A glucose tolerance test is one of the options for testing the functionality of the pancreas and diagnosing diabetes mellitus.
This type of research is used both for diagnosing the disease and for preventive purposes.
Its use is allowed for diabetics and absolutely healthy people, and does not require a lot of means for implementation, as well as increased safety measures when carrying out
This type of glucose test is identically called a glucose tolerance test (GTT). The test is available in almost all laboratories due to its simplicity. By following certain preparation recommendations, you can achieve the most accurate result.
Glucose tolerance in men and women
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that the following blood sugar levels be considered normal:
- on an empty stomach - less than 6.1 mmol/l (
- 1 hour after oral GTT - less than 7.8 mmol/l (
- 2 hours after oral GTT - less than 7.8 mmol/l (
According to the American Diabetes Association (ADA), these values differ slightly:
- on an empty stomach - less than 5.6 mmol/l (
- 2 hours after oral GTT - less than 7.0 mmol/l (
Glucose tolerance is considered impaired if fasting glucose is 6.1-6.9 mmol/l, 2 hours after exercise - 7.8-11.0 mmol/l according to WHO. The values proposed by the ADA are represented by the following values: on an empty stomach - 5.6-6.9 mmol/l, after 2 hours - 7.0-11.0 mmol/l.
Women
In women, glucose levels correspond to generally accepted standards. However, these values are more susceptible to fluctuations during the day, due to the influence of hormonal levels and more pronounced emotional perception. Sugar may rise slightly during menstrual periods and pregnancy, which is considered an absolutely physiological process.
Men
Men are also characterized by concentrations that do not differ from classical standards and age categories. If the subject is at risk for diabetes and all indicators are normal, it is advisable to conduct the examination at least once a year.
Children
Normal values in children under 14 years of age correspond to 3.3-5.6 mmol/l, in newborns - 2.8-4.4 mmol/l.
For children, the calculation of the required volume of dry anhydrous glucose for GTT is carried out as follows - 1.75 g per 1 kilogram of body weight, but in the total volume no more than 75 grams. If the child weighs 43 kilograms or more, use the usual dosage as for adults.
The risk of developing hyperglycemia is increased in children with excess body weight and an additional risk factor for diabetes mellitus (family history, low physical activity, poor diet, etc.). However, such disorders are often transient and require dynamic determination.
Glucose tolerance test during pregnancy
If someone says that pregnant women do not need to undergo GTT, this is completely wrong!
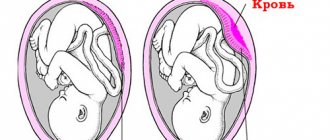
Pregnancy is a time of radical restructuring of the body to ensure good nutrition of the fetus and provide it with oxygen. Changes also occur in glucose metabolism. In the first half of the pregnancy, GTT gives lower values than usual. Then a special mechanism is activated - some muscle cells stop recognizing insulin, more sugar remains in the blood, and the child receives more energy through the bloodstream for growth.
If this mechanism fails, it is referred to as gestational diabetes. This is a separate type of diabetes that occurs exclusively during pregnancy and goes away immediately after birth.
It poses a danger to the fetus due to impaired blood flow through the vessels of the placenta, an increased risk of infections, and also leads to high weight of the child, which complicates the course of labor.
Criteria for diagnosing gestational diabetes
| Interpretation of the result | First blood draw | After an hour | 2 hours later |
| Norm | GLU < 5.1 | GLU < 10 | GLU < 8.5 |
| Gestational diabetes | 5.1 < GLU < 6.9 | GLU > 10 | 8.5 < GLU < 11 |
If fasting glucose is above 7, and after exercise – 11 mmol/l, it means that diabetes mellitus debuted during pregnancy. Such high rates will not be able to return to normal after the birth of the child.
Let's figure out how long it takes to do GTT in order to track metabolic disorders in time. The first time sugar tests are prescribed immediately after visiting a doctor. Blood glucose or glycated hemoglobin is determined. Based on the results of these studies, pregnant women with diabetes are identified (glucose above 7, glycated hemoglobin more than 6.5%). Their pregnancy is carried out in a special order. If questionable borderline results are obtained, pregnant women are considered to be at risk for gestational diabetes. An early glucose tolerance test is performed for women in this group, as well as for those who have a combination of several risk factors for diabetes.
The test at 24-28 weeks of pregnancy is mandatory for everyone; it is part of the screening examination.
