Heparin sodium is a drug (solution) that belongs to the pharmacological group of anticoagulants. The instructions for use highlight the following features:
How to dissolve vascular plaques, normalize blood circulation, blood pressure and forget the way to the pharmacy
- Sold only with a doctor's prescription
- During pregnancy: with caution
- When breastfeeding: with caution
- For liver dysfunction: contraindicated
- If renal function is impaired: with caution
- In old age: with caution
Release form and composition
Dosage forms of the drug:
- Solution for intravenous (IV) and subcutaneous (SC) administration: light yellow or colorless transparent liquid (bottle (bottle) 1 ml, 5 or 10 pcs. in blister or plastic (pallets) packaging, in a cardboard box 1 or 2 packages; 5 or 10 pieces in a cardboard pack without packaging. 1 ml ampoule with an ampoule knife, 5 or 10 pieces in a contour cell or plastic (pallets) package, in a cardboard pack 1 or 2 packages; 5 or 10 pcs in a cardboard pack without packaging. 2 ml ampoule with an ampoule knife, 5 pcs in a blister pack, 1 or 2 packs in a cardboard pack. 5 ml ampoule with an ampoule knife, 5 or 10 pcs in a blister pack or plastic (pallets) packaging, in a cardboard pack 1 or 2 packs. Ampoule 5 ml with ampoule knife, 5 or 10 pcs. in a cardboard pack. Ampoule 5 ml, 5 or 10 pcs. in a cardboard pack. Bottle (bottle) 5 ml, 5 or 10 pcs. in blister or plastic packaging (pallets), in a cardboard pack 1 or 2 packages. Bottle (bottle) 5 ml, 1, 5 or 10 pcs. in a cardboard pack. Polymer ampoule 5 ml, 5 pcs. in a cardboard pack. Bottle (bottle) 5 ml, 5 pcs. in a polystyrene container);
- Ointment for external use (10 or 25 g in aluminum tubes, 1 tube in a cardboard box);
- Gel for external use (15, 20, 30, 50 or 100 g in aluminum tubes, 1 tube in a cardboard pack).
Active ingredient: sodium heparin:
- 1 ml of solution – 5000 IU;
- 1 g ointment – 100 IU;
- 1 g of gel – 1000 IU.
Auxiliary components:
- Solution: sodium chloride – 3.4 mg, benzyl alcohol – 9 mg, water for injection up to 1 ml;
- Ointment: benzocaine – 40 mg, benzyl nicotinate – 0.8 mg.
Reviews about "Heparin"
Heparin is a very well studied, clinically tested, frequently used and effective antithrombotic drug; its mechanism of action is based on suppressing the activity of thrombin, which catalyzes a number of reactions occurring in the hemostatic system. Among them is the biotransformation of fibrinogen into fibrin.
The most common reviews are about Heparin in the form of gel and ointment. Patients note its high effectiveness against hemorrhoids, thrombophlebitis, bruises and localized infiltrates. Side effects occur quite rarely if you adhere to the doctor’s recommendations and the rules specified in the instructions for use of Heparin. There are reviews on this matter.
Indications for use
- Therapy and prevention: thrombophlebitis, pulmonary embolism (including in the case of peripheral vein diseases), deep vein thrombosis, coronary artery thrombosis, unstable angina, acute myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation (including accompanied by embolism), syndrome disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), microcirculation disorders and microthrombosis, renal vein thrombosis, hemolyticouremic syndrome, bacterial endocarditis, glomerulonephritis, lupus nephritis;
- Prevention: blood clotting during operations that use extracorporeal blood circulation methods, mitral heart disease, hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, hemosorption, forced diuresis, cytapheresis;
- Flushing venous catheters;
- Preparation of non-clotting blood samples for laboratory purposes and blood transfusions.
Contraindications
Contraindications to the use of Heparin in solution form:
- History or current heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, with or without thrombosis;
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding period;
- Bleeding, if the potential risk outweighs the intended benefit of use.
The solution is prescribed with caution for pathological conditions associated with an increased risk of bleeding:
- Traumatic brain injury, hemorrhagic stroke;
- Malignant neoplasms;
- Cardiovascular system: cerebral aneurysm, acute and subacute infective endocarditis, severe uncontrolled arterial hypertension, aortic dissection;
- Organs of the lymphatic system and hematopoiesis: hemorrhagic diathesis, leukemia, hemophilia, thrombocytopenia;
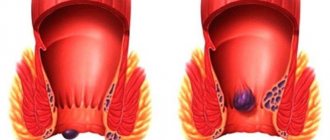
- Ulcerative colitis, erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), varicose veins of the esophagus, prolonged use of gastric and small intestinal drainage, hemorrhoids;
- Congenital deficiency of antithrombin III synthesis and replacement therapy with antithrombin III drugs (small doses of the drug should be used to reduce the risk of bleeding).
