumatic heart disease, additional medications may be prescribed.
Heart attack is a serious disease that is one of the main causes of death. And even in favorable cases, the patient faces difficult rehabilitation and consequences that go far into the future.
People who have had a heart attack are at high risk of cardiovascular events, so they are advised to take certain medications for life. With their help, it is possible to normalize basic blood parameters and cardiac function.
However, in addition to taking medications, patients should also reconsider their habits and lifestyle. This contributes to a significant improvement in the prognosis regarding coronary heart disease and the likelihood of recurrent heart attacks.
In addition, a healthy lifestyle helps the heart recover faster. Therefore, after a heart attack you should not despair. People should, on the contrary, seriously reconsider their attitude towards their own health, and not ask how long they live after a heart attack, assuming a negative answer.
Treatment of a heart attack takes place only in the cardiology department of a hospital. Indications for hospitalization are ECG results indicating a pathological process, symptoms of heart failure. The main tasks of this period:
- Eliminate pain
- Reducing the area of cardiac necrosis,
- Restoration of blood flow in the coronary arteries,
- Reducing the risk of blood clots,
- Unloading the heart, fighting arrhythmia,
- Maintaining optimal blood pressure levels.
They are administered intravenously in the first minutes of medical care and effectively relieve pain. If it is necessary to relieve fear or excessive excitement, then tranquilizers (Relanium, Diazepam) are used.
Dissolution of blood clots and restoration of blood flow in the coronary and small arteries of the myocardium is the goal of thrombolytic therapy. Timely administration of thrombolytics reduces the size of the focus of myocardial necrosis, which significantly improves the prognosis of the disease.
Streptokinase, Fiboinolysin, Alteplase have thrombolytic activity. Prevents thrombus formation Heparin prevents thromboembolism.
Such therapy should be carried out in the first 6 hours after a heart attack to quickly restore blood flow.
Therapy for the treatment of myocardial infarction includes the use of anticoagulants, the main drug from this group is Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid). Its use prevents platelets from sticking together and attaching to the walls of blood vessels, and red blood cells are able to be easily transported through the bloodstream.
An important part of drug therapy is the use of ACE inhibitors to slow down cardiac activity, reduce blood pressure, and dilate blood vessels. Indications for their use are acute heart failure. These are Captopril, Ranipril, Enalapril.
Additionally, cardioprotectors are prescribed to treat arrhythmia and limit the area of myocardial damage. These can be beta-blockers (Atenolol, Propranolol), nitrates in the form of intravenous infusion of Nitroglycerin, vitamins.
If drug treatment does not alleviate the patient’s condition, he is prepared for surgical treatment for aortic bypass surgery, angioplasty, or installation of a stent in the coronary artery.
The rehabilitation period requires constant use of medications to prevent thrombosis and arrhythmia, and maintain optimal blood pressure levels. In addition to them, you can use traditional medicine recipes in the form of tinctures and decoctions of aloe, hawthorn, calendula, and motherwort.
You need low-fat, easily digestible food that is beneficial for blood vessels and the heart muscle. These can be cereals, dairy products, dried fruits, juices, light vegetable and fruit salads.
To prevent congestion, it is recommended to engage in physical therapy, measured walking under the guidance of a specialist; these activities should be started as early as possible.
Life expectancy after myocardial infarction
Experts most often estimate survival after a heart attack using patient registries in different regions. Survival rates are typically analyzed at 1, 3, 5, and 8 years. It has been established that if patients do not have impaired renal function or diabetes mellitus, then almost all of them survive up to three years after suffering an MI 3-6.
Long-term survival largely depends on the quality of care provided and the type of treatment chosen at the hospital stage. According to the DANAMI-2 study, among all patients with myocardial infarction, the eight-year survival rate was: 15.6% after thrombolysis and 12.4% after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) 3 .
The greatest risk of death occurs in the first year of life after MI (up to 32%). The main causes: recurrent heart attack - 37%, chronic ischemic heart disease - 21%, sudden cardiac death, pulmonary embolism and acute cerebrovascular accident (stroke) 5 .