A glucose tolerance test is carried out during pregnancy with great caution, since high sugar after exercise can harm the fetus. A rapid test is preliminarily carried out to detect glucose levels, and only if its indicators are normal, GTT is allowed to be carried out
Glucose is used no more than 75 g, in case of the slightest infectious diseases the test is canceled, the test is performed with a load only up to 28 weeks, in exceptional cases - up to 32.
To sum it up - a brief description of the analysis
| Name | Glucose tolerance test |
| Chapter | Biochemical research |
| Object of analysis | Blood plasma or capillary blood |
| Peculiarities | Only as prescribed by a doctor in the absence of contraindications |
| Indications | Hereditary diabetes mellitus, obesity, metabolic disorders, diagnosis of predisposition to diabetes |
| Contraindications | Acute diseases, last weeks of pregnancy, age up to 14 years, endocrine disorders |
| Preparation | On an empty stomach, a period without food of 8 hours, the day before, do not change your diet, do not drink alcohol, avoid stress, discuss taking medications with your doctor |
| Test result | Glucose level in mmol/l |
| Test interpretation | Normal - with GLU < 6.1 (5.6 for capillary blood) for the first measurement, GLU < 7.8 for subsequent ones |
| lead time | 1-2 working days |
| Price | About 700 rubles + cost of blood drawing |
Stay healthy and monitor your blood sugar levels.
Diet for prediabetes
The diet consists of healthy dishes that help stabilize blood glucose levels. For prediabetes it is recommended:
- be sure to have breakfast;
- eat rationally throughout the day;
- do not use sweets and prohibited snacks for snacking;
- Before going to bed, drink a glass of fermented milk drink with a fat content of no more than 2.5%.
Sample menu that you can use as a basis
| Broths and soups | Main dishes | Side dishes | Salads |
| pea or bean soup (without adding smoked meats) | stewed cabbage with rabbit or poultry | buckwheat | “Vitamin” (cabbage with carrots and fresh herbs). |
| fish soup (preference should be given to lean fish) | steamed turkey meatballs | jacket potatoes | seaweed with cucumbers |
| cabbage soup or borscht in turkey (veal) broth | steamed fish cutlets | steamed broccoli (cauliflower) | Greek salad (feta cheese is recommended as a cheese component) |
| seafood soup | poultry cabbage rolls | white or Brussels sprouts cutlets | vegetable (cucumbers, green peppers, tomatoes, onions, greens) |
| chicken broth with chicken meatballs | stuffed green pepper | stewed vegetables or vegetable puree | “Pastelka” salad from raw vegetables (cabbage, beets, carrots) |
| mushroom soup | boiled meat or fish | pasta (category A) | beans (crab sticks, canned beans, garlic, tomatoes) |
| vegetable soup with chicken broth (the skin should be removed from the chicken) | stewed chicken with sour cream 10% fat | stewed beans or lentils with tomatoes and onions | sauerkraut with cranberries |
Salads should be dressed with natural yogurt, flax seed oil, olives, and low-fat sour cream. For a morning meal, cheesecakes or cottage cheese casserole (it is recommended to add fresh berries), an omelet with spinach or boiled eggs, a sandwich (whole grain bread + feta cheese), oatmeal, wheat or barley porridge with fruits (berries) are suitable. For an afternoon snack or lunch: fruit puree or fresh fruit, curdled milk, fermented baked milk or yogurt, biscuits, diabetic gingerbread, unleavened flatbread with cottage cheese.
Allowed drinks include: tea (oolong, black, green, red, hibiscus), freshly squeezed juice diluted with water (1:1), mineral water, decoctions and infusions of rose hips, roots: dandelion or burdock, blueberry leaves, currants, lingonberries, weak coffee with milk (no added sugar). The menu has enough products from which it is easy to prepare healthy, satisfying and tasty dishes. Prediabetes is a condition of the body that is dangerous to neglect. Sugar can only be normalized through proper nutrition. Otherwise, an incurable pathology develops – diabetes mellitus.
Types of dough
Sugar curve analysis has 2 types : oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) and intravenous glucose tolerance test (IGTT). The difference is in the method of introducing glucose into the body.
In the first case, the patient drinks a glass of warm water with glucose, in the second, glucose with saline is administered intravenously.
OGTT is done in rare cases: when the patient cannot drink water on his own (esophageal obstruction, loss of consciousness) or there are gastrointestinal pathologies due to which sugar is poorly absorbed from the intestines. In all other situations, an oral glucose tolerance test is used.