Other physiological conditions and pathologies in which Heparin solution should be used with caution: chronic renal failure; severe liver diseases with impaired protein-synthetic function; vasculitis; proliferative diabetic retinopathy; recent surgical interventions on the spinal cord, brain, eyes; early postpartum period; recent epidural anesthesia or lumbar puncture; threatened abortion; period of menstruation.
Under close medical supervision, it is recommended to use the solution when treating children under 3 years of age and patients over 60 years of age, especially women.
Contraindications to the use of ointment and gel:
- Diseases accompanied by impaired blood coagulation processes, bleeding, cerebral aneurysm, suspected intracranial hemorrhage, hemorrhagic stroke, dissecting aortic aneurysm, malignant arterial hypertension, subacute bacterial endocarditis, antiphospholipid syndrome;
- Erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, malignant neoplasms in the liver, severe damage to the liver parenchyma, cirrhosis of the liver with varicose veins of the esophagus, shock conditions;
- The recovery period after surgery on the liver and bile ducts, brain, eyes, prostate gland, spinal cord puncture;
- Recent childbirth, menstruation, threatened miscarriage.
Ointment and gel should not be applied to ulcerative-necrotic processes, to mucous membranes or open wounds.
Application of ointment or gel during pregnancy and during breastfeeding (lactation) is possible under close medical supervision, only under strict indications.
The use of all dosage forms of Heparin is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Analogues of "Heparin"
The main analogues of “Heparin” in gel form include the following products: “Trombless”, “Laventum”, “Lioton 1000”, “Heparin-Acrigel 1000”.
Generic injection forms are “Heparin-Sandoz”, “Heparin J”, “Heparin-Ferein”.
The tablets “Wessel Due F”, “Angioflux”, “Piyavit”, as well as injection solutions “Eniksum”, “Fraxiparin”, “Anfibra”, “Fluxum”, “Wessel Due F”, “Antitrombin III”, have a similar mechanism of action. "Hemapaxan", "Angioflux".
It is important to remember that any replacement of a therapeutic drug should be made only after consultation with a specialist.
Directions for use and dosage
The solution is administered intravenously by drip or bolus and subcutaneously into the abdominal area. Do not administer the drug intramuscularly! The dosage is prescribed by the doctor based on clinical indications and taking into account the patient’s age. Typically, treatment begins with intravenous administration of 5000 IU, then switches to subcutaneous injections or intravenous drips.
Maintenance dosing depending on the method of application of the solution:
- Continuous intravenous infusion – 24000-48000 IU per day at a rate of 1000-2000 IU per hour;
- Regular intravenous injections – 5000-10000 IU with an interval of 4-6 hours;
- Subcutaneous injections - 15,000-20,000 IU 2 times or 8,000-10,000 IU - 3 times a day.
For infusion administration, the drug is diluted with 0.9% sodium chloride solution. Each subsequent dose is adjusted based on regular studies of activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) and/or blood clotting time. With subcutaneous administration of 10,000-15,000 IU per day, regular monitoring of aPTT is not necessary.
The treatment period depends on the route of administration and indications. The drug is used intravenously for 7-10 days, then treatment should be continued with oral anticoagulants. Oral anticoagulants are recommended to be prescribed from the first or from 5 to 7 days of treatment; discontinuation of the solution is prescribed on the 4-5 day of combined treatment.
The use of Heparin in special clinical situations is carried out according to a special scheme.
Ointment and gel are used depending on the clinical indications and age of the patient.
Reviews of injections in the stomach to thin the blood during pregnancy
Elena, 26 years old: I had two miscarriages before, I became pregnant again, the doctor strongly advised me to do a hemostasiogram. It turned out that my blood is thick. It needs to be liquefied. I injected Fraxiparin from 12 to 28 weeks. At first I was very afraid, but then I got used to it. I ordered the drug in advance from the pharmacy, because one time it happened that I ran out of injections, and it was not available for sale at the nearest points of sale. Injections should not be skipped. Therefore, I advise everyone to keep the medicine in reserve.
Natalya, 31 years old: The injections are really not painful, but after them the stomach turned blue. Personally, I always had a fear that I would hit a child with a needle. The doctor assured me that there was no need to be afraid: the fetus was reliably protected, and the length of the needle was only one and a half centimeters. But every time I felt uneasy every time.
Katya, 19 years old: I was prescribed injections in the stomach in the last trimester. The stomach was stretched like a drum, it was impossible to make a fold. Well, there was a nurse living next door. I asked her to come in. I lay down on the floor on the carpet. She sat on her knees and did everything very quickly. The needle is very short, thin, it didn’t hurt, but my fear of an injection made me nervous. And then the baby kicked like mad. The course was like an execution, it’s good that it ended a month later and I switched to pills.