Depending on the medications that patients take after an MI, the lifespan also differs. Beta blockers have been shown to reduce mortality from 61% (in those not taking them) to 24% over 5 years 3 .
- Help the body recover after myocardial infarction/cardiac surgery and adapt to usual stress.
- Restore performance and quality of life.
- Reduce the risk of complications and recurrent heart attacks.
- 1 Stationary.
It is carried out in the intensive care unit or intensive care unit, and then in a specialized cardiology department or in a vascular center. - 2 Rehabilitation center or sanatorium.
Lasts up to 28 days after a heart attack in the rehabilitation department and in a cardiological sanatorium. - 3 Outpatient.
Observation in the clinic for 12 months by a cardiologist, rehabilitation specialist and physical therapy instructor. Continues independently at home.
The basis of rehabilitation is physical activity, which gradually increases under the supervision of specialists. So, if on the first day the patient is prescribed strict bed rest, then over time it expands with the ability to sit up in bed several times a day, walk around the ward and the corridor. After 8-18 days, depending on the severity of the MI, the patient is already able to walk up to 3 km at low speed and exercise on an exercise bike 7 .
The physical rehabilitation program is developed individually. Both an accelerated program (7-10 days) is possible for patients with low risk, and an extended one for those with a high risk of complications. At each stage, the patient's condition is monitored and assessed according to various criteria, including stress tests 7 .
Initial stage of recovery
A favorable prognosis for patients who have had a heart attack largely depends on the moment at which the recovery phase begins
Therefore, it is so important to carry out the rehabilitation period as early as possible.
Of course, such measures should be carried out taking into account the condition of the patient himself and the degree of damage to the heart muscle.
In the first days, that is, at the hospital stage, the following active loads are allowed:
- If the process is moderately severe, you can start training within 2-3 days. In severe MI, this is possible only after a week.
- On about 4-5 days, the patient is allowed to sit on the bed for several minutes with his legs down.
- If the patient’s condition does not cause concern, then after a week he is allowed to take a few steps near his bed.
- The patient is allowed to move freely around the ward two weeks after the attack.
- If the patient’s condition is satisfactory, the exercise therapy instructor may, in the third week of the hospital period, allow him to go out into the corridor and even master several steps of the stairs.
- Every day the walking distance gradually increases.
During this particularly important period, a patient with a heart attack should not be left alone. Relatives or someone from the medical staff must be with him.
To assess the patient’s condition, it is necessary to measure blood pressure and pulse rate before and after physical activity. If necessary, an electrocardiogram should be done. If the measurement data indicates a negative change in the patient's condition, then physical activity is reduced.
In the normal course of the recovery process, the person is sent for further rehabilitation to a sanatorium institution or a specialized cardiac center. And only after this the doctor gives the patient detailed instructions for carrying out activities at home.
How long do they live after a massive heart attack?
Kabardino-Balkarian State University named after. HM. Berbekova, Faculty of Medicine (KBSU)
Level of education – Specialist
State educational institution "Institute for Advanced Medical Studies" of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Chuvashia
According to medical research, life expectancy after a heart attack suffered by a person depends on the time of rehabilitation and its quality. If the patient was able to survive the first month, then the chance of living for another year increases to 85%, the next five years - 70%. Over the next ten years, the body of a person who has suffered a massive myocardial infarction recovers so much that his heart is not much different from the organ of a healthy person. Let's take a closer look at myocardial infarction - how long people live after it, as well as what needs to be done to prevent the body from causing problems in the future.
What is a microinfarction?
A microinfarction is necrosis of the heart muscle, which occurs due to inadequate blood supply or ischemia. The symptoms are similar to a normal myocardial infarction, but are much milder. A microinfarction can occur without symptoms. Often the cause of poor coordination of movement when walking is a small-focal heart attack, which can seriously harm the overall health. If one of the signs of the disease appears, it is important to undergo treatment in a hospital. The main cause of microinfarction is ischemia, which develops when blood vessels are blocked by blood clots. Acute heart attack is especially dangerous for the patient's life.