Ask your question to clinical laboratory diagnostics doctor Anna Poniaeva. Graduated from the Nizhny Novgorod Medical Academy (2007-2014) and Residency in Clinical Laboratory Diagnostics (2014-2016).Ask a question>>
Manifestations of tissue tolerance to glucose
Prediabetes, or as this condition was previously called - latent diabetes mellitus, is characterized by a normal concentration of glucose in the blood on an empty stomach, and there is no glucosuria (after diabetes mellitus develops, the concentration of glucose in the blood increases and, accordingly, it appears in urine). But at the same time, there is already a violation of carbohydrate metabolism, which consists of a violation of the absorption of glucose by body tissues.
Often, with the development of prediabetic disorders, patients experience paradiabetic symptoms.
- Furunculosis is multiple foci of purulent inflammation of the hair follicles.
- Problems with teeth and gums - periodontal disease, tooth loss, bleeding gums.
- Problems with the skin, which are manifested by dryness, itching, various damage and diseases that do not heal for a long time.
- There is a violation of sexual function, in women - a disorder of the menstrual cycle.
- Various angioneuropathies - atherosclerosis, vascular inflammation, retinopathy (non-inflammatory damage to the retina).
If any of these symptoms or several of them are noted, this is an indication for a glucose tolerance test.
At this stage of the disorder, the classic signs that characterize diabetes mellitus, such as thirst, frequent urination, weight loss, are still absent. Do not underestimate this condition - you must monitor the dynamics and do everything possible to prevent the increase in disorders and symptoms. At the stage of glucose tolerance, diet, exercise and weight loss (in the case of excess body weight) have a chance to prevent or delay the development of symptoms of the disease.
Survey methodology
The glucose tolerance test is carried out in the morning so as not to force the patient to fast for too long. The method of conducting a glucose tolerance test is that first of all, blood is taken from a vein from a patient on an empty stomach and submitted to calculate the sugar concentration in it. After five minutes, a person should drink about a glass of warm water in which glucose is diluted: 75 g. in the standard case and 1.75 g. per kg of body weight if the patient is a child. A glucose tolerance test during pregnancy is often complicated by the feeling of nausea that a woman experiences while taking such a sweet liquid, which is why glucose has to be administered intravenously.
When conducting a glucose tolerance test, it is very important to evaluate the changes occurring in the composition of the blood after the administration of glucose in order to create a dynamic curve and not miss a likely peak indicating the presence of latent diabetes. For this reason, the rules for conducting GTT state that subsequent blood draws should be carried out and analyzed every 30 minutes, the last of them two hours after loading the body with glucose.
During the entire period of organization of the study, the patient should be quietly in a sitting or lying position, without receiving physical activity, without smoking and without hypothermia (warming the body actively consumes glucose). Naturally, during this period you cannot consume any drinks or food.
Dishes subject to restrictions
To maintain the correct balance of nutrients, you should not completely eliminate meals made from foods with an average glycemic index. In the menu developed for the week, 2-3 times a week it is allowed to include jacket potatoes (boiled or baked), unleavened dough products (flatbread, pita bread), side dishes made from buckwheat pearl barley, canned corn, peas, beans, dishes from fatty fish, boiled eggs and omelet cooked in the microwave, vinaigrette (pickles should be replaced with sauerkraut). The fruit component is represented by: pineapple, banana, persimmon, kiwi, persimmon.
Reasons for violation
Diabetes fears this remedy like fire!
You just need to apply it.
The causes of disorders are both inherited predisposition and lifestyle.
Factors contributing to the development of the disease are:
In pregnant women, the likelihood of such a disorder occurs:
- with increased body weight;
- hereditary predisposition;
- reaching the age of 30 years;
- diagnosis of prediabetes in previous pregnancies;
- polycystic ovary syndrome.
The blood glucose level of even healthy people increases with age by 1 mg/% every 10 years.
When performing a glucose tolerance test - by 5 mg/%. Thus, almost 10% of older people have prediabetes. The main reason is considered to be changing chemical composition with age, physical activity, diet and changes in insulin action.
The aging process causes lean body mass to decrease and the amount of fat to increase. It turns out that the levels of glucose, insulin, glucagon and the percentage of fat directly depend on each other.