Side effects
- From the blood coagulation system: thrombocytopenia in a transient and severe form, in rare cases with a fatal outcome, can cause the development of skin necrosis, arterial thrombosis, gangrene, stroke, myocardial infarction; hemorrhagic complications in the form of bleeding of the gastrointestinal tract or urinary tract, retroperitoneal hemorrhages in the ovaries, adrenal glands with the risk of developing acute adrenal insufficiency;
- From the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, decreased appetite, increased levels of transaminases in the blood;
- From the musculoskeletal system: in case of long-term use - soft tissue calcification, osteoporosis and spontaneous fractures;
- Allergic reactions: urticaria, skin itching, skin hyperemia, bronchospasm, rhinitis, drug fever, anaphylactoid reactions, anaphylactic shock;
- Local reactions: pain, hematoma, bleeding, hyperemia or ulceration at the injection site;
- Other: inhibition of aldosterone synthesis, transient alopecia.
Injections in the stomach during pregnancy to thin the blood name
For each woman, the process of bearing a child proceeds differently. Some people tolerate pregnancy easily, while others experience various complications. The pregnant woman is monitored by a doctor all the way. It takes into account all the nuances of embryo development.
The doctor can advise the expectant mother which foods thin the blood during pregnancy. This will help both the expectant mother and the child stay healthy. Not only foods affect blood thinning. After all, during pregnancy, the doctor can prescribe a course of important medications that will reduce the thickness of the blood.
Throughout the pregnancy, the expectant mother undergoes examination almost every day. This allows you to monitor the condition of the mother and embryo. There is a special test after which you can find out whether a pregnant woman’s blood is thick or not. But such changes are not always safe. It is very important to thin the blood to avoid trouble.
In general, the entire pregnancy process carries with it certain risks. After all, thick blood does not flow well, which does not allow oxygen to flow to the tissues of the organs. The process of nutrient intake is also inhibited.
Another danger is that clots can form in thick blood. If measures are not taken in time, varicose veins, thrombophlebitis may form, hypertension and oxygen starvation of the baby may develop. The worst thing that can happen is a miscarriage.
There is another clearly visible reason that causes an increase in blood thickening - the result of the manifestation of antiphospholipid syndrome. As a result, high coagulation of blood vessels occurs, which can cause the fetus to die or premature birth to begin.
special instructions
Long-term treatment with large doses is recommended in a hospital setting.
The use of the solution should take into account blood clotting indicators; in case of a sharp decrease in the number of platelets, the use of the drug should be immediately discontinued.
If the drug is prescribed in high doses or in the absence of a response to Heparin, it is necessary to monitor the level of antithrombin III.
IM administration of other drugs while using the drug solution is not recommended.
In patients with arterial hypertension, treatment should be accompanied by regular monitoring of blood pressure.
The drug should be used with caution in patients undergoing radiation therapy, dental procedures, active tuberculosis, and in the presence of an intrauterine contraceptive device.
When treating women over 60 years of age, the use of sodium heparin may increase bleeding, so this category of patients should reduce the dose of the solution.
Adequate dosing, regular monitoring of blood clotting, and careful assessment of contraindications reduce the risk of bleeding.
Pharmacological properties
Sodium heparin is a proteoglycan and belongs to the medium molecular weight heparins. It forms a complex with the protein antithrombin III, increasing its activity in blood clotting. It is a natural physiological blocker of coagulation factors, being part of the anticoagulation system together with fibrinolysin. Injections of the drug inactivate thrombin synthesis and have a fibrinolytic effect.
Heparin is an anticoagulant that has a direct effect. Included in the group of heparins that slow down the development of fibrin. The anticoagulant effect can be achieved after intravenous administration.
After intravenous administration, maximum concentration occurs almost immediately. If the drug is administered subcutaneously, after about 4 hours.
It is worth noting that the components do not pass into breast milk. Mainly concentrated in the liver and spleen.
It is excreted from the body by the kidneys in a modified form. If a large amount of this medicine is administered for a long time, it may be excreted unchanged.
Drug interactions
Heparin solution is compatible only with 0.9% sodium chloride solution.
Sodium heparin enhances the effect of drugs containing benzodiazepine derivatives, phenytoin, propranolol, quinidine.
The activity of the drug is reduced by tricyclic antidepressants, protamine sulfates, and polypeptides.
The anticoagulant effect of the drug is enhanced by the simultaneous use of thrombolytic agents (alteplase, urokinase, streptokinase), antiplatelet agents (acetylsalicylic acid, dipyridamole, clopidogrel, ticlopidine, prasugrel), indirect anticoagulants (warfarin, acenocoumarol, phenindione), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
The risk of bleeding is increased by the simultaneous use of Heparin with dextran, glucocorticosteroids, cytostatics, hydroxychloroquine, cefamandole, valproic and ethacrynic acid, propylthiouracil.
The anticoagulant effect of the drug is reduced by the simultaneous use of corticotropin, ascorbic acid, nitroglycerin, ergot alkaloids, quinine, nicotine, tetracycline, cardiac glycosides, antihistamines or thyroxine.
The drug may reduce the effect of glucocorticosteroids, adrenocorticotropic hormone, and insulin.