The likelihood of a second heart attack: why can it happen?
High mortality after a heart attack is often caused by a relapse of the disease - in 60% of cases, it is a repeated heart attack that leads to the death of a person. That is why we consider it necessary to briefly consider the question of why such a phenomenon is possible and whether it is possible to live without fear of it in the future.
It is impossible to predict with 100% accuracy whether the disease will recur. Many people, after suffering a heart attack, lead a healthy lifestyle, adhering to the doctor’s instructions, but the disease returns again, while others return to their previous lifestyle, but the disease no longer makes itself felt. Doctors identify the following factors that can affect both relapse and a person’s life expectancy:
- Nature of the pathology. During a heart attack, the integrity of the heart muscle is compromised. This process occurs differently in all people - some have one large scar, others have multiple scars.
- In 80% of cases, relapse and repetition of a heart attack appears as a result of atherosclerosis and multiple atherosclerotic plaques, deposits of which block the lumen of the coronary arteries.
- Male gender. Men more often suffer from cardiovascular diseases (including the phenomenon under consideration), which is due to the lack of a large amount of estrogen in the body. This statistic is true up to age 70—after that, the incidence of the disease is the same in men and women.
- Obesity and diabetes mellitus, which place additional stress on the cardiovascular system.
- Arterial hypertension, which impairs the contractility of the heart muscle.
- Stresses that have a psychogenic nature of origin.
- Bad habits.
- Excessive physical activity during the rehabilitation period and low compliance (failure to comply with the rules and regulations for treatment).
How long a person will live after the disease largely depends on the last point - compliance with the instructions, regimen and rules of treatment.
Lifestyle change
Why is it important to follow the recommendations:
- after the first months, lifestyle must be changed to avoid possible complications;
- after this period - to minimize the possibility of a new attack.
Compliance with the recommendations makes the recovery process much more effective and significantly increases the quality of life after myocardial infarction.
During the first days he must remain on bed rest.
Contrary to myths, intimate life for men after a heart attack causes much less difficulty than for women. Statistics say that about 80% of women who have had an attack experience various difficulties in their sexual life. But there is no need to completely abandon intimate life
It is important to realize how to behave in new realities, and that the quality of intimacy may suffer
Possible consequences in men include:
- problems with potency;
- erectile disfunction;
- premature termination of sexual intercourse;
- significant reduction in desire.
Patients can begin sexual activity a month to a month and a half after the attack
Your doctor will tell you how to live after a heart attack
To improve your health, it is important to make lifestyle changes. Each patient should:
Watch your diet. Fatty and fried foods that contain a lot of cholesterol are strictly contraindicated. Meat and fish products can only be consumed boiled and steamed. The diet should include vegetables and fruits. In no case should you overeat, as this increases the load not only on the stomach, but also on the heart. Limit the amount of salt in food to five grams. Drink less liquid, no more than a liter. Stop drinking alcohol and smoking. Create an optimal daily routine. You can't overwork yourself
It is important to take time to rest during the day. Stabilize your emotional state. To do this you need to turn to psychotherapy
Talking to a doctor will help you get rid of the fear of death. If you are overweight, solve this problem. Since obesity creates additional stress on the heart muscle.
You need to start training immediately after the acute period has passed. But they do this under the supervision of a doctor. Gradually they are allowed to increase the load and walk in the fresh air. But, if symptoms appear in the form of increased blood pressure, tachycardia, chest pain and shortness of breath, you should reduce the intensity of your training.
What can you do to prolong life after a heart attack?
Doctors can make prognoses for future life from the available medical history. Unfortunately, we cannot give the exact lifespan. Statistical data will not provide reliable information on how long people live after a major heart attack since the sample is always of a purely individual nature - age, gender, previous diseases, medical history, treatment method, heredity, etc. Despite this, we can name factors that will not only prolong life, but also improve its quality.