If a person is not obese in old age, then there is no relationship between hormones. In old age, the process of counteracting hypoglycemia is disrupted, this is due to a weakening of the glucagon response.
There are no signs of such a violation at the initial stage.
The patient is usually overweight or obese, and examination reveals:
In a state of prediabetes, the following are observed:
As the situation worsens, the following are additionally observed:
Factors influencing the reliability of GTT
When taking the test, the first measurement of glucose is taken on an empty stomach. This result is considered the level to which other measurements will be compared. The second and subsequent indicators depend on the correctness of glucose administration and the accuracy of the equipment used. We cannot influence them. But the patients themselves are entirely responsible . A number of reasons can distort the results, so special attention should be paid to preparing for the GTT.
The following may lead to inaccurate data obtained:
- Alcohol on the eve of the study.
- Diarrhea, extreme heat, or not drinking enough water that has led to dehydration.
- Difficult physical work or intense training for 3 days before the test.
- Sudden changes in diet, especially those related to carbohydrate restriction and fasting.
- Smoking at night and in the morning before GTT.
- Stressful situations.
- Colds, including mild ones.
- Recovery processes in the body in the postoperative period.
- Bed rest or sudden reduction in usual physical activity.
When receiving a referral for analysis, the attending physician must be informed of all medications taken, including vitamins and contraceptives. He will choose which ones will have to be canceled 3 days before the GTT. Usually these are drugs that lower sugar, contraceptives and other hormonal drugs.
How to find out if you have diabetes
It is impossible to find out at home that you have prediabetes. The only possible option is to consult an endocrinologist after conducting a tolerance test in the laboratory.
The test is carried out after the rapid method, which is a standard test for blood sugar levels. Blood is taken on an empty stomach, preferably in the morning. Also, before conducting a test that will show impaired glucose tolerance, it is better to avoid stressful situations and too much physical activity. The test is carried out in three stages:
- the first is blood sampling before taking dissolved glucose;
- second - a person is given glucose dissolved in water (75 ml) to drink, and 50 minutes later (after the first blood draw) the procedure is repeated;
- the third is the last blood draw, which occurs another fifty minutes after the previous analysis.
If a person is healthy, then his indicators will be as follows:
- 1st blood draw – 5.49 mmol/liter;
- 2nd blood sampling – 11.09 mmol/liter;
- 3rd blood sampling – 7.79 mmol/liter.
Indicators that indicate impaired glucose tolerance are the following:
- 1st blood draw – 5.49–6.69 mmol/liter;
- 2nd blood sampling – less than 11.09 mmol/liter;
- 3rd blood sampling – rises to the level of 11.09 mmol/liter.
In children, as in adult men and women, the indicators do not differ. If the first test showed impaired glucose tolerance, then you should not be upset in advance, since the endocrinologist prescribes more than one such test. This is necessary to exclude factors that could affect blood sugar levels. These include:
- craving for sweet foods on the eve of analysis;
- the person was under stress;
- lack of sports activity;
- excessive alcohol consumption the day before the test;
- pregnancy or tests during menstruation;
- obesity.
Therefore, panic is inappropriate. Any test may also produce statistical error. This one is no exception.
What is GTT?
In order to examine the pancreas, which synthesizes insulin, a glucose tolerance test is performed. This hormone monitors sugar levels and helps the body regulate them within limits.
When a person is affected by diabetes, up to ninety percent of all beta cells of the pancreas are destroyed.
This study is carried out if the endocrinologist suspects the early stages of diabetes or problems with carbon metabolism.
Over the course of two hours, blood is drawn from the subject 4 times. The first approach is done in the morning, on an empty stomach. Then the person being studied must take water with glucose (70-110 grams, stirred in 150-200 ml of water). Blood samples are taken after 1 hour, 1.5 and 2 hours. You cannot eat or drink during the entire analysis.
General conditions for catering
A diet for prediabetes is based on eating healthy foods and foods and eating rationally. The main conditions for catering are:
- eliminating foods containing fast carbohydrates from the menu;
- replacing animal fats with vegetable oils (sunflower, olive, corn, flaxseed, etc.);
- observing the time interval between meals (no more than 3–4 hours);
- strict control over the calorie content of dishes and the volume of portions (a single meal should not exceed 350–400 grams);
- exclusion from the menu of dishes prepared by frying (including over charcoal);
- compliance with the drinking regime (1.5–2 liters per day);
- limited consumption of table salt;
- introduction into the diet of foods that stabilize glucose levels.