Undergoing rehabilitation
The first few months after a heart attack are the most dangerous, so the rehabilitation period should take place under the constant supervision of a doctor. The exact rehabilitation course should be determined by the attending physician and directly depends on the severity of the patient’s condition and other data. In some cases, rehabilitation at home is possible already from the first month after the illness, while in others it is recommended that the person be under the constant supervision of a doctor for a certain time.
Rejection of bad habits
This includes not only quitting smoking and alcohol, but also monitoring your own diet. Excess weight is a provoking factor that can cause relapse. Therefore, during the entire period after a heart attack, it is recommended to avoid excessive consumption of excessively fatty and heavy foods, coffee and other drinks that affect the functioning of the nervous and cardiovascular systems.
Special diet
The general recommendation is more vegetables, fruits and other foods containing large amounts of micro- and macroelements. It is recommended to eat foods rich in antioxidants - they inhibit oxidative processes in the body and also have a beneficial effect on the body’s recovery after illness. Note that a diet does not mean a complete rejection of usual foods and a menu of 10 products for life. The main rule is moderation in diet, combined with the maximum amount of healthy foods.
Physical exercise
Excessive physical activity is strictly prohibited, since the heart muscle in the first few months (and even years) does not have the same resource as it had before the heart attack. At the same time, moderate and constant physical activity will have a beneficial effect. A complete absence will weaken the body and lead to the fact that even minor stress in the future can be fatal for the heart. The mode of physical activity, exercises and acceptable sports (whether Nordic walking or swimming) are determined only by the attending physician.
Therapeutic and preventive exercises
If physical activity can be used only with a doctor’s prescription and only after a significant post-infarction period has passed, then over the next few months it is necessary to use special therapeutic and preventive exercises that will speed up the rehabilitation period and restore a person’s performance. There are many techniques that can be used for health care facilities - Propastin’s technique, Muravov’s technique, etc.
Traditional medicine
Note that traditional medicine does not have any pronounced effects. Among all the above rules, this one is not mandatory, but advisory. Some herbal mixtures and decoctions can be taken after discharge from the intensive care unit, others - after restoration of performance for preventive purposes. Treatment using only traditional medicine is contraindicated, since they are not able to have an effect similar to medications that are used to restore the body.
Please note that the above measures will not be able to fully restore the patient’s health. The damaged area in the area of the heart muscle becomes covered with connective tissue over time, and therefore the original structure of the muscle changes and its functionality decreases. Despite this, the above measures can prolong the life of a person who has experienced a massive heart attack, as well as minimize the likelihood of a relapse of the disease. Provided that all of the above rules are followed, a person will be able to live for a very long time after a major heart attack.
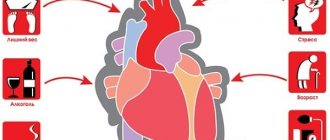
Causes of heart attack
A heart attack is a consequence of acute circulatory failure in the vessels of the heart. This may be due to the following reasons:
- Atherosclerotic vascular damage with subsequent thrombus formation.
- Vessel obstruction due to fat embolism or coagulopathy.
- Severe coronary spasm.
- Insufficiency of general blood flow, shock.
- Severe anemia.
- General hypoxia.
Atherosclerotic arterial disease is a chronic disease of the human cardiovascular system, which occurs due to fat metabolism disorders that accumulate over time. At the same time, over the course of several years, the functioning of the endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels, is gradually disrupted. In combination with an increase in the amount of lipoproteins circulating in the blood, this leads to the formation of lipid spots.
”alt=””>
This provokes the migration of leukocytes and further lipid infiltration, which leads to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, partially blocking the lumen of the vessel. If this process occurs in the coronary vessels, it leads to disruption of the blood supply to the heart. Plaques are a favorable place for the formation of blood clots, which can later break off and, moving with the blood flow, completely clog narrower areas of the vessel, causing a heart attack.
What determines life expectancy?
The second aspect, which is directly related to the length of years , is the types of complications after a heart attack. They are divided into early and late. If the lesion is small, then there will be fewer complications.
- Pulmonary edema.
- Heart rhythm failure.
- Acute heart failure.
- Thrombosis.
Most often, the disease affects the left ventricle of the heart, which is why failure occurs in this department. Its characteristic symptom is breathing problems. Forms of heart rhythm disturbances are also dangerous. Doctors say that long-term complications are not as dangerous to health as acute ones, but they appear much more often.
Cardiosclerosis is a characteristic disease for all heart patients, and directly affects life expectancy after an attack. This condition is associated with how quickly the cardiac scar heals; in the diffuse form, deviations in the activity of the heart muscle begin.
A separate list includes complications during the death of heart cells:
So, the maximum opportunity to live after a heart attack for a long number of years remains for patients whose health is not complicated by other diseases and unpleasant consequences. If you follow the recommendations during recovery, it is quite possible to significantly reduce the risk.
A procedure such as stenting, when the walls of the arteries are cleared of atherosclerotic plaques, also prolongs the life of heart attack patients. The blood flow is restored, the heart continues to work without overstrain.
What measures are necessary in the post-infarction period?
Immediately after a heart attack, to prevent complications, you must follow the following instructions:
- During the first two days, the patient must strictly adhere to bed rest. During this period, scars begin to form, so it is necessary to exclude all stress, as they can lead to changes in heart rate and surges in blood pressure.
- On the third day you are allowed to sit.
- Starting from the third day to the fifth day after a heart attack, if the patient feels better, with the doctor’s permission, you can walk around the room a little, go to the toilet, but with the help of a medical professional.
- Starting somewhere from the fourth to fifth days, you can already walk around the room and even along the street, the only thing is that you cannot climb the stairs, the duration of the walk should not exceed 20 minutes, and it must be done in the presence of medical personnel. The patient should not feel any fatigue.
- After 7 days, you can spend up to 30 minutes walking, you are allowed to take a shower, the water temperature should be pleasant for the body.
- In the second week, the patient is prepared for discharge. While still in the hospital, he is allowed to do various non-heavy exercises, using which doctors analyze how the body reacts to stress, decide on a course of rehabilitation measures for the patient, and check for symptoms of a second heart attack or signs of complications.
- If symptoms of heart failure or heart rhythm disturbances appear, the specialist makes adjustments in rehabilitation measures towards reducing the load.
By carrying out regular rehabilitation measures, the patient gradually avoids complications after a heart attack, and the functioning of the heart muscles is normalized.
How long do they live depending on the type of heart attack?
The first recommendations of doctors are to protect the patient from severe stress. Fear, joy, fright - any shock can become fatal for the body, even with positive prognosis. If such nervous shocks have happened often in the past, and promise to happen in the future, it is problematic to talk about the patient’s long life expectancy. But in their assessments, doctors also take into account the forms of the disease.
After a micro-infarction
Most often it occurs in men, starting from the age of 30, women last longer. In addition, they rarely pay attention to the symptoms of the disease, attributing it to general malaise or fatigue. Meanwhile, the consequences of a microinfarction are no less dangerous, since the next stage may already be a heart attack.
- pain behind the sternum, radiating to the left arm;
- shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air;
- nausea;
- heart rhythm disturbances.
With proper treatment, it is possible to recover and live for more than one year. The patient does not feel any sharp restrictions after a microinfarction; only strong physical activity and stress are prohibited.
After a heart attack
After a heart attack, recovery is much more problematic, because part of the heart tissue dies. During an extensive attack, most of the organ suffers, which affects the general condition of the patient. According to statistics, the process of destruction in most heart attack patients is observed in the right ventricle. If necrosis covers up to 10 cm in width, blood flow in the coronary artery is severely impaired.
The statistics of life after a heart attack are very sad. Only if the assistance was provided competently and at a high level, we can talk about good chances. If a person lives for 10 years after an attack, then his life expectancy is equal to that of a healthy person.
After another heart attack
The second attack is much more dangerous and most often occurs in those suffering from hypertension. This disease is detected in all heart attack patients and is often accompanied by asthma and heart rhythm disturbances. This time the symptoms will be less noticeable, since the affected organ reacts much weaker. In 80% of cases, a repeated heart attack is provoked by atherosclerosis.