In a prediabetic state, drinking alcohol can provoke the development of the disease. Alcoholic drinks must be avoided.
Treatments for Impaired Glucose Tolerance
Two treatment tactics are used: medication and alternative. With timely diagnosis, treatment with alternative methods, without taking medications, is often sufficient.
Non-drug treatment of impaired glucose tolerance is based on the following basic principles:
- Fractional meals in small portions. You need to eat 4-6 times a day, and evening meals should be low-calorie.
- Minimizing the consumption of flour products, baked goods, and sweets.
- Strictly control weight, preventing fat deposition.
- Make vegetables and fruits the main food products, excluding only those that contain large amounts of starch and carbohydrates - potatoes, rice, bananas, grapes.
- Be sure to drink at least 1.5 liters of mineral water per day.
- If possible, eliminate the consumption of animal fats, giving preference to vegetable oil.
Usually, following these nutritional rules gives good results. If it is not achieved, special drugs are prescribed to help normalize glucose metabolism and metabolism. Taking medications containing hormones is not necessary in this case.
The most popular and effective drugs prescribed to improve glucose metabolism in the body:
All prescriptions must be made strictly by a doctor. If for some reason taking medications is undesirable or impossible, for example, during pregnancy, impaired glucose tolerance is treated with folk recipes, in particular, various herbal infusions and decoctions.
The following medicinal plants are used: black currant leaves, horsetail, burdock root and inflorescences, blueberries. Steamed buckwheat is very popular in treatment.
There are a fairly large number of methods to combat unstable blood sugar levels.
But it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, especially during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Quitting smoking and drinking alcohol, walking in the fresh air, playing sports, following a diet - all this significantly affects the body's tolerance to glucose and can help avoid the transformation of a minor disorder into a pathology, especially during pregnancy.
An equally important point is the state of the nervous system. Constant stress and anxiety can be a decisive factor. Therefore, if necessary, you should consult a psychologist. He will help you pull yourself together, stop worrying, and if necessary, prescribe medications that help strengthen the nervous system.
And the last piece of advice: do not neglect your health and ignore scheduled annual check-ups, even if at the moment you are feeling quite satisfactory.
It is easier to prevent or cure any disease at the initial stage than to then fight it for many months and even years.
https://diabethelp.org
Test procedure
Although the glucose tolerance test is very simple, you will have to spend about 2 hours in the laboratory, during which changes in sugar levels will be analyzed. It will not be possible to go for a walk at this time, as staff supervision is required. Typically, patients are asked to wait on a bench in the laboratory hallway. Playing exciting games on your phone is also not worth it - emotional changes can affect the absorption of glucose. The best choice is an educational book.
Stages of identifying glucose tolerance:
- The first blood donation must be done in the morning, on an empty stomach. The period since the last meal is strictly regulated. It should not be less than 8 hours, so that the consumed carbohydrates have time to be utilized, and no more than 14, so that the body does not begin to starve and absorb glucose in non-standard quantities.
- A glucose load is a glass of sweet water that you drink within 5 minutes. The amount of glucose in it is determined strictly individually. Typically, 85 grams of glucose monohydrate is dissolved in water, which equates to 75 grams pure. For persons 14-18 years old, the required load is calculated based on their weight - 1.75 g of pure glucose per kilogram of weight. If you weigh more than 43 kg, the usual adult dose is allowed. For obese people, the load is increased to 100 g. With intravenous administration, the portion of glucose is greatly reduced, which makes it possible to take into account its losses during digestion.
- Blood is donated again 4 more times - every half hour after exercise. Based on the dynamics of sugar reduction, one can judge about disturbances in its metabolism. Some laboratories take blood twice - on an empty stomach and after 2 hours. The result of such an analysis may be unreliable. If your blood glucose peak occurs at an earlier time, it will not be recorded.
An interesting detail is that citric acid is added to the sweet syrup or simply given a slice of lemon. Why lemon and how does it affect the measurement of glucose tolerance? It does not have the slightest effect on sugar levels, but it allows you to eliminate nausea after a one-time intake of a large amount of carbohydrates.
Laboratory determination of glucose levels
Currently, blood is almost never taken from a finger. In modern laboratories, the standard is to work with venous blood. When analyzing it, the results are more accurate, since it is not mixed with intercellular fluid and lymph, like capillary blood from a finger. Nowadays, sampling from a vein is no less traumatic than the procedure - laser-sharpened needles make the puncture almost painless.