- pain radiating to the arm;
- severe suffocation;
- pressure decreases;
- fainting.
It is difficult for doctors to predict whether there will be a relapse or not, since it depends on the general health of the patient and how well he follows his diet and daily routine. A distinction is made between repeated and recurrent infarction. In the first case, a heart attack may occur a couple of months after the first one. In case of relapse, this may happen earlier. Moreover, the survival rate after a second or recurrent heart attack is low.
To avoid such manifestations and live for more than one year, you must try to reduce the amount of bad cholesterol in the blood, in medical terms - low-density lipoproteins. Dietary nutrition, drug treatment, and traditional methods will help with this.
Weight control and dieting
After an illness, the heart muscle is subjected to serious stress if the body weight is sufficiently higher than normal. Therefore, if you are overweight, you should try to reduce it. The first basic point for weight loss is dieting. It is strictly forbidden to use strict diets. The best option would be to eat small portions of food, but every 3 hours.
The diet should be varied, but you should avoid foods rich in cholesterol, since a third of cases of coronary heart disease are caused by high cholesterol levels. Fatty and fried foods are strictly contraindicated - they contribute to the further development of atherosclerosis.
To eliminate the risk of further development and recurrent attack, you should consume more:
- Whole grain breads and cereals;
- Fresh and processed vegetables - 200 g, fresh and frozen fruits - at least 5 servings per day (1 serving is 1 apple, or 1 banana, or 1 orange, or 1 pear, or 2 kiwis, or 2 plums, or 1 slice melons, or 1 glass of juice);
- All legumes (including soybeans and soy protein) – 300-400 g per week;
- Lean meats, lean and fatty fish should be consumed no more than twice a week, fish from the northern seas is preferable, seafood can be consumed in moderation;
- Skim milk or fermented milk products – 200 ml, cottage cheese or low-fat cheese – 30 g;
- Chicken egg white, yolk – 2-3 times a week;
- Low-calorie sweets;
- To season food, you can use vinegar, ketchup, mustard and fat-free dressings. Instead of animal fats, it is preferable to use vegetable oils, preferably olive oil.
It should be remembered that it is necessary to limit the consumption of table salt, completely avoid smoked meats, coffee, chocolate, and alcohol.
To maintain normal functioning of the heart muscle, you need to eat dried apricots, raisins, prunes, which are rich in potassium, and seafood rich in iodine.
Risk factors
There are a number of factors that affect how long a person can live after an attack.
- Nature of the disease. Some people have one large scar on their heart after a heart attack, while others have several small ones.
- The appearance of atherosclerotic plaques that block the arteries.
- In men, cardiovascular diseases are provoked by a lack of large amounts of estrogen in the blood, which is why heart attacks occur more often in them than in women. But this situation is typical only up to 70 years of age, then the incidence rate is the same.
- Diabetes or excess weight, which greatly overloads the heart muscle.
- Heavy loads during the recovery process.
Statistics
The introduction of surgical interventions (bypass surgery and stenting) into clinical practice is encouraging: the incidence of complications in the early period has decreased by 25% over the past 15 years. The most common causes of death after a heart attack:
- acute heart failure with the development of pulmonary edema;
- cardiogenic shock – systemic circulatory disorder with a drop in blood pressure;
- acute left ventricular aneurysm – thinning of the wall with protrusion. Its rupture is accompanied by cardiac tamponade: the cavities of the pericardial sac are filled with blood, disrupting the contractile function of the myocardium;
- rhythm and conduction disturbances (ventricular or atrial fibrillation, complete atrioventricular block and others);
- systemic thromboembolism - the spread of blood clots throughout the vascular bed with blockage of the arteries of the kidneys and brain (with the development of stroke);
- recurrence of heart attack.
How long do patients live on average?
The prognosis for myocardial infarction depends on the characteristics of the pathology and other factors, including age, gender, and the presence of concomitant diseases. The timeliness of care provided and systemic administration of medications (before an acute coronary event) also affect the outcome of the pathology.
Statistics on life expectancy after myocardial infarction are presented in the table.
In medical practice, there is an opinion that 25% of all deaths from a heart attack occur in the first minutes, 50% in the first hour, 75% in the first day. The absence of acute complications within 24 hours is the key to a favorable prognosis for the patient.
What determines the duration of future life?
How long and how long you can live after a heart attack is determined by the following indicators:
Q wave on the electrocardiogram (characterizes the presence, location and size of a scar in the myocardium);
- spread of the process: extensive (transmural) infarction has a more unfavorable prognosis compared to large focal ones;
- arterial hypertension – persistent increase in blood pressure;
- diabetes mellitus and the degree of its compensation;
- smoking and drinking alcohol;
- lipid metabolism disorders with increased levels of cholesterol and low-density lipoproteins;
- left ventricular dysfunction;
- the formation of heart failure;
- the presence of arrhythmias (atrial fibrillation, high-class extrasystole, atrioventricular block and others);
- timeliness of assistance - thrombolytic therapy or reperfusion (restoring blood flow) operations.
Statistical characteristics of 3-year survival of patients with acute myocardial infarction are presented in the table.
- Q-myocardial infarction: 93%
- Non-Q infarction: 95%
- Men – 93.5%.
- Women – 95.2%
- Young (40-49 years old) – 99%
- Average (50-69 years old) – 95%
- Elderly (over 70 years old) – 99%
How to maximize life after a heart attack?
It is difficult to give an exact figure for how many years people live after a heart attack, since personal characteristics of the body, the severity of the disease, and heredity are also taken into account.
Helps the body return to normal, live for several years with a competent menu and giving up alcohol and cigarettes. You also need to regularly do special exercises; swimming and walking can help restore recovery. But all physical activity is only on the recommendation of a specialist.
It is difficult to predict the chances after a heart attack; it all depends on how sensitive a person is to his health. It is very important to undergo diagnostics on time and consult with specialists. If the disease is recognized at an early stage, such a patient has a much greater chance of recovering quickly and without consequences.
What could be the consequences?
The most severe consequences of a heart attack are observed with extensive transmural tissue necrosis in the absence of timely medical or surgical assistance. Complications can be early (occur in the first hours and days after the onset of acute ischemia of the heart muscle) and late. The following consequences are possible:
- Extrasystole. This is a form of heart rhythm disorder characterized by extraordinary contractions of the myocardium. This condition is manifested by lack of air, a feeling of interruptions in heart function and anxiety.
- Paroxysmal tachycardia. It is characterized by a rapid (up to 200 or more beats) heartbeat. These people have normal sinus rhythm. An attack of tachycardia is manifested by tinnitus, dizziness, chest discomfort and autonomic symptoms.
- Atrial fibrillation. It is characterized by twitching of individual myocardial fibers or chaotic and frequent contractions of the atria.
- Impaired conduction of nerve impulses through the heart (blockade).
- Ventricular flutter. The most severe form of heart rhythm disorder, in which the ventricles contract frequently (200-300 times per minute) and in a disorganized manner. At the same time, the correct rhythm is maintained. Ventricular flutter is manifested by decreased pressure, respiratory distress, dilated pupils, pale skin and cyanosis. This condition can progress to fibrillation.
- Heart failure. Characterized by a decrease in cardiac output and oxygen deficiency of all organs and systems. With a heart attack, left ventricular failure most often develops.
- Cardiogenic shock. An emergency condition that develops as a result of acute disruption of blood flow. This is an extreme degree of heart failure, in which the mortality rate exceeds 60%. This complication develops when more than 40-50% of cardiomyocytes die. Symptoms of shock include chest pain, decreased respiratory rate, fear of death, pink foam at the mouth (if pulmonary edema has developed), severe hypotension, decreased urine output, and decreased consciousness.