When blood is collected for a glucose tolerance test, it is placed in special tubes treated with preservatives. The best option is to use vacuum systems, into which blood flows evenly due to the difference in pressure. This avoids the destruction of red blood cells and the formation of clots, which can distort the test results or make it impossible to perform it altogether.
The laboratory assistant’s task at this stage is to avoid blood damage - oxidation, glycolysis and coagulation. To prevent the oxidation of glucose, sodium fluoride is contained in the test tubes. Fluorine ions in it prevent the breakdown of the glucose molecule. Changes in glycated hemoglobin are avoided by using cool tubes and subsequent refrigeration of samples. EDTA or sodium citrate are used as anticoagulants.
The tube is then placed in a centrifuge, which separates the blood into plasma and formed elements. The plasma is transferred to a new tube, where the glucose level will be determined. Many methods have been developed for this purpose, but two of them are currently used in laboratories: glucose oxidase and hexokinase. Both methods are enzymatic, their action is based on chemical reactions of enzymes with glucose. The substances obtained as a result of these reactions are examined using a biochemical photometer or automatic analyzers. Such a well-established and proven blood analysis process allows you to obtain reliable data on its composition, compare results from different laboratories, and use uniform glucose levels.
Normal GTT indicators
Glucose norms for the first blood draw during GTT
| Interpretation of the result | Glucose level | |
| Whole capillary blood (finger prick) | Blood plasma (sampling from a vein) | |
| Normal level | GLU 6.1 | CLU > 7 |
Glucose norms for the second and subsequent blood draws during GTT
| Interpretation of the result | Glucose level | |
| Whole capillary blood (finger prick) | Blood plasma (sampling from a vein) | |
| Normal level | GLU 11.1 | GLU > 11.1 |
The data obtained is not a diagnosis, it is just information for the attending physician. To confirm the results, a repeat glucose tolerance test is performed, blood donation for other indicators, and additional organ studies are prescribed. Only after all these procedures can we talk about metabolic syndrome, impaired glucose absorption and, especially, diabetes mellitus.
If the diagnosis is confirmed, you will have to reconsider your entire lifestyle: bring your weight back to normal, limit carbohydrate foods, restore muscle tone through regular physical activity. In addition, patients are prescribed glucose-lowering drugs, and in severe cases, insulin injections. A large amount of glucose in the blood causes a feeling of constant fatigue and apathy, poisons the body from the inside, and provokes a difficult to overcome desire to overeat sweets. The body seems to resist recovery. And if you succumb to it and let the disease take its course, there is a high risk of getting irreversible changes in the eyes, kidneys, feet, and even disability within 5 years.
If you belong to a risk group, diabetes prevention should begin even before a glucose tolerance test shows abnormalities. In this case, the likelihood of a long and healthy life without diabetes increases significantly.
Symptoms of the disease
There are no symptoms of the disease as such; it is almost impossible to independently determine that glucose tolerance is impaired. This means that the symptoms develop with the onset of diabetes, so the manifestations sometimes include increased thirst, respectively, increased urination, and dry mouth. However, the symptoms are vague and in the summer can be regarded as a consequence of the heat.
With the deterioration of NGT, the body's protective barriers are reduced, which leads to disruption of metabolic processes, as a result of which the quality of hair, skin, and nail plate deteriorates. A person experiences low activity, apathy, the body succumbs to viral attacks, psycho-emotional exhaustion manifests itself, and endocrine functionality is often disrupted.
Indications
- high blood sugar levels recorded for the first time;
- prediabetes;
- control of the development of existing diabetes mellitus;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- initial examination of a pregnant woman.
By the way, the question “At what week of pregnancy is it better to do a glucose tolerance test?” still causes controversy because there are no reliable statistics on the timing of the onset of gestational diabetes mellitus.
It is believed that it is highly advisable to do the test before the 22nd week.
Watch a video on this topic
Diagnostics
Impaired glucose tolerance in most cases is detected incidentally, since patients do not present any complaints. The basis for diagnosis is usually the result of a blood sugar test, which shows an increase in fasting glucose levels to 6.0 mmol/l.
- anamnesis analysis (data on concomitant diseases and relatives with diabetes is clarified);
- a general examination, which in many cases reveals the presence of overweight or obesity.