- Cardiac tamponade. Occurs against the background of rupture of muscle fibers. Tamponade is characterized by hemorrhage into the pericardial sac.
- Pulmonary embolism. This complication occurs in 2-3% of people who have had a heart attack. Thromboembolism is more common in people with a tendency to thrombosis. A blood clot breaks off from the wall of the vessel and is carried away with the blood, clogging the main arteries.
- Sudden death.
- Formation of acute aneurysm. A heart attack is dangerous because scar tissue forms, which can bulge. A pathological expansion of the myocardium is formed. This section is thin and can tear. Most often, a cardiac aneurysm forms against the background of damage to the left ventricle.
- Post-infarction syndrome. With this pathology, the pericardial sac (pericardium) is affected. This complication occurs in 15-30% of patients. It is based on an autoimmune reaction in response to the release and entry into the blood of proteins from destroyed tissues. Post-infarction syndrome is manifested by cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, low-grade fever, rapid breathing, tachycardia, nausea and dizziness.
- Inflammation of the pleura.
- Pulmonary edema.
- Thrombosis.
- Ischemic stroke. It occurs due to blockage of the cerebral arteries by a detached thrombus and acute tissue ischemia. It manifests itself as motor and speech disorders, blurred vision and headaches.
- Joint damage. Possibly due to post-infarction syndrome.
- Collapse (sharp decrease in blood pressure).
Every cardiologist should know the danger of a heart attack and the consequences of this disease.
For men
When a heart attack develops in men, the consequences do not have specific features. They are similar to those in women. The consequences of a microinfarction are less dangerous, since the area of necrosis in this pathology is small. The male body ceases to function normally after myocardial necrosis. In the heart, the number of functional cells that are responsible for contractility decreases. As a result, the ventricles do not emit enough blood. Various organs (kidneys, brain, lungs) suffer from oxygen deficiency.
Or maybe it’s not a heart attack after all?
Chest pain should always alert a person, however, one should not immediately make the dire diagnosis of myocardial infarction.
Only a specialist can carry out an accurate differential diagnosis and make the correct diagnosis, because chest pain can be a sign of some other diseases, for example, intercostal neuralgia.
However, there are general signs that allow the exclusion of myocardial infarction:
- the pain is localized in a specific intercostal space;
- rash in the form of micro bubbles along the nerve;
- pain associated with breathing;
- the pain noticeably intensifies when coughing, sneezing, or turning the body;
- muscle twitching;
- the pain lasts for hours, even days.
Important! The listed symptoms are most often signs of intercostal neuralgia, but only a doctor can finally exclude myocardial infarction and make a diagnosis of neuralgia after the necessary research.
Prevention of recurrent heart attacks
Methods for monitoring the health of a person who has survived a heart attack are divided into two stages. The first refers to the initial 24 months of rehabilitation. Cardiologists monitor the patient and record the improvement in his condition. The person is restored physically and emotionally. After two years, the body’s functioning is completely normalized, and control over its health comes down to preventing relapses.
Drug therapy is actively used. To maintain heart function, the following medications are prescribed:
- blood thinners (for example, Aspirin);
- promoting unloading of the left ventricle - beta-blockers;
- ACE inhibitors, which prevent ventricular dysfunction;
- calcium antagonists, indicated for angina and coronary artery disease.
After an attack, patients adhere to medical recommendations, but must also independently control their lifestyle. The influence of negative factors on the body that can cause a heart attack is reduced by special preventive measures. They are divided into primary and secondary. The latter refer to people who have previously experienced a heart attack and suggest:
- Balanced diet.
- Training blood vessels and the heart through physical activity (walking, running, exercise).
- Complete cessation of bad habits.
- Control of sugar levels and blood pressure. These are some of the symptoms of an impending attack.
- Regular examination.
It is easier to prevent a second myocardial infarction (like the first one) than to later deal with its consequences, which can be fatal to a person. In preventing a dangerous disease, an integrated approach is important - medical supervision and independent preventive actions. As soon as alarming symptoms appear, you should immediately seek advice from a specialist.
Source: serdce.biz