The basis for the diagnosis of prediabetes is a glucose tolerance test, which assesses the body's ability to metabolize glucose. If you have infectious diseases, increased or decreased physical activity during the day before the test (does not correspond to the usual one), and are taking medications that affect your sugar level, the test is not performed.
Before taking the test, it is recommended not to restrict yourself in nutrition for 3 days, so that your carbohydrate intake is at least 150 g per day. Physical activity should not exceed standard loads. In the evening before the test, the amount of carbohydrates consumed should be from 30 to 50 g, after which food is not consumed for 8-14 hours (water is allowed to be drunk).
- fasting blood sampling for sugar testing;
- taking a glucose solution (for 75 g of glucose you need 250-300 ml of water);
- repeated blood sampling for sugar analysis 2 hours after taking the glucose solution.
In some cases, additional blood samples are taken every 30 minutes.
Smoking is prohibited during the test to avoid distorting the analysis results.
Impaired glucose tolerance in children is also determined using this test, but the “load” of glucose on a child is calculated based on his weight - 1.75 g of glucose is taken for each kilogram, but in total no more than 75 g.
Impaired glucose tolerance in pregnancy is checked using an oral test between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. The test is carried out using the same technique, but it involves an additional measurement of blood glucose levels an hour after the glucose solution has been taken.
Normally, the glucose level during repeated blood sampling should not exceed 7.8 mmol/l. A glucose level of 7.8 to 11.1 mmol/L indicates the presence of impaired glucose tolerance, and a level above 11.1 mmol/L is a sign of diabetes mellitus.
If the fasting glucose level is repeatedly detected above 7.0 mmol/l, the test is not advisable.
The test is contraindicated in individuals with a fasting glucose concentration greater than 11.1 mmol/L and in individuals with a recent history of myocardial infarction, surgery, or childbirth.
If it is necessary to determine the secretory reserve of insulin, the doctor can, in parallel with the glucose tolerance test, determine the level of C-peptide.
How to properly prepare for GTT?
To obtain accurate analysis results, all of the following requirements must be met:
- The test is taken on an empty stomach.,
- Food intake should be limited at least eight hours before blood sampling,
- In a few days (2-3) stop drinking alcohol and cigarettes,
- Moderate physical activity . You should not overload yourself on the eve of the test, and also lead a practically immobile lifestyle,
- It is recommended to stop consuming confectionery and sugary water for a few days,
- Avoid stressful situations , worries, worries, etc.
- Infectious diseases may affect the test results,
- Use of certain medications . It is necessary to inform your doctor about the use of medications.
Only by fulfilling the above requirements can you minimize the risk of false testimony.
Also, the results may deviate when carrying a child, since the expectant mother’s body undergoes significant changes that change hormonal levels.
Impaired glucose tolerance causes and symptoms
The reasons for increased glucose levels in the body are the same for all types of diabetes. The main ones that provoke the appearance of impaired glucose tolerance are:
- Genetic predisposition. If one of the family members has or has previously had diabetes, then the descendants are also at possible risk.
- Impaired sensitivity of body cells to insulin (insulin resistance).
- Pancreatic disease.
- Endocrine system disorder (Cushing's disease).
- Obesity.
- Lack of sports activity.
- Taking medications that increase sugar levels.
Unfortunately, there are no symptoms of the early phase, which indicate negative changes associated with blood glucose. The only recommendation that will help identify impaired glucose tolerance is to take a blood test in the hospital every six months to prevent serious consequences. Symptoms of this problem appear only as the disease progresses and are characteristic parameters for diabetes mellitus. Symptoms of high sugar levels in the body:
- feeling of constant thirst;
- feeling of dryness in the mouth;
- abnormal frequency of urination;
- increased or decreased appetite;
- predisposition to viral diseases.
Indications for use
- When examining patients with risk factors for diabetes (sedentary lifestyle, obesity, presence of a first-degree relative with diabetes, hypertension and other diseases of the cardiovascular system, lipid disorders, impaired glucose tolerance).
- Excess weight (body weight).
- Atherosclerosis.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Gout.
- Close relatives of patients with diabetes.
- Women who have had miscarriages, premature births, very large newborns or children with developmental defects, stillborn newborns, diabetes during pregnancy.
- Metabolic syndrome.
- Chronic liver diseases.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Neuropathies of unknown etiology.
- Long-term use of diuretics, glucocorticoids, synthetic estrogens.
- Chronic periodontal disease and furunculosis.